mirror of
https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus.git
synced 2025-06-24 14:43:22 +00:00
Compare commits
431 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| be6bc155eb | |||
| d0bbef74ef | |||
| a282ae22af | |||
| c83e8e1e62 | |||
| 452ec28761 | |||
| 8a78637719 | |||
| 1fdb75068d | |||
| 230c135d4e | |||
| bf544af690 | |||
| e7ab8be0cd | |||
| b1822f2602 | |||
| f4a74a3405 | |||
| 73da639654 | |||
| f2a1456e94 | |||
| c75abda571 | |||
| 1aec670c43 | |||
| 77695d75bb | |||
| 3dec452a8a | |||
| 97f5ce52d1 | |||
| 540de896e3 | |||
| dcfccb2a0d | |||
| ac5b0a3b34 | |||
| 8f854ee83a | |||
| bd312607a3 | |||
| 99f2abfd71 | |||
| 132ecc0580 | |||
| 5157a56803 | |||
| 33281b04e7 | |||
| a9404fe33f | |||
| 95bdb47f01 | |||
| ebf624772a | |||
| b33a6addcc | |||
| 1e4fb1f6fe | |||
| 287828fe0b | |||
| dc311b978e | |||
| bccaf93f8b | |||
| 61a84e15ea | |||
| f7bdb6555d | |||
| 125a59df91 | |||
| eae4a9e1f8 | |||
| 20f009e927 | |||
| 78d9fa280c | |||
| 45bb85cd8f | |||
| 16551643b3 | |||
| 5245ed2262 | |||
| 9e91b15b74 | |||
| b5c2646360 | |||
| 8cd7f3438f | |||
| e0ff431169 | |||
| a8ff64f704 | |||
| 9c105098dd | |||
| 9af6395e92 | |||
| 670316f997 | |||
| 4cf02a32a7 | |||
| 6b3a9b9dc0 | |||
| d544a5a947 | |||
| 973b0ac488 | |||
| baff2ce80f | |||
| 8a7fed5dfb | |||
| a962359993 | |||
| 5b45fc5921 | |||
| c8d3d813ff | |||
| 8eafa90105 | |||
| 8e2ee30c47 | |||
| 19afe50efa | |||
| 8f519e7959 | |||
| 293ff9d586 | |||
| 2109d37298 | |||
| fb31a3bf2e | |||
| 68fa95beb3 | |||
| 942245b985 | |||
| 6e25fde883 | |||
| 46955be305 | |||
| b89d10025d | |||
| edb33cba0c | |||
| 783e5fa42f | |||
| 9c31196610 | |||
| ca765b5ebb | |||
| 3f65f534aa | |||
| 1fc328b2ea | |||
| 1e93146b49 | |||
| 36fea4ba7b | |||
| 18a1a19deb | |||
| 1d52e1f41b | |||
| f0ec7635ab | |||
| 158d8a181e | |||
| f66c0a5d98 | |||
| a609b08c0a | |||
| e63c9ec05e | |||
| 4936322dbc | |||
| 9baee07c94 | |||
| 03ecf6e695 | |||
| 2b1b9f816c | |||
| 1b55df5848 | |||
| 7bec9e3804 | |||
| 06cb695cd7 | |||
| c08f4f5845 | |||
| c71fc74248 | |||
| 0b52d342f6 | |||
| a5acd32f56 | |||
| a7e45319c3 | |||
| e18caef4f6 | |||
| 149b7d9ee8 | |||
| d13592aea0 | |||
| 59d4b0aadb | |||
| 96c9fa0ccc | |||
| 7cdd0abfd5 | |||
| 74ef58e310 | |||
| 897fb9c2e4 | |||
| ff1f6af7e9 | |||
| 9aefe7a040 | |||
| 17bb51756f | |||
| 5044bb0332 | |||
| b4ca95a9fa | |||
| f097f780af | |||
| 99be294726 | |||
| 7adb7cf7f6 | |||
| e36e5f4fc9 | |||
| 1e503a586d | |||
| 6488400fbf | |||
| e423e0a0f1 | |||
| ad1750b53d | |||
| e909d5f5c2 | |||
| 6e6480c952 | |||
| ff5c7b155c | |||
| 123d97bfb8 | |||
| dd0a8c200c | |||
| 272a43be11 | |||
| 63677bb1f9 | |||
| 780a78c825 | |||
| c29af4aeba | |||
| 48e6e3ac45 | |||
| 74a984d75f | |||
| b55ea6409d | |||
| 68b3849d51 | |||
| ed7917e619 | |||
| 5e56d3bf36 | |||
| e2dfac08c0 | |||
| c8173eb9ec | |||
| 832c784a70 | |||
| 61b0a3775b | |||
| 5f50964176 | |||
| 428b88a82a | |||
| 46ac559003 | |||
| caba176c87 | |||
| f37e7c5240 | |||
| 252742ce20 | |||
| 3f3f03f715 | |||
| 4df1ad35b3 | |||
| 4e87c6af02 | |||
| fc277b736a | |||
| 278f4fd08e | |||
| df86816e7d | |||
| d8059cab6b | |||
| d1a2a3eee5 | |||
| 7856f09799 | |||
| 461e717157 | |||
| 8ee11fecc4 | |||
| 36020c41df | |||
| 6444bc6a71 | |||
| a67d86c6e2 | |||
| 924f3025f9 | |||
| 9690bb4b9c | |||
| 5d5ee85928 | |||
| 820621baa2 | |||
| 75d2881302 | |||
| 95b641198e | |||
| 6b40189045 | |||
| df379dfcf4 | |||
| 4721617fd6 | |||
| b82ff2d7e7 | |||
| efa2052896 | |||
| 52cbd650b7 | |||
| 4cb1d756f7 | |||
| 84161d7c9d | |||
| c8c5ec254a | |||
| 1a0b491ed6 | |||
| 3a4226a28b | |||
| 1a47a5a739 | |||
| 760416c1a0 | |||
| 5955dd4e25 | |||
| e0f9aa3508 | |||
| b31dff6bee | |||
| 1b3f971330 | |||
| abf61ecc8f | |||
| 71bf2d8826 | |||
| 52bfd1fc3d | |||
| a8d96967c4 | |||
| f7a400878a | |||
| e1f18f6212 | |||
| 9705ccee67 | |||
| 7151651ea9 | |||
| 0d7ecd4327 | |||
| 50530c144e | |||
| 45f00e45be | |||
| e969afc627 | |||
| f094908f54 | |||
| f3617bd83b | |||
| 3bfd88aabb | |||
| d47ef88fcd | |||
| b24639d011 | |||
| 2ae4ca91b4 | |||
| e9d968e060 | |||
| 1652831f1d | |||
| 39c4bb7a49 | |||
| 6cb07a9131 | |||
| e76ad2980f | |||
| af5fd8c819 | |||
| 3b3df4e3cb | |||
| c124576a4d | |||
| 659037eef5 | |||
| 500a378fdf | |||
| 4f3c417753 | |||
| 113fc168ab | |||
| 0ba49eacc9 | |||
| bbd9441fc6 | |||
| 22454ce60b | |||
| 5036cb54cc | |||
| 2eeb07d164 | |||
| ca6ac09dcc | |||
| eadd378f6c | |||
| 7b36afd5f1 | |||
| f677427f68 | |||
| 132ad08885 | |||
| d3e173b6e6 | |||
| 3f2a317af0 | |||
| 892513708b | |||
| 733c8e4c34 | |||
| 80f175daac | |||
| c5e0b29a22 | |||
| bec9b307db | |||
| aca63d4986 | |||
| bae398a9a4 | |||
| 0d001c09c3 | |||
| cd259fe118 | |||
| d7b707a71c | |||
| 17228d27e5 | |||
| 10df5ad0ac | |||
| 7338568125 | |||
| 4adca18337 | |||
| b6f5e1635c | |||
| 0e59a59169 | |||
| 6b45deaf97 | |||
| e72d4a96bf | |||
| b79adc01fa | |||
| 790d717543 | |||
| b1ebd62c78 | |||
| fcc349467f | |||
| cc55e5c6d8 | |||
| a51d4227b6 | |||
| 742aed4f2e | |||
| d3d0682310 | |||
| 53012ff41c | |||
| dd734a01dc | |||
| 2053731ebc | |||
| a3b863d312 | |||
| 7cb0658b00 | |||
| 96c76a8333 | |||
| 925cfba424 | |||
| f63318a20f | |||
| f5d4912ca8 | |||
| 642cf8b5ff | |||
| 0612aa2b65 | |||
| 3937764ac5 | |||
| ed603dcba2 | |||
| 41d2e7d6b6 | |||
| 73d02f3a80 | |||
| e1183be22e | |||
| 2971b5b315 | |||
| 65a3a9773d | |||
| 8b6a4e5759 | |||
| 07df1e3034 | |||
| 09c95b7ea7 | |||
| a6fe8ae0af | |||
| dc2c46e23c | |||
| 0f476a289f | |||
| ae3f058ff0 | |||
| 1315021388 | |||
| ccb231e4f4 | |||
| aad485128e | |||
| 54bb9f4b55 | |||
| af823d6486 | |||
| 487a87df02 | |||
| b14fead592 | |||
| ebf2c8caa5 | |||
| 84855737b3 | |||
| 7a608d1346 | |||
| 3e418ecb6e | |||
| 89769c836f | |||
| 7c8470b1dc | |||
| 81bab528b2 | |||
| d6beac5235 | |||
| a949b40d11 | |||
| 7ca22cd552 | |||
| 30586e634d | |||
| 2b6fe347ae | |||
| f97409dd2d | |||
| c384367f17 | |||
| eea1c6606c | |||
| 8f4f45c524 | |||
| db2392b778 | |||
| ce842648ae | |||
| ad1c4bf202 | |||
| 5969b7cdbc | |||
| 6013d20aef | |||
| dfb3bd8e33 | |||
| d6c2db9620 | |||
| 00dc8a0ad5 | |||
| 9246f21f2a | |||
| 2237319ebb | |||
| 6fa95008bc | |||
| 3789a56225 | |||
| 0a2d9af2a1 | |||
| 2b7a627181 | |||
| f697752b52 | |||
| 914426d887 | |||
| 302e717790 | |||
| 27928fbc94 | |||
| 253056b932 | |||
| 1d1d0d9b6f | |||
| c7887abb64 | |||
| 47525f0dd6 | |||
| 5ac5d91c6b | |||
| 322b5a736b | |||
| 907c054142 | |||
| 7b6d51a9d0 | |||
| d3eba93c7d | |||
| 866e22355c | |||
| fe084b9866 | |||
| 5f7e3025d9 | |||
| 13b8bc1a89 | |||
| 054cec8a5d | |||
| 8dc326e1f1 | |||
| 81dd1aea82 | |||
| 5b2cb426be | |||
| 5fa19f2801 | |||
| 4f5acb8f52 | |||
| cf71c53559 | |||
| 80c98f4d0c | |||
| 73f8ab3aa8 | |||
| da372335bf | |||
| 0af9f664db | |||
| 995eb0cd79 | |||
| 9f07965876 | |||
| 8a4cdd56d4 | |||
| 3252523823 | |||
| 2628f9f61b | |||
| 0d217e15d5 | |||
| 520c85c7b7 | |||
| 82d70e0720 | |||
| 054976c390 | |||
| da8e03e18a | |||
| 4a80dbdd10 | |||
| 013a1731d5 | |||
| e664024853 | |||
| 495f3b9a68 | |||
| 98a6963911 | |||
| c204efaaab | |||
| 0f13137616 | |||
| 864056fcaa | |||
| 5c0830f628 | |||
| e96a2dd681 | |||
| f45332e1ab | |||
| 5508e30854 | |||
| 3e14d63a0a | |||
| eddfddccb2 | |||
| c067ef0216 | |||
| f7d9019b8c | |||
| 519678192f | |||
| c3083a77d4 | |||
| 891ab3951b | |||
| 11251c77ca | |||
| 71e22d9263 | |||
| 3095d96715 | |||
| 198946231c | |||
| b2f0b6f2b4 | |||
| d9c70c7b8c | |||
| 7ae61e7393 | |||
| 984ae35948 | |||
| 0d6cddda4d | |||
| 18e031d346 | |||
| c0332ad98b | |||
| 7f6aaa5314 | |||
| 14aa5fe521 | |||
| 9199967022 | |||
| 04c92c8470 | |||
| 00b22e37df | |||
| aaa810c64a | |||
| b57b2073ac | |||
| 771a9e9cd2 | |||
| cc48f4499a | |||
| 3e2f2ddb56 | |||
| 0ca6df6f09 | |||
| 37a379f959 | |||
| 625d6c2ed7 | |||
| c2edb3e22f | |||
| fedbd54325 | |||
| 134d2bd766 | |||
| 9eb2cd7327 | |||
| c0347c80b2 | |||
| d9ff84e39e | |||
| 7256e6d203 | |||
| c083fd895c | |||
| 0cd7a3d216 | |||
| aa4fc44a80 | |||
| f07d49e877 | |||
| 45be91ff48 | |||
| c657b3d072 | |||
| 5dfb3ded17 | |||
| 0104e99caa | |||
| e16593c9b1 | |||
| 1cc69df0f4 | |||
| 2db576f52b | |||
| 421edce623 | |||
| 549b83504f | |||
| d10ebd1a68 | |||
| 4e3d921f1a | |||
| 1d6e1ec61c | |||
| db3cc11195 | |||
| d64efa6a68 | |||
| 7b5905bda6 | |||
| f5ba5ffe80 | |||
| 0113c4f834 | |||
| 1c2ed83960 | |||
| 7a236b11b8 | |||
| a0328bbcf8 | |||
| 46e58b434a | |||
| 7955f8a7cb | |||
| 263fd37590 | |||
| ba37bf13d6 | |||
| b59d71546b |
148
.clang-format
Normal file
148
.clang-format
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
Language: Cpp
|
||||
# BasedOnStyle: Google
|
||||
AccessModifierOffset: -1
|
||||
AlignAfterOpenBracket: Align
|
||||
AlignConsecutiveAssignments: false
|
||||
AlignConsecutiveDeclarations: true
|
||||
AlignEscapedNewlines: Left
|
||||
AlignOperands: true
|
||||
AlignTrailingComments: true
|
||||
AllowAllParametersOfDeclarationOnNextLine: true
|
||||
AllowShortBlocksOnASingleLine: true
|
||||
AllowShortCaseLabelsOnASingleLine: true
|
||||
AllowShortFunctionsOnASingleLine: false
|
||||
AllowShortIfStatementsOnASingleLine: true
|
||||
AllowShortLoopsOnASingleLine: false
|
||||
AlwaysBreakAfterDefinitionReturnType: None
|
||||
AlwaysBreakAfterReturnType: None
|
||||
AlwaysBreakBeforeMultilineStrings: true
|
||||
AlwaysBreakTemplateDeclarations: Yes
|
||||
BinPackArguments: true
|
||||
BinPackParameters: true
|
||||
BraceWrapping:
|
||||
AfterClass: false
|
||||
AfterControlStatement: false
|
||||
AfterEnum: false
|
||||
AfterFunction: false
|
||||
AfterNamespace: false
|
||||
AfterObjCDeclaration: false
|
||||
AfterStruct: false
|
||||
AfterUnion: false
|
||||
AfterExternBlock: false
|
||||
BeforeCatch: false
|
||||
BeforeElse: false
|
||||
IndentBraces: false
|
||||
SplitEmptyFunction: true
|
||||
SplitEmptyRecord: true
|
||||
SplitEmptyNamespace: true
|
||||
BreakBeforeBinaryOperators: None
|
||||
BreakBeforeBraces: Attach
|
||||
BreakBeforeInheritanceComma: false
|
||||
BreakInheritanceList: BeforeColon
|
||||
BreakBeforeTernaryOperators: true
|
||||
BreakConstructorInitializersBeforeComma: false
|
||||
BreakConstructorInitializers: BeforeColon
|
||||
BreakAfterJavaFieldAnnotations: false
|
||||
BreakStringLiterals: true
|
||||
ColumnLimit: 80
|
||||
CommentPragmas: '^ IWYU pragma:'
|
||||
CompactNamespaces: false
|
||||
ConstructorInitializerAllOnOneLineOrOnePerLine: true
|
||||
ConstructorInitializerIndentWidth: 4
|
||||
ContinuationIndentWidth: 4
|
||||
Cpp11BracedListStyle: true
|
||||
DerivePointerAlignment: true
|
||||
DisableFormat: false
|
||||
ExperimentalAutoDetectBinPacking: false
|
||||
FixNamespaceComments: true
|
||||
ForEachMacros:
|
||||
- foreach
|
||||
- Q_FOREACH
|
||||
- BOOST_FOREACH
|
||||
IncludeBlocks: Preserve
|
||||
IncludeCategories:
|
||||
- Regex: '^<ext/.*\.h>'
|
||||
Priority: 2
|
||||
- Regex: '^<.*\.h>'
|
||||
Priority: 1
|
||||
- Regex: '^<.*'
|
||||
Priority: 2
|
||||
- Regex: '.*'
|
||||
Priority: 3
|
||||
IncludeIsMainRegex: '([-_](test|unittest))?$'
|
||||
IndentCaseLabels: true
|
||||
IndentPPDirectives: None
|
||||
IndentWidth: 2
|
||||
IndentWrappedFunctionNames: false
|
||||
JavaScriptQuotes: Leave
|
||||
JavaScriptWrapImports: true
|
||||
KeepEmptyLinesAtTheStartOfBlocks: false
|
||||
MacroBlockBegin: ''
|
||||
MacroBlockEnd: ''
|
||||
MaxEmptyLinesToKeep: 1
|
||||
NamespaceIndentation: None
|
||||
ObjCBinPackProtocolList: Never
|
||||
ObjCBlockIndentWidth: 2
|
||||
ObjCSpaceAfterProperty: false
|
||||
ObjCSpaceBeforeProtocolList: true
|
||||
PenaltyBreakAssignment: 2
|
||||
PenaltyBreakBeforeFirstCallParameter: 1
|
||||
PenaltyBreakComment: 300
|
||||
PenaltyBreakFirstLessLess: 120
|
||||
PenaltyBreakString: 1000
|
||||
PenaltyBreakTemplateDeclaration: 10
|
||||
PenaltyExcessCharacter: 1000000
|
||||
PenaltyReturnTypeOnItsOwnLine: 200
|
||||
PointerAlignment: Right
|
||||
RawStringFormats:
|
||||
- Language: Cpp
|
||||
Delimiters:
|
||||
- cc
|
||||
- CC
|
||||
- cpp
|
||||
- Cpp
|
||||
- CPP
|
||||
- 'c++'
|
||||
- 'C++'
|
||||
CanonicalDelimiter: ''
|
||||
BasedOnStyle: google
|
||||
- Language: TextProto
|
||||
Delimiters:
|
||||
- pb
|
||||
- PB
|
||||
- proto
|
||||
- PROTO
|
||||
EnclosingFunctions:
|
||||
- EqualsProto
|
||||
- EquivToProto
|
||||
- PARSE_PARTIAL_TEXT_PROTO
|
||||
- PARSE_TEST_PROTO
|
||||
- PARSE_TEXT_PROTO
|
||||
- ParseTextOrDie
|
||||
- ParseTextProtoOrDie
|
||||
CanonicalDelimiter: ''
|
||||
BasedOnStyle: google
|
||||
ReflowComments: true
|
||||
SortIncludes: false
|
||||
SortUsingDeclarations: true
|
||||
SpaceAfterCStyleCast: false
|
||||
SpaceAfterTemplateKeyword: true
|
||||
SpaceBeforeAssignmentOperators: true
|
||||
SpaceBeforeCpp11BracedList: false
|
||||
SpaceBeforeCtorInitializerColon: true
|
||||
SpaceBeforeInheritanceColon: true
|
||||
SpaceBeforeParens: ControlStatements
|
||||
SpaceBeforeRangeBasedForLoopColon: true
|
||||
SpaceInEmptyParentheses: false
|
||||
SpacesBeforeTrailingComments: 2
|
||||
SpacesInAngles: false
|
||||
SpacesInContainerLiterals: true
|
||||
SpacesInCStyleCastParentheses: false
|
||||
SpacesInParentheses: false
|
||||
SpacesInSquareBrackets: false
|
||||
Standard: Auto
|
||||
TabWidth: 8
|
||||
UseTab: Never
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
117
.custom-format.py
Executable file
117
.custom-format.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
#
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop++ - custom code formatter
|
||||
# --------------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintaned by Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2015, 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
# string_re = re.compile('(\\"(\\\\.|[^"\\\\])*\\")') # future use
|
||||
|
||||
with open(".clang-format") as f:
|
||||
fmt = f.read()
|
||||
|
||||
CLANG_FORMAT_BIN = os.getenv("CLANG_FORMAT_BIN")
|
||||
if CLANG_FORMAT_BIN is None:
|
||||
p = subprocess.Popen(["clang-format", "--version"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
o, _ = p.communicate()
|
||||
o = str(o, "utf-8")
|
||||
o = o[len("clang-format version "):].strip()
|
||||
o = o[:o.find(".")]
|
||||
o = int(o)
|
||||
if o < 7:
|
||||
if subprocess.call(['which', 'clang-format-7'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE) == 0:
|
||||
CLANG_FORMAT_BIN = 'clang-format-7'
|
||||
elif subprocess.call(['which', 'clang-format-8'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE) == 0:
|
||||
CLANG_FORMAT_BIN = 'clang-format-8'
|
||||
elif subprocess.call(['which', 'clang-format-9'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE) == 0:
|
||||
CLANG_FORMAT_BIN = 'clang-format-9'
|
||||
elif subprocess.call(['which', 'clang-format-10'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE) == 0:
|
||||
CLANG_FORMAT_BIN = 'clang-format-10'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print ("clang-format 7 or above is needed. Aborted.")
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
CLANG_FORMAT_BIN = 'clang-format'
|
||||
|
||||
COLUMN_LIMIT = 80
|
||||
for line in fmt.split("\n"):
|
||||
line = line.split(":")
|
||||
if line[0].strip() == "ColumnLimit":
|
||||
COLUMN_LIMIT = int(line[1].strip())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def custom_format(filename):
|
||||
p = subprocess.Popen([CLANG_FORMAT_BIN, filename], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
src, _ = p.communicate()
|
||||
src = str(src, "utf-8")
|
||||
|
||||
in_define = False
|
||||
last_line = None
|
||||
out = ""
|
||||
|
||||
for line in src.split("\n"):
|
||||
if line.startswith("#"):
|
||||
if line.startswith("#define"):
|
||||
in_define = True
|
||||
|
||||
if "/*" in line and not line.strip().startswith("/*") and line.endswith("*/") and len(line) < (COLUMN_LIMIT-2):
|
||||
cmt_start = line.rfind("/*")
|
||||
line = line[:cmt_start] + " " * (COLUMN_LIMIT-2 - len(line)) + line[cmt_start:]
|
||||
|
||||
define_padding = 0
|
||||
if last_line is not None and in_define and last_line.endswith("\\"):
|
||||
last_line = last_line[:-1]
|
||||
define_padding = max(0, len(last_line[last_line.rfind("\n")+1:]))
|
||||
|
||||
if last_line is not None and last_line.strip().endswith("{") and line.strip() != "":
|
||||
line = (" " * define_padding + "\\" if in_define else "") + "\n" + line
|
||||
elif last_line is not None and last_line.strip().startswith("}") and line.strip() != "":
|
||||
line = (" " * define_padding + "\\" if in_define else "") + "\n" + line
|
||||
elif line.strip().startswith("}") and last_line is not None and last_line.strip() != "":
|
||||
line = (" " * define_padding + "\\" if in_define else "") + "\n" + line
|
||||
|
||||
if not line.endswith("\\"):
|
||||
in_define = False
|
||||
|
||||
out += line + "\n"
|
||||
last_line = line
|
||||
|
||||
return (out)
|
||||
|
||||
args = sys.argv[1:]
|
||||
if len(args) == 0:
|
||||
print ("Usage: ./format.py [-i] <filename>")
|
||||
print ()
|
||||
print (" The -i option, if specified, let the script to modify in-place")
|
||||
print (" the source files. By default the results are written to stdout.")
|
||||
print()
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
in_place = False
|
||||
if args[0] == "-i":
|
||||
in_place = True
|
||||
args = args[1:]
|
||||
|
||||
for filename in args:
|
||||
code = custom_format(filename)
|
||||
if in_place:
|
||||
with open(filename, "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(code)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(code)
|
||||
|
||||
39
.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
39
.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
.test
|
||||
.test2
|
||||
*.o
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
afl-analyze
|
||||
afl-as
|
||||
afl-clang
|
||||
afl-clang++
|
||||
afl-clang-fast
|
||||
afl-clang-fast++
|
||||
afl-fuzz
|
||||
afl-g++
|
||||
afl-gcc
|
||||
afl-gcc-fast
|
||||
afl-g++-fast
|
||||
afl-gotcpu
|
||||
afl-qemu-trace
|
||||
afl-showmap
|
||||
afl-tmin
|
||||
afl-analyze.8
|
||||
afl-clang-fast++.8
|
||||
afl-clang-fast.8
|
||||
afl-cmin.8
|
||||
afl-fuzz.8
|
||||
afl-gcc.8
|
||||
afl-gcc-fast.8
|
||||
afl-g++-fast.8
|
||||
afl-gotcpu.8
|
||||
afl-plot.8
|
||||
afl-showmap.8
|
||||
afl-system-config.8
|
||||
afl-tmin.8
|
||||
afl-whatsup.8
|
||||
qemu_mode/libcompcov/compcovtest
|
||||
as
|
||||
qemu_mode/qemu-*
|
||||
unicorn_mode/unicorn
|
||||
unicorn_mode/unicorn-*
|
||||
unicorn_mode/*.tar.gz
|
||||
11
.travis.yml
Normal file
11
.travis.yml
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
language: c
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
- AFL_I_DONT_CARE_ABOUT_MISSING_CRASHES=1 AFL_NO_UI=1
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- make
|
||||
- ./afl-gcc ./test-instr.c -o test-instr
|
||||
- mkdir seeds; mkdir out
|
||||
- echo "" > seeds/nil_seed
|
||||
- timeout --preserve-status 5s ./afl-fuzz -i seeds -o out/ -- ./test-instr
|
||||
1
Android.mk
Symbolic link
1
Android.mk
Symbolic link
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
Makefile
|
||||
14
CONTRIBUTING.md
Normal file
14
CONTRIBUTING.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
# How to submit a Pull Request to AFLplusplus
|
||||
|
||||
Each modified source file, before merging, must be formatted.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
make code-formatter
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This should be fine if you modified one of the file already present in the
|
||||
project, otherwise run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i file-that-you-have-created.c
|
||||
```
|
||||
296
Makefile
296
Makefile
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - makefile
|
||||
# -----------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -13,46 +13,127 @@
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# For Heiko:
|
||||
#TEST_MMAP=1
|
||||
|
||||
PROGNAME = afl
|
||||
VERSION = $(shell grep '^\#define VERSION ' config.h | cut -d '"' -f2)
|
||||
VERSION = $(shell grep '^\#define VERSION ' include/config.h | cut -d '"' -f2)
|
||||
|
||||
PREFIX ?= /usr/local
|
||||
BIN_PATH = $(PREFIX)/bin
|
||||
HELPER_PATH = $(PREFIX)/lib/afl
|
||||
DOC_PATH = $(PREFIX)/share/doc/afl
|
||||
MISC_PATH = $(PREFIX)/share/afl
|
||||
MAN_PATH = $(PREFIX)/man/man8
|
||||
|
||||
# PROGS intentionally omit afl-as, which gets installed elsewhere.
|
||||
|
||||
PROGS = afl-gcc afl-fuzz afl-showmap afl-tmin afl-gotcpu afl-analyze
|
||||
SH_PROGS = afl-plot afl-cmin afl-whatsup afl-system-config
|
||||
MANPAGES=$(foreach p, $(PROGS) $(SH_PROGS), $(p).8)
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign \
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign -I include/ \
|
||||
-DAFL_PATH=\"$(HELPER_PATH)\" -DDOC_PATH=\"$(DOC_PATH)\" \
|
||||
-DBIN_PATH=\"$(BIN_PATH)\"
|
||||
-DBIN_PATH=\"$(BIN_PATH)\" -Wno-unused-function
|
||||
|
||||
AFL_FUZZ_FILES = $(wildcard src/afl-fuzz*.c)
|
||||
|
||||
PYTHON_INCLUDE ?= /usr/include/python2.7
|
||||
|
||||
ifneq "$(filter Linux GNU%,$(shell uname))" ""
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -ldl
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifneq "$(findstring FreeBSD, $(shell uname))" ""
|
||||
CFLAGS += -pthread
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifneq "$(findstring NetBSD, $(shell uname))" ""
|
||||
CFLAGS += -pthread
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(findstring clang, $(shell $(CC) --version 2>/dev/null))" ""
|
||||
TEST_CC = afl-gcc
|
||||
else
|
||||
TEST_CC = afl-clang
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
COMM_HDR = alloc-inl.h config.h debug.h types.h
|
||||
COMM_HDR = include/alloc-inl.h include/config.h include/debug.h include/types.h
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell echo '\#include <Python.h>@int main() {return 0; }' | tr @ '\n' | $(CC) -x c - -o .test -I$(PYTHON_INCLUDE) -lpython2.7 2>/dev/null && echo 1 || echo 0 )" "1"
|
||||
PYTHON_OK=1
|
||||
PYFLAGS=-DUSE_PYTHON -I$(PYTHON_INCLUDE) -lpython2.7
|
||||
else
|
||||
PYTHON_OK=0
|
||||
PYFLAGS=
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifdef STATIC
|
||||
$(info Compiling static version of binaries)
|
||||
# Disable python for static compilation to simplify things
|
||||
PYTHON_OK=0
|
||||
PYFLAGS=
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS += -static
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lm -lrt -lpthread -lz -lutil
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell echo '\#include <sys/ipc.h>@\#include <sys/shm.h>@int main() { int _id = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 65536, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0600); shmctl(_id, IPC_RMID, 0); return 0;}' | tr @ '\n' | $(CC) -x c - -o .test2 2>/dev/null && echo 1 || echo 0 )" "1"
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=1
|
||||
else
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=0
|
||||
CFLAGS+=-DUSEMMAP=1
|
||||
LDFLAGS+=-Wno-deprecated-declarations -lrt
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(TEST_MMAP)" "1"
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=0
|
||||
CFLAGS+=-DUSEMMAP=1
|
||||
LDFLAGS+=-Wno-deprecated-declarations -lrt
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
all: test_x86 test_shm test_python27 ready $(PROGS) afl-as test_build all_done
|
||||
|
||||
man: $(MANPAGES)
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C llvm_mode
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C gcc_plugin
|
||||
|
||||
tests: source-only
|
||||
@cd test ; ./test.sh
|
||||
|
||||
performance-tests: performance-test
|
||||
test-performance: performance-test
|
||||
|
||||
performance-test: source-only
|
||||
@cd test ; ./test-performance.sh
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
help:
|
||||
@echo "HELP --- the following make targets exist:"
|
||||
@echo "=========================================="
|
||||
@echo "all: just the main afl++ binaries"
|
||||
@echo "binary-only: everything for binary-only fuzzing: qemu_mode, unicorn_mode, libdislocator, libtokencap"
|
||||
@echo "source-only: everything for source code fuzzing: llvm_mode, libdislocator, libtokencap"
|
||||
@echo "distrib: everything (for both binary-only and source code fuzzing)"
|
||||
@echo "man: creates simple man pages from the help option of the programs"
|
||||
@echo "install: installs everything you have compiled with the build option above"
|
||||
@echo "clean: cleans everything. for qemu_mode and unicorn_mode it means it deletes all downloads as well"
|
||||
@echo "tests: this runs the test framework. It is more catered for the developers, but if you run into problems this helps pinpointing the problem"
|
||||
@echo "document: creates afl-fuzz-document which will only do one run and save all manipulated inputs into out/queue/mutations"
|
||||
@echo "help: shows these build options :-)"
|
||||
@echo "=========================================="
|
||||
@echo "Recommended: \"distrib\" or \"source-only\", then \"install\""
|
||||
|
||||
all: test_x86 $(PROGS) afl-as test_build all_done
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef AFL_NO_X86
|
||||
|
||||
test_x86:
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for the ability to compile x86 code..."
|
||||
@echo 'main() { __asm__("xorb %al, %al"); }' | $(CC) -w -x c - -o .test || ( echo; echo "Oops, looks like your compiler can't generate x86 code."; echo; echo "Don't panic! You can use the LLVM or QEMU mode, but see docs/INSTALL first."; echo "(To ignore this error, set AFL_NO_X86=1 and try again.)"; echo; exit 1 )
|
||||
@rm -f .test
|
||||
@echo "[+] Everything seems to be working, ready to compile."
|
||||
@echo 'main() { __asm__("xorb %al, %al"); }' | $(CC) -w -x c - -o .test1 || ( echo; echo "Oops, looks like your compiler can't generate x86 code."; echo; echo "Don't panic! You can use the LLVM or QEMU mode, but see docs/INSTALL first."; echo "(To ignore this error, set AFL_NO_X86=1 and try again.)"; echo; exit 1 )
|
||||
@rm -f .test1
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,38 +142,105 @@ test_x86:
|
||||
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
afl-gcc: afl-gcc.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(SHMAT_OK)" "1"
|
||||
|
||||
test_shm:
|
||||
@echo "[+] shmat seems to be working."
|
||||
@rm -f .test2
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
|
||||
test_shm:
|
||||
@echo "[-] shmat seems not to be working, switching to mmap implementation"
|
||||
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(PYTHON_OK)" "1"
|
||||
|
||||
test_python27:
|
||||
@rm -f .test 2> /dev/null
|
||||
@echo "[+] Python 2.7 support seems to be working."
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
|
||||
test_python27:
|
||||
@echo "[-] You seem to need to install the package python2.7-dev, but it is optional so we continue"
|
||||
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ready:
|
||||
@echo "[+] Everything seems to be working, ready to compile."
|
||||
|
||||
afl-gcc: src/afl-gcc.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) src/$@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
set -e; for i in afl-g++ afl-clang afl-clang++; do ln -sf afl-gcc $$i; done
|
||||
|
||||
afl-as: afl-as.c afl-as.h $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
afl-as: src/afl-as.c include/afl-as.h $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) src/$@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
ln -sf afl-as as
|
||||
|
||||
afl-fuzz: afl-fuzz.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
src/afl-common.o : src/afl-common.c include/common.h
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c src/afl-common.c -o src/afl-common.o
|
||||
|
||||
afl-showmap: afl-showmap.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
src/afl-forkserver.o : src/afl-forkserver.c include/forkserver.h
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c src/afl-forkserver.c -o src/afl-forkserver.o
|
||||
|
||||
afl-tmin: afl-tmin.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
src/afl-sharedmem.o : src/afl-sharedmem.c include/sharedmem.h
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c src/afl-sharedmem.c -o src/afl-sharedmem.o
|
||||
|
||||
afl-analyze: afl-analyze.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
afl-fuzz: include/afl-fuzz.h $(AFL_FUZZ_FILES) src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(AFL_FUZZ_FILES) src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o -o $@ $(PYFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
afl-showmap: src/afl-showmap.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
afl-tmin: src/afl-tmin.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
afl-analyze: src/afl-analyze.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
afl-gotcpu: src/afl-gotcpu.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) src/$@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# document all mutations and only do one run (use with only one input file!)
|
||||
document: include/afl-fuzz.h $(AFL_FUZZ_FILES) src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(AFL_FUZZ_FILES) -D_AFL_DOCUMENT_MUTATIONS src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o -o afl-fuzz-document $(LDFLAGS) $(PYFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
code-format:
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i src/*.c
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i include/*.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i libdislocator/*.c
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i libtokencap/*.c
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i llvm_mode/*.c
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i llvm_mode/*.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i llvm_mode/*.cc
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i gcc_plugin/*.c
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i gcc_plugin/*.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i gcc_plugin/*.cc
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i qemu_mode/patches/*.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i qemu_mode/libcompcov/*.c
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i qemu_mode/libcompcov/*.cc
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i qemu_mode/libcompcov/*.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i unicorn_mode/patches/*.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i *.h
|
||||
./.custom-format.py -i *.c
|
||||
|
||||
afl-gotcpu: afl-gotcpu.c $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $@.c -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef AFL_NO_X86
|
||||
|
||||
test_build: afl-gcc afl-as afl-showmap
|
||||
@echo "[*] Testing the CC wrapper and instrumentation output..."
|
||||
unset AFL_USE_ASAN AFL_USE_MSAN; AFL_QUIET=1 AFL_INST_RATIO=100 AFL_PATH=. ./$(TEST_CC) $(CFLAGS) test-instr.c -o test-instr $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
echo 0 | ./afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr0 ./test-instr
|
||||
unset AFL_USE_ASAN AFL_USE_MSAN AFL_CC; AFL_QUIET=1 AFL_INST_RATIO=100 AFL_PATH=. ./$(TEST_CC) $(CFLAGS) test-instr.c -o test-instr $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
./afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr0 ./test-instr < /dev/null
|
||||
echo 1 | ./afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr1 ./test-instr
|
||||
@rm -f test-instr
|
||||
@cmp -s .test-instr0 .test-instr1; DR="$$?"; rm -f .test-instr0 .test-instr1; if [ "$$DR" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Oops, the instrumentation does not seem to be behaving correctly!"; echo; echo "Please ping <lcamtuf@google.com> to troubleshoot the issue."; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
@cmp -s .test-instr0 .test-instr1; DR="$$?"; rm -f .test-instr0 .test-instr1; if [ "$$DR" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Oops, the instrumentation does not seem to be behaving correctly!"; echo; echo "Please post to https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus/issues to troubleshoot the issue."; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
@echo "[+] All right, the instrumentation seems to be working!"
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
@ -102,29 +250,73 @@ test_build: afl-gcc afl-as afl-showmap
|
||||
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
all_done: test_build
|
||||
@if [ ! "`which clang 2>/dev/null`" = "" ]; then echo "[+] LLVM users: see llvm_mode/README.llvm for a faster alternative to afl-gcc."; fi
|
||||
@echo "[+] All done! Be sure to review README - it's pretty short and useful."
|
||||
@echo "[+] All done! Be sure to review the README.md - it's pretty short and useful."
|
||||
@if [ "`uname`" = "Darwin" ]; then printf "\nWARNING: Fuzzing on MacOS X is slow because of the unusually high overhead of\nfork() on this OS. Consider using Linux or *BSD. You can also use VirtualBox\n(virtualbox.org) to put AFL inside a Linux or *BSD VM.\n\n"; fi
|
||||
@! tty <&1 >/dev/null || printf "\033[0;30mNOTE: If you can read this, your terminal probably uses white background.\nThis will make the UI hard to read. See docs/status_screen.txt for advice.\033[0m\n" 2>/dev/null
|
||||
|
||||
.NOTPARALLEL: clean
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -f $(PROGS) afl-as as afl-g++ afl-clang afl-clang++ *.o *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]* *.stackdump test .test test-instr .test-instr0 .test-instr1 qemu_mode/qemu-2.10.0.tar.bz2 afl-qemu-trace
|
||||
rm -rf out_dir qemu_mode/qemu-2.10.0
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C llvm_mode clean
|
||||
rm -f $(PROGS) afl-as as afl-g++ afl-clang afl-clang++ *.o src/*.o *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]* *.stackdump .test .test1 .test2 test-instr .test-instr0 .test-instr1 qemu_mode/qemu-3.1.1.tar.xz afl-qemu-trace afl-gcc-fast afl-gcc-pass.so afl-gcc-rt.o afl-g++-fast *.so unicorn_mode/24f55a7973278f20f0de21b904851d99d4716263.tar.gz *.8
|
||||
rm -rf out_dir qemu_mode/qemu-3.1.1 unicorn_mode/unicorn *.dSYM */*.dSYM
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C llvm_mode clean
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C gcc_plugin clean
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libdislocator clean
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libtokencap clean
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/unsigaction clean
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/libcompcov clean
|
||||
|
||||
install: all
|
||||
distrib: all
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C llvm_mode
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C gcc_plugin
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libdislocator
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libtokencap
|
||||
cd qemu_mode && sh ./build_qemu_support.sh
|
||||
cd unicorn_mode && sh ./build_unicorn_support.sh
|
||||
|
||||
binary-only: all
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libdislocator
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libtokencap
|
||||
cd qemu_mode && sh ./build_qemu_support.sh
|
||||
cd unicorn_mode && sh ./build_unicorn_support.sh
|
||||
|
||||
source-only: all
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C llvm_mode
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C gcc_plugin
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libdislocator
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C libtokencap
|
||||
|
||||
%.8: %
|
||||
@echo .TH $* 8 `date -I` "afl++" > $@
|
||||
@echo .SH NAME >> $@
|
||||
@echo .B $* >> $@
|
||||
@echo >> $@
|
||||
@echo .SH SYNOPSIS >> $@
|
||||
@./$* -h 2>&1 | head -n 3 | tail -n 1 | sed 's/^\.\///' >> $@
|
||||
@echo >> $@
|
||||
@echo .SH OPTIONS >> $@
|
||||
@echo .nf >> $@
|
||||
@./$* -h 2>&1 | tail -n +4 >> $@
|
||||
@echo >> $@
|
||||
@echo .SH AUTHOR >> $@
|
||||
@echo "afl++ was written by Michal \"lcamtuf\" Zalewski and is maintained by Marc \"van Hauser\" Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>, Heiko \"hexcoder-\" Eissfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>" >> $@
|
||||
@echo The homepage of afl++ is: https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus >> $@
|
||||
@echo >> $@
|
||||
@echo .SH LICENSE >> $@
|
||||
@echo Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004 >> $@
|
||||
|
||||
install: all $(MANPAGES)
|
||||
mkdir -p -m 755 $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH) $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH) $${DESTDIR}$(DOC_PATH) $${DESTDIR}$(MISC_PATH)
|
||||
rm -f $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-plot.sh
|
||||
install -m 755 $(PROGS) $(SH_PROGS) $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)
|
||||
rm -f $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-as
|
||||
if [ -f afl-qemu-trace ]; then install -m 755 afl-qemu-trace $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f afl-gcc-fast ]; then set e; install -m 755 afl-gcc-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH); ln -sf afl-gcc-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-g++-fast; install -m 755 afl-gcc-pass.so afl-gcc-rt.o $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
ifndef AFL_TRACE_PC
|
||||
if [ -f afl-clang-fast -a -f afl-llvm-pass.so -a -f afl-llvm-rt.o ]; then set -e; install -m 755 afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH); ln -sf afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang-fast++; install -m 755 afl-llvm-pass.so afl-llvm-rt.o $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f afl-clang-fast -a -f libLLVMInsTrim.so -a -f afl-llvm-rt.o ]; then set -e; install -m 755 afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH); ln -sf afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang-fast++; install -m 755 libLLVMInsTrim.so afl-llvm-pass.so afl-llvm-rt.o $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
else
|
||||
if [ -f afl-clang-fast -a -f afl-llvm-rt.o ]; then set -e; install -m 755 afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH); ln -sf afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang-fast++; install -m 755 afl-llvm-rt.o $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
endif
|
||||
@ -133,25 +325,33 @@ endif
|
||||
if [ -f compare-transform-pass.so ]; then set -e; install -m 755 compare-transform-pass.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f split-compares-pass.so ]; then set -e; install -m 755 split-compares-pass.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f split-switches-pass.so ]; then set -e; install -m 755 split-switches-pass.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f libdislocator.so ]; then set -e; install -m 755 libdislocator.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f libtokencap.so ]; then set -e; install -m 755 libtokencap.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
if [ -f libcompcov.so ]; then set -e; install -m 755 libcompcov.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH); fi
|
||||
|
||||
set -e; ln -sf afl-gcc $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-g++
|
||||
set -e; if [ -f afl-clang-fast ] ; then ln -sf afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang ; ln -sf afl-clang-fast $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang++ ; else ln -sf afl-gcc $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang ; ln -sf afl-gcc $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/afl-clang++; fi
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -m 0755 -p ${DESTDIR}$(MAN_PATH)
|
||||
install -m0644 -D *.8 ${DESTDIR}$(MAN_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
set -e; for i in afl-g++ afl-clang afl-clang++; do ln -sf afl-gcc $${DESTDIR}$(BIN_PATH)/$$i; done
|
||||
install -m 755 afl-as $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
ln -sf afl-as $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)/as
|
||||
install -m 644 docs/README docs/ChangeLog docs/*.txt $${DESTDIR}$(DOC_PATH)
|
||||
install -m 644 docs/README.md docs/ChangeLog docs/*.txt $${DESTDIR}$(DOC_PATH)
|
||||
cp -r testcases/ $${DESTDIR}$(MISC_PATH)
|
||||
cp -r dictionaries/ $${DESTDIR}$(MISC_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
publish: clean
|
||||
test "`basename $$PWD`" = "afl" || exit 1
|
||||
test -f ~/www/afl/releases/$(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz; if [ "$$?" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Change program version in config.h, mmkay?"; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
cd ..; rm -rf $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION); cp -pr $(PROGNAME) $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION); \
|
||||
tar -cvz -f ~/www/afl/releases/$(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION)
|
||||
chmod 644 ~/www/afl/releases/$(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz
|
||||
( cd ~/www/afl/releases/; ln -s -f $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz $(PROGNAME)-latest.tgz )
|
||||
cat docs/README >~/www/afl/README.txt
|
||||
cat docs/status_screen.txt >~/www/afl/status_screen.txt
|
||||
cat docs/historical_notes.txt >~/www/afl/historical_notes.txt
|
||||
cat docs/technical_details.txt >~/www/afl/technical_details.txt
|
||||
cat docs/ChangeLog >~/www/afl/ChangeLog.txt
|
||||
cat docs/QuickStartGuide.txt >~/www/afl/QuickStartGuide.txt
|
||||
echo -n "$(VERSION)" >~/www/afl/version.txt
|
||||
#publish: clean
|
||||
# test "`basename $$PWD`" = "afl" || exit 1
|
||||
# test -f ~/www/afl/releases/$(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz; if [ "$$?" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Change program version in config.h, mmkay?"; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
# cd ..; rm -rf $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION); cp -pr $(PROGNAME) $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION); \
|
||||
# tar -cvz -f ~/www/afl/releases/$(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION)
|
||||
# chmod 644 ~/www/afl/releases/$(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz
|
||||
# ( cd ~/www/afl/releases/; ln -s -f $(PROGNAME)-$(VERSION).tgz $(PROGNAME)-latest.tgz )
|
||||
# cat docs/README.md >~/www/afl/README.txt
|
||||
# cat docs/status_screen.txt >~/www/afl/status_screen.txt
|
||||
# cat docs/historical_notes.txt >~/www/afl/historical_notes.txt
|
||||
# cat docs/technical_details.txt >~/www/afl/technical_details.txt
|
||||
# cat docs/ChangeLog >~/www/afl/ChangeLog.txt
|
||||
# cat docs/QuickStartGuide.txt >~/www/afl/QuickStartGuide.txt
|
||||
# echo -n "$(VERSION)" >~/www/afl/version.txt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,42 +1,120 @@
|
||||
============================
|
||||
american fuzzy lop plus plus
|
||||
============================
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop plus plus (afl++)
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Release Version: 2.58c
|
||||
|
||||
Repository: https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus
|
||||
Github Version: 2.58d
|
||||
|
||||
afl++ is maintained by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de> and Heiko Eissfeldt
|
||||
<heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> as there have been no updates to afl since
|
||||
November 2017.
|
||||
includes all necessary/interesting changes from Google's afl 2.56b
|
||||
|
||||
This version has several bug fixes, new features and speed enhancements
|
||||
based on community patches from https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-patches
|
||||
To see the list of which patches have been applied, see the PATCHES file.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally AFLfast's power schedules by Marcel Boehme from
|
||||
github.com/mboehme/aflfast have been incorporated.
|
||||
Originally developed by Michal "lcamtuf" Zalewski.
|
||||
|
||||
Repository: [https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus](https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus)
|
||||
|
||||
afl++ is maintained by Marc "van Hauser" Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko "hexcoder-" Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that although afl now has a Google afl repository [https://github.com/Google/afl](https://github.com/Google/afl),
|
||||
it is unlikely to receive any noteable enhancements: [https://twitter.com/Dor3s/status/1154737061787660288](https://twitter.com/Dor3s/status/1154737061787660288)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## The enhancements compared to the original stock afl
|
||||
|
||||
Many improvements were made over the official afl release - which did not
|
||||
get any feature improvements since November 2017.
|
||||
|
||||
Among other changes afl++ has a more performant llvm_mode, supports
|
||||
llvm up to version 9, QEMU 3.1, more speed and crashfixes for QEMU,
|
||||
better *BSD and Android support and much, much more.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally the following patches have been integrated:
|
||||
|
||||
* AFLfast's power schedules by Marcel Böhme: [https://github.com/mboehme/aflfast](https://github.com/mboehme/aflfast)
|
||||
|
||||
* The new excellent MOpt mutator: [https://github.com/puppet-meteor/MOpt-AFL](https://github.com/puppet-meteor/MOpt-AFL)
|
||||
|
||||
* InsTrim, a very effective CFG llvm_mode instrumentation implementation for large targets: [https://github.com/csienslab/instrim](https://github.com/csienslab/instrim)
|
||||
|
||||
* C. Holler's afl-fuzz Python mutator module and llvm_mode whitelist support: [https://github.com/choller/afl](https://github.com/choller/afl)
|
||||
|
||||
* Custom mutator by a library (instead of Python) by kyakdan
|
||||
|
||||
* unicorn_mode which allows fuzzing of binaries from completely different platforms (integration provided by domenukk)
|
||||
|
||||
* laf-intel or CompCov support for llvm_mode, qemu_mode and unicorn_mode
|
||||
|
||||
* NeverZero patch for afl-gcc, llvm_mode, qemu_mode and unicorn_mode which prevents a wrapping map value to zero, increases coverage
|
||||
|
||||
* Persistent mode and deferred forkserver for qemu_mode
|
||||
|
||||
* Win32 PE binary-only fuzzing with QEMU and Wine
|
||||
|
||||
A more thorough list is available in the PATCHES file.
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature/Instrumentation | AFL-GCC | LLVM_MODE | GCC_PLUGIN | QEMU_MODE | Unicorn |
|
||||
| ----------------------- |:-------:|:---------:|:----------:|:---------:|:-------:|
|
||||
| laf-intel / CompCov | | x | | x | x |
|
||||
| NeverZero | X | x(1) | | x | x |
|
||||
| Persistent mode | | x | X | x | |
|
||||
| Whitelist | | x | X | | |
|
||||
| InsTrim | | x | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
(1) only in LLVM >= 9.0 due to a bug in llvm in previous versions
|
||||
|
||||
Plus it was upgraded to qemu 3.1 from 2.1 with the work of
|
||||
https://github.com/andreafioraldi/afl and got the community patches applied
|
||||
to it.
|
||||
|
||||
So all in all this is the best-of AFL that is currently out there :-)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Released under terms and conditions of Apache License, Version 2.0.
|
||||
|
||||
For new versions and additional information, check out:
|
||||
http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl/
|
||||
[https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus](https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus)
|
||||
|
||||
To compare notes with other users or get notified about major new features,
|
||||
send a mail to <afl-users+subscribe@googlegroups.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
** See QuickStartGuide.txt if you don't have time to read this file. **
|
||||
See [docs/QuickStartGuide.txt](docs/QuickStartGuide.txt) if you don't have time to
|
||||
read this file.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Challenges of guided fuzzing
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 0) Building and installing afl++
|
||||
|
||||
afl++ has many build options.
|
||||
The easiest is to build and install everything:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ make distrib
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that "make distrib" also builds llvm_mode, qemu_mode, unicorn_mode and
|
||||
more. If you just want plain afl then do "make all", however compiling and
|
||||
using at least llvm_mode is highly recommended for much better results -
|
||||
hence in this case
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ make source-only
|
||||
```
|
||||
is what you should choose.
|
||||
|
||||
These build options exist:
|
||||
|
||||
* all: just the main afl++ binaries
|
||||
* binary-only: everything for binary-only fuzzing: qemu_mode, unicorn_mode, libdislocator, libtokencap
|
||||
* source-only: everything for source code fuzzing: llvm_mode, libdislocator, libtokencap
|
||||
* distrib: everything (for both binary-only and source code fuzzing)
|
||||
* install: installs everything you have compiled with the build options above
|
||||
* clean: cleans everything. for qemu_mode and unicorn_mode it means it deletes all downloads as well
|
||||
* tests: runs test cases to ensure that all features are still working as they should
|
||||
* help: shows these build options
|
||||
|
||||
[Unless you are on Mac OS X](https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/qa/qa1118/_index.html) you can also build statically linked versions of the
|
||||
afl++ binaries by passing the STATIC=1 argument to make:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ make all STATIC=1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Challenges of guided fuzzing
|
||||
|
||||
Fuzzing is one of the most powerful and proven strategies for identifying
|
||||
security issues in real-world software; it is responsible for the vast
|
||||
@ -62,8 +140,8 @@ All these methods are extremely promising in experimental settings, but tend
|
||||
to suffer from reliability and performance problems in practical uses - and
|
||||
currently do not offer a viable alternative to "dumb" fuzzing techniques.
|
||||
|
||||
2) The afl-fuzz approach
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) The afl-fuzz approach
|
||||
|
||||
American Fuzzy Lop is a brute-force fuzzer coupled with an exceedingly simple
|
||||
but rock-solid instrumentation-guided genetic algorithm. It uses a modified
|
||||
@ -101,8 +179,13 @@ closed-source tools.
|
||||
The fuzzer is thoroughly tested to deliver out-of-the-box performance far
|
||||
superior to blind fuzzing or coverage-only tools.
|
||||
|
||||
3) Instrumenting programs for use with AFL
|
||||
------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 3) Instrumenting programs for use with AFL
|
||||
|
||||
PLEASE NOTE: llvm_mode compilation with afl-clang-fast/afl-clang-fast++
|
||||
instead of afl-gcc/afl-g++ is much faster and has a few cool features.
|
||||
See llvm_mode/ - however few code does not compile with llvm.
|
||||
We support llvm versions 3.8.0 to 9.
|
||||
|
||||
When source code is available, instrumentation can be injected by a companion
|
||||
tool that works as a drop-in replacement for gcc or clang in any standard build
|
||||
@ -115,38 +198,45 @@ or even faster than possible with traditional tools.
|
||||
The correct way to recompile the target program may vary depending on the
|
||||
specifics of the build process, but a nearly-universal approach would be:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ CC=/path/to/afl/afl-gcc ./configure
|
||||
$ make clean all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For C++ programs, you'd would also want to set CXX=/path/to/afl/afl-g++.
|
||||
For C++ programs, you'd would also want to set `CXX=/path/to/afl/afl-g++`.
|
||||
|
||||
The clang wrappers (afl-clang and afl-clang++) can be used in the same way;
|
||||
clang users may also opt to leverage a higher-performance instrumentation mode,
|
||||
as described in llvm_mode/README.llvm.
|
||||
Clang/LLVM has a much better performance, but only works with LLVM up to and
|
||||
including 6.0.1.
|
||||
as described in [llvm_mode/README.md](llvm_mode/README.md).
|
||||
Clang/LLVM has a much better performance and works with LLVM version 3.8.0 to 9.
|
||||
|
||||
Using the LAF Intel performance enhancements are also recommended, see
|
||||
docs/README.laf-intel
|
||||
[llvm_mode/README.laf-intel.md](llvm_mode/README.laf-intel.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Using partial instrumentation is also recommended, see
|
||||
[llvm_mode/README.whitelist.md](llvm_mode/README.whitelist.md)
|
||||
|
||||
When testing libraries, you need to find or write a simple program that reads
|
||||
data from stdin or from a file and passes it to the tested library. In such a
|
||||
case, it is essential to link this executable against a static version of the
|
||||
instrumented library, or to make sure that the correct .so file is loaded at
|
||||
runtime (usually by setting LD_LIBRARY_PATH). The simplest option is a static
|
||||
runtime (usually by setting `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`). The simplest option is a static
|
||||
build, usually possible via:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ CC=/path/to/afl/afl-gcc ./configure --disable-shared
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Setting AFL_HARDEN=1 when calling 'make' will cause the CC wrapper to
|
||||
Setting `AFL_HARDEN=1` when calling 'make' will cause the CC wrapper to
|
||||
automatically enable code hardening options that make it easier to detect
|
||||
simple memory bugs. Libdislocator, a helper library included with AFL (see
|
||||
libdislocator/README.dislocator) can help uncover heap corruption issues, too.
|
||||
[libdislocator/README.md](libdislocator/README.md)) can help uncover heap corruption issues, too.
|
||||
|
||||
PS. ASAN users are advised to review notes_for_asan.txt file for important
|
||||
caveats.
|
||||
PS. ASAN users are advised to review [docs/notes_for_asan.txt](docs/notes_for_asan.txt)
|
||||
file for important caveats.
|
||||
|
||||
4) Instrumenting binary-only apps
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 4) Instrumenting binary-only apps
|
||||
|
||||
When source code is *NOT* available, the fuzzer offers experimental support for
|
||||
fast, on-the-fly instrumentation of black-box binaries. This is accomplished
|
||||
@ -155,23 +245,59 @@ with a version of QEMU running in the lesser-known "user space emulation" mode.
|
||||
QEMU is a project separate from AFL, but you can conveniently build the
|
||||
feature by doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ cd qemu_mode
|
||||
$ ./build_qemu_support.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For additional instructions and caveats, see qemu_mode/README.qemu.
|
||||
For additional instructions and caveats, see [qemu_mode/README.md](qemu_mode/README.md).
|
||||
|
||||
The mode is approximately 2-5x slower than compile-time instrumentation, is
|
||||
less conductive to parallelization, and may have some other quirks.
|
||||
|
||||
5) Choosing initial test cases
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
If [afl-dyninst](https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dyninst) works for
|
||||
your binary, then you can use afl-fuzz normally and it will have twice
|
||||
the speed compared to qemu_mode.
|
||||
|
||||
A more comprehensive description of these and other options can be found in
|
||||
[docs/binaryonly_fuzzing.txt](docs/binaryonly_fuzzing.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 5) Power schedules
|
||||
|
||||
The power schedules were copied from Marcel Böhme's excellent AFLfast
|
||||
implementation and expand on the ability to discover new paths and
|
||||
therefore may increase the code coverage.
|
||||
|
||||
The available schedules are:
|
||||
|
||||
- explore (default)
|
||||
- fast
|
||||
- coe
|
||||
- quad
|
||||
- lin
|
||||
- exploit
|
||||
|
||||
In parallel mode (-M/-S, several instances with shared queue), we suggest to
|
||||
run the master using the exploit schedule (-p exploit) and the slaves with a
|
||||
combination of cut-off-exponential (-p coe), exponential (-p fast; default),
|
||||
and explore (-p explore) schedules.
|
||||
|
||||
In single mode, using -p fast is usually more beneficial than the default
|
||||
explore mode.
|
||||
(We don't want to change the default behaviour of afl, so "fast" has not been
|
||||
made the default mode).
|
||||
|
||||
More details can be found in the paper published at the 23rd ACM Conference on
|
||||
Computer and Communications Security [CCS'16](https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2016/accepted-papers/)
|
||||
## 6) Choosing initial test cases
|
||||
|
||||
To operate correctly, the fuzzer requires one or more starting file that
|
||||
contains a good example of the input data normally expected by the targeted
|
||||
application. There are two basic rules:
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep the files small. Under 1 kB is ideal, although not strictly necessary.
|
||||
For a discussion of why size matters, see perf_tips.txt.
|
||||
For a discussion of why size matters, see [perf_tips.txt](docs/perf_tips.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
- Use multiple test cases only if they are functionally different from
|
||||
each other. There is no point in using fifty different vacation photos
|
||||
@ -184,8 +310,8 @@ PS. If a large corpus of data is available for screening, you may want to use
|
||||
the afl-cmin utility to identify a subset of functionally distinct files that
|
||||
exercise different code paths in the target binary.
|
||||
|
||||
6) Fuzzing binaries
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 7) Fuzzing binaries
|
||||
|
||||
The fuzzing process itself is carried out by the afl-fuzz utility. This program
|
||||
requires a read-only directory with initial test cases, a separate place to
|
||||
@ -193,13 +319,17 @@ store its findings, plus a path to the binary to test.
|
||||
|
||||
For target binaries that accept input directly from stdin, the usual syntax is:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ ./afl-fuzz -i testcase_dir -o findings_dir /path/to/program [...params...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For programs that take input from a file, use '@@' to mark the location in
|
||||
the target's command line where the input file name should be placed. The
|
||||
fuzzer will substitute this for you:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ ./afl-fuzz -i testcase_dir -o findings_dir /path/to/program @@
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the -f option to have the mutated data written to a specific
|
||||
file. This is useful if the program expects a particular file extension or so.
|
||||
@ -211,19 +341,19 @@ You can use -t and -m to override the default timeout and memory limit for the
|
||||
executed process; rare examples of targets that may need these settings touched
|
||||
include compilers and video decoders.
|
||||
|
||||
Tips for optimizing fuzzing performance are discussed in perf_tips.txt.
|
||||
Tips for optimizing fuzzing performance are discussed in [perf_tips.txt](docs/perf_tips.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
Note that afl-fuzz starts by performing an array of deterministic fuzzing
|
||||
steps, which can take several days, but tend to produce neat test cases. If you
|
||||
want quick & dirty results right away - akin to zzuf and other traditional
|
||||
fuzzers - add the -d option to the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
7) Interpreting output
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See the status_screen.txt file for information on how to interpret the
|
||||
displayed stats and monitor the health of the process. Be sure to consult this
|
||||
file especially if any UI elements are highlighted in red.
|
||||
## 8) Interpreting output
|
||||
|
||||
See the [docs/status_screen.txt](docs/status_screen.txt) file for information on
|
||||
how to interpret the displayed stats and monitor the health of the process. Be
|
||||
sure to consult this file especially if any UI elements are highlighted in red.
|
||||
|
||||
The fuzzing process will continue until you press Ctrl-C. At minimum, you want
|
||||
to allow the fuzzer to complete one queue cycle, which may take anywhere from a
|
||||
@ -261,34 +391,38 @@ queue entries. This should help with debugging.
|
||||
When you can't reproduce a crash found by afl-fuzz, the most likely cause is
|
||||
that you are not setting the same memory limit as used by the tool. Try:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ LIMIT_MB=50
|
||||
$ ( ulimit -Sv $[LIMIT_MB << 10]; /path/to/tested_binary ... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Change LIMIT_MB to match the -m parameter passed to afl-fuzz. On OpenBSD,
|
||||
also change -Sv to -Sd.
|
||||
|
||||
Any existing output directory can be also used to resume aborted jobs; try:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ ./afl-fuzz -i- -o existing_output_dir [...etc...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have gnuplot installed, you can also generate some pretty graphs for any
|
||||
active fuzzing task using afl-plot. For an example of how this looks like,
|
||||
see http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl/plot/.
|
||||
see [http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl/plot/](http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl/plot/).
|
||||
|
||||
8) Parallelized fuzzing
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 9) Parallelized fuzzing
|
||||
|
||||
Every instance of afl-fuzz takes up roughly one core. This means that on
|
||||
multi-core systems, parallelization is necessary to fully utilize the hardware.
|
||||
For tips on how to fuzz a common target on multiple cores or multiple networked
|
||||
machines, please refer to parallel_fuzzing.txt.
|
||||
machines, please refer to [docs/parallel_fuzzing.txt](docs/parallel_fuzzing.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
The parallel fuzzing mode also offers a simple way for interfacing AFL to other
|
||||
fuzzers, to symbolic or concolic execution engines, and so forth; again, see the
|
||||
last section of parallel_fuzzing.txt for tips.
|
||||
last section of [docs/parallel_fuzzing.txt](docs/parallel_fuzzing.txt) for tips.
|
||||
|
||||
9) Fuzzer dictionaries
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 10) Fuzzer dictionaries
|
||||
|
||||
By default, afl-fuzz mutation engine is optimized for compact data formats -
|
||||
say, images, multimedia, compressed data, regular expression syntax, or shell
|
||||
@ -298,13 +432,13 @@ redundant verbiage - notably including HTML, SQL, or JavaScript.
|
||||
To avoid the hassle of building syntax-aware tools, afl-fuzz provides a way to
|
||||
seed the fuzzing process with an optional dictionary of language keywords,
|
||||
magic headers, or other special tokens associated with the targeted data type
|
||||
- and use that to reconstruct the underlying grammar on the go:
|
||||
-- and use that to reconstruct the underlying grammar on the go:
|
||||
|
||||
http://lcamtuf.blogspot.com/2015/01/afl-fuzz-making-up-grammar-with.html
|
||||
[http://lcamtuf.blogspot.com/2015/01/afl-fuzz-making-up-grammar-with.html](http://lcamtuf.blogspot.com/2015/01/afl-fuzz-making-up-grammar-with.html)
|
||||
|
||||
To use this feature, you first need to create a dictionary in one of the two
|
||||
formats discussed in dictionaries/README.dictionaries; and then point the fuzzer
|
||||
to it via the -x option in the command line.
|
||||
formats discussed in [dictionaries/README.md](dictionaries/README.md);
|
||||
and then point the fuzzer to it via the -x option in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
(Several common dictionaries are already provided in that subdirectory, too.)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -312,7 +446,7 @@ There is no way to provide more structured descriptions of the underlying
|
||||
syntax, but the fuzzer will likely figure out some of this based on the
|
||||
instrumentation feedback alone. This actually works in practice, say:
|
||||
|
||||
http://lcamtuf.blogspot.com/2015/04/finding-bugs-in-sqlite-easy-way.html
|
||||
[http://lcamtuf.blogspot.com/2015/04/finding-bugs-in-sqlite-easy-way.html](http://lcamtuf.blogspot.com/2015/04/finding-bugs-in-sqlite-easy-way.html)
|
||||
|
||||
PS. Even when no explicit dictionary is given, afl-fuzz will try to extract
|
||||
existing syntax tokens in the input corpus by watching the instrumentation
|
||||
@ -321,10 +455,10 @@ parsers and grammars, but isn't nearly as good as the -x mode.
|
||||
|
||||
If a dictionary is really hard to come by, another option is to let AFL run
|
||||
for a while, and then use the token capture library that comes as a companion
|
||||
utility with AFL. For that, see libtokencap/README.tokencap.
|
||||
utility with AFL. For that, see [libtokencap/README.md](libtokencap/README.md).
|
||||
|
||||
10) Crash triage
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 11) Crash triage
|
||||
|
||||
The coverage-based grouping of crashes usually produces a small data set that
|
||||
can be quickly triaged manually or with a very simple GDB or Valgrind script.
|
||||
@ -352,7 +486,9 @@ beneath.
|
||||
Oh, one more thing: for test case minimization, give afl-tmin a try. The tool
|
||||
can be operated in a very simple way:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ ./afl-tmin -i test_case -o minimized_result -- /path/to/program [...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tool works with crashing and non-crashing test cases alike. In the crash
|
||||
mode, it will happily accept instrumented and non-instrumented binaries. In the
|
||||
@ -367,10 +503,10 @@ file, attempts to sequentially flip bytes, and observes the behavior of the
|
||||
tested program. It then color-codes the input based on which sections appear to
|
||||
be critical, and which are not; while not bulletproof, it can often offer quick
|
||||
insights into complex file formats. More info about its operation can be found
|
||||
near the end of technical_details.txt.
|
||||
near the end of [docs/technical_details.txt](docs/technical_details.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
11) Going beyond crashes
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 12) Going beyond crashes
|
||||
|
||||
Fuzzing is a wonderful and underutilized technique for discovering non-crashing
|
||||
design and implementation errors, too. Quite a few interesting bugs have been
|
||||
@ -390,11 +526,11 @@ found by modifying the target programs to call abort() when, say:
|
||||
|
||||
Implementing these or similar sanity checks usually takes very little time;
|
||||
if you are the maintainer of a particular package, you can make this code
|
||||
conditional with #ifdef FUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION (a flag also
|
||||
shared with libfuzzer) or #ifdef __AFL_COMPILER (this one is just for AFL).
|
||||
conditional with `#ifdef FUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION` (a flag also
|
||||
shared with libfuzzer) or `#ifdef __AFL_COMPILER` (this one is just for AFL).
|
||||
|
||||
12) Common-sense risks
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 13) Common-sense risks
|
||||
|
||||
Please keep in mind that, similarly to many other computationally-intensive
|
||||
tasks, fuzzing may put strain on your hardware and on the OS. In particular:
|
||||
@ -419,10 +555,12 @@ tasks, fuzzing may put strain on your hardware and on the OS. In particular:
|
||||
|
||||
A good way to monitor disk I/O on Linux is the 'iostat' command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ iostat -d 3 -x -k [...optional disk ID...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
13) Known limitations & areas for improvement
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
## 14) Known limitations & areas for improvement
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the most important caveats for AFL:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -439,35 +577,36 @@ Here are some of the most important caveats for AFL:
|
||||
To work around this, you can comment out the relevant checks (see
|
||||
experimental/libpng_no_checksum/ for inspiration); if this is not possible,
|
||||
you can also write a postprocessor, as explained in
|
||||
experimental/post_library/.
|
||||
experimental/post_library/ (with AFL_POST_LIBRARY)
|
||||
|
||||
- There are some unfortunate trade-offs with ASAN and 64-bit binaries. This
|
||||
isn't due to any specific fault of afl-fuzz; see notes_for_asan.txt for
|
||||
tips.
|
||||
isn't due to any specific fault of afl-fuzz; see [docs/notes_for_asan.txt](docs/notes_for_asan.txt)
|
||||
for tips.
|
||||
|
||||
- There is no direct support for fuzzing network services, background
|
||||
daemons, or interactive apps that require UI interaction to work. You may
|
||||
need to make simple code changes to make them behave in a more traditional
|
||||
way. Preeny may offer a relatively simple option, too - see:
|
||||
https://github.com/zardus/preeny
|
||||
[https://github.com/zardus/preeny](https://github.com/zardus/preeny)
|
||||
|
||||
Some useful tips for modifying network-based services can be also found at:
|
||||
https://www.fastly.com/blog/how-to-fuzz-server-american-fuzzy-lop
|
||||
[https://www.fastly.com/blog/how-to-fuzz-server-american-fuzzy-lop](https://www.fastly.com/blog/how-to-fuzz-server-american-fuzzy-lop)
|
||||
|
||||
- AFL doesn't output human-readable coverage data. If you want to monitor
|
||||
coverage, use afl-cov from Michael Rash: https://github.com/mrash/afl-cov
|
||||
coverage, use afl-cov from Michael Rash: [https://github.com/mrash/afl-cov](https://github.com/mrash/afl-cov)
|
||||
|
||||
- Occasionally, sentient machines rise against their creators. If this
|
||||
happens to you, please consult http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/prep/.
|
||||
happens to you, please consult [http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/prep/](http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/prep/).
|
||||
|
||||
Beyond this, see INSTALL for platform-specific tips.
|
||||
|
||||
14) Special thanks
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the improvements to afl-fuzz wouldn't be possible without feedback,
|
||||
bug reports, or patches from:
|
||||
## 15) Special thanks
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the improvements to the original afl and afl++ wouldn't be possible
|
||||
without feedback, bug reports, or patches from:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Jann Horn Hanno Boeck
|
||||
Felix Groebert Jakub Wilk
|
||||
Richard W. M. Jones Alexander Cherepanov
|
||||
@ -482,7 +621,7 @@ bug reports, or patches from:
|
||||
Jonathan Gray Filipe Cabecinhas
|
||||
Nico Weber Jodie Cunningham
|
||||
Andrew Griffiths Parker Thompson
|
||||
Jonathan Neuschfer Tyler Nighswander
|
||||
Jonathan Neuschaefer Tyler Nighswander
|
||||
Ben Nagy Samir Aguiar
|
||||
Aidan Thornton Aleksandar Nikolich
|
||||
Sam Hakim Laszlo Szekeres
|
||||
@ -501,33 +640,25 @@ bug reports, or patches from:
|
||||
Austin Seipp Daniel Komaromy
|
||||
Daniel Binderman Jonathan Metzman
|
||||
Vegard Nossum Jan Kneschke
|
||||
Kurt Roeckx Marcel Bohme
|
||||
Kurt Roeckx Marcel Boehme
|
||||
Van-Thuan Pham Abhik Roychoudhury
|
||||
Joshua J. Drake Toby Hutton
|
||||
Rene Freingruber Sergey Davidoff
|
||||
Sami Liedes Craig Young
|
||||
Andrzej Jackowski Daniel Hodson
|
||||
Nathan Voss Dominik Maier
|
||||
Andrea Biondo Vincent Le Garrec
|
||||
Khaled Yakdan Kuang-che Wu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you!
|
||||
|
||||
15) Contact
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
Questions? Concerns? Bug reports? The author can be usually reached at
|
||||
<lcamtuf@google.com>.
|
||||
## 16) Contact
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a mailing list for the project; to join, send a mail to
|
||||
Questions? Concerns? Bug reports? The contributors can be reached via
|
||||
[https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus](https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus)
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a mailing list for the afl project; to join, send a mail to
|
||||
<afl-users+subscribe@googlegroups.com>. Or, if you prefer to browse
|
||||
archives first, try:
|
||||
|
||||
https://groups.google.com/group/afl-users
|
||||
|
||||
PS. If you wish to submit raw code to be incorporated into the project, please
|
||||
be aware that the copyright on most of AFL is claimed by Google. While you do
|
||||
retain copyright on your contributions, they do ask people to agree to a simple
|
||||
CLA first:
|
||||
|
||||
https://cla.developers.google.com/clas
|
||||
|
||||
Sorry about the hassle. Of course, no CLA is required for feature requests or
|
||||
bug reports.
|
||||
archives first, try: [https://groups.google.com/group/afl-users](https://groups.google.com/group/afl-users)
|
||||
57
TODO
Normal file
57
TODO
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Roadmap 2.60:
|
||||
=============
|
||||
|
||||
afl-fuzz:
|
||||
- radamsa mutator
|
||||
- test the libmutator actually works and does not run infinite (need an example though)
|
||||
|
||||
gcc_plugin:
|
||||
- neverZero
|
||||
- laf-intel
|
||||
|
||||
qemu_mode:
|
||||
- update to 4.x (probably this will be skipped :( )
|
||||
- instrim for QEMU mode via static analysis (with r2pipe? or angr?)
|
||||
Idea: The static analyzer outputs a map in which each edge that must be
|
||||
skipped is marked with 1. QEMU loads it at startup in the parent process.
|
||||
|
||||
custom_mutators:
|
||||
- rip what Superion is doing into custom mutators for js, php, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
enhance test/test.sh script for checking if compcov features are working
|
||||
correctly (especially float splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The far away future:
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
Problem: Average targets (tiff, jpeg, unrar) go through 1500 edges.
|
||||
At afl's default map that means ~16 collisions and ~3 wrappings.
|
||||
Solution #1: increase map size.
|
||||
every +1 decreases fuzzing speed by ~10% and halfs the collisions
|
||||
birthday paradox predicts collisions at this # of edges:
|
||||
mapsize => collisions
|
||||
2^16 = 302
|
||||
2^17 = 427
|
||||
2^18 = 603
|
||||
2^19 = 853
|
||||
2^20 = 1207
|
||||
2^21 = 1706
|
||||
2^22 = 2412
|
||||
2^23 = 3411
|
||||
2^24 = 4823
|
||||
Increasing the map is an easy solution but also not a good one.
|
||||
Solution #2: use dynamic map size and collision free basic block IDs
|
||||
This only works in llvm_mode and llvm >= 9 though
|
||||
A potential good future solution. Heiko/hexcoder follows this up
|
||||
Solution #3: write instruction pointers to a big shared map
|
||||
512kb/1MB shared map and the instrumented code writes the instruction
|
||||
pointer into the map. Map must be big enough but could be command line
|
||||
controlled.
|
||||
Good: complete coverage information, nothing is lost. choice of analysis
|
||||
impacts speed, but this can be decided by user options
|
||||
Neutral: a little bit slower but no loss of coverage
|
||||
Bad: completely changes how afl uses the map and the scheduling.
|
||||
Overall another very good solution, Marc Heuse/vanHauser follows this up
|
||||
|
||||
21
afl-cmin
21
afl-cmin
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - corpus minimization tool
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2014, 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@
|
||||
# array sizes.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
echo "corpus minimization tool for afl-fuzz by <lcamtuf@google.com>"
|
||||
echo "corpus minimization tool for afl-fuzz by Michal Zalewski"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
#########
|
||||
@ -49,12 +49,15 @@ MEM_LIMIT=100
|
||||
TIMEOUT=none
|
||||
|
||||
unset IN_DIR OUT_DIR STDIN_FILE EXTRA_PAR MEM_LIMIT_GIVEN \
|
||||
AFL_CMIN_CRASHES_ONLY AFL_CMIN_ALLOW_ANY QEMU_MODE
|
||||
AFL_CMIN_CRASHES_ONLY AFL_CMIN_ALLOW_ANY QEMU_MODE UNICORN_MODE
|
||||
|
||||
while getopts "+i:o:f:m:t:eQC" opt; do
|
||||
while getopts "+i:o:f:m:t:eQUCh" opt; do
|
||||
|
||||
case "$opt" in
|
||||
|
||||
"h")
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
"i")
|
||||
IN_DIR="$OPTARG"
|
||||
;;
|
||||
@ -83,6 +86,11 @@ while getopts "+i:o:f:m:t:eQC" opt; do
|
||||
test "$MEM_LIMIT_GIVEN" = "" && MEM_LIMIT=250
|
||||
QEMU_MODE=1
|
||||
;;
|
||||
"U")
|
||||
EXTRA_PAR="$EXTRA_PAR -U"
|
||||
test "$MEM_LIMIT_GIVEN" = "" && MEM_LIMIT=250
|
||||
UNICORN_MODE=1
|
||||
;;
|
||||
"?")
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
;;
|
||||
@ -111,7 +119,8 @@ Execution control settings:
|
||||
-m megs - memory limit for child process ($MEM_LIMIT MB)
|
||||
-t msec - run time limit for child process (none)
|
||||
-Q - use binary-only instrumentation (QEMU mode)
|
||||
|
||||
-U - use unicorn-based instrumentation (Unicorn mode)
|
||||
|
||||
Minimization settings:
|
||||
|
||||
-C - keep crashing inputs, reject everything else
|
||||
@ -196,7 +205,7 @@ if [ ! -f "$TARGET_BIN" -o ! -x "$TARGET_BIN" ]; then
|
||||
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$AFL_SKIP_BIN_CHECK" = "" -a "$QEMU_MODE" = "" ]; then
|
||||
if [ "$AFL_SKIP_BIN_CHECK" = "" -a "$QEMU_MODE" = "" -a "$UNICORN_MODE" = "" ]; then
|
||||
|
||||
if ! grep -qF "__AFL_SHM_ID" "$TARGET_BIN"; then
|
||||
echo "[-] Error: binary '$TARGET_BIN' doesn't appear to be instrumented." 1>&2
|
||||
|
||||
8271
afl-fuzz.c
8271
afl-fuzz.c
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
8
afl-plot
8
afl-plot
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - Advanced Persistent Graphing
|
||||
# -------------------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
# Based on a design & prototype by Michael Rash.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2014, 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
@ -15,16 +15,16 @@
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
echo "progress plotting utility for afl-fuzz by <lcamtuf@google.com>"
|
||||
echo "progress plotting utility for afl-fuzz by Michal Zalewski"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
if [ ! "$#" = "2" ]; then
|
||||
|
||||
cat 1>&2 <<_EOF_
|
||||
This program generates gnuplot images from afl-fuzz output data. Usage:
|
||||
|
||||
$0 afl_state_dir graph_output_dir
|
||||
|
||||
This program generates gnuplot images from afl-fuzz output data. Usage:
|
||||
|
||||
The afl_state_dir parameter should point to an existing state directory for any
|
||||
active or stopped instance of afl-fuzz; while graph_output_dir should point to
|
||||
an empty directory where this tool can write the resulting plots to.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,24 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
test "$1" = "-h" && {
|
||||
echo afl-system-config by Marc Heuse
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo $0
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo afl-system-config has no command line options
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo afl-system reconfigures the system to a high performance fuzzing state
|
||||
echo WARNING: this reduces the security of the system
|
||||
echo
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PLATFORM=`uname -s`
|
||||
echo This reconfigures the system to have a better fuzzing performance
|
||||
if [ '!' "$EUID" = 0 ] && [ '!' `id -u` = 0 ] ; then
|
||||
echo Error you need to be root to run this
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ "$PLATFORM" = "Linux" ] ; then
|
||||
sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=core
|
||||
sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
|
||||
sysctl -w kernel.sched_child_runs_first=1
|
||||
@ -7,9 +26,41 @@ sysctl -w kernel.sched_autogroup_enabled=1
|
||||
sysctl -w kernel.sched_migration_cost_ns=50000000
|
||||
sysctl -w kernel.sched_latency_ns=250000000
|
||||
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
|
||||
echo performance | tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/cpufreq/scaling_governor > /dev/null
|
||||
test -e /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/scaling_governor && echo performance | tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/scaling_governor
|
||||
test -e /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/policy0/scaling_governor && echo performance | tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/policy*/scaling_governor
|
||||
test -e /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor && echo performance | tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/cpufreq/scaling_governor
|
||||
test -e /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo && echo 0 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo
|
||||
test -e /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/boost && echo 1 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/boost
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo It is recommended to boot the kernel with lots of security off - if you are running a machine that is in a secured network - so set this:
|
||||
echo '/etc/default/grub:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="ibpb=off ibrs=off kpti=off l1tf=off mds=off mitigations=off no_stf_barrier noibpb noibrs nopcid nopti nospec_store_bypass_disable nospectre_v1 nospectre_v2 pcid=off pti=off spec_store_bypass_disable=off spectre_v2=off stf_barrier=off"'
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ "$PLATFORM" = "FreeBSD" ] ; then
|
||||
sysctl kern.elf32.aslr.enable=0
|
||||
sysctl kern.elf64.aslr.enable=0
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo It is recommended to boot the kernel with lots of security off - if you are running a machine that is in a secured network - so set this:
|
||||
echo 'sysctl hw.ibrs_disable=1'
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo 'Setting kern.pmap.pg_ps_enabled=0 into /boot/loader.conf might be helpful too.'
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ "$PLATFORM" = "OpenBSD" ] ; then
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo 'System security features cannot be disabled on OpenBSD.'
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ "$PLATFORM" = "NetBSD" ] ; then
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo It is recommended to enable unprivileged users to set cpu affinity
|
||||
echo to be able to use afl-gotcpu meaningfully.
|
||||
/sbin/sysctl -w security.models.extensions.user_set_cpu_affinity=1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ "$PLATFORM" = "Darwin" ] ; then
|
||||
if [ $(launchctl list 2>/dev/null | grep -q '\.ReportCrash$') ] ; then
|
||||
echo We unload the default crash reporter here
|
||||
SL=/System/Library; PL=com.apple.ReportCrash
|
||||
launchctl unload -w ${SL}/LaunchAgents/${PL}.plist
|
||||
sudo launchctl unload -w ${SL}/LaunchDaemons/${PL}.Root.plist
|
||||
fi
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo Also use AFL_TMPDIR to use a tmpfs for the input file
|
||||
|
||||
13
afl-whatsup
13
afl-whatsup
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - status check tool
|
||||
# --------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -17,8 +17,15 @@
|
||||
# instances of afl-fuzz.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
echo "status check tool for afl-fuzz by <lcamtuf@google.com>"
|
||||
echo "status check tool for afl-fuzz by Michal Zalewski"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
test "$1" = "-h" && {
|
||||
echo $0
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo afl-whatsup has no command line options
|
||||
echo
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$1" = "-s" ]; then
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +61,7 @@ fi
|
||||
|
||||
CUR_TIME=`date +%s`
|
||||
|
||||
TMP=`mktemp -t .afl-whatsup-XXXXXXXX` || exit 1
|
||||
TMP=`mktemp -t .afl-whatsup-XXXXXXXX` || TMP=`mktemp -p /data/local/tmp .afl-whatsup-XXXXXXXX` || exit 1
|
||||
|
||||
ALIVE_CNT=0
|
||||
DEAD_CNT=0
|
||||
|
||||
61
afl-wine-trace
Executable file
61
afl-wine-trace
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import pefile
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
|
||||
print("[afl-wine-trace] usage: wine-cov binary [args...]\n")
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
if os.getenv("AFL_PATH"):
|
||||
my_dir = os.getenv("AFL_PATH")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
my_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["WINELOADERNOEXEC"] = "1"
|
||||
|
||||
pe = pefile.PE(sys.argv[1])
|
||||
|
||||
if "AFL_ENTRYPOINT" not in os.environ:
|
||||
os.environ["AFL_ENTRYPOINT"] = "0x%x" % (pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase + pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.AddressOfEntryPoint)
|
||||
if not os.getenv("AFL_INST_LIBS"):
|
||||
if "AFL_CODE_START" not in os.environ:
|
||||
os.environ["AFL_CODE_START"] = "0x%x" % (pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase + pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.BaseOfCode)
|
||||
if "AFL_CODE_END" not in os.environ:
|
||||
os.environ["AFL_CODE_END"] = "0x%x" % (pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase + pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.BaseOfCode + pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.SizeOfCode)
|
||||
|
||||
if pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_AMD64"] or pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_IA64"]:
|
||||
os.environ["LD_PRELOAD"] = os.path.join(my_dir, "qemu_mode/unsigaction/unsigaction64.so")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
os.environ["LD_PRELOAD"] = os.path.join(my_dir, "qemu_mode/unsigaction/unsigaction32.so")
|
||||
|
||||
if os.getenv("WINECOV_QEMU_PATH"):
|
||||
qemu_path = os.getenv("WINECOV_QEMU_PATH")
|
||||
elif os.path.exists(os.path.join(my_dir, "afl-qemu-trace")):
|
||||
qemu_path = os.path.join(my_dir, "afl-qemu-trace")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
qemu_path = "qemu-"
|
||||
if pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_AMD64"] or pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_IA64"]:
|
||||
qemu_path += "x86_64"
|
||||
elif pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_I386"]:
|
||||
qemu_path += "i386"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print ("[wine-cov] unsuppoted architecture\n")
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
qemu_path = shutil.which(qemu_path)
|
||||
|
||||
if os.getenv("WINECOV_WINE_PATH"):
|
||||
wine_path = os.getenv("WINECOV_WINE_PATH")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
wine_path = "/usr/lib/wine/wine"
|
||||
if pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_AMD64"] or pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_IA64"]:
|
||||
wine_path += "64"
|
||||
elif pe.FILE_HEADER.Machine == pefile.MACHINE_TYPE["IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_I386"]:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print ("[afl-wine-trace] unsopported architecture\n")
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
os.execve(qemu_path, [qemu_path, wine_path] + sys.argv[1:], os.environ)
|
||||
354
config.h
354
config.h
@ -1,354 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop plus plus - vaguely configurable bits
|
||||
----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _HAVE_CONFIG_H
|
||||
#define _HAVE_CONFIG_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Version string: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define VERSION "++2.52c"
|
||||
|
||||
/******************************************************
|
||||
* *
|
||||
* Settings that may be of interest to power users: *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
******************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Comment out to disable terminal colors (note that this makes afl-analyze
|
||||
a lot less nice): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define USE_COLOR
|
||||
|
||||
/* Comment out to disable fancy ANSI boxes and use poor man's 7-bit UI: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FANCY_BOXES
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default timeout for fuzzed code (milliseconds). This is the upper bound,
|
||||
also used for detecting hangs; the actual value is auto-scaled: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EXEC_TIMEOUT 1000
|
||||
|
||||
/* Timeout rounding factor when auto-scaling (milliseconds): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EXEC_TM_ROUND 20
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default memory limit for child process (MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __x86_64__
|
||||
# define MEM_LIMIT 25
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define MEM_LIMIT 50
|
||||
#endif /* ^!__x86_64__ */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default memory limit when running in QEMU mode (MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MEM_LIMIT_QEMU 200
|
||||
|
||||
/* Number of calibration cycles per every new test case (and for test
|
||||
cases that show variable behavior): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CAL_CYCLES 8
|
||||
#define CAL_CYCLES_LONG 40
|
||||
|
||||
/* Number of subsequent timeouts before abandoning an input file: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TMOUT_LIMIT 250
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum number of unique hangs or crashes to record: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define KEEP_UNIQUE_HANG 500
|
||||
#define KEEP_UNIQUE_CRASH 5000
|
||||
|
||||
/* Baseline number of random tweaks during a single 'havoc' stage: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_CYCLES 256
|
||||
#define HAVOC_CYCLES_INIT 1024
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum multiplier for the above (should be a power of two, beware
|
||||
of 32-bit int overflows): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_MAX_MULT 16
|
||||
|
||||
/* Absolute minimum number of havoc cycles (after all adjustments): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_MIN 16
|
||||
|
||||
/* Power Schedule Divisor */
|
||||
#define POWER_BETA 1
|
||||
#define MAX_FACTOR (POWER_BETA * 32)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum stacking for havoc-stage tweaks. The actual value is calculated
|
||||
like this:
|
||||
|
||||
n = random between 1 and HAVOC_STACK_POW2
|
||||
stacking = 2^n
|
||||
|
||||
In other words, the default (n = 7) produces 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or
|
||||
128 stacked tweaks: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_STACK_POW2 7
|
||||
|
||||
/* Caps on block sizes for cloning and deletion operations. Each of these
|
||||
ranges has a 33% probability of getting picked, except for the first
|
||||
two cycles where smaller blocks are favored: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_SMALL 32
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_MEDIUM 128
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_LARGE 1500
|
||||
|
||||
/* Extra-large blocks, selected very rarely (<5% of the time): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_XL 32768
|
||||
|
||||
/* Probabilities of skipping non-favored entries in the queue, expressed as
|
||||
percentages: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SKIP_TO_NEW_PROB 99 /* ...when there are new, pending favorites */
|
||||
#define SKIP_NFAV_OLD_PROB 95 /* ...no new favs, cur entry already fuzzed */
|
||||
#define SKIP_NFAV_NEW_PROB 75 /* ...no new favs, cur entry not fuzzed yet */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Splicing cycle count: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SPLICE_CYCLES 15
|
||||
|
||||
/* Nominal per-splice havoc cycle length: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SPLICE_HAVOC 32
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum offset for integer addition / subtraction stages: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ARITH_MAX 35
|
||||
|
||||
/* Limits for the test case trimmer. The absolute minimum chunk size; and
|
||||
the starting and ending divisors for chopping up the input file: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TRIM_MIN_BYTES 4
|
||||
#define TRIM_START_STEPS 16
|
||||
#define TRIM_END_STEPS 1024
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum size of input file, in bytes (keep under 100MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_FILE (1 * 1024 * 1024)
|
||||
|
||||
/* The same, for the test case minimizer: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TMIN_MAX_FILE (10 * 1024 * 1024)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Block normalization steps for afl-tmin: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TMIN_SET_MIN_SIZE 4
|
||||
#define TMIN_SET_STEPS 128
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum dictionary token size (-x), in bytes: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_DICT_FILE 128
|
||||
|
||||
/* Length limits for auto-detected dictionary tokens: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MIN_AUTO_EXTRA 3
|
||||
#define MAX_AUTO_EXTRA 32
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum number of user-specified dictionary tokens to use in deterministic
|
||||
steps; past this point, the "extras/user" step will be still carried out,
|
||||
but with proportionally lower odds: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_DET_EXTRAS 200
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum number of auto-extracted dictionary tokens to actually use in fuzzing
|
||||
(first value), and to keep in memory as candidates. The latter should be much
|
||||
higher than the former. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define USE_AUTO_EXTRAS 50
|
||||
#define MAX_AUTO_EXTRAS (USE_AUTO_EXTRAS * 10)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Scaling factor for the effector map used to skip some of the more
|
||||
expensive deterministic steps. The actual divisor is set to
|
||||
2^EFF_MAP_SCALE2 bytes: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EFF_MAP_SCALE2 3
|
||||
|
||||
/* Minimum input file length at which the effector logic kicks in: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EFF_MIN_LEN 128
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum effector density past which everything is just fuzzed
|
||||
unconditionally (%): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EFF_MAX_PERC 90
|
||||
|
||||
/* UI refresh frequency (Hz): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define UI_TARGET_HZ 5
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fuzzer stats file and plot update intervals (sec): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define STATS_UPDATE_SEC 60
|
||||
#define PLOT_UPDATE_SEC 5
|
||||
|
||||
/* Smoothing divisor for CPU load and exec speed stats (1 - no smoothing). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define AVG_SMOOTHING 16
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sync interval (every n havoc cycles): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SYNC_INTERVAL 5
|
||||
|
||||
/* Output directory reuse grace period (minutes): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define OUTPUT_GRACE 25
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment to use simple file names (id_NNNNNN): */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define SIMPLE_FILES
|
||||
|
||||
/* List of interesting values to use in fuzzing. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_8 \
|
||||
-128, /* Overflow signed 8-bit when decremented */ \
|
||||
-1, /* */ \
|
||||
0, /* */ \
|
||||
1, /* */ \
|
||||
16, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
32, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
64, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
100, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
127 /* Overflow signed 8-bit when incremented */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_16 \
|
||||
-32768, /* Overflow signed 16-bit when decremented */ \
|
||||
-129, /* Overflow signed 8-bit */ \
|
||||
128, /* Overflow signed 8-bit */ \
|
||||
255, /* Overflow unsig 8-bit when incremented */ \
|
||||
256, /* Overflow unsig 8-bit */ \
|
||||
512, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
1000, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
1024, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
4096, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
32767 /* Overflow signed 16-bit when incremented */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_32 \
|
||||
-2147483648LL, /* Overflow signed 32-bit when decremented */ \
|
||||
-100663046, /* Large negative number (endian-agnostic) */ \
|
||||
-32769, /* Overflow signed 16-bit */ \
|
||||
32768, /* Overflow signed 16-bit */ \
|
||||
65535, /* Overflow unsig 16-bit when incremented */ \
|
||||
65536, /* Overflow unsig 16 bit */ \
|
||||
100663045, /* Large positive number (endian-agnostic) */ \
|
||||
2147483647 /* Overflow signed 32-bit when incremented */
|
||||
|
||||
/***********************************************************
|
||||
* *
|
||||
* Really exotic stuff you probably don't want to touch: *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
***********************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Call count interval between reseeding the libc PRNG from /dev/urandom: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define RESEED_RNG 10000
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum line length passed from GCC to 'as' and used for parsing
|
||||
configuration files: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_LINE 8192
|
||||
|
||||
/* Environment variable used to pass SHM ID to the called program. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SHM_ENV_VAR "__AFL_SHM_ID"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Other less interesting, internal-only variables. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CLANG_ENV_VAR "__AFL_CLANG_MODE"
|
||||
#define AS_LOOP_ENV_VAR "__AFL_AS_LOOPCHECK"
|
||||
#define PERSIST_ENV_VAR "__AFL_PERSISTENT"
|
||||
#define DEFER_ENV_VAR "__AFL_DEFER_FORKSRV"
|
||||
|
||||
/* In-code signatures for deferred and persistent mode. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define PERSIST_SIG "##SIG_AFL_PERSISTENT##"
|
||||
#define DEFER_SIG "##SIG_AFL_DEFER_FORKSRV##"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Distinctive bitmap signature used to indicate failed execution: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EXEC_FAIL_SIG 0xfee1dead
|
||||
|
||||
/* Distinctive exit code used to indicate MSAN trip condition: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MSAN_ERROR 86
|
||||
|
||||
/* Designated file descriptors for forkserver commands (the application will
|
||||
use FORKSRV_FD and FORKSRV_FD + 1): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FORKSRV_FD 198
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fork server init timeout multiplier: we'll wait the user-selected
|
||||
timeout plus this much for the fork server to spin up. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FORK_WAIT_MULT 10
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calibration timeout adjustments, to be a bit more generous when resuming
|
||||
fuzzing sessions or trying to calibrate already-added internal finds.
|
||||
The first value is a percentage, the other is in milliseconds: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CAL_TMOUT_PERC 125
|
||||
#define CAL_TMOUT_ADD 50
|
||||
|
||||
/* Number of chances to calibrate a case before giving up: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CAL_CHANCES 3
|
||||
|
||||
/* Map size for the traced binary (2^MAP_SIZE_POW2). Must be greater than
|
||||
2; you probably want to keep it under 18 or so for performance reasons
|
||||
(adjusting AFL_INST_RATIO when compiling is probably a better way to solve
|
||||
problems with complex programs). You need to recompile the target binary
|
||||
after changing this - otherwise, SEGVs may ensue. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAP_SIZE_POW2 16
|
||||
#define MAP_SIZE (1 << MAP_SIZE_POW2)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum allocator request size (keep well under INT_MAX): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_ALLOC 0x40000000
|
||||
|
||||
/* A made-up hashing seed: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HASH_CONST 0xa5b35705
|
||||
|
||||
/* Constants for afl-gotcpu to control busy loop timing: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CTEST_TARGET_MS 5000
|
||||
#define CTEST_CORE_TRG_MS 1000
|
||||
#define CTEST_BUSY_CYCLES (10 * 1000 * 1000)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment this to use inferior block-coverage-based instrumentation. Note
|
||||
that you need to recompile the target binary for this to have any effect: */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define COVERAGE_ONLY
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment this to ignore hit counts and output just one bit per tuple.
|
||||
As with the previous setting, you will need to recompile the target
|
||||
binary: */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define SKIP_COUNTS
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment this to use instrumentation data to record newly discovered paths,
|
||||
but do not use them as seeds for fuzzing. This is useful for conveniently
|
||||
measuring coverage that could be attained by a "dumb" fuzzing algorithm: */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define IGNORE_FINDS
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_CONFIG_H */
|
||||
2
custom_mutators/README
Normal file
2
custom_mutators/README
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
This is a simple example for the AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_LIBRARY feature.
|
||||
For more information see docs/custom_mutator.txt
|
||||
49
custom_mutators/simple_mutator.c
Normal file
49
custom_mutators/simple_mutator.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Simple Custom Mutator for AFL
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Khaled Yakdan <yakdan@code-intelligence.de>
|
||||
|
||||
This a simple mutator that assumes that the generates messages starting with
|
||||
one of the three strings GET, PUT, or DEL followed by a payload. The mutator
|
||||
randomly selects a commend and mutates the payload of the seed provided as
|
||||
input.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
static const char *commands[] = {
|
||||
|
||||
"GET",
|
||||
"PUT",
|
||||
"DEL",
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
static size_t data_size = 100;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t afl_custom_mutator(uint8_t *data, size_t size, uint8_t *mutated_out,
|
||||
size_t max_size, unsigned int seed) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Seed the PRNG
|
||||
srand(seed);
|
||||
|
||||
// Make sure that the packet size does not exceed the maximum size expected by
|
||||
// the fuzzer
|
||||
size_t mutated_size = data_size <= max_size ? data_size : max_size;
|
||||
|
||||
// Randomly select a command string to add as a header to the packet
|
||||
memcpy(mutated_out, commands[rand() % 3], 3);
|
||||
|
||||
// Mutate the payload of the packet
|
||||
for (int i = 3; i < mutated_size; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
mutated_out[i] = (data[i] + rand() % 10) & 0xff;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return mutated_size;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
251
debug.h
251
debug.h
@ -1,251 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - debug / error handling macros
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _HAVE_DEBUG_H
|
||||
#define _HAVE_DEBUG_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <errno.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*******************
|
||||
* Terminal colors *
|
||||
*******************/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_COLOR
|
||||
|
||||
# define cBLK "\x1b[0;30m"
|
||||
# define cRED "\x1b[0;31m"
|
||||
# define cGRN "\x1b[0;32m"
|
||||
# define cBRN "\x1b[0;33m"
|
||||
# define cBLU "\x1b[0;34m"
|
||||
# define cMGN "\x1b[0;35m"
|
||||
# define cCYA "\x1b[0;36m"
|
||||
# define cLGR "\x1b[0;37m"
|
||||
# define cGRA "\x1b[1;90m"
|
||||
# define cLRD "\x1b[1;91m"
|
||||
# define cLGN "\x1b[1;92m"
|
||||
# define cYEL "\x1b[1;93m"
|
||||
# define cLBL "\x1b[1;94m"
|
||||
# define cPIN "\x1b[1;95m"
|
||||
# define cLCY "\x1b[1;96m"
|
||||
# define cBRI "\x1b[1;97m"
|
||||
# define cRST "\x1b[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
# define bgBLK "\x1b[40m"
|
||||
# define bgRED "\x1b[41m"
|
||||
# define bgGRN "\x1b[42m"
|
||||
# define bgBRN "\x1b[43m"
|
||||
# define bgBLU "\x1b[44m"
|
||||
# define bgMGN "\x1b[45m"
|
||||
# define bgCYA "\x1b[46m"
|
||||
# define bgLGR "\x1b[47m"
|
||||
# define bgGRA "\x1b[100m"
|
||||
# define bgLRD "\x1b[101m"
|
||||
# define bgLGN "\x1b[102m"
|
||||
# define bgYEL "\x1b[103m"
|
||||
# define bgLBL "\x1b[104m"
|
||||
# define bgPIN "\x1b[105m"
|
||||
# define bgLCY "\x1b[106m"
|
||||
# define bgBRI "\x1b[107m"
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
# define cBLK ""
|
||||
# define cRED ""
|
||||
# define cGRN ""
|
||||
# define cBRN ""
|
||||
# define cBLU ""
|
||||
# define cMGN ""
|
||||
# define cCYA ""
|
||||
# define cLGR ""
|
||||
# define cGRA ""
|
||||
# define cLRD ""
|
||||
# define cLGN ""
|
||||
# define cYEL ""
|
||||
# define cLBL ""
|
||||
# define cPIN ""
|
||||
# define cLCY ""
|
||||
# define cBRI ""
|
||||
# define cRST ""
|
||||
|
||||
# define bgBLK ""
|
||||
# define bgRED ""
|
||||
# define bgGRN ""
|
||||
# define bgBRN ""
|
||||
# define bgBLU ""
|
||||
# define bgMGN ""
|
||||
# define bgCYA ""
|
||||
# define bgLGR ""
|
||||
# define bgGRA ""
|
||||
# define bgLRD ""
|
||||
# define bgLGN ""
|
||||
# define bgYEL ""
|
||||
# define bgLBL ""
|
||||
# define bgPIN ""
|
||||
# define bgLCY ""
|
||||
# define bgBRI ""
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_COLOR */
|
||||
|
||||
/*************************
|
||||
* Box drawing sequences *
|
||||
*************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FANCY_BOXES
|
||||
|
||||
# define SET_G1 "\x1b)0" /* Set G1 for box drawing */
|
||||
# define RESET_G1 "\x1b)B" /* Reset G1 to ASCII */
|
||||
# define bSTART "\x0e" /* Enter G1 drawing mode */
|
||||
# define bSTOP "\x0f" /* Leave G1 drawing mode */
|
||||
# define bH "q" /* Horizontal line */
|
||||
# define bV "x" /* Vertical line */
|
||||
# define bLT "l" /* Left top corner */
|
||||
# define bRT "k" /* Right top corner */
|
||||
# define bLB "m" /* Left bottom corner */
|
||||
# define bRB "j" /* Right bottom corner */
|
||||
# define bX "n" /* Cross */
|
||||
# define bVR "t" /* Vertical, branch right */
|
||||
# define bVL "u" /* Vertical, branch left */
|
||||
# define bHT "v" /* Horizontal, branch top */
|
||||
# define bHB "w" /* Horizontal, branch bottom */
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
# define SET_G1 ""
|
||||
# define RESET_G1 ""
|
||||
# define bSTART ""
|
||||
# define bSTOP ""
|
||||
# define bH "-"
|
||||
# define bV "|"
|
||||
# define bLT "+"
|
||||
# define bRT "+"
|
||||
# define bLB "+"
|
||||
# define bRB "+"
|
||||
# define bX "+"
|
||||
# define bVR "+"
|
||||
# define bVL "+"
|
||||
# define bHT "+"
|
||||
# define bHB "+"
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^FANCY_BOXES */
|
||||
|
||||
/***********************
|
||||
* Misc terminal codes *
|
||||
***********************/
|
||||
|
||||
#define TERM_HOME "\x1b[H"
|
||||
#define TERM_CLEAR TERM_HOME "\x1b[2J"
|
||||
#define cEOL "\x1b[0K"
|
||||
#define CURSOR_HIDE "\x1b[?25l"
|
||||
#define CURSOR_SHOW "\x1b[?25h"
|
||||
|
||||
/************************
|
||||
* Debug & error macros *
|
||||
************************/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Just print stuff to the appropriate stream. */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef MESSAGES_TO_STDOUT
|
||||
# define SAYF(x...) printf(x)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define SAYF(x...) fprintf(stderr, x)
|
||||
#endif /* ^MESSAGES_TO_STDOUT */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed warning. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define WARNF(x...) do { \
|
||||
SAYF(cYEL "[!] " cBRI "WARNING: " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed "doing something" message. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ACTF(x...) do { \
|
||||
SAYF(cLBL "[*] " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed "success" message. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define OKF(x...) do { \
|
||||
SAYF(cLGN "[+] " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed fatal error message (not used in afl). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define BADF(x...) do { \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n[-] " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die with a verbose non-OS fatal error message. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FATAL(x...) do { \
|
||||
SAYF(bSTOP RESET_G1 CURSOR_SHOW cRST cLRD "\n[-] PROGRAM ABORT : " \
|
||||
cBRI x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n Location : " cRST "%s(), %s:%u\n\n", \
|
||||
__FUNCTION__, __FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
exit(1); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die by calling abort() to provide a core dump. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ABORT(x...) do { \
|
||||
SAYF(bSTOP RESET_G1 CURSOR_SHOW cRST cLRD "\n[-] PROGRAM ABORT : " \
|
||||
cBRI x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n Stop location : " cRST "%s(), %s:%u\n\n", \
|
||||
__FUNCTION__, __FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
abort(); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die while also including the output of perror(). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define PFATAL(x...) do { \
|
||||
fflush(stdout); \
|
||||
SAYF(bSTOP RESET_G1 CURSOR_SHOW cRST cLRD "\n[-] SYSTEM ERROR : " \
|
||||
cBRI x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n Stop location : " cRST "%s(), %s:%u\n", \
|
||||
__FUNCTION__, __FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD " OS message : " cRST "%s\n", strerror(errno)); \
|
||||
exit(1); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die with FAULT() or PFAULT() depending on the value of res (used to
|
||||
interpret different failure modes for read(), write(), etc). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define RPFATAL(res, x...) do { \
|
||||
if (res < 0) PFATAL(x); else FATAL(x); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Error-checking versions of read() and write() that call RPFATAL() as
|
||||
appropriate. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_write(fd, buf, len, fn) do { \
|
||||
u32 _len = (len); \
|
||||
s32 _res = write(fd, buf, _len); \
|
||||
if (_res != _len) RPFATAL(_res, "Short write to %s", fn); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_read(fd, buf, len, fn) do { \
|
||||
u32 _len = (len); \
|
||||
s32 _res = read(fd, buf, _len); \
|
||||
if (_res != _len) RPFATAL(_res, "Short read from %s", fn); \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_DEBUG_H */
|
||||
@ -1,19 +1,17 @@
|
||||
================
|
||||
AFL dictionaries
|
||||
================
|
||||
# AFL dictionaries
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
(See [../docs/README.md](../docs/README.md) for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
|
||||
This subdirectory contains a set of dictionaries that can be used in
|
||||
conjunction with the -x option to allow the fuzzer to effortlessly explore the
|
||||
grammar of some of the more verbose data formats or languages. The basic
|
||||
principle behind the operation of fuzzer dictionaries is outlined in section 9
|
||||
of the "main" README for the project.
|
||||
principle behind the operation of fuzzer dictionaries is outlined in section 10
|
||||
of the "main" README.md for the project.
|
||||
|
||||
Custom dictionaries can be added at will. They should consist of a
|
||||
reasonably-sized set of rudimentary syntax units that the fuzzer will then try
|
||||
to clobber together in various ways. Snippets between 2 and 16 bytes are usually
|
||||
the sweet spot.
|
||||
to clobber together in various ways. Snippets between 2 and 16 bytes are
|
||||
usually the sweet spot.
|
||||
|
||||
Custom dictionaries can be created in two ways:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,12 +30,12 @@ parameter is a file or a directory.
|
||||
|
||||
In the file mode, every name field can be optionally followed by @<num>, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
keyword_foo@1 = "foo"
|
||||
`keyword_foo@1 = "foo"`
|
||||
|
||||
Such entries will be loaded only if the requested dictionary level is equal or
|
||||
higher than this number. The default level is zero; a higher value can be set
|
||||
by appending @<num> to the dictionary file name, like so:
|
||||
|
||||
-x path/to/dictionary.dct@2
|
||||
`-x path/to/dictionary.dct@2`
|
||||
|
||||
Good examples of dictionaries can be found in xml.dict and png.dict.
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
# AFL dictionary for GIF images
|
||||
# -----------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
header_87a="87a"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
|
||||
# A basic collection of HTML tags likely to matter to HTML parsers. Does *not*
|
||||
# include any attributes or attribute values.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
tag_a="<a>"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
# AFL dictionary for JPEG images
|
||||
# ------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
header_jfif="JFIF\x00"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Contains basic reserved keywords and syntax building blocks.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
keyword_arguments="arguments"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
|
||||
# Just the basic, standard-originating sections; does not include vendor
|
||||
# extensions.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
header_png="\x89PNG\x0d\x0a\x1a\x0a"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
|
||||
# standpoint, because they are usually not allowed in non-privileged
|
||||
# contexts).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
function_abs=" abs(1)"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
|
||||
# Just the basic, standard-originating sections; does not include vendor
|
||||
# extensions.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
header_ii="II*\x00"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
# AFL dictionary for WebP images
|
||||
# ------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
header_RIFF="RIFF"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Several basic syntax elements and attributes, modeled on libxml2.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Created by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
attr_encoding=" encoding=\"1\""
|
||||
|
||||
122
docs/ChangeLog
122
docs/ChangeLog
@ -13,14 +13,132 @@ Want to stay in the loop on major new features? Join our mailing list by
|
||||
sending a mail to <afl-users+subscribe@googlegroups.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
Version ++2.58c (release):
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- reverted patch to not unlink and recreate the input file, it resulted in
|
||||
performance loss of ~10%
|
||||
- added test/test-performance.sh script
|
||||
- (re)added gcc_plugin, fast inline instrumentation is not yet finished,
|
||||
however it includes the whitelisting and persistance feature! by hexcoder-
|
||||
- gcc_plugin tests added to testing framework
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
Version ++2.54d-2.57c (release):
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- we jump to 2.57 instead of 2.55 to catch up with Google's versioning
|
||||
- persistent mode for QEMU (see qemu_mode/README.md)
|
||||
- custom mutator library is now an additional mutator, to exclusivly use it
|
||||
add AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY (that will trigger the previous behaviour)
|
||||
- new library qemu_mode/unsigaction which filters sigaction events
|
||||
- afl-fuzz: new command line option -I to execute a command on a new crash
|
||||
- no more unlinking the input file, this way the input file can also be a
|
||||
FIFO or disk partition
|
||||
- setting LLVM_CONFIG for llvm_mode will now again switch to the selected
|
||||
llvm version. If your setup is correct.
|
||||
- fuzzing strategy yields for custom mutator were missing from the UI, added them :)
|
||||
- added "make tests" which will perform checks to see that all functionality
|
||||
is working as expected. this is currently the starting point, its not complete :)
|
||||
- added mutation documentation feature ("make document"), creates afl-fuzz-document
|
||||
and saves all mutations of the first run on the first file into out/queue/mutations
|
||||
- libtokencap and libdislocator now compile to the afl_root directory and are
|
||||
installed to the .../lib/afl directory when present during make install
|
||||
- more BSD support, e.g. free CPU binding code for FreeBSD (thanks to devnexen)
|
||||
- reducing duplicate code in afl-fuzz
|
||||
- added "make help"
|
||||
- removed compile warnings from python internal stuff
|
||||
- added man page for afl-clang-fast[++]
|
||||
- updated documentation
|
||||
- Wine mode to run Win32 binaries with the QEMU instrumentation (-W)
|
||||
- CompareCoverage for ARM target in QEMU/Unicorn
|
||||
- laf-intel in llvm_mode now also handles floating point comparisons
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
Version ++2.54c (release):
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- big code refactoring:
|
||||
* all includes are now in include/
|
||||
* all afl sources are now in src/ - see src/README.src
|
||||
* afl-fuzz was splitted up in various individual files for including
|
||||
functionality in other programs (e.g. forkserver, memory map, etc.)
|
||||
for better readability.
|
||||
* new code indention everywhere
|
||||
- auto-generating man pages for all (main) tools
|
||||
- added AFL_FORCE_UI to show the UI even if the terminal is not detected
|
||||
- llvm 9 is now supported (still needs testing)
|
||||
- Android is now supported (thank to JoeyJiao!) - still need to modify the Makefile though
|
||||
- fix building qemu on some Ubuntus (thanks to floyd!)
|
||||
- custom mutator by a loaded library is now supported (thanks to kyakdan!)
|
||||
- added PR that includes peak_rss_mb and slowest_exec_ms in the fuzzer_stats report
|
||||
- more support for *BSD (thanks to devnexen!)
|
||||
- fix building on *BSD (thanks to tobias.kortkamp for the patch)
|
||||
- fix for a few features to support different map sized than 2^16
|
||||
- afl-showmap: new option -r now shows the real values in the buckets (stock
|
||||
afl never did), plus shows tuple content summary information now
|
||||
- small docu updates
|
||||
- NeverZero counters for QEMU
|
||||
- NeverZero counters for Unicorn
|
||||
- CompareCoverage Unicorn
|
||||
- immediates-only instrumentation for CompareCoverage
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
Version ++2.53c (release):
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- README is now README.md
|
||||
- imported the few minor changes from the 2.53b release
|
||||
- unicorn_mode got added - thanks to domenukk for the patch!
|
||||
- fix llvm_mode AFL_TRACE_PC with modern llvm
|
||||
- fix a crash in qemu_mode which also exists in stock afl
|
||||
- added libcompcov, a laf-intel implementation for qemu! :)
|
||||
see qemu_mode/libcompcov/README.libcompcov
|
||||
- afl-fuzz now displays the selected core in the status screen (blue {#})
|
||||
- updated afl-fuzz and afl-system-config for new scaling governor location
|
||||
in modern kernels
|
||||
- using the old ineffective afl-gcc will now show a deprecation warning
|
||||
- all queue, hang and crash files now have their discovery time in their name
|
||||
- if llvm_mode was compiled, afl-clang/afl-clang++ will point to these
|
||||
instead of afl-gcc
|
||||
- added instrim, a much faster llvm_mode instrumentation at the cost of
|
||||
path discovery. See llvm_mode/README.instrim (https://github.com/csienslab/instrim)
|
||||
- added MOpt (github.com/puppet-meteor/MOpt-AFL) mode, see docs/README.MOpt
|
||||
- added code to make it more portable to other platforms than Intel Linux
|
||||
- added never zero counters for afl-gcc and optionally (because of an
|
||||
optimization issue in llvm < 9) for llvm_mode (AFL_LLVM_NEVER_ZERO=1)
|
||||
- added a new doc about binary only fuzzing: docs/binaryonly_fuzzing.txt
|
||||
- more cpu power for afl-system-config
|
||||
- added forkserver patch to afl-tmin, makes it much faster (originally from
|
||||
github.com/nccgroup/TriforceAFL)
|
||||
- added whitelist support for llvm_mode via AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST to allow
|
||||
only to instrument what is actually interesting. Gives more speed and less
|
||||
map pollution (originally by choller@mozilla)
|
||||
- added Python Module mutator support, python2.7-dev is autodetected.
|
||||
see docs/python_mutators.txt (originally by choller@mozilla)
|
||||
- added AFL_CAL_FAST for slow applications and AFL_DEBUG_CHILD_OUTPUT for
|
||||
debugging
|
||||
- added -V time and -E execs option to better comparison runs, runs afl-fuzz
|
||||
for a specific time/executions.
|
||||
- added a -s seed switch to allow afl run with a fixed initial
|
||||
seed that is not updated. This is good for performance and path discovery
|
||||
tests as the random numbers are deterministic then
|
||||
- llvm_mode LAF_... env variables can now be specified as AFL_LLVM_LAF_...
|
||||
that is longer but in line with other llvm specific env vars
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
Version ++2.52c (2019-05-28):
|
||||
Version ++2.52c (2019-06-05):
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Applied community patches. See docs/PATCHES for the full list.
|
||||
LLVM and Qemu modes are now faster.
|
||||
Important changes:
|
||||
afl-fuzz: -e EXTENSION commandline option
|
||||
afl-fuzz: -e EXTENSION commandline option
|
||||
llvm_mode: LAF-intel performance (needs activation, see llvm/README.laf-intel)
|
||||
a few new environment variables for afl-fuzz, llvm and qemu, see docs/env_variables.txt
|
||||
- Added the power schedules of AFLfast by Marcel Boehme, but set the default
|
||||
|
||||
10
docs/PATCHES
10
docs/PATCHES
@ -17,7 +17,15 @@ afl-qemu-optimize-entrypoint.diff by mh(at)mh-sec(dot)de
|
||||
afl-qemu-speed.diff by abiondo on github
|
||||
afl-qemu-optimize-map.diff by mh(at)mh-sec(dot)de
|
||||
|
||||
additionally AFLfast additions (github.com/mboehme/aflfast) were incorporated.
|
||||
+ Custom mutator (native library) (by kyakdan)
|
||||
+ unicorn_mode (modernized and updated by domenukk)
|
||||
+ instrim (https://github.com/csienslab/instrim) was integrated
|
||||
+ MOpt (github.com/puppet-meteor/MOpt-AFL) was imported
|
||||
+ AFLfast additions (github.com/mboehme/aflfast) were incorporated.
|
||||
+ Qemu 3.1 upgrade with enhancement patches (github.com/andreafioraldi/afl)
|
||||
+ Python mutator modules support (github.com/choller/afl)
|
||||
+ Whitelisting in LLVM mode (github.com/choller/afl)
|
||||
+ forkserver patch for afl-tmin (github.com/nccgroup/TriforceAFL)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
NOT INSTALLED
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
AFL quick start guide
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
You should read docs/README. It's pretty short. If you really can't, here's
|
||||
You should read docs/README.md - it's pretty short. If you really can't, here's
|
||||
how to hit the ground running:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Compile AFL with 'make'. If build fails, see docs/INSTALL for tips.
|
||||
@ -12,10 +12,12 @@ how to hit the ground running:
|
||||
If testing a network service, modify it to run in the foreground and read
|
||||
from stdin. When fuzzing a format that uses checksums, comment out the
|
||||
checksum verification code, too.
|
||||
If this is not possible (e.g. in -Q(emu) mode) then use AFL_POST_LIBRARY
|
||||
to calculate the values with your own library.
|
||||
|
||||
The program must crash properly when a fault is encountered. Watch out for
|
||||
custom SIGSEGV or SIGABRT handlers and background processes. For tips on
|
||||
detecting non-crashing flaws, see section 11 in docs/README.
|
||||
detecting non-crashing flaws, see section 11 in docs/README.md .
|
||||
|
||||
3) Compile the program / library to be fuzzed using afl-gcc. A common way to
|
||||
do this would be:
|
||||
@ -40,10 +42,13 @@ how to hit the ground running:
|
||||
6) Investigate anything shown in red in the fuzzer UI by promptly consulting
|
||||
docs/status_screen.txt.
|
||||
|
||||
7) compile and use llvm_mode (afl-clang-fast/afl-clang-fast++) as it is way
|
||||
faster and has a few cool features
|
||||
|
||||
That's it. Sit back, relax, and - time permitting - try to skim through the
|
||||
following files:
|
||||
|
||||
- docs/README - A general introduction to AFL,
|
||||
- docs/README.md - A general introduction to AFL,
|
||||
- docs/perf_tips.txt - Simple tips on how to fuzz more quickly,
|
||||
- docs/status_screen.txt - An explanation of the tidbits shown in the UI,
|
||||
- docs/parallel_fuzzing.txt - Advice on running AFL on multiple cores.
|
||||
|
||||
51
docs/README.MOpt
Normal file
51
docs/README.MOpt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
# MOpt(imized) AFL by <puppet@zju.edu.cn>
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Description
|
||||
MOpt-AFL is a AFL-based fuzzer that utilizes a customized Particle Swarm
|
||||
Optimization (PSO) algorithm to find the optimal selection probability
|
||||
distribution of operators with respect to fuzzing effectiveness.
|
||||
More details can be found in the technical report.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Cite Information
|
||||
Chenyang Lyu, Shouling Ji, Chao Zhang, Yuwei Li, Wei-Han Lee, Yu Song and
|
||||
Raheem Beyah, MOPT: Optimized Mutation Scheduling for Fuzzers,
|
||||
USENIX Security 2019.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Seed Sets
|
||||
We open source all the seed sets used in the paper
|
||||
"MOPT: Optimized Mutation Scheduling for Fuzzers".
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Experiment Results
|
||||
The experiment results can be found in
|
||||
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/184GOzkZGls1H2NuLuUfSp9gfqp1E2-lL?usp=sharing.
|
||||
We only open source the crash files since the space is limited.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Technical Report
|
||||
MOpt_TechReport.pdf is the technical report of the paper
|
||||
"MOPT: Optimized Mutation Scheduling for Fuzzers", which contains more deatails.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Parameter Introduction
|
||||
Most important, you must add the parameter `-L` (e.g., `-L 0`) to launch the
|
||||
MOpt scheme.
|
||||
|
||||
Option '-L' controls the time to move on to the pacemaker fuzzing mode.
|
||||
'-L t': when MOpt-AFL finishes the mutation of one input, if it has not
|
||||
discovered any new unique crash or path for more than t minutes, MOpt-AFL will
|
||||
enter the pacemaker fuzzing mode.
|
||||
|
||||
Setting 0 will enter the pacemaker fuzzing mode at first, which is
|
||||
recommended in a short time-scale evaluation.
|
||||
|
||||
Other important parameters can be found in afl-fuzz.c, for instance,
|
||||
|
||||
'swarm_num': the number of the PSO swarms used in the fuzzing process.
|
||||
'period_pilot': how many times MOpt-AFL will execute the target program
|
||||
in the pilot fuzzing module, then it will enter the core fuzzing module.
|
||||
'period_core': how many times MOpt-AFL will execute the target program in the
|
||||
core fuzzing module, then it will enter the PSO updating module.
|
||||
'limit_time_bound': control how many interesting test cases need to be found
|
||||
before MOpt-AFL quits the pacemaker fuzzing mode and reuses the deterministic stage.
|
||||
0 < 'limit_time_bound' < 1, MOpt-AFL-tmp.
|
||||
'limit_time_bound' >= 1, MOpt-AFL-ever.
|
||||
|
||||
Have fun with MOpt in AFL!
|
||||
1
docs/README.md
Symbolic link
1
docs/README.md
Symbolic link
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
../README.md
|
||||
144
docs/binaryonly_fuzzing.txt
Normal file
144
docs/binaryonly_fuzzing.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Fuzzing binary-only programs with afl++
|
||||
=======================================
|
||||
|
||||
afl++, libfuzzer and others are great if you have the source code, and
|
||||
it allows for very fast and coverage guided fuzzing.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if there is only the binary program and not source code available,
|
||||
then standard afl++ (dumb mode) is not effective.
|
||||
|
||||
The following is a description of how these can be fuzzed with afl++
|
||||
|
||||
!!!!!
|
||||
TL;DR: try DYNINST with afl-dyninst. If it produces too many crashes then
|
||||
use afl -Q qemu_mode, or better: use both in parallel.
|
||||
!!!!!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU
|
||||
----
|
||||
Qemu is the "native" solution to the program.
|
||||
It is available in the ./qemu_mode/ directory and once compiled it can
|
||||
be accessed by the afl-fuzz -Q command line option.
|
||||
The speed decrease is at about 50%
|
||||
It is the easiest to use alternative and even works for cross-platform binaries.
|
||||
|
||||
As it is included in afl++ this needs no URL.
|
||||
|
||||
WINE+QEMU
|
||||
---------
|
||||
Wine mode can run Win32 PE with the QEMU instrumentation.
|
||||
It needs Wine, python3 and the pefile python package installed.
|
||||
|
||||
UNICORN
|
||||
-------
|
||||
Unicorn is a fork of QEMU. The instrumentation is, therefore, very similar.
|
||||
In contrast to QEMU, Unicorn does not offer a full system or even userland emulation.
|
||||
Runtime environment and/or loaders have to be written from scratch, if needed.
|
||||
On top, block chaining has been removed. This means the speed boost introduced in
|
||||
to the patched QEMU Mode of afl++ cannot simply be ported over to Unicorn.
|
||||
For further information, check out ./unicorn_mode.txt.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DYNINST
|
||||
-------
|
||||
Dyninst is a binary instrumentation framework similar to Pintool and Dynamorio
|
||||
(see far below). However whereas Pintool and Dynamorio work at runtime, dyninst
|
||||
instruments the target at load time, and then let it run.
|
||||
This is great for some things, e.g. fuzzing, and not so effective for others,
|
||||
e.g. malware analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
So what we can do with dyninst is taking every basic block, and put afl's
|
||||
instrumention code in there - and then save the binary.
|
||||
Afterwards we can just fuzz the newly saved target binary with afl-fuzz.
|
||||
Sounds great? It is. The issue though - it is a non-trivial problem to
|
||||
insert instructions, which change addresses in the process space, so
|
||||
everything is still working afterwards. Hence more often than not binaries
|
||||
crash when they are run (because of instrumentation).
|
||||
|
||||
The speed decrease is about 15-35%, depending on the optimization options
|
||||
used with afl-dyninst.
|
||||
|
||||
So if dyninst works, it is the best option available. Otherwise it just doesn't
|
||||
work well.
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dyninst
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
INTEL-PT
|
||||
--------
|
||||
If you have a newer Intel CPU, you can make use of Intels processor trace.
|
||||
The big issue with Intel's PT is the small buffer size and the complex
|
||||
encoding of the debug information collected through PT.
|
||||
This makes the decoding very CPU intensive and hence slow.
|
||||
As a result, the overall speed decrease is about 70-90% (depending on
|
||||
the implementation and other factors).
|
||||
|
||||
There are two afl intel-pt implementations:
|
||||
|
||||
1. https://github.com/junxzm1990/afl-pt
|
||||
=> this needs Ubuntu 14.04.05 without any updates and the 4.4 kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
2. https://github.com/hunter-ht-2018/ptfuzzer
|
||||
=> this needs a 4.14 or 4.15 kernel. the "nopti" kernel boot option must
|
||||
be used. This one is faster than the other.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
CORESIGHT
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
Coresight is ARM's answer to Intel's PT.
|
||||
There is no implementation so far which handle coresight and getting
|
||||
it working on an ARM Linux is very difficult due to custom kernel building
|
||||
on embedded systems is difficult. And finding one that has coresight in
|
||||
the ARM chip is difficult too.
|
||||
My guess is that it is slower than Qemu, but faster than Intel PT.
|
||||
If anyone finds any coresight implementation for afl please ping me:
|
||||
vh@thc.org
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PIN & DYNAMORIO
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
||||
Pintool and Dynamorio are dynamic instrumentation engines, and they can be
|
||||
used for getting basic block information at runtime.
|
||||
Pintool is only available for Intel x32/x64 on Linux, Mac OS and Windows
|
||||
whereas Dynamorio is additionally available for ARM and AARCH64.
|
||||
Dynamorio is also 10x faster than Pintool.
|
||||
|
||||
The big issue with Dynamorio (and therefore Pintool too) is speed.
|
||||
Dynamorio has a speed decrease of 98-99%
|
||||
Pintool has a speed decrease of 99.5%
|
||||
|
||||
Hence Dynamorio is the option to go for if everything fails, and Pintool
|
||||
only if Dynamorio fails too.
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamorio solutions:
|
||||
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dynamorio
|
||||
https://github.com/mxmssh/drAFL
|
||||
https://github.com/googleprojectzero/winafl/ <= very good but windows only
|
||||
|
||||
Pintool solutions:
|
||||
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-pin
|
||||
https://github.com/mothran/aflpin
|
||||
https://github.com/spinpx/afl_pin_mode <= only old Pintool version supported
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Non-AFL solutions
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
There are many binary-only fuzzing frameworks. Some are great for CTFs but don't
|
||||
work with large binaries, others are very slow but have good path discovery,
|
||||
some are very hard to set-up ...
|
||||
|
||||
QSYM: https://github.com/sslab-gatech/qsym
|
||||
Manticore: https://github.com/trailofbits/manticore
|
||||
S2E: https://github.com/S2E
|
||||
<please send me any missing that are good>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That's it!
|
||||
News, corrections, updates?
|
||||
Email vh@thc.org
|
||||
39
docs/custom_mutator.txt
Normal file
39
docs/custom_mutator.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
Adding custom mutators to AFL using
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
This file describes how you can implement custom mutations to be used in AFL.
|
||||
|
||||
Implemented by Khaled Yakdan from Code Intelligence <yakdan@code-intelligence.de>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1) Description
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
Custom mutator libraries can be passed to afl-fuzz to perform custom mutations
|
||||
on test cases beyond those available in AFL - for example, to enable structure-aware
|
||||
fuzzing by using libraries that perform mutations according to a given grammar.
|
||||
|
||||
The custom mutator library is passed to afl-fuzz via the AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_LIBRARY
|
||||
environment variable. The library must export the afl_custom_mutator() function and
|
||||
must be compiled as a shared object. For example:
|
||||
$CC -shared -Wall -O3 <lib-name>.c -o <lib-name>.so
|
||||
|
||||
Note: unless AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY is set, its state mutator like any others,
|
||||
so it will be used for some test cases, and other mutators for others.
|
||||
|
||||
Only if AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY is set the afl_custom_mutator() function will
|
||||
be called every time it needs to mutate test case!
|
||||
|
||||
For some cases, the format of the mutated data returned from
|
||||
the custom mutator is not suitable to directly execute the target with this input.
|
||||
For example, when using libprotobuf-mutator, the data returned is in a protobuf
|
||||
format which corresponds to a given grammar. In order to execute the target,
|
||||
the protobuf data must be converted to the plain-text format expected by the target.
|
||||
In such scenarios, the user can define the afl_pre_save_handler() function. This function
|
||||
is then transforms the data into the format expected by the API before executing the target.
|
||||
afl_pre_save_handler is optional and does not have to be implemented if its functionality
|
||||
is not needed.
|
||||
|
||||
2) Example
|
||||
----------
|
||||
A simple example is provided in ../custom_mutators/
|
||||
@ -7,8 +7,8 @@ Environmental variables
|
||||
users or for some types of custom fuzzing setups. See README for the general
|
||||
instruction manual.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Settings for afl-gcc, afl-clang, and afl-as
|
||||
----------------------------------------------
|
||||
1) Settings for afl-gcc, afl-clang, and afl-as - and gcc_plugin afl-gcc-fast
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Because they can't directly accept command-line options, the compile-time
|
||||
tools make fairly broad use of environmental variables:
|
||||
@ -68,20 +68,83 @@ tools make fairly broad use of environmental variables:
|
||||
- Setting AFL_QUIET will prevent afl-cc and afl-as banners from being
|
||||
displayed during compilation, in case you find them distracting.
|
||||
|
||||
2) Settings for afl-clang-fast
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
- Setting AFL_CAL_FAST will speed up the initial calibration, if the
|
||||
application is very slow
|
||||
|
||||
The native LLVM instrumentation helper accepts a subset of the settings
|
||||
discussed in section #1, with the exception of:
|
||||
2) Settings for afl-clang-fast / afl-clang-fast++ / afl-gcc-fast / afl-g++-fast
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The native instrumentation helpers (llvm_mode and gcc_plugin) accept a subset
|
||||
of the settings discussed in section #1, with the exception of:
|
||||
|
||||
- AFL_AS, since this toolchain does not directly invoke GNU as.
|
||||
|
||||
- TMPDIR and AFL_KEEP_ASSEMBLY, since no temporary assembly files are
|
||||
created.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that AFL_INST_RATIO will behave a bit differently than for afl-gcc,
|
||||
because functions are *not* instrumented unconditionally - so low values
|
||||
will have a more striking effect. For this tool, 0 is not a valid choice.
|
||||
- AFL_INST_RATIO, as we switched for instrim instrumentation which
|
||||
is more effective but makes not much sense together with this option.
|
||||
|
||||
Then there are a few specific features that are only available in llvm_mode:
|
||||
|
||||
LAF-INTEL
|
||||
=========
|
||||
This great feature will split compares to series of single byte comparisons
|
||||
to allow afl-fuzz to find otherwise rather impossible paths. It is not
|
||||
restricted to Intel CPUs ;-)
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES will split switch()es
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES will split string compare functions
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES will split all floating point and
|
||||
64, 32 and 16 bit integer CMP instructions
|
||||
|
||||
See llvm_mode/README.laf-intel.md for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
WHITELIST
|
||||
=========
|
||||
This feature allows selectively instrumentation of the source
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST with a filename will only instrument those
|
||||
files that match the names listed in this file.
|
||||
|
||||
See llvm_mode/README.whitelist.md for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
INSTRIM
|
||||
=======
|
||||
This feature increases the speed by whopping 20% but at the cost of a
|
||||
lower path discovery and therefore coverage.
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM activates this mode
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM_LOOPHEAD=1 expands on INSTRIM to optimize loops.
|
||||
afl-fuzz will only be able to see the path the loop took, but not how
|
||||
many times it was called (unless it is a complex loop).
|
||||
|
||||
See llvm_mode/README.instrim.md
|
||||
|
||||
NOT_ZERO
|
||||
========
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_LLVM_NOT_ZERO=1 during compilation will use counters
|
||||
that skip zero on overflow. This is the default for llvm >= 9,
|
||||
however for llvm versions below that this will increase an unnecessary
|
||||
slowdown due a performance issue that is only fixed in llvm 9+.
|
||||
This feature increases path discovery by a little bit.
|
||||
|
||||
See llvm_mode/README.neverzero.md
|
||||
|
||||
Then there are a few specific features that are only available in the gcc_plugin:
|
||||
|
||||
WHITELIST
|
||||
=========
|
||||
This feature allows selective instrumentation of the source
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_GCC_WHITELIST with a filename will only instrument those
|
||||
files that match the names listed in this file (one filename per line).
|
||||
|
||||
See gcc_plugin/README.whitelist.md for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
3) Settings for afl-fuzz
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
@ -132,8 +195,8 @@ checks or alter some of the more exotic semantics of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- AFL_TMPDIR is used to write the .cur_input file to if exists, and in
|
||||
the normal output directory otherwise. You would use this to point to
|
||||
a ramdisk/tmpfs. This increases the speed by a very minimal value but
|
||||
also reduces the stress on SSDs.
|
||||
a ramdisk/tmpfs. This increases the speed by a small value but also
|
||||
reduces the stress on SSDs.
|
||||
|
||||
- When developing custom instrumentation on top of afl-fuzz, you can use
|
||||
AFL_SKIP_BIN_CHECK to inhibit the checks for non-instrumented binaries
|
||||
@ -150,6 +213,16 @@ checks or alter some of the more exotic semantics of the tool:
|
||||
mutated files - say, to fix up checksums. See experimental/post_library/
|
||||
for more.
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_LIBRARY to a shared library with
|
||||
afl_custom_mutator() export run additional mutations though this library.
|
||||
If AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY is also set, all mutations will solely be
|
||||
performed with/from the libary. see docs/custom_mutator.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- For AFL_PYTHON_MODULE and AFL_PYTHON_ONLY - they require to be compiled
|
||||
with -DUSE_PYTHON. Please see docs/python_mutators.txt
|
||||
This feature allows to configure custom mutators which can be very helpful
|
||||
in e.g. fuzzing XML or other highly flexible structured input.
|
||||
|
||||
- AFL_FAST_CAL keeps the calibration stage about 2.5x faster (albeit less
|
||||
precise), which can help when starting a session against a slow target.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -167,6 +240,9 @@ checks or alter some of the more exotic semantics of the tool:
|
||||
some basic stats. This behavior is also automatically triggered when the
|
||||
output from afl-fuzz is redirected to a file or to a pipe.
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_FORCE_UI will force painting the UI on the screen even if
|
||||
no valid terminal was detected (for virtual consoles)
|
||||
|
||||
- If you are Jakub, you may need AFL_I_DONT_CARE_ABOUT_MISSING_CRASHES.
|
||||
Others need not apply.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -174,6 +250,9 @@ checks or alter some of the more exotic semantics of the tool:
|
||||
processing the first queue entry; and AFL_BENCH_UNTIL_CRASH causes it to
|
||||
exit soon after the first crash is found.
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_DEBUG_CHILD_OUTPUT will not suppress the child output.
|
||||
Not pretty but good for debugging purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
4) Settings for afl-qemu-trace
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -185,6 +264,20 @@ The QEMU wrapper used to instrument binary-only code supports several settings:
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_INST_LIBS causes the translator to also instrument the code
|
||||
inside any dynamically linked libraries (notably including glibc).
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL enables the CompareCoverage tracing of all cmp
|
||||
and sub in x86 and x86_64 and memory comparions functions (e.g. strcmp,
|
||||
memcmp, ...) when libcompcov is preloaded using AFL_PRELOAD.
|
||||
More info at qemu_mode/libcompcov/README.md.
|
||||
There are two levels at the moment, AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL=1 that instruments
|
||||
only comparisons with immediate values / read-only memory and
|
||||
AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL=2 that instruments all the comparions. Level 2 is more
|
||||
accurate but may need a larger shared memory.
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting AFL_QEMU_COMPCOV enables the CompareCoverage tracing of all
|
||||
cmp and sub in x86 and x86_64.
|
||||
This is an alias of AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL=1 when AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL is
|
||||
not specified.
|
||||
|
||||
- The underlying QEMU binary will recognize any standard "user space
|
||||
emulation" variables (e.g., QEMU_STACK_SIZE), but there should be no
|
||||
@ -194,9 +287,10 @@ The QEMU wrapper used to instrument binary-only code supports several settings:
|
||||
Use this if you are unsure if the entrypoint might be wrong - but
|
||||
use it directly, e.g. afl-qemu-trace ./program
|
||||
|
||||
- If you want to specify a specific entrypoint into the binary (this can
|
||||
be very good for the performance!), use AFL_ENTRYPOINT for this.
|
||||
- AFL_ENTRYPOINT allows you to specify a specific entrypoint into the
|
||||
binary (this can be very good for the performance!).
|
||||
The entrypoint is specified as hex address, e.g. 0x4004110
|
||||
Note that the address must be the address of a basic block.
|
||||
|
||||
5) Settings for afl-cmin
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
@ -235,7 +329,7 @@ of decimal.
|
||||
8) Settings for libdislocator.so
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The library honors three environmental variables:
|
||||
The library honors these environmental variables:
|
||||
|
||||
- AFL_LD_LIMIT_MB caps the size of the maximum heap usage permitted by the
|
||||
library, in megabytes. The default value is 1 GB. Once this is exceeded,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,6 +64,14 @@ that can offer huge benefits for programs with high startup overhead. Both
|
||||
modes require you to edit the source code of the fuzzed program, but the
|
||||
changes often amount to just strategically placing a single line or two.
|
||||
|
||||
If there are important data comparisons performed (e.g. strcmp(ptr, MAGIC_HDR)
|
||||
then using laf-intel (see llvm_mode/README.laf-intel) will help afl-fuzz a lot
|
||||
to get to the important parts in the code.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are only intested in specific parts of the code being fuzzed, you can
|
||||
whitelist the files that are actually relevant. This improves the speed and
|
||||
accuracy of afl. See llvm_mode/README.whitelist
|
||||
|
||||
4) Profile and optimize the binary
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -191,7 +199,7 @@ There are several OS-level factors that may affect fuzzing speed:
|
||||
- Use the afl-system-config script to set all proc/sys settings above
|
||||
|
||||
- Disable all the spectre, meltdown etc. security countermeasures in the
|
||||
kernel if your machine is properly seperated:
|
||||
kernel if your machine is properly separated:
|
||||
"ibpb=off ibrs=off kpti=off l1tf=off mds=off mitigations=off
|
||||
no_stf_barrier noibpb noibrs nopcid nopti nospec_store_bypass_disable
|
||||
nospectre_v1 nospectre_v2 pcid=off pti=off spec_store_bypass_disable=off
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,31 +1,26 @@
|
||||
This document was copied and modified from AFLfast at github.com/mboehme/aflfast
|
||||
afl++'s power schedules based on AFLfast
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://comp.nus.edu.sg/~mboehme/paper/CCS16.pdf"><img src="https://comp.nus.edu.sg/~mboehme/paper/CCS16.png" align="right" width="250"></a>
|
||||
Power schedules implemented by Marcel Böhme \<marcel.boehme@acm.org\>.
|
||||
AFLFast is an extension of AFL which was written by Michal Zalewski.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, we observed that most generated inputs exercise the same few
|
||||
"high-frequency" paths and developed strategies to gravitate towards
|
||||
low-frequency paths, to stress significantly more program behavior in the
|
||||
same amount of time. We devised several **search strategies** that decide
|
||||
in which order the seeds should be fuzzed and **power schedules** that
|
||||
smartly regulate the number of inputs generated from a seed (i.e., the
|
||||
time spent fuzzing a seed). We call the number of inputs generated from a
|
||||
seed, the seed's **energy**.
|
||||
AFLfast has helped in the success of Team Codejitsu at the finals of the DARPA Cyber Grand Challenge where their bot Galactica took **2nd place** in terms of #POVs proven (see red bar at https://www.cybergrandchallenge.com/event#results). AFLFast exposed several previously unreported CVEs that could not be exposed by AFL in 24 hours and otherwise exposed vulnerabilities significantly faster than AFL while generating orders of magnitude more unique crashes.
|
||||
|
||||
Old AFL used -p exploit which had a too high cost, current AFL uses -p explore.
|
||||
Essentially, we observed that most generated inputs exercise the same few "high-frequency" paths and developed strategies to gravitate towards low-frequency paths, to stress significantly more program behavior in the same amount of time. We devised several **search strategies** that decide in which order the seeds should be fuzzed and **power schedules** that smartly regulate the number of inputs generated from a seed (i.e., the time spent fuzzing a seed). We call the number of inputs generated from a seed, the seed's **energy**.
|
||||
|
||||
AFLfast implemented 4 new power schedules which are highly recommended to run
|
||||
in parallel.
|
||||
We find that AFL's exploitation-based constant schedule assigns **too much energy to seeds exercising high-frequency paths** (e.g., paths that reject invalid inputs) and not enough energy to seeds exercising low-frequency paths (e.g., paths that stress interesting behaviors). Technically, we modified the computation of a seed's performance score (`calculate_score`), which seed is marked as favourite (`update_bitmap_score`), and which seed is chosen next from the circular queue (`main`). We implemented the following schedules (in the order of their effectiveness, best first):
|
||||
|
||||
| AFL flag | Power Schedule |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------------------------- |
|
||||
| `-p fast` (default)| 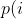=\\min\\left(\\frac{\\alpha(i)}{\\beta}\\cdot\\frac{2^{s(i)}}{f(i)},M\\right)) |
|
||||
| `-p explore` (default)| 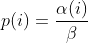 |
|
||||
| `-p fast` | 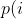=\\min\\left(\\frac{\\alpha(i)}{\\beta}\\cdot\\frac{2^{s(i)}}{f(i)},M\\right)) |
|
||||
| `-p coe` | 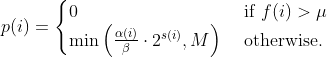 |
|
||||
| `-p explore` | 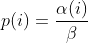 |
|
||||
| `-p quad` | 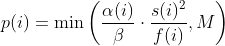 |
|
||||
| `-p lin` | 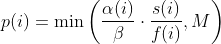 |
|
||||
| `-p exploit` (AFL) | 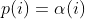 |
|
||||
where *α(i)* is the performance score that AFL uses to compute for the seed input *i*, *β(i)>1* is a constant, *s(i)* is the number of times that seed *i* has been chosen from the queue, *f(i)* is the number of generated inputs that exercise the same path as seed *i*, and *μ* is the average number of generated inputs exercising a path.
|
||||
|
||||
More details can be found in our paper that was recently accepted at the [23rd ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS'16)](https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2016/accepted-papers/).
|
||||
More details can be found in the paper that was accepted at the [23rd ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS'16)](https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2016/accepted-papers/).
|
||||
|
||||
PS: In parallel mode (several instances with shared queue), we suggest to run the master using the exploit schedule (-p exploit) and the slaves with a combination of cut-off-exponential (-p coe), exponential (-p fast; default), and explore (-p explore) schedules. In single mode, the default settings will do. **EDIT:** In parallel mode, AFLFast seems to perform poorly because the path probability estimates are incorrect for the imported seeds. Pull requests to fix this issue by syncing the estimates accross instances are appreciated :)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
152
docs/python_mutators.txt
Normal file
152
docs/python_mutators.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
Adding custom mutators to AFL using Python modules
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
This file describes how you can utilize the external Python API to write
|
||||
your own custom mutation routines.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This feature is highly experimental. Use at your own risk.
|
||||
|
||||
Implemented by Christian Holler (:decoder) <choller@mozilla.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This is for Python 2.7 !
|
||||
Anyone who wants to add Python 3.7 support is happily welcome :)
|
||||
|
||||
For an example and a template see ../python_mutators/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1) Description and purpose
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
While AFLFuzz comes with a good selection of generic deterministic and
|
||||
non-deterministic mutation operations, it sometimes might make sense to extend
|
||||
these to implement strategies more specific to the target you are fuzzing.
|
||||
|
||||
For simplicity and in order to allow people without C knowledge to extend
|
||||
AFLFuzz, I implemented a "Python" stage that can make use of an external
|
||||
module (written in Python) that implements a custom mutation stage.
|
||||
|
||||
The main motivation behind this is to lower the barrier for people
|
||||
experimenting with this tool. Hopefully, someone will be able to do useful
|
||||
things with this extension.
|
||||
|
||||
If you find it useful, have questions or need additional features added to the
|
||||
interface, feel free to send a mail to <choller@mozilla.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
See the following information to get a better pictures:
|
||||
https://www.agarri.fr/docs/XML_Fuzzing-NullCon2017-PUBLIC.pdf
|
||||
https://bugs.chromium.org/p/chromium/issues/detail?id=930663
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2) How the Python module looks like
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a simple example in pymodules/example.py including documentation
|
||||
explaining each function. In the same directory, you can find another simple
|
||||
module that performs simple mutations.
|
||||
|
||||
Right now, "init" is called at program startup and can be used to perform any
|
||||
kinds of one-time initializations while "fuzz" is called each time a mutation
|
||||
is requested.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also optional support for a trimming API, see the section below for
|
||||
further information about this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3) How to compile AFLFuzz with Python support
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You must install the python 2.7 development package of your Linux distribution
|
||||
before this will work. On Debian/Ubuntu/Kali this can be done with:
|
||||
apt install python2.7-dev
|
||||
|
||||
A prerequisite for using this mode is to compile AFLFuzz with Python support.
|
||||
|
||||
The afl Makefile performs some magic and detects Python 2.7 if it is in the
|
||||
default path and compiles afl-fuzz with the feature if available (which is
|
||||
/usr/include/python2.7 for the Python.h include and /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
|
||||
for the libpython2.7.a library)
|
||||
|
||||
In case your setup is different set the necessary variables like this:
|
||||
PYTHON_INCLUDE=/path/to/python2.7/include LDFLAGS=-L/path/to/python2.7/lib make
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4) How to run AFLFuzz with your custom module
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You must pass the module name inside the env variable AFL_PYTHON_MODULE.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, if you are trying to load the module from the local directory,
|
||||
you must adjust your PYTHONPATH to reflect this circumstance. The following
|
||||
command should work if you are inside the aflfuzz directory:
|
||||
|
||||
$ AFL_PYTHON_MODULE="pymodules.test" PYTHONPATH=. ./afl-fuzz
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, the following environment variables are supported:
|
||||
|
||||
AFL_PYTHON_ONLY - Disable all other mutation stages. This can prevent broken
|
||||
testcases (those that your Python module can't work with
|
||||
anymore) to fill up your queue. Best combined with a custom
|
||||
trimming routine (see below) because trimming can cause the
|
||||
same test breakage like havoc and splice.
|
||||
|
||||
AFL_DEBUG - When combined with AFL_NO_UI, this causes the C trimming code
|
||||
to emit additional messages about the performance and actions
|
||||
of your custom Python trimmer. Use this to see if it works :)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
5) Order and statistics
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The Python stage is set to be the first non-deterministic stage (right before
|
||||
the havoc stage). In the statistics however, it shows up as the third number
|
||||
under "havoc". That's because I'm lazy and I didn't want to mess with the UI
|
||||
too much ;)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
6) Trimming support
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The generic trimming routines implemented in AFLFuzz can easily destroy the
|
||||
structure of complex formats, possibly leading to a point where you have a lot
|
||||
of testcases in the queue that your Python module cannot process anymore but
|
||||
your target application still accepts. This is especially the case when your
|
||||
target can process a part of the input (causing coverage) and then errors out
|
||||
on the remaining input.
|
||||
|
||||
In such cases, it makes sense to implement a custom trimming routine in Python.
|
||||
The API consists of multiple methods because after each trimming step, we have
|
||||
to go back into the C code to check if the coverage bitmap is still the same
|
||||
for the trimmed input. Here's a quick API description:
|
||||
|
||||
init_trim: This method is called at the start of each trimming operation
|
||||
and receives the initial buffer. It should return the amount
|
||||
of iteration steps possible on this input (e.g. if your input
|
||||
has n elements and you want to remove them one by one, return n,
|
||||
if you do a binary search, return log(n), and so on...).
|
||||
|
||||
If your trimming algorithm doesn't allow you to determine the
|
||||
amount of (remaining) steps easily (esp. while running), then you
|
||||
can alternatively return 1 here and always return 0 in post_trim
|
||||
until you are finished and no steps remain. In that case,
|
||||
returning 1 in post_trim will end the trimming routine. The whole
|
||||
current index/max iterations stuff is only used to show progress.
|
||||
|
||||
trim: This method is called for each trimming operation. It doesn't
|
||||
have any arguments because we already have the initial buffer
|
||||
from init_trim and we can memorize the current state in global
|
||||
variables. This can also save reparsing steps for each iteration.
|
||||
It should return the trimmed input buffer, where the returned data
|
||||
must not exceed the initial input data in length. Returning anything
|
||||
that is larger than the original data (passed to init_trim) will
|
||||
result in a fatal abort of AFLFuzz.
|
||||
|
||||
post_trim: This method is called after each trim operation to inform you
|
||||
if your trimming step was successful or not (in terms of coverage).
|
||||
If you receive a failure here, you should reset your input to the
|
||||
last known good state.
|
||||
In any case, this method must return the next trim iteration index
|
||||
(from 0 to the maximum amount of steps you returned in init_trim).
|
||||
|
||||
Omitting any of the methods will cause Python trimming to be disabled and
|
||||
trigger a fallback to the builtin default trimming routine.
|
||||
@ -6,6 +6,10 @@ Sister projects
|
||||
designed for, or meant to integrate with AFL. See README for the general
|
||||
instruction manual.
|
||||
|
||||
!!!
|
||||
!!! This list is outdated and needs an update, missing: e.g. Angora, FairFuzz
|
||||
!!!
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------
|
||||
Support for other languages / environments:
|
||||
-------------------------------------------
|
||||
@ -263,7 +267,7 @@ Static binary-only instrumentation (Aleksandar Nikolich)
|
||||
reports better performance compared to QEMU, but occasional translation
|
||||
errors with stripped binaries.
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/vrtadmin/moflow/tree/master/afl-dyninst
|
||||
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dyninst
|
||||
|
||||
AFL PIN (Parker Thompson)
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,6 +33,16 @@ other side effects - sorry about that.
|
||||
|
||||
With that out of the way, let's talk about what's actually on the screen...
|
||||
|
||||
0) The status bar
|
||||
|
||||
The top line shows you which mode afl-fuzz is running in
|
||||
(normal: "american fuzy lop", crash exploration mode: "peruvian rabbit mode")
|
||||
and the version of afl++.
|
||||
Next to the version is the banner, which, if not set with -T by hand, will
|
||||
either show the binary name being fuzzed, or the -M/-S master/slave name for
|
||||
parallel fuzzing.
|
||||
Finally, the last item is the power schedule mode being run (default: explore).
|
||||
|
||||
1) Process timing
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -397,6 +407,9 @@ directory. This includes:
|
||||
- variable_paths - number of test cases showing variable behavior
|
||||
- unique_crashes - number of unique crashes recorded
|
||||
- unique_hangs - number of unique hangs encountered
|
||||
- command_line - full command line used for the fuzzing session
|
||||
- slowest_exec_ms- real time of the slowest execution in seconds
|
||||
- peak_rss_mb - max rss usage reached during fuzzing in MB
|
||||
|
||||
Most of these map directly to the UI elements discussed earlier on.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - sample argv fuzzing wrapper
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
# David A. Wheeler <dwheeler@ida.org>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Edits to bring the script in line with afl-cmin and other companion scripts
|
||||
# by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>. All bugs are my fault.
|
||||
# by Michal Zalewski. All bugs are my fault.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2015 Institute for Defense Analyses.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - <canvas> harness
|
||||
-------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - clang assembly normalizer
|
||||
# ----------------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
# The idea for this wrapper comes from Ryan Govostes.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2013, 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - crash triage utility
|
||||
# -----------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2013, 2014, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
||||
# necessary.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
echo "crash triage utility for afl-fuzz by <lcamtuf@google.com>"
|
||||
echo "crash triage utility for afl-fuzz by Michal Zalewski"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
ulimit -v 100000 2>/dev/null
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - fuzzer synchronization tool
|
||||
# ------------------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - persistent mode example
|
||||
--------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,6 +33,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
ssize_t len; /* how much input did we read? */
|
||||
char buf[100]; /* Example-only buffer, you'd replace it with other global or
|
||||
local variables appropriate for your use case. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,11 +58,15 @@ int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
Beware of reading from buffered FILE* objects such as stdin. Use
|
||||
raw file descriptors or call fopen() / fdopen() in every pass. */
|
||||
|
||||
read(0, buf, 100);
|
||||
len = read(0, buf, 100);
|
||||
|
||||
/* STEP 3: This is where we'd call the tested library on the read data.
|
||||
We just have some trivial inline code that faults on 'foo!'. */
|
||||
|
||||
/* do we have enough data? */
|
||||
if (len < 4)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (buf[0] == 'f') {
|
||||
printf("one\n");
|
||||
if (buf[1] == 'o') {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - postprocessor library example
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - postprocessor for PNG
|
||||
------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
130
gcc_plugin/Makefile
Normal file
130
gcc_plugin/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - GCC plugin instrumentation
|
||||
# -----------------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written by Austin Seipp <aseipp@pobox.com> and
|
||||
# Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
# Michal Zalewski and
|
||||
# Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko@hexco.de>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# GCC integration design is based on the LLVM design, which comes
|
||||
# from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
PREFIX ?= /usr/local
|
||||
HELPER_PATH = $(PREFIX)/lib/afl
|
||||
BIN_PATH = $(PREFIX)/bin
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -g -funroll-loops
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -Wno-pointer-sign \
|
||||
-DAFL_PATH=\"$(HELPER_PATH)\" -DBIN_PATH=\"$(BIN_PATH)\" \
|
||||
|
||||
CXXFLAGS ?= -O3 -g -funroll-loops
|
||||
CXXEFLAGS := $(CXXFLAGS) -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2
|
||||
|
||||
CC ?= gcc
|
||||
CXX ?= g++
|
||||
|
||||
PLUGIN_FLAGS = -fPIC -fno-rtti -I"$(shell $(CC) -print-file-name=plugin)/include"
|
||||
|
||||
PROGS = ../afl-gcc-fast ../afl-gcc-pass.so ../afl-gcc-rt.o
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell echo '\#include <sys/ipc.h>@\#include <sys/shm.h>@int main() { int _id = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 65536, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0600); shmctl(_id, IPC_RMID, 0); return 0;}' | tr @ '\n' | $(CC) -x c - -o .test2 2>/dev/null && echo 1 || echo 0 )" "1"
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=1
|
||||
else
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=0
|
||||
CFLAGS+=-DUSEMMAP=1
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lrt
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(TEST_MMAP)" "1"
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=0
|
||||
CFLAGS+=-DUSEMMAP=1
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lrt
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
all: test_shm test_deps $(PROGS) afl-gcc-fast.8 test_build all_done
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(SHMAT_OK)" "1"
|
||||
|
||||
test_shm:
|
||||
@echo "[+] shmat seems to be working."
|
||||
@rm -f .test2
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
|
||||
test_shm:
|
||||
@echo "[-] shmat seems not to be working, switching to mmap implementation"
|
||||
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
test_deps:
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for working '$(CC)'..."
|
||||
@which $(CC) >/dev/null 2>&1 || ( echo "[-] Oops, can't find '$(CC)'. Make sure that it's in your \$$PATH (or set \$$CC and \$$CXX)."; exit 1 )
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for gcc for plugin support..."
|
||||
@$(CC) -v 2>&1 | grep -q -- --enable-plugin || ( echo "[-] Oops, this gcc has not been configured with plugin support."; exit 1 )
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for gcc plugin development header files..."
|
||||
@test -d `$(CC) -print-file-name=plugin`/include || ( echo "[-] Oops, can't find gcc header files. Be sure to install 'gcc-X-plugin-dev'."; exit 1 )
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for '../afl-showmap'..."
|
||||
@test -f ../afl-showmap || ( echo "[-] Oops, can't find '../afl-showmap'. Be sure to compile AFL first."; exit 1 )
|
||||
@echo "[+] All set and ready to build."
|
||||
|
||||
../afl-gcc-fast: afl-gcc-fast.c | test_deps
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $< -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
ln -sf afl-gcc-fast ../afl-g++-fast
|
||||
|
||||
../afl-gcc-pass.so: afl-gcc-pass.so.cc | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXEFLAGS) $(PLUGIN_FLAGS) -shared $< -o $@
|
||||
|
||||
../afl-gcc-rt.o: afl-gcc-rt.o.c | test_deps
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -fPIC -c $< -o $@
|
||||
|
||||
test_build: $(PROGS)
|
||||
@echo "[*] Testing the CC wrapper and instrumentation output..."
|
||||
unset AFL_USE_ASAN AFL_USE_MSAN; AFL_QUIET=1 AFL_INST_RATIO=100 AFL_PATH=. AFL_CC=$(CC) ../afl-gcc-fast $(CFLAGS) ../test-instr.c -o test-instr $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
# unset AFL_USE_ASAN AFL_USE_MSAN; AFL_INST_RATIO=100 AFL_PATH=. AFL_CC=$(CC) ../afl-gcc-fast $(CFLAGS) ../test-instr.c -o test-instr $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
../afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr0 ./test-instr </dev/null
|
||||
echo 1 | ../afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr1 ./test-instr
|
||||
@rm -f test-instr
|
||||
@cmp -s .test-instr0 .test-instr1; DR="$$?"; rm -f .test-instr0 .test-instr1; if [ "$$DR" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Oops, the instrumentation does not seem to be behaving correctly!"; echo; echo "Please post to https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus/issues to troubleshoot the issue."; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
@echo "[+] All right, the instrumentation seems to be working!"
|
||||
|
||||
all_done: test_build
|
||||
@echo "[+] All done! You can now use '../afl-gcc-fast' to compile programs."
|
||||
|
||||
.NOTPARALLEL: clean
|
||||
|
||||
vpath % ..
|
||||
%.8: %
|
||||
@echo .TH $* 8 `date "+%Y-%m-%d"` "afl++" > ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH NAME >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .B $* >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH SYNOPSIS >> ../$@
|
||||
@../$* -h 2>&1 | head -n 3 | tail -n 1 | sed 's/^\.\///' >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH OPTIONS >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .nf >> ../$@
|
||||
@../$* -h 2>&1 | tail -n +4 >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH AUTHOR >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo "afl++ was written by Michal \"lcamtuf\" Zalewski and is maintained by Marc \"van Hauser\" Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>, Heiko \"hexcoder-\" Eissfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>" >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo The homepage of afl++ is: https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH LICENSE >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004 >> ../$@
|
||||
ln -sf afl-gcc-fast.8 ../afl-g++-fast.8
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -f *.o *.so *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]* test-instr .test-instr0 .test-instr1
|
||||
rm -f $(PROGS) ../afl-g++-fast ../afl-g*-fast.8
|
||||
158
gcc_plugin/README.gcc.md
Normal file
158
gcc_plugin/README.gcc.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
|
||||
===========================================
|
||||
GCC-based instrumentation for afl-fuzz
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README.md for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
(See ../llvm_mode/README.md for the LLVM-based instrumentation.)
|
||||
|
||||
!!! TODO items are:
|
||||
!!! => inline instrumentation has to work!
|
||||
!!!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
The code in this directory allows you to instrument programs for AFL using
|
||||
true compiler-level instrumentation, instead of the more crude
|
||||
assembly-level rewriting approach taken by afl-gcc and afl-clang. This has
|
||||
several interesting properties:
|
||||
|
||||
- The compiler can make many optimizations that are hard to pull off when
|
||||
manually inserting assembly. As a result, some slow, CPU-bound programs will
|
||||
run up to around faster.
|
||||
|
||||
The gains are less pronounced for fast binaries, where the speed is limited
|
||||
chiefly by the cost of creating new processes. In such cases, the gain will
|
||||
probably stay within 10%.
|
||||
|
||||
- The instrumentation is CPU-independent. At least in principle, you should
|
||||
be able to rely on it to fuzz programs on non-x86 architectures (after
|
||||
building afl-fuzz with AFL_NOX86=1).
|
||||
|
||||
- Because the feature relies on the internals of GCC, it is gcc-specific
|
||||
and will *not* work with LLVM (see ../llvm_mode for an alternative).
|
||||
|
||||
Once this implementation is shown to be sufficiently robust and portable, it
|
||||
will probably replace afl-gcc. For now, it can be built separately and
|
||||
co-exists with the original code.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea and much of the implementation comes from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) How to use
|
||||
|
||||
In order to leverage this mechanism, you need to have modern enough GCC
|
||||
(>= version 4.5.0) and the plugin headers installed on your system. That
|
||||
should be all you need. On Debian machines, these headers can be acquired by
|
||||
installing the `gcc-<VERSION>-plugin-dev` packages.
|
||||
|
||||
To build the instrumentation itself, type 'make'. This will generate binaries
|
||||
called afl-gcc-fast and afl-g++-fast in the parent directory. Once this
|
||||
is done, you can instrument third-party code in a way similar to the standard
|
||||
operating mode of AFL, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
CC=/path/to/afl/afl-gcc-fast ./configure [...options...]
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||
Be sure to also include CXX set to afl-g++-fast for C++ code.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool honors roughly the same environmental variables as afl-gcc (see
|
||||
../docs/env_variables.txt). This includes AFL_INST_RATIO, AFL_USE_ASAN,
|
||||
AFL_HARDEN, and AFL_DONT_OPTIMIZE.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: if you want the GCC plugin to be installed on your system for all
|
||||
users, you need to build it before issuing 'make install' in the parent
|
||||
directory.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3) Gotchas, feedback, bugs
|
||||
|
||||
This is an early-stage mechanism, so field reports are welcome. You can send bug
|
||||
reports to <hexcoder-@github.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
## 4) Bonus feature #1: deferred initialization
|
||||
|
||||
AFL tries to optimize performance by executing the targeted binary just once,
|
||||
stopping it just before main(), and then cloning this "master" process to get
|
||||
a steady supply of targets to fuzz.
|
||||
|
||||
Although this approach eliminates much of the OS-, linker- and libc-level
|
||||
costs of executing the program, it does not always help with binaries that
|
||||
perform other time-consuming initialization steps - say, parsing a large config
|
||||
file before getting to the fuzzed data.
|
||||
|
||||
In such cases, it's beneficial to initialize the forkserver a bit later, once
|
||||
most of the initialization work is already done, but before the binary attempts
|
||||
to read the fuzzed input and parse it; in some cases, this can offer a 10x+
|
||||
performance gain. You can implement delayed initialization in LLVM mode in a
|
||||
fairly simple way.
|
||||
|
||||
First, locate a suitable location in the code where the delayed cloning can
|
||||
take place. This needs to be done with *extreme* care to avoid breaking the
|
||||
binary. In particular, the program will probably malfunction if you select
|
||||
a location after:
|
||||
|
||||
- The creation of any vital threads or child processes - since the forkserver
|
||||
can't clone them easily.
|
||||
|
||||
- The initialization of timers via setitimer() or equivalent calls.
|
||||
|
||||
- The creation of temporary files, network sockets, offset-sensitive file
|
||||
descriptors, and similar shared-state resources - but only provided that
|
||||
their state meaningfully influences the behavior of the program later on.
|
||||
|
||||
- Any access to the fuzzed input, including reading the metadata about its
|
||||
size.
|
||||
|
||||
With the location selected, add this code in the appropriate spot:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#ifdef __AFL_HAVE_MANUAL_CONTROL
|
||||
__AFL_INIT();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You don't need the #ifdef guards, but they will make the program still work as
|
||||
usual when compiled with a tool other than afl-gcc-fast/afl-clang-fast.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, recompile the program with afl-gcc-fast (afl-gcc or afl-clang will
|
||||
*not* generate a deferred-initialization binary) - and you should be all set!
|
||||
|
||||
## 5) Bonus feature #2: persistent mode
|
||||
|
||||
Some libraries provide APIs that are stateless, or whose state can be reset in
|
||||
between processing different input files. When such a reset is performed, a
|
||||
single long-lived process can be reused to try out multiple test cases,
|
||||
eliminating the need for repeated fork() calls and the associated OS overhead.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic structure of the program that does this would be:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
while (__AFL_LOOP(1000)) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Read input data. */
|
||||
/* Call library code to be fuzzed. */
|
||||
/* Reset state. */
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Exit normally */
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The numerical value specified within the loop controls the maximum number
|
||||
of iterations before AFL will restart the process from scratch. This minimizes
|
||||
the impact of memory leaks and similar glitches; 1000 is a good starting point.
|
||||
|
||||
A more detailed template is shown in ../experimental/persistent_demo/.
|
||||
Similarly to the previous mode, the feature works only with afl-gcc-fast or
|
||||
afl-clang-fast; #ifdef guards can be used to suppress it when using other
|
||||
compilers.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that as with the previous mode, the feature is easy to misuse; if you
|
||||
do not reset the critical state fully, you may end up with false positives or
|
||||
waste a whole lot of CPU power doing nothing useful at all. Be particularly
|
||||
wary of memory leaks and the state of file descriptors.
|
||||
|
||||
When running in this mode, the execution paths will inherently vary a bit
|
||||
depending on whether the input loop is being entered for the first time or
|
||||
executed again. To avoid spurious warnings, the feature implies
|
||||
AFL_NO_VAR_CHECK and hides the "variable path" warnings in the UI.
|
||||
|
||||
73
gcc_plugin/README.whitelist.md
Normal file
73
gcc_plugin/README.whitelist.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
Using afl++ with partial instrumentation
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
|
||||
This file describes how you can selectively instrument only the source files
|
||||
that are interesting to you using the gcc instrumentation provided by
|
||||
afl++.
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin by hexcoder-.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Description and purpose
|
||||
|
||||
When building and testing complex programs where only a part of the program is
|
||||
the fuzzing target, it often helps to only instrument the necessary parts of
|
||||
the program, leaving the rest uninstrumented. This helps to focus the fuzzer
|
||||
on the important parts of the program, avoiding undesired noise and
|
||||
disturbance by uninteresting code being exercised.
|
||||
|
||||
For this purpose, I have added a "partial instrumentation" support to the gcc
|
||||
plugin of AFLFuzz that allows you to specify on a source file level which files
|
||||
should be compiled with or without instrumentation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) Building the gcc plugin
|
||||
|
||||
The new code is part of the existing afl++ gcc plugin in the gcc_plugin/
|
||||
subdirectory. There is nothing specifically to do :)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 3) How to use the partial instrumentation mode
|
||||
|
||||
In order to build with partial instrumentation, you need to build with
|
||||
afl-gcc-fast and afl-g++-fast respectively. The only required change is
|
||||
that you need to set the environment variable AFL_GCC_WHITELIST when calling
|
||||
the compiler.
|
||||
|
||||
The environment variable must point to a file containing all the filenames
|
||||
that should be instrumented. For matching, the filename that is being compiled
|
||||
must end in the filename entry contained in this whitelist (to avoid breaking
|
||||
the matching when absolute paths are used during compilation).
|
||||
|
||||
For example if your source tree looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
project/
|
||||
project/feature_a/a1.cpp
|
||||
project/feature_a/a2.cpp
|
||||
project/feature_b/b1.cpp
|
||||
project/feature_b/b2.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and you only want to test feature_a, then create a whitelist file containing:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
feature_a/a1.cpp
|
||||
feature_a/a2.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However if the whitelist file contains only this, it works as well:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
a1.cpp
|
||||
a2.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
but it might lead to files being unwantedly instrumented if the same filename
|
||||
exists somewhere else in the project directories.
|
||||
|
||||
The created whitelist file is then set to AFL_GCC_WHITELIST when you compile
|
||||
your program. For each file that didn't match the whitelist, the compiler will
|
||||
issue a warning at the end stating that no blocks were instrumented. If you
|
||||
didn't intend to instrument that file, then you can safely ignore that warning.
|
||||
333
gcc_plugin/afl-gcc-fast.c
Normal file
333
gcc_plugin/afl-gcc-fast.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,333 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - GCC wrapper for GCC plugin
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Austin Seipp <aseipp@pobox.com> and
|
||||
Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
GCC integration design is based on the LLVM design, which comes
|
||||
from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
This program is a drop-in replacement for gcc, similar in most
|
||||
respects to ../afl-gcc, but with compiler instrumentation through a
|
||||
plugin. It tries to figure out compilation mode, adds a bunch of
|
||||
flags, and then calls the real compiler.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define AFL_MAIN
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../types.h"
|
||||
#include "../include/debug.h"
|
||||
#include "../include/alloc-inl.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
static u8* obj_path; /* Path to runtime libraries */
|
||||
static u8** cc_params; /* Parameters passed to the real CC */
|
||||
static u32 cc_par_cnt = 1; /* Param count, including argv0 */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Try to find the runtime libraries. If that fails, abort. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void find_obj(u8* argv0) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* afl_path = getenv("AFL_PATH");
|
||||
u8 *slash, *tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl_path) {
|
||||
|
||||
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/afl-gcc-rt.o", afl_path);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!access(tmp, R_OK)) {
|
||||
|
||||
obj_path = afl_path;
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
slash = strrchr(argv0, '/');
|
||||
|
||||
if (slash) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* dir;
|
||||
|
||||
*slash = 0;
|
||||
dir = ck_strdup(argv0);
|
||||
*slash = '/';
|
||||
|
||||
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/afl-gcc-rt.o", dir);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!access(tmp, R_OK)) {
|
||||
|
||||
obj_path = dir;
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
ck_free(dir);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!access(AFL_PATH "/afl-gcc-rt.o", R_OK)) {
|
||||
|
||||
obj_path = AFL_PATH;
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL(
|
||||
"Unable to find 'afl-gcc-rt.o' or 'afl-gcc-pass.so'. Please set "
|
||||
"AFL_PATH");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Copy argv to cc_params, making the necessary edits. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 fortify_set = 0, asan_set = 0, x_set = 0, maybe_linking = 1;
|
||||
u8* name;
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params = ck_alloc((argc + 64) * sizeof(u8*));
|
||||
|
||||
name = strrchr(argv[0], '/');
|
||||
if (!name)
|
||||
name = argv[0];
|
||||
else
|
||||
++name;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(name, "afl-g++-fast")) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* alt_cxx = getenv("AFL_CXX");
|
||||
cc_params[0] = alt_cxx ? alt_cxx : (u8*)"g++";
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* alt_cc = getenv("AFL_CC");
|
||||
cc_params[0] = alt_cc ? alt_cc : (u8*)"gcc";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
char* fplugin_arg = alloc_printf("-fplugin=%s/afl-gcc-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = fplugin_arg;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Detect stray -v calls from ./configure scripts. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc == 1 && !strcmp(argv[1], "-v")) maybe_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
while (--argc) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* cur = *(++argv);
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__x86_64__)
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-m32")) FATAL("-m32 is not supported");
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-x")) x_set = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-c") || !strcmp(cur, "-S") || !strcmp(cur, "-E") ||
|
||||
!strcmp(cur, "-v"))
|
||||
maybe_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-fsanitize=address") || !strcmp(cur, "-fsanitize=memory"))
|
||||
asan_set = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (strstr(cur, "FORTIFY_SOURCE")) fortify_set = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-shared")) maybe_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = cur;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_HARDEN")) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-fstack-protector-all";
|
||||
|
||||
if (!fortify_set) cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!asan_set) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN")) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN")) FATAL("ASAN and MSAN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_HARDEN"))
|
||||
FATAL("ASAN and AFL_HARDEN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-U_FORTIFY_SOURCE";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-fsanitize=address";
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN")) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN")) FATAL("ASAN and MSAN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_HARDEN"))
|
||||
FATAL("MSAN and AFL_HARDEN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-U_FORTIFY_SOURCE";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-fsanitize=memory";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!getenv("AFL_DONT_OPTIMIZE")) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-g";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-O3";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-funroll-loops";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USEMMAP
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-lrt";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D__AFL_HAVE_MANUAL_CONTROL=1";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D__AFL_COMPILER=1";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-DFUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION=1";
|
||||
|
||||
/* When the user tries to use persistent or deferred forkserver modes by
|
||||
appending a single line to the program, we want to reliably inject a
|
||||
signature into the binary (to be picked up by afl-fuzz) and we want
|
||||
to call a function from the runtime .o file. This is unnecessarily
|
||||
painful for three reasons:
|
||||
|
||||
1) We need to convince the compiler not to optimize out the signature.
|
||||
This is done with __attribute__((used)).
|
||||
|
||||
2) We need to convince the linker, when called with -Wl,--gc-sections,
|
||||
not to do the same. This is done by forcing an assignment to a
|
||||
'volatile' pointer.
|
||||
|
||||
3) We need to declare __afl_persistent_loop() in the global namespace,
|
||||
but doing this within a method in a class is hard - :: and extern "C"
|
||||
are forbidden and __attribute__((alias(...))) doesn't work. Hence the
|
||||
__asm__ aliasing trick.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
"-D__AFL_LOOP(_A)="
|
||||
"({ static volatile char *_B __attribute__((used)); "
|
||||
" _B = (char*)\"" PERSIST_SIG
|
||||
"\"; "
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
"int _L(unsigned int) __asm__(\"___afl_persistent_loop\"); "
|
||||
#else
|
||||
"int _L(unsigned int) __asm__(\"__afl_persistent_loop\"); "
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
"_L(_A); })";
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
"-D__AFL_INIT()="
|
||||
"do { static volatile char *_A __attribute__((used)); "
|
||||
" _A = (char*)\"" DEFER_SIG
|
||||
"\"; "
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
"void _I(void) __asm__(\"___afl_manual_init\"); "
|
||||
#else
|
||||
"void _I(void) __asm__(\"__afl_manual_init\"); "
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
"_I(); } while (0)";
|
||||
|
||||
if (maybe_linking) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (x_set) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-x";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "none";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/afl-gcc-rt.o", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt] = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Main entry point */
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "-h") == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
printf(
|
||||
cCYA
|
||||
"afl-gcc-fast" VERSION cRST
|
||||
" initially by <aseipp@pobox.com>, maintainer: hexcoder-\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"This is a helper application for afl-fuzz. It serves as a drop-in "
|
||||
"replacement\n"
|
||||
"for gcc, letting you recompile third-party code with the required "
|
||||
"runtime\n"
|
||||
"instrumentation. A common use pattern would be one of the "
|
||||
"following:\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
" CC=%s/afl-gcc-fast ./configure\n"
|
||||
" CXX=%s/afl-g++-fast ./configure\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
"In contrast to the traditional afl-gcc tool, this version is "
|
||||
"implemented as\n"
|
||||
"a GCC plugin and tends to offer improved performance with slow "
|
||||
"programs\n"
|
||||
"(similarly to the LLVM plugin used by afl-clang-fast).\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
"You can specify custom next-stage toolchain via AFL_CC and AFL_CXX. "
|
||||
"Setting\n"
|
||||
"AFL_HARDEN enables hardening optimizations in the compiled code.\n\n",
|
||||
BIN_PATH, BIN_PATH);
|
||||
|
||||
exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (isatty(2) && !getenv("AFL_QUIET")) {
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "afl-gcc-fast" VERSION cRST
|
||||
" initially by <aseipp@pobox.com>, maintainer: hexcoder-\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
find_obj(argv[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
edit_params(argc, argv);
|
||||
/*if (isatty(2) && !getenv("AFL_QUIET")) {
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Calling \"%s\" with:\n", cc_params[0]);
|
||||
for(int i=1; i<cc_par_cnt; i++) printf("%s\n", cc_params[i]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
execvp(cc_params[0], (char**)cc_params);
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Oops, failed to execute '%s' - check your PATH", cc_params[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
565
gcc_plugin/afl-gcc-pass.so.cc
Normal file
565
gcc_plugin/afl-gcc-pass.so.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,565 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There are some TODOs in this file:
|
||||
// - fix instrumentation via external call
|
||||
// - fix inline instrumentation
|
||||
// - implement whitelist feature
|
||||
// - dont instrument blocks that are uninteresting
|
||||
// - implement neverZero
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - GCC instrumentation pass
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Austin Seipp <aseipp@pobox.com> with bits from
|
||||
Emese Revfy <re.emese@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Fixed by Heiko Eißfeldt 2019 for AFL++
|
||||
|
||||
GCC integration design is based on the LLVM design, which comes
|
||||
from Laszlo Szekeres. Some of the boilerplate code below for
|
||||
afl_pass to adapt to different GCC versions was taken from Emese
|
||||
Revfy's Size Overflow plugin for GCC, licensed under the GPLv2/v3.
|
||||
|
||||
(NOTE: this plugin code is under GPLv3, in order to comply with the
|
||||
GCC runtime library exception, which states that you may distribute
|
||||
"Target Code" from the compiler under a license of your choice, as
|
||||
long as the "Compilation Process" is "Eligible", and contains no
|
||||
GPL-incompatible software in GCC "during the process of
|
||||
transforming high level code to target code". In this case, the
|
||||
plugin will be used to generate "Target Code" during the
|
||||
"Compilation Process", and thus it must be GPLv3 to be "eligible".)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (C) 2015 Austin Seipp
|
||||
|
||||
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
||||
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
|
||||
(at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
GNU General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
||||
along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define BUILD_INLINE_INST
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../include/debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* clear helper AFL types pulls in, which intervene with gcc-plugin geaders from
|
||||
* GCC-8 */
|
||||
#ifdef likely
|
||||
#undef likely
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef unlikely
|
||||
#undef unlikely
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <gcc-plugin.h>
|
||||
#include <plugin-version.h>
|
||||
#include <diagnostic.h>
|
||||
#include <tree.h>
|
||||
#include <tree-ssa.h>
|
||||
#include <tree-pass.h>
|
||||
#include <tree-ssa-alias.h>
|
||||
#include <basic-block.h>
|
||||
#include <gimple-expr.h>
|
||||
#include <gimple.h>
|
||||
#include <gimple-iterator.h>
|
||||
#include <gimple-ssa.h>
|
||||
#include <version.h>
|
||||
#include <toplev.h>
|
||||
#include <intl.h>
|
||||
#include <context.h>
|
||||
#include <stringpool.h>
|
||||
#include <cgraph.h>
|
||||
#include <cfgloop.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
|
||||
/* -- AFL instrumentation pass ---------------------------------------------- */
|
||||
|
||||
static int be_quiet = 0;
|
||||
static unsigned int inst_ratio = 100;
|
||||
static bool inst_ext = true;
|
||||
static std::list<std::string> myWhitelist;
|
||||
|
||||
static unsigned int ext_call_instrument(function *fun) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Instrument all the things! */
|
||||
basic_block bb;
|
||||
unsigned finst_blocks = 0;
|
||||
unsigned fcnt_blocks = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
tree fntype = build_function_type_list(void_type_node, /* return */
|
||||
uint32_type_node, /* args */
|
||||
NULL_TREE); /* done */
|
||||
tree fndecl = build_fn_decl("__afl_trace", fntype);
|
||||
TREE_STATIC(fndecl) = 1; /* Defined elsewhere */
|
||||
TREE_PUBLIC(fndecl) = 1; /* Public */
|
||||
DECL_EXTERNAL(fndecl) = 1; /* External linkage */
|
||||
DECL_ARTIFICIAL(fndecl) = 1; /* Injected by compiler */
|
||||
|
||||
FOR_EACH_BB_FN(bb, fun) {
|
||||
|
||||
gimple_seq fcall;
|
||||
gimple_seq seq = NULL;
|
||||
gimple_stmt_iterator bentry;
|
||||
++fcnt_blocks;
|
||||
|
||||
// only instrument if this basic block is the destination of a previous
|
||||
// basic block that has multiple successors
|
||||
// this gets rid of ~5-10% of instrumentations that are unnecessary
|
||||
// result: a little more speed and less map pollution
|
||||
|
||||
int more_than_one = -1;
|
||||
edge ep;
|
||||
edge_iterator eip;
|
||||
FOR_EACH_EDGE(ep, eip, bb->preds) {
|
||||
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
if (more_than_one == -1) more_than_one = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
basic_block Pred = ep->src;
|
||||
edge es;
|
||||
edge_iterator eis;
|
||||
FOR_EACH_EDGE(es, eis, Pred->succs) {
|
||||
|
||||
basic_block Succ = es->dest;
|
||||
if (Succ != NULL) count++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (count > 1) more_than_one = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (more_than_one != 1) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Bail on this block if we trip the specified ratio */
|
||||
if (R(100) >= inst_ratio) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make up cur_loc */
|
||||
unsigned int rand_loc = R(MAP_SIZE);
|
||||
tree cur_loc = build_int_cst(uint32_type_node, rand_loc);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Update bitmap via external call */
|
||||
/* to quote:
|
||||
* /+ Trace a basic block with some ID +/
|
||||
* void __afl_trace(u32 x);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
fcall = gimple_build_call(
|
||||
fndecl, 1,
|
||||
cur_loc); /* generate the function _call_ to above built reference, with
|
||||
*1* parameter -> the random const for the location */
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, fcall); /* and insert into a sequence */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Done - grab the entry to the block and insert sequence */
|
||||
bentry = gsi_after_labels(bb);
|
||||
gsi_insert_seq_before(&bentry, seq, GSI_SAME_STMT);
|
||||
|
||||
++finst_blocks;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Say something nice. */
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!finst_blocks)
|
||||
WARNF(G_("No instrumentation targets found in " cBRI "%s" cRST),
|
||||
function_name(fun));
|
||||
else if (finst_blocks < fcnt_blocks)
|
||||
OKF(G_("Instrumented %2u /%2u locations in " cBRI "%s" cRST),
|
||||
finst_blocks, fcnt_blocks, function_name(fun));
|
||||
else
|
||||
OKF(G_("Instrumented %2u locations in " cBRI "%s" cRST), finst_blocks,
|
||||
function_name(fun));
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static unsigned int inline_instrument(function *fun) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Instrument all the things! */
|
||||
basic_block bb;
|
||||
unsigned finst_blocks = 0;
|
||||
unsigned fcnt_blocks = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set up global type declarations */
|
||||
tree map_type = build_pointer_type(unsigned_char_type_node);
|
||||
tree map_ptr_g =
|
||||
build_decl(UNKNOWN_LOCATION, VAR_DECL,
|
||||
get_identifier_with_length("__afl_area_ptr", 14), map_type);
|
||||
TREE_USED(map_ptr_g) = 1;
|
||||
TREE_STATIC(map_ptr_g) = 1; /* Defined elsewhere */
|
||||
DECL_EXTERNAL(map_ptr_g) = 1; /* External linkage */
|
||||
DECL_PRESERVE_P(map_ptr_g) = 1;
|
||||
DECL_ARTIFICIAL(map_ptr_g) = 1; /* Injected by compiler */
|
||||
rest_of_decl_compilation(map_ptr_g, 1, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
tree prev_loc_g = build_decl(UNKNOWN_LOCATION, VAR_DECL,
|
||||
get_identifier_with_length("__afl_prev_loc", 14),
|
||||
uint32_type_node);
|
||||
TREE_USED(prev_loc_g) = 1;
|
||||
TREE_STATIC(prev_loc_g) = 1; /* Defined elsewhere */
|
||||
DECL_EXTERNAL(prev_loc_g) = 1; /* External linkage */
|
||||
DECL_PRESERVE_P(prev_loc_g) = 1;
|
||||
DECL_ARTIFICIAL(prev_loc_g) = 1; /* Injected by compiler */
|
||||
rest_of_decl_compilation(prev_loc_g, 1, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
FOR_EACH_BB_FN(bb, fun) {
|
||||
|
||||
gimple_seq seq = NULL;
|
||||
gimple_stmt_iterator bentry;
|
||||
++fcnt_blocks;
|
||||
|
||||
// only instrument if this basic block is the destination of a previous
|
||||
// basic block that has multiple successors
|
||||
// this gets rid of ~5-10% of instrumentations that are unnecessary
|
||||
// result: a little more speed and less map pollution
|
||||
|
||||
int more_than_one = -1;
|
||||
edge ep;
|
||||
edge_iterator eip;
|
||||
FOR_EACH_EDGE(ep, eip, bb->preds) {
|
||||
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
if (more_than_one == -1) more_than_one = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
basic_block Pred = ep->src;
|
||||
edge es;
|
||||
edge_iterator eis;
|
||||
FOR_EACH_EDGE(es, eis, Pred->succs) {
|
||||
|
||||
basic_block Succ = es->dest;
|
||||
if (Succ != NULL) count++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (count > 1) more_than_one = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (more_than_one != 1) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Bail on this block if we trip the specified ratio */
|
||||
if (R(100) >= inst_ratio) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make up cur_loc */
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned int rand_loc = R(MAP_SIZE);
|
||||
tree cur_loc = build_int_cst(uint32_type_node, rand_loc);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Load prev_loc, xor with cur_loc */
|
||||
// gimple_assign <var_decl, prev_loc.0_1, prev_loc, NULL, NULL>
|
||||
tree prev_loc = create_tmp_var_raw(uint32_type_node, "prev_loc");
|
||||
gassign *g = gimple_build_assign(prev_loc, VAR_DECL, prev_loc_g);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // load prev_loc
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
// gimple_assign <bit_xor_expr, _2, prev_loc.0_1, 47231, NULL>
|
||||
tree area_off = create_tmp_var_raw(uint32_type_node, "area_off");
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(area_off, BIT_XOR_EXPR, prev_loc, cur_loc);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // area_off = prev_loc ^ cur_loc
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Update bitmap */
|
||||
|
||||
tree one = build_int_cst(unsigned_char_type_node, 1);
|
||||
// tree zero = build_int_cst(unsigned_char_type_node, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
// gimple_assign <addr_expr, p_6, &map[_2], NULL, NULL>
|
||||
tree map_ptr = create_tmp_var(map_type, "map_ptr");
|
||||
tree map_ptr2 = create_tmp_var(map_type, "map_ptr2");
|
||||
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(map_ptr, map_ptr_g);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // map_ptr = __afl_area_ptr
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
#if 0
|
||||
tree addr = build2(ADDR_EXPR, map_type, map_ptr, area_off);
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(map_ptr2, MODIFY_EXPR, addr);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // map_ptr2 = map_ptr + area_off
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(map_ptr2, PLUS_EXPR, map_ptr, area_off);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // map_ptr2 = map_ptr + area_off
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
// gimple_assign <mem_ref, _3, *p_6, NULL, NULL>
|
||||
tree tmp1 = create_tmp_var_raw(unsigned_char_type_node, "tmp1");
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(tmp1, MEM_REF, map_ptr2);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // tmp1 = *map_ptr2
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
// gimple_assign <plus_expr, _4, _3, 1, NULL>
|
||||
tree tmp2 = create_tmp_var_raw(unsigned_char_type_node, "tmp2");
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(tmp2, PLUS_EXPR, tmp1, one);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // tmp2 = tmp1 + 1
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: neverZero: here we have to check if tmp3 == 0
|
||||
// and add 1 if so
|
||||
|
||||
// gimple_assign <ssa_name, *p_6, _4, NULL, NULL>
|
||||
// tree map_ptr3 = create_tmp_var_raw(map_type, "map_ptr3");
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(map_ptr_g, INDIRECT_REF, tmp2);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // *map_ptr3 = tmp2
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set prev_loc to cur_loc >> 1 */
|
||||
|
||||
// gimple_assign <integer_cst, prev_loc, 23615, NULL, NULL>
|
||||
tree shifted_loc = build_int_cst(TREE_TYPE(prev_loc_g), rand_loc >> 1);
|
||||
tree prev_loc2 = create_tmp_var_raw(uint32_type_node, "prev_loc2");
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(prev_loc2, shifted_loc);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // __afl_prev_loc = cur_loc >> 1
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
g = gimple_build_assign(prev_loc_g, prev_loc2);
|
||||
gimple_seq_add_stmt(&seq, g); // __afl_prev_loc = cur_loc >> 1
|
||||
update_stmt(g);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Done - grab the entry to the block and insert sequence */
|
||||
|
||||
bentry = gsi_after_labels(bb);
|
||||
gsi_insert_seq_before(&bentry, seq, GSI_NEW_STMT);
|
||||
|
||||
++finst_blocks;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Say something nice. */
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!finst_blocks)
|
||||
WARNF(G_("No instrumentation targets found in " cBRI "%s" cRST),
|
||||
function_name(fun));
|
||||
else if (finst_blocks < fcnt_blocks)
|
||||
OKF(G_("Instrumented %2u /%2u locations in " cBRI "%s" cRST),
|
||||
finst_blocks, fcnt_blocks, function_name(fun));
|
||||
else
|
||||
OKF(G_("Instrumented %2u locations in " cBRI "%s" cRST), finst_blocks,
|
||||
function_name(fun));
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
|
||||
/* -- Boilerplate and initialization ---------------------------------------- */
|
||||
|
||||
static const struct pass_data afl_pass_data = {
|
||||
|
||||
.type = GIMPLE_PASS,
|
||||
.name = "afl-inst",
|
||||
.optinfo_flags = OPTGROUP_NONE,
|
||||
|
||||
.tv_id = TV_NONE,
|
||||
.properties_required = 0,
|
||||
.properties_provided = 0,
|
||||
.properties_destroyed = 0,
|
||||
.todo_flags_start = 0,
|
||||
// NOTE(aseipp): it's very, very important to include
|
||||
// at least 'TODO_update_ssa' here so that GCC will
|
||||
// properly update the resulting SSA form, e.g., to
|
||||
// include new PHI nodes for newly added symbols or
|
||||
// names. Do not remove this. Do not taunt Happy Fun
|
||||
// Ball.
|
||||
.todo_flags_finish = TODO_update_ssa | TODO_verify_il | TODO_cleanup_cfg,
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
class afl_pass : public gimple_opt_pass {
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool do_ext_call;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
afl_pass(bool ext_call, gcc::context *g)
|
||||
: gimple_opt_pass(afl_pass_data, g), do_ext_call(ext_call) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
virtual unsigned int execute(function *fun) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!myWhitelist.empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool instrumentBlock = false;
|
||||
|
||||
/* EXPR_FILENAME
|
||||
This macro returns the name of the file in which the entity was declared,
|
||||
as a char*. For an entity declared implicitly by the compiler (like
|
||||
__builtin_ memcpy), this will be the string "<internal>".
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const char *fname = DECL_SOURCE_FILE(fun->decl);
|
||||
|
||||
if (0 != strncmp("<internal>", fname, 10) &&
|
||||
0 != strncmp("<built-in>", fname, 10)) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::string instFilename(fname);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Continue only if we know where we actually are */
|
||||
if (!instFilename.empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::list<std::string>::iterator it = myWhitelist.begin();
|
||||
it != myWhitelist.end(); ++it) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* We don't check for filename equality here because
|
||||
* filenames might actually be full paths. Instead we
|
||||
* check that the actual filename ends in the filename
|
||||
* specified in the list. */
|
||||
if (instFilename.length() >= it->length()) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (instFilename.compare(instFilename.length() - it->length(),
|
||||
it->length(), *it) == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrumentBlock = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Either we couldn't figure out our location or the location is
|
||||
* not whitelisted, so we skip instrumentation. */
|
||||
if (!instrumentBlock) return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return do_ext_call ? ext_call_instrument(fun) : inline_instrument(fun);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}; /* class afl_pass */
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
static struct opt_pass *make_afl_pass(bool ext_call, gcc::context *ctxt) {
|
||||
|
||||
return new afl_pass(ext_call, ctxt);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
|
||||
/* -- Initialization -------------------------------------------------------- */
|
||||
|
||||
int plugin_is_GPL_compatible = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
static struct plugin_info afl_plugin_info = {
|
||||
|
||||
.version = "20191015",
|
||||
.help = "AFL++ gcc plugin\n",
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
int plugin_init(struct plugin_name_args * plugin_info,
|
||||
struct plugin_gcc_version *version) {
|
||||
|
||||
struct register_pass_info afl_pass_info;
|
||||
struct timeval tv;
|
||||
struct timezone tz;
|
||||
u32 rand_seed;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Setup random() so we get Actually Random(TM) outputs from R() */
|
||||
gettimeofday(&tv, &tz);
|
||||
rand_seed = tv.tv_sec ^ tv.tv_usec ^ getpid();
|
||||
srandom(rand_seed);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Pass information */
|
||||
afl_pass_info.pass = make_afl_pass(inst_ext, g);
|
||||
afl_pass_info.reference_pass_name = "ssa";
|
||||
afl_pass_info.ref_pass_instance_number = 1;
|
||||
afl_pass_info.pos_op = PASS_POS_INSERT_AFTER;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!plugin_default_version_check(version, &gcc_version)) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL(G_("Incompatible gcc/plugin versions!"));
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a banner */
|
||||
if (isatty(2) && !getenv("AFL_QUIET")) {
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF(G_(cCYA "afl-gcc-pass" VERSION cRST
|
||||
" initially by <aseipp@pobox.com>, maintainer: hexcoder-\n"));
|
||||
|
||||
} else
|
||||
|
||||
be_quiet = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Decide instrumentation ratio */
|
||||
char *inst_ratio_str = getenv("AFL_INST_RATIO");
|
||||
|
||||
if (inst_ratio_str) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (sscanf(inst_ratio_str, "%u", &inst_ratio) != 1 || !inst_ratio ||
|
||||
inst_ratio > 100)
|
||||
FATAL(G_("Bad value of AFL_INST_RATIO (must be between 1 and 100)"));
|
||||
else {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet)
|
||||
ACTF(G_("%s instrumentation at ratio of %u%% in %s mode."),
|
||||
inst_ext ? G_("Call-based") : G_("Inline"), inst_ratio,
|
||||
getenv("AFL_HARDEN") ? G_("hardened") : G_("non-hardened"));
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
char *instWhiteListFilename = getenv("AFL_GCC_WHITELIST");
|
||||
if (instWhiteListFilename) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::string line;
|
||||
std::ifstream fileStream;
|
||||
fileStream.open(instWhiteListFilename);
|
||||
if (!fileStream) fatal_error(0, "Unable to open AFL_GCC_WHITELIST");
|
||||
getline(fileStream, line);
|
||||
while (fileStream) {
|
||||
|
||||
myWhitelist.push_back(line);
|
||||
getline(fileStream, line);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (!be_quiet && getenv("AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST"))
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF(cYEL "[-] " cRST
|
||||
"AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST environment variable detected - did you mean "
|
||||
"AFL_GCC_WHITELIST?\n");
|
||||
|
||||
/* Go go gadget */
|
||||
register_callback(plugin_info->base_name, PLUGIN_INFO, NULL,
|
||||
&afl_plugin_info);
|
||||
register_callback(plugin_info->base_name, PLUGIN_PASS_MANAGER_SETUP, NULL,
|
||||
&afl_pass_info);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
224
gcc_plugin/afl-gcc-rt.o.c
Normal file
224
gcc_plugin/afl-gcc-rt.o.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - GCC plugin instrumentation bootstrap
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Austin Seipp <aseipp@pobox.com> and
|
||||
Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
GCC integration design is based on the LLVM design, which comes
|
||||
from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
This code is the rewrite of afl-as.h's main_payload.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <signal.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <sys/mman.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/shm.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/wait.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/types.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/* Globals needed by the injected instrumentation. The __afl_area_initial region
|
||||
is used for instrumentation output before __afl_map_shm() has a chance to
|
||||
run. It will end up as .comm, so it shouldn't be too wasteful. */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 __afl_area_initial[MAP_SIZE];
|
||||
u8 *__afl_area_ptr = __afl_area_initial;
|
||||
u32 __afl_prev_loc;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Running in persistent mode? */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 is_persistent;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Trace a basic block with some ID */
|
||||
void __afl_trace(u32 x) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 l = __afl_prev_loc;
|
||||
u32 n = l ^ x;
|
||||
*(__afl_area_ptr + n) += 1;
|
||||
__afl_prev_loc = (x >> 1);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* SHM setup. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void __afl_map_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *id_str = getenv(SHM_ENV_VAR);
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we're running under AFL, attach to the appropriate region, replacing the
|
||||
early-stage __afl_area_initial region that is needed to allow some really
|
||||
hacky .init code to work correctly in projects such as OpenSSL. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (id_str) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 shm_id = atoi(id_str);
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr = shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Whooooops. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_area_ptr == (void *)-1) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write something into the bitmap so that even with low AFL_INST_RATIO,
|
||||
our parent doesn't give up on us. */
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr[0] = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fork server logic. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 tmp[4];
|
||||
s32 child_pid;
|
||||
|
||||
u8 child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Phone home and tell the parent that we're OK. If parent isn't there,
|
||||
assume we're not running in forkserver mode and just execute program. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, tmp, 4) != 4) return;
|
||||
|
||||
while (1) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 was_killed;
|
||||
int status;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Wait for parent by reading from the pipe. Abort if read fails. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we stopped the child in persistent mode, but there was a race
|
||||
condition and afl-fuzz already issued SIGKILL, write off the old
|
||||
process. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_stopped && was_killed) {
|
||||
|
||||
child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) < 0) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!child_stopped) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. */
|
||||
|
||||
child_pid = fork();
|
||||
if (child_pid < 0) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (!child_pid) {
|
||||
|
||||
close(FORKSRV_FD);
|
||||
close(FORKSRV_FD + 1);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Special handling for persistent mode: if the child is alive but
|
||||
currently stopped, simply restart it with SIGCONT. */
|
||||
|
||||
kill(child_pid, SIGCONT);
|
||||
child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &child_pid, 4) != 4) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, is_persistent ? WUNTRACED : 0) < 0) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* In persistent mode, the child stops itself with SIGSTOP to indicate
|
||||
a successful run. In this case, we want to wake it up without forking
|
||||
again. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (WIFSTOPPED(status)) child_stopped = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &status, 4) != 4) exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* A simplified persistent mode handler, used as explained in README.llvm. */
|
||||
|
||||
int __afl_persistent_loop(unsigned int max_cnt) {
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 first_pass = 1;
|
||||
static u32 cycle_cnt;
|
||||
|
||||
if (first_pass) {
|
||||
|
||||
cycle_cnt = max_cnt;
|
||||
first_pass = 0;
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (is_persistent && --cycle_cnt) {
|
||||
|
||||
raise(SIGSTOP);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
} else
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* This one can be called from user code when deferred forkserver mode
|
||||
is enabled. */
|
||||
|
||||
void __afl_manual_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 init_done;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!init_done) {
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_map_shm();
|
||||
__afl_start_forkserver();
|
||||
init_done = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Proper initialization routine. */
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((constructor(101))) void __afl_auto_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
is_persistent = !!getenv(PERSIST_ENV_VAR);
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv(DEFER_ENV_VAR)) return;
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_manual_init();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,15 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - injectable parts
|
||||
-------------------------------------
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - injectable parts
|
||||
---------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Forkserver design by Jann Horn <jannhorn@googlemail.com>
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
@ -37,7 +40,7 @@
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
/*
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
Performances notes
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
@ -106,47 +109,47 @@
|
||||
|
||||
static const u8* trampoline_fmt_32 =
|
||||
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- AFL TRAMPOLINE (32-BIT) --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
".align 4\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"leal -16(%%esp), %%esp\n"
|
||||
"movl %%edi, 0(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl %%edx, 4(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl %%ecx, 8(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl %%eax, 12(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl $0x%08x, %%ecx\n"
|
||||
"call __afl_maybe_log\n"
|
||||
"movl 12(%%esp), %%eax\n"
|
||||
"movl 8(%%esp), %%ecx\n"
|
||||
"movl 4(%%esp), %%edx\n"
|
||||
"movl 0(%%esp), %%edi\n"
|
||||
"leal 16(%%esp), %%esp\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- END --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n";
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- AFL TRAMPOLINE (32-BIT) --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
".align 4\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"leal -16(%%esp), %%esp\n"
|
||||
"movl %%edi, 0(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl %%edx, 4(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl %%ecx, 8(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl %%eax, 12(%%esp)\n"
|
||||
"movl $0x%08x, %%ecx\n"
|
||||
"call __afl_maybe_log\n"
|
||||
"movl 12(%%esp), %%eax\n"
|
||||
"movl 8(%%esp), %%ecx\n"
|
||||
"movl 4(%%esp), %%edx\n"
|
||||
"movl 0(%%esp), %%edi\n"
|
||||
"leal 16(%%esp), %%esp\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- END --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n";
|
||||
|
||||
static const u8* trampoline_fmt_64 =
|
||||
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- AFL TRAMPOLINE (64-BIT) --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
".align 4\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"leaq -(128+24)(%%rsp), %%rsp\n"
|
||||
"movq %%rdx, 0(%%rsp)\n"
|
||||
"movq %%rcx, 8(%%rsp)\n"
|
||||
"movq %%rax, 16(%%rsp)\n"
|
||||
"movq $0x%08x, %%rcx\n"
|
||||
"call __afl_maybe_log\n"
|
||||
"movq 16(%%rsp), %%rax\n"
|
||||
"movq 8(%%rsp), %%rcx\n"
|
||||
"movq 0(%%rsp), %%rdx\n"
|
||||
"leaq (128+24)(%%rsp), %%rsp\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- END --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n";
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- AFL TRAMPOLINE (64-BIT) --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
".align 4\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"leaq -(128+24)(%%rsp), %%rsp\n"
|
||||
"movq %%rdx, 0(%%rsp)\n"
|
||||
"movq %%rcx, 8(%%rsp)\n"
|
||||
"movq %%rax, 16(%%rsp)\n"
|
||||
"movq $0x%08x, %%rcx\n"
|
||||
"call __afl_maybe_log\n"
|
||||
"movq 16(%%rsp), %%rax\n"
|
||||
"movq 8(%%rsp), %%rcx\n"
|
||||
"movq 0(%%rsp), %%rdx\n"
|
||||
"leaq (128+24)(%%rsp), %%rsp\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"/* --- END --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n";
|
||||
|
||||
static const u8* main_payload_32 =
|
||||
|
||||
@ -183,13 +186,14 @@ static const u8* main_payload_32 =
|
||||
" movl %ecx, __afl_prev_loc\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" movl %ecx, %edi\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#ifdef SKIP_COUNTS
|
||||
" orb $1, (%edx, %edi, 1)\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" incb (%edx, %edi, 1)\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
|
||||
" adcb $0, (%edx, %edi, 1)\n" // never zero counter implementation. slightly better path discovery and little performance impact
|
||||
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"__afl_return:\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
@ -220,6 +224,29 @@ static const u8* main_payload_32 =
|
||||
" testl %eax, %eax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#ifdef USEMMAP
|
||||
" pushl $384 /* shm_open mode 0600 */\n"
|
||||
" pushl $2 /* flags O_RDWR */\n"
|
||||
" pushl %eax /* SHM file path */\n"
|
||||
" call shm_open\n"
|
||||
" addl $12, %esp\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" cmpl $-1, %eax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" pushl $0 /* mmap off */\n"
|
||||
" pushl %eax /* shm fd */\n"
|
||||
" pushl $1 /* mmap flags */\n"
|
||||
" pushl $3 /* mmap prot */\n"
|
||||
" pushl $"STRINGIFY(MAP_SIZE)" /* mmap len */\n"
|
||||
" pushl $0 /* mmap addr */\n"
|
||||
" call mmap\n"
|
||||
" addl $12, %esp\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" cmpl $-1, %eax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" pushl %eax\n"
|
||||
" call atoi\n"
|
||||
" addl $4, %esp\n"
|
||||
@ -233,6 +260,7 @@ static const u8* main_payload_32 =
|
||||
" cmpl $-1, %eax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
" /* Store the address of the SHM region. */\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" movl %eax, __afl_area_ptr\n"
|
||||
@ -354,7 +382,7 @@ static const u8* main_payload_32 =
|
||||
" .comm __afl_setup_failure, 1, 32\n"
|
||||
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
|
||||
" .comm __afl_prev_loc, 4, 32\n"
|
||||
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
" .comm __afl_fork_pid, 4, 32\n"
|
||||
" .comm __afl_temp, 4, 32\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
@ -373,10 +401,10 @@ static const u8* main_payload_32 =
|
||||
recognize .string. */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
# define CALL_L64(str) "call _" str "\n"
|
||||
#define CALL_L64(str) "call _" str "\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define CALL_L64(str) "call " str "@PLT\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
#define CALL_L64(str) "call " str "@PLT\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
|
||||
static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
|
||||
@ -390,11 +418,11 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"__afl_maybe_log:\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#if defined(__OpenBSD__) || (defined(__FreeBSD__) && (__FreeBSD__ < 9))
|
||||
#if defined(__OpenBSD__) || (defined(__FreeBSD__) && (__FreeBSD__ < 9))
|
||||
" .byte 0x9f /* lahf */\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" lahf\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^__OpenBSD__, etc */
|
||||
#endif /* ^__OpenBSD__, etc */
|
||||
" seto %al\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" /* Check if SHM region is already mapped. */\n"
|
||||
@ -411,22 +439,23 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
" xorq __afl_prev_loc(%rip), %rcx\n"
|
||||
" xorq %rcx, __afl_prev_loc(%rip)\n"
|
||||
" shrq $1, __afl_prev_loc(%rip)\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
#endif /* ^!COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#ifdef SKIP_COUNTS
|
||||
" orb $1, (%rdx, %rcx, 1)\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" incb (%rdx, %rcx, 1)\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
|
||||
" adcb $0, (%rdx, %rcx, 1)\n" // never zero counter implementation. slightly better path discovery and little performance impact
|
||||
#endif /* ^SKIP_COUNTS */
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"__afl_return:\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" addb $127, %al\n"
|
||||
#if defined(__OpenBSD__) || (defined(__FreeBSD__) && (__FreeBSD__ < 9))
|
||||
#if defined(__OpenBSD__) || (defined(__FreeBSD__) && (__FreeBSD__ < 9))
|
||||
" .byte 0x9e /* sahf */\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" sahf\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^__OpenBSD__, etc */
|
||||
#endif /* ^__OpenBSD__, etc */
|
||||
" ret\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
".align 8\n"
|
||||
@ -445,7 +474,7 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
" movq (%rdx), %rdx\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" movq __afl_global_area_ptr(%rip), %rdx\n"
|
||||
#endif /* !^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
#endif /* !^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
" testq %rdx, %rdx\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_first\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
@ -501,6 +530,27 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
" testq %rax, %rax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#ifdef USEMMAP
|
||||
" movl $384, %edx /* shm_open mode 0600 */\n"
|
||||
" movl $2, %esi /* flags O_RDWR */\n"
|
||||
" movq %rax, %rdi /* SHM file path */\n"
|
||||
CALL_L64("shm_open")
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" cmpq $-1, %rax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" movl $0, %r9d\n"
|
||||
" movl %eax, %r8d\n"
|
||||
" movl $1, %ecx\n"
|
||||
" movl $3, %edx\n"
|
||||
" movl $"STRINGIFY(MAP_SIZE)", %esi\n"
|
||||
" movl $0, %edi\n"
|
||||
CALL_L64("mmap")
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" cmpq $-1, %rax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" movq %rax, %rdi\n"
|
||||
CALL_L64("atoi")
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
@ -512,6 +562,7 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
" cmpq $-1, %rax\n"
|
||||
" je __afl_setup_abort\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
" /* Store the address of the SHM region. */\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
" movq %rax, %rdx\n"
|
||||
@ -522,7 +573,7 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
#else
|
||||
" movq __afl_global_area_ptr@GOTPCREL(%rip), %rdx\n"
|
||||
" movq %rax, (%rdx)\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
" movq %rax, %rdx\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"__afl_forkserver:\n"
|
||||
@ -691,7 +742,7 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
" .comm __afl_area_ptr, 8\n"
|
||||
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
|
||||
" .comm __afl_prev_loc, 8\n"
|
||||
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
" .comm __afl_fork_pid, 4\n"
|
||||
" .comm __afl_temp, 4\n"
|
||||
" .comm __afl_setup_failure, 1\n"
|
||||
@ -701,12 +752,12 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
" .lcomm __afl_area_ptr, 8\n"
|
||||
#ifndef COVERAGE_ONLY
|
||||
" .lcomm __afl_prev_loc, 8\n"
|
||||
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
#endif /* !COVERAGE_ONLY */
|
||||
" .lcomm __afl_fork_pid, 4\n"
|
||||
" .lcomm __afl_temp, 4\n"
|
||||
" .lcomm __afl_setup_failure, 1\n"
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
|
||||
" .comm __afl_global_area_ptr, 8, 8\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
@ -716,4 +767,5 @@ static const u8* main_payload_64 =
|
||||
"/* --- END --- */\n"
|
||||
"\n";
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* !_HAVE_AFL_AS_H */
|
||||
#endif /* !_HAVE_AFL_AS_H */
|
||||
|
||||
703
include/afl-fuzz.h
Normal file
703
include/afl-fuzz.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,703 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - fuzzer header
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
This is the real deal: the program takes an instrumented binary and
|
||||
attempts a variety of basic fuzzing tricks, paying close attention to
|
||||
how they affect the execution path.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _AFL_FUZZ_H
|
||||
#define _AFL_FUZZ_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define AFL_MAIN
|
||||
#define MESSAGES_TO_STDOUT
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _GNU_SOURCE
|
||||
#define _GNU_SOURCE 1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define _FILE_OFFSET_BITS 64
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __ANDROID__
|
||||
#include "android-ashmem.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
#include "alloc-inl.h"
|
||||
#include "hash.h"
|
||||
#include "sharedmem.h"
|
||||
#include "forkserver.h"
|
||||
#include "common.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <time.h>
|
||||
#include <errno.h>
|
||||
#include <signal.h>
|
||||
#include <dirent.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <termios.h>
|
||||
#include <dlfcn.h>
|
||||
#include <sched.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <sys/wait.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/time.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/shm.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/stat.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/types.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/resource.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/mman.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/file.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__APPLE__) || defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__OpenBSD__) || \
|
||||
defined(__NetBSD__)
|
||||
#include <sys/sysctl.h>
|
||||
#endif /* __APPLE__ || __FreeBSD__ || __OpenBSD__ */
|
||||
|
||||
/* For systems that have sched_setaffinity; right now just Linux, but one
|
||||
can hope... */
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__linux__) || defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__NetBSD__)
|
||||
#define HAVE_AFFINITY 1
|
||||
#if defined(__FreeBSD__)
|
||||
#include <sys/param.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/cpuset.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/user.h>
|
||||
#include <pthread.h>
|
||||
#include <pthread_np.h>
|
||||
#define cpu_set_t cpuset_t
|
||||
#elif defined(__NetBSD__)
|
||||
#include <pthread.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif /* __linux__ */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef SIMPLE_FILES
|
||||
#define CASE_PREFIX "id:"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define CASE_PREFIX "id_"
|
||||
#endif /* ^!SIMPLE_FILES */
|
||||
|
||||
struct queue_entry {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* fname; /* File name for the test case */
|
||||
u32 len; /* Input length */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 cal_failed, /* Calibration failed? */
|
||||
trim_done, /* Trimmed? */
|
||||
was_fuzzed, /* historical, but needed for MOpt */
|
||||
passed_det, /* Deterministic stages passed? */
|
||||
has_new_cov, /* Triggers new coverage? */
|
||||
var_behavior, /* Variable behavior? */
|
||||
favored, /* Currently favored? */
|
||||
fs_redundant; /* Marked as redundant in the fs? */
|
||||
|
||||
u32 bitmap_size, /* Number of bits set in bitmap */
|
||||
fuzz_level, /* Number of fuzzing iterations */
|
||||
exec_cksum; /* Checksum of the execution trace */
|
||||
|
||||
u64 exec_us, /* Execution time (us) */
|
||||
handicap, /* Number of queue cycles behind */
|
||||
n_fuzz, /* Number of fuzz, does not overflow */
|
||||
depth; /* Path depth */
|
||||
|
||||
u8* trace_mini; /* Trace bytes, if kept */
|
||||
u32 tc_ref; /* Trace bytes ref count */
|
||||
|
||||
struct queue_entry *next, /* Next element, if any */
|
||||
*next_100; /* 100 elements ahead */
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct extra_data {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* data; /* Dictionary token data */
|
||||
u32 len; /* Dictionary token length */
|
||||
u32 hit_cnt; /* Use count in the corpus */
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fuzzing stages */
|
||||
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
|
||||
/* 00 */ STAGE_FLIP1,
|
||||
/* 01 */ STAGE_FLIP2,
|
||||
/* 02 */ STAGE_FLIP4,
|
||||
/* 03 */ STAGE_FLIP8,
|
||||
/* 04 */ STAGE_FLIP16,
|
||||
/* 05 */ STAGE_FLIP32,
|
||||
/* 06 */ STAGE_ARITH8,
|
||||
/* 07 */ STAGE_ARITH16,
|
||||
/* 08 */ STAGE_ARITH32,
|
||||
/* 09 */ STAGE_INTEREST8,
|
||||
/* 10 */ STAGE_INTEREST16,
|
||||
/* 11 */ STAGE_INTEREST32,
|
||||
/* 12 */ STAGE_EXTRAS_UO,
|
||||
/* 13 */ STAGE_EXTRAS_UI,
|
||||
/* 14 */ STAGE_EXTRAS_AO,
|
||||
/* 15 */ STAGE_HAVOC,
|
||||
/* 16 */ STAGE_SPLICE,
|
||||
/* 17 */ STAGE_PYTHON,
|
||||
/* 18 */ STAGE_CUSTOM_MUTATOR
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* Stage value types */
|
||||
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
|
||||
/* 00 */ STAGE_VAL_NONE,
|
||||
/* 01 */ STAGE_VAL_LE,
|
||||
/* 02 */ STAGE_VAL_BE
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* Execution status fault codes */
|
||||
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
|
||||
/* 00 */ FAULT_NONE,
|
||||
/* 01 */ FAULT_TMOUT,
|
||||
/* 02 */ FAULT_CRASH,
|
||||
/* 03 */ FAULT_ERROR,
|
||||
/* 04 */ FAULT_NOINST,
|
||||
/* 05 */ FAULT_NOBITS
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* MOpt:
|
||||
Lots of globals, but mostly for the status UI and other things where it
|
||||
really makes no sense to haul them around as function parameters. */
|
||||
extern u64 limit_time_puppet, orig_hit_cnt_puppet, last_limit_time_start,
|
||||
tmp_pilot_time, total_pacemaker_time, total_puppet_find, temp_puppet_find,
|
||||
most_time_key, most_time, most_execs_key, most_execs, old_hit_count;
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 SPLICE_CYCLES_puppet, limit_time_sig, key_puppet, key_module;
|
||||
|
||||
extern double w_init, w_end, w_now;
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 g_now;
|
||||
extern s32 g_max;
|
||||
|
||||
#define operator_num 16
|
||||
#define swarm_num 5
|
||||
#define period_core 500000
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 tmp_core_time;
|
||||
extern s32 swarm_now;
|
||||
|
||||
extern double x_now[swarm_num][operator_num], L_best[swarm_num][operator_num],
|
||||
eff_best[swarm_num][operator_num], G_best[operator_num],
|
||||
v_now[swarm_num][operator_num], probability_now[swarm_num][operator_num],
|
||||
swarm_fitness[swarm_num];
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 stage_finds_puppet[swarm_num][operator_num], /* Patterns found per
|
||||
fuzz stage */
|
||||
stage_finds_puppet_v2[swarm_num][operator_num],
|
||||
stage_cycles_puppet_v2[swarm_num][operator_num],
|
||||
stage_cycles_puppet_v3[swarm_num][operator_num],
|
||||
stage_cycles_puppet[swarm_num][operator_num],
|
||||
operator_finds_puppet[operator_num],
|
||||
core_operator_finds_puppet[operator_num],
|
||||
core_operator_finds_puppet_v2[operator_num],
|
||||
core_operator_cycles_puppet[operator_num],
|
||||
core_operator_cycles_puppet_v2[operator_num],
|
||||
core_operator_cycles_puppet_v3[operator_num]; /* Execs per fuzz stage */
|
||||
|
||||
#define RAND_C (rand() % 1000 * 0.001)
|
||||
#define v_max 1
|
||||
#define v_min 0.05
|
||||
#define limit_time_bound 1.1
|
||||
#define SPLICE_CYCLES_puppet_up 25
|
||||
#define SPLICE_CYCLES_puppet_low 5
|
||||
#define STAGE_RANDOMBYTE 12
|
||||
#define STAGE_DELETEBYTE 13
|
||||
#define STAGE_Clone75 14
|
||||
#define STAGE_OverWrite75 15
|
||||
#define period_pilot 50000
|
||||
|
||||
extern double period_pilot_tmp;
|
||||
extern s32 key_lv;
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 *in_dir, /* Input directory with test cases */
|
||||
*out_dir, /* Working & output directory */
|
||||
*tmp_dir, /* Temporary directory for input */
|
||||
*sync_dir, /* Synchronization directory */
|
||||
*sync_id, /* Fuzzer ID */
|
||||
*power_name, /* Power schedule name */
|
||||
*use_banner, /* Display banner */
|
||||
*in_bitmap, /* Input bitmap */
|
||||
*file_extension, /* File extension */
|
||||
*orig_cmdline, /* Original command line */
|
||||
*doc_path, /* Path to documentation dir */
|
||||
*infoexec, /* Command to execute on a new crash */
|
||||
*out_file; /* File to fuzz, if any */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u32 exec_tmout; /* Configurable exec timeout (ms) */
|
||||
extern u32 hang_tmout; /* Timeout used for hang det (ms) */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 mem_limit; /* Memory cap for child (MB) */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 cal_cycles, /* Calibration cycles defaults */
|
||||
cal_cycles_long, debug, /* Debug mode */
|
||||
custom_only, /* Custom mutator only mode */
|
||||
python_only; /* Python-only mode */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u32 stats_update_freq; /* Stats update frequency (execs) */
|
||||
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
|
||||
/* 00 */ EXPLORE, /* AFL default, Exploration-based constant schedule */
|
||||
/* 01 */ FAST, /* Exponential schedule */
|
||||
/* 02 */ COE, /* Cut-Off Exponential schedule */
|
||||
/* 03 */ LIN, /* Linear schedule */
|
||||
/* 04 */ QUAD, /* Quadratic schedule */
|
||||
/* 05 */ EXPLOIT, /* AFL's exploitation-based const. */
|
||||
|
||||
POWER_SCHEDULES_NUM
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
extern char* power_names[POWER_SCHEDULES_NUM];
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 schedule; /* Power schedule (default: EXPLORE)*/
|
||||
extern u8 havoc_max_mult;
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 skip_deterministic, /* Skip deterministic stages? */
|
||||
force_deterministic, /* Force deterministic stages? */
|
||||
use_splicing, /* Recombine input files? */
|
||||
dumb_mode, /* Run in non-instrumented mode? */
|
||||
score_changed, /* Scoring for favorites changed? */
|
||||
kill_signal, /* Signal that killed the child */
|
||||
resuming_fuzz, /* Resuming an older fuzzing job? */
|
||||
timeout_given, /* Specific timeout given? */
|
||||
not_on_tty, /* stdout is not a tty */
|
||||
term_too_small, /* terminal dimensions too small */
|
||||
no_forkserver, /* Disable forkserver? */
|
||||
crash_mode, /* Crash mode! Yeah! */
|
||||
in_place_resume, /* Attempt in-place resume? */
|
||||
auto_changed, /* Auto-generated tokens changed? */
|
||||
no_cpu_meter_red, /* Feng shui on the status screen */
|
||||
no_arith, /* Skip most arithmetic ops */
|
||||
shuffle_queue, /* Shuffle input queue? */
|
||||
bitmap_changed, /* Time to update bitmap? */
|
||||
qemu_mode, /* Running in QEMU mode? */
|
||||
unicorn_mode, /* Running in Unicorn mode? */
|
||||
use_wine, /* Use WINE with QEMU mode */
|
||||
skip_requested, /* Skip request, via SIGUSR1 */
|
||||
run_over10m, /* Run time over 10 minutes? */
|
||||
persistent_mode, /* Running in persistent mode? */
|
||||
deferred_mode, /* Deferred forkserver mode? */
|
||||
fixed_seed, /* do not reseed */
|
||||
fast_cal, /* Try to calibrate faster? */
|
||||
uses_asan; /* Target uses ASAN? */
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 out_fd, /* Persistent fd for out_file */
|
||||
#ifndef HAVE_ARC4RANDOM
|
||||
dev_urandom_fd, /* Persistent fd for /dev/urandom */
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
dev_null_fd, /* Persistent fd for /dev/null */
|
||||
fsrv_ctl_fd, /* Fork server control pipe (write) */
|
||||
fsrv_st_fd; /* Fork server status pipe (read) */
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 forksrv_pid, /* PID of the fork server */
|
||||
child_pid, /* PID of the fuzzed program */
|
||||
out_dir_fd; /* FD of the lock file */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8* trace_bits; /* SHM with instrumentation bitmap */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 virgin_bits[MAP_SIZE], /* Regions yet untouched by fuzzing */
|
||||
virgin_tmout[MAP_SIZE], /* Bits we haven't seen in tmouts */
|
||||
virgin_crash[MAP_SIZE]; /* Bits we haven't seen in crashes */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 var_bytes[MAP_SIZE]; /* Bytes that appear to be variable */
|
||||
|
||||
extern volatile u8 stop_soon, /* Ctrl-C pressed? */
|
||||
clear_screen, /* Window resized? */
|
||||
child_timed_out; /* Traced process timed out? */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u32 queued_paths, /* Total number of queued testcases */
|
||||
queued_variable, /* Testcases with variable behavior */
|
||||
queued_at_start, /* Total number of initial inputs */
|
||||
queued_discovered, /* Items discovered during this run */
|
||||
queued_imported, /* Items imported via -S */
|
||||
queued_favored, /* Paths deemed favorable */
|
||||
queued_with_cov, /* Paths with new coverage bytes */
|
||||
pending_not_fuzzed, /* Queued but not done yet */
|
||||
pending_favored, /* Pending favored paths */
|
||||
cur_skipped_paths, /* Abandoned inputs in cur cycle */
|
||||
cur_depth, /* Current path depth */
|
||||
max_depth, /* Max path depth */
|
||||
useless_at_start, /* Number of useless starting paths */
|
||||
var_byte_count, /* Bitmap bytes with var behavior */
|
||||
current_entry, /* Current queue entry ID */
|
||||
havoc_div; /* Cycle count divisor for havoc */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 total_crashes, /* Total number of crashes */
|
||||
unique_crashes, /* Crashes with unique signatures */
|
||||
total_tmouts, /* Total number of timeouts */
|
||||
unique_tmouts, /* Timeouts with unique signatures */
|
||||
unique_hangs, /* Hangs with unique signatures */
|
||||
total_execs, /* Total execve() calls */
|
||||
slowest_exec_ms, /* Slowest testcase non hang in ms */
|
||||
start_time, /* Unix start time (ms) */
|
||||
last_path_time, /* Time for most recent path (ms) */
|
||||
last_crash_time, /* Time for most recent crash (ms) */
|
||||
last_hang_time, /* Time for most recent hang (ms) */
|
||||
last_crash_execs, /* Exec counter at last crash */
|
||||
queue_cycle, /* Queue round counter */
|
||||
cycles_wo_finds, /* Cycles without any new paths */
|
||||
trim_execs, /* Execs done to trim input files */
|
||||
bytes_trim_in, /* Bytes coming into the trimmer */
|
||||
bytes_trim_out, /* Bytes coming outa the trimmer */
|
||||
blocks_eff_total, /* Blocks subject to effector maps */
|
||||
blocks_eff_select; /* Blocks selected as fuzzable */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u32 subseq_tmouts; /* Number of timeouts in a row */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 *stage_name, /* Name of the current fuzz stage */
|
||||
*stage_short, /* Short stage name */
|
||||
*syncing_party; /* Currently syncing with... */
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 stage_cur, stage_max; /* Stage progression */
|
||||
extern s32 splicing_with; /* Splicing with which test case? */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u32 master_id, master_max; /* Master instance job splitting */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u32 syncing_case; /* Syncing with case #... */
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 stage_cur_byte, /* Byte offset of current stage op */
|
||||
stage_cur_val; /* Value used for stage op */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8 stage_val_type; /* Value type (STAGE_VAL_*) */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 stage_finds[32], /* Patterns found per fuzz stage */
|
||||
stage_cycles[32]; /* Execs per fuzz stage */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef HAVE_ARC4RANDOM
|
||||
extern u32 rand_cnt; /* Random number counter */
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 total_cal_us, /* Total calibration time (us) */
|
||||
total_cal_cycles; /* Total calibration cycles */
|
||||
|
||||
extern u64 total_bitmap_size, /* Total bit count for all bitmaps */
|
||||
total_bitmap_entries; /* Number of bitmaps counted */
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 cpu_core_count; /* CPU core count */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef HAVE_AFFINITY
|
||||
|
||||
extern s32 cpu_aff; /* Selected CPU core */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* HAVE_AFFINITY */
|
||||
|
||||
extern FILE* plot_file; /* Gnuplot output file */
|
||||
|
||||
extern struct queue_entry *queue, /* Fuzzing queue (linked list) */
|
||||
*queue_cur, /* Current offset within the queue */
|
||||
*queue_top, /* Top of the list */
|
||||
*q_prev100; /* Previous 100 marker */
|
||||
|
||||
extern struct queue_entry*
|
||||
top_rated[MAP_SIZE]; /* Top entries for bitmap bytes */
|
||||
|
||||
extern struct extra_data* extras; /* Extra tokens to fuzz with */
|
||||
extern u32 extras_cnt; /* Total number of tokens read */
|
||||
|
||||
extern struct extra_data* a_extras; /* Automatically selected extras */
|
||||
extern u32 a_extras_cnt; /* Total number of tokens available */
|
||||
|
||||
u8* (*post_handler)(u8* buf, u32* len);
|
||||
|
||||
/* hooks for the custom mutator function */
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Perform custom mutations on a given input
|
||||
* @param data Input data to be mutated
|
||||
* @param size Size of input data
|
||||
* @param mutated_out Buffer to store the mutated input
|
||||
* @param max_size Maximum size of the mutated output. The mutation must not
|
||||
* produce data larger than max_size.
|
||||
* @param seed Seed used for the mutation. The mutation should produce the same
|
||||
* output given the same seed.
|
||||
* @return Size of the mutated output.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
size_t (*custom_mutator)(u8* data, size_t size, u8* mutated_out,
|
||||
size_t max_size, unsigned int seed);
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A post-processing function to use right before AFL writes the test case to
|
||||
* disk in order to execute the target. If this functionality is not needed,
|
||||
* Simply don't define this function.
|
||||
* @param data Buffer containing the test case to be executed.
|
||||
* @param size Size of the test case.
|
||||
* @param new_data Buffer to store the test case after processing
|
||||
* @return Size of data after processing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
size_t (*pre_save_handler)(u8* data, size_t size, u8** new_data);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Interesting values, as per config.h */
|
||||
|
||||
extern s8 interesting_8[INTERESTING_8_LEN];
|
||||
extern s16 interesting_16[INTERESTING_8_LEN + INTERESTING_16_LEN];
|
||||
extern s32
|
||||
interesting_32[INTERESTING_8_LEN + INTERESTING_16_LEN + INTERESTING_32_LEN];
|
||||
|
||||
/* Python stuff */
|
||||
#ifdef USE_PYTHON
|
||||
|
||||
// because Python sets stuff it should not ...
|
||||
#ifdef _POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#define _SAVE_POSIX_C_SOURCE _POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#undef _POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef _XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#define _SAVE_XOPEN_SOURCE _XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#undef _XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Python.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _SAVE_POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#ifdef _POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#undef _POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE _SAVE_POSIX_C_SOURCE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef _SAVE_XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#ifdef _XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#undef _XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define _XOPEN_SOURCE _SAVE_XOPEN_SOURCE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
extern PyObject* py_module;
|
||||
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
|
||||
/* 00 */ PY_FUNC_INIT,
|
||||
/* 01 */ PY_FUNC_FUZZ,
|
||||
/* 02 */ PY_FUNC_INIT_TRIM,
|
||||
/* 03 */ PY_FUNC_POST_TRIM,
|
||||
/* 04 */ PY_FUNC_TRIM,
|
||||
PY_FUNC_COUNT
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
extern PyObject* py_functions[PY_FUNC_COUNT];
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/**** Prototypes ****/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Python */
|
||||
#ifdef USE_PYTHON
|
||||
int init_py();
|
||||
void finalize_py();
|
||||
void fuzz_py(char*, size_t, char*, size_t, char**, size_t*);
|
||||
u32 init_trim_py(char*, size_t);
|
||||
u32 post_trim_py(char);
|
||||
void trim_py(char**, size_t*);
|
||||
u8 trim_case_python(char**, struct queue_entry*, u8*);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Queue */
|
||||
|
||||
void mark_as_det_done(struct queue_entry*);
|
||||
void mark_as_variable(struct queue_entry*);
|
||||
void mark_as_redundant(struct queue_entry*, u8);
|
||||
void add_to_queue(u8*, u32, u8);
|
||||
void destroy_queue(void);
|
||||
void update_bitmap_score(struct queue_entry*);
|
||||
void cull_queue(void);
|
||||
u32 calculate_score(struct queue_entry*);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Bitmap */
|
||||
|
||||
void write_bitmap(void);
|
||||
void read_bitmap(u8*);
|
||||
u8 has_new_bits(u8*);
|
||||
u32 count_bits(u8*);
|
||||
u32 count_bytes(u8*);
|
||||
u32 count_non_255_bytes(u8*);
|
||||
#ifdef __x86_64__
|
||||
void simplify_trace(u64*);
|
||||
void classify_counts(u64*);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
void simplify_trace(u32*);
|
||||
void classify_counts(u32*);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
void init_count_class16(void);
|
||||
void minimize_bits(u8*, u8*);
|
||||
#ifndef SIMPLE_FILES
|
||||
u8* describe_op(u8);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
u8 save_if_interesting(char**, void*, u32, u8);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Misc */
|
||||
|
||||
u8* DI(u64);
|
||||
u8* DF(double);
|
||||
u8* DMS(u64);
|
||||
u8* DTD(u64, u64);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Extras */
|
||||
|
||||
void load_extras_file(u8*, u32*, u32*, u32);
|
||||
void load_extras(u8*);
|
||||
void maybe_add_auto(u8*, u32);
|
||||
void save_auto(void);
|
||||
void load_auto(void);
|
||||
void destroy_extras(void);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Stats */
|
||||
|
||||
void write_stats_file(double, double, double);
|
||||
void maybe_update_plot_file(double, double);
|
||||
void show_stats(void);
|
||||
void show_init_stats(void);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Run */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 run_target(char**, u32);
|
||||
void write_to_testcase(void*, u32);
|
||||
void write_with_gap(void*, u32, u32, u32);
|
||||
u8 calibrate_case(char**, struct queue_entry*, u8*, u32, u8);
|
||||
void sync_fuzzers(char**);
|
||||
u8 trim_case(char**, struct queue_entry*, u8*);
|
||||
u8 common_fuzz_stuff(char**, u8*, u32);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fuzz one */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 fuzz_one_original(char**);
|
||||
u8 pilot_fuzzing(char**);
|
||||
u8 core_fuzzing(char**);
|
||||
void pso_updating(void);
|
||||
u8 fuzz_one(char**);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Init */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef HAVE_AFFINITY
|
||||
void bind_to_free_cpu(void);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
void setup_post(void);
|
||||
void setup_custom_mutator(void);
|
||||
void read_testcases(void);
|
||||
void perform_dry_run(char**);
|
||||
void pivot_inputs(void);
|
||||
u32 find_start_position(void);
|
||||
void find_timeout(void);
|
||||
double get_runnable_processes(void);
|
||||
void nuke_resume_dir(void);
|
||||
void maybe_delete_out_dir(void);
|
||||
void setup_dirs_fds(void);
|
||||
void setup_cmdline_file(char**);
|
||||
void setup_stdio_file(void);
|
||||
void check_crash_handling(void);
|
||||
void check_cpu_governor(void);
|
||||
void get_core_count(void);
|
||||
void fix_up_sync(void);
|
||||
void check_asan_opts(void);
|
||||
void check_binary(u8*);
|
||||
void fix_up_banner(u8*);
|
||||
void check_if_tty(void);
|
||||
void setup_signal_handlers(void);
|
||||
char** get_qemu_argv(u8*, char**, int);
|
||||
char** get_wine_argv(u8*, char**, int);
|
||||
void save_cmdline(u32, char**);
|
||||
|
||||
/**** Inline routines ****/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Generate a random number (from 0 to limit - 1). This may
|
||||
have slight bias. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline u32 UR(u32 limit) {
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef HAVE_ARC4RANDOM
|
||||
if (fixed_seed) { return random() % limit; }
|
||||
|
||||
/* The boundary not being necessarily a power of 2,
|
||||
we need to ensure the result uniformity. */
|
||||
return arc4random_uniform(limit);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
if (!fixed_seed && unlikely(!rand_cnt--)) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 seed[2];
|
||||
|
||||
ck_read(dev_urandom_fd, &seed, sizeof(seed), "/dev/urandom");
|
||||
srandom(seed[0]);
|
||||
rand_cnt = (RESEED_RNG / 2) + (seed[1] % RESEED_RNG);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return random() % limit;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Find first power of two greater or equal to val (assuming val under
|
||||
2^63). */
|
||||
|
||||
static u64 next_p2(u64 val) {
|
||||
|
||||
u64 ret = 1;
|
||||
while (val > ret)
|
||||
ret <<= 1;
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Get unix time in milliseconds */
|
||||
|
||||
static u64 get_cur_time(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
struct timeval tv;
|
||||
struct timezone tz;
|
||||
|
||||
gettimeofday(&tv, &tz);
|
||||
|
||||
return (tv.tv_sec * 1000ULL) + (tv.tv_usec / 1000);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Get unix time in microseconds */
|
||||
|
||||
static u64 get_cur_time_us(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
struct timeval tv;
|
||||
struct timezone tz;
|
||||
|
||||
gettimeofday(&tv, &tz);
|
||||
|
||||
return (tv.tv_sec * 1000000ULL) + tv.tv_usec;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _AFL_DOCUMENT_MUTATIONS
|
||||
extern u8 do_document;
|
||||
extern u32 document_counter;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,15 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - error-checking, memory-zeroing alloc routines
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - error-checking, memory-zeroing alloc routines
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
@ -31,76 +36,109 @@
|
||||
|
||||
/* User-facing macro to sprintf() to a dynamically allocated buffer. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define alloc_printf(_str...) ({ \
|
||||
u8* _tmp; \
|
||||
s32 _len = snprintf(NULL, 0, _str); \
|
||||
#define alloc_printf(_str...) \
|
||||
({ \
|
||||
\
|
||||
u8* _tmp; \
|
||||
s32 _len = snprintf(NULL, 0, _str); \
|
||||
if (_len < 0) FATAL("Whoa, snprintf() fails?!"); \
|
||||
_tmp = ck_alloc(_len + 1); \
|
||||
snprintf((char*)_tmp, _len + 1, _str); \
|
||||
_tmp; \
|
||||
_tmp = ck_alloc(_len + 1); \
|
||||
snprintf((char*)_tmp, _len + 1, _str); \
|
||||
_tmp; \
|
||||
\
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
/* Macro to enforce allocation limits as a last-resort defense against
|
||||
integer overflows. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CHECK_SIZE(_s) do { \
|
||||
if ((_s) > MAX_ALLOC) \
|
||||
ABORT("Bad alloc request: %u bytes", (_s)); \
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CHECK_SIZE(_s) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if ((_s) > MAX_ALLOC) ABORT("Bad alloc request: %u bytes", (_s)); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Macro to check malloc() failures and the like. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CHECK_RESULT(_r, _s) do { \
|
||||
if (!(_r)) \
|
||||
ABORT("Out of memory: can't allocate %u bytes", (_s)); \
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CHECK_RESULT(_r, _s) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (!(_r)) ABORT("Out of memory: can't allocate %u bytes", (_s)); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Magic tokens used to mark used / freed chunks. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_MAGIC_C1 0xFF00FF00 /* Used head (dword) */
|
||||
#define ALLOC_MAGIC_F 0xFE00FE00 /* Freed head (dword) */
|
||||
#define ALLOC_MAGIC_C2 0xF0 /* Used tail (byte) */
|
||||
#define ALLOC_MAGIC_C1 0xFF00FF00 /* Used head (dword) */
|
||||
#define ALLOC_MAGIC_F 0xFE00FE00 /* Freed head (dword) */
|
||||
#define ALLOC_MAGIC_C2 0xF0 /* Used tail (byte) */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Positions of guard tokens in relation to the user-visible pointer. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_C1(_ptr) (((u32*)(_ptr))[-2])
|
||||
#define ALLOC_S(_ptr) (((u32*)(_ptr))[-1])
|
||||
#define ALLOC_C2(_ptr) (((u8*)(_ptr))[ALLOC_S(_ptr)])
|
||||
#define ALLOC_C1(_ptr) (((u32*)(_ptr))[-2])
|
||||
#define ALLOC_S(_ptr) (((u32*)(_ptr))[-1])
|
||||
#define ALLOC_C2(_ptr) (((u8*)(_ptr))[ALLOC_S(_ptr)])
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_OFF_HEAD 8
|
||||
#define ALLOC_OFF_HEAD 8
|
||||
#define ALLOC_OFF_TOTAL (ALLOC_OFF_HEAD + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Allocator increments for ck_realloc_block(). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_BLK_INC 256
|
||||
#define ALLOC_BLK_INC 256
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sanity-checking macros for pointers. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CHECK_PTR(_p) do { \
|
||||
#define CHECK_PTR(_p) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (_p) { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (ALLOC_C1(_p) ^ ALLOC_MAGIC_C1) { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (ALLOC_C1(_p) == ALLOC_MAGIC_F) \
|
||||
ABORT("Use after free."); \
|
||||
else \
|
||||
ABORT("Corrupted head alloc canary."); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* #define CHECK_PTR(_p) do { \
|
||||
if (_p) { \
|
||||
if (ALLOC_C1(_p) ^ ALLOC_MAGIC_C1) {\
|
||||
if (ALLOC_C1(_p) == ALLOC_MAGIC_F) \
|
||||
ABORT("Use after free."); \
|
||||
else ABORT("Corrupted head alloc canary."); \
|
||||
|
||||
} \
|
||||
|
||||
if (ALLOC_C2(_p) ^ ALLOC_MAGIC_C2) \
|
||||
ABORT("Corrupted tail alloc canary."); \
|
||||
|
||||
} \
|
||||
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#define CHECK_PTR_EXPR(_p) ({ \
|
||||
typeof (_p) _tmp = (_p); \
|
||||
CHECK_PTR(_tmp); \
|
||||
_tmp; \
|
||||
})
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define CHECK_PTR_EXPR(_p) \
|
||||
({ \
|
||||
\
|
||||
typeof(_p) _tmp = (_p); \
|
||||
CHECK_PTR(_tmp); \
|
||||
_tmp; \
|
||||
\
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
/* Allocate a buffer, explicitly not zeroing it. Returns NULL for zero-sized
|
||||
requests. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* DFL_ck_alloc_nozero(u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
void* ret;
|
||||
u8* ret;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!size) return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -111,14 +149,13 @@ static inline void* DFL_ck_alloc_nozero(u32 size) {
|
||||
ret += ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C1;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_C2(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C2;
|
||||
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
return (void*)ret;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Allocate a buffer, returning zeroed memory. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* DFL_ck_alloc(u32 size) {
|
||||
@ -132,7 +169,6 @@ static inline void* DFL_ck_alloc(u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Free memory, checking for double free and corrupted heap. When DEBUG_BUILD
|
||||
is set, the old memory will be also clobbered with 0xFF. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -147,23 +183,23 @@ static inline void DFL_ck_free(void* mem) {
|
||||
/* Catch pointer issues sooner. */
|
||||
memset(mem, 0xFF, ALLOC_S(mem));
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
#endif /* DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(mem) = ALLOC_MAGIC_F;
|
||||
|
||||
free(mem - ALLOC_OFF_HEAD);
|
||||
u8* realStart = mem;
|
||||
free(realStart - ALLOC_OFF_HEAD);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Re-allocate a buffer, checking for issues and zeroing any newly-added tail.
|
||||
With DEBUG_BUILD, the buffer is always reallocated to a new addresses and the
|
||||
old memory is clobbered with 0xFF. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* DFL_ck_realloc(void* orig, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
void* ret;
|
||||
u32 old_size = 0;
|
||||
u8* ret;
|
||||
u32 old_size = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!size) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -178,10 +214,12 @@ static inline void* DFL_ck_realloc(void* orig, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef DEBUG_BUILD
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(orig) = ALLOC_MAGIC_F;
|
||||
#endif /* !DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
#endif /* !DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
|
||||
old_size = ALLOC_S(orig);
|
||||
orig -= ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
old_size = ALLOC_S(orig);
|
||||
u8* origu8 = orig;
|
||||
origu8 -= ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
orig = origu8;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_CHECK_SIZE(old_size);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -204,31 +242,30 @@ static inline void* DFL_ck_realloc(void* orig, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (orig) {
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(ret + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD, orig + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD, MIN(size, old_size));
|
||||
memset(orig + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD, 0xFF, old_size);
|
||||
u8* origu8 = orig;
|
||||
memcpy(ret + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD, origu8 + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD, MIN(size, old_size));
|
||||
memset(origu8 + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD, 0xFF, old_size);
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(orig + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD) = ALLOC_MAGIC_F;
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(origu8 + ALLOC_OFF_HEAD) = ALLOC_MAGIC_F;
|
||||
|
||||
free(orig);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^!DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
#endif /* ^!DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
|
||||
ret += ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C1;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_C2(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C2;
|
||||
|
||||
if (size > old_size)
|
||||
memset(ret + old_size, 0, size - old_size);
|
||||
if (size > old_size) memset(ret + old_size, 0, size - old_size);
|
||||
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
return (void*)ret;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Re-allocate a buffer with ALLOC_BLK_INC increments (used to speed up
|
||||
repeated small reallocs without complicating the user code). */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,19 +283,18 @@ static inline void* DFL_ck_realloc_block(void* orig, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* !DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
#endif /* !DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
|
||||
return DFL_ck_realloc(orig, size);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Create a buffer with a copy of a string. Returns NULL for NULL inputs. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline u8* DFL_ck_strdup(u8* str) {
|
||||
|
||||
void* ret;
|
||||
u32 size;
|
||||
u8* ret;
|
||||
u32 size;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!str) return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -271,38 +307,36 @@ static inline u8* DFL_ck_strdup(u8* str) {
|
||||
ret += ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C1;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_C2(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C2;
|
||||
|
||||
return memcpy(ret, str, size);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Create a buffer with a copy of a memory block. Returns NULL for zero-sized
|
||||
or NULL inputs. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* DFL_ck_memdup(void* mem, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
void* ret;
|
||||
u8* ret;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!mem || !size) return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_CHECK_SIZE(size);
|
||||
ret = malloc(size + ALLOC_OFF_TOTAL);
|
||||
ALLOC_CHECK_RESULT(ret, size);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ret += ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C1;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_C2(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C2;
|
||||
|
||||
return memcpy(ret, mem, size);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Create a buffer with a block of text, appending a NUL terminator at the end.
|
||||
Returns NULL for zero-sized or NULL inputs. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -315,11 +349,11 @@ static inline u8* DFL_ck_memdup_str(u8* mem, u32 size) {
|
||||
ALLOC_CHECK_SIZE(size);
|
||||
ret = malloc(size + ALLOC_OFF_TOTAL + 1);
|
||||
ALLOC_CHECK_RESULT(ret, size);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ret += ALLOC_OFF_HEAD;
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOC_C1(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C1;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_S(ret) = size;
|
||||
ALLOC_C2(ret) = ALLOC_MAGIC_C2;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(ret, mem, size);
|
||||
@ -329,20 +363,19 @@ static inline u8* DFL_ck_memdup_str(u8* mem, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef DEBUG_BUILD
|
||||
|
||||
/* In non-debug mode, we just do straightforward aliasing of the above functions
|
||||
to user-visible names such as ck_alloc(). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_alloc DFL_ck_alloc
|
||||
#define ck_alloc_nozero DFL_ck_alloc_nozero
|
||||
#define ck_realloc DFL_ck_realloc
|
||||
#define ck_realloc_block DFL_ck_realloc_block
|
||||
#define ck_strdup DFL_ck_strdup
|
||||
#define ck_memdup DFL_ck_memdup
|
||||
#define ck_memdup_str DFL_ck_memdup_str
|
||||
#define ck_free DFL_ck_free
|
||||
#define ck_alloc DFL_ck_alloc
|
||||
#define ck_alloc_nozero DFL_ck_alloc_nozero
|
||||
#define ck_realloc DFL_ck_realloc
|
||||
#define ck_realloc_block DFL_ck_realloc_block
|
||||
#define ck_strdup DFL_ck_strdup
|
||||
#define ck_memdup DFL_ck_memdup
|
||||
#define ck_memdup_str DFL_ck_memdup_str
|
||||
#define ck_free DFL_ck_free
|
||||
|
||||
#define alloc_report()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -353,12 +386,14 @@ static inline u8* DFL_ck_memdup_str(u8* mem, u32 size) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Alloc tracking data structures: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_BUCKETS 4096
|
||||
#define ALLOC_BUCKETS 4096
|
||||
|
||||
struct TRK_obj {
|
||||
void *ptr;
|
||||
|
||||
void* ptr;
|
||||
char *file, *func;
|
||||
u32 line;
|
||||
u32 line;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef AFL_MAIN
|
||||
@ -366,22 +401,21 @@ struct TRK_obj {
|
||||
struct TRK_obj* TRK[ALLOC_BUCKETS];
|
||||
u32 TRK_cnt[ALLOC_BUCKETS];
|
||||
|
||||
# define alloc_report() TRK_report()
|
||||
#define alloc_report() TRK_report()
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
extern struct TRK_obj* TRK[ALLOC_BUCKETS];
|
||||
extern u32 TRK_cnt[ALLOC_BUCKETS];
|
||||
extern u32 TRK_cnt[ALLOC_BUCKETS];
|
||||
|
||||
# define alloc_report()
|
||||
#define alloc_report()
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^AFL_MAIN */
|
||||
#endif /* ^AFL_MAIN */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Bucket-assigning function for a given pointer: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TRKH(_ptr) (((((u32)(_ptr)) >> 16) ^ ((u32)(_ptr))) % ALLOC_BUCKETS)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Add a new entry to the list of allocated objects. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void TRK_alloc_buf(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
@ -399,7 +433,7 @@ static inline void TRK_alloc_buf(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
|
||||
if (!TRK[bucket][i].ptr) {
|
||||
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].ptr = ptr;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].ptr = ptr;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].file = (char*)file;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].func = (char*)func;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].line = line;
|
||||
@ -409,10 +443,10 @@ static inline void TRK_alloc_buf(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
|
||||
/* No space available - allocate more. */
|
||||
|
||||
TRK[bucket] = DFL_ck_realloc_block(TRK[bucket],
|
||||
(TRK_cnt[bucket] + 1) * sizeof(struct TRK_obj));
|
||||
TRK[bucket] = DFL_ck_realloc_block(
|
||||
TRK[bucket], (TRK_cnt[bucket] + 1) * sizeof(struct TRK_obj));
|
||||
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].ptr = ptr;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].ptr = ptr;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].file = (char*)file;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].func = (char*)func;
|
||||
TRK[bucket][i].line = line;
|
||||
@ -421,7 +455,6 @@ static inline void TRK_alloc_buf(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Remove entry from the list of allocated objects. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void TRK_free_buf(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
@ -444,12 +477,11 @@ static inline void TRK_free_buf(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
WARNF("ALLOC: Attempt to free non-allocated memory in %s (%s:%u)",
|
||||
func, file, line);
|
||||
WARNF("ALLOC: Attempt to free non-allocated memory in %s (%s:%u)", func, file,
|
||||
line);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Do a final report on all non-deallocated objects. */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void TRK_report(void) {
|
||||
@ -466,7 +498,6 @@ static inline void TRK_report(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Simple wrappers for non-debugging functions: */
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* TRK_ck_alloc(u32 size, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
@ -478,7 +509,6 @@ static inline void* TRK_ck_alloc(u32 size, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* TRK_ck_realloc(void* orig, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
const char* func, u32 line) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -489,7 +519,6 @@ static inline void* TRK_ck_realloc(void* orig, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* TRK_ck_realloc_block(void* orig, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
const char* func, u32 line) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -500,7 +529,6 @@ static inline void* TRK_ck_realloc_block(void* orig, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* TRK_ck_strdup(u8* str, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
u32 line) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -510,7 +538,6 @@ static inline void* TRK_ck_strdup(u8* str, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* TRK_ck_memdup(void* mem, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
const char* func, u32 line) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -520,7 +547,6 @@ static inline void* TRK_ck_memdup(void* mem, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void* TRK_ck_memdup_str(void* mem, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
const char* func, u32 line) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -530,9 +556,8 @@ static inline void* TRK_ck_memdup_str(void* mem, u32 size, const char* file,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void TRK_ck_free(void* ptr, const char* file,
|
||||
const char* func, u32 line) {
|
||||
static inline void TRK_ck_free(void* ptr, const char* file, const char* func,
|
||||
u32 line) {
|
||||
|
||||
TRK_free_buf(ptr, file, func, line);
|
||||
DFL_ck_free(ptr);
|
||||
@ -541,11 +566,9 @@ static inline void TRK_ck_free(void* ptr, const char* file,
|
||||
|
||||
/* Aliasing user-facing names to tracking functions: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_alloc(_p1) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_alloc(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
#define ck_alloc(_p1) TRK_ck_alloc(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_alloc_nozero(_p1) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_alloc(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
#define ck_alloc_nozero(_p1) TRK_ck_alloc(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_realloc(_p1, _p2) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_realloc(_p1, _p2, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
@ -553,8 +576,7 @@ static inline void TRK_ck_free(void* ptr, const char* file,
|
||||
#define ck_realloc_block(_p1, _p2) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_realloc_block(_p1, _p2, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_strdup(_p1) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_strdup(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
#define ck_strdup(_p1) TRK_ck_strdup(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_memdup(_p1, _p2) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_memdup(_p1, _p2, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
@ -562,9 +584,9 @@ static inline void TRK_ck_free(void* ptr, const char* file,
|
||||
#define ck_memdup_str(_p1, _p2) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_memdup_str(_p1, _p2, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_free(_p1) \
|
||||
TRK_ck_free(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
#define ck_free(_p1) TRK_ck_free(_p1, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^!DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
#endif /* ^!DEBUG_BUILD */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_ALLOC_INL_H */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_ALLOC_INL_H */
|
||||
104
include/android-ashmem.h
Normal file
104
include/android-ashmem.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - android shared memory compatibility layer
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
This header re-defines the shared memory routines used by AFL++
|
||||
using the Andoid API.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _ANDROID_ASHMEM_H
|
||||
#define _ANDROID_ASHMEM_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <linux/shm.h>
|
||||
#include <linux/ashmem.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/mman.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#if __ANDROID_API__ >= 26
|
||||
#define shmat bionic_shmat
|
||||
#define shmctl bionic_shmctl
|
||||
#define shmdt bionic_shmdt
|
||||
#define shmget bionic_shmget
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#include <sys/shm.h>
|
||||
#undef shmat
|
||||
#undef shmctl
|
||||
#undef shmdt
|
||||
#undef shmget
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#define ASHMEM_DEVICE "/dev/ashmem"
|
||||
|
||||
static inline int shmctl(int __shmid, int __cmd, struct shmid_ds *__buf) {
|
||||
|
||||
int ret = 0;
|
||||
if (__cmd == IPC_RMID) {
|
||||
|
||||
int length = ioctl(__shmid, ASHMEM_GET_SIZE, NULL);
|
||||
struct ashmem_pin pin = {0, length};
|
||||
ret = ioctl(__shmid, ASHMEM_UNPIN, &pin);
|
||||
close(__shmid);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static inline int shmget(key_t __key, size_t __size, int __shmflg) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd, ret;
|
||||
char ourkey[11];
|
||||
|
||||
fd = open(ASHMEM_DEVICE, O_RDWR);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) return fd;
|
||||
|
||||
sprintf(ourkey, "%d", __key);
|
||||
ret = ioctl(fd, ASHMEM_SET_NAME, ourkey);
|
||||
if (ret < 0) goto error;
|
||||
|
||||
ret = ioctl(fd, ASHMEM_SET_SIZE, __size);
|
||||
if (ret < 0) goto error;
|
||||
|
||||
return fd;
|
||||
|
||||
error:
|
||||
close(fd);
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static inline void *shmat(int __shmid, const void *__shmaddr, int __shmflg) {
|
||||
|
||||
int size;
|
||||
void *ptr;
|
||||
|
||||
size = ioctl(__shmid, ASHMEM_GET_SIZE, NULL);
|
||||
if (size < 0) { return NULL; }
|
||||
|
||||
ptr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, __shmid, 0);
|
||||
if (ptr == MAP_FAILED) { return NULL; }
|
||||
|
||||
return ptr;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
37
include/common.h
Normal file
37
include/common.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - common routines header
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Gather some functions common to multiple executables
|
||||
|
||||
- detect_file_args
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __AFLCOMMON_H
|
||||
#define __AFLCOMMON_H
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
extern u8* target_path; /* Path to target binary */
|
||||
|
||||
void detect_file_args(char** argv, u8* prog_in);
|
||||
|
||||
char** get_qemu_argv(u8* own_loc, char** argv, int argc);
|
||||
char** get_wine_argv(u8* own_loc, char** argv, int argc);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
382
include/config.h
Normal file
382
include/config.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,382 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - vaguely configurable bits
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _HAVE_CONFIG_H
|
||||
#define _HAVE_CONFIG_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Version string: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define VERSION "++2.58c" // c = release, d = volatile github dev
|
||||
|
||||
/******************************************************
|
||||
* *
|
||||
* Settings that may be of interest to power users: *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
******************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Comment out to disable terminal colors (note that this makes afl-analyze
|
||||
a lot less nice): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define USE_COLOR
|
||||
|
||||
/* Comment out to disable fancy ANSI boxes and use poor man's 7-bit UI: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FANCY_BOXES
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default timeout for fuzzed code (milliseconds). This is the upper bound,
|
||||
also used for detecting hangs; the actual value is auto-scaled: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EXEC_TIMEOUT 1000
|
||||
|
||||
/* Timeout rounding factor when auto-scaling (milliseconds): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EXEC_TM_ROUND 20
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default memory limit for child process (MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __x86_64__
|
||||
#define MEM_LIMIT 25
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define MEM_LIMIT 50
|
||||
#endif /* ^!__x86_64__ */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default memory limit when running in QEMU mode (MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MEM_LIMIT_QEMU 200
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default memory limit when running in Unicorn mode (MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MEM_LIMIT_UNICORN 200
|
||||
|
||||
/* Number of calibration cycles per every new test case (and for test
|
||||
cases that show variable behavior): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CAL_CYCLES 8
|
||||
#define CAL_CYCLES_LONG 40
|
||||
|
||||
/* Number of subsequent timeouts before abandoning an input file: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TMOUT_LIMIT 250
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum number of unique hangs or crashes to record: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define KEEP_UNIQUE_HANG 500
|
||||
#define KEEP_UNIQUE_CRASH 5000
|
||||
|
||||
/* Baseline number of random tweaks during a single 'havoc' stage: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_CYCLES 256
|
||||
#define HAVOC_CYCLES_INIT 1024
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum multiplier for the above (should be a power of two, beware
|
||||
of 32-bit int overflows): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_MAX_MULT 16
|
||||
#define HAVOC_MAX_MULT_MOPT 32
|
||||
|
||||
/* Absolute minimum number of havoc cycles (after all adjustments): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_MIN 16
|
||||
|
||||
/* Power Schedule Divisor */
|
||||
#define POWER_BETA 1
|
||||
#define MAX_FACTOR (POWER_BETA * 32)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum stacking for havoc-stage tweaks. The actual value is calculated
|
||||
like this:
|
||||
|
||||
n = random between 1 and HAVOC_STACK_POW2
|
||||
stacking = 2^n
|
||||
|
||||
In other words, the default (n = 7) produces 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or
|
||||
128 stacked tweaks: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_STACK_POW2 7
|
||||
|
||||
/* Caps on block sizes for cloning and deletion operations. Each of these
|
||||
ranges has a 33% probability of getting picked, except for the first
|
||||
two cycles where smaller blocks are favored: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_SMALL 32
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_MEDIUM 128
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_LARGE 1500
|
||||
|
||||
/* Extra-large blocks, selected very rarely (<5% of the time): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HAVOC_BLK_XL 32768
|
||||
|
||||
/* Probabilities of skipping non-favored entries in the queue, expressed as
|
||||
percentages: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SKIP_TO_NEW_PROB 99 /* ...when there are new, pending favorites */
|
||||
#define SKIP_NFAV_OLD_PROB 95 /* ...no new favs, cur entry already fuzzed */
|
||||
#define SKIP_NFAV_NEW_PROB 75 /* ...no new favs, cur entry not fuzzed yet */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Splicing cycle count: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SPLICE_CYCLES 15
|
||||
|
||||
/* Nominal per-splice havoc cycle length: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SPLICE_HAVOC 32
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum offset for integer addition / subtraction stages: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ARITH_MAX 35
|
||||
|
||||
/* Limits for the test case trimmer. The absolute minimum chunk size; and
|
||||
the starting and ending divisors for chopping up the input file: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TRIM_MIN_BYTES 4
|
||||
#define TRIM_START_STEPS 16
|
||||
#define TRIM_END_STEPS 1024
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum size of input file, in bytes (keep under 100MB): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_FILE (1 * 1024 * 1024)
|
||||
|
||||
/* The same, for the test case minimizer: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TMIN_MAX_FILE (10 * 1024 * 1024)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Block normalization steps for afl-tmin: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define TMIN_SET_MIN_SIZE 4
|
||||
#define TMIN_SET_STEPS 128
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum dictionary token size (-x), in bytes: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_DICT_FILE 128
|
||||
|
||||
/* Length limits for auto-detected dictionary tokens: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MIN_AUTO_EXTRA 3
|
||||
#define MAX_AUTO_EXTRA 32
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum number of user-specified dictionary tokens to use in deterministic
|
||||
steps; past this point, the "extras/user" step will be still carried out,
|
||||
but with proportionally lower odds: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_DET_EXTRAS 200
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum number of auto-extracted dictionary tokens to actually use in fuzzing
|
||||
(first value), and to keep in memory as candidates. The latter should be much
|
||||
higher than the former. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define USE_AUTO_EXTRAS 50
|
||||
#define MAX_AUTO_EXTRAS (USE_AUTO_EXTRAS * 10)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Scaling factor for the effector map used to skip some of the more
|
||||
expensive deterministic steps. The actual divisor is set to
|
||||
2^EFF_MAP_SCALE2 bytes: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EFF_MAP_SCALE2 3
|
||||
|
||||
/* Minimum input file length at which the effector logic kicks in: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EFF_MIN_LEN 128
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum effector density past which everything is just fuzzed
|
||||
unconditionally (%): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EFF_MAX_PERC 90
|
||||
|
||||
/* UI refresh frequency (Hz): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define UI_TARGET_HZ 5
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fuzzer stats file and plot update intervals (sec): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define STATS_UPDATE_SEC 60
|
||||
#define PLOT_UPDATE_SEC 5
|
||||
|
||||
/* Smoothing divisor for CPU load and exec speed stats (1 - no smoothing). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define AVG_SMOOTHING 16
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sync interval (every n havoc cycles): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SYNC_INTERVAL 5
|
||||
|
||||
/* Output directory reuse grace period (minutes): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define OUTPUT_GRACE 25
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment to use simple file names (id_NNNNNN): */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define SIMPLE_FILES
|
||||
|
||||
/* List of interesting values to use in fuzzing. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_8 \
|
||||
-128, /* Overflow signed 8-bit when decremented */ \
|
||||
-1, /* */ \
|
||||
0, /* */ \
|
||||
1, /* */ \
|
||||
16, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
32, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
64, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
100, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
127 /* Overflow signed 8-bit when incremented */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_8_LEN 9
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_16 \
|
||||
-32768, /* Overflow signed 16-bit when decremented */ \
|
||||
-129, /* Overflow signed 8-bit */ \
|
||||
128, /* Overflow signed 8-bit */ \
|
||||
255, /* Overflow unsig 8-bit when incremented */ \
|
||||
256, /* Overflow unsig 8-bit */ \
|
||||
512, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
1000, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
1024, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
4096, /* One-off with common buffer size */ \
|
||||
32767 /* Overflow signed 16-bit when incremented */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_16_LEN 10
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_32 \
|
||||
-2147483648LL, /* Overflow signed 32-bit when decremented */ \
|
||||
-100663046, /* Large negative number (endian-agnostic) */ \
|
||||
-32769, /* Overflow signed 16-bit */ \
|
||||
32768, /* Overflow signed 16-bit */ \
|
||||
65535, /* Overflow unsig 16-bit when incremented */ \
|
||||
65536, /* Overflow unsig 16 bit */ \
|
||||
100663045, /* Large positive number (endian-agnostic) */ \
|
||||
2147483647 /* Overflow signed 32-bit when incremented */
|
||||
|
||||
#define INTERESTING_32_LEN 8
|
||||
|
||||
/***********************************************************
|
||||
* *
|
||||
* Really exotic stuff you probably don't want to touch: *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
***********************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Call count interval between reseeding the libc PRNG from /dev/urandom: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define RESEED_RNG 10000
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum line length passed from GCC to 'as' and used for parsing
|
||||
configuration files: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_LINE 8192
|
||||
|
||||
/* Environment variable used to pass SHM ID to the called program. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SHM_ENV_VAR "__AFL_SHM_ID"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Other less interesting, internal-only variables. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CLANG_ENV_VAR "__AFL_CLANG_MODE"
|
||||
#define AS_LOOP_ENV_VAR "__AFL_AS_LOOPCHECK"
|
||||
#define PERSIST_ENV_VAR "__AFL_PERSISTENT"
|
||||
#define DEFER_ENV_VAR "__AFL_DEFER_FORKSRV"
|
||||
|
||||
/* In-code signatures for deferred and persistent mode. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define PERSIST_SIG "##SIG_AFL_PERSISTENT##"
|
||||
#define DEFER_SIG "##SIG_AFL_DEFER_FORKSRV##"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Distinctive bitmap signature used to indicate failed execution: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define EXEC_FAIL_SIG 0xfee1dead
|
||||
|
||||
/* Distinctive exit code used to indicate MSAN trip condition: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MSAN_ERROR 86
|
||||
|
||||
/* Designated file descriptors for forkserver commands (the application will
|
||||
use FORKSRV_FD and FORKSRV_FD + 1): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FORKSRV_FD 198
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fork server init timeout multiplier: we'll wait the user-selected
|
||||
timeout plus this much for the fork server to spin up. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FORK_WAIT_MULT 10
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calibration timeout adjustments, to be a bit more generous when resuming
|
||||
fuzzing sessions or trying to calibrate already-added internal finds.
|
||||
The first value is a percentage, the other is in milliseconds: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CAL_TMOUT_PERC 125
|
||||
#define CAL_TMOUT_ADD 50
|
||||
|
||||
/* Number of chances to calibrate a case before giving up: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CAL_CHANCES 3
|
||||
|
||||
/* Map size for the traced binary (2^MAP_SIZE_POW2). Must be greater than
|
||||
2; you probably want to keep it under 18 or so for performance reasons
|
||||
(adjusting AFL_INST_RATIO when compiling is probably a better way to solve
|
||||
problems with complex programs). You need to recompile the target binary
|
||||
after changing this - otherwise, SEGVs may ensue. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAP_SIZE_POW2 16
|
||||
#define MAP_SIZE (1 << MAP_SIZE_POW2)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Maximum allocator request size (keep well under INT_MAX): */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_ALLOC 0x40000000
|
||||
|
||||
/* A made-up hashing seed: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define HASH_CONST 0xa5b35705
|
||||
|
||||
/* Constants for afl-gotcpu to control busy loop timing: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define CTEST_TARGET_MS 5000
|
||||
#define CTEST_CORE_TRG_MS 1000
|
||||
#define CTEST_BUSY_CYCLES (10 * 1000 * 1000)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Enable NeverZero counters in QEMU mode */
|
||||
|
||||
#define AFL_QEMU_NOT_ZERO
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment this to use inferior block-coverage-based instrumentation. Note
|
||||
that you need to recompile the target binary for this to have any effect: */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define COVERAGE_ONLY
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment this to ignore hit counts and output just one bit per tuple.
|
||||
As with the previous setting, you will need to recompile the target
|
||||
binary: */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define SKIP_COUNTS
|
||||
|
||||
/* Uncomment this to use instrumentation data to record newly discovered paths,
|
||||
but do not use them as seeds for fuzzing. This is useful for conveniently
|
||||
measuring coverage that could be attained by a "dumb" fuzzing algorithm: */
|
||||
|
||||
// #define IGNORE_FINDS
|
||||
|
||||
/* for *BSD: use ARC4RANDOM and save a file descriptor */
|
||||
#if defined(__APPLE__) || defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__OpenBSD__)
|
||||
#ifndef HAVE_ARC4RANDOM
|
||||
#define HAVE_ARC4RANDOM 1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif /* __APPLE__ || __FreeBSD__ || __OpenBSD__ */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_CONFIG_H */
|
||||
|
||||
290
include/debug.h
Normal file
290
include/debug.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - debug / error handling macros
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _HAVE_DEBUG_H
|
||||
#define _HAVE_DEBUG_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <errno.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*******************
|
||||
* Terminal colors *
|
||||
*******************/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_COLOR
|
||||
|
||||
#define cBLK "\x1b[0;30m"
|
||||
#define cRED "\x1b[0;31m"
|
||||
#define cGRN "\x1b[0;32m"
|
||||
#define cBRN "\x1b[0;33m"
|
||||
#define cBLU "\x1b[0;34m"
|
||||
#define cMGN "\x1b[0;35m"
|
||||
#define cCYA "\x1b[0;36m"
|
||||
#define cLGR "\x1b[0;37m"
|
||||
#define cGRA "\x1b[1;90m"
|
||||
#define cLRD "\x1b[1;91m"
|
||||
#define cLGN "\x1b[1;92m"
|
||||
#define cYEL "\x1b[1;93m"
|
||||
#define cLBL "\x1b[1;94m"
|
||||
#define cPIN "\x1b[1;95m"
|
||||
#define cLCY "\x1b[1;96m"
|
||||
#define cBRI "\x1b[1;97m"
|
||||
#define cRST "\x1b[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
#define bgBLK "\x1b[40m"
|
||||
#define bgRED "\x1b[41m"
|
||||
#define bgGRN "\x1b[42m"
|
||||
#define bgBRN "\x1b[43m"
|
||||
#define bgBLU "\x1b[44m"
|
||||
#define bgMGN "\x1b[45m"
|
||||
#define bgCYA "\x1b[46m"
|
||||
#define bgLGR "\x1b[47m"
|
||||
#define bgGRA "\x1b[100m"
|
||||
#define bgLRD "\x1b[101m"
|
||||
#define bgLGN "\x1b[102m"
|
||||
#define bgYEL "\x1b[103m"
|
||||
#define bgLBL "\x1b[104m"
|
||||
#define bgPIN "\x1b[105m"
|
||||
#define bgLCY "\x1b[106m"
|
||||
#define bgBRI "\x1b[107m"
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
#define cBLK ""
|
||||
#define cRED ""
|
||||
#define cGRN ""
|
||||
#define cBRN ""
|
||||
#define cBLU ""
|
||||
#define cMGN ""
|
||||
#define cCYA ""
|
||||
#define cLGR ""
|
||||
#define cGRA ""
|
||||
#define cLRD ""
|
||||
#define cLGN ""
|
||||
#define cYEL ""
|
||||
#define cLBL ""
|
||||
#define cPIN ""
|
||||
#define cLCY ""
|
||||
#define cBRI ""
|
||||
#define cRST ""
|
||||
|
||||
#define bgBLK ""
|
||||
#define bgRED ""
|
||||
#define bgGRN ""
|
||||
#define bgBRN ""
|
||||
#define bgBLU ""
|
||||
#define bgMGN ""
|
||||
#define bgCYA ""
|
||||
#define bgLGR ""
|
||||
#define bgGRA ""
|
||||
#define bgLRD ""
|
||||
#define bgLGN ""
|
||||
#define bgYEL ""
|
||||
#define bgLBL ""
|
||||
#define bgPIN ""
|
||||
#define bgLCY ""
|
||||
#define bgBRI ""
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_COLOR */
|
||||
|
||||
/*************************
|
||||
* Box drawing sequences *
|
||||
*************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FANCY_BOXES
|
||||
|
||||
#define SET_G1 "\x1b)0" /* Set G1 for box drawing */
|
||||
#define RESET_G1 "\x1b)B" /* Reset G1 to ASCII */
|
||||
#define bSTART "\x0e" /* Enter G1 drawing mode */
|
||||
#define bSTOP "\x0f" /* Leave G1 drawing mode */
|
||||
#define bH "q" /* Horizontal line */
|
||||
#define bV "x" /* Vertical line */
|
||||
#define bLT "l" /* Left top corner */
|
||||
#define bRT "k" /* Right top corner */
|
||||
#define bLB "m" /* Left bottom corner */
|
||||
#define bRB "j" /* Right bottom corner */
|
||||
#define bX "n" /* Cross */
|
||||
#define bVR "t" /* Vertical, branch right */
|
||||
#define bVL "u" /* Vertical, branch left */
|
||||
#define bHT "v" /* Horizontal, branch top */
|
||||
#define bHB "w" /* Horizontal, branch bottom */
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
#define SET_G1 ""
|
||||
#define RESET_G1 ""
|
||||
#define bSTART ""
|
||||
#define bSTOP ""
|
||||
#define bH "-"
|
||||
#define bV "|"
|
||||
#define bLT "+"
|
||||
#define bRT "+"
|
||||
#define bLB "+"
|
||||
#define bRB "+"
|
||||
#define bX "+"
|
||||
#define bVR "+"
|
||||
#define bVL "+"
|
||||
#define bHT "+"
|
||||
#define bHB "+"
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^FANCY_BOXES */
|
||||
|
||||
/***********************
|
||||
* Misc terminal codes *
|
||||
***********************/
|
||||
|
||||
#define TERM_HOME "\x1b[H"
|
||||
#define TERM_CLEAR TERM_HOME "\x1b[2J"
|
||||
#define cEOL "\x1b[0K"
|
||||
#define CURSOR_HIDE "\x1b[?25l"
|
||||
#define CURSOR_SHOW "\x1b[?25h"
|
||||
|
||||
/************************
|
||||
* Debug & error macros *
|
||||
************************/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Just print stuff to the appropriate stream. */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef MESSAGES_TO_STDOUT
|
||||
#define SAYF(x...) printf(x)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define SAYF(x...) fprintf(stderr, x)
|
||||
#endif /* ^MESSAGES_TO_STDOUT */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed warning. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define WARNF(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
SAYF(cYEL "[!] " cBRI "WARNING: " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed "doing something" message. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ACTF(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
SAYF(cLBL "[*] " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed "success" message. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define OKF(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
SAYF(cLGN "[+] " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a prefixed fatal error message (not used in afl). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define BADF(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n[-] " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cRST "\n"); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die with a verbose non-OS fatal error message. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define FATAL(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
SAYF(bSTOP RESET_G1 CURSOR_SHOW cRST cLRD \
|
||||
"\n[-] PROGRAM ABORT : " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n Location : " cRST "%s(), %s:%u\n\n", __FUNCTION__, \
|
||||
__FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
exit(1); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die by calling abort() to provide a core dump. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ABORT(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
SAYF(bSTOP RESET_G1 CURSOR_SHOW cRST cLRD \
|
||||
"\n[-] PROGRAM ABORT : " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n Stop location : " cRST "%s(), %s:%u\n\n", __FUNCTION__, \
|
||||
__FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
abort(); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die while also including the output of perror(). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define PFATAL(x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
fflush(stdout); \
|
||||
SAYF(bSTOP RESET_G1 CURSOR_SHOW cRST cLRD \
|
||||
"\n[-] SYSTEM ERROR : " cRST x); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD "\n Stop location : " cRST "%s(), %s:%u\n", __FUNCTION__, \
|
||||
__FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
SAYF(cLRD " OS message : " cRST "%s\n", strerror(errno)); \
|
||||
exit(1); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Die with FAULT() or PFAULT() depending on the value of res (used to
|
||||
interpret different failure modes for read(), write(), etc). */
|
||||
|
||||
#define RPFATAL(res, x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (res < 0) \
|
||||
PFATAL(x); \
|
||||
else \
|
||||
FATAL(x); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Error-checking versions of read() and write() that call RPFATAL() as
|
||||
appropriate. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_write(fd, buf, len, fn) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
u32 _len = (len); \
|
||||
s32 _res = write(fd, buf, _len); \
|
||||
if (_res != _len) RPFATAL(_res, "Short write to %s", fn); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ck_read(fd, buf, len, fn) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
u32 _len = (len); \
|
||||
s32 _res = read(fd, buf, _len); \
|
||||
if (_res != _len) RPFATAL(_res, "Short read from %s", fn); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_DEBUG_H */
|
||||
|
||||
51
include/forkserver.h
Normal file
51
include/forkserver.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - forkserver header
|
||||
----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Forkserver design by Jann Horn <jannhorn@googlemail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Shared code that implements a forkserver. This is used by the fuzzer
|
||||
as well the other components like afl-tmin.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __AFL_FORKSERVER_H
|
||||
#define __AFL_FORKSERVER_H
|
||||
|
||||
void handle_timeout(int sig);
|
||||
void init_forkserver(char **argv);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
#define MSG_FORK_ON_APPLE \
|
||||
" - On MacOS X, the semantics of fork() syscalls are non-standard and " \
|
||||
"may\n" \
|
||||
" break afl-fuzz performance optimizations when running " \
|
||||
"platform-specific\n" \
|
||||
" targets. To fix this, set AFL_NO_FORKSRV=1 in the environment.\n\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define MSG_FORK_ON_APPLE ""
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef RLIMIT_AS
|
||||
#define MSG_ULIMIT_USAGE " ( ulimit -Sv $[%llu << 10];"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define MSG_ULIMIT_USAGE " ( ulimit -Sd $[%llu << 10];"
|
||||
#endif /* ^RLIMIT_AS */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - hashing function
|
||||
-------------------------------------
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - hashing function
|
||||
---------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The hash32() function is a variant of MurmurHash3, a good
|
||||
non-cryptosafe hashing function developed by Austin Appleby.
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Austin's original code is public domain.
|
||||
|
||||
Other code written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Other code written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,12 +31,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __x86_64__
|
||||
|
||||
#define ROL64(_x, _r) ((((u64)(_x)) << (_r)) | (((u64)(_x)) >> (64 - (_r))))
|
||||
#define ROL64(_x, _r) ((((u64)(_x)) << (_r)) | (((u64)(_x)) >> (64 - (_r))))
|
||||
|
||||
static inline u32 hash32(const void* key, u32 len, u32 seed) {
|
||||
|
||||
const u64* data = (u64*)key;
|
||||
u64 h1 = seed ^ len;
|
||||
u64 h1 = seed ^ len;
|
||||
|
||||
len >>= 3;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,12 +45,12 @@ static inline u32 hash32(const void* key, u32 len, u32 seed) {
|
||||
u64 k1 = *data++;
|
||||
|
||||
k1 *= 0x87c37b91114253d5ULL;
|
||||
k1 = ROL64(k1, 31);
|
||||
k1 = ROL64(k1, 31);
|
||||
k1 *= 0x4cf5ad432745937fULL;
|
||||
|
||||
h1 ^= k1;
|
||||
h1 = ROL64(h1, 27);
|
||||
h1 = h1 * 5 + 0x52dce729;
|
||||
h1 = ROL64(h1, 27);
|
||||
h1 = h1 * 5 + 0x52dce729;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,14 +64,14 @@ static inline u32 hash32(const void* key, u32 len, u32 seed) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
#define ROL32(_x, _r) ((((u32)(_x)) << (_r)) | (((u32)(_x)) >> (32 - (_r))))
|
||||
#define ROL32(_x, _r) ((((u32)(_x)) << (_r)) | (((u32)(_x)) >> (32 - (_r))))
|
||||
|
||||
static inline u32 hash32(const void* key, u32 len, u32 seed) {
|
||||
|
||||
const u32* data = (u32*)key;
|
||||
u32 h1 = seed ^ len;
|
||||
const u32* data = (u32*)key;
|
||||
u32 h1 = seed ^ len;
|
||||
|
||||
len >>= 2;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,12 +80,12 @@ static inline u32 hash32(const void* key, u32 len, u32 seed) {
|
||||
u32 k1 = *data++;
|
||||
|
||||
k1 *= 0xcc9e2d51;
|
||||
k1 = ROL32(k1, 15);
|
||||
k1 = ROL32(k1, 15);
|
||||
k1 *= 0x1b873593;
|
||||
|
||||
h1 ^= k1;
|
||||
h1 = ROL32(h1, 13);
|
||||
h1 = h1 * 5 + 0xe6546b64;
|
||||
h1 = ROL32(h1, 13);
|
||||
h1 = h1 * 5 + 0xe6546b64;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -99,6 +99,7 @@ static inline u32 hash32(const void* key, u32 len, u32 seed) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^__x86_64__ */
|
||||
#endif /* ^__x86_64__ */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* !_HAVE_HASH_H */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* !_HAVE_HASH_H */
|
||||
34
include/sharedmem.h
Normal file
34
include/sharedmem.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - shared memory related header
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Forkserver design by Jann Horn <jannhorn@googlemail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Shared code to handle the shared memory. This is used by the fuzzer
|
||||
as well the other components like afl-tmin, afl-showmap, etc...
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __AFL_SHAREDMEM_H
|
||||
#define __AFL_SHAREDMEM_H
|
||||
|
||||
void setup_shm(unsigned char dumb_mode);
|
||||
void remove_shm(void);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
101
include/types.h
Normal file
101
include/types.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - type definitions and minor macros
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Now maintained by by Marc Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>,
|
||||
Heiko Eißfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _HAVE_TYPES_H
|
||||
#define _HAVE_TYPES_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
typedef uint8_t u8;
|
||||
typedef uint16_t u16;
|
||||
typedef uint32_t u32;
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
|
||||
Ugh. There is an unintended compiler / glibc #include glitch caused by
|
||||
combining the u64 type an %llu in format strings, necessitating a workaround.
|
||||
|
||||
In essence, the compiler is always looking for 'unsigned long long' for %llu.
|
||||
On 32-bit systems, the u64 type (aliased to uint64_t) is expanded to
|
||||
'unsigned long long' in <bits/types.h>, so everything checks out.
|
||||
|
||||
But on 64-bit systems, it is #ifdef'ed in the same file as 'unsigned long'.
|
||||
Now, it only happens in circumstances where the type happens to have the
|
||||
expected bit width, *but* the compiler does not know that... and complains
|
||||
about 'unsigned long' being unsafe to pass to %llu.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __x86_64__
|
||||
typedef unsigned long long u64;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
typedef uint64_t u64;
|
||||
#endif /* ^__x86_64__ */
|
||||
|
||||
typedef int8_t s8;
|
||||
typedef int16_t s16;
|
||||
typedef int32_t s32;
|
||||
typedef int64_t s64;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef MIN
|
||||
#define MIN(_a, _b) ((_a) > (_b) ? (_b) : (_a))
|
||||
#define MAX(_a, _b) ((_a) > (_b) ? (_a) : (_b))
|
||||
#endif /* !MIN */
|
||||
|
||||
#define SWAP16(_x) \
|
||||
({ \
|
||||
\
|
||||
u16 _ret = (_x); \
|
||||
(u16)((_ret << 8) | (_ret >> 8)); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
#define SWAP32(_x) \
|
||||
({ \
|
||||
\
|
||||
u32 _ret = (_x); \
|
||||
(u32)((_ret << 24) | (_ret >> 24) | ((_ret << 8) & 0x00FF0000) | \
|
||||
((_ret >> 8) & 0x0000FF00)); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef AFL_LLVM_PASS
|
||||
#define AFL_R(x) (random() % (x))
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define R(x) (random() % (x))
|
||||
#endif /* ^AFL_LLVM_PASS */
|
||||
|
||||
#define STRINGIFY_INTERNAL(x) #x
|
||||
#define STRINGIFY(x) STRINGIFY_INTERNAL(x)
|
||||
|
||||
#define MEM_BARRIER() __asm__ volatile("" ::: "memory")
|
||||
|
||||
#if __GNUC__ < 6
|
||||
#define likely(_x) (_x)
|
||||
#define unlikely(_x) (_x)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define likely(_x) __builtin_expect(!!(_x), 1)
|
||||
#define unlikely(_x) __builtin_expect(!!(_x), 0)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ! _HAVE_TYPES_H */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - libdislocator
|
||||
# ----------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -18,21 +18,21 @@ HELPER_PATH = $(PREFIX)/lib/afl
|
||||
|
||||
VERSION = $(shell grep '^\#define VERSION ' ../config.h | cut -d '"' -f2)
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops -I ../include/
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign
|
||||
|
||||
all: libdislocator.so
|
||||
|
||||
libdislocator.so: libdislocator.so.c ../config.h
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC $< -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC $< -o ../$@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
.NOTPARALLEL: clean
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -f *.o *.so *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]*
|
||||
rm -f libdislocator.so
|
||||
rm -f ../libdislocator.so
|
||||
|
||||
install: all
|
||||
install -m 755 libdislocator.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
install -m 755 ../libdislocator.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
install -m 644 README.dislocator $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
libdislocator, an abusive allocator
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
# libdislocator, an abusive allocator
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,7 +43,9 @@ when fuzzing small, self-contained binaries.
|
||||
|
||||
To use this library, run AFL like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
AFL_PRELOAD=/path/to/libdislocator.so ./afl-fuzz [...other params...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You *have* to specify path, even if it's just ./libdislocator.so or
|
||||
$PWD/libdislocator.so.
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - dislocator, an abusive allocator
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,36 +25,48 @@
|
||||
#include <limits.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/mman.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../types.h"
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef PAGE_SIZE
|
||||
# define PAGE_SIZE 4096
|
||||
#endif /* !PAGE_SIZE */
|
||||
#define PAGE_SIZE 4096
|
||||
#endif /* !PAGE_SIZE */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef MAP_ANONYMOUS
|
||||
# define MAP_ANONYMOUS MAP_ANON
|
||||
#endif /* !MAP_ANONYMOUS */
|
||||
#define MAP_ANONYMOUS MAP_ANON
|
||||
#endif /* !MAP_ANONYMOUS */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Error / message handling: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define DEBUGF(_x...) do { \
|
||||
if (alloc_verbose) { \
|
||||
if (++call_depth == 1) { \
|
||||
#define DEBUGF(_x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (alloc_verbose) { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (++call_depth == 1) { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "[AFL] " _x); \
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n"); \
|
||||
} \
|
||||
call_depth--; \
|
||||
} \
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n"); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} \
|
||||
call_depth--; \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#define FATAL(_x...) do { \
|
||||
if (++call_depth == 1) { \
|
||||
#define FATAL(_x...) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
if (++call_depth == 1) { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "*** [AFL] " _x); \
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " ***\n"); \
|
||||
abort(); \
|
||||
} \
|
||||
call_depth--; \
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " ***\n"); \
|
||||
abort(); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} \
|
||||
call_depth--; \
|
||||
\
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
/* Macro to count the number of pages needed to store a buffer: */
|
||||
@ -63,7 +75,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
/* Canary & clobber bytes: */
|
||||
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CANARY 0xAACCAACC
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CANARY 0xAACCAACC
|
||||
#define ALLOC_CLOBBER 0xCC
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTR_C(_p) (((u32*)(_p))[-1])
|
||||
@ -73,14 +85,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
static u32 max_mem = MAX_ALLOC; /* Max heap usage to permit */
|
||||
static u8 alloc_verbose, /* Additional debug messages */
|
||||
hard_fail, /* abort() when max_mem exceeded? */
|
||||
no_calloc_over; /* abort() on calloc() overflows? */
|
||||
hard_fail, /* abort() when max_mem exceeded? */
|
||||
no_calloc_over; /* abort() on calloc() overflows? */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __OpenBSD__
|
||||
#define __thread
|
||||
#warning no thread support available
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
static __thread size_t total_mem; /* Currently allocated mem */
|
||||
|
||||
static __thread u32 call_depth; /* To avoid recursion via fprintf() */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* This is the main alloc function. It allocates one page more than necessary,
|
||||
sets that tailing page to PROT_NONE, and then increments the return address
|
||||
so that it is right-aligned to that boundary. Since it always uses mmap(),
|
||||
@ -90,14 +105,11 @@ static void* __dislocator_alloc(size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
void* ret;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (total_mem + len > max_mem || total_mem + len < total_mem) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (hard_fail)
|
||||
FATAL("total allocs exceed %u MB", max_mem / 1024 / 1024);
|
||||
if (hard_fail) FATAL("total allocs exceed %u MB", max_mem / 1024 / 1024);
|
||||
|
||||
DEBUGF("total allocs exceed %u MB, returning NULL",
|
||||
max_mem / 1024 / 1024);
|
||||
DEBUGF("total allocs exceed %u MB, returning NULL", max_mem / 1024 / 1024);
|
||||
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -142,7 +154,6 @@ static void* __dislocator_alloc(size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* The "user-facing" wrapper for calloc(). This just checks for overflows and
|
||||
displays debug messages if requested. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -157,8 +168,11 @@ void* calloc(size_t elem_len, size_t elem_cnt) {
|
||||
if (elem_cnt && len / elem_cnt != elem_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (no_calloc_over) {
|
||||
DEBUGF("calloc(%zu, %zu) would overflow, returning NULL", elem_len, elem_cnt);
|
||||
|
||||
DEBUGF("calloc(%zu, %zu) would overflow, returning NULL", elem_len,
|
||||
elem_cnt);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("calloc(%zu, %zu) would overflow", elem_len, elem_cnt);
|
||||
@ -174,7 +188,6 @@ void* calloc(size_t elem_len, size_t elem_cnt) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* The wrapper for malloc(). Roughly the same, also clobbers the returned
|
||||
memory (unlike calloc(), malloc() is not guaranteed to return zeroed
|
||||
memory). */
|
||||
@ -193,7 +206,6 @@ void* malloc(size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* The wrapper for free(). This simply marks the entire region as PROT_NONE.
|
||||
If the region is already freed, the code will segfault during the attempt to
|
||||
read the canary. Not very graceful, but works, right? */
|
||||
@ -224,7 +236,6 @@ void free(void* ptr) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Realloc is pretty straightforward, too. We forcibly reallocate the buffer,
|
||||
move data, and then free (aka mprotect()) the original one. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -249,7 +260,6 @@ void* realloc(void* ptr, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((constructor)) void __dislocator_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* tmp = getenv("AFL_LD_LIMIT_MB");
|
||||
@ -266,3 +276,4 @@ __attribute__((constructor)) void __dislocator_init(void) {
|
||||
no_calloc_over = !!getenv("AFL_LD_NO_CALLOC_OVER");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
# american fuzzy lop - libtokencap
|
||||
# --------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -18,21 +18,24 @@ HELPER_PATH = $(PREFIX)/lib/afl
|
||||
|
||||
VERSION = $(shell grep '^\#define VERSION ' ../config.h | cut -d '"' -f2)
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops -I ../include/
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign
|
||||
|
||||
all: libtokencap.so
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "Linux"
|
||||
TARGETS = libtokencap.so
|
||||
endif
|
||||
all: $(TARGETS)
|
||||
|
||||
libtokencap.so: libtokencap.so.c ../config.h
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC $< -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC $< -o ../$@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
.NOTPARALLEL: clean
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -f *.o *.so *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]*
|
||||
rm -f libtokencap.so
|
||||
rm -f ../libtokencap.so
|
||||
|
||||
install: all
|
||||
install -m 755 libtokencap.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
install -m 755 ../libtokencap.so $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
install -m 644 README.tokencap $${DESTDIR}$(HELPER_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
|
||||
=========================================
|
||||
strcmp() / memcmp() token capture library
|
||||
=========================================
|
||||
# strcmp() / memcmp() token capture library
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
|
||||
This Linux-only companion library allows you to instrument strcmp(), memcmp(),
|
||||
This Linux-only companion library allows you to instrument `strcmp()`, `memcmp()`,
|
||||
and related functions to automatically extract syntax tokens passed to any of
|
||||
these libcalls. The resulting list of tokens may be then given as a starting
|
||||
dictionary to afl-fuzz (the -x option) to improve coverage on subsequent
|
||||
@ -31,15 +29,18 @@ with -fno-builtin and is linked dynamically. If you wish to automate the first
|
||||
part without mucking with CFLAGS in Makefiles, you can set AFL_NO_BUILTIN=1
|
||||
when using afl-gcc. This setting specifically adds the following flags:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-fno-builtin-strcmp -fno-builtin-strncmp -fno-builtin-strcasecmp
|
||||
-fno-builtin-strcasencmp -fno-builtin-memcmp -fno-builtin-strstr
|
||||
-fno-builtin-strcasestr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is simply loading this library via LD_PRELOAD. The optimal usage
|
||||
pattern is to allow afl-fuzz to fuzz normally for a while and build up a corpus,
|
||||
and then fire off the target binary, with libtokencap.so loaded, on every file
|
||||
found by AFL in that earlier run. This demonstrates the basic principle:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export AFL_TOKEN_FILE=$PWD/temp_output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
for i in <out_dir>/queue/id*; do
|
||||
@ -48,6 +49,7 @@ found by AFL in that earlier run. This demonstrates the basic principle:
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
sort -u temp_output.txt >afl_dictionary.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't get any results, the target library is probably not using strcmp()
|
||||
and memcmp() to parse input; or you haven't compiled it with -fno-builtin; or
|
||||
@ -55,7 +57,7 @@ the whole thing isn't dynamically linked, and LD_PRELOAD is having no effect.
|
||||
|
||||
PS. The library is Linux-only because there is probably no particularly portable
|
||||
and non-invasive way to distinguish between read-only and read-write memory
|
||||
mappings. The __tokencap_load_mappings() function is the only thing that would
|
||||
mappings. The `__tokencap_load_mappings()` function is the only thing that would
|
||||
need to be changed for other OSes. Porting to platforms with /proc/<pid>/maps
|
||||
(e.g., FreeBSD) should be trivial.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
american fuzzy lop - extract tokens passed to strcmp / memcmp
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written and maintained by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,30 +27,26 @@
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __linux__
|
||||
# error "Sorry, this library is Linux-specific for now!"
|
||||
#endif /* !__linux__ */
|
||||
|
||||
#error "Sorry, this library is Linux-specific for now!"
|
||||
#endif /* !__linux__ */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Mapping data and such */
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_MAPPINGS 1024
|
||||
|
||||
static struct mapping {
|
||||
void *st, *en;
|
||||
} __tokencap_ro[MAX_MAPPINGS];
|
||||
static struct mapping { void *st, *en; } __tokencap_ro[MAX_MAPPINGS];
|
||||
|
||||
static u32 __tokencap_ro_cnt;
|
||||
static u8 __tokencap_ro_loaded;
|
||||
static FILE* __tokencap_out_file;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Identify read-only regions in memory. Only parameters that fall into these
|
||||
ranges are worth dumping when passed to strcmp() and so on. Read-write
|
||||
regions are far more likely to contain user input instead. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void __tokencap_load_mappings(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 buf[MAX_LINE];
|
||||
u8 buf[MAX_LINE];
|
||||
FILE* f = fopen("/proc/self/maps", "r");
|
||||
|
||||
__tokencap_ro_loaded = 1;
|
||||
@ -59,8 +55,8 @@ static void __tokencap_load_mappings(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
while (fgets(buf, MAX_LINE, f)) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 rf, wf;
|
||||
void* st, *en;
|
||||
u8 rf, wf;
|
||||
void *st, *en;
|
||||
|
||||
if (sscanf(buf, "%p-%p %c%c", &st, &en, &rf, &wf) != 4) continue;
|
||||
if (wf == 'w' || rf != 'r') continue;
|
||||
@ -76,7 +72,6 @@ static void __tokencap_load_mappings(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Check an address against the list of read-only mappings. */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 __tokencap_is_ro(const void* ptr) {
|
||||
@ -85,20 +80,19 @@ static u8 __tokencap_is_ro(const void* ptr) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!__tokencap_ro_loaded) __tokencap_load_mappings();
|
||||
|
||||
for (i = 0; i < __tokencap_ro_cnt; i++)
|
||||
for (i = 0; i < __tokencap_ro_cnt; i++)
|
||||
if (ptr >= __tokencap_ro[i].st && ptr <= __tokencap_ro[i].en) return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Dump an interesting token to output file, quoting and escaping it
|
||||
properly. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void __tokencap_dump(const u8* ptr, size_t len, u8 is_text) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 buf[MAX_AUTO_EXTRA * 4 + 1];
|
||||
u8 buf[MAX_AUTO_EXTRA * 4 + 1];
|
||||
u32 i;
|
||||
u32 pos = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -120,9 +114,7 @@ static void __tokencap_dump(const u8* ptr, size_t len, u8 is_text) {
|
||||
pos += 4;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
|
||||
buf[pos++] = ptr[i];
|
||||
default: buf[pos++] = ptr[i];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -130,11 +122,10 @@ static void __tokencap_dump(const u8* ptr, size_t len, u8 is_text) {
|
||||
|
||||
buf[pos] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(__tokencap_out_file, "\"%s\"\n", buf);
|
||||
fprintf(__tokencap_out_file, "\"%s\"\n", buf);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Replacements for strcmp(), memcmp(), and so on. Note that these will be used
|
||||
only if the target is compiled with -fno-builtins and linked dynamically. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -151,13 +142,13 @@ int strcmp(const char* str1, const char* str2) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (c1 != c2) return (c1 > c2) ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
if (!c1) return 0;
|
||||
str1++; str2++;
|
||||
str1++;
|
||||
str2++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#undef strncmp
|
||||
|
||||
int strncmp(const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t len) {
|
||||
@ -171,7 +162,8 @@ int strncmp(const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!c1) return 0;
|
||||
if (c1 != c2) return (c1 > c2) ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
str1++; str2++;
|
||||
str1++;
|
||||
str2++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +171,6 @@ int strncmp(const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#undef strcasecmp
|
||||
|
||||
int strcasecmp(const char* str1, const char* str2) {
|
||||
@ -193,13 +184,13 @@ int strcasecmp(const char* str1, const char* str2) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (c1 != c2) return (c1 > c2) ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
if (!c1) return 0;
|
||||
str1++; str2++;
|
||||
str1++;
|
||||
str2++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#undef strncasecmp
|
||||
|
||||
int strncasecmp(const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t len) {
|
||||
@ -213,7 +204,8 @@ int strncasecmp(const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!c1) return 0;
|
||||
if (c1 != c2) return (c1 > c2) ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
str1++; str2++;
|
||||
str1++;
|
||||
str2++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -221,7 +213,6 @@ int strncasecmp(const char* str1, const char* str2, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#undef memcmp
|
||||
|
||||
int memcmp(const void* mem1, const void* mem2, size_t len) {
|
||||
@ -233,7 +224,8 @@ int memcmp(const void* mem1, const void* mem2, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned char c1 = *(const char*)mem1, c2 = *(const char*)mem2;
|
||||
if (c1 != c2) return (c1 > c2) ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
mem1++; mem2++;
|
||||
mem1++;
|
||||
mem2++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -241,7 +233,6 @@ int memcmp(const void* mem1, const void* mem2, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#undef strstr
|
||||
|
||||
char* strstr(const char* haystack, const char* needle) {
|
||||
@ -249,16 +240,17 @@ char* strstr(const char* haystack, const char* needle) {
|
||||
if (__tokencap_is_ro(haystack))
|
||||
__tokencap_dump(haystack, strlen(haystack), 1);
|
||||
|
||||
if (__tokencap_is_ro(needle))
|
||||
__tokencap_dump(needle, strlen(needle), 1);
|
||||
if (__tokencap_is_ro(needle)) __tokencap_dump(needle, strlen(needle), 1);
|
||||
|
||||
do {
|
||||
|
||||
const char* n = needle;
|
||||
const char* h = haystack;
|
||||
|
||||
while(*n && *h && *n == *h) n++, h++;
|
||||
while (*n && *h && *n == *h)
|
||||
n++, h++;
|
||||
|
||||
if(!*n) return (char*)haystack;
|
||||
if (!*n) return (char*)haystack;
|
||||
|
||||
} while (*(haystack++));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -266,7 +258,6 @@ char* strstr(const char* haystack, const char* needle) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#undef strcasestr
|
||||
|
||||
char* strcasestr(const char* haystack, const char* needle) {
|
||||
@ -274,25 +265,24 @@ char* strcasestr(const char* haystack, const char* needle) {
|
||||
if (__tokencap_is_ro(haystack))
|
||||
__tokencap_dump(haystack, strlen(haystack), 1);
|
||||
|
||||
if (__tokencap_is_ro(needle))
|
||||
__tokencap_dump(needle, strlen(needle), 1);
|
||||
if (__tokencap_is_ro(needle)) __tokencap_dump(needle, strlen(needle), 1);
|
||||
|
||||
do {
|
||||
|
||||
const char* n = needle;
|
||||
const char* h = haystack;
|
||||
|
||||
while(*n && *h && tolower(*n) == tolower(*h)) n++, h++;
|
||||
while (*n && *h && tolower(*n) == tolower(*h))
|
||||
n++, h++;
|
||||
|
||||
if(!*n) return (char*)haystack;
|
||||
if (!*n) return (char*)haystack;
|
||||
|
||||
} while(*(haystack++));
|
||||
} while (*(haystack++));
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Init code to open the output file (or default to stderr). */
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((constructor)) void __tokencap_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
443
llvm_mode/LLVMInsTrim.so.cc
Normal file
443
llvm_mode/LLVMInsTrim.so.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,443 @@
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <stdarg.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "llvm/ADT/DenseMap.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/ADT/DenseSet.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/CFG.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Dominators.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/IRBuilder.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Instructions.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/LegacyPassManager.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Module.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Pass.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Support/raw_ostream.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Transforms/IPO/PassManagerBuilder.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Transforms/Utils/BasicBlockUtils.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/DebugInfo.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/BasicBlock.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/CFG.h"
|
||||
#include <unordered_set>
|
||||
#include <random>
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "MarkNodes.h"
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace llvm;
|
||||
|
||||
static cl::opt<bool> MarkSetOpt("markset", cl::desc("MarkSet"),
|
||||
cl::init(false));
|
||||
static cl::opt<bool> LoopHeadOpt("loophead", cl::desc("LoopHead"),
|
||||
cl::init(false));
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
struct InsTrim : public ModulePass {
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
std::list<std::string> myWhitelist;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
std::mt19937 generator;
|
||||
int total_instr = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned int genLabel() {
|
||||
|
||||
return generator() & (MAP_SIZE - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
InsTrim() : ModulePass(ID), generator(0) {
|
||||
|
||||
char *instWhiteListFilename = getenv("AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST");
|
||||
if (instWhiteListFilename) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::string line;
|
||||
std::ifstream fileStream;
|
||||
fileStream.open(instWhiteListFilename);
|
||||
if (!fileStream) report_fatal_error("Unable to open AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST");
|
||||
getline(fileStream, line);
|
||||
while (fileStream) {
|
||||
|
||||
myWhitelist.push_back(line);
|
||||
getline(fileStream, line);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void getAnalysisUsage(AnalysisUsage &AU) const override {
|
||||
|
||||
AU.addRequired<DominatorTreeWrapperPass>();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 4
|
||||
const char *
|
||||
#else
|
||||
StringRef
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
return "InstTrim Instrumentation";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override {
|
||||
|
||||
char be_quiet = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (isatty(2) && !getenv("AFL_QUIET")) {
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "LLVMInsTrim" VERSION cRST " by csienslab\n");
|
||||
|
||||
} else
|
||||
|
||||
be_quiet = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
char *neverZero_counters_str;
|
||||
if ((neverZero_counters_str = getenv("AFL_LLVM_NOT_ZERO")) != NULL)
|
||||
OKF("LLVM neverZero activated (by hexcoder)\n");
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM_LOOPHEAD") != NULL ||
|
||||
getenv("LOOPHEAD") != NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
LoopHeadOpt = true;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// this is our default
|
||||
MarkSetOpt = true;
|
||||
|
||||
/* // I dont think this makes sense to port into LLVMInsTrim
|
||||
char* inst_ratio_str = getenv("AFL_INST_RATIO");
|
||||
unsigned int inst_ratio = 100;
|
||||
if (inst_ratio_str) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (sscanf(inst_ratio_str, "%u", &inst_ratio) != 1 || !inst_ratio ||
|
||||
inst_ratio > 100) FATAL("Bad value of AFL_INST_RATIO (must be between 1
|
||||
and 100)");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMContext &C = M.getContext();
|
||||
IntegerType *Int8Ty = IntegerType::getInt8Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int32Ty = IntegerType::getInt32Ty(C);
|
||||
|
||||
GlobalVariable *CovMapPtr = new GlobalVariable(
|
||||
M, PointerType::getUnqual(Int8Ty), false, GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage,
|
||||
nullptr, "__afl_area_ptr");
|
||||
|
||||
GlobalVariable *OldPrev = new GlobalVariable(
|
||||
M, Int32Ty, false, GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage, 0, "__afl_prev_loc", 0,
|
||||
GlobalVariable::GeneralDynamicTLSModel, 0, false);
|
||||
|
||||
u64 total_rs = 0;
|
||||
u64 total_hs = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (Function &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!F.size()) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
if (!myWhitelist.empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool instrumentBlock = false;
|
||||
DebugLoc Loc;
|
||||
StringRef instFilename;
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock::iterator IP = BB.getFirstInsertionPt();
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&(*IP));
|
||||
if (!Loc) Loc = IP->getDebugLoc();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (Loc) {
|
||||
|
||||
DILocation *cDILoc = dyn_cast<DILocation>(Loc.getAsMDNode());
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned int instLine = cDILoc->getLine();
|
||||
instFilename = cDILoc->getFilename();
|
||||
|
||||
if (instFilename.str().empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* If the original location is empty, try using the inlined location
|
||||
*/
|
||||
DILocation *oDILoc = cDILoc->getInlinedAt();
|
||||
if (oDILoc) {
|
||||
|
||||
instFilename = oDILoc->getFilename();
|
||||
instLine = oDILoc->getLine();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Continue only if we know where we actually are */
|
||||
if (!instFilename.str().empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::list<std::string>::iterator it = myWhitelist.begin();
|
||||
it != myWhitelist.end(); ++it) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (instFilename.str().length() >= it->length()) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (instFilename.str().compare(
|
||||
instFilename.str().length() - it->length(),
|
||||
it->length(), *it) == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrumentBlock = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Either we couldn't figure out our location or the location is
|
||||
* not whitelisted, so we skip instrumentation. */
|
||||
if (!instrumentBlock) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!instFilename.str().empty())
|
||||
SAYF(cYEL "[!] " cBRI "Not in whitelist, skipping %s ...\n",
|
||||
instFilename.str().c_str());
|
||||
else
|
||||
SAYF(cYEL "[!] " cBRI "No filename information found, skipping it");
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::unordered_set<BasicBlock *> MS;
|
||||
if (!MarkSetOpt) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
MS.insert(&BB);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
total_rs += F.size();
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
auto Result = markNodes(&F);
|
||||
auto RS = Result.first;
|
||||
auto HS = Result.second;
|
||||
|
||||
MS.insert(RS.begin(), RS.end());
|
||||
if (!LoopHeadOpt) {
|
||||
|
||||
MS.insert(HS.begin(), HS.end());
|
||||
total_rs += MS.size();
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
DenseSet<std::pair<BasicBlock *, BasicBlock *>> EdgeSet;
|
||||
DominatorTreeWrapperPass * DTWP =
|
||||
&getAnalysis<DominatorTreeWrapperPass>(F);
|
||||
auto DT = &DTWP->getDomTree();
|
||||
|
||||
total_rs += RS.size();
|
||||
total_hs += HS.size();
|
||||
|
||||
for (BasicBlock *BB : HS) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool Inserted = false;
|
||||
for (auto BI = pred_begin(BB), BE = pred_end(BB); BI != BE; ++BI) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto Edge = BasicBlockEdge(*BI, BB);
|
||||
if (Edge.isSingleEdge() && DT->dominates(Edge, BB)) {
|
||||
|
||||
EdgeSet.insert({*BI, BB});
|
||||
Inserted = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!Inserted) {
|
||||
|
||||
MS.insert(BB);
|
||||
total_rs += 1;
|
||||
total_hs -= 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto I = EdgeSet.begin(), E = EdgeSet.end(); I != E; ++I) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto PredBB = I->first;
|
||||
auto SuccBB = I->second;
|
||||
auto NewBB =
|
||||
SplitBlockPredecessors(SuccBB, {PredBB}, ".split", DT, nullptr,
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR >= 8
|
||||
nullptr,
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
false);
|
||||
MS.insert(NewBB);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto *EBB = &F.getEntryBlock();
|
||||
if (succ_begin(EBB) == succ_end(EBB)) {
|
||||
|
||||
MS.insert(EBB);
|
||||
total_rs += 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (BasicBlock &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (MS.find(&BB) == MS.end()) { continue; }
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&*BB.getFirstInsertionPt());
|
||||
IRB.CreateStore(ConstantInt::get(Int32Ty, genLabel()), OldPrev);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (BasicBlock &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto PI = pred_begin(&BB);
|
||||
auto PE = pred_end(&BB);
|
||||
if (MarkSetOpt && MS.find(&BB) == MS.end()) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&*BB.getFirstInsertionPt());
|
||||
Value * L = NULL;
|
||||
if (PI == PE) {
|
||||
|
||||
L = ConstantInt::get(Int32Ty, genLabel());
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
auto *PN = PHINode::Create(Int32Ty, 0, "", &*BB.begin());
|
||||
DenseMap<BasicBlock *, unsigned> PredMap;
|
||||
for (auto PI = pred_begin(&BB), PE = pred_end(&BB); PI != PE; ++PI) {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock *PBB = *PI;
|
||||
auto It = PredMap.insert({PBB, genLabel()});
|
||||
unsigned Label = It.first->second;
|
||||
PN->addIncoming(ConstantInt::get(Int32Ty, Label), PBB);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
L = PN;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Load prev_loc */
|
||||
LoadInst *PrevLoc = IRB.CreateLoad(OldPrev);
|
||||
PrevLoc->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
Value *PrevLocCasted = IRB.CreateZExt(PrevLoc, IRB.getInt32Ty());
|
||||
|
||||
/* Load SHM pointer */
|
||||
LoadInst *MapPtr = IRB.CreateLoad(CovMapPtr);
|
||||
MapPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
Value *MapPtrIdx =
|
||||
IRB.CreateGEP(MapPtr, IRB.CreateXor(PrevLocCasted, L));
|
||||
|
||||
/* Update bitmap */
|
||||
LoadInst *Counter = IRB.CreateLoad(MapPtrIdx);
|
||||
Counter->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
|
||||
Value *Incr = IRB.CreateAdd(Counter, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1));
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
if (neverZero_counters_str !=
|
||||
NULL) // with llvm 9 we make this the default as the bug in llvm is
|
||||
// then fixed
|
||||
#else
|
||||
if (1) // with llvm 9 we make this the default as the bug in llvm is
|
||||
// then fixed
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
/* hexcoder: Realize a counter that skips zero during overflow.
|
||||
* Once this counter reaches its maximum value, it next increments to
|
||||
* 1
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Instead of
|
||||
* Counter + 1 -> Counter
|
||||
* we inject now this
|
||||
* Counter + 1 -> {Counter, OverflowFlag}
|
||||
* Counter + OverflowFlag -> Counter
|
||||
*/
|
||||
auto cf = IRB.CreateICmpEQ(Incr, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 0));
|
||||
auto carry = IRB.CreateZExt(cf, Int8Ty);
|
||||
Incr = IRB.CreateAdd(Incr, carry);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
IRB.CreateStore(Incr, MapPtrIdx)
|
||||
->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set prev_loc to cur_loc >> 1 */
|
||||
/*
|
||||
StoreInst *Store = IRB.CreateStore(ConstantInt::get(Int32Ty, L >> 1),
|
||||
OldPrev); Store->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C,
|
||||
None));
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
total_instr++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
OKF("Instrumented %u locations (%llu, %llu) (%s mode)\n" /*", ratio
|
||||
%u%%)."*/
|
||||
,
|
||||
total_instr, total_rs, total_hs,
|
||||
getenv("AFL_HARDEN")
|
||||
? "hardened"
|
||||
: ((getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN") || getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN"))
|
||||
? "ASAN/MSAN"
|
||||
: "non-hardened") /*, inst_ratio*/);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}; // end of struct InsTrim
|
||||
|
||||
} // end of anonymous namespace
|
||||
|
||||
char InsTrim::ID = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
static void registerAFLPass(const PassManagerBuilder &,
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
|
||||
PM.add(new InsTrim());
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterAFLPass(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_OptimizerLast, registerAFLPass);
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterAFLPass0(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_EnabledOnOptLevel0, registerAFLPass);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
# -----------------------------------------
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Written by Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
# Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
# Michal Zalewski
|
||||
#
|
||||
# LLVM integration design comes from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
#
|
||||
@ -16,57 +16,131 @@
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# For Heiko:
|
||||
#TEST_MMAP=1
|
||||
|
||||
PREFIX ?= /usr/local
|
||||
HELPER_PATH = $(PREFIX)/lib/afl
|
||||
BIN_PATH = $(PREFIX)/bin
|
||||
|
||||
VERSION = $(shell grep '^\#define VERSION ' ../config.h | cut -d '"' -f2)
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM_CONFIG ?= llvm-config
|
||||
#LLVM_OK = $(shell $(LLVM_CONFIG) --version | egrep -q '^[5-6]' && echo 0 || echo 1 )
|
||||
LLVM_UNSUPPORTED = $(shell $(LLVM_CONFIG) --version | egrep -q '^9|3.0' && echo 1 || echo 0 )
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "OpenBSD"
|
||||
LLVM_CONFIG ?= $(BIN_PATH)/llvm-config
|
||||
HAS_OPT = $(shell test -x $(BIN_PATH)/opt && echo 0 || echo 1)
|
||||
ifeq "$(HAS_OPT)" "1"
|
||||
$(error llvm_mode needs a complete llvm installation (versions 3.8.0 up to 9) -> e.g. "pkg_add llvm-7.0.1p9")
|
||||
endif
|
||||
else
|
||||
LLVM_CONFIG ?= llvm-config
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMVER = $(shell $(LLVM_CONFIG) --version 2>/dev/null)
|
||||
LLVM_UNSUPPORTED = $(shell $(LLVM_CONFIG) --version 2>/dev/null | egrep -q '^[12]|^3\.0|^1[0-9]' && echo 1 || echo 0 )
|
||||
LLVM_MAJOR = $(shell $(LLVM_CONFIG) --version 2>/dev/null | sed 's/\..*//')
|
||||
LLVM_BINDIR = $(shell $(LLVM_CONFIG) --bindir 2>/dev/null)
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(LLVM_UNSUPPORTED)" "1"
|
||||
$(warn llvm_mode only supports versions 3.8.0 up to 8.x )
|
||||
$(warn llvm_mode only supports versions 3.8.0 up to 9)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
# this is not visible yet:
|
||||
ifeq "$(LLVM_MAJOR)" "9"
|
||||
$(info llvm_mode detected llvm 9, enabling neverZero implementation)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign \
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign -I ../include/ \
|
||||
-DAFL_PATH=\"$(HELPER_PATH)\" -DBIN_PATH=\"$(BIN_PATH)\" \
|
||||
-DVERSION=\"$(VERSION)\"
|
||||
-DVERSION=\"$(VERSION)\"
|
||||
ifdef AFL_TRACE_PC
|
||||
CFLAGS += -DUSE_TRACE_PC=1
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
CXXFLAGS ?= -O3 -funroll-loops
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -Wno-pointer-sign \
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -Wall -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -g -I ../include/ \
|
||||
-DVERSION=\"$(VERSION)\" -Wno-variadic-macros
|
||||
|
||||
CLANG_CFL = `$(LLVM_CONFIG) --cxxflags` -Wl,-znodelete -fno-rtti -fpic $(CXXFLAGS)
|
||||
CLANG_LFL = `$(LLVM_CONFIG) --ldflags` $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
# User teor2345 reports that this is required to make things work on MacOS X.
|
||||
|
||||
# User teor2345 reports that this is required to make things work on MacOS X.
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "Darwin"
|
||||
CLANG_LFL += -Wl,-flat_namespace -Wl,-undefined,suppress
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "OpenBSD"
|
||||
CLANG_LFL += `$(LLVM_CONFIG) --libdir`/libLLVM.so
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
# We were using llvm-config --bindir to get the location of clang, but
|
||||
# this seems to be busted on some distros, so using the one in $PATH is
|
||||
# probably better.
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(origin CC)" "default"
|
||||
CC = clang
|
||||
CXX = clang++
|
||||
CC = $(LLVM_BINDIR)/clang
|
||||
CXX = $(LLVM_BINDIR)/clang++
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell test -e $(CC) || echo 1 )" "1"
|
||||
# llvm-config --bindir is not providing a valid path, so ...
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell test -e '$(BIN_DIR)/clang' && echo 1)" "1"
|
||||
# we found one in the local install directory, lets use these
|
||||
CC = $(BIN_DIR)/clang
|
||||
CXX = $(BIN_DIR)/clang++
|
||||
else
|
||||
# hope for the best
|
||||
$(warn we have trouble finding clang/clang++ - llvm-config is not helping us)
|
||||
CC = clang
|
||||
CXX = clang++
|
||||
endif
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
# sanity check.
|
||||
# Are versions of clang --version and llvm-config --version equal?
|
||||
CLANGVER = $(shell $(CC) --version | sed -E -ne '/^.*version\ ([0-9]\.[0-9]\.[0-9]).*/s//\1/p')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell echo '\#include <sys/ipc.h>@\#include <sys/shm.h>@int main() { int _id = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 65536, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0600); shmctl(_id, IPC_RMID, 0); return 0;}' | tr @ '\n' | $(CC) -x c - -o .test2 2>/dev/null && echo 1 || echo 0 )" "1"
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=1
|
||||
else
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=0
|
||||
CFLAGS+=-DUSEMMAP=1
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lrt
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(TEST_MMAP)" "1"
|
||||
SHMAT_OK=0
|
||||
CFLAGS+=-DUSEMMAP=1
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lrt
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef AFL_TRACE_PC
|
||||
PROGS = ../afl-clang-fast ../afl-llvm-pass.so ../afl-llvm-rt.o ../afl-llvm-rt-32.o ../afl-llvm-rt-64.o ../compare-transform-pass.so ../split-compares-pass.so ../split-switches-pass.so
|
||||
PROGS = ../afl-clang-fast ../afl-llvm-pass.so ../libLLVMInsTrim.so ../afl-llvm-rt.o ../afl-llvm-rt-32.o ../afl-llvm-rt-64.o ../compare-transform-pass.so ../split-compares-pass.so ../split-switches-pass.so
|
||||
else
|
||||
PROGS = ../afl-clang-fast ../afl-llvm-rt.o ../afl-llvm-rt-32.o ../afl-llvm-rt-64.o ../compare-transform-pass.so ../split-compares-pass.so ../split-switches-pass.so
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
all: test_deps $(PROGS) test_build all_done
|
||||
ifneq "$(CLANGVER)" "$(LLVMVER)"
|
||||
CC = $(shell llvm-config --bindir)/clang
|
||||
CXX = $(shell llvm-config --bindir)/clang++
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
all: test_shm test_deps $(PROGS) afl-clang-fast.8 test_build all_done
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(SHMAT_OK)" "1"
|
||||
|
||||
test_shm:
|
||||
@echo "[+] shmat seems to be working."
|
||||
@rm -f .test2
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
|
||||
test_shm:
|
||||
@echo "[-] shmat seems not to be working, switching to mmap implementation"
|
||||
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
test_deps:
|
||||
ifndef AFL_TRACE_PC
|
||||
@ -77,6 +151,13 @@ else
|
||||
endif
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for working '$(CC)'..."
|
||||
@which $(CC) >/dev/null 2>&1 || ( echo "[-] Oops, can't find '$(CC)'. Make sure that it's in your \$$PATH (or set \$$CC and \$$CXX)."; exit 1 )
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for matching versions of '$(CC)' and '$(LLVM_CONFIG)'"
|
||||
ifneq "$(CLANGVER)" "$(LLVMVER)"
|
||||
@echo "[!] WARNING: we have llvm-config version $(LLVMVER) and a clang version $(CLANGVER)"
|
||||
@echo "[!] Retrying with the clang compiler from llvm: CC=`llvm-config --bindir`/clang"
|
||||
else
|
||||
@echo "[*] We have llvm-config version $(LLVMVER) with a clang version $(CLANGVER), good."
|
||||
endif
|
||||
@echo "[*] Checking for '../afl-showmap'..."
|
||||
@test -f ../afl-showmap || ( echo "[-] Oops, can't find '../afl-showmap'. Be sure to compile AFL first."; exit 1 )
|
||||
@echo "[+] All set and ready to build."
|
||||
@ -85,8 +166,11 @@ endif
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $< -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
ln -sf afl-clang-fast ../afl-clang-fast++
|
||||
|
||||
../libLLVMInsTrim.so: LLVMInsTrim.so.cc MarkNodes.cc | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CLANG_CFL) -DLLVMInsTrim_EXPORTS -fno-rtti -fPIC -std=gnu++11 -shared $< MarkNodes.cc -o $@ $(CLANG_LFL)
|
||||
|
||||
../afl-llvm-pass.so: afl-llvm-pass.so.cc | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CLANG_CFL) -shared $< -o $@ $(CLANG_LFL)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CLANG_CFL) -DLLVMInsTrim_EXPORTS -fno-rtti -fPIC -std=gnu++11 -shared $< -o $@ $(CLANG_LFL)
|
||||
|
||||
# laf
|
||||
../split-switches-pass.so: split-switches-pass.so.cc | test_deps
|
||||
@ -110,11 +194,11 @@ endif
|
||||
|
||||
test_build: $(PROGS)
|
||||
@echo "[*] Testing the CC wrapper and instrumentation output..."
|
||||
unset AFL_USE_ASAN AFL_USE_MSAN AFL_INST_RATIO; AFL_QUIET=1 AFL_PATH=. AFL_CC=$(CC) LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES=1 LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES=1 LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES=1 ../afl-clang-fast $(CFLAGS) ../test-instr.c -o test-instr $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
echo 0 | ../afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr0 ./test-instr
|
||||
unset AFL_USE_ASAN AFL_USE_MSAN AFL_INST_RATIO; AFL_QUIET=1 AFL_PATH=. AFL_CC=$(CC) AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES=1 AFL_LLVM_LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES=1 AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES=1 ../afl-clang-fast $(CFLAGS) ../test-instr.c -o test-instr $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
../afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr0 ./test-instr < /dev/null
|
||||
echo 1 | ../afl-showmap -m none -q -o .test-instr1 ./test-instr
|
||||
@rm -f test-instr
|
||||
@cmp -s .test-instr0 .test-instr1; DR="$$?"; rm -f .test-instr0 .test-instr1; if [ "$$DR" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Oops, the instrumentation does not seem to be behaving correctly!"; echo; echo "Please ping <lcamtuf@google.com> to troubleshoot the issue."; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
@cmp -s .test-instr0 .test-instr1; DR="$$?"; rm -f .test-instr0 .test-instr1; if [ "$$DR" = "0" ]; then echo; echo "Oops, the instrumentation does not seem to be behaving correctly!"; echo; echo "Please post to https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus/issues to troubleshoot the issue."; echo; exit 1; fi
|
||||
@echo "[+] All right, the instrumentation seems to be working!"
|
||||
|
||||
all_done: test_build
|
||||
@ -122,6 +206,27 @@ all_done: test_build
|
||||
|
||||
.NOTPARALLEL: clean
|
||||
|
||||
vpath % ..
|
||||
%.8: %
|
||||
@echo .TH $* 8 `date "+%Y-%m-%d"` "afl++" > ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH NAME >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .B $* >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH SYNOPSIS >> ../$@
|
||||
@../$* -h 2>&1 | head -n 3 | tail -n 1 | sed 's/^\.\///' >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH OPTIONS >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .nf >> ../$@
|
||||
@../$* -h 2>&1 | tail -n +4 >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH AUTHOR >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo "afl++ was written by Michal \"lcamtuf\" Zalewski and is maintained by Marc \"van Hauser\" Heuse <mh@mh-sec.de>, Heiko \"hexcoder-\" Eissfeldt <heiko.eissfeldt@hexco.de> and Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>" >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo The homepage of afl++ is: https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/AFLplusplus >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo .SH LICENSE >> ../$@
|
||||
@echo Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004 >> ../$@
|
||||
ln -sf afl-clang-fast.8 ../afl-clang-fast++.8
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -f *.o *.so *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]* test-instr .test-instr0 .test-instr1
|
||||
rm -f $(PROGS) ../afl-clang-fast++
|
||||
rm -f *.o *.so *~ a.out core core.[1-9][0-9]* .test2 test-instr .test-instr0 .test-instr1
|
||||
rm -f $(PROGS) ../afl-clang-fast++ ../afl-clang-fast*.8
|
||||
|
||||
465
llvm_mode/MarkNodes.cc
Normal file
465
llvm_mode/MarkNodes.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,465 @@
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <map>
|
||||
#include <queue>
|
||||
#include <set>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include "llvm/ADT/DenseMap.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/ADT/DenseSet.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/ADT/SmallVector.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/BasicBlock.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/CFG.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Constants.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Function.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/IRBuilder.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Instructions.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Module.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Pass.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Support/Debug.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Support/raw_ostream.h"
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace llvm;
|
||||
|
||||
DenseMap<BasicBlock *, uint32_t> LMap;
|
||||
std::vector<BasicBlock *> Blocks;
|
||||
std::set<uint32_t> Marked, Markabove;
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t> > Succs, Preds;
|
||||
|
||||
void reset() {
|
||||
|
||||
LMap.clear();
|
||||
Blocks.clear();
|
||||
Marked.clear();
|
||||
Markabove.clear();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t start_point;
|
||||
|
||||
void labelEachBlock(Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Fake single endpoint;
|
||||
LMap[NULL] = Blocks.size();
|
||||
Blocks.push_back(NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
// Assign the unique LabelID to each block;
|
||||
for (auto I = F->begin(), E = F->end(); I != E; ++I) {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock *BB = &*I;
|
||||
LMap[BB] = Blocks.size();
|
||||
Blocks.push_back(BB);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
start_point = LMap[&F->getEntryBlock()];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void buildCFG(Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
Succs.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
Preds.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < Succs.size(); i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
Succs[i].clear();
|
||||
Preds[i].clear();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// uint32_t FakeID = 0;
|
||||
for (auto S = F->begin(), E = F->end(); S != E; ++S) {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock *BB = &*S;
|
||||
uint32_t MyID = LMap[BB];
|
||||
// if (succ_begin(BB) == succ_end(BB)) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Succs[MyID].push_back(FakeID);
|
||||
// Marked.insert(MyID);
|
||||
//}
|
||||
for (auto I = succ_begin(BB), E = succ_end(BB); I != E; ++I) {
|
||||
|
||||
Succs[MyID].push_back(LMap[*I]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t> > tSuccs;
|
||||
std::vector<bool> tag, indfs;
|
||||
|
||||
void DFStree(size_t now_id) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (tag[now_id]) return;
|
||||
tag[now_id] = true;
|
||||
indfs[now_id] = true;
|
||||
for (auto succ : tSuccs[now_id]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (tag[succ] and indfs[succ]) {
|
||||
|
||||
Marked.insert(succ);
|
||||
Markabove.insert(succ);
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Succs[now_id].push_back(succ);
|
||||
Preds[succ].push_back(now_id);
|
||||
DFStree(succ);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
indfs[now_id] = false;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void turnCFGintoDAG(Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
tSuccs = Succs;
|
||||
tag.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
indfs.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < Blocks.size(); ++i) {
|
||||
|
||||
Succs[i].clear();
|
||||
tag[i] = false;
|
||||
indfs[i] = false;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
DFStree(start_point);
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < Blocks.size(); ++i)
|
||||
if (Succs[i].empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
Succs[i].push_back(0);
|
||||
Preds[0].push_back(i);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t timeStamp;
|
||||
namespace DominatorTree {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t> > cov;
|
||||
std::vector<uint32_t> dfn, nfd, par, sdom, idom, mom, mn;
|
||||
|
||||
bool Compare(uint32_t u, uint32_t v) {
|
||||
|
||||
return dfn[u] < dfn[v];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t eval(uint32_t u) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (mom[u] == u) return u;
|
||||
uint32_t res = eval(mom[u]);
|
||||
if (Compare(sdom[mn[mom[u]]], sdom[mn[u]])) { mn[u] = mn[mom[u]]; }
|
||||
return mom[u] = res;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void DFS(uint32_t now) {
|
||||
|
||||
timeStamp += 1;
|
||||
dfn[now] = timeStamp;
|
||||
nfd[timeStamp - 1] = now;
|
||||
for (auto succ : Succs[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (dfn[succ] == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
par[succ] = now;
|
||||
DFS(succ);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void DominatorTree(Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (Blocks.empty()) return;
|
||||
uint32_t s = start_point;
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialization
|
||||
mn.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
cov.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
dfn.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
nfd.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
par.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
mom.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
sdom.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
idom.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < Blocks.size(); i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
dfn[i] = 0;
|
||||
nfd[i] = Blocks.size();
|
||||
cov[i].clear();
|
||||
idom[i] = mom[i] = mn[i] = sdom[i] = i;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
timeStamp = 0;
|
||||
DFS(s);
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = Blocks.size() - 1; i >= 1u; i--) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t now = nfd[i];
|
||||
if (now == Blocks.size()) { continue; }
|
||||
for (uint32_t pre : Preds[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (dfn[pre]) {
|
||||
|
||||
eval(pre);
|
||||
if (Compare(sdom[mn[pre]], sdom[now])) { sdom[now] = sdom[mn[pre]]; }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cov[sdom[now]].push_back(now);
|
||||
mom[now] = par[now];
|
||||
for (uint32_t x : cov[par[now]]) {
|
||||
|
||||
eval(x);
|
||||
if (Compare(sdom[mn[x]], par[now])) {
|
||||
|
||||
idom[x] = mn[x];
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
idom[x] = par[now];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = 1; i < Blocks.size(); i += 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t now = nfd[i];
|
||||
if (now == Blocks.size()) { continue; }
|
||||
if (idom[now] != sdom[now]) idom[now] = idom[idom[now]];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace DominatorTree
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<uint32_t> Visited, InStack;
|
||||
std::vector<uint32_t> TopoOrder, InDeg;
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t> > t_Succ, t_Pred;
|
||||
|
||||
void Go(uint32_t now, uint32_t tt) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (now == tt) return;
|
||||
Visited[now] = InStack[now] = timeStamp;
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t nxt : Succs[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (Visited[nxt] == timeStamp and InStack[nxt] == timeStamp) {
|
||||
|
||||
Marked.insert(nxt);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
t_Succ[now].push_back(nxt);
|
||||
t_Pred[nxt].push_back(now);
|
||||
InDeg[nxt] += 1;
|
||||
if (Visited[nxt] == timeStamp) { continue; }
|
||||
Go(nxt, tt);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
InStack[now] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void TopologicalSort(uint32_t ss, uint32_t tt) {
|
||||
|
||||
timeStamp += 1;
|
||||
|
||||
Go(ss, tt);
|
||||
|
||||
TopoOrder.clear();
|
||||
std::queue<uint32_t> wait;
|
||||
wait.push(ss);
|
||||
while (not wait.empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t now = wait.front();
|
||||
wait.pop();
|
||||
TopoOrder.push_back(now);
|
||||
for (uint32_t nxt : t_Succ[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
InDeg[nxt] -= 1;
|
||||
if (InDeg[nxt] == 0u) { wait.push(nxt); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::set<uint32_t> > NextMarked;
|
||||
bool Indistinguish(uint32_t node1, uint32_t node2) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (NextMarked[node1].size() > NextMarked[node2].size()) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t _swap = node1;
|
||||
node1 = node2;
|
||||
node2 = _swap;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t x : NextMarked[node1]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (NextMarked[node2].find(x) != NextMarked[node2].end()) { return true; }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void MakeUniq(uint32_t now) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool StopFlag = false;
|
||||
if (Marked.find(now) == Marked.end()) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t pred1 : t_Pred[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t pred2 : t_Pred[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (pred1 == pred2) continue;
|
||||
if (Indistinguish(pred1, pred2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
Marked.insert(now);
|
||||
StopFlag = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (StopFlag) { break; }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (Marked.find(now) != Marked.end()) {
|
||||
|
||||
NextMarked[now].insert(now);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t pred : t_Pred[now]) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t x : NextMarked[pred]) {
|
||||
|
||||
NextMarked[now].insert(x);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void MarkSubGraph(uint32_t ss, uint32_t tt) {
|
||||
|
||||
TopologicalSort(ss, tt);
|
||||
if (TopoOrder.empty()) return;
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t i : TopoOrder) {
|
||||
|
||||
NextMarked[i].clear();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
NextMarked[TopoOrder[0]].insert(TopoOrder[0]);
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = 1; i < TopoOrder.size(); i += 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
MakeUniq(TopoOrder[i]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void MarkVertice(Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t s = start_point;
|
||||
|
||||
InDeg.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
Visited.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
InStack.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
t_Succ.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
t_Pred.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
NextMarked.resize(Blocks.size());
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < Blocks.size(); i += 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
Visited[i] = InStack[i] = InDeg[i] = 0;
|
||||
t_Succ[i].clear();
|
||||
t_Pred[i].clear();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
timeStamp = 0;
|
||||
uint32_t t = 0;
|
||||
// MarkSubGraph(s, t);
|
||||
// return;
|
||||
|
||||
while (s != t) {
|
||||
|
||||
MarkSubGraph(DominatorTree::idom[t], t);
|
||||
t = DominatorTree::idom[t];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// return {marked nodes}
|
||||
std::pair<std::vector<BasicBlock *>, std::vector<BasicBlock *> > markNodes(
|
||||
Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
assert(F->size() > 0 && "Function can not be empty");
|
||||
|
||||
reset();
|
||||
labelEachBlock(F);
|
||||
buildCFG(F);
|
||||
turnCFGintoDAG(F);
|
||||
DominatorTree::DominatorTree(F);
|
||||
MarkVertice(F);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<BasicBlock *> Result, ResultAbove;
|
||||
for (uint32_t x : Markabove) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto it = Marked.find(x);
|
||||
if (it != Marked.end()) Marked.erase(it);
|
||||
if (x) ResultAbove.push_back(Blocks[x]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint32_t x : Marked) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (x == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
Result.push_back(Blocks[x]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return {Result, ResultAbove};
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
12
llvm_mode/MarkNodes.h
Normal file
12
llvm_mode/MarkNodes.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
#ifndef __MARK_NODES__
|
||||
#define __MARK_NODES__
|
||||
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/BasicBlock.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Function.h"
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
std::pair<std::vector<llvm::BasicBlock *>, std::vector<llvm::BasicBlock *>>
|
||||
markNodes(llvm::Function *F);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
25
llvm_mode/README.instrim.md
Normal file
25
llvm_mode/README.instrim.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
# InsTrim
|
||||
|
||||
InsTrim: Lightweight Instrumentation for Coverage-guided Fuzzing
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
InsTrim uses CFG and markers to instrument just what is necessary in the
|
||||
binary in llvm_mode. It is about 20-25% faster but as a cost has a lower
|
||||
path discovery.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Set the environment variable `AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM=1` during compilation of
|
||||
the target.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an advanced mode which instruments loops in a way so that
|
||||
afl-fuzz can see which loop path has been selected but not being able to
|
||||
see how often the loop has been rerun.
|
||||
This again is a tradeoff for speed for less path information.
|
||||
To enable this mode set `AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM_LOOPHEAD=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Background
|
||||
|
||||
The paper: [InsTrim: Lightweight Instrumentation for Coverage-guided Fuzzing]
|
||||
(https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/bar2018_14_Hsu_paper.pdf)
|
||||
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Usage
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
By default the passes will not run when you compile programs using
|
||||
afl-clang-fast. Hence, you can use AFL as usual.
|
||||
To enable the passes you must set environment variables before you
|
||||
compile the target project.
|
||||
|
||||
The following options exist:
|
||||
|
||||
export LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES=1 Enables the split-switches pass.
|
||||
|
||||
export LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES=1 Enables the transform-compares pass
|
||||
(strcmp, memcmp, strncmp, strcasecmp, strncasecmp).
|
||||
|
||||
export LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES=1 Enables the split-compares pass.
|
||||
By default it will split all compares with a bit width <= 64 bits.
|
||||
You can change this behaviour by setting
|
||||
export LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES_BITW=<bit_width>.
|
||||
|
||||
38
llvm_mode/README.laf-intel.md
Normal file
38
llvm_mode/README.laf-intel.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
# laf-intel instrumentation
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
By default these passes will not run when you compile programs using
|
||||
afl-clang-fast. Hence, you can use AFL as usual.
|
||||
To enable the passes you must set environment variables before you
|
||||
compile the target project.
|
||||
|
||||
The following options exist:
|
||||
|
||||
`export AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES=1`
|
||||
|
||||
Enables the split-switches pass.
|
||||
|
||||
`export AFL_LLVM_LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES=1`
|
||||
|
||||
Enables the transform-compares pass (strcmp, memcmp, strncmp,
|
||||
strcasecmp, strncasecmp).
|
||||
|
||||
`export AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES=1`
|
||||
|
||||
Enables the split-compares pass.
|
||||
By default it will
|
||||
1. simplify operators >= (and <=) into chains of > (<) and == comparisons
|
||||
2. change signed integer comparisons to a chain of sign-only comparison
|
||||
and unsigned comparisons
|
||||
3. split all unsigned integer comparisons with bit widths of
|
||||
64, 32 or 16 bits to chains of 8 bits comparisons.
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the behaviour of the last step by setting
|
||||
`export AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES_BITW=<bit_width>`, where
|
||||
bit_width may be 64, 32 or 16.
|
||||
|
||||
A new experimental feature is splitting floating point comparisons into a
|
||||
series of sign, exponent and mantissa comparisons followed by splitting each
|
||||
of them into 8 bit comparisons when necessary.
|
||||
It is activated with the `AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES` setting.
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,11 @@
|
||||
============================================
|
||||
Fast LLVM-based instrumentation for afl-fuzz
|
||||
============================================
|
||||
# Fast LLVM-based instrumentation for afl-fuzz
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
(See ../gcc_plugin/README.gcc for the GCC-based instrumentation.)
|
||||
|
||||
1) Introduction
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
## 1) Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
! llvm_mode works with llvm version 3.8.1 up to 8.x !
|
||||
! llvm version 9 does not work yet !
|
||||
! llvm_mode works with llvm versions 3.8.0 up to 9 !
|
||||
|
||||
The code in this directory allows you to instrument programs for AFL using
|
||||
true compiler-level instrumentation, instead of the more crude
|
||||
@ -30,7 +27,8 @@ several interesting properties:
|
||||
- The instrumentation can cope a bit better with multi-threaded targets.
|
||||
|
||||
- Because the feature relies on the internals of LLVM, it is clang-specific
|
||||
and will *not* work with GCC.
|
||||
and will *not* work with GCC (see ../gcc_plugin/ for an alternative once
|
||||
it is available).
|
||||
|
||||
Once this implementation is shown to be sufficiently robust and portable, it
|
||||
will probably replace afl-clang. For now, it can be built separately and
|
||||
@ -38,13 +36,16 @@ co-exists with the original code.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea and much of the implementation comes from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
|
||||
2) How to use
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
## 2) How to use this
|
||||
|
||||
In order to leverage this mechanism, you need to have clang installed on your
|
||||
system. You should also make sure that the llvm-config tool is in your path
|
||||
(or pointed to via LLVM_CONFIG in the environment).
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if you have several LLVM versions installed, pointing LLVM_CONFIG
|
||||
to the version you want to use will switch compiling to this specific
|
||||
version - if you installation is set up correctly :-)
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, some systems that do have clang come without llvm-config or the
|
||||
LLVM development headers; one example of this is FreeBSD. FreeBSD users will
|
||||
also run into problems with clang being built statically and not being able to
|
||||
@ -63,27 +64,52 @@ called afl-clang-fast and afl-clang-fast++ in the parent directory. Once this
|
||||
is done, you can instrument third-party code in a way similar to the standard
|
||||
operating mode of AFL, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
CC=/path/to/afl/afl-clang-fast ./configure [...options...]
|
||||
make
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Be sure to also include CXX set to afl-clang-fast++ for C++ code.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool honors roughly the same environmental variables as afl-gcc (see
|
||||
../docs/env_variables.txt). This includes AFL_INST_RATIO, AFL_USE_ASAN,
|
||||
AFL_HARDEN, and AFL_DONT_OPTIMIZE.
|
||||
../docs/env_variables.txt). This includes AFL_USE_ASAN,
|
||||
AFL_HARDEN, and AFL_DONT_OPTIMIZE. However AFL_INST_RATIO is not honored
|
||||
as it does not serve a good purpose with the more effective instrim CFG
|
||||
analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: if you want the LLVM helper to be installed on your system for all
|
||||
users, you need to build it before issuing 'make install' in the parent
|
||||
directory.
|
||||
|
||||
3) Gotchas, feedback, bugs
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
## 3) Options
|
||||
|
||||
Several options are present to make llvm_mode faster or help it rearrange
|
||||
the code to make afl-fuzz path discovery easier.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need just to instrument specific parts of the code, you can whitelist
|
||||
which C/C++ files to actually instrument. See README.whitelist
|
||||
|
||||
For splitting memcmp, strncmp, etc. please see README.laf-intel
|
||||
|
||||
Then there is an optimized instrumentation strategy that uses CFGs and
|
||||
markers to just instrument what is needed. This increases speed by 20-25%
|
||||
however has a lower path discovery.
|
||||
If you want to use this, set AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM=1
|
||||
See README.instrim
|
||||
|
||||
Finally if your llvm version is 8 or lower, you can activate a mode that
|
||||
prevents that a counter overflow result in a 0 value. This is good for
|
||||
path discovery, but the llvm implementation for x86 for this functionality
|
||||
is not optimal and was only fixed in llvm 9.
|
||||
You can set this with AFL_LLVM_NOT_ZERO=1
|
||||
See README.neverzero
|
||||
|
||||
## 4) Gotchas, feedback, bugs
|
||||
|
||||
This is an early-stage mechanism, so field reports are welcome. You can send bug
|
||||
reports to <afl-users@googlegroups.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
4) Bonus feature #1: deferred instrumentation
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
## 5) Bonus feature #1: deferred initialization
|
||||
|
||||
AFL tries to optimize performance by executing the targeted binary just once,
|
||||
stopping it just before main(), and then cloning this "master" process to get
|
||||
@ -119,9 +145,11 @@ a location after:
|
||||
|
||||
With the location selected, add this code in the appropriate spot:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
#ifdef __AFL_HAVE_MANUAL_CONTROL
|
||||
__AFL_INIT();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You don't need the #ifdef guards, but including them ensures that the program
|
||||
will keep working normally when compiled with a tool other than afl-clang-fast.
|
||||
@ -129,8 +157,7 @@ will keep working normally when compiled with a tool other than afl-clang-fast.
|
||||
Finally, recompile the program with afl-clang-fast (afl-gcc or afl-clang will
|
||||
*not* generate a deferred-initialization binary) - and you should be all set!
|
||||
|
||||
5) Bonus feature #2: persistent mode
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
## 6) Bonus feature #2: persistent mode
|
||||
|
||||
Some libraries provide APIs that are stateless, or whose state can be reset in
|
||||
between processing different input files. When such a reset is performed, a
|
||||
@ -139,6 +166,7 @@ eliminating the need for repeated fork() calls and the associated OS overhead.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic structure of the program that does this would be:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
while (__AFL_LOOP(1000)) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Read input data. */
|
||||
@ -148,6 +176,7 @@ The basic structure of the program that does this would be:
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Exit normally */
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The numerical value specified within the loop controls the maximum number
|
||||
of iterations before AFL will restart the process from scratch. This minimizes
|
||||
@ -156,8 +185,8 @@ and going much higher increases the likelihood of hiccups without giving you
|
||||
any real performance benefits.
|
||||
|
||||
A more detailed template is shown in ../experimental/persistent_demo/.
|
||||
Similarly to the previous mode, the feature works only with afl-clang-fast;
|
||||
#ifdef guards can be used to suppress it when using other compilers.
|
||||
Similarly to the previous mode, the feature works only with afl-clang-fast; #ifdef
|
||||
guards can be used to suppress it when using other compilers.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that as with the previous mode, the feature is easy to misuse; if you
|
||||
do not fully reset the critical state, you may end up with false positives or
|
||||
@ -169,8 +198,7 @@ PS. Because there are task switches still involved, the mode isn't as fast as
|
||||
faster than the normal fork() model, and compared to in-process fuzzing,
|
||||
should be a lot more robust.
|
||||
|
||||
6) Bonus feature #3: new 'trace-pc-guard' mode
|
||||
----------------------------------------------
|
||||
## 8) Bonus feature #3: new 'trace-pc-guard' mode
|
||||
|
||||
Recent versions of LLVM are shipping with a built-in execution tracing feature
|
||||
that provides AFL with the necessary tracing data without the need to
|
||||
@ -178,12 +206,12 @@ post-process the assembly or install any compiler plugins. See:
|
||||
|
||||
http://clang.llvm.org/docs/SanitizerCoverage.html#tracing-pcs-with-guards
|
||||
|
||||
As of this writing, the feature is only available on SVN trunk, and is yet to
|
||||
make it to an official release of LLVM. Nevertheless, if you have a
|
||||
sufficiently recent compiler and want to give it a try, build afl-clang-fast
|
||||
this way:
|
||||
If you have a sufficiently recent compiler and want to give it a try, build
|
||||
afl-clang-fast this way:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
AFL_TRACE_PC=1 make clean all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this mode is currently about 20% slower than "vanilla" afl-clang-fast,
|
||||
and about 5-10% slower than afl-clang. This is likely because the
|
||||
27
llvm_mode/README.neverzero.md
Normal file
27
llvm_mode/README.neverzero.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
# NeverZero counters for LLVM instrumentation
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
In larger, complex or reiterative programs the counters that collect the edge
|
||||
coverage can easily fill up and wrap around.
|
||||
This is not that much of an issue - unless by chance it wraps just to a value
|
||||
of zero when the program execution ends.
|
||||
In this case afl-fuzz is not able to see that the edge has been accessed and
|
||||
will ignore it.
|
||||
|
||||
NeverZero prevents this behaviour. If a counter wraps, it jumps over the value
|
||||
0 directly to a 1. This improves path discovery (by a very little amount)
|
||||
at a very little cost (one instruction per edge).
|
||||
|
||||
(The alternative of saturated counters has been tested also and proved to be
|
||||
inferior in terms of path discovery.)
|
||||
|
||||
This is implemented in afl-gcc, however for llvm_mode this is optional if
|
||||
the llvm version is below 9 - as there is a perfomance bug that is only fixed
|
||||
in version 9 and onwards.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to enable this for llvm < 9 then set
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export AFL_LLVM_NOT_ZERO=1
|
||||
```
|
||||
75
llvm_mode/README.whitelist.md
Normal file
75
llvm_mode/README.whitelist.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
# Using afl++ with partial instrumentation
|
||||
|
||||
This file describes how you can selectively instrument only the source files
|
||||
that are interesting to you using the LLVM instrumentation provided by
|
||||
afl++
|
||||
|
||||
Originally developed by Christian Holler (:decoder) <choller@mozilla.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Description and purpose
|
||||
|
||||
When building and testing complex programs where only a part of the program is
|
||||
the fuzzing target, it often helps to only instrument the necessary parts of
|
||||
the program, leaving the rest uninstrumented. This helps to focus the fuzzer
|
||||
on the important parts of the program, avoiding undesired noise and
|
||||
disturbance by uninteresting code being exercised.
|
||||
|
||||
For this purpose, I have added a "partial instrumentation" support to the LLVM
|
||||
mode of AFLFuzz that allows you to specify on a source file level which files
|
||||
should be compiled with or without instrumentation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) Building the LLVM module
|
||||
|
||||
The new code is part of the existing afl++ LLVM module in the llvm_mode/
|
||||
subdirectory. There is nothing specifically to do :)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 3) How to use the partial instrumentation mode
|
||||
|
||||
In order to build with partial instrumentation, you need to build with
|
||||
afl-clang-fast and afl-clang-fast++ respectively. The only required change is
|
||||
that you need to set the environment variable AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST when calling
|
||||
the compiler.
|
||||
|
||||
The environment variable must point to a file containing all the filenames
|
||||
that should be instrumented. For matching, the filename that is being compiled
|
||||
must end in the filename entry contained in this whitelist (to avoid breaking
|
||||
the matching when absolute paths are used during compilation).
|
||||
|
||||
For example if your source tree looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
project/
|
||||
project/feature_a/a1.cpp
|
||||
project/feature_a/a2.cpp
|
||||
project/feature_b/b1.cpp
|
||||
project/feature_b/b2.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and you only want to test feature_a, then create a whitelist file containing:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
feature_a/a1.cpp
|
||||
feature_a/a2.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However if the whitelist file contains only this, it works as well:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
a1.cpp
|
||||
a2.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
but it might lead to files being unwantedly instrumented if the same filename
|
||||
exists somewhere else in the project directories.
|
||||
|
||||
The created whitelist file is then set to AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST when you compile
|
||||
your program. For each file that didn't match the whitelist, the compiler will
|
||||
issue a warning at the end stating that no blocks were instrumented. If you
|
||||
didn't intend to instrument that file, then you can safely ignore that warning.
|
||||
|
||||
For old LLVM versions this feature might require to be compiled with debug
|
||||
information (-g), however at least from llvm version 6.0 onwards this is not
|
||||
required anymore (and might hurt performance and crash detection, so better not
|
||||
use -g).
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM integration design comes from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,26 +23,26 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#define AFL_MAIN
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../types.h"
|
||||
#include "../debug.h"
|
||||
#include "../alloc-inl.h"
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
#include "alloc-inl.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
|
||||
static u8* obj_path; /* Path to runtime libraries */
|
||||
static u8** cc_params; /* Parameters passed to the real CC */
|
||||
static u32 cc_par_cnt = 1; /* Param count, including argv0 */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8* obj_path; /* Path to runtime libraries */
|
||||
static u8** cc_params; /* Parameters passed to the real CC */
|
||||
static u32 cc_par_cnt = 1; /* Param count, including argv0 */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Try to find the runtime libraries. If that fails, abort. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void find_obj(u8* argv0) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *afl_path = getenv("AFL_PATH");
|
||||
u8* afl_path = getenv("AFL_PATH");
|
||||
u8 *slash, *tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl_path) {
|
||||
@ -50,9 +50,11 @@ static void find_obj(u8* argv0) {
|
||||
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/afl-llvm-rt.o", afl_path);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!access(tmp, R_OK)) {
|
||||
|
||||
obj_path = afl_path;
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
@ -63,7 +65,7 @@ static void find_obj(u8* argv0) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (slash) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *dir;
|
||||
u8* dir;
|
||||
|
||||
*slash = 0;
|
||||
dir = ck_strdup(argv0);
|
||||
@ -72,9 +74,11 @@ static void find_obj(u8* argv0) {
|
||||
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/afl-llvm-rt.o", dir);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!access(tmp, R_OK)) {
|
||||
|
||||
obj_path = dir;
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ck_free(tmp);
|
||||
@ -83,75 +87,103 @@ static void find_obj(u8* argv0) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!access(AFL_PATH "/afl-llvm-rt.o", R_OK)) {
|
||||
|
||||
obj_path = AFL_PATH;
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Unable to find 'afl-llvm-rt.o' or 'afl-llvm-pass.so'. Please set AFL_PATH");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
FATAL(
|
||||
"Unable to find 'afl-llvm-rt.o' or 'afl-llvm-pass.so.cc'. Please set "
|
||||
"AFL_PATH");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Copy argv to cc_params, making the necessary edits. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 fortify_set = 0, asan_set = 0, x_set = 0, maybe_linking = 1, bit_mode = 0;
|
||||
u8 *name;
|
||||
u8 fortify_set = 0, asan_set = 0, x_set = 0, maybe_linking = 1, bit_mode = 0;
|
||||
u8* name;
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params = ck_alloc((argc + 128) * sizeof(u8*));
|
||||
|
||||
name = strrchr(argv[0], '/');
|
||||
if (!name) name = argv[0]; else name++;
|
||||
if (!name)
|
||||
name = argv[0];
|
||||
else
|
||||
++name;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(name, "afl-clang-fast++")) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* alt_cxx = getenv("AFL_CXX");
|
||||
cc_params[0] = alt_cxx ? alt_cxx : (u8*)"clang++";
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* alt_cc = getenv("AFL_CC");
|
||||
cc_params[0] = alt_cc ? alt_cc : (u8*)"clang";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* There are two ways to compile afl-clang-fast. In the traditional mode, we
|
||||
use afl-llvm-pass.so to inject instrumentation. In the experimental
|
||||
/* There are three ways to compile with afl-clang-fast. In the traditional
|
||||
mode, we use afl-llvm-pass.so, then there is libLLVMInsTrim.so which is
|
||||
much faster but has less coverage. Finally there is the experimental
|
||||
'trace-pc-guard' mode, we use native LLVM instrumentation callbacks
|
||||
instead. The latter is a very recent addition - see:
|
||||
|
||||
http://clang.llvm.org/docs/SanitizerCoverage.html#tracing-pcs-with-guards */
|
||||
instead. For trace-pc-guard see:
|
||||
http://clang.llvm.org/docs/SanitizerCoverage.html#tracing-pcs-with-guards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// laf
|
||||
if (getenv("LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES")) {
|
||||
if (getenv("LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES") || getenv("AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_SWITCHES")) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-load";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/split-switches-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/split-switches-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES")) {
|
||||
if (getenv("LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES") ||
|
||||
getenv("AFL_LLVM_LAF_TRANSFORM_COMPARES")) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-load";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/compare-transform-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/compare-transform-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES")) {
|
||||
if (getenv("LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES") || getenv("AFL_LLVM_LAF_SPLIT_COMPARES")) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-load";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/split-compares-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/split-compares-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// /laf
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_TRACE_PC
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-fsanitize-coverage=trace-pc-guard";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-mllvm";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-sanitizer-coverage-block-threshold=0";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
"-fsanitize-coverage=trace-pc-guard"; // edge coverage by default
|
||||
// cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-mllvm";
|
||||
// cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
// "-fsanitize-coverage=trace-cmp,trace-div,trace-gep";
|
||||
// cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-sanitizer-coverage-block-threshold=0";
|
||||
#else
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-load";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/afl-llvm-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_LLVM_INSTRIM") != NULL || getenv("INSTRIM_LIB") != NULL)
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/libLLVMInsTrim.so", obj_path);
|
||||
else
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf("%s/afl-llvm-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Qunused-arguments";
|
||||
|
||||
@ -160,6 +192,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
if (argc == 1 && !strcmp(argv[1], "-v")) maybe_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
while (--argc) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8* cur = *(++argv);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-m32")) bit_mode = 32;
|
||||
@ -170,15 +203,15 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-c") || !strcmp(cur, "-S") || !strcmp(cur, "-E"))
|
||||
maybe_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-fsanitize=address") ||
|
||||
!strcmp(cur, "-fsanitize=memory")) asan_set = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-fsanitize=address") || !strcmp(cur, "-fsanitize=memory"))
|
||||
asan_set = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (strstr(cur, "FORTIFY_SOURCE")) fortify_set = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-shared")) maybe_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-Wl,-z,defs") ||
|
||||
!strcmp(cur, "-Wl,--no-undefined")) continue;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-Wl,-z,defs") || !strcmp(cur, "-Wl,--no-undefined"))
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = cur;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -188,8 +221,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-fstack-protector-all";
|
||||
|
||||
if (!fortify_set)
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2";
|
||||
if (!fortify_set) cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -197,8 +229,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN")) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN"))
|
||||
FATAL("ASAN and MSAN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN")) FATAL("ASAN and MSAN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_HARDEN"))
|
||||
FATAL("ASAN and AFL_HARDEN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
@ -208,8 +239,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN")) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN"))
|
||||
FATAL("ASAN and MSAN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN")) FATAL("ASAN and MSAN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_HARDEN"))
|
||||
FATAL("MSAN and AFL_HARDEN are mutually exclusive");
|
||||
@ -226,7 +256,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_INST_RATIO"))
|
||||
FATAL("AFL_INST_RATIO not available at compile time with 'trace-pc'.");
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
#endif /* USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
|
||||
if (!getenv("AFL_DONT_OPTIMIZE")) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,6 +276,10 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USEMMAP
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-lrt";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D__AFL_HAVE_MANUAL_CONTROL=1";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D__AFL_COMPILER=1";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-DFUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION=1";
|
||||
@ -270,35 +304,41 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D__AFL_LOOP(_A)="
|
||||
"({ static volatile char *_B __attribute__((used)); "
|
||||
" _B = (char*)\"" PERSIST_SIG "\"; "
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
"-D__AFL_LOOP(_A)="
|
||||
"({ static volatile char *_B __attribute__((used)); "
|
||||
" _B = (char*)\"" PERSIST_SIG
|
||||
"\"; "
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"int _L(unsigned int) __asm__(\"___afl_persistent_loop\"); "
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"int _L(unsigned int) __asm__(\"___afl_persistent_loop\"); "
|
||||
#else
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"int _L(unsigned int) __asm__(\"__afl_persistent_loop\"); "
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
"_L(_A); })";
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"int _L(unsigned int) __asm__(\"__afl_persistent_loop\"); "
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
"_L(_A); })";
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-D__AFL_INIT()="
|
||||
"do { static volatile char *_A __attribute__((used)); "
|
||||
" _A = (char*)\"" DEFER_SIG "\"; "
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
"-D__AFL_INIT()="
|
||||
"do { static volatile char *_A __attribute__((used)); "
|
||||
" _A = (char*)\"" DEFER_SIG
|
||||
"\"; "
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"void _I(void) __asm__(\"___afl_manual_init\"); "
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"void _I(void) __asm__(\"___afl_manual_init\"); "
|
||||
#else
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"void _I(void) __asm__(\"__afl_manual_init\"); "
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
"_I(); } while (0)";
|
||||
"__attribute__((visibility(\"default\"))) "
|
||||
"void _I(void) __asm__(\"__afl_manual_init\"); "
|
||||
#endif /* ^__APPLE__ */
|
||||
"_I(); } while (0)";
|
||||
|
||||
if (maybe_linking) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (x_set) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-x";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "none";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch (bit_mode) {
|
||||
@ -331,54 +371,70 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Main entry point */
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (isatty(2) && !getenv("AFL_QUIET")) {
|
||||
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "-h") == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_TRACE_PC
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "afl-clang-fast" VERSION cRST " [tpcg] by <lszekeres@google.com>\n");
|
||||
printf(
|
||||
cCYA
|
||||
"afl-clang-fast" VERSION cRST
|
||||
" [tpcg] by <lszekeres@google.com>\n"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "afl-clang-fast" VERSION cRST " by <lszekeres@google.com>\n");
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
printf(
|
||||
cCYA
|
||||
"afl-clang-fast" VERSION cRST
|
||||
" by <lszekeres@google.com>\n"
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"afl-clang-fast[++] [options]\n"
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"This is a helper application for afl-fuzz. It serves as a drop-in "
|
||||
"replacement\n"
|
||||
"for clang, letting you recompile third-party code with the required "
|
||||
"runtime\n"
|
||||
"instrumentation. A common use pattern would be one of the "
|
||||
"following:\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
" CC=%s/afl-clang-fast ./configure\n"
|
||||
" CXX=%s/afl-clang-fast++ ./configure\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc < 2) {
|
||||
"In contrast to the traditional afl-clang tool, this version is "
|
||||
"implemented as\n"
|
||||
"an LLVM pass and tends to offer improved performance with slow "
|
||||
"programs.\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF("\n"
|
||||
"This is a helper application for afl-fuzz. It serves as a drop-in replacement\n"
|
||||
"for clang, letting you recompile third-party code with the required runtime\n"
|
||||
"instrumentation. A common use pattern would be one of the following:\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
" CC=%s/afl-clang-fast ./configure\n"
|
||||
" CXX=%s/afl-clang-fast++ ./configure\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
"In contrast to the traditional afl-clang tool, this version is implemented as\n"
|
||||
"an LLVM pass and tends to offer improved performance with slow programs.\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
"You can specify custom next-stage toolchain via AFL_CC and AFL_CXX. Setting\n"
|
||||
"AFL_HARDEN enables hardening optimizations in the compiled code.\n\n",
|
||||
BIN_PATH, BIN_PATH);
|
||||
"You can specify custom next-stage toolchain via AFL_CC and AFL_CXX. "
|
||||
"Setting\n"
|
||||
"AFL_HARDEN enables hardening optimizations in the compiled code.\n\n",
|
||||
BIN_PATH, BIN_PATH);
|
||||
|
||||
exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (isatty(2) && !getenv("AFL_QUIET")) {
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_TRACE_PC
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "afl-clang-fast" VERSION cRST
|
||||
" [tpcg] by <lszekeres@google.com>\n");
|
||||
#else
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "afl-clang-fast" VERSION cRST " by <lszekeres@google.com>\n");
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
find_obj(argv[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
edit_params(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
printf("EXEC:");
|
||||
while (cc_params[i] != NULL)
|
||||
printf(" %s", cc_params[i++]);
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
printf("EXEC:");
|
||||
while (cc_params[i] != NULL)
|
||||
printf(" %s", cc_params[i++]);
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
execvp(cc_params[0], (char**)cc_params);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -387,3 +443,4 @@ int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM integration design comes from Laszlo Szekeres. C bits copied-and-pasted
|
||||
from afl-as.c are Michal's fault.
|
||||
@ -24,13 +24,18 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#define AFL_LLVM_PASS
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../debug.h"
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/DebugInfo.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/BasicBlock.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/IRBuilder.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/LegacyPassManager.h"
|
||||
@ -43,32 +48,52 @@ using namespace llvm;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
class AFLCoverage : public ModulePass {
|
||||
class AFLCoverage : public ModulePass {
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
AFLCoverage() : ModulePass(ID) {
|
||||
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
AFLCoverage() : ModulePass(ID) { }
|
||||
char *instWhiteListFilename = getenv("AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST");
|
||||
if (instWhiteListFilename) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
std::string line;
|
||||
std::ifstream fileStream;
|
||||
fileStream.open(instWhiteListFilename);
|
||||
if (!fileStream) report_fatal_error("Unable to open AFL_LLVM_WHITELIST");
|
||||
getline(fileStream, line);
|
||||
while (fileStream) {
|
||||
|
||||
// StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
// return "American Fuzzy Lop Instrumentation";
|
||||
// }
|
||||
myWhitelist.push_back(line);
|
||||
getline(fileStream, line);
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
|
||||
// StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
// return "American Fuzzy Lop Instrumentation";
|
||||
// }
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
std::list<std::string> myWhitelist;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
char AFLCoverage::ID = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMContext &C = M.getContext();
|
||||
|
||||
IntegerType *Int8Ty = IntegerType::getInt8Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int8Ty = IntegerType::getInt8Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int32Ty = IntegerType::getInt32Ty(C);
|
||||
unsigned int cur_loc = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,11 +105,13 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF(cCYA "afl-llvm-pass" VERSION cRST " by <lszekeres@google.com>\n");
|
||||
|
||||
} else be_quiet = 1;
|
||||
} else if (getenv("AFL_QUIET"))
|
||||
|
||||
be_quiet = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Decide instrumentation ratio */
|
||||
|
||||
char* inst_ratio_str = getenv("AFL_INST_RATIO");
|
||||
char * inst_ratio_str = getenv("AFL_INST_RATIO");
|
||||
unsigned int inst_ratio = 100;
|
||||
|
||||
if (inst_ratio_str) {
|
||||
@ -95,6 +122,10 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
char *neverZero_counters_str = getenv("AFL_LLVM_NOT_ZERO");
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Get globals for the SHM region and the previous location. Note that
|
||||
__afl_prev_loc is thread-local. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,9 +133,14 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
new GlobalVariable(M, PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0), false,
|
||||
GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage, 0, "__afl_area_ptr");
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __ANDROID__
|
||||
GlobalVariable *AFLPrevLoc = new GlobalVariable(
|
||||
M, Int32Ty, false, GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage, 0, "__afl_prev_loc",
|
||||
0, GlobalVariable::GeneralDynamicTLSModel, 0, false);
|
||||
M, Int32Ty, false, GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage, 0, "__afl_prev_loc");
|
||||
#else
|
||||
GlobalVariable *AFLPrevLoc = new GlobalVariable(
|
||||
M, Int32Ty, false, GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage, 0, "__afl_prev_loc", 0,
|
||||
GlobalVariable::GeneralDynamicTLSModel, 0, false);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Instrument all the things! */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,39 +150,112 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock::iterator IP = BB.getFirstInsertionPt();
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&(*IP));
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&(*IP));
|
||||
|
||||
if (!myWhitelist.empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool instrumentBlock = false;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Get the current location using debug information.
|
||||
* For now, just instrument the block if we are not able
|
||||
* to determine our location. */
|
||||
DebugLoc Loc = IP->getDebugLoc();
|
||||
if (Loc) {
|
||||
|
||||
DILocation *cDILoc = dyn_cast<DILocation>(Loc.getAsMDNode());
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned int instLine = cDILoc->getLine();
|
||||
StringRef instFilename = cDILoc->getFilename();
|
||||
|
||||
if (instFilename.str().empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* If the original location is empty, try using the inlined location
|
||||
*/
|
||||
DILocation *oDILoc = cDILoc->getInlinedAt();
|
||||
if (oDILoc) {
|
||||
|
||||
instFilename = oDILoc->getFilename();
|
||||
instLine = oDILoc->getLine();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Continue only if we know where we actually are */
|
||||
if (!instFilename.str().empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::list<std::string>::iterator it = myWhitelist.begin();
|
||||
it != myWhitelist.end(); ++it) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* We don't check for filename equality here because
|
||||
* filenames might actually be full paths. Instead we
|
||||
* check that the actual filename ends in the filename
|
||||
* specified in the list. */
|
||||
if (instFilename.str().length() >= it->length()) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (instFilename.str().compare(
|
||||
instFilename.str().length() - it->length(),
|
||||
it->length(), *it) == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrumentBlock = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Either we couldn't figure out our location or the location is
|
||||
* not whitelisted, so we skip instrumentation. */
|
||||
if (!instrumentBlock) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (AFL_R(100) >= inst_ratio) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make up cur_loc */
|
||||
|
||||
//cur_loc++;
|
||||
// cur_loc++;
|
||||
cur_loc = AFL_R(MAP_SIZE);
|
||||
|
||||
/* There is a problem with Ubuntu 18.04 and llvm 6.0 (see issue #63).
|
||||
The inline function successors() is not inlined and also not found at runtime
|
||||
:-( As I am unable to detect Ubuntu18.04 heree, the next best thing is to
|
||||
disable this optional optimization for LLVM 6.0.0 and Linux */
|
||||
#if !(LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR == 6 && LLVM_VERSION_MINOR == 0) || !defined __linux__
|
||||
// only instrument if this basic block is the destination of a previous
|
||||
// basic block that has multiple successors
|
||||
// this gets rid of ~5-10% of instrumentations that are unnecessary
|
||||
// result: a little more speed and less map pollution
|
||||
int more_than_one = -1;
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, "BB %u: ", cur_loc);
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "BB %u: ", cur_loc);
|
||||
for (BasicBlock *Pred : predecessors(&BB)) {
|
||||
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
if (more_than_one == -1)
|
||||
more_than_one = 0;
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, " %p=>", Pred);
|
||||
if (more_than_one == -1) more_than_one = 0;
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, " %p=>", Pred);
|
||||
|
||||
for (BasicBlock *Succ : successors(Pred)) {
|
||||
//if (count > 0)
|
||||
|
||||
// if (count > 0)
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "|");
|
||||
if (Succ != NULL) count++;
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, "%p", Succ);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (count > 1)
|
||||
more_than_one = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, " == %d\n", more_than_one);
|
||||
if (more_than_one != 1)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "%p", Succ);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (count > 1) more_than_one = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, " == %d\n", more_than_one);
|
||||
if (more_than_one != 1) continue;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
ConstantInt *CurLoc = ConstantInt::get(Int32Ty, cur_loc);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Load prev_loc */
|
||||
@ -166,7 +275,77 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *Counter = IRB.CreateLoad(MapPtrIdx);
|
||||
Counter->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
|
||||
Value *Incr = IRB.CreateAdd(Counter, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1));
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
if (neverZero_counters_str !=
|
||||
NULL) { // with llvm 9 we make this the default as the bug in llvm is
|
||||
// then fixed
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
/* hexcoder: Realize a counter that skips zero during overflow.
|
||||
* Once this counter reaches its maximum value, it next increments to 1
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Instead of
|
||||
* Counter + 1 -> Counter
|
||||
* we inject now this
|
||||
* Counter + 1 -> {Counter, OverflowFlag}
|
||||
* Counter + OverflowFlag -> Counter
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/* // we keep the old solutions just in case
|
||||
// Solution #1
|
||||
if (neverZero_counters_str[0] == '1') {
|
||||
|
||||
CallInst *AddOv =
|
||||
IRB.CreateBinaryIntrinsic(Intrinsic::uadd_with_overflow, Counter,
|
||||
ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1));
|
||||
AddOv->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"),
|
||||
MDNode::get(C, None)); Value *SumWithOverflowBit = AddOv; Incr =
|
||||
IRB.CreateAdd(IRB.CreateExtractValue(SumWithOverflowBit, 0), // sum
|
||||
IRB.CreateZExt( // convert from one bit
|
||||
type to 8 bits type IRB.CreateExtractValue(SumWithOverflowBit, 1), //
|
||||
overflow Int8Ty));
|
||||
// Solution #2
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (neverZero_counters_str[0] == '2') {
|
||||
|
||||
auto cf = IRB.CreateICmpEQ(Counter,
|
||||
ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 255)); Value *HowMuch =
|
||||
IRB.CreateAdd(ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1), cf); Incr =
|
||||
IRB.CreateAdd(Counter, HowMuch);
|
||||
// Solution #3
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (neverZero_counters_str[0] == '3') {
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
// this is the solution we choose because llvm9 should do the right
|
||||
// thing here
|
||||
auto cf = IRB.CreateICmpEQ(Incr, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 0));
|
||||
auto carry = IRB.CreateZExt(cf, Int8Ty);
|
||||
Incr = IRB.CreateAdd(Incr, carry);
|
||||
/*
|
||||
// Solution #4
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (neverZero_counters_str[0] == '4') {
|
||||
|
||||
auto cf = IRB.CreateICmpULT(Incr, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1));
|
||||
auto carry = IRB.CreateZExt(cf, Int8Ty);
|
||||
Incr = IRB.CreateAdd(Incr, carry);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "Error: unknown value for AFL_NZERO_COUNTS: %s
|
||||
(valid is 1-4)\n", neverZero_counters_str); exit(-1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
IRB.CreateStore(Incr, MapPtrIdx)
|
||||
->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -184,11 +363,16 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!inst_blocks) WARNF("No instrumentation targets found.");
|
||||
else OKF("Instrumented %u locations (%s mode, ratio %u%%).",
|
||||
inst_blocks, getenv("AFL_HARDEN") ? "hardened" :
|
||||
((getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN") || getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN")) ?
|
||||
"ASAN/MSAN" : "non-hardened"), inst_ratio);
|
||||
if (!inst_blocks)
|
||||
WARNF("No instrumentation targets found.");
|
||||
else
|
||||
OKF("Instrumented %u locations (%s mode, ratio %u%%).", inst_blocks,
|
||||
getenv("AFL_HARDEN")
|
||||
? "hardened"
|
||||
: ((getenv("AFL_USE_ASAN") || getenv("AFL_USE_MSAN"))
|
||||
? "ASAN/MSAN"
|
||||
: "non-hardened"),
|
||||
inst_ratio);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -196,7 +380,6 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static void registerAFLPass(const PassManagerBuilder &,
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -204,9 +387,9 @@ static void registerAFLPass(const PassManagerBuilder &,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterAFLPass(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_OptimizerLast, registerAFLPass);
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterAFLPass0(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_EnabledOnOptLevel0, registerAFLPass);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Laszlo Szekeres <lszekeres@google.com> and
|
||||
Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com>
|
||||
Michal Zalewski
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM integration design comes from Laszlo Szekeres.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,8 +19,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../config.h"
|
||||
#include "../types.h"
|
||||
#ifdef __ANDROID__
|
||||
#include "android-ashmem.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
@ -39,32 +42,36 @@
|
||||
the LLVM-generated runtime initialization pass, not before. */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_TRACE_PC
|
||||
# define CONST_PRIO 5
|
||||
#define CONST_PRIO 5
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define CONST_PRIO 0
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
#define CONST_PRIO 0
|
||||
#endif /* ^USE_TRACE_PC */
|
||||
|
||||
#include <sys/mman.h>
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/* Globals needed by the injected instrumentation. The __afl_area_initial region
|
||||
is used for instrumentation output before __afl_map_shm() has a chance to run.
|
||||
It will end up as .comm, so it shouldn't be too wasteful. */
|
||||
is used for instrumentation output before __afl_map_shm() has a chance to
|
||||
run. It will end up as .comm, so it shouldn't be too wasteful. */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 __afl_area_initial[MAP_SIZE];
|
||||
u8* __afl_area_ptr = __afl_area_initial;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __ANDROID__
|
||||
u32 __afl_prev_loc;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
__thread u32 __afl_prev_loc;
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Running in persistent mode? */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 is_persistent;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* SHM setup. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void __afl_map_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *id_str = getenv(SHM_ENV_VAR);
|
||||
u8* id_str = getenv(SHM_ENV_VAR);
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we're running under AFL, attach to the appropriate region, replacing the
|
||||
early-stage __afl_area_initial region that is needed to allow some really
|
||||
@ -72,13 +79,42 @@ static void __afl_map_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (id_str) {
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USEMMAP
|
||||
const char* shm_file_path = id_str;
|
||||
int shm_fd = -1;
|
||||
unsigned char* shm_base = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
/* create the shared memory segment as if it was a file */
|
||||
shm_fd = shm_open(shm_file_path, O_RDWR, 0600);
|
||||
if (shm_fd == -1) {
|
||||
|
||||
printf("shm_open() failed\n");
|
||||
exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* map the shared memory segment to the address space of the process */
|
||||
shm_base = mmap(0, MAP_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
|
||||
if (shm_base == MAP_FAILED) {
|
||||
|
||||
close(shm_fd);
|
||||
shm_fd = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
printf("mmap() failed\n");
|
||||
exit(2);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr = shm_base;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
u32 shm_id = atoi(id_str);
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr = shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Whooooops. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_area_ptr == (void *)-1) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (__afl_area_ptr == (void*)-1) _exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write something into the bitmap so that even with low AFL_INST_RATIO,
|
||||
our parent doesn't give up on us. */
|
||||
@ -89,16 +125,15 @@ static void __afl_map_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fork server logic. */
|
||||
|
||||
static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 tmp[4];
|
||||
s32 child_pid;
|
||||
s32 child_pid;
|
||||
|
||||
u8 child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
u8 child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
void (*old_sigchld_handler)(int) = signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_DFL);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Phone home and tell the parent that we're OK. If parent isn't there,
|
||||
@ -120,8 +155,10 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
process. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_stopped && was_killed) {
|
||||
|
||||
child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) < 0) _exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!child_stopped) {
|
||||
@ -134,12 +171,13 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (!child_pid) {
|
||||
|
||||
signal(SIGCHLD, old_sigchld_handler);
|
||||
|
||||
close(FORKSRV_FD);
|
||||
close(FORKSRV_FD + 1);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
@ -173,7 +211,6 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* A simplified persistent mode handler, used as explained in README.llvm. */
|
||||
|
||||
int __afl_persistent_loop(unsigned int max_cnt) {
|
||||
@ -193,9 +230,10 @@ int __afl_persistent_loop(unsigned int max_cnt) {
|
||||
memset(__afl_area_ptr, 0, MAP_SIZE);
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr[0] = 1;
|
||||
__afl_prev_loc = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cycle_cnt = max_cnt;
|
||||
cycle_cnt = max_cnt;
|
||||
first_pass = 0;
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -228,7 +266,6 @@ int __afl_persistent_loop(unsigned int max_cnt) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* This one can be called from user code when deferred forkserver mode
|
||||
is enabled. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,7 +283,6 @@ void __afl_manual_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Proper initialization routine. */
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((constructor(CONST_PRIO))) void __afl_auto_init(void) {
|
||||
@ -259,7 +295,6 @@ __attribute__((constructor(CONST_PRIO))) void __afl_auto_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* The following stuff deals with supporting -fsanitize-coverage=trace-pc-guard.
|
||||
It remains non-operational in the traditional, plugin-backed LLVM mode.
|
||||
For more info about 'trace-pc-guard', see README.llvm.
|
||||
@ -268,9 +303,10 @@ __attribute__((constructor(CONST_PRIO))) void __afl_auto_init(void) {
|
||||
edge (as opposed to every basic block). */
|
||||
|
||||
void __sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard(uint32_t* guard) {
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr[*guard]++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr[*guard]++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Init callback. Populates instrumentation IDs. Note that we're using
|
||||
ID of 0 as a special value to indicate non-instrumented bits. That may
|
||||
@ -287,8 +323,10 @@ void __sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard_init(uint32_t* start, uint32_t* stop) {
|
||||
if (x) inst_ratio = atoi(x);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!inst_ratio || inst_ratio > 100) {
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "[-] ERROR: Invalid AFL_INST_RATIO (must be 1-100).\n");
|
||||
abort();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make sure that the first element in the range is always set - we use that
|
||||
@ -299,11 +337,14 @@ void __sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard_init(uint32_t* start, uint32_t* stop) {
|
||||
|
||||
while (start < stop) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (R(100) < inst_ratio) *start = R(MAP_SIZE - 1) + 1;
|
||||
else *start = 0;
|
||||
if (R(100) < inst_ratio)
|
||||
*start = R(MAP_SIZE - 1) + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
*start = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
start++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,191 +36,236 @@ using namespace llvm;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
class CompareTransform : public ModulePass {
|
||||
class CompareTransform : public ModulePass {
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
CompareTransform() : ModulePass(ID) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
CompareTransform() : ModulePass(ID) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 4
|
||||
const char * getPassName() const override {
|
||||
#else
|
||||
StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return "transforms compare functions";
|
||||
}
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp, const bool processMemcmp
|
||||
,const bool processStrncmp, const bool processStrcasecmp, const bool processStrncasecmp);
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
const char *getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return "transforms compare functions";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp,
|
||||
const bool processMemcmp, const bool processStrncmp,
|
||||
const bool processStrcasecmp,
|
||||
const bool processStrncasecmp);
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
char CompareTransform::ID = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
bool CompareTransform::transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp, const bool processMemcmp
|
||||
, const bool processStrncmp, const bool processStrcasecmp, const bool processStrncasecmp) {
|
||||
bool CompareTransform::transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp,
|
||||
const bool processMemcmp,
|
||||
const bool processStrncmp,
|
||||
const bool processStrcasecmp,
|
||||
const bool processStrncasecmp) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<CallInst*> calls;
|
||||
LLVMContext &C = M.getContext();
|
||||
IntegerType *Int8Ty = IntegerType::getInt8Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int32Ty = IntegerType::getInt32Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int64Ty = IntegerType::getInt64Ty(C);
|
||||
std::vector<CallInst *> calls;
|
||||
LLVMContext & C = M.getContext();
|
||||
IntegerType * Int8Ty = IntegerType::getInt8Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType * Int32Ty = IntegerType::getInt32Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType * Int64Ty = IntegerType::getInt64Ty(C);
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Constant*
|
||||
Constant *
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
c = M.getOrInsertFunction("tolower",
|
||||
Int32Ty,
|
||||
Int32Ty
|
||||
c = M.getOrInsertFunction("tolower", Int32Ty, Int32Ty
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
, nullptr
|
||||
,
|
||||
nullptr
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
);
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Function *tolowerFn = cast<Function>(c);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee tolowerFn = c;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
);
|
||||
Function* tolowerFn = cast<Function>(c);
|
||||
|
||||
/* iterate over all functions, bbs and instruction and add suitable calls to strcmp/memcmp/strncmp/strcasecmp/strncasecmp */
|
||||
/* iterate over all functions, bbs and instruction and add suitable calls to
|
||||
* strcmp/memcmp/strncmp/strcasecmp/strncasecmp */
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
for(auto &IN: BB) {
|
||||
CallInst* callInst = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &IN : BB) {
|
||||
|
||||
CallInst *callInst = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
if ((callInst = dyn_cast<CallInst>(&IN))) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool isStrcmp = processStrcmp;
|
||||
bool isMemcmp = processMemcmp;
|
||||
bool isStrncmp = processStrncmp;
|
||||
bool isStrcasecmp = processStrcasecmp;
|
||||
bool isStrcmp = processStrcmp;
|
||||
bool isMemcmp = processMemcmp;
|
||||
bool isStrncmp = processStrncmp;
|
||||
bool isStrcasecmp = processStrcasecmp;
|
||||
bool isStrncasecmp = processStrncasecmp;
|
||||
|
||||
Function *Callee = callInst->getCalledFunction();
|
||||
if (!Callee)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
if (callInst->getCallingConv() != llvm::CallingConv::C)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
if (!Callee) continue;
|
||||
if (callInst->getCallingConv() != llvm::CallingConv::C) continue;
|
||||
StringRef FuncName = Callee->getName();
|
||||
isStrcmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strcmp"));
|
||||
isMemcmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("memcmp"));
|
||||
isStrncmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strncmp"));
|
||||
isStrcasecmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strcasecmp"));
|
||||
isStrcmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strcmp"));
|
||||
isMemcmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("memcmp"));
|
||||
isStrncmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strncmp"));
|
||||
isStrcasecmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strcasecmp"));
|
||||
isStrncasecmp &= !FuncName.compare(StringRef("strncasecmp"));
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isStrcmp && !isMemcmp && !isStrncmp && !isStrcasecmp && !isStrncasecmp)
|
||||
if (!isStrcmp && !isMemcmp && !isStrncmp && !isStrcasecmp &&
|
||||
!isStrncasecmp)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Verify the strcmp/memcmp/strncmp/strcasecmp/strncasecmp function prototype */
|
||||
/* Verify the strcmp/memcmp/strncmp/strcasecmp/strncasecmp function
|
||||
* prototype */
|
||||
FunctionType *FT = Callee->getFunctionType();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
isStrcmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 2 &&
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext());
|
||||
isStrcasecmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 2 &&
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext());
|
||||
isMemcmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 3 &&
|
||||
isStrcmp &=
|
||||
FT->getNumParams() == 2 && FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext());
|
||||
isStrcasecmp &=
|
||||
FT->getNumParams() == 2 && FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext());
|
||||
isMemcmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 3 &&
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0)->isPointerTy() &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(1)->isPointerTy() &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(2)->isIntegerTy();
|
||||
isStrncmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 3 &&
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext()) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(2)->isIntegerTy();
|
||||
isStrncmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 3 &&
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) ==
|
||||
IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext()) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(2)->isIntegerTy();
|
||||
isStrncasecmp &= FT->getNumParams() == 3 &&
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext()) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(2)->isIntegerTy();
|
||||
FT->getReturnType()->isIntegerTy(32) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) == FT->getParamType(1) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(0) ==
|
||||
IntegerType::getInt8PtrTy(M.getContext()) &&
|
||||
FT->getParamType(2)->isIntegerTy();
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isStrcmp && !isMemcmp && !isStrncmp && !isStrcasecmp && !isStrncasecmp)
|
||||
if (!isStrcmp && !isMemcmp && !isStrncmp && !isStrcasecmp &&
|
||||
!isStrncasecmp)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
/* is a str{n,}{case,}cmp/memcmp, check is we have
|
||||
/* is a str{n,}{case,}cmp/memcmp, check if we have
|
||||
* str{case,}cmp(x, "const") or str{case,}cmp("const", x)
|
||||
* strn{case,}cmp(x, "const", ..) or strn{case,}cmp("const", x, ..)
|
||||
* memcmp(x, "const", ..) or memcmp("const", x, ..) */
|
||||
Value *Str1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *Str2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
Value *Str1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0),
|
||||
*Str2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
StringRef Str1, Str2;
|
||||
bool HasStr1 = getConstantStringInfo(Str1P, Str1);
|
||||
bool HasStr2 = getConstantStringInfo(Str2P, Str2);
|
||||
bool HasStr1 = getConstantStringInfo(Str1P, Str1);
|
||||
bool HasStr2 = getConstantStringInfo(Str2P, Str2);
|
||||
|
||||
/* handle cases of one string is const, one string is variable */
|
||||
if (!(HasStr1 ^ HasStr2))
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
if (!(HasStr1 ^ HasStr2)) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
if (isMemcmp || isStrncmp || isStrncasecmp) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* check if third operand is a constant integer
|
||||
* strlen("constStr") and sizeof() are treated as constant */
|
||||
Value *op2 = callInst->getArgOperand(2);
|
||||
ConstantInt* ilen = dyn_cast<ConstantInt>(op2);
|
||||
if (!ilen)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
/* final precaution: if size of compare is larger than constant string skip it*/
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = HasStr1 ? GetStringLength(Str1P) : GetStringLength(Str2P);
|
||||
if (literalLength < ilen->getZExtValue())
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
Value * op2 = callInst->getArgOperand(2);
|
||||
ConstantInt *ilen = dyn_cast<ConstantInt>(op2);
|
||||
if (!ilen) continue;
|
||||
/* final precaution: if size of compare is larger than constant
|
||||
* string skip it*/
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength =
|
||||
HasStr1 ? GetStringLength(Str1P) : GetStringLength(Str2P);
|
||||
if (literalLength < ilen->getZExtValue()) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
calls.push_back(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!calls.size())
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
errs() << "Replacing " << calls.size() << " calls to strcmp/memcmp/strncmp/strcasecmp/strncasecmp\n";
|
||||
if (!calls.size()) return false;
|
||||
errs() << "Replacing " << calls.size()
|
||||
<< " calls to strcmp/memcmp/strncmp/strcasecmp/strncasecmp\n";
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &callInst: calls) {
|
||||
for (auto &callInst : calls) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value *Str1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *Str2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
StringRef Str1, Str2, ConstStr;
|
||||
Value *VarStr;
|
||||
bool HasStr1 = getConstantStringInfo(Str1P, Str1);
|
||||
Value *Str1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0),
|
||||
*Str2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
StringRef Str1, Str2, ConstStr;
|
||||
std::string TmpConstStr;
|
||||
Value * VarStr;
|
||||
bool HasStr1 = getConstantStringInfo(Str1P, Str1);
|
||||
getConstantStringInfo(Str2P, Str2);
|
||||
uint64_t constLen, sizedLen;
|
||||
bool isMemcmp = !callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(StringRef("memcmp"));
|
||||
bool isSizedcmp = isMemcmp
|
||||
|| !callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(StringRef("strncmp"))
|
||||
|| !callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(StringRef("strncasecmp"));
|
||||
bool isCaseInsensitive = !callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(StringRef("strcasecmp"))
|
||||
|| !callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(StringRef("strncasecmp"));
|
||||
bool isMemcmp =
|
||||
!callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(StringRef("memcmp"));
|
||||
bool isSizedcmp = isMemcmp ||
|
||||
!callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(
|
||||
StringRef("strncmp")) ||
|
||||
!callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(
|
||||
StringRef("strncasecmp"));
|
||||
bool isCaseInsensitive = !callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(
|
||||
StringRef("strcasecmp")) ||
|
||||
!callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName().compare(
|
||||
StringRef("strncasecmp"));
|
||||
|
||||
if (isSizedcmp) {
|
||||
Value *op2 = callInst->getArgOperand(2);
|
||||
ConstantInt* ilen = dyn_cast<ConstantInt>(op2);
|
||||
|
||||
Value * op2 = callInst->getArgOperand(2);
|
||||
ConstantInt *ilen = dyn_cast<ConstantInt>(op2);
|
||||
sizedLen = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (HasStr1) {
|
||||
ConstStr = Str1;
|
||||
|
||||
TmpConstStr = Str1.str();
|
||||
VarStr = Str2P;
|
||||
constLen = isMemcmp ? sizedLen : GetStringLength(Str1P);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
ConstStr = Str2;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
TmpConstStr = Str2.str();
|
||||
VarStr = Str1P;
|
||||
constLen = isMemcmp ? sizedLen : GetStringLength(Str2P);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (isSizedcmp && constLen > sizedLen) {
|
||||
constLen = sizedLen;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
errs() << callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName() << ": len " << constLen << ": " << ConstStr << "\n";
|
||||
/* properly handle zero terminated C strings by adding the terminating 0 to
|
||||
* the StringRef (in comparison to std::string a StringRef has built-in
|
||||
* runtime bounds checking, which makes debugging easier) */
|
||||
TmpConstStr.append("\0", 1);
|
||||
ConstStr = StringRef(TmpConstStr);
|
||||
|
||||
if (isSizedcmp && constLen > sizedLen) { constLen = sizedLen; }
|
||||
|
||||
errs() << callInst->getCalledFunction()->getName() << ": len " << constLen
|
||||
<< ": " << ConstStr << "\n";
|
||||
|
||||
/* split before the call instruction */
|
||||
BasicBlock *bb = callInst->getParent();
|
||||
BasicBlock *end_bb = bb->splitBasicBlock(BasicBlock::iterator(callInst));
|
||||
BasicBlock *next_bb = BasicBlock::Create(C, "cmp_added", end_bb->getParent(), end_bb);
|
||||
BasicBlock *next_bb =
|
||||
BasicBlock::Create(C, "cmp_added", end_bb->getParent(), end_bb);
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(end_bb, next_bb);
|
||||
PHINode *PN = PHINode::Create(Int32Ty, constLen + 1, "cmp_phi");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -238,74 +283,81 @@ bool CompareTransform::transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp, const
|
||||
|
||||
char c = isCaseInsensitive ? tolower(ConstStr[i]) : ConstStr[i];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock::iterator IP = next_bb->getFirstInsertionPt();
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&*IP);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(&*IP);
|
||||
|
||||
Value* v = ConstantInt::get(Int64Ty, i);
|
||||
Value *ele = IRB.CreateInBoundsGEP(VarStr, v, "empty");
|
||||
Value *v = ConstantInt::get(Int64Ty, i);
|
||||
Value *ele = IRB.CreateInBoundsGEP(VarStr, v, "empty");
|
||||
Value *load = IRB.CreateLoad(ele);
|
||||
if (isCaseInsensitive) {
|
||||
|
||||
// load >= 'A' && load <= 'Z' ? load | 0x020 : load
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
args.push_back(load);
|
||||
load = IRB.CreateCall(tolowerFn, args, "tmp");
|
||||
load = IRB.CreateTrunc(load, Int8Ty);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Value *isub;
|
||||
if (HasStr1)
|
||||
isub = IRB.CreateSub(ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, c), load);
|
||||
else
|
||||
isub = IRB.CreateSub(load, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, c));
|
||||
|
||||
Value *sext = IRB.CreateSExt(isub, Int32Ty);
|
||||
Value *sext = IRB.CreateSExt(isub, Int32Ty);
|
||||
PN->addIncoming(sext, cur_bb);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < constLen - 1) {
|
||||
next_bb = BasicBlock::Create(C, "cmp_added", end_bb->getParent(), end_bb);
|
||||
|
||||
next_bb =
|
||||
BasicBlock::Create(C, "cmp_added", end_bb->getParent(), end_bb);
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(end_bb, next_bb);
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 8
|
||||
TerminatorInst *term = cur_bb->getTerminator();
|
||||
#else
|
||||
Instruction *term = cur_bb->getTerminator();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
Value *icmp = IRB.CreateICmpEQ(isub, ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 0));
|
||||
IRB.CreateCondBr(icmp, next_bb, end_bb);
|
||||
term->eraseFromParent();
|
||||
cur_bb->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
//IRB.CreateBr(end_bb);
|
||||
|
||||
// IRB.CreateBr(end_bb);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//add offset to varstr
|
||||
//create load
|
||||
//create signed isub
|
||||
//create icmp
|
||||
//create jcc
|
||||
//create next_bb
|
||||
// add offset to varstr
|
||||
// create load
|
||||
// create signed isub
|
||||
// create icmp
|
||||
// create jcc
|
||||
// create next_bb
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* since the call is the first instruction of the bb it is safe to
|
||||
* replace it with a phi instruction */
|
||||
BasicBlock::iterator ii(callInst);
|
||||
ReplaceInstWithInst(callInst->getParent()->getInstList(), ii, PN);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool CompareTransform::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
llvm::errs() << "Running compare-transform-pass by laf.intel@gmail.com, extended by heiko@hexco.de\n";
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_QUIET") == NULL)
|
||||
llvm::errs() << "Running compare-transform-pass by laf.intel@gmail.com, "
|
||||
"extended by heiko@hexco.de\n";
|
||||
transformCmps(M, true, true, true, true, true);
|
||||
verifyModule(M);
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void registerCompTransPass(const PassManagerBuilder &,
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto p = new CompareTransform();
|
||||
PM.add(p);
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -36,95 +36,120 @@ using namespace llvm;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
class SplitSwitchesTransform : public ModulePass {
|
||||
class SplitSwitchesTransform : public ModulePass {
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
SplitSwitchesTransform() : ModulePass(ID) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
SplitSwitchesTransform() : ModulePass(ID) {
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR >= 4
|
||||
StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
const char * getPassName() const override {
|
||||
const char *getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return "splits switch constructs";
|
||||
}
|
||||
struct CaseExpr {
|
||||
ConstantInt* Val;
|
||||
BasicBlock* BB;
|
||||
return "splits switch constructs";
|
||||
|
||||
CaseExpr(ConstantInt *val = nullptr, BasicBlock *bb = nullptr) :
|
||||
Val(val), BB(bb) { }
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
typedef std::vector<CaseExpr> CaseVector;
|
||||
struct CaseExpr {
|
||||
|
||||
ConstantInt *Val;
|
||||
BasicBlock * BB;
|
||||
|
||||
CaseExpr(ConstantInt *val = nullptr, BasicBlock *bb = nullptr)
|
||||
: Val(val), BB(bb) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool splitSwitches(Module &M);
|
||||
bool transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp, const bool processMemcmp);
|
||||
BasicBlock* switchConvert(CaseVector Cases, std::vector<bool> bytesChecked,
|
||||
BasicBlock* OrigBlock, BasicBlock* NewDefault,
|
||||
Value* Val, unsigned level);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
typedef std::vector<CaseExpr> CaseVector;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool splitSwitches(Module &M);
|
||||
bool transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp,
|
||||
const bool processMemcmp);
|
||||
BasicBlock *switchConvert(CaseVector Cases, std::vector<bool> bytesChecked,
|
||||
BasicBlock *OrigBlock, BasicBlock *NewDefault,
|
||||
Value *Val, unsigned level);
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
char SplitSwitchesTransform::ID = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* switchConvert - Transform simple list of Cases into list of CaseRange's */
|
||||
BasicBlock* SplitSwitchesTransform::switchConvert(CaseVector Cases, std::vector<bool> bytesChecked,
|
||||
BasicBlock* OrigBlock, BasicBlock* NewDefault,
|
||||
Value* Val, unsigned level) {
|
||||
BasicBlock *SplitSwitchesTransform::switchConvert(
|
||||
CaseVector Cases, std::vector<bool> bytesChecked, BasicBlock *OrigBlock,
|
||||
BasicBlock *NewDefault, Value *Val, unsigned level) {
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned ValTypeBitWidth = Cases[0].Val->getBitWidth();
|
||||
IntegerType *ValType = IntegerType::get(OrigBlock->getContext(), ValTypeBitWidth);
|
||||
IntegerType *ByteType = IntegerType::get(OrigBlock->getContext(), 8);
|
||||
unsigned BytesInValue = bytesChecked.size();
|
||||
unsigned ValTypeBitWidth = Cases[0].Val->getBitWidth();
|
||||
IntegerType *ValType =
|
||||
IntegerType::get(OrigBlock->getContext(), ValTypeBitWidth);
|
||||
IntegerType * ByteType = IntegerType::get(OrigBlock->getContext(), 8);
|
||||
unsigned BytesInValue = bytesChecked.size();
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> setSizes;
|
||||
std::vector<std::set<uint8_t>> byteSets(BytesInValue, std::set<uint8_t>());
|
||||
|
||||
assert(ValTypeBitWidth >= 8 && ValTypeBitWidth <= 64);
|
||||
|
||||
/* for each of the possible cases we iterate over all bytes of the values
|
||||
* build a set of possible values at each byte position in byteSets */
|
||||
for (CaseExpr& Case: Cases) {
|
||||
for (CaseExpr &Case : Cases) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (unsigned i = 0; i < BytesInValue; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t byte = (Case.Val->getZExtValue() >> (i*8)) & 0xFF;
|
||||
uint8_t byte = (Case.Val->getZExtValue() >> (i * 8)) & 0xFF;
|
||||
byteSets[i].insert(byte);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* find the index of the first byte position that was not yet checked. then
|
||||
* save the number of possible values at that byte position */
|
||||
unsigned smallestIndex = 0;
|
||||
unsigned smallestSize = 257;
|
||||
for(unsigned i = 0; i < byteSets.size(); i++) {
|
||||
if (bytesChecked[i])
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
for (unsigned i = 0; i < byteSets.size(); i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (bytesChecked[i]) continue;
|
||||
if (byteSets[i].size() < smallestSize) {
|
||||
|
||||
smallestIndex = i;
|
||||
smallestSize = byteSets[i].size();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
assert(bytesChecked[smallestIndex] == false);
|
||||
|
||||
/* there are only smallestSize different bytes at index smallestIndex */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Instruction *Shift, *Trunc;
|
||||
Function* F = OrigBlock->getParent();
|
||||
BasicBlock* NewNode = BasicBlock::Create(Val->getContext(), "NodeBlock", F);
|
||||
Shift = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::LShr, Val, ConstantInt::get(ValType, smallestIndex * 8));
|
||||
Function * F = OrigBlock->getParent();
|
||||
BasicBlock * NewNode = BasicBlock::Create(Val->getContext(), "NodeBlock", F);
|
||||
Shift = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::LShr, Val,
|
||||
ConstantInt::get(ValType, smallestIndex * 8));
|
||||
NewNode->getInstList().push_back(Shift);
|
||||
|
||||
if (ValTypeBitWidth > 8) {
|
||||
|
||||
Trunc = new TruncInst(Shift, ByteType);
|
||||
NewNode->getInstList().push_back(Trunc);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
/* not necessary to trunc */
|
||||
Trunc = Shift;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* this is a trivial case, we can directly check for the byte,
|
||||
@ -132,113 +157,155 @@ BasicBlock* SplitSwitchesTransform::switchConvert(CaseVector Cases, std::vector<
|
||||
* mark the byte as checked. if this was the last byte to check
|
||||
* we can finally execute the block belonging to this case */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (smallestSize == 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t byte = *(byteSets[smallestIndex].begin());
|
||||
|
||||
/* insert instructions to check whether the value we are switching on is equal to byte */
|
||||
ICmpInst* Comp = new ICmpInst(ICmpInst::ICMP_EQ, Trunc, ConstantInt::get(ByteType, byte), "byteMatch");
|
||||
/* insert instructions to check whether the value we are switching on is
|
||||
* equal to byte */
|
||||
ICmpInst *Comp =
|
||||
new ICmpInst(ICmpInst::ICMP_EQ, Trunc, ConstantInt::get(ByteType, byte),
|
||||
"byteMatch");
|
||||
NewNode->getInstList().push_back(Comp);
|
||||
|
||||
bytesChecked[smallestIndex] = true;
|
||||
if (std::all_of(bytesChecked.begin(), bytesChecked.end(), [](bool b){return b;} )) {
|
||||
if (std::all_of(bytesChecked.begin(), bytesChecked.end(),
|
||||
[](bool b) { return b; })) {
|
||||
|
||||
assert(Cases.size() == 1);
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(Cases[0].BB, NewDefault, Comp, NewNode);
|
||||
|
||||
/* we have to update the phi nodes! */
|
||||
for (BasicBlock::iterator I = Cases[0].BB->begin(); I != Cases[0].BB->end(); ++I) {
|
||||
if (!isa<PHINode>(&*I)) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (BasicBlock::iterator I = Cases[0].BB->begin();
|
||||
I != Cases[0].BB->end(); ++I) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isa<PHINode>(&*I)) { continue; }
|
||||
PHINode *PN = cast<PHINode>(I);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Only update the first occurence. */
|
||||
/* Only update the first occurrence. */
|
||||
unsigned Idx = 0, E = PN->getNumIncomingValues();
|
||||
for (; Idx != E; ++Idx) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (PN->getIncomingBlock(Idx) == OrigBlock) {
|
||||
|
||||
PN->setIncomingBlock(Idx, NewNode);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
BasicBlock* BB = switchConvert(Cases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val, level + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock *BB = switchConvert(Cases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault,
|
||||
Val, level + 1);
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(BB, NewDefault, Comp, NewNode);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* there is no byte which we can directly check on, split the tree */
|
||||
else {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> byteVector;
|
||||
std::copy(byteSets[smallestIndex].begin(), byteSets[smallestIndex].end(), std::back_inserter(byteVector));
|
||||
std::copy(byteSets[smallestIndex].begin(), byteSets[smallestIndex].end(),
|
||||
std::back_inserter(byteVector));
|
||||
std::sort(byteVector.begin(), byteVector.end());
|
||||
uint8_t pivot = byteVector[byteVector.size() / 2];
|
||||
|
||||
/* we already chose to divide the cases based on the value of byte at index smallestIndex
|
||||
* the pivot value determines the threshold for the decicion; if a case value
|
||||
* is smaller at this byte index move it to the LHS vector, otherwise to the RHS vector */
|
||||
/* we already chose to divide the cases based on the value of byte at index
|
||||
* smallestIndex the pivot value determines the threshold for the decicion;
|
||||
* if a case value
|
||||
* is smaller at this byte index move it to the LHS vector, otherwise to the
|
||||
* RHS vector */
|
||||
|
||||
CaseVector LHSCases, RHSCases;
|
||||
|
||||
for (CaseExpr& Case: Cases) {
|
||||
uint8_t byte = (Case.Val->getZExtValue() >> (smallestIndex*8)) & 0xFF;
|
||||
for (CaseExpr &Case : Cases) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t byte = (Case.Val->getZExtValue() >> (smallestIndex * 8)) & 0xFF;
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte < pivot) {
|
||||
LHSCases.push_back(Case);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
RHSCases.push_back(Case);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BasicBlock *LBB, *RBB;
|
||||
LBB = switchConvert(LHSCases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val, level + 1);
|
||||
RBB = switchConvert(RHSCases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val, level + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* insert instructions to check whether the value we are switching on is equal to byte */
|
||||
ICmpInst* Comp = new ICmpInst(ICmpInst::ICMP_ULT, Trunc, ConstantInt::get(ByteType, pivot), "byteMatch");
|
||||
LHSCases.push_back(Case);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
RHSCases.push_back(Case);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock *LBB, *RBB;
|
||||
LBB = switchConvert(LHSCases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val,
|
||||
level + 1);
|
||||
RBB = switchConvert(RHSCases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val,
|
||||
level + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
/* insert instructions to check whether the value we are switching on is
|
||||
* equal to byte */
|
||||
ICmpInst *Comp =
|
||||
new ICmpInst(ICmpInst::ICMP_ULT, Trunc,
|
||||
ConstantInt::get(ByteType, pivot), "byteMatch");
|
||||
NewNode->getInstList().push_back(Comp);
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(LBB, RBB, Comp, NewNode);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return NewNode;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool SplitSwitchesTransform::splitSwitches(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<SwitchInst*> switches;
|
||||
std::vector<SwitchInst *> switches;
|
||||
|
||||
/* iterate over all functions, bbs and instruction and add
|
||||
* all switches to switches vector for later processing */
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
SwitchInst* switchInst = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
SwitchInst *switchInst = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
if ((switchInst = dyn_cast<SwitchInst>(BB.getTerminator()))) {
|
||||
if (switchInst->getNumCases() < 1)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
switches.push_back(switchInst);
|
||||
|
||||
if (switchInst->getNumCases() < 1) continue;
|
||||
switches.push_back(switchInst);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!switches.size())
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
errs() << "Rewriting " << switches.size() << " switch statements " << "\n";
|
||||
if (!switches.size()) return false;
|
||||
errs() << "Rewriting " << switches.size() << " switch statements "
|
||||
<< "\n";
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &SI: switches) {
|
||||
for (auto &SI : switches) {
|
||||
|
||||
BasicBlock *CurBlock = SI->getParent();
|
||||
BasicBlock *OrigBlock = CurBlock;
|
||||
Function *F = CurBlock->getParent();
|
||||
Function * F = CurBlock->getParent();
|
||||
/* this is the value we are switching on */
|
||||
Value *Val = SI->getCondition();
|
||||
BasicBlock* Default = SI->getDefaultDest();
|
||||
Value * Val = SI->getCondition();
|
||||
BasicBlock *Default = SI->getDefaultDest();
|
||||
unsigned bitw = Val->getType()->getIntegerBitWidth();
|
||||
|
||||
/* If there is only the default destination, don't bother with the code below. */
|
||||
if (!SI->getNumCases()) {
|
||||
errs() << "switch: " << SI->getNumCases() << " cases " << bitw << " bit\n";
|
||||
|
||||
/* If there is only the default destination or the condition checks 8 bit or
|
||||
* less, don't bother with the code below. */
|
||||
if (!SI->getNumCases() || bitw <= 8) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_QUIET") == NULL) errs() << "skip trivial switch..\n";
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Create a new, empty default block so that the new hierarchy of
|
||||
@ -250,17 +317,21 @@ bool SplitSwitchesTransform::splitSwitches(Module &M) {
|
||||
NewDefault->insertInto(F, Default);
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(Default, NewDefault);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Prepare cases vector. */
|
||||
CaseVector Cases;
|
||||
for (SwitchInst::CaseIt i = SI->case_begin(), e = SI->case_end(); i != e; ++i)
|
||||
for (SwitchInst::CaseIt i = SI->case_begin(), e = SI->case_end(); i != e;
|
||||
++i)
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
Cases.push_back(CaseExpr(i.getCaseValue(), i.getCaseSuccessor()));
|
||||
#else
|
||||
Cases.push_back(CaseExpr(i->getCaseValue(), i->getCaseSuccessor()));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
std::vector<bool> bytesChecked(Cases[0].Val->getBitWidth() / 8, false);
|
||||
BasicBlock* SwitchBlock = switchConvert(Cases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val, 0);
|
||||
/* bugfix thanks to pbst
|
||||
* round up bytesChecked (in case getBitWidth() % 8 != 0) */
|
||||
std::vector<bool> bytesChecked((7 + Cases[0].Val->getBitWidth()) / 8,
|
||||
false);
|
||||
BasicBlock * SwitchBlock =
|
||||
switchConvert(Cases, bytesChecked, OrigBlock, NewDefault, Val, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Branch to our shiny new if-then stuff... */
|
||||
BranchInst::Create(SwitchBlock, OrigBlock);
|
||||
@ -268,40 +339,47 @@ bool SplitSwitchesTransform::splitSwitches(Module &M) {
|
||||
/* We are now done with the switch instruction, delete it. */
|
||||
CurBlock->getInstList().erase(SI);
|
||||
|
||||
/* we have to update the phi nodes! */
|
||||
for (BasicBlock::iterator I = Default->begin(); I != Default->end(); ++I) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* we have to update the phi nodes! */
|
||||
for (BasicBlock::iterator I = Default->begin(); I != Default->end(); ++I) {
|
||||
if (!isa<PHINode>(&*I)) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
PHINode *PN = cast<PHINode>(I);
|
||||
if (!isa<PHINode>(&*I)) { continue; }
|
||||
PHINode *PN = cast<PHINode>(I);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Only update the first occurence. */
|
||||
unsigned Idx = 0, E = PN->getNumIncomingValues();
|
||||
for (; Idx != E; ++Idx) {
|
||||
if (PN->getIncomingBlock(Idx) == OrigBlock) {
|
||||
PN->setIncomingBlock(Idx, NewDefault);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Only update the first occurrence. */
|
||||
unsigned Idx = 0, E = PN->getNumIncomingValues();
|
||||
for (; Idx != E; ++Idx) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (PN->getIncomingBlock(Idx) == OrigBlock) {
|
||||
|
||||
PN->setIncomingBlock(Idx, NewDefault);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
verifyModule(M);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
verifyModule(M);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool SplitSwitchesTransform::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
llvm::errs() << "Running split-switches-pass by laf.intel@gmail.com\n";
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_QUIET") == NULL)
|
||||
llvm::errs() << "Running split-switches-pass by laf.intel@gmail.com\n";
|
||||
splitSwitches(M);
|
||||
verifyModule(M);
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void registerSplitSwitchesTransPass(const PassManagerBuilder &,
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto p = new SplitSwitchesTransform();
|
||||
PM.add(p);
|
||||
@ -313,3 +391,4 @@ static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterSplitSwitchesTransPass(
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterSplitSwitchesTransPass0(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_EnabledOnOptLevel0, registerSplitSwitchesTransPass);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
15
python_mutators/README
Normal file
15
python_mutators/README
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
These are example and helper files for the AFL_PYTHON_MODULE feature.
|
||||
See docs/python_mutators.txt for more information
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
example.py - this is the template you can use, the functions are there
|
||||
but they are empty
|
||||
|
||||
simple-chunk-replace.py - this is a simple example where chunks are replaced
|
||||
|
||||
common.py - this can be used for common functions and helpers.
|
||||
the examples do not use this though. But you can :)
|
||||
|
||||
wrapper_afl_min.py - mutation of XML documents, loads XmlMutatorMin.py
|
||||
|
||||
XmlMutatorMin.py - module for XML mutation
|
||||
331
python_mutators/XmlMutatorMin.py
Normal file
331
python_mutators/XmlMutatorMin.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,331 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
|
||||
""" Mutation of XML documents, should be called from one of its wrappers (CLI, AFL, ...) """
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
from copy import deepcopy
|
||||
from lxml import etree as ET
|
||||
import random, re, io
|
||||
|
||||
###########################
|
||||
# The XmlMutatorMin class #
|
||||
###########################
|
||||
|
||||
class XmlMutatorMin:
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Optionals parameters:
|
||||
seed Seed used by the PRNG (default: "RANDOM")
|
||||
verbose Verbosity (default: False)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, seed="RANDOM", verbose=False):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Initialize seed, database and mutators """
|
||||
|
||||
# Verbosity
|
||||
self.verbose = verbose
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize PRNG
|
||||
self.seed = str(seed)
|
||||
if self.seed == "RANDOM":
|
||||
random.seed()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("Static seed '%s'" % self.seed)
|
||||
random.seed(self.seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize input and output documents
|
||||
self.input_tree = None
|
||||
self.tree = None
|
||||
|
||||
# High-level mutators (no database needed)
|
||||
hl_mutators_delete = [ "del_node_and_children", "del_node_but_children", "del_attribute", "del_content" ] # Delete items
|
||||
hl_mutators_fuzz = ["fuzz_attribute"] # Randomly change attribute values
|
||||
|
||||
# Exposed mutators
|
||||
self.hl_mutators_all = hl_mutators_fuzz + hl_mutators_delete
|
||||
|
||||
def __parse_xml (self, xml):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Parse an XML string. Basic wrapper around lxml.parse() """
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Function parse() takes care of comments / DTD / processing instructions / ...
|
||||
tree = ET.parse(io.BytesIO(xml))
|
||||
except ET.ParseError:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError("XML isn't well-formed!")
|
||||
except LookupError as e:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(e)
|
||||
|
||||
# Return a document wrapper
|
||||
return tree
|
||||
|
||||
def __exec_among (self, module, functions, min_times, max_times):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Randomly execute $functions between $min and $max times """
|
||||
|
||||
for i in xrange (random.randint (min_times, max_times)):
|
||||
# Function names are mangled because they are "private"
|
||||
getattr (module, "_XmlMutatorMin__" + random.choice(functions)) ()
|
||||
|
||||
def __serialize_xml (self, tree):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Serialize a XML document. Basic wrapper around lxml.tostring() """
|
||||
|
||||
return ET.tostring(tree, with_tail=False, xml_declaration=True, encoding=tree.docinfo.encoding)
|
||||
|
||||
def __ver (self, version):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Helper for displaying lxml version numbers """
|
||||
|
||||
return ".".join(map(str, version))
|
||||
|
||||
def reset (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Reset the mutator """
|
||||
|
||||
self.tree = deepcopy(self.input_tree)
|
||||
|
||||
def init_from_string (self, input_string):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Initialize the mutator from a XML string """
|
||||
|
||||
# Get a pointer to the top-element
|
||||
self.input_tree = self.__parse_xml(input_string)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get a working copy
|
||||
self.tree = deepcopy(self.input_tree)
|
||||
|
||||
def save_to_string (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Return the current XML document as UTF-8 string """
|
||||
|
||||
# Return a text version of the tree
|
||||
return self.__serialize_xml(self.tree)
|
||||
|
||||
def __pick_element (self, exclude_root_node = False):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Pick a random element from the current document """
|
||||
|
||||
# Get a list of all elements, but nodes like PI and comments
|
||||
elems = list(self.tree.getroot().iter(tag=ET.Element))
|
||||
|
||||
# Is the root node excluded?
|
||||
if exclude_root_node:
|
||||
start = 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
start = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Pick a random element
|
||||
try:
|
||||
elem_id = random.randint (start, len(elems) - 1)
|
||||
elem = elems[elem_id]
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
# Should only occurs if "exclude_root_node = True"
|
||||
return (None, None)
|
||||
|
||||
return (elem_id, elem)
|
||||
|
||||
def __fuzz_attribute (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Fuzz (part of) an attribute value """
|
||||
|
||||
# Select a node to modify
|
||||
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get all the attributes
|
||||
attribs = rand_elem.keys()
|
||||
|
||||
# Is there attributes?
|
||||
if len(attribs) < 1:
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("No attribute: can't replace!")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Pick a random attribute
|
||||
rand_attrib_id = random.randint (0, len(attribs) - 1)
|
||||
rand_attrib = attribs[rand_attrib_id]
|
||||
|
||||
# We have the attribute to modify
|
||||
# Get its value
|
||||
attrib_value = rand_elem.get(rand_attrib);
|
||||
# print("- Value: " + attrib_value)
|
||||
|
||||
# Should we work on the whole value?
|
||||
func_call = "(?P<func>[a-zA-Z:\-]+)\((?P<args>.*?)\)"
|
||||
p = re.compile(func_call)
|
||||
l = p.findall(attrib_value)
|
||||
if random.choice((True,False)) and l:
|
||||
# Randomly pick one the function calls
|
||||
(func, args) = random.choice(l)
|
||||
# Split by "," and randomly pick one of the arguments
|
||||
value = random.choice(args.split(','))
|
||||
# Remove superfluous characters
|
||||
unclean_value = value
|
||||
value = value.strip(" ").strip("'")
|
||||
# print("Selected argument: [%s]" % value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
value = attrib_value
|
||||
|
||||
# For each type, define some possible replacement values
|
||||
choices_number = ( \
|
||||
"0", \
|
||||
"11111", \
|
||||
"-128", \
|
||||
"2", \
|
||||
"-1", \
|
||||
"1/3", \
|
||||
"42/0", \
|
||||
"1094861636 idiv 1.0", \
|
||||
"-1123329771506872 idiv 3.8", \
|
||||
"17=$numericRTF", \
|
||||
str(3 + random.randrange(0, 100)), \
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
choices_letter = ( \
|
||||
"P" * (25 * random.randrange(1, 100)), \
|
||||
"%s%s%s%s%s%s", \
|
||||
"foobar", \
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
choices_alnum = ( \
|
||||
"Abc123", \
|
||||
"020F0302020204030204", \
|
||||
"020F0302020204030204" * (random.randrange(5, 20)), \
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Fuzz the value
|
||||
if random.choice((True,False)) and value == "":
|
||||
|
||||
# Empty
|
||||
new_value = value
|
||||
|
||||
elif random.choice((True,False)) and value.isdigit():
|
||||
|
||||
# Numbers
|
||||
new_value = random.choice(choices_number)
|
||||
|
||||
elif random.choice((True,False)) and value.isalpha():
|
||||
|
||||
# Letters
|
||||
new_value = random.choice(choices_letter)
|
||||
|
||||
elif random.choice((True,False)) and value.isalnum():
|
||||
|
||||
# Alphanumeric
|
||||
new_value = random.choice(choices_alnum)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
# Default type
|
||||
new_value = random.choice(choices_alnum + choices_letter + choices_number)
|
||||
|
||||
# If we worked on a substring, apply changes to the whole string
|
||||
if value != attrib_value:
|
||||
# No ' around empty values
|
||||
if new_value != "" and value != "":
|
||||
new_value = "'" + new_value + "'"
|
||||
# Apply changes
|
||||
new_value = attrib_value.replace(unclean_value, new_value)
|
||||
|
||||
# Log something
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("Fuzzing attribute #%i '%s' of tag #%i '%s'" % (rand_attrib_id, rand_attrib, rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag))
|
||||
|
||||
# Modify the attribute
|
||||
rand_elem.set(rand_attrib, new_value.decode("utf-8"))
|
||||
|
||||
def __del_node_and_children (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" High-level minimizing mutator
|
||||
Delete a random node and its children (i.e. delete a random tree) """
|
||||
|
||||
self.__del_node(True)
|
||||
|
||||
def __del_node_but_children (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" High-level minimizing mutator
|
||||
Delete a random node but its children (i.e. link them to the parent of the deleted node) """
|
||||
|
||||
self.__del_node(False)
|
||||
|
||||
def __del_node (self, delete_children):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Called by the __del_node_* mutators """
|
||||
|
||||
# Select a node to modify (but the root one)
|
||||
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element (exclude_root_node = True)
|
||||
|
||||
# If the document includes only a top-level element
|
||||
# Then we can't pick a element (given that "exclude_root_node = True")
|
||||
|
||||
# Is the document deep enough?
|
||||
if rand_elem is None:
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("Can't delete a node: document not deep enough!")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Log something
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
but_or_and = "and" if delete_children else "but"
|
||||
print("Deleting tag #%i '%s' %s its children" % (rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag, but_or_and))
|
||||
|
||||
if delete_children is False:
|
||||
# Link children of the random (soon to be deleted) node to its parent
|
||||
for child in rand_elem:
|
||||
rand_elem.getparent().append(child)
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove the node
|
||||
rand_elem.getparent().remove(rand_elem)
|
||||
|
||||
def __del_content (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" High-level minimizing mutator
|
||||
Delete the attributes and children of a random node """
|
||||
|
||||
# Select a node to modify
|
||||
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element()
|
||||
|
||||
# Log something
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("Reseting tag #%i '%s'" % (rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag))
|
||||
|
||||
# Reset the node
|
||||
rand_elem.clear()
|
||||
|
||||
def __del_attribute (self):
|
||||
|
||||
""" High-level minimizing mutator
|
||||
Delete a random attribute from a random node """
|
||||
|
||||
# Select a node to modify
|
||||
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get all the attributes
|
||||
attribs = rand_elem.keys()
|
||||
|
||||
# Is there attributes?
|
||||
if len(attribs) < 1:
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("No attribute: can't delete!")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Pick a random attribute
|
||||
rand_attrib_id = random.randint (0, len(attribs) - 1)
|
||||
rand_attrib = attribs[rand_attrib_id]
|
||||
|
||||
# Log something
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
print("Deleting attribute #%i '%s' of tag #%i '%s'" % (rand_attrib_id, rand_attrib, rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag))
|
||||
|
||||
# Delete the attribute
|
||||
rand_elem.attrib.pop(rand_attrib)
|
||||
|
||||
def mutate (self, min=1, max=5):
|
||||
|
||||
""" Execute some high-level mutators between $min and $max times, then some medium-level ones """
|
||||
|
||||
# High-level mutation
|
||||
self.__exec_among(self, self.hl_mutators_all, min, max)
|
||||
|
||||
37
python_mutators/common.py
Normal file
37
python_mutators/common.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# encoding: utf-8
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Module containing functions shared between multiple AFL modules
|
||||
|
||||
@author: Christian Holler (:decoder)
|
||||
|
||||
@license:
|
||||
|
||||
This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public
|
||||
License, v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed with this
|
||||
file, You can obtain one at http://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.
|
||||
|
||||
@contact: choller@mozilla.com
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
def randel(l):
|
||||
if not l:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return l[random.randint(0,len(l)-1)]
|
||||
|
||||
def randel_pop(l):
|
||||
if not l:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return l.pop(random.randint(0,len(l)-1))
|
||||
|
||||
def write_exc_example(data, exc):
|
||||
exc_name = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z0-9]', '_', repr(exc))
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(exc_name):
|
||||
with open(exc_name, 'w') as f:
|
||||
f.write(data)
|
||||
103
python_mutators/example.py
Normal file
103
python_mutators/example.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# encoding: utf-8
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Example Python Module for AFLFuzz
|
||||
|
||||
@author: Christian Holler (:decoder)
|
||||
|
||||
@license:
|
||||
|
||||
This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public
|
||||
License, v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed with this
|
||||
file, You can obtain one at http://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.
|
||||
|
||||
@contact: choller@mozilla.com
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
def init(seed):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Called once when AFLFuzz starts up. Used to seed our RNG.
|
||||
|
||||
@type seed: int
|
||||
@param seed: A 32-bit random value
|
||||
'''
|
||||
random.seed(seed)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def fuzz(buf, add_buf):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Called per fuzzing iteration.
|
||||
|
||||
@type buf: bytearray
|
||||
@param buf: The buffer that should be mutated.
|
||||
|
||||
@type add_buf: bytearray
|
||||
@param add_buf: A second buffer that can be used as mutation source.
|
||||
|
||||
@rtype: bytearray
|
||||
@return: A new bytearray containing the mutated data
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ret = bytearray(buf)
|
||||
# Do something interesting with ret
|
||||
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
|
||||
# Uncomment and implement the following methods if you want to use a custom
|
||||
# trimming algorithm. See also the documentation for a better API description.
|
||||
|
||||
# def init_trim(buf):
|
||||
# '''
|
||||
# Called per trimming iteration.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# @type buf: bytearray
|
||||
# @param buf: The buffer that should be trimmed.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# @rtype: int
|
||||
# @return: The maximum number of trimming steps.
|
||||
# '''
|
||||
# global ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# # Initialize global variables
|
||||
#
|
||||
# # Figure out how many trimming steps are possible.
|
||||
# # If this is not possible for your trimming, you can
|
||||
# # return 1 instead and always return 0 in post_trim
|
||||
# # until you are done (then you return 1).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# return steps
|
||||
#
|
||||
# def trim():
|
||||
# '''
|
||||
# Called per trimming iteration.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# @rtype: bytearray
|
||||
# @return: A new bytearray containing the trimmed data.
|
||||
# '''
|
||||
# global ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# # Implement the actual trimming here
|
||||
#
|
||||
# return bytearray(...)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# def post_trim(success):
|
||||
# '''
|
||||
# Called after each trimming operation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# @type success: bool
|
||||
# @param success: Indicates if the last trim operation was successful.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# @rtype: int
|
||||
# @return: The next trim index (0 to max number of steps) where max
|
||||
# number of steps indicates the trimming is done.
|
||||
# '''
|
||||
# global ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# if not success:
|
||||
# # Restore last known successful input, determine next index
|
||||
# else:
|
||||
# # Just determine the next index, based on what was successfully
|
||||
# # removed in the last step
|
||||
#
|
||||
# return next_index
|
||||
59
python_mutators/simple-chunk-replace.py
Normal file
59
python_mutators/simple-chunk-replace.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# encoding: utf-8
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Simple Chunk Cross-Over Replacement Module for AFLFuzz
|
||||
|
||||
@author: Christian Holler (:decoder)
|
||||
|
||||
@license:
|
||||
|
||||
This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public
|
||||
License, v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed with this
|
||||
file, You can obtain one at http://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.
|
||||
|
||||
@contact: choller@mozilla.com
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
def init(seed):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Called once when AFLFuzz starts up. Used to seed our RNG.
|
||||
|
||||
@type seed: int
|
||||
@param seed: A 32-bit random value
|
||||
'''
|
||||
# Seed our RNG
|
||||
random.seed(seed)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def fuzz(buf, add_buf):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Called per fuzzing iteration.
|
||||
|
||||
@type buf: bytearray
|
||||
@param buf: The buffer that should be mutated.
|
||||
|
||||
@type add_buf: bytearray
|
||||
@param add_buf: A second buffer that can be used as mutation source.
|
||||
|
||||
@rtype: bytearray
|
||||
@return: A new bytearray containing the mutated data
|
||||
'''
|
||||
# Make a copy of our input buffer for returning
|
||||
ret = bytearray(buf)
|
||||
|
||||
# Take a random fragment length between 2 and 32 (or less if add_buf is shorter)
|
||||
fragment_len = random.randint(1, min(len(add_buf), 32))
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine a random source index where to take the data chunk from
|
||||
rand_src_idx = random.randint(0, len(add_buf) - fragment_len)
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine a random destination index where to put the data chunk
|
||||
rand_dst_idx = random.randint(0, len(buf))
|
||||
|
||||
# Make the chunk replacement
|
||||
ret[rand_dst_idx:rand_dst_idx + fragment_len] = add_buf[rand_src_idx:rand_src_idx + fragment_len]
|
||||
|
||||
# Return data
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
117
python_mutators/wrapper_afl_min.py
Normal file
117
python_mutators/wrapper_afl_min.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
|
||||
from XmlMutatorMin import XmlMutatorMin
|
||||
|
||||
# Default settings (production mode)
|
||||
|
||||
__mutator__ = None
|
||||
__seed__ = "RANDOM"
|
||||
__log__ = False
|
||||
__log_file__ = "wrapper.log"
|
||||
|
||||
# AFL functions
|
||||
|
||||
def log(text):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Logger
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
global __seed__
|
||||
global __log__
|
||||
global __log_file__
|
||||
|
||||
if __log__:
|
||||
with open(__log_file__, "a") as logf:
|
||||
logf.write("[%s] %s\n" % (__seed__, text))
|
||||
|
||||
def init(seed):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Called once when AFL starts up. Seed is used to identify the AFL instance in log files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
global __mutator__
|
||||
global __seed__
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the seed
|
||||
__seed__ = seed
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a global mutation class
|
||||
try:
|
||||
__mutator__ = XmlMutatorMin(__seed__, verbose=__log__)
|
||||
log("init(): Mutator created")
|
||||
except RuntimeError as e:
|
||||
log("init(): Can't create mutator: %s" % e.message)
|
||||
|
||||
def fuzz(buf, add_buf):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Called for each fuzzing iteration.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
global __mutator__
|
||||
|
||||
# Do we have a working mutator object?
|
||||
if __mutator__ is None:
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Can't fuzz, no mutator available")
|
||||
return buf
|
||||
|
||||
# Try to use the AFL buffer
|
||||
via_buffer = True
|
||||
|
||||
# Interpret the AFL buffer (an array of bytes) as a string
|
||||
if via_buffer:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
buf_str = str(buf)
|
||||
log("fuzz(): AFL buffer converted to a string")
|
||||
except:
|
||||
via_buffer = False
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Can't convert AFL buffer to a string")
|
||||
|
||||
# Load XML from the AFL string
|
||||
if via_buffer:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
__mutator__.init_from_string(buf_str)
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Mutator successfully initialized with AFL buffer (%d bytes)" % len(buf_str))
|
||||
except:
|
||||
via_buffer = False
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Can't initialize mutator with AFL buffer")
|
||||
|
||||
# If init from AFL buffer wasn't succesful
|
||||
if not via_buffer:
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Returning unmodified AFL buffer")
|
||||
return buf
|
||||
|
||||
# Sucessful initialization -> mutate
|
||||
try:
|
||||
__mutator__.mutate(max=5)
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Input mutated")
|
||||
except:
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Can't mutate input => returning buf")
|
||||
return buf
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert mutated data to a array of bytes
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = bytearray(__mutator__.save_to_string())
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Mutated data converted as bytes")
|
||||
except:
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Can't convert mutated data to bytes => returning buf")
|
||||
return buf
|
||||
|
||||
# Everything went fine, returning mutated content
|
||||
log("fuzz(): Returning %d bytes" % len(data))
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
# Main (for debug)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
|
||||
__log__ = True
|
||||
__log_file__ = "/dev/stdout"
|
||||
__seed__ = "RANDOM"
|
||||
|
||||
init(__seed__)
|
||||
|
||||
in_1 = bytearray("<foo ddd='eeee'>ffff<a b='c' d='456' eee='ffffff'>zzzzzzzzzzzz</a><b yyy='YYY' zzz='ZZZ'></b></foo>")
|
||||
in_2 = bytearray("<abc abc123='456' abcCBA='ppppppppppppppppppppppppppppp'/>")
|
||||
out = fuzz(in_1, in_2)
|
||||
print(out)
|
||||
|
||||
187
qemu_mode/README.md
Normal file
187
qemu_mode/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,187 @@
|
||||
# High-performance binary-only instrumentation for afl-fuzz
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
The code in this directory allows you to build a standalone feature that
|
||||
leverages the QEMU "user emulation" mode and allows callers to obtain
|
||||
instrumentation output for black-box, closed-source binaries. This mechanism
|
||||
can be then used by afl-fuzz to stress-test targets that couldn't be built
|
||||
with afl-gcc.
|
||||
|
||||
The usual performance cost is 2-5x, which is considerably better than
|
||||
seen so far in experiments with tools such as DynamoRIO and PIN.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea and much of the initial implementation comes from Andrew Griffiths.
|
||||
The actual implementation on QEMU 3 (shipped with afl++) is from
|
||||
Andrea Fioraldi. Special thanks to abiondo that re-enabled TCG chaining.
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) How to use
|
||||
|
||||
The feature is implemented with a patch to QEMU 3.1.1. The simplest way
|
||||
to build it is to run ./build_qemu_support.sh. The script will download,
|
||||
configure, and compile the QEMU binary for you.
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU is a big project, so this will take a while, and you may have to
|
||||
resolve a couple of dependencies (most notably, you will definitely need
|
||||
libtool and glib2-devel).
|
||||
|
||||
Once the binaries are compiled, you can leverage the QEMU tool by calling
|
||||
afl-fuzz and all the related utilities with -Q in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that QEMU requires a generous memory limit to run; somewhere around
|
||||
200 MB is a good starting point, but considerably more may be needed for
|
||||
more complex programs. The default -m limit will be automatically bumped up
|
||||
to 200 MB when specifying -Q to afl-fuzz; be careful when overriding this.
|
||||
|
||||
In principle, if you set CPU_TARGET before calling ./build_qemu_support.sh,
|
||||
you should get a build capable of running non-native binaries (say, you
|
||||
can try CPU_TARGET=arm). This is also necessary for running 32-bit binaries
|
||||
on a 64-bit system (CPU_TARGET=i386). If you're trying to run QEMU on a
|
||||
different architecture you can also set HOST to the cross-compiler prefix
|
||||
to use (for example HOST=arm-linux-gnueabi to use arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc).
|
||||
|
||||
You can also compile statically-linked binaries by setting STATIC=1. This
|
||||
can be useful when compiling QEMU on a different system than the one you're
|
||||
planning to run the fuzzer on and is most often used with the HOST variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: if you want the QEMU helper to be installed on your system for all
|
||||
users, you need to build it before issuing 'make install' in the parent
|
||||
directory.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3) Bonus feature #1: deferred initialization
|
||||
|
||||
As for LLVM mode (refer to its README for mode details) QEMU mode supports
|
||||
the deferred initialization.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be enabled setting the environment variable AFL_ENTRYPOINT which allows
|
||||
to move the forkserver to a different part, e.g. just before the file is
|
||||
opened (e.g. way after command line parsing and config file loading, etc.)
|
||||
which can be a huge speed improvement. Note that the specified address
|
||||
must be an address of a basic block.
|
||||
|
||||
## 4) Bonus feature #2: persistent mode
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU mode supports also persistent mode for x86 and x86_64 targets.
|
||||
The environment variable to enable it is AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR=`start addr`.
|
||||
In this variable you must specify the address of the function that
|
||||
has to be the body of the persistent loop.
|
||||
The code in this function must be stateless like in the LLVM persistent mode.
|
||||
The return address on stack is patched like in WinAFL in order to repeat the
|
||||
execution of such function.
|
||||
Another modality to execute the persistent loop is to specify also the
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_RET=`end addr` env variable.
|
||||
With this variable assigned, instead of patching the return address, the
|
||||
specified instruction is transformed to a jump towards `start addr`.
|
||||
Note that the format of the addresses in such variables is hex.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the base address of PIE binaries in QEMU user mode is 0x4000000000.
|
||||
|
||||
With the env variable AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_GPR you can tell QEMU to save the
|
||||
original value of general purpose registers and restore them in each cycle.
|
||||
This allows to use as persistent loop functions that make use of arguments on
|
||||
x86_64.
|
||||
|
||||
With AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_RETADDR_OFFSET you can specify the offset from the
|
||||
stack pointer in which QEMU can find the return address when `start addr` is
|
||||
hitted.
|
||||
|
||||
Use this mode with caution, probably it will not work at the first shot.
|
||||
|
||||
## 5) Bonus feature #3: CompareCoverage
|
||||
|
||||
CompareCoverage is a sub-instrumentation with effects similar to laf-intel.
|
||||
|
||||
The option that enables QEMU CompareCoverage is AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL.
|
||||
There is also ./libcompcov/ which implements CompareCoverage for *cmp functions
|
||||
(splitting memcmp, strncmp, etc. to make these conditions easier solvable by
|
||||
afl-fuzz).
|
||||
AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL=1 is to instrument comparisons with only immediate
|
||||
values / read-only memory. AFL_COMPCOV_LEVEL=2 instruments all
|
||||
comparison instructions and memory comparison functions when libcompcov
|
||||
is preloaded. Comparison instructions are currently instrumented only
|
||||
on the x86, x86_64 and ARM targets.
|
||||
|
||||
Highly recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
## 6) Bonus feature #4: Wine mode
|
||||
|
||||
AFL++ QEMU can use Wine to fuzz WIn32 PE binaries. Use the -W flag of afl-fuzz.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that some binaries require user interaction with the GUI and must be patched.
|
||||
|
||||
For examples look [here](https://github.com/andreafioraldi/WineAFLplusplusDEMO).
|
||||
|
||||
## 7) Notes on linking
|
||||
|
||||
The feature is supported only on Linux. Supporting BSD may amount to porting
|
||||
the changes made to linux-user/elfload.c and applying them to
|
||||
bsd-user/elfload.c, but I have not looked into this yet.
|
||||
|
||||
The instrumentation follows only the .text section of the first ELF binary
|
||||
encountered in the linking process. It does not trace shared libraries. In
|
||||
practice, this means two things:
|
||||
|
||||
- Any libraries you want to analyze *must* be linked statically into the
|
||||
executed ELF file (this will usually be the case for closed-source
|
||||
apps).
|
||||
|
||||
- Standard C libraries and other stuff that is wasteful to instrument
|
||||
should be linked dynamically - otherwise, AFL will have no way to avoid
|
||||
peeking into them.
|
||||
|
||||
Setting AFL_INST_LIBS=1 can be used to circumvent the .text detection logic
|
||||
and instrument every basic block encountered.
|
||||
|
||||
## 8) Benchmarking
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to compare the performance of the QEMU instrumentation with that of
|
||||
afl-gcc compiled code against the same target, you need to build the
|
||||
non-instrumented binary with the same optimization flags that are normally
|
||||
injected by afl-gcc, and make sure that the bits to be tested are statically
|
||||
linked into the binary. A common way to do this would be:
|
||||
|
||||
$ CFLAGS="-O3 -funroll-loops" ./configure --disable-shared
|
||||
$ make clean all
|
||||
|
||||
Comparative measurements of execution speed or instrumentation coverage will be
|
||||
fairly meaningless if the optimization levels or instrumentation scopes don't
|
||||
match.
|
||||
|
||||
## 9) Gotchas, feedback, bugs
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to fix up checksums or do other cleanup on mutated test cases, see
|
||||
experimental/post_library/ for a viable solution.
|
||||
|
||||
Do not mix QEMU mode with ASAN, MSAN, or the likes; QEMU doesn't appreciate
|
||||
the "shadow VM" trick employed by the sanitizers and will probably just
|
||||
run out of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Compared to fully-fledged virtualization, the user emulation mode is *NOT* a
|
||||
security boundary. The binaries can freely interact with the host OS. If you
|
||||
somehow need to fuzz an untrusted binary, put everything in a sandbox first.
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU does not necessarily support all CPU or hardware features that your
|
||||
target program may be utilizing. In particular, it does not appear to have
|
||||
full support for AVX2 / FMA3. Using binaries for older CPUs, or recompiling them
|
||||
with -march=core2, can help.
|
||||
|
||||
Beyond that, this is an early-stage mechanism, so fields reports are welcome.
|
||||
You can send them to <afl-users@googlegroups.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
## 10) Alternatives: static rewriting
|
||||
|
||||
Statically rewriting binaries just once, instead of attempting to translate
|
||||
them at run time, can be a faster alternative. That said, static rewriting is
|
||||
fraught with peril, because it depends on being able to properly and fully model
|
||||
program control flow without actually executing each and every code path.
|
||||
|
||||
The best implementation is this one:
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dyninst
|
||||
|
||||
The issue however is Dyninst which is not rewriting the binaries so that
|
||||
they run stable. A lot of crashes happen, especially in C++ programs that
|
||||
use throw/catch. Try it first, and if it works for you be happy as it is
|
||||
2-3x as fast as qemu_mode.
|
||||
@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
|
||||
=========================================================
|
||||
High-performance binary-only instrumentation for afl-fuzz
|
||||
=========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
(See ../docs/README for the general instruction manual.)
|
||||
|
||||
1) Introduction
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
||||
The code in this directory allows you to build a standalone feature that
|
||||
leverages the QEMU "user emulation" mode and allows callers to obtain
|
||||
instrumentation output for black-box, closed-source binaries. This mechanism
|
||||
can be then used by afl-fuzz to stress-test targets that couldn't be built
|
||||
with afl-gcc.
|
||||
|
||||
The usual performance cost is 2-5x, which is considerably better than
|
||||
seen so far in experiments with tools such as DynamoRIO and PIN.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea and much of the implementation comes from Andrew Griffiths.
|
||||
|
||||
2) How to use
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
The feature is implemented with a fairly simple patch to QEMU 2.10.0. The
|
||||
simplest way to build it is to run ./build_qemu_support.sh. The script will
|
||||
download, configure, and compile the QEMU binary for you.
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU is a big project, so this will take a while, and you may have to
|
||||
resolve a couple of dependencies (most notably, you will definitely need
|
||||
libtool and glib2-devel).
|
||||
|
||||
Once the binaries are compiled, you can leverage the QEMU tool by calling
|
||||
afl-fuzz and all the related utilities with -Q in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that QEMU requires a generous memory limit to run; somewhere around
|
||||
200 MB is a good starting point, but considerably more may be needed for
|
||||
more complex programs. The default -m limit will be automatically bumped up
|
||||
to 200 MB when specifying -Q to afl-fuzz; be careful when overriding this.
|
||||
|
||||
In principle, if you set CPU_TARGET before calling ./build_qemu_support.sh,
|
||||
you should get a build capable of running non-native binaries (say, you
|
||||
can try CPU_TARGET=arm). This is also necessary for running 32-bit binaries
|
||||
on a 64-bit system (CPU_TARGET=i386).
|
||||
|
||||
Note: if you want the QEMU helper to be installed on your system for all
|
||||
users, you need to build it before issuing 'make install' in the parent
|
||||
directory.
|
||||
|
||||
3) Notes on linking
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The feature is supported only on Linux. Supporting BSD may amount to porting
|
||||
the changes made to linux-user/elfload.c and applying them to
|
||||
bsd-user/elfload.c, but I have not looked into this yet.
|
||||
|
||||
The instrumentation follows only the .text section of the first ELF binary
|
||||
encountered in the linking process. It does not trace shared libraries. In
|
||||
practice, this means two things:
|
||||
|
||||
- Any libraries you want to analyze *must* be linked statically into the
|
||||
executed ELF file (this will usually be the case for closed-source
|
||||
apps).
|
||||
|
||||
- Standard C libraries and other stuff that is wasteful to instrument
|
||||
should be linked dynamically - otherwise, AFL will have no way to avoid
|
||||
peeking into them.
|
||||
|
||||
Setting AFL_INST_LIBS=1 can be used to circumvent the .text detection logic
|
||||
and instrument every basic block encountered.
|
||||
|
||||
4) Benchmarking
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to compare the performance of the QEMU instrumentation with that of
|
||||
afl-gcc compiled code against the same target, you need to build the
|
||||
non-instrumented binary with the same optimization flags that are normally
|
||||
injected by afl-gcc, and make sure that the bits to be tested are statically
|
||||
linked into the binary. A common way to do this would be:
|
||||
|
||||
$ CFLAGS="-O3 -funroll-loops" ./configure --disable-shared
|
||||
$ make clean all
|
||||
|
||||
Comparative measurements of execution speed or instrumentation coverage will be
|
||||
fairly meaningless if the optimization levels or instrumentation scopes don't
|
||||
match.
|
||||
|
||||
5) Gotchas, feedback, bugs
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to fix up checksums or do other cleanup on mutated test cases, see
|
||||
experimental/post_library/ for a viable solution.
|
||||
|
||||
Do not mix QEMU mode with ASAN, MSAN, or the likes; QEMU doesn't appreciate
|
||||
the "shadow VM" trick employed by the sanitizers and will probably just
|
||||
run out of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Compared to fully-fledged virtualization, the user emulation mode is *NOT* a
|
||||
security boundary. The binaries can freely interact with the host OS. If you
|
||||
somehow need to fuzz an untrusted binary, put everything in a sandbox first.
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU does not necessarily support all CPU or hardware features that your
|
||||
target program may be utilizing. In particular, it does not appear to have
|
||||
full support for AVX2 / FMA3. Using binaries for older CPUs, or recompiling them
|
||||
with -march=core2, can help.
|
||||
|
||||
Beyond that, this is an early-stage mechanism, so fields reports are welcome.
|
||||
You can send them to <afl-users@googlegroups.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
6) Alternatives: static rewriting
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Statically rewriting binaries just once, instead of attempting to translate
|
||||
them at run time, can be a faster alternative. That said, static rewriting is
|
||||
fraught with peril, because it depends on being able to properly and fully model
|
||||
program control flow without actually executing each and every code path.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to experiment with this mode of operation, there is a module
|
||||
contributed by Aleksandar Nikolich:
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/vrtadmin/moflow/tree/master/afl-dyninst
|
||||
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/afl-users/HlSQdbOTlpg
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, the author reports the possibility of hiccups with stripped
|
||||
binaries. That said, if we can get it to be comparably reliable to QEMU, we may
|
||||
decide to switch to this mode, but I had no time to play with it yet.
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user