Search for direct_reg_access location.
openwifi
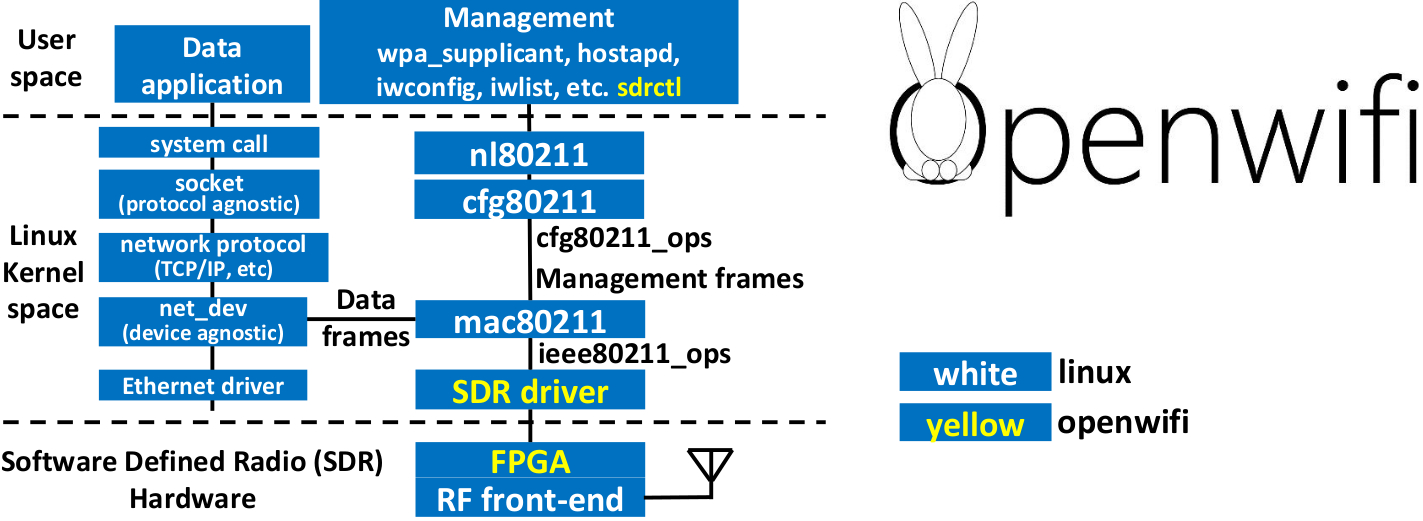
openwifi: Linux mac80211 compatible full-stack IEEE802.11/Wi-Fi design based on SDR (Software Defined Radio).
This repository includes Linux driver and software. openwifi-hw repository has the FPGA design. It is YOUR RESPONSIBILITY to follow your LOCAL SPECTRUM REGULATION or use CABLE to avoid potential interference over the air.
[Quick start] [Project document] [Application notes] [Videos] [Publications and How to Cite] [maillist]
Openwifi code has dual licenses. AGPLv3 is the opensource license. For non-opensource and advanced feature license, please contact Filip.Louagie@UGent.be. Openwifi project also leverages some 3rd party modules. It is user's duty to check and follow licenses of those modules according to the purpose/usage. You can find an example explanation from Analog Devices for this compound license conditions. [How to contribute].
Features:
- 802.11a/g/n [IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4)]
- 20MHz bandwidth; 70 MHz to 6 GHz frequency range
- Mode tested: Ad-hoc; Station; AP, Monitor
- DCF (CSMA/CA) low MAC layer in FPGA (10us SIFS is achieved)
- 802.11 packet injection and fuzzing
- CSI: Channel State Information, freq offset, equalizer to computer
- CSI fuzzer: Create artificial channel response in WiFi transmitter
- [IQ capture]: real-time AGC, RSSI, IQ sample to computer. [Dual antenna version]
- Configurable channel access priority parameters:
- duration of RTS/CTS, CTS-to-self
- SIFS/DIFS/xIFS/slot-time/CW/etc
- Time slicing based on MAC address (time gated/scheduled FPGA queues)
- Easy to change bandwidth and frequency:
- 2MHz for 802.11ah in sub-GHz
- 10MHz for 802.11p/vehicle in 5.9GHz
- 802.11ax under development
Performance (AP: openwifi at channel 44, client: TL-WDN4200 N900 USB Dongle):
- AP --> client: 30.6Mbps(TCP), 38.8Mbps(UDP)
- client --> AP: 17.0Mbps(TCP), 21.5Mbps(UDP)
Supported SDR platforms: (Check Porting guide for your new board if it isn't in the list)
| board_name | board combination | status | SD card img | Vivado license |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| zc706_fmcs2 | Xilinx ZC706 board + FMCOMMS2/3/4 | Done | 32bit img | Need |
| zed_fmcs2 | Xilinx zed board + FMCOMMS2/3/4 | Done | 32bit img | NO need |
| adrv9364z7020 | ADRV9364-Z7020 + ADRV1CRR-BOB | Done | 32bit img | NO need |
| adrv9361z7035 | ADRV9361-Z7035 + ADRV1CRR-BOB/FMC | Done | 32bit img | Need |
| zc702_fmcs2 | Xilinx ZC702 board + FMCOMMS2/3/4 | Done | 32bit img | NO need |
| antsdr | MicroPhase enhanced ADALM-PLUTO Notes | Done | 32bit img | NO need |
| zcu102_fmcs2 | Xilinx ZCU102 board + FMCOMMS2/3/4 | Done | 64bit img | Need |
| zcu102_9371 | Xilinx ZCU102 board + ADRV9371 | Future | Future | Need |
- board_name is used to identify FPGA design in openwifi-hw/boards/
- Don't have any boards? Or you like JTAG boot instead of SD card? Check our test bed w-iLab.t tutorial.
[Quick start] [Basic operations] [Update FPGA] [Update Driver] [Update sdrctl] [Easy Access and etc]
[Build openwifi Linux img from scratch] [Special note for 11b] [Porting guide] [Project document] [Application notes]
Quick start
-
Restore openwifi board specific img file (from the table) into a SD card. To do this, program "Disks" in Ubuntu can be used (Install: "sudo apt install gnome-disk-utility"). After restoring, the SD card should have two partitions: BOOT and rootfs. You need to config the correct files in the BOOT partition according to the board you have by operation on your computer:
- Copy files in openwifi/board_name to the base directory of BOOT partition.
- Copy openwifi/zynqmp-common/Image (zcu102 board) or openwifi/zynq-common/uImage (other boards) to the base directory of BOOT partition
-
Connect two antennas to RXA/TXA ports. Config the board to SD card boot mode (check the board manual). Insert the SD card to the board. Power on.
-
Login to the board from your PC (PC Ethernet should have IP 192.168.10.1) with password openwifi.
ssh root@192.168.10.122 -
On board, run openwifi AP and the on board webserver
~/openwifi/fosdem.sh (Use "./fosdem.sh 1" to enable experimental AMPDU aggregation on top of 11n) (Use "./fosdem-11ag.sh" to force 11a/g mode)NOTE adrv9361z7035 has ultra low TX power in 5GHz. Move CLOSER when you use that board in 5GHz!!!
-
After you see the "openwifi" SSID on your device (Phone/Laptop/etc), connect it. Browser to 192.168.13.1 on your device, you should see the webpage hosted by the webserver on board.
- Note 1: If your device doesn't support 5GHz (ch44), please change the hostapd-openwifi.conf on board and re-run fosdem.sh.
- Note 2: After ~2 hours, the Viterbi decoder will halt (Xilinx Evaluation License). Just power cycle the board if it happens. (If output of "./sdrctl dev sdr0 get reg rx 20" is always the same, it means the decoder halts)
-
To give the Wi-Fi client internet access, configure routing/NAT on the PC:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o NICY -j MASQUERADE sudo ip route add 192.168.13.0/24 via 192.168.10.122 dev ethXethX is the PC NIC name connecting the board ethernet. NICY is the PC NIC name connecting internet (WiFi or another ethernet).
If you want, uncommenting "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" in /etc/sysctl.conf to make IP forwarding persistent on PC.
-
To monitor real-time CSI (Chip State Information), such as timestamp, frequency offset, channel state, equalizer, please refer to [CSI notes].
Basic operations
The board actually is an Linux/Ubuntu computer which is running hostapd to offer Wi-Fi AP functionality over the Wi-Fi Network Interface (NIC). The NIC is implemented by openwifi-hw FPGA design. We use the term "On board" to indicate that the commands should be executed after ssh login to the board. "On PC" means the commands should run on PC.
- Bring up the openwifi NIC sdr0:
cd ~/openwifi && ./wgd.sh (Use "./wgd.sh 1" to enable experimental AMPDU aggregation) - Use openwifi as client to connect other AP (Change wpa-connect.conf on board firstly):
route del default gw 192.168.10.1 wpa_supplicant -i sdr0 -c wpa-connect.conf & dhclient sdr0 - Use openwifi in ad-hoc mode: Please check sdr-ad-hoc-up.sh and sdr-ad-hoc-join.sh.
- Use openwifi in monitor mode: Please check monitor_ch.sh.
- The Linux native Wi-Fi tools/Apps (iwconfig/ifconfig/iwlist/iw/hostapd/wpa_supplicant/etc) can run over openwifi NIC in the same way as commercial Wi-Fi chip.
- sdrctl is a dedicated tool to access openwifi driver/FPGA, please check doc directory for more information.
Update FPGA
Since the pre-built SD card image might not have the latest bug-fixes/updates, it is recommended to update the fpga bitstream on board.
- Install Vivado/SDK 2018.3 (Vivado Design Suite - HLx Editions - 2018.3 Full Product Installation. If you don't need to generate new FPGA bitstream, WebPack version without license is enough)
- Setup environment variables (use absolute path):
export XILINX_DIR=your_Xilinx_install_directory (Example: export XILINX_DIR=/opt/Xilinx. The Xilinx directory should include sth like: Downloads, SDK, Vivado, xic) export OPENWIFI_HW_DIR=your_openwifi-hw_directory (The directory where you store the open-sdr/openwifi-hw repo via git clone) export BOARD_NAME=your_board_name - Pick the FPGA bitstream from openwifi-hw, and generate BOOT.BIN and transfer it on board via ssh channel:
For Zynq 7000: cd openwifi/user_space; ./boot_bin_gen.sh $OPENWIFI_HW_DIR $XILINX_DIR $BOARD_NAME For Zynq MPSoC (like zcu102 board): cd openwifi/user_space; ./boot_bin_gen_zynqmp.sh $OPENWIFI_HW_DIR $XILINX_DIR $BOARD_NAME cd openwifi/kernel_boot/boards/$BOARD_NAME/output_boot_bin; scp ./BOOT.BIN root@192.168.10.122: - On board: Put the BOOT.BIN into the BOOT partition.
Power cycle the board to load new FPGA bitstream.mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt cp ~/BOOT.BIN /mnt cd /mnt sync cd ~ umount /mnt
Update Driver
Since the pre-built SD card image might not have the latest bug-fixes/updates, it is recommended to update the driver on board.
- Prepare Analog Devices Linux kernel source code (only need to run once):
Note: In Ubuntu, gcc-10 might have issue ('yylloc' error), so use gcc-9 if you encounter error.cd openwifi/user_space; ./prepare_kernel.sh $XILINX_DIR ARCH_BIT build (For Zynq 7000, ARCH_BIT should be 32, for Zynq MPSoC, ARCH_BIT should be 64) - Compile the latest openwifi driver
cd openwifi/driver; ./make_all.sh $XILINX_DIR ARCH_BIT (For Zynq 7000, ARCH_BIT should be 32, for Zynq MPSoC, ARCH_BIT should be 64) - Copy the driver files to the board via ssh channel
Now you can use wgd.sh on board to load the new openwifi driver. Note: If you have symbol or version error while loadng the driver, it could be because the kernel in the SD card image is too old. In this case, you need to follow [Build openwifi Linux img from scratch] to generate your new SD card image.cd openwifi/driver; scp `find ./ -name \*.ko` root@192.168.10.122:openwifi/
Update sdrctl
- Copy the sdrctl source files to the board via ssh channel
cd openwifi/user_space/sdrctl_src; scp `find ./ -name \*` root@192.168.10.122:openwifi/sdrctl_src/ - Compile the sdrctl on board:
cd ~/openwifi/sdrctl_src/ && make && cp sdrctl ../ && cd ..
Easy Access and etc
- FPGA and driver on board update scripts
- Setup ftp server on PC, allow anonymous and change ftp root directory to the openwifi directory.
- On board:
./sdcard_boot_update.sh $BOARD_NAME (Above command downloads uImage, BOOT.BIN and devicetree.dtb, then copy them into boot partition. Remember to power cycle) ./wgd.sh remote (Above command downloads driver files, and brings up sdr0) - Access the board disk/rootfs like a disk:
- On PC: "File manager --> Connect to Server...", input: sftp://root@192.168.10.122/root
- Input password "openwifi"
Build openwifi Linux img from scratch
-
Install the devicetree compiler -- dtc. (For Ubuntu: sudo apt install device-tree-compiler)
-
Install the mkimage tool. (For Ubuntu: sudo apt install u-boot-tools)
-
Download 2019_R1-2020_06_22.img.xz from Analog Devices Wiki. Burn it to a SD card.
-
Insert the SD card to your Linux PC. Find out the mount point (that has two sub directories BOOT and rootfs), and setup environment variables (use absolute path):
export SDCARD_DIR=sdcard_mount_point export XILINX_DIR=your_Xilinx_install_directory export OPENWIFI_HW_DIR=your_openwifi-hw_directory export BOARD_NAME=your_board_name -
Run script to update SD card:
cd openwifi/user_space; ./update_sdcard.sh $OPENWIFI_HW_DIR $XILINX_DIR $BOARD_NAME $SDCARD_DIR -
Config your board to SD card boot mode (check the board manual). Insert the SD card to the board. Power on.
-
Login to the board from your PC (PC Ethernet should have IP 192.168.10.1) with one time password analog.
ssh root@192.168.10.122 -
Setup routing/NAT on the PC for your board -- this internet connection is important for post installation/config.
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o NICY -j MASQUERADE sudo ip route add 192.168.13.0/24 via 192.168.10.122 dev ethXethX is the PC NIC name connecting the board ethernet. NICY is the PC NIC name connecting internet (WiFi or another ethernet).
If you want, uncommenting "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" in /etc/sysctl.conf to make IP forwarding persistent on PC.
-
Run one time script on board to complete post installation/config (After this, password becomes openwifi)
cd ~/openwifi && ./post_config.sh -
Now you can start from Quick start (Skip the image download and burn step)
Special note for 11b
Openwifi only applies OFDM as its modulation scheme and as a result, it is not backward compatible with 802.11b clients or modes of operation. This is usually the case during beacon transmission, connection establishment, and robust communication.
As a solution to this problem, openwifi can be fully controlled only if communicating with APs/clients instantiated using hostapd/wpa_supplicant userspace programs respectively.
For hostapd program, 802.11b rates can be suppressed using configuration commands (i.e. supported_rates, basic_rates) and an example configuration file is provided (i.e. hostapd-openwifi.conf). One small caveat to this one comes from fullMAC Wi-Fi cards as they must implement the NL80211_TXRATE_LEGACY NetLink handler at the device driver level.
On the other hand, the wpa_supplicant program on the client side (commercial Wi-Fi dongle/board) cannot suppress 802.11b rates out of the box in 2.4GHz band, so there will be an issue when connecting openwifi (OFDM only). A patched wpa_supplicant should be used at the client side.
sudo apt-get install libssl1.0-dev
cd openwifi/user_space; ./build_wpa_supplicant_wo11b.sh
Porting guide
This section explains the porting work by showing the differences between openwifi and Analog Devices reference design. openwifi is based on 2019_R1 of HDL Reference Designs.
- Open the fmcomms2 + zc706 reference design at hdl/projects/fmcomms2/zc706 (Please read Analog Devices help)
- Open the openwifi design zc706_fmcs2 at openwifi-hw/boards/zc706_fmcs2 (Please read openwifi-hw repository)
- "Open Block Design", you will see the differences between openwifi and the reference design. Both in "diagram" and in "Address Editor".
- The address/interrupts of FPGA blocks hooked to the ARM bus should be put/aligned to the devicetree file openwifi/kernel_boot/boards/zc706_fmcs2/devicetree.dts. Linux will parse the devicetree.dtb when booting to know information of attached device (FPGA blocks in our case).
- We use dtc command to get devicetree.dts converted from devicetree.dtb in Analog Devices Linux image, then do modification according to what we have added/modified to the reference design.
- Please learn the script in [Build openwifi Linux img from scratch] to understand how we generate devicetree.dtb, BOOT.BIN and Linux kernel uImage and put them together to build the full SD card image.
License
This project is available as open source under the terms of the AGPL 3.0 Or later. However, some elements are being licensed under GPL 2-0 or later and BSD 3 license . For accurate information, please check individual files.