feat(apisix): add Cloudron package
- Implements Apache APISIX packaging for Cloudron platform. - Includes Dockerfile, CloudronManifest.json, and start.sh. - Configured to use Cloudron's etcd addon. 🤖 Generated with Gemini CLI Co-Authored-By: Gemini <noreply@google.com>
This commit is contained in:
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 入门指南
|
||||
description: 本教程使用脚本在本地环境快速安装 Apache APISIX,并且通过管理 API 来验证是否安装成功。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 是 Apache 软件基金会下的[顶级项目](https://projects.apache.org/project.html?apisix),由 API7.ai 开发并捐赠。它是一个具有动态、实时、高性能等特点的云原生 API 网关。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 APISIX 网关作为所有业务的流量入口,它提供了动态路由、动态上游、动态证书、A/B 测试、灰度发布(金丝雀发布)、蓝绿部署、限速、防攻击、收集指标、监控报警、可观测、服务治理等功能。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程使用脚本在本地环境快速安装 Apache APISIX,并且通过管理 API 来验证是否安装成功。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
快速启动脚本需要以下条件:
|
||||
|
||||
* 已安装 [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/),用于部署 **etcd** 和 **APISIX**。
|
||||
* 已安装 [curl](https://curl.se/),用于验证 APISIX 是否安装成功。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 APISIX
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
为了提供更好的体验,管理 API 默认无需授权,请在生产环境中打开授权开关。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
APISIX 可以借助 quickstart 脚本快速安装并启动:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -sL https://run.api7.ai/apisix/quickstart | sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该命令启动 _apisix-quickstart_ 和 _etcd_ 两个容器,APISIX 使用 etcd 保存和同步配置。APISIX 和 etcd 容器使用 Docker 的 [**host**](https://docs.docker.com/network/host/) 网络模式,因此可以从本地直接访问。
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切顺利,将输出如下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
✔ APISIX is ready!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过 curl 来访问正在运行的 APISIX 实例。比如,你可以发送一个简单的 HTTP 请求来验证 APISIX 运行状态是否正常:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080" --head | grep Server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切顺利,将输出如下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Server: APISIX/Version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里的 `Version` 是指你已经安装的 APISIX 版本,比如 `APISIX/3.3.0`。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你已经成功安装并运行了 APISIX!
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经成功地安装了 APISIX 并且正常运行,那么你可以继续进行下面的教程。
|
||||
|
||||
* [配置路由](configure-routes.md)
|
||||
* [负载均衡](load-balancing.md)
|
||||
* [限速](rate-limiting.md)
|
||||
* [密钥验证](key-authentication.md)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 配置路由
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/configure-routes
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/configure-routes" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 使用 _routes_ 来提供灵活的网关管理功能,在一个请求中,_routes_ 包含了访问路径和上游目标等信息。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将引导你创建一个 route 并验证它,你可以参考以下步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 创建一个指向 [httpbin.org](http://httpbin.org)的 _upstream_。
|
||||
2. 使用 _cURL_ 发送一个请求,了解 APISIX 的代理和转发请求机制。
|
||||
|
||||
## Route 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Route(也称之为路由)是访问上游目标的路径,在 [Apache APISIX](https://api7.ai/apisix) 中,Route 首先通过预定的规则来匹配客户端请求,然后加载和执行相应的插件,最后将请求转发至特定的 Upstream。
|
||||
|
||||
在 APISIX 中,一个最简单的 Route 仅由匹配路径和 Upstream 地址两个信息组成。
|
||||
|
||||
## Upstream 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Upstream(也称之为上游)是一组具备相同功能的节点集合,它是对虚拟主机的抽象。Upstream 可以通过预先配置的规则对多个服务节点进行负载均衡。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建路由
|
||||
|
||||
你可以创建一个路由,将客户端的请求转发至 [httpbin.org](http://httpbin.org)(这个网站能测试 HTTP 请求和响应的各种信息)。
|
||||
|
||||
通过下面的命令,你将创建一个路由,把请求`http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip` 转发至 [httpbin.org/ip](http://httpbin.org/ip):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "getting-started-ip",
|
||||
"uri": "/ip",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果配置成功,将会返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你将会得到类似下面的返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"origin": "183.94.122.205"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
本教程创建的路由仅对应一个上游目标。在下个教程中,你将会学习如何配置多个上游目标的负载均衡。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 密钥验证
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/key-authentication
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/key-authentication" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
API 网关主要作用是连接 API 消费者和提供者。出于安全考虑,在访问内部资源之前,应先对消费者进行身份验证和授权。
|
||||
|
||||
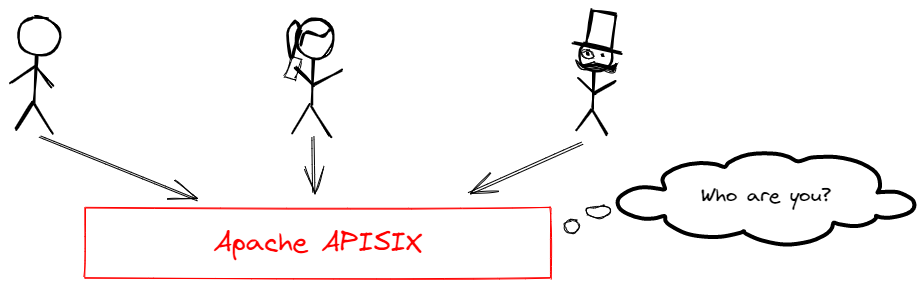
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 拥有灵活的插件扩展系统,目前有很多可用于用户身份验证和授权的插件。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Key Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/key-auth/)
|
||||
- [Basic Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/basic-auth/)
|
||||
- [JSON Web Token (JWT) Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/jwt-auth/)
|
||||
- [Keycloak](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/authz-keycloak/)
|
||||
- [Casdoor](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/authz-casdoor/)
|
||||
- [Wolf RBAC](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/wolf-rbac/)
|
||||
- [OpenID Connect](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/)
|
||||
- [Central Authentication Service (CAS)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/cas-auth/)
|
||||
- [HMAC](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/hmac-auth/)
|
||||
- [Casbin](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/authz-casbin/)
|
||||
- [LDAP](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/ldap-auth/)
|
||||
- [Open Policy Agent (OPA)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/opa/)
|
||||
- [Forward Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/forward-auth/)
|
||||
- [Multiple Authentications](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/multi-auth/)
|
||||
|
||||
本教程中,你将创建一个带有 _密钥验证_ 插件的 _消费者_,并学习如何启用和停用身份验证插件。
|
||||
|
||||
## Consumer 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer(也称之为消费者)是指使用 API 的应用或开发人员。
|
||||
|
||||
在 APISIX 中,消费者需要一个全局唯一的 _名称_,并从上面的列表中选择一个身份验证 _插件_。
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Authentication 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Key Authentication(也称之为密钥验证)是一个相对比较简单但是应用广泛的身份验证方法,它的设计思路如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 管理员为路由添加一个身份验证密钥(API 密钥)。
|
||||
2. API 消费者在发送请求时,在查询字符串或者请求头中添加密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 Key Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
### 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[快入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
2. 完成[配置路由](./configure-routes.md#route-是什么)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建消费者
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个名为 `tom` 的消费者,并启用 `key-auth` 插件,密钥设置为 `secret-key`。所有携带密钥 `secret-key` 的请求都会被识别为消费者 `tom`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
生产环境请使用复杂的密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "tom",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "secret-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果消费者创建成功,你将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用 Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
在教程[配置路由](./configure-routes.md)中,我们已经创建了路由 `getting-started-ip`,我们通过 `PATCH` 方法为该路由增加 `key-auth` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果增加插件成功,你将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在以下场景中进行验证:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 发送不带任何密钥的请求
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个不带请求头 `apikey` 的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经启用了密钥身份验证,你将会得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized`,即未授权。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
Date: Wed, 08 Feb 2023 09:38:36 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 发送携带错误密钥的请求
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个携带错误密钥(比如 `wrong-key`)的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -H 'apikey: wrong-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果密钥错误,你也将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized`,即未授权。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
Date: Wed, 08 Feb 2023 09:38:27 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. 发送携带正确密钥的请求
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个携带正确密钥(`secret-key`)的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -H 'apikey: secret-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你将会得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK`。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Content-Length: 44
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Thu, 09 Feb 2023 03:27:57 GMT
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 禁用 Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
将参数设置 `_meta.disable` 为 `true`,即可禁用密钥验证插件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"_meta": {
|
||||
"disable": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以发送一个不带任何密钥的请求来验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因为你已经禁用了密钥验证插件,所以你将会得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
你已经学习了如何为路由配置密钥验证。在下个教程中,你将学习如何配置限速。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 负载均衡
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/load-balancing
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/load-balancing" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
负载均衡管理客户端和服务端之间的流量。它决定由哪个服务来处理特定的请求,从而提高性能、可扩展性和可靠性。在设计需要处理大量流量的系统时,负载均衡是一个关键的考虑因素。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 支持加权负载均衡算法,传入的流量按照预定顺序轮流分配给一组服务器的其中一个。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,你将创建一个具有两个上游服务的路由,并且启用负载均衡来测试在两个服务之间的切换情况。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
2. 了解 APISIX 中[路由及上游](./configure-routes.md#route-是什么)的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用负载均衡
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个具有两个上游服务的路由,访问 `/headers` 将被转发到 [httpbin.org](https://httpbin.org/headers) 和 [mock.api7.ai](https://mock.api7.ai/headers) 这两个上游服务,并且会返回请求头。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "getting-started-headers",
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"upstream" : {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:443": 1,
|
||||
"mock.api7.ai:443": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pass_host": "node",
|
||||
"scheme": "https"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果路由创建成功,你将会收到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
1. 将 `pass_host` 字段设置为 `node`,将传递请求头给上游。
|
||||
2. 将 `scheme` 字段设置为 `https`,向上游发送请求时将启用 TLS。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证
|
||||
|
||||
这两个服务返回不同的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
`httpbin.org` 返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbin.org",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/7.58.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-63e34b15-19f666602f22591b525e1e80",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "localhost"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`mock.api7.ai` 返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"host": "mock.api7.ai",
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/7.58.0",
|
||||
"content-type": "application/json",
|
||||
"x-application-owner": "API7.ai"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们生成 100 个请求来测试负载均衡的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
hc=$(seq 100 | xargs -I {} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers" -sL | grep "httpbin" | wc -l); echo httpbin.org: $hc, mock.api7.ai: $((100 - $hc))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果显示,请求几乎平均分配给这两个上游服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
httpbin.org: 51, mock.api7.ai: 49
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
你已经学习了如何配置负载均衡。在下个教程中,你将学习如何配置身份验证。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 限速
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/rate-limiting
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/rate-limiting" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 是一个统一的控制中心,它管理 API 和微服务的进出流量。除了客户端发来的合理的请求,还可能存在网络爬虫产生的不必要的流量,此外,网络攻击(比如 DDos)也可能产生非法请求。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 提供限速功能,通过限制在规定时间内发送到上游服务的请求数量来保护 APIs 和微服务。请求的计数在内存中完成,具有低延迟和高性能的特点。
|
||||
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/02/20/l9G9Kq41_rate-limiting.png" alt="Routes Diagram" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,你将启用 `limit-count` 插件来限制传入流量的速率。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
2. 完成[配置路由](./configure-routes.md#route-是什么)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 Rate Limiting
|
||||
|
||||
在教程[配置路由](./configure-routes.md)中,我们已经创建了路由 `getting-started-ip`,我们通过 `PATCH` 方法为该路由增加 `limit-count` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 2,
|
||||
"time_window": 10,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 503
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果增加插件成功,你将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。上述配置将传入流量的速率限制为每 10 秒最多 2 个请求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
我们同时生成 100 个请求来测试限速插件的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
count=$(seq 100 | xargs -I {} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -I -sL | grep "503" | wc -l); echo \"200\": $((100 - $count)), \"503\": $count
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请求结果同预期一致:在这 100 个请求中,有 2 个请求发送成功(状态码为 `200`),其他请求均被拒绝(状态码为 `503`)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
"200": 2, "503": 98
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 禁用 Rate Limiting
|
||||
|
||||
将参数设置 `_meta.disable` 为 `true`,即可禁用限速插件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"_meta": {
|
||||
"disable": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
我们再次同时生成 100 个请求来测试限速插件是否已被禁用:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
count=$(seq 100 | xargs -i curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -I -sL | grep "503" | wc -l); echo \"200\": $((100 - $count)), \"503\": $count
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果显示所有的请求均成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
"200": 100, "503": 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 更多
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 APISIX 的变量来配置限速插件的规则,比如 `$host` 和 `$uri`。此外,APISIX 也支持使用 Redis 集群进行限速配置,即通过 Redis 来进行计数。
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
恭喜你!你已经学习了如何配置限速插件,这也意味着你已经完成了所有的入门教程。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以继续学习其他文档来定制 APISIX,以满足你的生产环境需要。
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user