feat(apisix): add Cloudron package
- Implements Apache APISIX packaging for Cloudron platform. - Includes Dockerfile, CloudronManifest.json, and start.sh. - Configured to use Cloudron's etcd addon. 🤖 Generated with Gemini CLI Co-Authored-By: Gemini <noreply@google.com>
This commit is contained in:
1593
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/CHANGELOG.md
Normal file
1593
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/CHANGELOG.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@@ -0,0 +1,426 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: APISIX Lua 编码风格指南
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 缩进
|
||||
|
||||
使用 4 个空格作为缩进的标记:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
if a then
|
||||
ngx.say("hello")
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
if a then
|
||||
ngx.say("hello")
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在使用的编辑器中把 tab 改为 4 个空格来简化操作。
|
||||
|
||||
## 空格
|
||||
|
||||
在操作符的两边,都需要用一个空格来做分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local i=1
|
||||
local s = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local i = 1
|
||||
local s = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 空行
|
||||
|
||||
不少开发者会在行尾增加一个分号:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
if a then
|
||||
ngx.say("hello");
|
||||
end;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
增加分号会让 Lua 代码显得非常丑陋,也是没有必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,不要为了显得“简洁”节省代码行数,而把多行代码变为一行。这样会在定位错误的时候不知道到底哪一段代码出了问题:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
if a then ngx.say("hello") end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
if a then
|
||||
ngx.say("hello")
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
函数之间需要用两个空行来做分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
end
|
||||
local function bar()
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
local function bar()
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果有多个 if elseif 的分支,它们之间需要一个空行来做分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
if a == 1 then
|
||||
foo()
|
||||
elseif a== 2 then
|
||||
bar()
|
||||
elseif a == 3 then
|
||||
run()
|
||||
else
|
||||
error()
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
if a == 1 then
|
||||
foo()
|
||||
|
||||
elseif a== 2 then
|
||||
bar()
|
||||
|
||||
elseif a == 3 then
|
||||
run()
|
||||
|
||||
else
|
||||
error()
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 每行最大长度
|
||||
|
||||
每行不能超过 80 个字符,超过的话,需要换行并对齐:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
return limit_conn_new("plugin-limit-conn", conf.conn, conf.burst, conf.default_conn_delay)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
return limit_conn_new("plugin-limit-conn", conf.conn, conf.burst,
|
||||
conf.default_conn_delay)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在换行对齐的时候,要体现出上下两行的对应关系。
|
||||
|
||||
就上面示例而言,第二行函数的参数,要在第一行左括号的右边。
|
||||
|
||||
如果是字符串拼接的对齐,需要把 `..` 放到下一行中:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
return limit_conn_new("plugin-limit-conn" .. "plugin-limit-conn" ..
|
||||
"plugin-limit-conn")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
return limit_conn_new("plugin-limit-conn" .. "plugin-limit-conn"
|
||||
.. "plugin-limit-conn")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
return "param1", "plugin-limit-conn"
|
||||
.. "plugin-limit-conn")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 变量
|
||||
|
||||
应该永远使用局部变量,不要使用全局变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
i = 1
|
||||
s = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local i = 1
|
||||
local s = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
变量命名使用 `snake_case`(蛇形命名法)风格:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local IndexArr = 1
|
||||
local str_Name = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local index_arr = 1
|
||||
local str_name = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于常量要使用全部大写:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local max_int = 65535
|
||||
local server_name = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local MAX_INT = 65535
|
||||
local SERVER_NAME = "apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 表格/数组
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `table.new` 来预先分配数组:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local t = {}
|
||||
for i = 1, 100 do
|
||||
t[i] = i
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local new_tab = require "table.new"
|
||||
local t = new_tab(100, 0)
|
||||
for i = 1, 100 do
|
||||
t[i] = i
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
不要在数组中使用 `nil`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local t = {1, 2, nil, 3}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果一定要使用空值,请用 `ngx.null` 来表示:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local t = {1, 2, ngx.null, 3}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 字符串
|
||||
|
||||
不要在热代码路径上拼接字符串:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local s = ""
|
||||
for i = 1, 100000 do
|
||||
s = s .. "a"
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local new_tab = require "table.new"
|
||||
local t = new_tab(100000, 0)
|
||||
for i = 1, 100000 do
|
||||
t[i] = "a"
|
||||
end
|
||||
local s = table.concat(t, "")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 函数
|
||||
|
||||
函数的命名也同样遵循 `snake_case`(蛇形命名法):
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local function testNginx()
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local function test_nginx()
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
函数应该尽可能早的返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local function check(age, name)
|
||||
local ret = true
|
||||
if age < 20 then
|
||||
ret = false
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
if name == "a" then
|
||||
ret = false
|
||||
end
|
||||
-- do something else
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local function check(age, name)
|
||||
if age < 20 then
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
if name == "a" then
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end
|
||||
-- do something else
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 模块
|
||||
|
||||
所有 `require` 的库都要 `local` 化:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = ngx.timer.at(delay, handler)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local timer_at = ngx.timer.at
|
||||
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = timer_at(delay, handler)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了风格的统一,`require` 和 `ngx` 也需要 `local` 化:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local core = require("apisix.core")
|
||||
local timer_at = ngx.timer.at
|
||||
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = timer_at(delay, handler)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local ngx = ngx
|
||||
local require = require
|
||||
local core = require("apisix.core")
|
||||
local timer_at = ngx.timer.at
|
||||
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = timer_at(delay, handler)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 错误处理
|
||||
|
||||
对于有错误信息返回的函数,必须对错误信息进行判断和处理:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local sock = ngx.socket.tcp()
|
||||
local ok = sock:connect("www.google.com", 80)
|
||||
ngx.say("successfully connected to google!")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local sock = ngx.socket.tcp()
|
||||
local ok, err = sock:connect("www.google.com", 80)
|
||||
if not ok then
|
||||
ngx.say("failed to connect to google: ", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
end
|
||||
ngx.say("successfully connected to google!")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
自己编写的函数,错误信息要作为第二个参数,用字符串的格式返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = func()
|
||||
if not ok then
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--No
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = func()
|
||||
if not ok then
|
||||
return false, {msg = err}
|
||||
end
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
--Yes
|
||||
local function foo()
|
||||
local ok, err = func()
|
||||
if not ok then
|
||||
return false, "failed to call func(): " .. err
|
||||
end
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
777
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/FAQ.md
Normal file
777
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/FAQ.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,777 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 常见问题
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 常见问题
|
||||
- FAQ
|
||||
description: 本文列举了使用 Apache APISIX 时常见问题解决方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 为什么需要一个新的 API 网关?不是已经有其他的开源网关了吗?
|
||||
|
||||
随着企业向云本地微服务的发展,企业对高性能、灵活、安全、可扩展的 API 网关的需求越来越大。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 在这些指标表现上优于其它 API 网关,同时具有平台无关性和完全动态的特性,如支持多种协议、细粒度路由和多语言支持。
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 和其他的 API 网关有什么不同之处?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 在以下方面有所不同:
|
||||
|
||||
— 它使用 etcd 来保存和同步配置,而不是使用如 PostgreSQL 或 MySQL 这类的关系数据库。etcd 中的实时事件通知系统比这些替代方案更容易扩展。这允许 APISIX 实时同步配置,使代码简洁,并避免单点故障。
|
||||
|
||||
- 完全动态
|
||||
- 支持[热加载插件](./terminology/plugin.md#热加载)。
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 所展现出的性能如何?
|
||||
|
||||
与其它 API 网关相比,Apache APISIX 提供了更好的性能,其单核 QPS 高达 18,000,平均延迟仅为 0.2 ms。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想获取性能基准测试的具体结果,请查看 [benchmark](benchmark.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## Apache APISIX 支持哪些平台?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 是一个开源的云原生 API 网关,它支持在裸金属服务器上运行,也支持在 Kubernetes 上使用,甚至也可以运行在 Apple Silicon ARM 芯片上。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何理解“Apache APISIX 是全动态的”?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 是全动态的 API 网关,意味着当你在更改一个配置后,只需要重新加载配置文件就可以使其生效。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 可以动态处理以下行为:
|
||||
|
||||
- 重新加载插件
|
||||
- 代理重写
|
||||
- 对请求进⾏镜像复制
|
||||
- 对请求进⾏修改
|
||||
- 健康状态的检查
|
||||
- 动态控制指向不同上游服务的流量⽐
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 是否有控制台界面?
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 具有功能强大的 Dashboard,并且 [APISIX Dashboard](https://github.com/apache/apisix-dashboard) 是一个独立的项目。你可以通过 [APISIX Dashboard](https://github.com/apache/apisix-dashboard) 用户操作界面来部署 APISIX Dashboard。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我可以为 Apache APISIX 开发适合自身业务的插件吗?
|
||||
|
||||
当然可以,APISIX 提供了灵活的自定义插件,方便开发者和企业编写自己的逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想开发符合自身业务逻辑的插件,请参考:[如何开发插件](plugin-develop.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为什么 Apache APISIX 选择 etcd 作为配置中心?
|
||||
|
||||
对于配置中心,配置存储只是最基本功能,APISIX 还需要下面几个特性:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 集群中的分布式部署
|
||||
2. 通过比较来监视业务
|
||||
3. 多版本并发控制
|
||||
4. 变化通知
|
||||
5. 高性能和最小的读/写延迟
|
||||
|
||||
etcd 提供了这些特性,并且使它比 PostgreSQL 和 MySQL 等其他数据库更理想。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解更多关于 etcd 与其他替代方案的比较,请参考[对比图表](https://etcd.io/docs/latest/learning/why/#comparison-chart)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用 LuaRocks 安装 Apache APISIX 依赖项时,为什么会导致超时、安装缓慢或安装失败?
|
||||
|
||||
可能是因为使用的 LuaRocks 服务器延迟过高。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,你可以使用 https_proxy 或者使用 `--server` 参数指定一个更快的 LuaRocks 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行如下命令来查看可用的服务器(需要 LuaRocks 3.0+):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
luarocks config rocks_servers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
中国大陆用户可以使用 `luarocks.cn` 作为 LuaRocks 的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
以下命令可以帮助你更快速的安装依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make deps ENV_LUAROCKS_SERVER=https://luarocks.cn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果通过上述操作仍然无法解决问题,可以尝试使用 `--verbose` 或 `-v` 参数获取详细的日志来诊断问题。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何构建 APISIX-Runtime 环境?
|
||||
|
||||
有些功能需要引入额外的 NGINX 模块,这就要求 APISIX 需要运行在 APISIX-Runtime 上。如果你需要这些功能,你可以参考 [api7/apisix-build-tools](https://github.com/api7/apisix-build-tools) 中的代码,构建自己的 APISIX-Runtime 环境。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我该如何使用 Apache APISIX 进行灰度发布?
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,比如:`foo.com/product/index.html?id=204&page=2`,并考虑您需要根据查询字符串中的 `id` 在此条件下进行灰度发布:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Group A:`id <= 1000`
|
||||
2. Group B:`id > 1000`
|
||||
|
||||
在 Apache APISIX 中有两种不同的方法来实现这一点:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 创建一个[Route](terminology/route.md)并配置 `vars` 字段:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
["arg_id", "<=", "1000"]
|
||||
],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"redirect": {
|
||||
"uri": "/test?group_id=1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/2 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
["arg_id", ">", "1000"]
|
||||
],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"redirect": {
|
||||
"uri": "/test?group_id=2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
更多 `lua-resty-radixtree` 匹配操作,请参考:[lua-resty-radixtree](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-radixtree#operator-list)。
|
||||
|
||||
2、通过 [traffic-split](plugins/traffic-split.md) 插件来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我如何通过 Apache APISIX 实现从 HTTP 自动跳转到 HTTPS?
|
||||
|
||||
比如,将 `http://foo.com` 重定向到 `https://foo.com`。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 提供了几种不同的方法来实现:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在 [redirect](plugins/redirect.md) 插件中将 `http_to_https` 设置为 `true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"host": "foo.com",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"redirect": {
|
||||
"http_to_https": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 结合高级路由规则 `vars` 和 `redirect` 插件一起使用:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"host": "foo.com",
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
[
|
||||
"scheme",
|
||||
"==",
|
||||
"http"
|
||||
]
|
||||
],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"redirect": {
|
||||
"uri": "https://$host$request_uri",
|
||||
"ret_code": 301
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 使用 `serverless` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"serverless-pre-function": {
|
||||
"phase": "rewrite",
|
||||
"functions": ["return function() if ngx.var.scheme == \"http\" and ngx.var.host == \"foo.com\" then ngx.header[\"Location\"] = \"https://foo.com\" .. ngx.var.request_uri; ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_MOVED_PERMANENTLY); end; end"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后测试下是否生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -H 'Host: foo.com' http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应信息应该是:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
|
||||
Date: Mon, 18 May 2020 02:56:04 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/html
|
||||
Content-Length: 166
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Location: https://foo.com/hello
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head><title>301 Moved Permanently</title></head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<center><h1>301 Moved Permanently</h1></center>
|
||||
<hr><center>openresty</center>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 我应该如何更改 Apache APISIX 的日志等级?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 默认的日志等级为 `warn`,你需要将日志等级调整为 `info` 来查看 `core.log.info` 的打印结果。
|
||||
|
||||
你需要将 `./conf/config.yaml` 中的 `nginx_config` 配置参数 `error_log_level: "warn"` 修改为 `error_log_level: "info"`,然后重新加载 Apache APISIX 使其生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
nginx_config:
|
||||
error_log_level: "info"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 我应该如何重新加载 Apache APISIX 的自定义插件?
|
||||
|
||||
所有的 Apache APISIX 的插件都支持热加载的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解更多关于热加载的内容,请参考[热加载](./terminology/plugin.md#热加载)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 在处理 HTTP 或 HTTPS 请求时,我该如何配置 Apache APISIX 来监听多个端口?
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,APISIX 在处理 HTTP 请求时只监听 9080 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
要配置 Apache APISIX 监听多个端口,你可以:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 修改 `conf/config.yaml` 中 HTTP 端口监听的参数 `node_listen`,示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
node_listen:
|
||||
- 9080
|
||||
- 9081
|
||||
- 9082
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
处理 HTTPS 请求也类似,修改 `conf/config.yaml` 中 HTTPS 端口监听的参数 `ssl.listen`,示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
enable: true
|
||||
listen:
|
||||
- port: 9443
|
||||
- port: 9444
|
||||
- port: 9445
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 重启或者重新加载 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 SSL 证书后,为什么无法通过 HTTPS + IP 访问对应的路由?
|
||||
|
||||
如果直接使用 HTTPS + IP 地址访问服务器,服务器将会使用 IP 地址与绑定的 SNI 进行比对,由于 SSL 证书是和域名进行绑定的,无法在 SNI 中找到对应的资源,因此证书就会校验失败,进而导致用户无法通过 HTTPS + IP 访问网关。
|
||||
|
||||
此时你可以通过在配置文件中设置 `fallback_sni` 参数,并配置域名,实现该功能。当用户使用 HTTPS + IP 访问网关时,SNI 为空时,则 fallback 到默认 SNI,从而实现 HTTPS + IP 访问网关。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
apisix
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
fallback_sni: "${your sni}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 如何利用 etcd 如何实现毫秒级别的配置同步?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 使用 etcd 作为它的配置中心。etcd 提供以下订阅功能(比如:[watch](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-etcd/blob/master/api_v3.md#watch)、[watchdir](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-etcd/blob/master/api_v3.md#watchdir))。它可以监视对特定关键字或目录的更改。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 主要使用 [etcd.watchdir](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-etcd/blob/master/api_v3.md#watchdir) 监视目录内容变更:
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果监听目录没有数据更新:则该调用会被阻塞,直到超时或其他错误返回。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果监听目录有数据更新:etcd 将立刻返回订阅(毫秒级)到的新数据,APISIX 将它更新到内存缓存。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我应该如何自定义 APISIX 实例 id?
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,APISIX 从 `conf/apisix.uid` 中读取实例 id。如果找不到,且没有配置 id,APISIX 会生成一个 `uuid` 作为实例 id。
|
||||
|
||||
要指定一个有意义的 id 来绑定 Apache APISIX 到你的内部系统,请在你的 `./conf/config.yaml` 中设置 id:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
id: "your-id"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 为什么 `error.log` 中会出现 "failed to fetch data from etcd, failed to read etcd dir, etcd key: xxxxxx" 的错误?
|
||||
|
||||
请按照以下步骤进行故障排除:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 确保 Apache APISIX 和集群中的 etcd 部署之间没有任何网络问题。
|
||||
2. 如果网络正常,请检查是否为 etcd 启用了[gRPC gateway](https://etcd.io/docs/v3.4.0/dev-guide/api_grpc_gateway/)。默认状态取决于你是使用命令行还是配置文件来启动 etcd 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果使用命令行选项,默认启用 gRPC 网关。可以手动启用,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
etcd --enable-grpc-gateway --data-dir=/path/to/data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:当运行 `etcd --help` 时,这个参数不会显示。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果使用配置文件,默认关闭 gRPC 网关。你可以手动启用,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
在 `etcd.json` 配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"enable-grpc-gateway": true,
|
||||
"data-dir": "/path/to/data"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 `etcd.conf.yml` 配置
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
enable-grpc-gateway: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:事实上这种差别已经在 etcd 的 master 分支中消除,但并没有向后兼容到已经发布的版本中,所以在部署 etcd 集群时,依然需要小心。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我应该如何创建高可用的 Apache APISIX 集群?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 可以通过在其前面添加一个负载均衡器来实现高可用性,因为 APISIX 的数据面是无状态的,并且可以在需要时进行扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 的控制平面是依赖于 `etcd cluster` 的高可用实现的,它只依赖于 etcd 集群。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为什么使用源码安装 Apache APISIX 时,执行 `make deps` 命令会失败?
|
||||
|
||||
当使用源代码安装 Apache APISIX 时,执行 `make deps` 命令可能会出现如下错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ make deps
|
||||
......
|
||||
Error: Failed installing dependency: https://luarocks.org/luasec-0.9-1.src.rock - Could not find header file for OPENSSL
|
||||
No file openssl/ssl.h in /usr/local/include
|
||||
You may have to install OPENSSL in your system and/or pass OPENSSL_DIR or OPENSSL_INCDIR to the luarocks command.
|
||||
Example: luarocks install luasec OPENSSL_DIR=/usr/local
|
||||
make: *** [deps] Error 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这是由于缺少 OpenResty openssl 开发工具包。要安装它,请参考[installation dependencies](install-dependencies.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我如何通过 APISIX 代理访问 APISIX Dashboard?
|
||||
|
||||
你可以按照以下步骤进行配置:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 为 Apache APISIX 代理和 Admin API 配置不同的端口,或者禁用 Admin API。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
admin:
|
||||
admin_listen: # use a separate port
|
||||
ip: 127.0.0.1
|
||||
port: 9180
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2、添加 APISIX Dashboard 的代理路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uris":[ "/*" ],
|
||||
"name":"apisix_proxy_dashboard",
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"nodes":[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host":"127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port":9000,
|
||||
"weight":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: Apache APISIX Dashboard 正在监听 `127.0.0.1:9000`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何使用正则表达式 (regex) 匹配 Route 中的 `uri`?
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 Route 中使用 `vars` 字段来匹配正则表达式:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/*",
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
["uri", "~~", "^/[a-z]+$"]
|
||||
],
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# uri 匹配成功
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -i
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
# uri 匹配失败
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/12ab -i
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解 `vars` 字段的更多信息,请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。
|
||||
|
||||
## Upstream 节点是否支持配置 [FQDN](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fully_qualified_domain_name) 地址?
|
||||
|
||||
这是支持的,下面是一个 `FQDN` 为 `httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local`(一个 Kubernetes Service)的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/ip",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令测试路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin API 的 `X-API-KEY` 指的是什么?是否可以修改?
|
||||
|
||||
Admin API 的 `X-API-KEY` 指的是 `./conf/config.yaml` 文件中的 `deployment.admin.admin_key.key`,默认值是 `edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1`。它是 Admin API 的访问 token。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,它被设置为 `edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1`,也可以通过修改 `./conf/conf/config` 中的参数来修改,如下示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
admin:
|
||||
admin_key
|
||||
- name: "admin"
|
||||
key: newkey
|
||||
role: admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后访问 Admin API:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY: newkey' -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uris":[ "/*" ],
|
||||
"name":"admin-token-test",
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"nodes":[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host":"127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port":1980,
|
||||
"weight":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
......
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:通过使用默认令牌,可能会面临安全风险。在将其部署到生产环境时,需要对其进行更新。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何允许所有 IP 访问 Apache APISIX 的 Admin API?
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 默认只允许 `127.0.0.0/24` 的 IP 段范围访问 `Admin API`,
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想允许所有的 IP 访问,只需在 `./conf/config.yaml` 配置文件中添加如下的配置,然后重启或重新加载 APISIX 就可以让所有 IP 访问 `Admin API`。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
admin:
|
||||
allow_admin:
|
||||
- 0.0.0.0/0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:你可以在非生产环境中使用此方法,以允许所有客户端从任何地方访问 Apache APISIX 实例,但是在生产环境中该设置并不安全。在生产环境中,请仅授权特定的 IP 地址或地址范围访问 Apache APISIX 实例。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何基于 acme.sh 自动更新 APISIX SSL 证书?
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行以下命令来实现这一点:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --output /root/.acme.sh/renew-hook-update-apisix.sh --silent https://gist.githubusercontent.com/anjia0532/9ebf8011322f43e3f5037bc2af3aeaa6/raw/65b359a4eed0ae990f9188c2afa22bacd8471652/renew-hook-update-apisix.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
chmod +x /root/.acme.sh/renew-hook-update-apisix.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
acme.sh --issue --staging -d demo.domain --renew-hook "/root/.acme.sh/renew-hook-update-apisix.sh -h http://apisix-admin:port -p /root/.acme.sh/demo.domain/demo.domain.cer -k /root/.acme.sh/demo.domain/demo.domain.key -a xxxxxxxxxxxxx"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
acme.sh --renew --domain demo.domain
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
详细步骤,请参考 [APISIX 基于 acme.sh 自动更新 HTTPS 证书](https://juejin.cn/post/6965778290619449351)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 在 Apache APISIX 中,我如何在转发到上游之前从路径中删除一个前缀?
|
||||
|
||||
在转发至上游之前移除请求路径中的前缀,比如说从 `/foo/get` 改成 `/get`,可以通过 `[proxy-rewrite](plugins/proxy-rewrite.md)` 插件来实现:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/foo/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"regex_uri": ["^/foo/(.*)","/$1"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试这个配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/foo/get -i
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
{
|
||||
...
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 我应该如何解决 `unable to get local issuer certificate` 这个错误?
|
||||
|
||||
你可以手动设置证书的路径,将其添加到 `./conf/config.yaml` 文件中,具体操作如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
ssl_trusted_certificate: /path/to/certs/ca-certificates.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:**当你尝试使用 cosocket 连接任何 TLS 服务时,如果 APISIX 不信任对端 TLS 服务证书,都需要配置 `apisix.ssl.ssl_trusted_certificate`。
|
||||
|
||||
例如:如果在 APISIX 中使用 Nacos 作为服务发现时,Nacos 开启了 TLS 协议,即 Nacos 配置的 `host` 是 `https://` 开头,就需要配置 `apisix.ssl.ssl_trusted_certificate`,并且使用和 Nacos 相同的 CA 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 我应该如何解决 `module 'resty.worker.events' not found` 这个错误?
|
||||
|
||||
引起这个错误的原因是在 `/root` 目录下安装了 APISIX。因为 worker 进程的用户是 nobody,无权访问 `/root` 目录下的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
解决办法是改变 APISIX 的安装目录,推荐安装在 `/usr/local` 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
## 在 Apache APISIX 中,`plugin-metadata` 和 `plugin-configs` 有什么区别?
|
||||
|
||||
两者之间的差异如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| `plugin-metadata` | `plugin-config` |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 当更改该 Plugin 属性后,需要应用到配置该插件的所有路由上时使用。 | 当你需要复用一组通用的插件配置时使用,可以把 Plugin 配置提取到一个 `plugin-config` 并绑定到不同的路由。 |
|
||||
| 对绑定到 Plugin 的配置实例的所有实体生效。 | 对绑定到 `plugin-config` 的路由生效。 |
|
||||
| 对绑定到 Plugin 的配置实例的所有实体生效。 | 对绑定到 `plugin-config` 的路由生效。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署了 Apache APISIX 之后,如何检测 APISIX 数据平面的存活情况(如何探活)?
|
||||
|
||||
可以创建一个名为 `health-info` 的路由,并开启 [fault-injection](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/fault-injection/) 插件(其中 YOUR-TOKEN 是用户自己的 token;127.0.0.1 是控制平面的 IP 地址,可以自行修改):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/health-info \
|
||||
-H 'X-API-KEY: YOUR-TOKEN' -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"fault-injection": {
|
||||
"abort": {
|
||||
"http_status": 200,
|
||||
"body": "fine"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/status"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
验证方式:
|
||||
|
||||
访问 Apache APISIX 数据平面的 `/status` 来探测 APISIX,如果 response code 是 200 就代表 APISIX 存活。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
这个方式只是探测 APISIX 数据平面是否存活,并不代表 APISIX 的路由和其他功能是正常的,这些需要更多路由级别的探测。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 与 [etcd](https://etcd.io/) 相关的延迟较高的问题有哪些,如何修复?
|
||||
|
||||
etcd 作为 APISIX 的数据存储组件,它的稳定性关乎 APISIX 的稳定性。在实际场景中,如果 APISIX 使用证书通过 HTTPS 的方式连接 etcd,可能会出现以下 2 种数据查询或写入延迟较高的问题:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过接口操作 APISIX Admin API 进行数据的查询或写入,延迟较高。
|
||||
2. 在监控系统中,Prometheus 抓取 APISIX 数据面 Metrics 接口超时。
|
||||
|
||||
这些延迟问题,严重影响了 APISIX 的服务稳定性,而之所以会出现这类问题,主要是因为 etcd 对外提供了 2 种操作方式:HTTP(HTTPS)、gRPC。而 APISIX 默认是基于 HTTP(HTTPS)协议来操作 etcd 的。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个场景中,etcd 存在一个关于 HTTP/2 的 BUG:如果通过 HTTPS 操作 etcd(HTTP 不受影响),HTTP/2 的连接数上限为 Golang 默认的 `250` 个。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,当 APISIX 数据面节点数较多时,一旦所有 APISIX 节点与 etcd 连接数超过这个上限,则 APISIX 的接口响应会非常的慢。
|
||||
|
||||
Golang 中,默认的 HTTP/2 上限为 `250`,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package http2
|
||||
|
||||
import ...
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
prefaceTimeout = 10 * time.Second
|
||||
firstSettingsTimeout = 2 * time.Second // should be in-flight with preface anyway
|
||||
handlerChunkWriteSize = 4 << 10
|
||||
defaultMaxStreams = 250 // TODO: make this 100 as the GFE seems to?
|
||||
maxQueuedControlFrames = 10000
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
目前,etcd 官方主要维护了 `3.4` 和 `3.5` 这两个主要版本。在 `3.4` 系列中,近期发布的 `3.4.20` 版本已修复了这个问题。至于 `3.5` 版本,其实,官方很早之前就在筹备发布 `3.5.5` 版本了,但截止目前(2022.09.13)仍尚未发布。所以,如果你使用的是 etcd 的版本小于 `3.5.5`,可以参考以下几种方式解决这个问题:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 将 APISIX 与 etcd 的通讯方式由 HTTPS 改为 HTTP。
|
||||
2. 将 etcd 版本回退到 `3.4.20`。
|
||||
3. 将 etcd 源码克隆下来,直接编译 `release-3.5` 分支(此分支已修复,只是尚未发布新版本而已)。
|
||||
|
||||
重新编译 etcd 的方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git checkout release-3.5
|
||||
make GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编译的二进制在 `bin` 目录下,将其替换掉你服务器环境的 etcd 二进制后,然后重启 etcd 即可。
|
||||
|
||||
更多信息,请参考:
|
||||
|
||||
- [when etcd node have many http long polling connections, it may cause etcd to respond slowly to http requests.](https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/issues/14185)
|
||||
- [bug: when apisix starts for a while, its communication with etcd starts to time out](https://github.com/apache/apisix/issues/7078)
|
||||
- [the prometheus metrics API is tool slow](https://github.com/apache/apisix/issues/7353)
|
||||
- [Support configuring `MaxConcurrentStreams` for http2](https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/pull/14169)
|
||||
|
||||
另外一种解决办法是改用实验性的基于 gRPC 的配置同步。需要在配置文件 `conf/config.yaml` 中设置 `use_grpc: true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
etcd:
|
||||
use_grpc: true
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "http://127.0.0.1:2379"
|
||||
prefix: "/apisix"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 为什么 file-logger 记录日志会出现乱码?
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用的是 `file-logger` 插件,但是在日志文件中出现了乱码,那么可能是因为上游服务的响应体被进行了压缩。你可以将请求头带上不接收压缩响应参数(`gzip;q=0,deflate,sdch`)以解决这个问题,你可以使用 [proxy-rewirte](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/proxy-rewrite/) 插件将请求头中的 `accept-encoding` 设置为不接收压缩响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H 'X-API-KEY: YOUR-TOKEN' -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods":[
|
||||
"GET"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"uri":"/test/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins":{
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite":{
|
||||
"headers":{
|
||||
"set":{
|
||||
"accept-encoding":"gzip;q=0,deflate,sdch"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes":{
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:80":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 如何配置带认证的 ETCD?
|
||||
|
||||
假设您有一个启用身份验证的 ETCD 集群。要访问该集群,需要在 `conf/config.yaml` 中为 Apache APISIX 配置正确的用户名和密码:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
etcd:
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "http://127.0.0.1:2379"
|
||||
user: etcd_user # username for etcd
|
||||
password: etcd_password # password for etcd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
关于 ETCD 的其他配置,比如过期时间、重试次数等等,你可以参考 `conf/config.yaml.example` 文件中的 `etcd` 部分。
|
||||
|
||||
## SSLs 对象与 `upstream` 对象中的 `tls.client_cert` 以及 `config.yaml` 中的 `ssl_trusted_certificate` 区别是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Admin API 中 `/apisix/admin/ssls` 用于管理 SSL 对象,如果 APISIX 需要接收来自外网的 HTTPS 请求,那就需要用到存放在这里的证书完成握手。SSL 对象中支持配置多个证书,不同域名的证书 APISIX 将使用 Server Name Indication (SNI) 进行区分。
|
||||
|
||||
Upstream 对象中的 `tls.client_cert`、`tls.client_key` 与 `tls.client_cert_id` 用于存放客户端的证书,适用于需要与上游进行 [mTLS 通信](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/tutorials/client-to-apisix-mtls/)的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
`config.yaml` 中的 `ssl_trusted_certificate` 用于配置一个受信任的根证书。它仅用于在 APISIX 内部访问某些具有自签名证书的服务时,避免提示拒绝对方的 SSL 证书。注意:它不用于信任 APISIX 上游的证书,因为 APISIX 不会验证上游证书的合法性。因此,即使上游使用了无效的 TLS 证书,APISIX 仍然可以与其通信,而无需配置根证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如果在使用 APISIX 过程中遇到问题,我可以在哪里寻求更多帮助?
|
||||
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX Slack Channel](/docs/general/join/#加入-slack-频道):加入后请选择 channel-apisix 频道,即可通过此频道进行 APISIX 相关问题的提问。
|
||||
- [邮件列表](/docs/general/join/#订阅邮件列表):任何问题或对项目提议都可以通过社区邮件进行讨论。
|
||||
- [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/apache/apisix/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+sort%3Aupdated-desc) 与 [GitHub Discussions](https://github.com/apache/apisix/discussions):也可直接在 GitHub 中进行相关 issue 创建进行问题的表述。
|
||||
259
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/README.md
Normal file
259
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,259 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Apache APISIX
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/comdev/project-logos/originals/apisix.svg" alt="APISIX logo" height="150px" align="right" />
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/apache/apisix/actions)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
**Apache APISIX** 是一个动态、实时、高性能的 API 网关,
|
||||
提供负载均衡、动态上游、灰度发布、服务熔断、身份认证、可观测性等丰富的流量管理功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 Apache APISIX 来处理传统的南北向流量,以及服务间的东西向流量,
|
||||
也可以当做 [k8s ingress controller](https://github.com/apache/apisix-ingress-controller) 来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 的技术架构如下图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 社区
|
||||
|
||||
- 邮件列表 - 发送任意内容到 dev-subscribe@apisix.apache.org 后,根据回复以订阅邮件列表。
|
||||
- QQ 群 - 781365357
|
||||
- Slack - [查看加入方式](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/general/join/#join-the-slack-channel)
|
||||
-  - 使用标签 `#ApacheAPISIX` 关注我们并与我们互动。
|
||||
- [哔哩哔哩](https://space.bilibili.com/551921247)
|
||||
- **新手任务列表**
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX®](https://github.com/apache/apisix/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® Ingress Controller](https://github.com/apache/apisix-ingress-controller/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® dashboard](https://github.com/apache/apisix-dashboard/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® Helm Chart](https://github.com/apache/apisix-helm-chart/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Docker distribution for Apache APISIX®](https://github.com/apache/apisix-docker/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® Website](https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® Java Plugin Runner](https://github.com/apache/apisix-java-plugin-runner/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® Go Plugin Runner](https://github.com/apache/apisix-go-plugin-runner/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX® Python Plugin Runner](https://github.com/apache/apisix-python-plugin-runner/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
|
||||
- **微信公众号**
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
- **微信视频号**
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
## 特性
|
||||
|
||||
你可以把 Apache APISIX 当做流量入口,来处理所有的业务数据,包括动态路由、动态上游、动态证书、
|
||||
A/B 测试、金丝雀发布(灰度发布)、蓝绿部署、限流限速、抵御恶意攻击、监控报警、服务可观测性、服务治理等。
|
||||
|
||||
- **全平台**
|
||||
|
||||
- 云原生:平台无关,没有供应商锁定,无论裸机还是 Kubernetes,APISIX 都可以运行。
|
||||
- 支持 ARM64:不用担心底层技术的锁定。
|
||||
|
||||
- **多协议**
|
||||
|
||||
- [TCP/UDP 代理](stream-proxy.md):动态 TCP/UDP 代理。
|
||||
- [Dubbo 代理](plugins/dubbo-proxy.md):动态代理 HTTP 请求到 Dubbo 后端。
|
||||
- [动态 MQTT 代理](plugins/mqtt-proxy.md):支持用 `client_id` 对 MQTT 进行负载均衡,同时支持 MQTT [3.1.\*](http://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v3.1.1/os/mqtt-v3.1.1-os.html) 和 [5.0](https://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v5.0/mqtt-v5.0.html) 两个协议标准。
|
||||
- [gRPC 代理](grpc-proxy.md):通过 APISIX 代理 gRPC 连接,并使用 APISIX 的大部分特性管理你的 gRPC 服务。
|
||||
- [gRPC Web 代理](plugins/grpc-web.md):通过 APISIX 代理 gRPC Web 请求到上游 gRPC 服务。
|
||||
- [gRPC 协议转换](plugins/grpc-transcode.md):支持协议的转换,这样客户端可以通过 HTTP/JSON 来访问你的 gRPC API。
|
||||
- Websocket 代理
|
||||
- Proxy Protocol
|
||||
- HTTP(S) 反向代理
|
||||
- [SSL](certificate.md):动态加载 SSL 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
- **全动态能力**
|
||||
|
||||
- [热更新和热插件](terminology/plugin.md):无需重启服务,就可以持续更新配置和插件。
|
||||
- [代理请求重写](plugins/proxy-rewrite.md):支持重写请求上游的`host`、`uri`、`schema`、`method`、`headers`信息。
|
||||
- [输出内容重写](plugins/response-rewrite.md):支持自定义修改返回内容的 `status code`、`body`、`headers`。
|
||||
- [Serverless](plugins/serverless.md):在 APISIX 的每一个阶段,你都可以添加并调用自己编写的函数。
|
||||
- 动态负载均衡:动态支持有权重的 round-robin 负载平衡。
|
||||
- 支持一致性 hash 的负载均衡:动态支持一致性 hash 的负载均衡。
|
||||
- [健康检查](./tutorials/health-check.md):启用上游节点的健康检查,将在负载均衡期间自动过滤不健康的节点,以确保系统稳定性。
|
||||
- 熔断器:智能跟踪不健康上游服务。
|
||||
- [代理镜像](plugins/proxy-mirror.md):提供镜像客户端请求的能力。
|
||||
- [流量拆分](plugins/traffic-split.md):允许用户逐步控制各个上游之间的流量百分比。
|
||||
|
||||
- **精细化路由**
|
||||
|
||||
- [支持全路径匹配和前缀匹配](../../en/latest/router-radixtree.md#how-to-use-libradixtree-in-apisix)
|
||||
- [支持使用 Nginx 所有内置变量做为路由的条件](../../en/latest/router-radixtree.md#how-to-filter-route-by-nginx-builtin-variable),所以你可以使用 `cookie`, `args` 等做为路由的条件,来实现灰度发布、A/B 测试等功能
|
||||
- 支持[各类操作符做为路由的判断条件](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-radixtree#operator-list),比如 `{"arg_age", ">", 24}`
|
||||
- 支持[自定义路由匹配函数](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-radixtree/blob/master/t/filter-fun.t#L10)
|
||||
- IPv6:支持使用 IPv6 格式匹配路由
|
||||
- 支持路由的[自动过期 (TTL)](admin-api.md#route)
|
||||
- [支持路由的优先级](../../en/latest/router-radixtree.md#3-match-priority)
|
||||
- [支持批量 Http 请求](plugins/batch-requests.md)
|
||||
- [支持通过 GraphQL 属性过滤路由](../../en/latest/router-radixtree.md#how-to-filter-route-by-graphql-attributes)
|
||||
|
||||
- **安全防护**
|
||||
|
||||
- 丰富的认证、鉴权支持:
|
||||
* [key-auth](plugins/key-auth.md)
|
||||
* [JWT](plugins/jwt-auth.md)
|
||||
* [basic-auth](plugins/basic-auth.md)
|
||||
* [wolf-rbac](plugins/wolf-rbac.md)
|
||||
* [casbin](plugins/authz-casbin.md)
|
||||
* [keycloak](plugins/authz-keycloak.md)
|
||||
* [casdoor](../../en/latest/plugins/authz-casdoor.md)
|
||||
- [IP 黑白名单](plugins/ip-restriction.md)
|
||||
- [Referer 黑白名单](plugins/referer-restriction.md)
|
||||
- [IdP 支持](plugins/openid-connect.md):支持外部的身份认证平台,比如 Auth0,Okta,Authing 等。
|
||||
- [限制速率](plugins/limit-req.md)
|
||||
- [限制请求数](plugins/limit-count.md)
|
||||
- [限制并发](plugins/limit-conn.md)
|
||||
- 防御 ReDoS(正则表达式拒绝服务):内置策略,无需配置即可抵御 ReDoS。
|
||||
- [CORS](plugins/cors.md):为你的 API 启用 CORS。
|
||||
- [URI 拦截器](plugins/uri-blocker.md):根据 URI 拦截用户请求。
|
||||
- [请求验证器](plugins/request-validation.md)。
|
||||
- [CSRF](plugins/csrf.md):基于 [`Double Submit Cookie`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-site_request_forgery#Double_Submit_Cookie) 的方式保护你的 API 远离 CSRF 攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
- **运维友好**
|
||||
|
||||
- OpenTracing 可观测性:支持 [Apache Skywalking](plugins/skywalking.md) 和 [Zipkin](plugins/zipkin.md)。
|
||||
- 对接外部服务发现:除了内置的 etcd 外,还支持 [Consul](../../en/latest/discovery/consul_kv.md)、[Nacos](discovery/nacos.md)、[Eureka](discovery/eureka.md) 和 [Zookeeper(CP)](https://github.com/api7/apisix-seed/blob/main/docs/en/latest/zookeeper.md)。
|
||||
- 监控和指标:[Prometheus](plugins/prometheus.md)
|
||||
- 集群:APISIX 节点是无状态的,创建配置中心集群请参考 [etcd Clustering Guide](https://etcd.io/docs/v3.5/op-guide/clustering/)。
|
||||
- 高可用:支持配置同一个集群内的多个 etcd 地址。
|
||||
- [控制台](https://github.com/apache/apisix-dashboard): 操作 APISIX 集群。
|
||||
- 版本控制:支持操作的多次回滚。
|
||||
- CLI:使用命令行来启动、关闭和重启 APISIX。
|
||||
- [单机模式](../../en/latest/deployment-modes.md#standalone):支持从本地配置文件中加载路由规则,在 kubernetes(k8s) 等环境下更友好。
|
||||
- [全局规则](terminology/global-rule.md):允许对所有请求执行插件,比如黑白名单、限流限速等。
|
||||
- 高性能:在单核上 QPS 可以达到 18k,同时延迟只有 0.2 毫秒。
|
||||
- [故障注入](plugins/fault-injection.md)
|
||||
- [REST Admin API](admin-api.md):使用 REST Admin API 来控制 Apache APISIX,默认只允许 127.0.0.1 访问,你可以修改 `conf/config.yaml` 中的 `allow_admin` 字段,指定允许调用 Admin API 的 IP 列表。同时需要注意的是,Admin API 使用 key auth 来校验调用者身份,**在部署前需要修改 `conf/config.yaml` 中的 `admin_key` 字段,来保证安全。**
|
||||
- 外部日志记录器:将访问日志导出到外部日志管理工具。([HTTP Logger](plugins/http-logger.md)、[TCP Logger](plugins/tcp-logger.md)、[Kafka Logger](plugins/kafka-logger.md)、[UDP Logger](plugins/udp-logger.md)、[RocketMQ Logger](plugins/rocketmq-logger.md)、[SkyWalking Logger](plugins/skywalking-logger.md)、[Alibaba Cloud Logging(SLS)](plugins/sls-logger.md)、[Google Cloud Logging](plugins/google-cloud-logging.md)、[Splunk HEC Logging](plugins/splunk-hec-logging.md)、[File Logger](plugins/file-logger.md)、[Elasticsearch Logger](plugins/elasticsearch-logger.md)、[TencentCloud CLS](plugins/tencent-cloud-cls.md))
|
||||
- [Helm charts](https://github.com/apache/apisix-helm-chart)
|
||||
|
||||
- **高度可扩展**
|
||||
- [自定义插件](plugin-develop.md):允许挂载常见阶段,例如`init`,`rewrite`,`access`,`balancer`,`header filter`,`body filter` 和 `log` 阶段。
|
||||
- [插件可以用 Java/Go/Python 编写](../../zh/latest/external-plugin.md)
|
||||
- 自定义负载均衡算法:可以在 `balancer` 阶段使用自定义负载均衡算法。
|
||||
- 自定义路由:支持用户自己实现路由算法。
|
||||
|
||||
- **多语言支持**
|
||||
- Apache APISIX 是一个通过 `RPC` 和 `Wasm` 支持不同语言来进行插件开发的网关。
|
||||

|
||||
- RPC 是当前采用的开发方式。开发者可以使用他们需要的语言来进行 RPC 服务的开发,该 RPC 通过本地通讯来跟 APISIX 进行数据交换。到目前为止,APISIX 已支持[Java](https://github.com/apache/apisix-java-plugin-runner), [Golang](https://github.com/apache/apisix-go-plugin-runner), [Python](https://github.com/apache/apisix-python-plugin-runner) 和 Node.js。
|
||||
- Wasm 或 WebAssembly 是实验性的开发方式。APISIX 能加载运行使用[Proxy Wasm SDK](https://github.com/proxy-wasm/spec#sdks)编译的 Wasm 字节码。开发者仅需要使用该 SDK 编写代码,然后编译成 Wasm 字节码,即可运行在 APISIX 中的 Wasm 虚拟机中。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Serverless**
|
||||
- [Lua functions](plugins/serverless.md):能在 APISIX 每个阶段调用 lua 函数。
|
||||
- [Azure functions](./plugins/azure-functions.md):能无缝整合进 Azure Serverless Function 中。作为动态上游,能将特定的 URI 请求全部代理到微软 Azure 云中。
|
||||
- [Apache OpenWhisk](./plugins/openwhisk.md):与 Apache OpenWhisk 集成。作为动态上游,能将特定的 URI 请求代理到你自己的 OpenWhisk 集群。
|
||||
|
||||
## 立刻开始
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装
|
||||
|
||||
请参考[APISIX 安装指南](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/installation-guide/)。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 入门指南
|
||||
|
||||
入门指南是学习 APISIX 基础知识的好方法。按照 [入门指南](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/getting-started/)的步骤即可。
|
||||
|
||||
更进一步,你可以跟着文档来尝试更多的[插件](plugins)。
|
||||
|
||||
3. Admin API
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 提供了 [REST Admin API](admin-api.md),方便动态控制 Apache APISIX 集群。
|
||||
|
||||
4. 插件二次开发
|
||||
|
||||
可以参考[插件开发指南](plugin-develop.md),以及示例插件 `example-plugin` 的代码实现。
|
||||
阅读[插件概念](terminology/plugin.md) 会帮助你学到更多关于插件的知识。
|
||||
|
||||
更多文档请参考 [Apache APISIX 文档站](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/getting-started/)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 性能测试
|
||||
|
||||
使用 AWS 的 8 核心服务器来压测 APISIX,QPS 可以达到 140000,同时延时只有 0.2 毫秒。
|
||||
|
||||
[性能测试脚本](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/benchmark/run.sh) 已经开源,欢迎补充。
|
||||
|
||||
## 贡献者变化
|
||||
|
||||
> [访问此处](https://www.apiseven.com/contributor-graph) 使用贡献者数据服务。
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://www.apiseven.com/en/contributor-graph?repo=apache/apisix)
|
||||
|
||||
## 视频和文章
|
||||
|
||||
- 2020.10.16 [Apache APISIX: How to implement plugin orchestration in API Gateway](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iEegNXOtEhQ)
|
||||
- 2020.10.16 [Improve Apache APISIX observability with Apache Skywalking](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DleVJwPs4i4)
|
||||
- 2020.1.17 [API 网关 Apache APISIX 和 Kong 的选型对比](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/c51apneVj0O9yxiZAHF34Q)
|
||||
- 2019.12.14 [从 0 到 1:Apache APISIX 的 Apache 之路](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/99620158)
|
||||
- 2019.12.14 [基于 Apache APISIX 的下一代微服务架构](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/445.html)
|
||||
- 2019.10.30 [Apache APISIX 微服务架构极致性能架构解析](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/440.html)
|
||||
- 2019.9.27 [想把 APISIX 运行在 ARM64 平台上?只要三步](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84467919)
|
||||
- 2019.8.31 [APISIX 技术选型、测试和持续集成](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/433.html)
|
||||
- 2019.8.31 [APISIX 高性能实战 2](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/437.html)
|
||||
- 2019.7.6 [APISIX 高性能实战](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/429.html)
|
||||
|
||||
## 用户实际使用案例
|
||||
|
||||
- [新浪微博:基于 Apache APISIX,新浪微博 API 网关的定制化开发之路](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/blog/2021/07/06/the-road-to-customization-of-sina-weibo-api-gateway-based-on-apache-apisix/)
|
||||
- [欧盟数字工厂平台:API Security Gateway – Using APISIX in the eFactory Platform](https://www.efactory-project.eu/post/api-security-gateway-using-apisix-in-the-efactory-platform)
|
||||
- [贝壳找房:如何基于 Apache APISIX 搭建网关](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yZl9MWPyF1-gOyCp8plflA)
|
||||
- [360:Apache APISIX 在基础运维平台项目中的实践](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/mF8w8hW4alIMww0MSu9Sjg)
|
||||
- [HelloTalk:基于 OpenResty 和 Apache APISIX 的全球化探索之路](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/447.html)
|
||||
- [腾讯云:为什么选择 Apache APISIX 来实现 k8s ingress controller?](https://www.upyun.com/opentalk/448.html)
|
||||
- [思必驰:为什么我们重新写了一个 k8s ingress controller?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bmm2ibk2V7-XYneLo9XAPQ)
|
||||
|
||||
更多用户案例,请查看 [Case Studies](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/blog/tags/case-studies/)。
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 的用户有哪些?
|
||||
|
||||
有很多公司和组织把 APISIX 用于学习、研究、生产环境和商业产品中,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/40708551/109484046-f7c4e280-7aa5-11eb-9d71-aab90830773a.png" width="725" height="1700" />
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎用户把自己加入到 [Powered By](../../../powered-by.md) 页面。
|
||||
|
||||
## 全景图
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://landscape.cncf.io/images/left-logo.svg" width="150" /> <img src="https://landscape.cncf.io/images/right-logo.svg" width="200" />
|
||||
<br /><br />
|
||||
APISIX 被纳入 <a href="https://landscape.cncf.io/card-mode?category=api-gateway&grouping=category"> 云原生软件基金会 API 网关全景图</a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Logo
|
||||
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX logo(PNG)](../../../logos/apache-apisix.png)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX logo 源文件](https://apache.org/logos/#apisix)
|
||||
|
||||
## 贡献
|
||||
|
||||
我们欢迎来自开源社区、个人和合作伙伴的各种贡献。
|
||||
|
||||
- [贡献指南](../../../CONTRIBUTING.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 致谢
|
||||
|
||||
灵感来自 Kong 和 Orange。
|
||||
|
||||
## 协议
|
||||
|
||||
[Apache 2.0 License](../../../LICENSE)
|
||||
1717
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/admin-api.md
Normal file
1717
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/admin-api.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: APISIX 变量
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- APISIX variable
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 Apache APISIX 支持的变量。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 除了支持 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)外,自身也提供了一些变量。
|
||||
|
||||
## 变量列表
|
||||
|
||||
| 变量名称 | 来源 | 描述 | 示例 |
|
||||
|---------------------|----------- |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------- |
|
||||
| balancer_ip | core | 上游服务器的 IP 地址。 | 192.168.1.2 |
|
||||
| balancer_port | core | 上游服务器的端口。 | 80 |
|
||||
| consumer_name | core | 消费者的名称。 | |
|
||||
| consumer_group_id | core | 消费者所在的组的 ID。 | |
|
||||
| graphql_name | core | GraphQL 的 [operation name](https://graphql.org/learn/queries/#operation-name)。 | HeroComparison |
|
||||
| graphql_operation | core | GraphQL 的操作类型。 | mutation |
|
||||
| graphql_root_fields | core | GraphQL 最高级别的字段。 | ["hero"] |
|
||||
| mqtt_client_id | mqtt-proxy | MQTT 协议中的客户端 ID。 | |
|
||||
| route_id | core | APISIX 路由的 ID。 | |
|
||||
| route_name | core | APISIX 路由的名称。 | |
|
||||
| service_id | core | APISIX 服务的 ID。 | |
|
||||
| service_name | core | APISIX 服务的名称。 | |
|
||||
| redis_cmd_line | Redis | Redis 命令的内容。 | |
|
||||
| resp_body | core | 在 logger 插件中,如果部分插件支持记录响应的 body 信息,比如配置 `include_resp_body: true`,那可以在 log format 中使用该变量。| |
|
||||
| rpc_time | xRPC | 在 RPC 请求级别所花费的时间。 | |
|
||||
|
||||
当然,除上述变量外,你也可以创建自定义[变量](./plugin-develop.md#register-custom-variable)。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 软件架构
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- 网关
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- APISIX 架构
|
||||
description: 云原生网关 Apache APISIX 的软件架构
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 是一个动态、实时、高性能的云原生 API 网关。它构建于 NGINX + ngx_lua 的技术基础之上,充分利用了 LuaJIT 所提供的强大性能。 [为什么 Apache APISIX 选择 NGINX+Lua 技术栈?](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/blog/2021/08/25/why-apache-apisix-chose-nginx-and-lua/)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 主要分为两个部分:
|
||||
|
||||
1. APISIX 核心:包括 Lua 插件、多语言插件运行时(Plugin Runner)、Wasm 插件运行时等;
|
||||
2. 功能丰富的各种内置插件:包括可观测性、安全、流量控制等。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 在其核心中,提供了路由匹配、负载均衡、服务发现、API 管理等重要功能,以及配置管理等基础性模块。除此之外,APISIX 插件运行时也包含其中,提供原生 Lua 插件的运行框架和多语言插件的运行框架,以及实验性的 Wasm 插件运行时等。APISIX 多语言插件运行时提供多种开发语言的支持,比如 Golang、Java、Python、JS 等。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 目前也内置了各类插件,覆盖了 API 网关的各种领域,如认证鉴权、安全、可观测性、流量管理、多协议接入等。当前 APISIX 内置的插件使用原生 Lua 实现,关于各个插件的介绍与使用方式,可以查看相关[插件文档](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/batch-requests)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件加载流程
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 插件内部结构
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 批处理器
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
批处理器可用于聚合条目(日志/任何数据)并进行批处理。
|
||||
当 `batch_max_size` 设置为 1 时,处理器将立即执行每个条目。将批处理的最大值设置为大于 1 将开始聚合条目,直到达到最大值或超时。
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置
|
||||
|
||||
创建批处理器的唯一必需参数是函数。当批处理达到最大值或缓冲区持续时间超过时,函数将被执行。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------ | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| name | string | 可选 | xxx logger | ["http logger", "Some strings",...] | 用于标识批处理器的唯一标识符,默认为调用批处理器的日志插件名字,如配置插件为 `http logger`,name 默认为 http logger。 |
|
||||
| batch_max_size | integer | 可选 | 1000 | [1,...] | 设置每批发送日志的最大条数,当日志条数达到设置的最大值时,会自动推送全部日志到 HTTP/HTTPS 服务。 |
|
||||
| inactive_timeout | integer | 可选 | 5 | [1,...] | 刷新缓冲区的最大时间(以秒为单位),当达到最大的刷新时间时,无论缓冲区中的日志数量是否达到设置的最大条数,也会自动将全部日志推送到 HTTP/HTTPS 服务。 |
|
||||
| buffer_duration | integer | 可选 | 60 | [1,...] | 必须先处理批次中最旧条目的最长期限(以秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| max_retry_count | integer | 可选 | 0 | [0,...] | 从处理管道中移除之前的最大重试次数。 |
|
||||
| retry_delay | integer | 可选 | 1 | [0,...] | 如果执行失败,则应延迟执行流程的秒数。 |
|
||||
以下代码显示了如何在你的插件中使用批处理器:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local bp_manager_mod = require("apisix.utils.batch-processor-manager")
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
local plugin_name = "xxx-logger"
|
||||
local batch_processor_manager = bp_manager_mod.new(plugin_name)
|
||||
local schema = {...}
|
||||
local _M = {
|
||||
...
|
||||
name = plugin_name,
|
||||
schema = batch_processor_manager:wrap_schema(schema),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.log(conf, ctx)
|
||||
local entry = {...} -- data to log
|
||||
|
||||
if batch_processor_manager:add_entry(conf, entry) then
|
||||
return
|
||||
end
|
||||
-- create a new processor if not found
|
||||
|
||||
-- entries is an array table of entry, which can be processed in batch
|
||||
local func = function(entries)
|
||||
-- serialize to json array core.json.encode(entries)
|
||||
-- process/send data
|
||||
return true
|
||||
-- return false, err_msg, first_fail if failed
|
||||
-- first_fail(optional) indicates first_fail-1 entries have been successfully processed
|
||||
-- and during processing of entries[first_fail], the error occurred. So the batch processor
|
||||
-- only retries for the entries having index >= first_fail as per the retry policy.
|
||||
end
|
||||
batch_processor_manager:add_entry_to_new_processor(conf, entry, ctx, func)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
批处理器的配置将通过该插件的配置设置。
|
||||
举个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"http-logger": {
|
||||
"uri": "http://mockbin.org/bin/:ID",
|
||||
"batch_max_size": 10,
|
||||
"max_retry_count": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的插件只使用一个全局的批处理器,
|
||||
你可以直接使用它:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local entry = {...} -- data to log
|
||||
if log_buffer then
|
||||
log_buffer:push(entry)
|
||||
return
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
local config_bat = {
|
||||
name = config.name,
|
||||
retry_delay = config.retry_delay,
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
local err
|
||||
-- entries is an array table of entry, which can be processed in batch
|
||||
local func = function(entries)
|
||||
...
|
||||
return true
|
||||
-- return false, err_msg, first_fail if failed
|
||||
end
|
||||
log_buffer, err = batch_processor:new(func, config_bat)
|
||||
|
||||
if not log_buffer then
|
||||
core.log.warn("error when creating the batch processor: ", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
log_buffer:push(entry)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:请确保批处理的最大值(条目数)在函数执行的范围内。
|
||||
刷新批处理的计时器基于 `inactive_timeout` 配置运行。因此,为了获得最佳使用效果,
|
||||
保持 `inactive_timeout` 小于 `buffer_duration`。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 压力测试
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试环境
|
||||
|
||||
使用谷歌云的服务器进行测试,型号为 n1-highcpu-8 (8 vCPUs, 7.2 GB memory)
|
||||
|
||||
我们最多只使用 4 核去运行 APISIX,剩下的 4 核用于系统和压力测试工具 [wrk](https://github.com/wg/wrk)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试反向代理
|
||||
|
||||
我们把 APISIX 当做反向代理来使用,不开启任何插件,响应体的大小为 1KB。
|
||||
|
||||
#### QPS
|
||||
|
||||
下图中 x 轴为 CPU 的使用个数,y 轴为每秒处理的请求数:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 延时
|
||||
|
||||
请注意 y 轴延时的单位是**微秒(μs)**,而不是毫秒:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 火焰图
|
||||
|
||||
火焰图的采样结果:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要在本地服务器上运行基准测试,你需要同时运行另一个 NGINX 实例来监听 80 端口:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:80": 1,
|
||||
"127.0.0.2:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在完成配置并安装 [wrk](https://github.com/wg/wrk/) 之后,可以使用以下命令进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wrk -d 60 --latency http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试反向代理,开启 2 个插件
|
||||
|
||||
我们把 APISIX 当做反向代理来使用,开启限速和 prometheus 插件,响应体的大小为 1KB。
|
||||
|
||||
#### QPS
|
||||
|
||||
下图中 x 轴为 CPU 的使用个数,y 轴为每秒处理的请求数:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Latency
|
||||
|
||||
请注意 y 轴延时的单位是**微秒(μs)**,而不是毫秒:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 火焰图
|
||||
|
||||
火焰图的采样结果:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要在本地服务器上运行基准测试,你需要同时运行另一个 NGINX 实例来监听 80 端口:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 999999999,
|
||||
"time_window": 60,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 503,
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"prometheus":{}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:80": 1,
|
||||
"127.0.0.2:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在完成配置并安装 [wrk](https://github.com/wg/wrk/) 之后,可以使用以下命令进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wrk -d 60 --latency http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有关如何运行基准测试的更多参考,你可以查看此[PR](https://github.com/apache/apisix/pull/6136)和此[脚本](https://gist.github.com/membphis/137db97a4bf64d3653aa42f3e016bd01)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想使用大量连接运行基准测试,您可能需要更新 [**keepalive**](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/conf/config.yaml.example#L241) 配置,将配置添加到 [`config.yaml`](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/conf/config.yaml) 并重新加载 APISIX。否则超过配置数量的连接将成为短连接。你可以使用以下命令运行大量连接的基准测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wrk -t200 -c5000 -d30s http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要了解更多信息,请参考:[ngx_http_upstream_module](http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_module.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: build-apisix-dev-environment-on-mac
|
||||
title: 在 Mac 上构建开发环境
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了如何用 Docker 的方式在 Mac 上快速构建 API 网关 Apache APISIX 的开发环境。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
如果你希望快速的在你的 Mac 平台上构建和开发 APISIX,你可以参考本教程。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
本教程适合需要在 Mac 平台快速开始入门阶段开发的情况,如果你想要更进一步,有更好的开发体验,更好的选择是 Linux-based 虚拟机,或是直接使用这类系统作为你的开发环境。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在[这里](install-dependencies.md#安装)看到具体支持的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 快速构建 Apache APISIX 开发环境
|
||||
|
||||
### 实现思路
|
||||
|
||||
我们通过 Docker 来构建 Apache APISIX 的测试环境,在容器启动时将 Apache APISIX 的源代码挂载到容器内,就可以做到在容器内构建以及运行测试用例。
|
||||
|
||||
### 实现步骤
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要拉取 APISIX 源码,并构建一个可以运行测试用例以及编译运行 Apache APISIX 的镜像:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/apache/apisix.git
|
||||
cd apisix
|
||||
docker build -t apisix-dev-env -f example/build-dev-image.dockerfile .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们要启动 Etcd:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d --name etcd-apisix --net=host pachyderm/etcd:v3.5.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
挂载 APISIX 目录并启动开发环境容器:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d --name apisix-dev-env --net=host -v $(pwd):/apisix:rw apisix-dev-env:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最后,构建 Apache APISIX 运行时并配置测试环境:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker exec -it apisix-dev-env make deps
|
||||
docker exec -it apisix-dev-env ln -s /usr/bin/openresty /usr/bin/nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动和停止 APISIX
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker exec -it apisix-dev-env make run
|
||||
docker exec -it apisix-dev-env make stop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在运行 `make run` 时收到类似 `nginx: [emerg] bind() to unix:/apisix/logs/worker_events.sock failed (95: Operation not supported)` 的错误消息,请使用此解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
更改你的 Docker-Desktop 的 `File Sharing` 设置:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
修改为 `gRPC FUSE` 或 `osxfs` 都可以解决此问题。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 运行指定测试用例
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker exec -it apisix-dev-env prove t/admin/routes.t
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,265 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: building-apisix
|
||||
title: 源码安装 APISIX
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- 贡献代码
|
||||
- 构建 APISIX
|
||||
- 源码安装 APISIX
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了如何在本地使用源码安装 API 网关 Apache APISIX 来构建开发环境。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
|
||||
如果你希望为 APISIX 做出贡献或配置开发环境,你可以参考本教程。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想通过其他方式安装 APISIX,你可以参考[安装指南](./installation-guide.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想为特定的环境或打包 APISIX,请参考 [apisix-build-tools](https://github.com/api7/apisix-build-tools)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 源码安装 APISIX
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要指定需要安装的版本`APISIX_VERSION`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
APISIX_BRANCH='release/3.13'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,你可以运行以下命令,从 Github 克隆 APISIX 源码:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone --depth 1 --branch ${APISIX_BRANCH} https://github.com/apache/apisix.git apisix-${APISIX_BRANCH}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从[下载页面](https://apisix.apache.org/downloads/)下载源码包。但是官网的源码包缺少测试用例,可能会对你后续操作产生困扰。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,你也可以在该页面找到 APISIX Dashboard 和 APISIX Ingress Controller 的源码包。
|
||||
|
||||
安装之前,请安装[OpenResty](https://openresty.org/en/installation.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
然后切换到 APISIX 源码的目录,创建依赖项并安装 APISIX,命令如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd apisix-${APISIX_BRANCH}
|
||||
make deps
|
||||
make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该命令将安装 APISIX 运行时依赖的 Lua 库以及 `apisix-runtime` 和 `apisix` 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在运行 `make deps` 时收到类似 `Could not find header file for LDAP/PCRE/openssl` 的错误消息,请使用此解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
`luarocks` 支持自定义编译时依赖项(请参考:[配置文件格式](https://github.com/luarocks/luarocks/wiki/Config-file-format))。你可以使用第三方工具安装缺少的软件包并将其安装目录添加到 `luarocks` 变量表中。此方法适用于 macOS、Ubuntu、CentOS 和其他类似操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
此处仅给出 macOS 的具体解决步骤,其他操作系统的解决方案类似:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 `openldap`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
brew install openldap
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 使用以下命令命令找到本地安装目录:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
brew --prefix openldap
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 将路径添加到项目配置文件中(选择两种方法中的一种即可):
|
||||
1. 你可以使用 `luarocks config` 命令设置 `LDAP_DIR`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
luarocks config variables.LDAP_DIR /opt/homebrew/cellar/openldap/2.6.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 你还可以更改 `luarocks` 的默认配置文件。打开 `~/.luaorcks/config-5.1.lua` 文件并添加以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
variables = { LDAP_DIR = "/opt/homebrew/cellar/openldap/2.6.1", LDAP_INCDIR = "/opt/homebrew/cellar/openldap/2.6.1/include", }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`/opt/homebrew/cellar/openldap/` 是 `brew` 在 macOS(Apple Silicon) 上安装 `openldap` 的默认位置。`/usr/local/opt/openldap/` 是 brew 在 macOS(Intel) 上安装 openldap 的默认位置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不再需要 APISIX,可以执行以下命令卸载:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make uninstall && make undeps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger
|
||||
|
||||
该操作将删除所有相关文件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 etcd
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 默认使用 [etcd](https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd) 来保存和同步配置。在运行 APISIX 之前,你需要在你的机器上安装 etcd。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="os"
|
||||
defaultValue="linux"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Linux', value: 'linux'},
|
||||
{label: 'macOS', value: 'mac'},
|
||||
]}>
|
||||
<TabItem value="linux">
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ETCD_VERSION='3.4.18'
|
||||
wget https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/releases/download/v${ETCD_VERSION}/etcd-v${ETCD_VERSION}-linux-amd64.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -xvf etcd-v${ETCD_VERSION}-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
|
||||
cd etcd-v${ETCD_VERSION}-linux-amd64 && \
|
||||
sudo cp -a etcd etcdctl /usr/bin/
|
||||
nohup etcd >/tmp/etcd.log 2>&1 &
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="mac">
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
brew install etcd
|
||||
brew services start etcd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 管理 APISIX 服务
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令初始化 NGINX 配置文件和 etcd。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行 `apisix help` 命令,查看返回结果,获取其他操作命令及其描述。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令测试配置文件,APISIX 将根据 `config.yaml` 生成 `nginx.conf`,并检查 `nginx.conf` 的语法是否正确。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最后,你可以使用以下命令运行 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要停止 APISIX,你可以使用 `apisix quit` 或者 `apisix stop` 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
`apisix quit` 将正常关闭 APISIX,该指令确保在停止之前完成所有收到的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix quit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`apisix stop` 命令会强制关闭 APISIX 并丢弃所有请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix stop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 为 APISIX 构建 APISIX-Runtime
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 的一些特性需要在 OpenResty 中引入额外的 NGINX 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
如果要使用这些功能,你需要构建一个自定义的 OpenResty 发行版(APISIX-Runtime)。请参考 [apisix-build-tools](https://github.com/api7/apisix-build-tools) 配置你的构建环境并进行构建。
|
||||
|
||||
## 运行测试用例
|
||||
|
||||
以下步骤展示了如何运行 APISIX 的测试用例:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 `perl` 的包管理器 [cpanminus](https://metacpan.org/pod/App::cpanminus#INSTALLATION)。
|
||||
2. 通过 `cpanm` 来安装 [test-nginx](https://github.com/openresty/test-nginx) 的依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo cpanm --notest Test::Nginx IPC::Run > build.log 2>&1 || (cat build.log && exit 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 将 `test-nginx` 源码克隆到本地:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/openresty/test-nginx.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. 运行以下命令将当前目录添加到 Perl 的模块目录:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
export PERL5LIB=.:$PERL5LIB
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过运行以下命令指定 NGINX 二进制路径:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
TEST_NGINX_BINARY=/usr/local/bin/openresty prove -Itest-nginx/lib -r t
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 运行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
部分测试需要依赖外部服务和修改系统配置。如果想要完整地构建测试环境,请参考 [ci/linux_openresty_common_runner.sh](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/ci/linux_openresty_common_runner.sh)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 故障排查
|
||||
|
||||
以下是运行 APISIX 测试用例的常见故障排除步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
出现 `Error unknown directive "lua_package_path" in /API_ASPIX/apisix/t/servroot/conf/nginx.conf` 报错,是因为默认的 NGINX 安装路径未找到,解决方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux 默认安装路径:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
export PATH=/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin:$PATH
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 运行指定的测试用例
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令运行指定的测试用例:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
prove -Itest-nginx/lib -r t/plugin/openid-connect.t
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要了解更多信息,请参考 [testing framework](../../en/latest/internal/testing-framework.md)。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,324 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 证书
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
`APISIX` 支持通过 TLS 扩展 SNI 实现加载特定的 SSL 证书以实现对 https 的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
SNI(Server Name Indication)是用来改善 SSL 和 TLS 的一项特性,它允许客户端在服务器端向其发送证书之前向服务器端发送请求的域名,服务器端根据客户端请求的域名选择合适的 SSL 证书发送给客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
### 单一域名指定
|
||||
|
||||
通常情况下一个 SSL 证书只包含一个静态域名,配置一个 `ssl` 参数对象,它包括 `cert`、`key`和`sni`三个属性,详细如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* `cert`:SSL 密钥对的公钥,pem 格式
|
||||
* `key`:SSL 密钥对的私钥,pem 格式
|
||||
* `snis`:SSL 证书所指定的一个或多个域名,注意在设置这个参数之前,你需要确保这个证书对应的私钥是有效的。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个包含证书和密钥,单一域名 SNI 的 SSL 对象:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cert" : "'"$(cat t/certs/apisix.crt)"'",
|
||||
"key": "'"$(cat t/certs/apisix.key)"'",
|
||||
"snis": ["test.com"]
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"hosts": ["test.com"],
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --resolve 'test.com:9443:127.0.0.1' https://test.com:9443/get -k -vvv
|
||||
|
||||
* Added test.com:9443:127.0.0.1 to DNS cache
|
||||
* About to connect() to test.com port 9443 (#0)
|
||||
* Trying 127.0.0.1...
|
||||
* Connected to test.com (127.0.0.1) port 9443 (#0)
|
||||
* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
|
||||
* ALPN, server accepted to use h2
|
||||
* Server certificate:
|
||||
* subject: C=CN; ST=GuangDong; L=ZhuHai; O=iresty; CN=test.com
|
||||
* start date: Jun 24 22:18:05 2019 GMT
|
||||
* expire date: May 31 22:18:05 2119 GMT
|
||||
* issuer: C=CN; ST=GuangDong; L=ZhuHai; O=iresty; CN=test.com
|
||||
* SSL certificate verify result: self-signed certificate (18), continuing anyway.
|
||||
> GET /get HTTP/2
|
||||
> Host: test.com:9443
|
||||
> user-agent: curl/7.81.0
|
||||
> accept: */*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 泛域名
|
||||
|
||||
一个 SSL 证书的域名也可能包含泛域名,如 `*.test.com`,它代表所有以 `test.com` 结尾的域名都可以使用该证书。比如 `*.test.com`,可以匹配 `www.test.com`、`mail.test.com`。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是在 APISIX 中配置泛域名 SNI 的 SSL 证书的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个包含证书和密钥,泛域名 SNI 的 SSL 对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cert" : "'"$(cat t/certs/apisix.crt)"'",
|
||||
"key": "'"$(cat t/certs/apisix.key)"'",
|
||||
"snis": ["*.test.com"]
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"hosts": ["*.test.com"],
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --resolve 'www.test.com:9443:127.0.0.1' https://www.test.com:9443/get -k -vvv
|
||||
|
||||
* Added www.test.com:9443:127.0.0.1 to DNS cache
|
||||
* Hostname www.test.com was found in DNS cache
|
||||
* Trying 127.0.0.1:9443...
|
||||
* Connected to www.test.com (127.0.0.1) port 9443 (#0)
|
||||
* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
|
||||
* ALPN, server accepted to use h2
|
||||
* Server certificate:
|
||||
* subject: C=CN; ST=GuangDong; L=ZhuHai; O=iresty; CN=test.com
|
||||
* start date: Jun 24 22:18:05 2019 GMT
|
||||
* expire date: May 31 22:18:05 2119 GMT
|
||||
* issuer: C=CN; ST=GuangDong; L=ZhuHai; O=iresty; CN=test.com
|
||||
* SSL certificate verify result: self signed certificate (18), continuing anyway.
|
||||
> GET /get HTTP/2
|
||||
> Host: www.test.com:9443
|
||||
> user-agent: curl/7.74.0
|
||||
> accept: */*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 多域名的情况
|
||||
|
||||
如果一个 SSL 证书包含多个独立域名,比如 `www.test.com` 和 `mail.test.com`,你可以把它们都放入 `snis` 数组中,就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"snis": ["www.test.com", "mail.test.com"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 单域名多证书的情况
|
||||
|
||||
如果你期望为一个域名配置多张证书,例如以此来同时支持使用 ECC 和 RSA
|
||||
的密钥交换算法,那么你可以将额外的证书和私钥(第一张证书和其私钥依然使用 `cert` 和 `key`)配置在 `certs` 和 `keys` 中。
|
||||
|
||||
* `certs`:PEM 格式的 SSL 证书列表
|
||||
* `keys`:PEM 格式的 SSL 证书私钥列表
|
||||
|
||||
`APISIX` 会将相同下标的证书和私钥配对使用,因此 `certs` 和 `keys` 列表的长度必须一致。
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置多个 CA 证书
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 目前支持在多处设置 CA 证书,比如 [保护 Admin API](./mtls.md#保护-admin-api),[保护 ETCD](./mtls.md#保护-etcd),以及 [部署模式](../../en/latest/deployment-modes.md) 等。
|
||||
|
||||
在这些地方,使用 `ssl_trusted_certificate` 或 `trusted_ca_cert` 来配置 CA 证书,但是这些配置最终将转化为 OpenResty 的 [lua_ssl_trusted_certificate](https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module#lua_ssl_trusted_certificate) 指令。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要在不同的地方指定不同的 CA 证书,你可以将这些 CA 证书制作成一个 CA bundle 文件,在需要用到 CA 证书的地方将配置指向这个文件。这样可以避免生成的 `lua_ssl_trusted_certificate` 存在多处并且互相覆盖的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
下面用一个完整的例子来展示如何在 APISIX 设置多个 CA 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
假设让 client 与 APISIX Admin API,APISIX 与 ETCD 之间都使用 mTLS 协议进行通信,目前有两张 CA 证书,分别是 `foo_ca.crt` 和 `bar_ca.crt`,用这两张 CA 证书各自签发 client 与 server 证书对,`foo_ca.crt` 及其签发的证书对用于保护 Admin API,`bar_ca.crt` 及其签发的证书对用于保护 ETCD。
|
||||
|
||||
下表详细列出这个示例所涉及到的配置及其作用:
|
||||
|
||||
| 配置 | 类型 | 用途 |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| foo_ca.crt | CA 证书 | 签发客户端与 APISIX Admin API 进行 mTLS 通信所需的次级证书。 |
|
||||
| foo_client.crt | 证书 | 由 `foo_ca.crt` 签发,客户端使用,访问 APISIX Admin API 时证明自身身份的证书。 |
|
||||
| foo_client.key | 密钥文件 | 由 `foo_ca.crt` 签发,客户端使用,访问 APISIX Admin API 所需的密钥文件。 |
|
||||
| foo_server.crt | 证书 | 由 `foo_ca.crt` 签发,APISIX 使用,对应 `admin_api_mtls.admin_ssl_cert` 配置项。 |
|
||||
| foo_server.key | 密钥文件 | 由 `foo_ca.crt` 签发,APISIX 使用,对应 `admin_api_mtls.admin_ssl_cert_key` 配置项。 |
|
||||
| admin.apisix.dev | 域名 | 签发 `foo_server.crt` 证书时使用的 Common Name,客户端通过该域名访问 APISIX Admin API |
|
||||
| bar_ca.crt | CA 证书 | 签发 APISIX 与 ETCD 进行 mTLS 通信所需的次级证书。 |
|
||||
| bar_etcd.crt | 证书 | 由 `bar_ca.crt` 签发,ETCD 使用,对应 ETCD 启动命令中的 `--cert-file` 选项。 |
|
||||
| bar_etcd.key | 密钥文件 | 由 `bar_ca.crt` 签发,ETCD 使用,对应 ETCD 启动命令中的 `--key-file` 选项。 |
|
||||
| bar_apisix.crt | 证书 | 由 `bar_ca.crt` 签发,APISIX 使用,对应 `etcd.tls.cert` 配置项。 |
|
||||
| bar_apisix.key | 密钥文件 | 由 `bar_ca.crt` 签发,APISIX 使用,对应 `etcd.tls.key` 配置项。 |
|
||||
| etcd.cluster.dev | 域名 | 签发 `bar_etcd.crt` 证书时使用的 Common Name,APISIX 与 ETCD 进行 mTLS 通信时,使用该域名作为 SNI。对应 `etcd.tls.sni` 配置项。|
|
||||
| apisix.ca-bundle | CA bundle | 由 `foo_ca.crt` 与 `bar_ca.crt` 合并而成,替代 `foo_ca.crt` 与 `bar_ca.crt`。 |
|
||||
|
||||
1. 制作 CA bundle 文件
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cat /path/to/foo_ca.crt /path/to/bar_ca.crt > apisix.ca-bundle
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 启动 ETCD 集群,并开启客户端验证
|
||||
|
||||
先编写 `goreman` 配置,命名为 `Procfile-single-enable-mtls`,内容如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# 运行 `go get github.com/mattn/goreman` 安装 goreman,用 goreman 执行以下命令:
|
||||
etcd1: etcd --name infra1 --listen-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:12379 --advertise-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:12379 --listen-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:12380 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:12380 --initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1 --initial-cluster 'infra1=http://127.0.0.1:12380,infra2=http://127.0.0.1:22380,infra3=http://127.0.0.1:32380' --initial-cluster-state new --cert-file /path/to/bar_etcd.crt --key-file /path/to/bar_etcd.key --client-cert-auth --trusted-ca-file /path/to/apisix.ca-bundle
|
||||
etcd2: etcd --name infra2 --listen-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:22379 --advertise-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:22379 --listen-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:22380 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:22380 --initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1 --initial-cluster 'infra1=http://127.0.0.1:12380,infra2=http://127.0.0.1:22380,infra3=http://127.0.0.1:32380' --initial-cluster-state new --cert-file /path/to/bar_etcd.crt --key-file /path/to/bar_etcd.key --client-cert-auth --trusted-ca-file /path/to/apisix.ca-bundle
|
||||
etcd3: etcd --name infra3 --listen-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:32379 --advertise-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:32379 --listen-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:32380 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:32380 --initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1 --initial-cluster 'infra1=http://127.0.0.1:12380,infra2=http://127.0.0.1:22380,infra3=http://127.0.0.1:32380' --initial-cluster-state new --cert-file /path/to/bar_etcd.crt --key-file /path/to/bar_etcd.key --client-cert-auth --trusted-ca-file /path/to/apisix.ca-bundle
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `goreman` 来启动 ETCD 集群:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
goreman -f Procfile-single-enable-mtls start > goreman.log 2>&1 &
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 更新 `config.yaml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
admin:
|
||||
admin_key
|
||||
- name: admin
|
||||
key: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1
|
||||
role: admin
|
||||
admin_listen:
|
||||
ip: 127.0.0.1
|
||||
port: 9180
|
||||
https_admin: true
|
||||
admin_api_mtls:
|
||||
admin_ssl_ca_cert: /path/to/apisix.ca-bundle
|
||||
admin_ssl_cert: /path/to/foo_server.crt
|
||||
admin_ssl_cert_key: /path/to/foo_server.key
|
||||
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
ssl_trusted_certificate: /path/to/apisix.ca-bundle
|
||||
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
role: traditional
|
||||
role_traditional:
|
||||
config_provider: etcd
|
||||
etcd:
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "https://127.0.0.1:12379"
|
||||
- "https://127.0.0.1:22379"
|
||||
- "https://127.0.0.1:32379"
|
||||
tls:
|
||||
cert: /path/to/bar_apisix.crt
|
||||
key: /path/to/bar_apisix.key
|
||||
sni: etcd.cluster.dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. 测试 Admin API
|
||||
|
||||
启动 APISIX,如果 APISIX 启动成功,`logs/error.log` 中没有异常输出,表示 APISIX 与 ETCD 之间进行 mTLS 通信正常。
|
||||
|
||||
用 curl 模拟客户端,与 APISIX Admin API 进行 mTLS 通信,并创建一条路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -vvv \
|
||||
--resolve 'admin.apisix.dev:9180:127.0.0.1' https://admin.apisix.dev:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
--cert /path/to/foo_client.crt \
|
||||
--key /path/to/foo_client.key \
|
||||
--cacert /path/to/apisix.ca-bundle \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果输出以下 SSL 握手过程,表示 curl 与 APISIX Admin API 之间 mTLS 通信成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Encrypted Extensions (8):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Request CERT (13):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Change cipher spec (1):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
|
||||
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
|
||||
* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 验证 APISIX 代理
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/get -i
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Content-Length: 298
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Tue, 26 Jul 2022 16:31:00 GMT
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
|
||||
Server: APISIX/2.14.1
|
||||
|
||||
……
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 将请求代理到了上游 `httpbin.org` 的 `/get` 路径,并返回了 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK`。整个过程使用 CA bundle 替代 CA 证书是正常可用的。
|
||||
357
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/config.json
Normal file
357
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/config.json
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,357 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"version": "3.13.0",
|
||||
"sidebar": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "快速开始",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"getting-started/README",
|
||||
"getting-started/configure-routes",
|
||||
"getting-started/load-balancing",
|
||||
"getting-started/key-authentication",
|
||||
"getting-started/rate-limiting"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "installation-guide"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "architecture-design/apisix"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "教程",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"tutorials/expose-api",
|
||||
"tutorials/protect-api",
|
||||
"tutorials/observe-your-api",
|
||||
"tutorials/health-check",
|
||||
"tutorials/client-to-apisix-mtls",
|
||||
"tutorials/keycloak-oidc"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "APISIX 术语",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"terminology/api-gateway",
|
||||
"terminology/consumer",
|
||||
"terminology/consumer-group",
|
||||
"terminology/credential",
|
||||
"terminology/global-rule",
|
||||
"terminology/plugin",
|
||||
"terminology/plugin-config",
|
||||
"terminology/plugin-metadata",
|
||||
"terminology/route",
|
||||
"terminology/router",
|
||||
"terminology/script",
|
||||
"terminology/service",
|
||||
"terminology/upstream",
|
||||
"terminology/secret"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "插件",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "普通插件",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/batch-requests",
|
||||
"plugins/redirect",
|
||||
"plugins/echo",
|
||||
"plugins/gzip",
|
||||
"plugins/brotli",
|
||||
"plugins/real-ip",
|
||||
"plugins/server-info",
|
||||
"plugins/ext-plugin-pre-req",
|
||||
"plugins/ext-plugin-post-req",
|
||||
"plugins/ext-plugin-post-resp",
|
||||
"plugins/ocsp-stapling"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "转换请求",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/response-rewrite",
|
||||
"plugins/proxy-rewrite",
|
||||
"plugins/grpc-transcode",
|
||||
"plugins/grpc-web",
|
||||
"plugins/fault-injection",
|
||||
"plugins/mocking",
|
||||
"plugins/body-transformer",
|
||||
"plugins/attach-consumer-label"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "身份认证",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/authz-keycloak",
|
||||
"plugins/authz-casdoor",
|
||||
"plugins/wolf-rbac",
|
||||
"plugins/key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins/jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins/jwe-decrypt",
|
||||
"plugins/basic-auth",
|
||||
"plugins/openid-connect",
|
||||
"plugins/hmac-auth",
|
||||
"plugins/authz-casbin",
|
||||
"plugins/ldap-auth",
|
||||
"plugins/opa",
|
||||
"plugins/forward-auth",
|
||||
"plugins/multi-auth"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "安全防护",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/cors",
|
||||
"plugins/uri-blocker",
|
||||
"plugins/ip-restriction",
|
||||
"plugins/ua-restriction",
|
||||
"plugins/referer-restriction",
|
||||
"plugins/consumer-restriction",
|
||||
"plugins/csrf",
|
||||
"plugins/public-api",
|
||||
"plugins/gm",
|
||||
"plugins/chaitin-waf"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "流量控制",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/limit-req",
|
||||
"plugins/limit-conn",
|
||||
"plugins/limit-count",
|
||||
"plugins/proxy-cache",
|
||||
"plugins/request-validation",
|
||||
"plugins/proxy-mirror",
|
||||
"plugins/api-breaker",
|
||||
"plugins/traffic-split",
|
||||
"plugins/request-id",
|
||||
"plugins/proxy-control",
|
||||
"plugins/client-control",
|
||||
"plugins/workflow"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "可观测性",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "数据链路",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/zipkin",
|
||||
"plugins/skywalking",
|
||||
"plugins/opentelemetry"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "数据指标",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/prometheus",
|
||||
"plugins/node-status",
|
||||
"plugins/datadog"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "日志采集",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/http-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/skywalking-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/tcp-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/kafka-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/rocketmq-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/udp-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/clickhouse-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/syslog",
|
||||
"plugins/log-rotate",
|
||||
"plugins/error-log-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/sls-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/google-cloud-logging",
|
||||
"plugins/splunk-hec-logging",
|
||||
"plugins/file-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/loggly",
|
||||
"plugins/elasticsearch-logger",
|
||||
"plugins/tencent-cloud-cls",
|
||||
"plugins/loki-logger"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "无服务器架构",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/serverless",
|
||||
"plugins/azure-functions",
|
||||
"plugins/openwhisk",
|
||||
"plugins/aws-lambda",
|
||||
"plugins/openfunction"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "其它协议",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"plugins/dubbo-proxy",
|
||||
"plugins/mqtt-proxy",
|
||||
"plugins/http-dubbo"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "相关 API",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "admin-api"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "control-api"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "status-api"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "开发者",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "building-apisix"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "build-apisix-dev-environment-on-mac"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "support-fips-in-apisix"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "external-plugin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "wasm"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "CODE_STYLE"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "plugin-develop"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "debug-mode"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "FAQ"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "其它",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "category",
|
||||
"label": "服务发现",
|
||||
"items": [
|
||||
"discovery",
|
||||
"discovery/dns",
|
||||
"discovery/nacos",
|
||||
"discovery/eureka",
|
||||
"discovery/control-plane-service-discovery",
|
||||
"discovery/kubernetes"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "router-radixtree"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "stream-proxy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "grpc-proxy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "customize-nginx-configuration"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "certificate"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "apisix-variable"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "batch-processor"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "benchmark"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "install-dependencies"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "mtls"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "debug-function"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "profile"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "ssl-protocol"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "http3"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "CHANGELOG"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "doc",
|
||||
"id": "upgrade-guide-from-2.15.x-to-3.0.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Control API
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
control API 可以被用来:
|
||||
|
||||
* 暴露 APISIX 内部状态信息
|
||||
* 控制单个 APISIX 的数据平面的行为
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,control API 是启用的,监听 `127.0.0.1:9090`。你可以通过修改 `apisix/conf/config.yaml` 中的 control 部分来更改设置,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
...
|
||||
enable_control: true
|
||||
control:
|
||||
ip: "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
port: 9090
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
插件的 control API 在默认情况下不支持参数匹配,如果想启用参数匹配功能可以在 control 部分添加 `router: 'radixtree_uri_with_parameter'`
|
||||
|
||||
注意:control API server 不应该被配置成监听公网地址。
|
||||
|
||||
## 通过插件添加的 control API
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 中一些插件添加了自己的 control API。如果你对他们感兴趣,请参阅对应插件的文档。
|
||||
|
||||
## 独立于插件的 control API
|
||||
|
||||
以下是支持的 API:
|
||||
|
||||
### GET /v1/schema
|
||||
|
||||
引入自 2.2 版本
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下格式返回被该 APISIX 实例使用的 json schema:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"main": {
|
||||
"route": {
|
||||
"properties": {...}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"properties": {...}
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"example-plugin": {
|
||||
"consumer_schema": {...},
|
||||
"metadata_schema": {...},
|
||||
"schema": {...},
|
||||
"type": ...,
|
||||
"priority": 0,
|
||||
"version": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"stream-plugins": {
|
||||
"mqtt-proxy": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
只有启用了的插件才会被包含在返回结果中 `plugins` 部分。(返回结果中的)一些插件可能会缺失如 `consumer_schema` 或者 `type` 字段,这取决于插件的定义。
|
||||
|
||||
### GET /v1/healthcheck
|
||||
|
||||
引入自 2.3 版本
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下格式返回当前的 [health check](./tutorials/health-check.md) 状态
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"nodes": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ip": "52.86.68.46",
|
||||
"counter": {
|
||||
"http_failure": 0,
|
||||
"success": 0,
|
||||
"timeout_failure": 0,
|
||||
"tcp_failure": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"port": 80,
|
||||
"status": "healthy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ip": "100.24.156.8",
|
||||
"counter": {
|
||||
"http_failure": 5,
|
||||
"success": 0,
|
||||
"timeout_failure": 0,
|
||||
"tcp_failure": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"port": 80,
|
||||
"status": "unhealthy"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"name": "/apisix/routes/1",
|
||||
"type": "http"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
每个 entry 包含以下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
* name: 资源 ID,健康检查的报告对象。
|
||||
* type: 健康检查类型,取值为 `["http", "https", "tcp"]`。
|
||||
* nodes: 检查节点列表。
|
||||
* nodes[i].ip: IP 地址。
|
||||
* nodes[i].port: 端口。
|
||||
* nodes[i].status: 状态:`["healthy", "unhealthy", "mostly_healthy", "mostly_unhealthy"]`。
|
||||
* nodes[i].counter.success: 成功计数器。
|
||||
* nodes[i].counter.http_failure: HTTP 访问失败计数器。
|
||||
* nodes[i].counter.tcp_failure: TCP 连接或读写的失败计数器。
|
||||
* nodes[i].counter.timeout_failure: 超时计数器。
|
||||
|
||||
用户也可以通过 `/v1/healthcheck/$src_type/$src_id` 来获取指定 health checker 的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,`GET /v1/healthcheck/upstreams/1` 返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"nodes": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ip": "52.86.68.46",
|
||||
"counter": {
|
||||
"http_failure": 0,
|
||||
"success": 2,
|
||||
"timeout_failure": 0,
|
||||
"tcp_failure": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"port": 80,
|
||||
"status": "healthy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ip": "100.24.156.8",
|
||||
"counter": {
|
||||
"http_failure": 5,
|
||||
"success": 0,
|
||||
"timeout_failure": 0,
|
||||
"tcp_failure": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"port": 80,
|
||||
"status": "unhealthy"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"type": "http"
|
||||
"name": "/apisix/routes/1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
只有一个上游满足以下条件时,它的健康检查状态才会出现在结果里面:
|
||||
|
||||
* 上游配置了健康检查。
|
||||
* 上游在任何一个 worker 进程处理过客户端请求。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用浏览器访问该 API,你将得到一个网页:
|
||||
|
||||
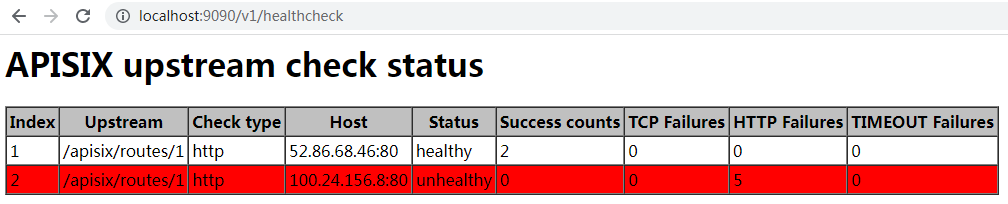
|
||||
|
||||
### POST /v1/gc
|
||||
|
||||
引入自 2.8 版本
|
||||
|
||||
在 http 子系统中触发一次全量 GC
|
||||
|
||||
注意,当你启用 stream proxy 时,APISIX 将为 stream 子系统运行另一个 Lua 虚拟机。它不会触发这个 Lua 虚拟机中的全量 GC。
|
||||
|
||||
### GET /v1/plugin_metadatas
|
||||
|
||||
引入自 3.0.0 版本
|
||||
|
||||
打印所有插件的元数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"upstream_response_time": "$upstream_response_time"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "file-logger"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ikey": 1,
|
||||
"skey": "val",
|
||||
"id": "example-plugin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### GET /v1/plugin_metadata/{plugin_name}
|
||||
|
||||
引入自 3.0.0 版本
|
||||
|
||||
打印指定插件的元数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"upstream_response_time": "$upstream_response_time"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "file-logger"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 自定义 Nginx 配置
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 使用的 Nginx 配置是通过模板文件 `apisix/cli/ngx_tpl.lua` 以及 `apisix/cli/config.lua` 和`conf/config.yaml` 中的参数生成的。
|
||||
|
||||
在执行完 `./bin/apisix start`,你可以在 `conf/nginx.conf` 看到生成的 Nginx 配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要自定义 Nginx 配置,请阅读 `conf/config.default.example` 中的 `nginx_config`。你可以在 `conf/config.yaml` 中覆盖默认值。例如,你可以在 `conf/nginx.conf` 中通过配置 `xxx_snippet` 条目注入一些代码片段:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
...
|
||||
# config.yaml 里面的内容
|
||||
nginx_config:
|
||||
main_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
daemon on;
|
||||
http_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
server
|
||||
{
|
||||
listen 45651;
|
||||
server_name _;
|
||||
access_log off;
|
||||
|
||||
location /ysec_status {
|
||||
req_status_show;
|
||||
allow 127.0.0.1;
|
||||
deny all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
chunked_transfer_encoding on;
|
||||
|
||||
http_server_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
set $my "var";
|
||||
http_admin_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
log_format admin "$request_time $pipe";
|
||||
http_end_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
|
||||
stream_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
tcp_nodelay off;
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意`nginx_config`及其子项的格式缩进,在执行`./bin/apisix start`时,错误的缩进将导致更新`conf/nginx.conf`文件失败。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 调试功能
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## `5xx` 响应状态码
|
||||
|
||||
500、502、503 等类似的 `5xx` 状态码,是由于服务器错误而响应的状态码,当一个请求出现 `5xx` 状态码时;它可能来源于 `APISIX` 或 `Upstream` 。如何识别这些响应状态码的来源,是一件很有意义的事,它能够快速的帮助我们确定问题的所在。(当修改 `conf/config.yaml` 的配置 `show_upstream_status_in_response_header` 为 `true` 时,会返回所有上游状态码,不仅仅是 `5xx` 状态。)
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何识别 `5xx` 响应状态码的来源
|
||||
|
||||
在请求的响应头中,通过 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status` 这个响应头,我们可以有效的识别 `5xx` 状态码的来源。当 `5xx` 状态码来源于 `Upstream` 时,在响应头中可以看到 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status` 这个响应头,并且这个响应头的值为响应的状态码。当 `5xx` 状态码来源于 `APISIX` 时,响应头中没有 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status` 的响应头信息。也就是只有 `5xx` 状态码来源于 `Upstream` 时,才会有 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status` 响应头。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:`502` 响应状态码来源于 `Upstream` (IP 地址不可用)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -v
|
||||
......
|
||||
< HTTP/1.1 502 Bad Gateway
|
||||
< Date: Wed, 25 Nov 2020 14:40:22 GMT
|
||||
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
|
||||
< Content-Length: 154
|
||||
< Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
< Server: APISIX/2.0
|
||||
< X-APISIX-Upstream-Status: 502
|
||||
<
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head><title>502 Bad Gateway</title></head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<center><h1>502 Bad Gateway</h1></center>
|
||||
<hr><center>openresty</center>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
具有 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status: 502` 的响应头。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:`502` 响应状态码来源于 `APISIX`
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"fault-injection": {
|
||||
"abort": {
|
||||
"http_status": 500,
|
||||
"body": "Fault Injection!\n"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -v
|
||||
......
|
||||
< HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
|
||||
< Date: Wed, 25 Nov 2020 14:50:20 GMT
|
||||
< Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
< Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
< Server: APISIX/2.0
|
||||
<
|
||||
Fault Injection!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
没有 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status` 的响应头。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 3:`Upstream` 具有多节点,并且所有节点不可用
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/upstreams/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.3:1": 1,
|
||||
"127.0.0.2:1": 1,
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"retries": 2,
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"upstream_id": "1"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -v
|
||||
< HTTP/1.1 502 Bad Gateway
|
||||
< Date: Wed, 25 Nov 2020 15:07:34 GMT
|
||||
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
|
||||
< Content-Length: 154
|
||||
< Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
< Server: APISIX/2.0
|
||||
< X-APISIX-Upstream-Status: 502, 502, 502
|
||||
<
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head><title>502 Bad Gateway</title></head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<center><h1>502 Bad Gateway</h1></center>
|
||||
<hr><center>openresty</center>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
具有 `X-APISIX-Upstream-Status: 502, 502, 502` 的响应头。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 调试模式
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本调试模式
|
||||
|
||||
设置 `conf/debug.yaml` 即可开启基本调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
basic:
|
||||
enable: true
|
||||
#END
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:在 APISIX 2.10 之前,开启基本调试模式曾经是设置 `conf/config.yaml` 中的 `apisix.enable_debug` 为 `true`。
|
||||
|
||||
比如对 `/hello` 开启了 `limit-conn` 和 `limit-count` 插件,这时候应答头中会有 `Apisix-Plugins: limit-conn, limit-count`。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:1984/hello -i
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Apisix-Plugins: limit-conn, limit-count
|
||||
X-RateLimit-Limit: 2
|
||||
X-RateLimit-Remaining: 1
|
||||
Server: openresty
|
||||
|
||||
hello world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果这个信息无法通过 HTTP 应答头传递,比如插件在 stream 子系统里面执行,
|
||||
那么这个信息会以 warn 等级日志写入到错误日志中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 高级调试模式
|
||||
|
||||
设置 `conf/debug.yaml` 中的选项,开启高级调试模式。由于 APISIX 服务启动后是每秒定期检查该文件,
|
||||
当可以正常读取到 `#END` 结尾时,才认为文件处于写完关闭状态。
|
||||
|
||||
根据文件最后修改时间判断文件内容是否有变化,如有变化则重新加载,如没变化则跳过本次检查。
|
||||
所以高级调试模式的开启、关闭都是热更新方式完成。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 必选项 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------- | ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ------ |
|
||||
| hook_conf.enable | 是 | 是否开启 hook 追踪调试。开启后将打印指定模块方法的请求参数或返回值。 | false |
|
||||
| hook_conf.name | 是 | 开启 hook 追踪调试的模块列表名称。 | |
|
||||
| hook_conf.log_level | 是 | 打印请求参数和返回值的日志级别。 | warn |
|
||||
| hook_conf.is_print_input_args | 是 | 是否打印输入参数。 | true |
|
||||
| hook_conf.is_print_return_value | 是 | 是否打印返回值。 | true |
|
||||
|
||||
请看下面示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
hook_conf:
|
||||
enable: false # 是否开启 hook 追踪调试
|
||||
name: hook_phase # 开启 hook 追踪调试的模块列表名称
|
||||
log_level: warn # 日志级别
|
||||
is_print_input_args: true # 是否打印输入参数
|
||||
is_print_return_value: true # 是否打印返回值
|
||||
|
||||
hook_phase: # 模块函数列表,名字:hook_phase
|
||||
apisix: # 引用的模块名称
|
||||
- http_access_phase # 函数名:数组
|
||||
- http_header_filter_phase
|
||||
- http_body_filter_phase
|
||||
- http_log_phase
|
||||
#END
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 动态高级调试模式
|
||||
|
||||
动态高级调试模式是基于高级调试模式,可以由单个请求动态开启高级调试模式。设置 `conf/debug.yaml` 中的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
http_filter:
|
||||
enable: true # 是否动态开启高级调试模式
|
||||
enable_header_name: X-APISIX-Dynamic-Debug # 追踪携带此 header 的请求
|
||||
......
|
||||
#END
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
动态开启高级调试模式,示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 127.0.0.1:9090/hello --header 'X-APISIX-Dynamic-Debug: foo'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:动态高级调试模式无法调试 `apisix.http_access_phase`,模块(因为请求进入 `apisix.http_access_phase` 模块后,才会判断是否动态开启高级调试模式)。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 集成服务发现注册中心
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 摘要
|
||||
|
||||
当业务量发生变化时,需要对上游服务进行扩缩容,或者因服务器硬件故障需要更换服务器。如果网关是通过配置来维护上游服务信息,在微服务架构模式下,其带来的维护成本可想而知。再者因不能及时更新这些信息,也会对业务带来一定的影响,还有人为误操作带来的影响也不可忽视,所以网关非常必要通过服务注册中心动态获取最新的服务实例信息。架构图如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 服务启动时将自身的一些信息,比如服务名、IP、端口等信息上报到注册中心;各个服务与注册中心使用一定机制(例如心跳)通信,如果注册中心与服务长时间无法通信,就会注销该实例;当服务下线时,会删除注册中心的实例信息;
|
||||
2. 网关会准实时地从注册中心获取服务实例信息;
|
||||
3. 当用户通过网关请求服务时,网关从注册中心获取的实例列表中选择一个进行代理;
|
||||
|
||||
常见的注册中心:Eureka, Etcd, Consul, Nacos, Zookeeper 等
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何扩展注册中心?
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本步骤
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 要扩展注册中心其实是件非常容易的事情,其基本步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在 `apisix/discovery/` 目录中添加注册中心客户端的实现;
|
||||
2. 实现用于初始化的 `_M.init_worker()` 函数以及用于获取服务实例节点列表的 `_M.nodes(service_name)` 函数;
|
||||
3. 将注册中心数据转换为 APISIX 格式的数据;
|
||||
|
||||
### 以 Eureka 举例
|
||||
|
||||
#### 实现 eureka 客户端
|
||||
|
||||
首先,在 `apisix/discovery` 下创建 `eureka` 目录;
|
||||
|
||||
其次,在 `apisix/discovery/eureka` 目录中添加 [`init.lua`](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/discovery/init.lua);
|
||||
|
||||
然后在 `init.lua` 实现用于初始化的 `init_worker` 函数以及用于获取服务实例节点列表的 `nodes` 函数即可:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local _M = {
|
||||
version = 0.1,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.nodes(service_name)
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.init_worker()
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return _M
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最后,在 `apisix/discovery/eureka` 下的 `schema.lua` 里面提供 YAML 配置的 schema。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Eureka 与 APISIX 之间数据转换逻辑
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 是通过 `upstream.nodes` 来配置上游服务的,所以使用注册中心后,通过注册中心获取服务的所有 node 后,赋值给 `upstream.nodes` 来达到相同的效果。那么 APISIX 是怎么将 Eureka 的数据转成 node 的呢?假如从 Eureka 获取如下数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"applications": {
|
||||
"application": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "USER-SERVICE", # 服务名称
|
||||
"instance": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"instanceId": "192.168.1.100:8761",
|
||||
"hostName": "192.168.1.100",
|
||||
"app": "USER-SERVICE", # 服务名称
|
||||
"ipAddr": "192.168.1.100", # 实例 IP 地址
|
||||
"status": "UP", # 状态
|
||||
"overriddenStatus": "UNKNOWN", # 覆盖状态
|
||||
"port": {
|
||||
"$": 8761, # 端口
|
||||
"@enabled": "true" # 开始端口
|
||||
},
|
||||
"securePort": {
|
||||
"$": 443,
|
||||
"@enabled": "false"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"management.port": "8761",
|
||||
"weight": 100 # 权重,需要通过 spring boot 应用的 eureka.instance.metadata-map.weight 进行配置
|
||||
},
|
||||
"homePageUrl": "http://192.168.1.100:8761/",
|
||||
"statusPageUrl": "http://192.168.1.100:8761/actuator/info",
|
||||
"healthCheckUrl": "http://192.168.1.100:8761/actuator/health",
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
解析 instance 数据步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先要选择状态为“UP”的实例:overriddenStatus 值不为 "UNKNOWN" 以 overriddenStatus 为准,否则以 status 的值为准;
|
||||
2. IP 地址:以 ipAddr 的值为 IP; 并且必须是 IPv4 或 IPv6 格式的;
|
||||
3. 端口:端口取值规则是,如果 port["@enabled"] 等于 "true" 那么使用 port["\$"] 的值;如果 securePort["@enabled"] 等于 "true" 那么使用 securePort["$"] 的值;
|
||||
4. 权重:权重取值顺序是,先判断 `metadata.weight` 是否有值,如果没有,则取配置中的 `eureka.weight` 的值,如果还没有,则取默认值`100`;
|
||||
|
||||
这个例子转成 APISIX nodes 的结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host": "192.168.1.100",
|
||||
"port": 8761,
|
||||
"weight": 100,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"management.port": "8761"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 注册中心配置
|
||||
|
||||
### 初始化服务发现
|
||||
|
||||
首先要在 `conf/config.yaml` 文件中增加如下配置,添加不同的服务发现客户端,以便在使用过程中动态选择:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
eureka: ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此名称要与 `apisix/discovery/` 目录中实现对应注册中心的文件名保持一致。
|
||||
|
||||
现已支持注册中心有:Eureka。
|
||||
|
||||
### Eureka 的配置
|
||||
|
||||
在 `conf/config.yaml` 增加如下格式的配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
eureka:
|
||||
host: # it's possible to define multiple eureka hosts addresses of the same eureka cluster.
|
||||
- "http://${username}:${password}@${eureka_host1}:${eureka_port1}"
|
||||
- "http://${username}:${password}@${eureka_host2}:${eureka_port2}"
|
||||
prefix: "/eureka/"
|
||||
fetch_interval: 30 # 从 eureka 中拉取数据的时间间隔,默认 30 秒
|
||||
weight: 100 # default weight for node
|
||||
timeout:
|
||||
connect: 2000 # 连接 eureka 的超时时间,默认 2000ms
|
||||
send: 2000 # 向 eureka 发送数据的超时时间,默认 2000ms
|
||||
read: 5000 # 从 eureka 读数据的超时时间,默认 5000ms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过 `discovery.eureka.host` 配置 eureka 的服务器地址。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 eureka 的地址是 `http://127.0.0.1:8761/` ,并且不需要用户名和密码验证的话,配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
eureka:
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "http://127.0.0.1:8761"
|
||||
prefix: "/eureka/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## upstream 配置
|
||||
|
||||
### 七层
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 是通过 `upstream.discovery_type` 选择使用的服务发现,`upstream.service_name` 与注册中心的服务名进行关联。下面是将 URL 为 "/user/\*" 的请求路由到注册中心名为 "USER-SERVICE" 的服务上例子:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/user/*",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "USER-SERVICE",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "eureka"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
|
||||
Date: Sat, 31 Aug 2019 01:17:15 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
|
||||
{"node":{"value":{"uri":"\/user\/*","upstream": {"service_name": "USER-SERVICE", "type": "roundrobin", "discovery_type": "eureka"}},"createdIndex":61925,"key":"\/apisix\/routes\/1","modifiedIndex":61925}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因为上游的接口 URL 可能会有冲突,通常会在网关通过前缀来进行区分:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/a/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite" : {
|
||||
"regex_uri": ["^/a/(.*)", "/${1}"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "A-SERVICE",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "eureka"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/2 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/b/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite" : {
|
||||
"regex_uri": ["^/b/(.*)", "/${1}"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "B-SERVICE",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "eureka"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
假如 A-SERVICE 和 B-SERVICE 都提供了一个 `/test` 的接口,通过上面的配置,可以通过 `/a/test` 访问 A-SERVICE 的 `/test` 接口,通过 `/b/test` 访问 B-SERVICE 的 `/test` 接口。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:配置 `upstream.service_name` 后 `upstream.nodes` 将不再生效,而是使用从注册中心的数据来替换,即使注册中心的数据是空的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 四层
|
||||
|
||||
eureka 服务发现也支持在四层中使用,配置方式与七层的类似。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"remote_addr": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "tcp",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "eureka",
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-EUREKA",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Date: Fri, 30 Dec 2022 03:52:19 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.0.0
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
|
||||
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600
|
||||
X-API-VERSION: v3
|
||||
|
||||
{"key":"\/apisix\/stream_routes\/1","value":{"remote_addr":"127.0.0.1","upstream":{"hash_on":"vars","type":"roundrobin","discovery_type":"eureka","scheme":"tcp","pass_host":"pass","service_name":"APISIX-EUREKA"},"id":"1","create_time":1672106762,"update_time":1672372339}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 控制面服务发现
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- ZooKeeper
|
||||
- Nacos
|
||||
- APISIX-Seed
|
||||
description: 本文档介绍了如何在 API 网关 Apache APISIX 控制面通过 Nacos 和 Zookeeper 实现服务发现。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
本文档介绍了如何在 APISIX 控制面通过 Nacos 和 Zookeeper 实现服务发现。
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX-Seed 架构
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 在早期已经支持了数据面服务发现,现在 APISIX 也通过 [APISIX-Seed](https://github.com/api7/apisix-seed) 项目实现了控制面服务发现,下图为 APISIX-Seed 架构图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
图中的数字代表的具体信息如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过 Admin API 向 APISIX 注册上游并指定服务发现类型。APISIX-Seed 将监听 etcd 中的 APISIX 资源变化,过滤服务发现类型并获取服务名称(如 ZooKeeper);
|
||||
2. APISIX-Seed 将在服务注册中心(如 ZooKeeper)订阅指定的服务名称,以监控和更新对应的服务信息;
|
||||
3. 客户端向服务注册中心注册服务后,APISIX-Seed 会获取新的服务信息,并将更新后的服务节点写入 etcd;
|
||||
4. 当 APISIX-Seed 在 etcd 中更新相应的服务节点信息时,APISIX 会将最新的服务节点信息同步到内存中。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
引入 APISIX-Seed 后,如果注册中心的服务变化频繁,etcd 中的数据也会频繁变化。因此,需要在启动 etcd 时设置 `--auto-compaction` 选项,用来定期压缩历史记录,避免耗尽 etcd 存储空间。详细信息请参考 [revisions](https://etcd.io/docs/v3.5/learning/api/#revisions)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 为什么需要 APISIX-Seed?
|
||||
|
||||
- 网络拓扑变得更简单
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 不需要与每个注册中心保持网络连接,只需要关注 etcd 中的配置信息即可。这将大大简化网络拓扑。
|
||||
|
||||
- 上游服务总数据量变小
|
||||
|
||||
由于 `registry` 的特性,APISIX 可能会在 Worker 中存储全量的 `registry` 服务数据,例如 Consul_KV。通过引入 APISIX-Seed,APISIX 的每个进程将不需要额外缓存上游服务相关信息。
|
||||
|
||||
- 更容易管理
|
||||
|
||||
服务发现配置需要为每个 APISIX 实例配置一次。通过引入 APISIX-Seed,APISIX 将对服务注册中心的配置变化无感知。
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持的服务发现类型
|
||||
|
||||
目前已经支持了 ZooKeeper 和 Nacos,后续还将支持更多的服务注册中心,更多信息请参考:[APISIX Seed](https://github.com/api7/apisix-seed#apisix-seed-for-apache-apisix)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果你想启用控制面 ZooKeeper 服务发现,请参考:[ZooKeeper 部署教程](https://github.com/api7/apisix-seed/blob/main/docs/zh/latest/zookeeper.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果你想启用控制面 Nacos 服务发现,请参考:[Nacos 部署教程](https://github.com/api7/apisix-seed/blob/main/docs/zh/latest/nacos.md)。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: DNS
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 基于 DNS 的服务发现
|
||||
|
||||
某些服务发现系统如 Consul,支持通过 DNS 提供系统信息。我们可以使用这种方法直接实现服务发现,七层与四层均支持。
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们需要配置 DNS 服务器的地址:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# 添加到 config.yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
dns:
|
||||
servers:
|
||||
- "127.0.0.1:8600" # 使用 DNS 服务器的真实地址
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
与在 Upstream 的 `nodes` 对象中配置域名不同的是,DNS 服务发现将返回所有的记录。例如按照以下的 upstream 配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": 1,
|
||||
"discovery_type": "dns",
|
||||
"service_name": "test.consul.service",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后 `test.consul.service` 将被解析为 `1.1.1.1` 和 `1.1.1.2`,这个结果等同于:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": 1,
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": [
|
||||
{"host": "1.1.1.1", "weight": 1},
|
||||
{"host": "1.1.1.2", "weight": 1}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意所有来自 `test.consul.service` 的 IP 都有相同的权重。
|
||||
|
||||
解析的记录将根据它们的 TTL 来进行缓存。对于记录不在缓存中的服务,我们将默认按照 `SRV -> A -> AAAA -> CNAME` 的顺序进行查询,刷新缓存记录时,我们将从上次成功的类型开始尝试。也可以通过修改配置文件来自定义 DNS 的解析顺序。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# 添加到 config.yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
dns:
|
||||
servers:
|
||||
- "127.0.0.1:8600" # 使用 DNS 服务器的真实地址
|
||||
order: # DNS 解析的顺序
|
||||
- last # "last" 表示从上次成功的类型开始
|
||||
- SRV
|
||||
- A
|
||||
- AAAA
|
||||
- CNAME
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想指定 upstream 服务器的端口,可以把以下内容添加到 `service_name`:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": 1,
|
||||
"discovery_type": "dns",
|
||||
"service_name": "test.consul.service:1980",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方法是通过 SRV 记录,见如下。
|
||||
|
||||
### SRV 记录
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用 SRV 记录你可以指定一个服务的端口和权重。
|
||||
|
||||
假设你有一条这样的 SRV 记录:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
; under the section of blah.service
|
||||
A 300 IN A 1.1.1.1
|
||||
B 300 IN A 1.1.1.2
|
||||
B 300 IN A 1.1.1.3
|
||||
|
||||
; name TTL type priority weight port
|
||||
srv 86400 IN SRV 10 60 1980 A
|
||||
srv 86400 IN SRV 20 20 1981 B
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upstream 配置是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": 1,
|
||||
"discovery_type": "dns",
|
||||
"service_name": "srv.blah.service",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
效果等同于:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": 1,
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": [
|
||||
{"host": "1.1.1.1", "port": 1980, "weight": 60, "priority": -10},
|
||||
{"host": "1.1.1.2", "port": 1981, "weight": 10, "priority": -20},
|
||||
{"host": "1.1.1.3", "port": 1981, "weight": 10, "priority": -20}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意 B 域名的两条记录均分权重。
|
||||
对于 SRV 记录,低优先级的节点被先选中,所以最后一项的优先级是负数。
|
||||
|
||||
关于 0 权重的 SRV 记录,在 [RFC 2782](https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2782.txt) 中是这么描述的:
|
||||
|
||||
> 当没有任何候选服务器时,域管理员应使用权重为 0 的,使 RR 更为易读(噪音更少)。当存在权重大于 0 的记录时,权重为 0 的记录被选中的可能性很小。
|
||||
|
||||
我们把权重为 0 的记录当作权重为 1,因此节点“被选中的可能性很小”,这也是处理此类记录的常用方法。
|
||||
|
||||
对于端口为 0 的 SRV 记录,我们会使用上游协议的默认端口。
|
||||
你也可以在“service_name”字段中直接指定端口,比如“srv.blah.service:8848”。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: eureka
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 支持使用 [Eureka](https://github.com/Netflix/eureka#eureka) 做服务发现。
|
||||
详情请阅读 [支持的服务注册发现](../discovery.md#当前支持的注册中心) 。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,403 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Kubernetes
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Kubernetes
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- 服务发现
|
||||
- 集群
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
description: 本文将介绍如何在 Apache APISIX 中基于 Kubernetes 进行服务发现以及相关问题汇总。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 基于 Kubernetes 的服务发现
|
||||
|
||||
Kubernetes 服务发现以 [_List-Watch_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/using-api/api-concepts) 方式监听 [_Kubernetes_](https://kubernetes.io) 集群 [_Endpoints_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service) 资源的实时变化,并将其值存储到 ngx.shared.DICT 中。
|
||||
|
||||
同时遵循 [_APISIX Discovery 规范_](../discovery.md) 提供了节点查询接口。
|
||||
|
||||
## Kubernetes 服务发现的使用
|
||||
|
||||
目前 Kubernetes 服务发现支持单集群和多集群模式,分别适用于待发现的服务分布在单个或多个 Kubernetes 的场景。
|
||||
|
||||
### 单集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现的配置格式
|
||||
|
||||
单集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现的完整配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
kubernetes:
|
||||
service:
|
||||
# apiserver schema, options [http, https]
|
||||
schema: https #default https
|
||||
|
||||
# apiserver host, options [ipv4, ipv6, domain, environment variable]
|
||||
host: ${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST} #default ${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST}
|
||||
|
||||
# apiserver port, options [port number, environment variable]
|
||||
port: ${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT} #default ${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT}
|
||||
|
||||
client:
|
||||
# serviceaccount token or token_file
|
||||
token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
|
||||
|
||||
#token: |-
|
||||
# eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ikx5ME1DNWdnbmhQNkZCNlZYMXBsT3pYU3BBS2swYzBPSkN3ZnBESGpkUEEif
|
||||
# 6Ikx5ME1DNWdnbmhQNkZCNlZYMXBsT3pYU3BBS2swYzBPSkN3ZnBESGpkUEEifeyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI
|
||||
|
||||
default_weight: 50 # weight assigned to each discovered endpoint. default 50, minimum 0
|
||||
|
||||
# kubernetes discovery support namespace_selector
|
||||
# you can use one of [equal, not_equal, match, not_match] filter namespace
|
||||
namespace_selector:
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace equal default
|
||||
equal: default
|
||||
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace not equal default
|
||||
#not_equal: default
|
||||
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace match one of [default, ^my-[a-z]+$]
|
||||
#match:
|
||||
#- default
|
||||
#- ^my-[a-z]+$
|
||||
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace not match one of [default, ^my-[a-z]+$]
|
||||
#not_match:
|
||||
#- default
|
||||
#- ^my-[a-z]+$
|
||||
|
||||
# kubernetes discovery support label_selector
|
||||
# for the expression of label_selector, please refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels
|
||||
label_selector: |-
|
||||
first="a",second="b"
|
||||
|
||||
# reserved lua shared memory size, 1m memory can store about 1000 pieces of endpoint
|
||||
shared_size: 1m #default 1m
|
||||
|
||||
# if watch_endpoint_slices setting true, watch apiserver with endpointslices instead of endpoints
|
||||
watch_endpoint_slices: false #default false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果 Kubernetes 服务发现运行在 Pod 内,你可以使用如下最简配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
kubernetes: { }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果 Kubernetes 服务发现运行在 Pod 外,你需要新建或选取指定的 [_ServiceAccount_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/), 获取其 Token 值,然后使用如下配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
kubernetes:
|
||||
service:
|
||||
schema: https
|
||||
host: # enter apiserver host value here
|
||||
port: # enter apiServer port value here
|
||||
client:
|
||||
token: # enter serviceaccount token value here
|
||||
#token_file: # enter token file path here
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 单集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现的查询接口
|
||||
|
||||
单集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现遵循 [_APISIX Discovery 规范_](../discovery.md) 提供节点查询接口。
|
||||
|
||||
**函数:**
|
||||
nodes(service_name)
|
||||
|
||||
**说明:**
|
||||
service_name 必须满足格式:[namespace]/[name]:[portName]
|
||||
|
||||
+ namespace: Endpoints 所在的命名空间
|
||||
|
||||
+ name: Endpoints 的资源名
|
||||
|
||||
+ portName: Endpoints 定义包含的 `ports.name` 值,如果 Endpoints 没有定义 `ports.name`,请依次使用 `targetPort`, `port` 代替。设置了 `ports.name` 的情况下,不能使用后两者。
|
||||
|
||||
**返回值:**
|
||||
以如下 Endpoints 为例:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: v1
|
||||
kind: Endpoints
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: plat-dev
|
||||
namespace: default
|
||||
subsets:
|
||||
- addresses:
|
||||
- ip: "10.5.10.109"
|
||||
- ip: "10.5.10.110"
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- port: 3306
|
||||
name: port
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
nodes("default/plat-dev:port") 调用会得到如下的返回值:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
{
|
||||
host="10.5.10.109",
|
||||
port= 3306,
|
||||
weight= 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
host="10.5.10.110",
|
||||
port= 3306,
|
||||
weight= 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 多集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现的配置格式
|
||||
|
||||
多集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现的完整配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
kubernetes:
|
||||
- id: release # a custom name refer to the cluster, pattern ^[a-z0-9]{1,8}
|
||||
service:
|
||||
# apiserver schema, options [http, https]
|
||||
schema: https #default https
|
||||
|
||||
# apiserver host, options [ipv4, ipv6, domain, environment variable]
|
||||
host: "1.cluster.com"
|
||||
|
||||
# apiserver port, options [port number, environment variable]
|
||||
port: "6443"
|
||||
|
||||
client:
|
||||
# serviceaccount token or token_file
|
||||
token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
|
||||
|
||||
#token: |-
|
||||
# eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ikx5ME1DNWdnbmhQNkZCNlZYMXBsT3pYU3BBS2swYzBPSkN3ZnBESGpkUEEif
|
||||
# 6Ikx5ME1DNWdnbmhQNkZCNlZYMXBsT3pYU3BBS2swYzBPSkN3ZnBESGpkUEEifeyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI
|
||||
|
||||
default_weight: 50 # weight assigned to each discovered endpoint. default 50, minimum 0
|
||||
|
||||
# kubernetes discovery support namespace_selector
|
||||
# you can use one of [equal, not_equal, match, not_match] filter namespace
|
||||
namespace_selector:
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace equal default
|
||||
equal: default
|
||||
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace not equal default
|
||||
#not_equal: default
|
||||
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace match one of [default, ^my-[a-z]+$]
|
||||
#match:
|
||||
#- default
|
||||
#- ^my-[a-z]+$
|
||||
|
||||
# only save endpoints with namespace not match one of [default, ^my-[a-z]+$]
|
||||
#not_match:
|
||||
#- default
|
||||
#- ^my-[a-z]+$
|
||||
|
||||
# kubernetes discovery support label_selector
|
||||
# for the expression of label_selector, please refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels
|
||||
label_selector: |-
|
||||
first="a",second="b"
|
||||
|
||||
# reserved lua shared memory size,1m memory can store about 1000 pieces of endpoint
|
||||
shared_size: 1m #default 1m
|
||||
|
||||
# if watch_endpoint_slices setting true, watch apiserver with endpointslices instead of endpoints
|
||||
watch_endpoint_slices: false #default false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
多集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现没有为 `service` 和 `client` 域填充默认值,你需要根据集群配置情况自行填充。
|
||||
|
||||
### 多集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现的查询接口
|
||||
|
||||
多集群模式 Kubernetes 服务发现遵循 [_APISIX Discovery 规范_](../discovery.md) 提供节点查询接口。
|
||||
|
||||
**函数:**
|
||||
nodes(service_name)
|
||||
|
||||
**说明:**
|
||||
service_name 必须满足格式:[id]/[namespace]/[name]:[portName]
|
||||
|
||||
+ id: Kubernetes 服务发现配置中定义的集群 id 值
|
||||
|
||||
+ namespace: Endpoints 所在的命名空间
|
||||
|
||||
+ name: Endpoints 的资源名
|
||||
|
||||
+ portName: Endpoints 定义包含的 `ports.name` 值,如果 Endpoints 没有定义 `ports.name`,请依次使用 `targetPort`, `port` 代替。设置了 `ports.name` 的情况下,不能使用后两者。
|
||||
|
||||
**返回值:**
|
||||
以如下 Endpoints 为例:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: v1
|
||||
kind: Endpoints
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: plat-dev
|
||||
namespace: default
|
||||
subsets:
|
||||
- addresses:
|
||||
- ip: "10.5.10.109"
|
||||
- ip: "10.5.10.110"
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- port: 3306
|
||||
name: port
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
nodes("release/default/plat-dev:port") 调用会得到如下的返回值:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
{
|
||||
host="10.5.10.109",
|
||||
port= 3306,
|
||||
weight= 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
host="10.5.10.110",
|
||||
port= 3306,
|
||||
weight= 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Q&A
|
||||
|
||||
**Q: 为什么只支持配置 token 来访问 Kubernetes APIServer?**
|
||||
|
||||
A: 一般情况下,我们有三种方式可以完成与 Kubernetes APIServer 的认证:
|
||||
|
||||
- mTLS
|
||||
- Token
|
||||
- Basic authentication
|
||||
|
||||
因为 lua-resty-http 目前不支持 mTLS, Basic authentication 不被推荐使用,所以当前只实现了 Token 认证方式。
|
||||
|
||||
**Q: APISIX 继承了 NGINX 的多进程模型,是否意味着每个 APISIX 工作进程都会监听 Kubernetes Endpoints?**
|
||||
|
||||
A: Kubernetes 服务发现只使用特权进程监听 Kubernetes Endpoints,然后将其值存储到 `ngx.shared.DICT` 中,工作进程通过查询 `ngx.shared.DICT` 来获取结果。
|
||||
|
||||
**Q: [_ServiceAccount_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/) 需要的权限有哪些?**
|
||||
|
||||
A: [_ServiceAccount_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/) 需要集群级 [ get,list,watch ] endpoints 资源的的权限,其声明式定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
kind: ServiceAccount
|
||||
apiVersion: v1
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: apisix-test
|
||||
namespace: default
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
kind: ClusterRole
|
||||
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: apisix-test
|
||||
rules:
|
||||
- apiGroups: [ "" ]
|
||||
resources: [ endpoints,endpointslices ]
|
||||
verbs: [ get,list,watch ]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
|
||||
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: apisix-test
|
||||
roleRef:
|
||||
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
|
||||
kind: ClusterRole
|
||||
name: apisix-test
|
||||
subjects:
|
||||
- kind: ServiceAccount
|
||||
name: apisix-test
|
||||
namespace: default
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Q: 怎样获取指定 [_ServiceAccount_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/) 的 Token 值?**
|
||||
|
||||
A: 假定你指定的 [_ServiceAccount_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/) 资源名为“kubernetes-discovery“, 命名空间为“apisix”, 请按如下步骤获取其 Token 值。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 获取 _Secret_ 资源名。执行以下命令,输出的第一列内容就是目标 _Secret_ 资源名:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
kubectl -n apisix get secrets | grep kubernetes-discovery
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 获取 Token 值。假定你获取到的 _Secret_ 资源名为 "kubernetes-discovery-token-c64cv", 执行以下命令,输出内容就是目标 Token 值:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
kubectl -n apisix get secret kubernetes-discovery-token-c64cv -o jsonpath={.data.token} | base64 -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 调试 API
|
||||
|
||||
它还提供了用于调试的控制 api。
|
||||
|
||||
### 内存 Dump API
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
GET /v1/discovery/kubernetes/dump
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
例子
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# curl http://127.0.0.1:9090/v1/discovery/kubernetes/dump | jq
|
||||
{
|
||||
"endpoints": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"endpoints": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"value": "{\"https\":[{\"host\":\"172.18.164.170\",\"port\":6443,\"weight\":50},{\"host\":\"172.18.164.171\",\"port\":6443,\"weight\":50},{\"host\":\"172.18.164.172\",\"port\":6443,\"weight\":50}]}",
|
||||
"name": "default/kubernetes"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"value": "{\"metrics\":[{\"host\":\"172.18.164.170\",\"port\":2379,\"weight\":50},{\"host\":\"172.18.164.171\",\"port\":2379,\"weight\":50},{\"host\":\"172.18.164.172\",\"port\":2379,\"weight\":50}]}",
|
||||
"name": "kube-system/etcd"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"value": "{\"http-85\":[{\"host\":\"172.64.89.2\",\"port\":85,\"weight\":50}]}",
|
||||
"name": "test-ws/testing"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"id": "first"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"config": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"default_weight": 50,
|
||||
"id": "first",
|
||||
"client": {
|
||||
"token": "xxx"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"service": {
|
||||
"host": "172.18.164.170",
|
||||
"port": "6443",
|
||||
"schema": "https"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"shared_size": "1m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,283 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: nacos
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 基于 [Nacos](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/what-is-nacos.html) 的服务发现
|
||||
|
||||
当前模块的性能有待改进:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 并行发送请求。
|
||||
|
||||
### Nacos 配置
|
||||
|
||||
在文件 `conf/config.yaml` 中添加以下配置到:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
nacos:
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "http://${username}:${password}@${host1}:${port1}"
|
||||
prefix: "/nacos/v1/"
|
||||
fetch_interval: 30 # default 30 sec
|
||||
weight: 100 # default 100
|
||||
timeout:
|
||||
connect: 2000 # default 2000 ms
|
||||
send: 2000 # default 2000 ms
|
||||
read: 5000 # default 5000 ms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
也可以这样简洁配置(未配置项使用默认值):
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
discovery:
|
||||
nacos:
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "http://192.168.33.1:8848"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Upstream 设置
|
||||
|
||||
#### 七层
|
||||
|
||||
例如,转发 URI 匹配 "/nacos/*" 的请求到一个上游服务,
|
||||
该服务在 Nacos 中的服务名是 APISIX-NACOS,查询地址是 http://192.168.33.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS,创建路由时指定服务发现类型为 nacos。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/nacos/*",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"node": {
|
||||
"key": "\/apisix\/routes\/1",
|
||||
"value": {
|
||||
"id": "1",
|
||||
"create_time": 1615796097,
|
||||
"status": 1,
|
||||
"update_time": 1615799165,
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"hash_on": "vars",
|
||||
"pass_host": "pass",
|
||||
"scheme": "http",
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"priority": 0,
|
||||
"uri": "\/nacos\/*"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 四层
|
||||
|
||||
nacos 服务发现也支持在四层中使用,配置方式与七层的类似。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"remote_addr": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "tcp",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 参数
|
||||
|
||||
| 名字 | 类型 | 可选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ------------ | ------ | ----------- | ------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| namespace_id | string | 可选 | public | | 服务所在的命名空间 |
|
||||
| group_name | string | 可选 | DEFAULT_GROUP | | 服务所在的组 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 指定命名空间
|
||||
|
||||
例如,转发 URI 匹配 "/nacosWithNamespaceId/*" 的请求到一个上游服务,
|
||||
该服务在 Nacos 中的服务名是 APISIX-NACOS,命名空间是 test_ns,查询地址是 http://192.168.33.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&namespaceId=test_ns,创建路由时指定服务发现类型为 nacos。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/2 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/nacosWithNamespaceId/*",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"discovery_args": {
|
||||
"namespace_id": "test_ns"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"node": {
|
||||
"key": "\/apisix\/routes\/2",
|
||||
"value": {
|
||||
"id": "2",
|
||||
"create_time": 1615796097,
|
||||
"status": 1,
|
||||
"update_time": 1615799165,
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"hash_on": "vars",
|
||||
"pass_host": "pass",
|
||||
"scheme": "http",
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"discovery_args": {
|
||||
"namespace_id": "test_ns"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"priority": 0,
|
||||
"uri": "\/nacosWithNamespaceId\/*"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 指定组
|
||||
|
||||
例如,转发 URI 匹配 "/nacosWithGroupName/*" 的请求到一个上游服务,
|
||||
该服务在 Nacos 中的服务名是 APISIX-NACOS,组名是 test_group,查询地址是 http://192.168.33.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&groupName=test_group,创建路由时指定服务发现类型为 nacos。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/3 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/nacosWithGroupName/*",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"discovery_args": {
|
||||
"group_name": "test_group"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"node": {
|
||||
"key": "\/apisix\/routes\/3",
|
||||
"value": {
|
||||
"id": "3",
|
||||
"create_time": 1615796097,
|
||||
"status": 1,
|
||||
"update_time": 1615799165,
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"hash_on": "vars",
|
||||
"pass_host": "pass",
|
||||
"scheme": "http",
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"discovery_args": {
|
||||
"group_name": "test_group"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"priority": 0,
|
||||
"uri": "\/nacosWithGroupName\/*"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 同时指定命名空间和组
|
||||
|
||||
例如,转发 URI 匹配 "/nacosWithNamespaceIdAndGroupName/*" 的请求到一个上游服务,
|
||||
该服务在 Nacos 中的服务名是 APISIX-NACOS,命名空间是 test_ns,组名是 test_group,查询地址是 http://192.168.33.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&namespaceId=test_ns&groupName=test_group,创建路由时指定服务发现类型为 nacos。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/4 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/nacosWithNamespaceIdAndGroupName/*",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"discovery_args": {
|
||||
"namespace_id": "test_ns",
|
||||
"group_name": "test_group"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"node": {
|
||||
"key": "\/apisix\/routes\/4",
|
||||
"value": {
|
||||
"id": "4",
|
||||
"create_time": 1615796097,
|
||||
"status": 1,
|
||||
"update_time": 1615799165,
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"hash_on": "vars",
|
||||
"pass_host": "pass",
|
||||
"scheme": "http",
|
||||
"service_name": "APISIX-NACOS",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"discovery_type": "nacos",
|
||||
"discovery_args": {
|
||||
"namespace_id": "test_ns",
|
||||
"group_name": "test_group"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"priority": 0,
|
||||
"uri": "\/nacosWithNamespaceIdAndGroupName\/*"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 外部插件
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 什么是 External Plugin 和 Plugin Runner
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 支持使用 Lua 语言编写插件,这种类型的插件在 APISIX 内部执行。
|
||||
有时候你想使用其他语言来开发插件,因此,APISIX 支持以 `Sidecar` 的方式加载和运行你写的插件。
|
||||
这里的 `Sidecar` 就是 Plugin Runner,你写的插件叫做 External Plugin。
|
||||
|
||||
## 它是如何工作的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当你在 APISIX 中配置了一个 Plugin Runner,APISIX 将以子进程的方式运行该 Plugin Runner。
|
||||
|
||||
该子进程与 APISIX 进程从属相同用户。当重启或者重新加载 APISIX 时,该 Plugin Runner 也将被重启。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你为指定路由配置了 `ext-plugin-*` 插件,
|
||||
匹配该路由的请求将触发从 APISIX 到 Plugin Runner 的 RPC 调用。
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin Runner 将处理该 RPC 调用,在其侧创建一个请求,运行 External Plugin 并将结果返回给 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
External Plugin 及其执行顺序在这里 `ext-plugin-*` 配置。与其他插件一样,External Plugin 可以动态启用和重新配置。
|
||||
|
||||
## 它是如何实现的
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对 Plugin Runner 内部实现感兴趣,请参考这份文档:
|
||||
[The Implementation of Plugin Runner](../../en/latest/internal/plugin-runner.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持的 Plugin Runner
|
||||
|
||||
- Java: https://github.com/apache/apisix-java-plugin-runner
|
||||
- Go: https://github.com/apache/apisix-go-plugin-runner
|
||||
- Python: https://github.com/apache/apisix-python-plugin-runner
|
||||
- JavaScript: https://github.com/zenozeng/apisix-javascript-plugin-runner
|
||||
|
||||
## 在 APISIX 中配置 Plugin Runner
|
||||
|
||||
在生产环境运行 Plugin Runner,添加以下配置到 `config.yaml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
ext-plugin:
|
||||
cmd: ["blah"] # replace it to the real runner executable according to the runner you choice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 将以子进程的方式管理该 Plugin Runner。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:在 Mac 上,APISIX `v2.6` 无法管理该 Plugin Runner。
|
||||
|
||||
在开发过程中,我们希望单独运行 Plugin Runner,这样就可以重新启动它,而无需先重新启动 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
通过指定环境变量 `APISIX_LISTEN_ADDRESS`, 我们可以使 Plugin Runner 监听一个固定的地址。
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
APISIX_LISTEN_ADDRESS=unix:/tmp/x.sock
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时,Plugin Runner 将监听 `/tmp/x.sock`
|
||||
|
||||
同时,你需要配置 APISIX 发送 RPC 请求到该固定的地址:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
ext-plugin:
|
||||
# cmd: ["blah"] # don't configure the executable!
|
||||
path_for_test: "/tmp/x.sock" # without 'unix:' prefix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在生产环境,不应该使用 `path_for_test`,此时监听的地址将动态生成。
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 由 APISIX 管理时,Plugin Runner 无法访问我的环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
自 `v2.7`,APISIX 可以将环境变量传递给 Plugin Runner。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,默认情况下,Nginx 将隐藏所有环境变量。所以你需要首先在 `conf/config.yaml` 中声明环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
nginx_config:
|
||||
envs:
|
||||
- MY_ENV_VAR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### APISIX 使用 SIGKILL 终止 Plugin Runner,而不是使用 SIGTERM!
|
||||
|
||||
自 `v2.7`,当跑在 OpenResty 1.19+ 时,APISIX 将使用 SIGTERM 来停止 Plugin Runner。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,APISIX 需要等待 Plugin Runner 退出,这样我们才能确保资源得以被释放。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,我们先发送 SIGTERM。然后在 1 秒后,如果 Plugin Runner 仍然在运行,我们将发送 SIGKILL。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 入门指南
|
||||
description: 本教程使用脚本在本地环境快速安装 Apache APISIX,并且通过管理 API 来验证是否安装成功。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 是 Apache 软件基金会下的[顶级项目](https://projects.apache.org/project.html?apisix),由 API7.ai 开发并捐赠。它是一个具有动态、实时、高性能等特点的云原生 API 网关。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 APISIX 网关作为所有业务的流量入口,它提供了动态路由、动态上游、动态证书、A/B 测试、灰度发布(金丝雀发布)、蓝绿部署、限速、防攻击、收集指标、监控报警、可观测、服务治理等功能。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程使用脚本在本地环境快速安装 Apache APISIX,并且通过管理 API 来验证是否安装成功。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
快速启动脚本需要以下条件:
|
||||
|
||||
* 已安装 [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/),用于部署 **etcd** 和 **APISIX**。
|
||||
* 已安装 [curl](https://curl.se/),用于验证 APISIX 是否安装成功。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 APISIX
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
为了提供更好的体验,管理 API 默认无需授权,请在生产环境中打开授权开关。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
APISIX 可以借助 quickstart 脚本快速安装并启动:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -sL https://run.api7.ai/apisix/quickstart | sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该命令启动 _apisix-quickstart_ 和 _etcd_ 两个容器,APISIX 使用 etcd 保存和同步配置。APISIX 和 etcd 容器使用 Docker 的 [**host**](https://docs.docker.com/network/host/) 网络模式,因此可以从本地直接访问。
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切顺利,将输出如下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
✔ APISIX is ready!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过 curl 来访问正在运行的 APISIX 实例。比如,你可以发送一个简单的 HTTP 请求来验证 APISIX 运行状态是否正常:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080" --head | grep Server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切顺利,将输出如下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Server: APISIX/Version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里的 `Version` 是指你已经安装的 APISIX 版本,比如 `APISIX/3.3.0`。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你已经成功安装并运行了 APISIX!
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经成功地安装了 APISIX 并且正常运行,那么你可以继续进行下面的教程。
|
||||
|
||||
* [配置路由](configure-routes.md)
|
||||
* [负载均衡](load-balancing.md)
|
||||
* [限速](rate-limiting.md)
|
||||
* [密钥验证](key-authentication.md)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 配置路由
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/configure-routes
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/configure-routes" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 使用 _routes_ 来提供灵活的网关管理功能,在一个请求中,_routes_ 包含了访问路径和上游目标等信息。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将引导你创建一个 route 并验证它,你可以参考以下步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 创建一个指向 [httpbin.org](http://httpbin.org)的 _upstream_。
|
||||
2. 使用 _cURL_ 发送一个请求,了解 APISIX 的代理和转发请求机制。
|
||||
|
||||
## Route 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Route(也称之为路由)是访问上游目标的路径,在 [Apache APISIX](https://api7.ai/apisix) 中,Route 首先通过预定的规则来匹配客户端请求,然后加载和执行相应的插件,最后将请求转发至特定的 Upstream。
|
||||
|
||||
在 APISIX 中,一个最简单的 Route 仅由匹配路径和 Upstream 地址两个信息组成。
|
||||
|
||||
## Upstream 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Upstream(也称之为上游)是一组具备相同功能的节点集合,它是对虚拟主机的抽象。Upstream 可以通过预先配置的规则对多个服务节点进行负载均衡。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建路由
|
||||
|
||||
你可以创建一个路由,将客户端的请求转发至 [httpbin.org](http://httpbin.org)(这个网站能测试 HTTP 请求和响应的各种信息)。
|
||||
|
||||
通过下面的命令,你将创建一个路由,把请求`http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip` 转发至 [httpbin.org/ip](http://httpbin.org/ip):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "getting-started-ip",
|
||||
"uri": "/ip",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果配置成功,将会返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你将会得到类似下面的返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"origin": "183.94.122.205"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
本教程创建的路由仅对应一个上游目标。在下个教程中,你将会学习如何配置多个上游目标的负载均衡。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 密钥验证
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/key-authentication
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/key-authentication" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
API 网关主要作用是连接 API 消费者和提供者。出于安全考虑,在访问内部资源之前,应先对消费者进行身份验证和授权。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 拥有灵活的插件扩展系统,目前有很多可用于用户身份验证和授权的插件。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Key Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/key-auth/)
|
||||
- [Basic Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/basic-auth/)
|
||||
- [JSON Web Token (JWT) Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/jwt-auth/)
|
||||
- [Keycloak](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/authz-keycloak/)
|
||||
- [Casdoor](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/authz-casdoor/)
|
||||
- [Wolf RBAC](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/wolf-rbac/)
|
||||
- [OpenID Connect](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/)
|
||||
- [Central Authentication Service (CAS)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/cas-auth/)
|
||||
- [HMAC](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/hmac-auth/)
|
||||
- [Casbin](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/authz-casbin/)
|
||||
- [LDAP](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/ldap-auth/)
|
||||
- [Open Policy Agent (OPA)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/opa/)
|
||||
- [Forward Authentication](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/plugins/forward-auth/)
|
||||
- [Multiple Authentications](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/multi-auth/)
|
||||
|
||||
本教程中,你将创建一个带有 _密钥验证_ 插件的 _消费者_,并学习如何启用和停用身份验证插件。
|
||||
|
||||
## Consumer 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer(也称之为消费者)是指使用 API 的应用或开发人员。
|
||||
|
||||
在 APISIX 中,消费者需要一个全局唯一的 _名称_,并从上面的列表中选择一个身份验证 _插件_。
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Authentication 是什么
|
||||
|
||||
Key Authentication(也称之为密钥验证)是一个相对比较简单但是应用广泛的身份验证方法,它的设计思路如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 管理员为路由添加一个身份验证密钥(API 密钥)。
|
||||
2. API 消费者在发送请求时,在查询字符串或者请求头中添加密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 Key Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
### 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[快入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
2. 完成[配置路由](./configure-routes.md#route-是什么)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建消费者
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个名为 `tom` 的消费者,并启用 `key-auth` 插件,密钥设置为 `secret-key`。所有携带密钥 `secret-key` 的请求都会被识别为消费者 `tom`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
生产环境请使用复杂的密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "tom",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "secret-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果消费者创建成功,你将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用 Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
在教程[配置路由](./configure-routes.md)中,我们已经创建了路由 `getting-started-ip`,我们通过 `PATCH` 方法为该路由增加 `key-auth` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果增加插件成功,你将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在以下场景中进行验证:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 发送不带任何密钥的请求
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个不带请求头 `apikey` 的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经启用了密钥身份验证,你将会得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized`,即未授权。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
Date: Wed, 08 Feb 2023 09:38:36 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 发送携带错误密钥的请求
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个携带错误密钥(比如 `wrong-key`)的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -H 'apikey: wrong-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果密钥错误,你也将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized`,即未授权。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
Date: Wed, 08 Feb 2023 09:38:27 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. 发送携带正确密钥的请求
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个携带正确密钥(`secret-key`)的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -H 'apikey: secret-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你将会得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK`。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Content-Length: 44
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Thu, 09 Feb 2023 03:27:57 GMT
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 禁用 Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
将参数设置 `_meta.disable` 为 `true`,即可禁用密钥验证插件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"_meta": {
|
||||
"disable": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以发送一个不带任何密钥的请求来验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因为你已经禁用了密钥验证插件,所以你将会得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
你已经学习了如何为路由配置密钥验证。在下个教程中,你将学习如何配置限速。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 负载均衡
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/load-balancing
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/load-balancing" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
负载均衡管理客户端和服务端之间的流量。它决定由哪个服务来处理特定的请求,从而提高性能、可扩展性和可靠性。在设计需要处理大量流量的系统时,负载均衡是一个关键的考虑因素。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache APISIX 支持加权负载均衡算法,传入的流量按照预定顺序轮流分配给一组服务器的其中一个。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,你将创建一个具有两个上游服务的路由,并且启用负载均衡来测试在两个服务之间的切换情况。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
2. 了解 APISIX 中[路由及上游](./configure-routes.md#route-是什么)的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用负载均衡
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个具有两个上游服务的路由,访问 `/headers` 将被转发到 [httpbin.org](https://httpbin.org/headers) 和 [mock.api7.ai](https://mock.api7.ai/headers) 这两个上游服务,并且会返回请求头。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "getting-started-headers",
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"upstream" : {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:443": 1,
|
||||
"mock.api7.ai:443": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pass_host": "node",
|
||||
"scheme": "https"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果路由创建成功,你将会收到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
1. 将 `pass_host` 字段设置为 `node`,将传递请求头给上游。
|
||||
2. 将 `scheme` 字段设置为 `https`,向上游发送请求时将启用 TLS。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证
|
||||
|
||||
这两个服务返回不同的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
`httpbin.org` 返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbin.org",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/7.58.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-63e34b15-19f666602f22591b525e1e80",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "localhost"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`mock.api7.ai` 返回:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"host": "mock.api7.ai",
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/7.58.0",
|
||||
"content-type": "application/json",
|
||||
"x-application-owner": "API7.ai"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们生成 100 个请求来测试负载均衡的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
hc=$(seq 100 | xargs -I {} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers" -sL | grep "httpbin" | wc -l); echo httpbin.org: $hc, mock.api7.ai: $((100 - $hc))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果显示,请求几乎平均分配给这两个上游服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
httpbin.org: 51, mock.api7.ai: 49
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
你已经学习了如何配置负载均衡。在下个教程中,你将学习如何配置身份验证。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 限速
|
||||
slug: /getting-started/rate-limiting
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/rate-limiting" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
> 本教程由 [API7.ai](https://api7.ai/) 编写。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 是一个统一的控制中心,它管理 API 和微服务的进出流量。除了客户端发来的合理的请求,还可能存在网络爬虫产生的不必要的流量,此外,网络攻击(比如 DDos)也可能产生非法请求。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 提供限速功能,通过限制在规定时间内发送到上游服务的请求数量来保护 APIs 和微服务。请求的计数在内存中完成,具有低延迟和高性能的特点。
|
||||
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/02/20/l9G9Kq41_rate-limiting.png" alt="Routes Diagram" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,你将启用 `limit-count` 插件来限制传入流量的速率。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置条件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[入门指南](./README.md)完成 APISIX 的安装。
|
||||
2. 完成[配置路由](./configure-routes.md#route-是什么)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 Rate Limiting
|
||||
|
||||
在教程[配置路由](./configure-routes.md)中,我们已经创建了路由 `getting-started-ip`,我们通过 `PATCH` 方法为该路由增加 `limit-count` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 2,
|
||||
"time_window": 10,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 503
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果增加插件成功,你将得到返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created`。上述配置将传入流量的速率限制为每 10 秒最多 2 个请求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
我们同时生成 100 个请求来测试限速插件的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
count=$(seq 100 | xargs -I {} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -I -sL | grep "503" | wc -l); echo \"200\": $((100 - $count)), \"503\": $count
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请求结果同预期一致:在这 100 个请求中,有 2 个请求发送成功(状态码为 `200`),其他请求均被拒绝(状态码为 `503`)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
"200": 2, "503": 98
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 禁用 Rate Limiting
|
||||
|
||||
将参数设置 `_meta.disable` 为 `true`,即可禁用限速插件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/getting-started-ip" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"_meta": {
|
||||
"disable": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
我们再次同时生成 100 个请求来测试限速插件是否已被禁用:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
count=$(seq 100 | xargs -i curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ip" -I -sL | grep "503" | wc -l); echo \"200\": $((100 - $count)), \"503\": $count
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果显示所有的请求均成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
"200": 100, "503": 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 更多
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 APISIX 的变量来配置限速插件的规则,比如 `$host` 和 `$uri`。此外,APISIX 也支持使用 Redis 集群进行限速配置,即通过 Redis 来进行计数。
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
恭喜你!你已经学习了如何配置限速插件,这也意味着你已经完成了所有的入门教程。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以继续学习其他文档来定制 APISIX,以满足你的生产环境需要。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: gRPC 代理
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
通过 APISIX 代理 gRPC 连接,并使用 APISIX 的大部分特性管理你的 gRPC 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参数
|
||||
|
||||
* `scheme`: Route 对应的 Upstream 的 `scheme` 必须设置为 `grpc` 或者 `grpcs`
|
||||
* `uri`: 格式为 /service/method 如:/helloworld.Greeter/SayHello
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建代理 gRPC 的 Route
|
||||
|
||||
在指定 Route 中,代理 gRPC 服务接口:
|
||||
|
||||
* 注意:这个 Route 对应的 Upstream 的 `scheme` 必须设置为 `grpc` 或者 `grpcs`。
|
||||
* 注意:APISIX 使用 TLS 加密的 HTTP/2 暴露 gRPC 服务,所以需要先 [配置 SSL 证书](certificate.md);
|
||||
* 注意:APISIX 也支持通过纯文本的 HTTP/2 暴露 gRPC 服务,这不需要依赖 SSL,通常用于内网环境代理 gRPC 服务
|
||||
* 下面例子所代理的 gRPC 服务可供参考:[grpc_server_example](https://github.com/api7/grpc_server_example)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["POST", "GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/helloworld.Greeter/SayHello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpc",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:50051": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试 TLS 加密的 HTTP/2
|
||||
|
||||
访问上面配置的 Route:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
grpcurl -insecure -import-path /pathtoprotos -proto helloworld.proto \
|
||||
-d '{"name":"apisix"}' 127.0.0.1:9443 helloworld.Greeter.SayHello
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello apisix"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> grpcurl 是一个 CLI 工具,类似于 curl,充当 gRPC 客户端并让您与 gRPC 服务器进行交互。安装方式请查看官方[文档](https://github.com/fullstorydev/grpcurl#installation)
|
||||
|
||||
这表示已成功代理。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试纯文本的 HTTP/2
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,APISIX 只在 `9443` 端口支持 TLS 加密的 HTTP/2。你也可以支持纯本文的 HTTP/2,只需要修改 `conf/config.yaml` 文件中的 `node_listen` 配置即可。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
node_listen:
|
||||
- port: 9080
|
||||
- port: 9081
|
||||
enable_http2: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问上面配置的 Route:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
grpcurl -plaintext -import-path /pathtoprotos -proto helloworld.proto \
|
||||
-d '{"name":"apisix"}' 127.0.0.1:9081 helloworld.Greeter.SayHello
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello apisix"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这表示已成功代理。
|
||||
|
||||
### gRPCS
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的 gRPC 服务使用了自己的 TLS 加密,即所谓的 `gPRCS` (gRPC + TLS),那么需要修改 scheme 为 `grpcs`。继续上面的例子,50052 端口上跑的是 gPRCS 的服务,这时候应该这么配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["POST", "GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/helloworld.Greeter/SayHello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpcs",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:50052": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
186
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/http3.md
Normal file
186
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/http3.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: HTTP3 协议
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[HTTP/3](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP/3) 是 Hypertext Transfer Protocol(HTTP) 的第三个主要版本。与依赖 TCP 的前辈不同,HTTP/3 基于 [QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) protocol](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QUIC)。它带来了多项好处,减少了延迟并提高了性能:
|
||||
|
||||
* 实现不同网络连接之间的无缝过渡,例如从 Wi-Fi 切换到移动数据。
|
||||
* 消除队头阻塞,以便丢失的数据包不会阻塞所有流。
|
||||
* 在 TLS 握手的同时协商 TLS 版本,从而实现更快的连接。
|
||||
* 默认提供加密,确保通过 HTTP/3 连接传输的所有数据都受到保护和保密。
|
||||
* 在与客户端已建立连接的服务器通信时提供零往返时间 (0-RTT)。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 目前支持下游客户端和 APISIX 之间的 HTTP/3 连接。尚不支持与上游服务的 HTTP/3 连接。欢迎社区贡献。
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
此功能尚未经过大规模测试,因此不建议用于生产使用。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
本文档将向您展示如何配置 APISIX 以在客户端和 APISIX 之间启用 HTTP/3 连接,并记录一些已知问题。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用 HTTP/3
|
||||
|
||||
将以下配置添加到 APISIX 的配置文件。该配置将在端口 `9443`(或其他端口)上启用 HTTP/3:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="config.yaml"
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
listen:
|
||||
- port: 9443
|
||||
enable_http3: true
|
||||
ssl_protocols: TLSv1.3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
如果您使用 Docker 部署 APISIX,请确保在 HTTP3 端口中允许 UDP,例如 `-p 9443:9443/udp`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
然后重新加载 APISIX 以使配置更改生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 生成证书和密钥
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/3 需要 TLS。您可以利用购买的证书或自行生成证书。
|
||||
|
||||
如自行生成,首先生成证书颁发机构 (CA) 密钥和证书:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048 && \
|
||||
openssl req -new -sha256 -key ca.key -out ca.csr -subj "/CN=ROOTCA" && \
|
||||
openssl x509 -req -days 36500 -sha256 -extensions v3_ca -signkey ca.key -in ca.csr -out ca.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,生成具有 APISIX 通用名称的密钥和证书,并使用 CA 证书进行签名:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048 && \
|
||||
openssl req -new -sha256 -key server.key -out server.csr -subj "/CN=test.com" && \
|
||||
openssl x509 -req -days 36500 -sha256 -extensions v3_req \
|
||||
-CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAserial ca.srl -CAcreateserial \
|
||||
-in server.csr -out server.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
可选择性地将存储在 `server.crt` 和 `server.key` 中的内容加载到环境变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
server_cert=$(cat server.crt)
|
||||
server_key=$(cat server.key)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个保存服务器证书及其密钥的 SSL 对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "quickstart-tls-client-ssl",
|
||||
"sni": "test.com",
|
||||
"cert": "'"${server_cert}"'",
|
||||
"key": "'"${server_key}"'"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建路由
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个路由至 `httpbin.org`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id":"httpbin-route",
|
||||
"uri":"/get",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证 HTTP/3 连接
|
||||
|
||||
验证前需要安装支持 HTTP/3 的 curl,如 [static-curl](https://github.com/stunnel/static-curl) 或其他支持 HTTP/3 的 curl。
|
||||
|
||||
发送一个请求到路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -kv --http3-only \
|
||||
-H "Host: test.com" \
|
||||
--resolve "test.com:9443:127.0.0.1" "https://test.com:9443/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
应收到 `HTTP/3 200` 相应如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
* Added test.com:9443:127.0.0.1 to DNS cache
|
||||
* Hostname test.com was found in DNS cache
|
||||
* Trying 127.0.0.1:9443...
|
||||
* QUIC cipher selection: TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256:TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384:TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256:TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256
|
||||
* Skipped certificate verification
|
||||
* Connected to test.com (127.0.0.1) port 9443
|
||||
* using HTTP/3
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] OPENED stream for https://test.com:9443/get
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] [:method: GET]
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] [:scheme: https]
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] [:authority: test.com]
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] [:path: /get]
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] [user-agent: curl/8.7.1]
|
||||
* [HTTP/3] [0] [accept: */*]
|
||||
> GET /get HTTP/3
|
||||
> Host: test.com
|
||||
> User-Agent: curl/8.7.1
|
||||
> Accept: */*
|
||||
>
|
||||
* Request completely sent off
|
||||
< HTTP/3 200
|
||||
...
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Content-Length": "0",
|
||||
"Host": "test.com",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.7.1",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6656013a-27da6b6a34d98e3e79baaf5b",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "test.com"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "172.19.0.1, 123.40.79.456",
|
||||
"url": "http://test.com/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
* Connection #0 to host test.com left intact
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 已知问题
|
||||
|
||||
- 对于 APISIX-3.9, Tongsuo 相关测试用例会失败,因为 Tongsuo 不支持 QUIC TLS。
|
||||
- APISIX-3.9 基于 NGINX-1.25.3,存在 HTTP/3 漏洞(CVE-2024-24989、CVE-2024-24990)。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 安装依赖
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意
|
||||
|
||||
- Apache APISIX 从 v2.0 开始不再支持 `v2` 版本的 etcd,并且 etcd 最低支持版本为 v3.4.0,因此请使用 etcd 3.4.0+。更重要的是,因为 etcd v3 使用 gRPC 作为消息传递协议,而 Apache APISIX 使用 HTTP(S) 与 etcd 集群通信,因此请确保启用 [etcd gRPC gateway](https://etcd.io/docs/v3.4.0/dev-guide/api_grpc_gateway/) 功能。
|
||||
|
||||
- 目前 Apache APISIX 默认使用 HTTP 协议与 etcd 集群通信,这并不安全,如果希望保障数据的安全性和完整性。请为您的 etcd 集群配置证书及对应私钥,并在您的 Apache APISIX etcd endpoints 配置列表中明确使用 `https` 协议前缀。请查阅 `conf/config.yaml.example` 中 `etcd` 一节相关的配置来了解更多细节。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果是 OpenResty 1.19,APISIX 会使用 OpenResty 内置的 LuaJIT 来运行 `bin/apisix`;否则会使用 Lua 5.1。如果运行过程中遇到 `luajit: lj_asm_x86.h:2819: asm_loop_fixup: Assertion '((intptr_t)target & 15) == 0' failed`,这是低版本 OpenResty 内置的 LuaJIT 在特定编译条件下的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
- 在某些平台上,通过包管理器安装 LuaRocks 会导致 Lua 被升级为 Lua 5.3,所以我们建议通过源代码的方式安装 LuaRocks。如果你通过官方仓库安装 OpenResty 和 OpenResty 的 OpenSSL 开发库(rpm 版本:openresty-openssl111-devel,deb 版本:openresty-openssl111-dev),那么 [我们提供了自动安装的脚本](https://github.com/apache/apisix/tree/master/utils/linux-install-luarocks.sh)。如果你是自己编译的 OpenResty,可以参考上述脚本并修改里面的路径。如果编译时没有指定 OpenSSL 库的路径,那么无需配置 LuaRocks 内跟 OpenSSL 相关的变量,因为默认都是用的系统自带的 OpenSSL。如果编译时指定了 OpenSSL 库,那么需要保证 LuaRocks 的 OpenSSL 配置跟 OpenResty 的相一致。
|
||||
|
||||
- OpenResty 是 APISIX 的一个依赖项,如果是第一次部署 APISIX 并且不需要使用 OpenResty 部署其他服务,可以在 OpenResty 安装完成后停止并禁用 OpenResty,这不会影响 APISIX 的正常工作,请根据自己的业务谨慎操作。例如 Ubuntu:`systemctl stop openresty && systemctl disable openresty`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装
|
||||
|
||||
在支持的操作系统上运行以下指令即可安装 Apache APISIX dependencies。
|
||||
|
||||
支持的操作系统版本:CentOS 7, Fedora 31 & 32, Ubuntu 16.04 & 18.04, Debian 9 & 10, Arch Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,对于 Arch Linux 来说,我们使用 AUR 源中的 `openresty`,所以需要 AUR Helper 才能正常安装。目前支持 `yay` 和 `pacaur`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/apisix/master/utils/install-dependencies.sh -sL | bash -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经克隆了 Apache APISIX 仓库,在根目录运行以下指令安装 Apache APISIX dependencies。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bash utils/install-dependencies.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,330 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: APISIX 安装指南
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- APISIX 安装教程
|
||||
- 部署 APISIX
|
||||
description: 本文档主要介绍了 APISIX 多种安装方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
|
||||
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
|
||||
|
||||
本文将介绍如何在你的环境中安装并运行 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
关于如何快速运行 Apache APISIX,请参考[入门指南](./getting-started/README.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 APISIX
|
||||
|
||||
你可以选择以下任意一种方式安装 APISIX:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="install-method"
|
||||
defaultValue="docker"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Docker', value: 'docker'},
|
||||
{label: 'Helm', value: 'helm'},
|
||||
{label: 'RPM', value: 'rpm'},
|
||||
{label: 'DEB', value: 'deb'},
|
||||
{label: 'Source Code', value: 'source code'},
|
||||
]}>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker">
|
||||
|
||||
使用此方法安装 APISIX,你需要安装 [Docker](https://www.docker.com/) 和 [Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/)。
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载 [apisix-docker](https://github.com/apache/apisix-docker) 仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/apache/apisix-docker.git
|
||||
cd apisix-docker/example
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,使用 `docker-compose` 启用 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="cpu-arch"
|
||||
defaultValue="x86"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'x86', value: 'x86'},
|
||||
{label: 'ARM/M1', value: 'arm'},
|
||||
]}>
|
||||
<TabItem value="x86">
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker-compose -p docker-apisix up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="arm">
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker-compose -p docker-apisix -f docker-compose-arm64.yml up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="helm">
|
||||
|
||||
通过 Helm 安装 APISIX,请执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
helm repo add apisix https://charts.apiseven.com
|
||||
helm repo update
|
||||
helm install apisix apisix/apisix --create-namespace --namespace apisix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从 [apisix-helm-chart](https://github.com/apache/apisix-helm-chart) 仓库找到其他组件。
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="rpm">
|
||||
|
||||
该安装方法适用于 CentOS 7 和 CentOS 8。如果你选择该方法安装 APISIX,需要先安装 etcd。具体安装方法请参考 [安装 etcd](#安装-etcd)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 RPM 仓库安装
|
||||
|
||||
如果当前系统**没有安装 OpenResty**,请使用以下命令来安装 OpenResty 和 APISIX 仓库:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo yum install -y https://repos.apiseven.com/packages/centos/apache-apisix-repo-1.0-1.noarch.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果已安装 OpenResty 的官方 RPM 仓库,请使用以下命令安装 APISIX 的 RPM 仓库:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://repos.apiseven.com/packages/centos/apache-apisix.repo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
完成上述操作后使用以下命令安装 APISIX:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo yum install apisix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以安装指定版本的 APISIX(本示例为 APISIX v3.8.0 版本):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo yum install apisix-3.8.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 RPM 包离线安装:
|
||||
|
||||
将 APISIX 离线 RPM 包下载到 `apisix` 文件夹:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p apisix
|
||||
sudo yum install -y https://repos.apiseven.com/packages/centos/apache-apisix-repo-1.0-1.noarch.rpm
|
||||
sudo yum clean all && yum makecache
|
||||
sudo yum install -y --downloadonly --downloaddir=./apisix apisix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后将 `apisix` 文件夹复制到目标主机并运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo yum install ./apisix/*.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 管理 APISIX 服务
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 安装完成后,你可以运行以下命令初始化 NGINX 配置文件和 etcd:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令启动 APISIX:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行 `apisix help` 命令,通过查看返回结果,获取其他操作的命令及描述。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="deb">
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 DEB 仓库安装
|
||||
|
||||
目前 APISIX 支持的 DEB 仓库仅支持 Debian 11(Bullseye),并且支持 amd64 和 arm64 架构。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# amd64
|
||||
wget -O - http://repos.apiseven.com/pubkey.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
echo "deb http://repos.apiseven.com/packages/debian bullseye main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/apisix.list
|
||||
|
||||
# arm64
|
||||
wget -O - http://repos.apiseven.com/pubkey.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
echo "deb http://repos.apiseven.com/packages/arm64/debian bullseye main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/apisix.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
完成上述操作后使用以下命令安装 APISIX:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y apisix=3.8.0-0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 管理 APISIX 服务
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 安装完成后,你可以运行以下命令初始化 NGINX 配置文件和 etcd:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo apisix init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令启动 APISIX:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo apisix start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行 `apisix help` 命令,通过查看返回结果,获取其他操作的命令及描述。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="source code">
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要使用源码构建 APISIX,请参考 [源码安装 APISIX](./building-apisix.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 etcd
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 使用 [etcd](https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd) 作为配置中心进行保存和同步配置。在安装 APISIX 之前,需要在你的主机上安装 etcd。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在安装 APISIX 时选择了 Docker 或 Helm 安装,那么 etcd 将会自动安装;如果你选择其他方法或者需要手动安装 APISIX,请参考以下步骤安装 etcd:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs
|
||||
groupId="os"
|
||||
defaultValue="linux"
|
||||
values={[
|
||||
{label: 'Linux', value: 'linux'},
|
||||
{label: 'macOS', value: 'mac'},
|
||||
]}>
|
||||
<TabItem value="linux">
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ETCD_VERSION='3.5.4'
|
||||
wget https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/releases/download/v${ETCD_VERSION}/etcd-v${ETCD_VERSION}-linux-amd64.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -xvf etcd-v${ETCD_VERSION}-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
|
||||
cd etcd-v${ETCD_VERSION}-linux-amd64 && \
|
||||
sudo cp -a etcd etcdctl /usr/bin/
|
||||
nohup etcd >/tmp/etcd.log 2>&1 &
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="mac">
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
brew install etcd
|
||||
brew services start etcd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 后续操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 APISIX
|
||||
|
||||
通过修改本地 `./conf/config.yaml` 文件,或者在启动 APISIX 时使用 `-c` 或 `--config` 添加文件路径参数 `apisix start -c <path string>`,完成对 APISIX 服务本身的基本配置。默认配置不应修改,可以在 `apisix/cli/config.lua` 中找到。
|
||||
|
||||
比如将 APISIX 默认监听端口修改为 8000,其他配置保持默认,在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中只需这样配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
node_listen: 8000 # APISIX listening port
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
比如指定 APISIX 默认监听端口为 8000,并且设置 etcd 地址为 `http://foo:2379`,其他配置保持默认。在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中只需这样配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
node_listen: 8000 # APISIX listening port
|
||||
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
role: traditional
|
||||
role_traditional:
|
||||
config_provider: etcd
|
||||
etcd:
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- "http://foo:2379"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
|
||||
请不要手动修改 APISIX 安装目录下的 `./conf/nginx.conf` 文件。当 APISIX 启动时,会根据 `config.yaml` 的配置自动生成新的 `nginx.conf` 并自动启动服务。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 更新 Admin API key
|
||||
|
||||
建议修改 Admin API 的 key,保护 APISIX 的安全。
|
||||
|
||||
请参考如下信息更新配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
admin:
|
||||
admin_key:
|
||||
- name: "admin"
|
||||
key: newsupersecurekey # 请修改 key 的值
|
||||
role: admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
更新完成后,你可以使用新的 key 访问 Admin API:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes?api_key=newsupersecurekey -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 APISIX 添加 systemd 配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是通过 RPM 包安装 APISIX,配置文件已经自动安装,你可以直接使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
systemctl start apisix
|
||||
systemctl stop apisix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是通过其他方法安装的 APISIX,可以参考[配置文件模板](https://github.com/api7/apisix-build-tools/blob/master/usr/lib/systemd/system/apisix.service)进行修改,并将其添加在 `/usr/lib/systemd/system/apisix.service` 路径下。
|
||||
|
||||
如需了解 APISIX 后续使用,请参考[入门指南](./getting-started/README.md)获取更多信息。
|
||||
205
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/mtls.md
Normal file
205
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/mtls.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: TLS 双向认证
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 保护 Admin API
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么使用
|
||||
|
||||
双向认证提供了一种更好的方法来阻止未经授权的对 APISIX Admin API 的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
客户端需要向服务器提供证书,服务器将检查该客户端证书是否由受信的 CA 签名,并决定是否响应其请求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何配置
|
||||
|
||||
1. 生成自签证书对,包括 CA、server、client 证书对。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 修改 `conf/config.yaml` 中的配置项:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
admin_listen:
|
||||
ip: 127.0.0.1
|
||||
port: 9180
|
||||
https_admin: true
|
||||
|
||||
admin_api_mtls:
|
||||
admin_ssl_ca_cert: "/data/certs/mtls_ca.crt" # Path of your self-signed ca cert.
|
||||
admin_ssl_cert: "/data/certs/mtls_server.crt" # Path of your self-signed server side cert.
|
||||
admin_ssl_cert_key: "/data/certs/mtls_server.key" # Path of your self-signed server side key.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 执行命令,使配置生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
apisix init
|
||||
apisix reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 客户端如何调用
|
||||
|
||||
需要将证书文件的路径与域名按实际情况替换。
|
||||
|
||||
* 注意:提供的 CA 证书需要与服务端的相同。*
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --cacert /data/certs/mtls_ca.crt --key /data/certs/mtls_client.key --cert /data/certs/mtls_client.crt https://admin.apisix.dev:9180/apisix/admin/routes -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 保护 ETCD
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何配置
|
||||
|
||||
你需要构建 [APISIX-runtime](./FAQ.md#如何构建-APISIX-runtime-环境?),并且需要在配置文件中设定 `etcd.tls` 来使 ETCD 的双向认证功能正常工作。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
deployment:
|
||||
role: traditional
|
||||
role_traditional:
|
||||
config_provider: etcd
|
||||
etcd:
|
||||
tls:
|
||||
cert: /data/certs/etcd_client.pem # path of certificate used by the etcd client
|
||||
key: /data/certs/etcd_client.key # path of key used by the etcd client
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果 APISIX 不信任 etcd server 使用的 CA 证书,我们需要设置 CA 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
ssl_trusted_certificate: /path/to/certs/ca-certificates.crt # path of CA certificate used by the etcd server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 保护路由
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么使用
|
||||
|
||||
双向认证是一种密码学安全的验证客户端身份的手段。当你需要加密并保护流量的双向安全时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
* 注意:双向认证只发生在 HTTPS 中。如果你的路由也可以通过 HTTP 访问,你应该在 HTTP 中添加额外的保护,或者禁止通过 HTTP 访问。*
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何配置
|
||||
|
||||
我们提供了一个[演示教程](./tutorials/client-to-apisix-mtls.md),详细地讲解了如何配置客户端和 APISIX 之间的 mTLS。
|
||||
|
||||
在配置 `ssl` 资源时,同时需要配置 `client.ca` 和 `client.depth` 参数,分别代表为客户端证书签名的 CA 列表,和证书链的最大深度。可参考:[SSL API 文档](./admin-api.md#ssl)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个可用于生成带双向认证配置的 SSL 资源的 shell 脚本示例(如果需要,可修改 API 地址、API Key 和 SSL 资源的 ID。):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
"cert": "'"$(cat t/certs/mtls_server.crt)"'",
|
||||
"key": "'"$(cat t/certs/mtls_server.key)"'",
|
||||
"snis": [
|
||||
"admin.apisix.dev"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"client": {
|
||||
"ca": "'"$(cat t/certs/mtls_ca.crt)"'",
|
||||
"depth": 10
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -vvv --resolve 'admin.apisix.dev:9443:127.0.0.1' https://admin.apisix.dev:9443/hello --cert t/certs/mtls_client.crt --key t/certs/mtls_client.key --cacert t/certs/mtls_ca.crt
|
||||
|
||||
* Added admin.apisix.dev:9443:127.0.0.1 to DNS cache
|
||||
* Hostname admin.apisix.dev was found in DNS cache
|
||||
* Trying 127.0.0.1:9443...
|
||||
* Connected to admin.apisix.dev (127.0.0.1) port 9443 (#0)
|
||||
* ALPN: offers h2
|
||||
* ALPN: offers http/1.1
|
||||
* CAfile: t/certs/mtls_ca.crt
|
||||
* CApath: none
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Unknown (8):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Request CERT (13):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
|
||||
* [CONN-0-0][CF-SSL] (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
|
||||
* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / AEAD-AES256-GCM-SHA384
|
||||
* ALPN: server accepted h2
|
||||
* Server certificate:
|
||||
* subject: C=cn; ST=GuangDong; L=ZhuHai; CN=admin.apisix.dev; OU=ops
|
||||
* start date: Dec 1 10:17:24 2022 GMT
|
||||
* expire date: Aug 18 10:17:24 2042 GMT
|
||||
* subjectAltName: host "admin.apisix.dev" matched cert's "admin.apisix.dev"
|
||||
* issuer: C=cn; ST=GuangDong; L=ZhuHai; CN=ca.apisix.dev; OU=ops
|
||||
* SSL certificate verify ok.
|
||||
* Using HTTP2, server supports multiplexing
|
||||
* Copying HTTP/2 data in stream buffer to connection buffer after upgrade: len=0
|
||||
* h2h3 [:method: GET]
|
||||
* h2h3 [:path: /hello]
|
||||
* h2h3 [:scheme: https]
|
||||
* h2h3 [:authority: admin.apisix.dev:9443]
|
||||
* h2h3 [user-agent: curl/7.87.0]
|
||||
* h2h3 [accept: */*]
|
||||
* Using Stream ID: 1 (easy handle 0x13000bc00)
|
||||
> GET /hello HTTP/2
|
||||
> Host: admin.apisix.dev:9443
|
||||
> user-agent: curl/7.87.0
|
||||
> accept: */*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意,测试时使用的域名需要符合证书的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX 与上游间的双向认证
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么使用
|
||||
|
||||
有时候上游的服务启用了双向认证。在这种情况下,APISIX 作为上游服务的客户端,需要提供客户端证书来正常与其进行通信。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何配置
|
||||
|
||||
在配置 upstream 资源时,可以使用参数 `tls.client_cert` 和 `tls.client_key` 来配置 APISIX 用于与上游进行通讯时使用的证书。可参考 [Upstream API 文档](./admin-api.md#upstream)。
|
||||
|
||||
该功能需要 APISIX 运行在 [APISIX-Runtime](./FAQ.md#如何构建-apisix-runtime-环境) 上。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个与配置 SSL 时相似的 shell 脚本,可为一个已存在的 upstream 资源配置双向认证。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/upstreams/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"tls": {
|
||||
"client_cert": "'"$(cat t/certs/mtls_client.crt)"'",
|
||||
"client_key": "'"$(cat t/certs/mtls_client.key)"'"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,480 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 插件开发
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
此文档是关于 lua 语言的插件开发,其他语言请看:[external plugin](./external-plugin.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件放置路径
|
||||
|
||||
通过在 `conf/config.yaml` 中配置 `extra_lua_path` 来加载你自定义的 lua 插件代码 (或者配置 `extra_lua_cpath` 指定编译的 .so 或 .dll 文件)。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,你可以创建一个目录 `/path/to/example` 作为 `extra_lua_path` 配置的值:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
...
|
||||
extra_lua_path: "/path/to/example/?.lua"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`example` 目录的结构应该像下面这样:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
├── example
|
||||
│ └── apisix
|
||||
│ ├── plugins
|
||||
│ │ └── 3rd-party.lua
|
||||
│ └── stream
|
||||
│ └── plugins
|
||||
│ └── 3rd-party.lua
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
该目录 (`/path/to/example`) 下必须包含 `/apisix/plugins` 的子目录。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::important
|
||||
|
||||
你应该给自己的代码文件起一个与内置插件代码文件 (在 `apisix/plugins` 目录下) 不同的名字。但是如果有需要,你可以使用相同名称的代码文件覆盖内置的代码文件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
要启用您的自定义插件,请将插件列表添加到 `conf/config.yaml` 并附加您的插件名称。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins: # 请参阅 `conf/config.yaml.example` 示例
|
||||
- ... # 添加现有插件
|
||||
- your-plugin # 添加您的自定义插件名称 (名称是在代码中定义的插件名称)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
|
||||
特别注意的是,在默认情况下 plugins 字段配置没有定义的情况下,大多数 APISIX 插件都是启用的状态 (默认启用的插件请参考[apisix/cli/config.lua](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/cli/config.lua))。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦在 `conf/config.yaml` 中定义了 plugins 配置,新的 plugins 列表将会替代默认的配置,而是不是合并,因此在新增配置`plugins`字段时请确保包含正在使用的内置插件。为了在定义 plugins 配置的同时与默认行为保持一致,可以在 plugins 中包含 `apisix/cli/config.lua` 定义的所有默认启用的插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 编写插件
|
||||
|
||||
[example-plugin](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/plugins/example-plugin.lua) 插件 (本地位置: **apisix/plugins/example-plugin.lua**) 提供了一个示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### 命名和优先级
|
||||
|
||||
在代码里指定插件名称(名称是插件的唯一标识,不可重名)和加载优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local plugin_name = "example-plugin"
|
||||
|
||||
local _M = {
|
||||
version = 0.1,
|
||||
priority = 0,
|
||||
name = plugin_name,
|
||||
schema = schema,
|
||||
metadata_schema = metadata_schema,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注:新插件的优先级(priority 属性)不能与现有插件的优先级相同,您可以使用 [control API](./control-api.md#get-v1schema) 的 `/v1/schema` 方法查看所有插件的优先级。另外,同一个阶段里面,优先级 ( priority ) 值大的插件,会优先执行,比如 `example-plugin` 的优先级是 0,`ip-restriction` 的优先级是 3000,所以在每个阶段,会先执行 `ip-restriction` 插件,再去执行 `example-plugin` 插件。这里的“阶段”的定义,参见后续的 [确定执行阶段](#确定执行阶段) 这一节。对于你的插件,建议采用 1 到 99 之间的优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
注:先后顺序与执行顺序无关。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置描述与校验
|
||||
|
||||
定义插件的配置项,以及对应的 [JSON Schema](https://json-schema.org) 描述,并完成对 JSON 的校验,这样方便对配置的数据规格进行验证,以确保数据的完整性以及程序的健壮性。同样,我们以 example-plugin 插件为例,看看他的配置数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"example-plugin": {
|
||||
"i": 1,
|
||||
"s": "s",
|
||||
"t": [1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们看下他的 Schema 描述:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local schema = {
|
||||
type = "object",
|
||||
properties = {
|
||||
i = {type = "number", minimum = 0},
|
||||
s = {type = "string"},
|
||||
t = {type = "array", minItems = 1},
|
||||
ip = {type = "string"},
|
||||
port = {type = "integer"},
|
||||
},
|
||||
required = {"i"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个 schema 定义了一个非负数 `i`,字符串 `s`,非空数组 `t`,和 `ip` 跟 `port`。只有 `i` 是必需的。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,需要实现 **check_schema(conf, schema_type)** 方法,完成配置参数的合法性校验。
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
function _M.check_schema(conf)
|
||||
return core.schema.check(schema, conf)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
项目已经提供了 **core.schema.check** 公共方法,直接使用即可完成配置参数校验。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
通过函数输入参数 **schema_type** 可以对不同类型的 schema 进行对应的校验。例如很多插件需要使用一些[元数据](./terminology/plugin-metadata.md),可以定义插件的 `metadata_schema`。
|
||||
|
||||
```lua title="example-plugin.lua"
|
||||
-- schema definition for metadata
|
||||
local metadata_schema = {
|
||||
type = "object",
|
||||
properties = {
|
||||
ikey = {type = "number", minimum = 0},
|
||||
skey = {type = "string"},
|
||||
},
|
||||
required = {"ikey", "skey"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.check_schema(conf, schema_type)
|
||||
--- check schema for metadata
|
||||
if schema_type == core.schema.TYPE_METADATA then
|
||||
return core.schema.check(metadata_schema, conf)
|
||||
end
|
||||
return core.schema.check(schema, conf)
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再比如 [key-auth](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/plugins/key-auth.lua) 插件为了跟 [Consumer](./admin-api.md#consumer) 资源一起使用,认证插件需要提供一个 `consumer_schema` 来检验 `Consumer` 资源的 `plugins` 属性里面的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```lua title="key-auth.lua"
|
||||
|
||||
local consumer_schema = {
|
||||
type = "object",
|
||||
properties = {
|
||||
key = {type = "string"},
|
||||
},
|
||||
required = {"key"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.check_schema(conf, schema_type)
|
||||
if schema_type == core.schema.TYPE_CONSUMER then
|
||||
return core.schema.check(consumer_schema, conf)
|
||||
else
|
||||
return core.schema.check(schema, conf)
|
||||
end
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 确定执行阶段
|
||||
|
||||
根据业务功能,确定你的插件需要在哪个[阶段](./terminology/plugin.md#插件执行生命周期)执行。
|
||||
|
||||
以 `key-auth` 为例, `key-auth`是一个认证插件,所以需要在 rewrite 阶段执行。在 APISIX,只有认证逻辑可以在 rewrite 阶段里面完成,其他需要在代理到上游之前执行的逻辑都是在 access 阶段完成的。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:我们不能在 rewrite 和 access 阶段调用 `ngx.exit`、`ngx.redirect` 或者 `core.respond.exit`。如果确实需要退出,只需要 return 状态码和正文,插件引擎将使用返回的状态码和正文进行退出。[例子](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/35269581e21473e1a27b11cceca6f773cad0192a/apisix/plugins/limit-count.lua#L177)**
|
||||
|
||||
#### APISIX 的自定义阶段
|
||||
|
||||
除了 OpenResty 的阶段,我们还提供额外的阶段来满足特定的目的:
|
||||
|
||||
- `delayed_body_filter`
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
function _M.delayed_body_filter(conf, ctx)
|
||||
-- delayed_body_filter 在 body_filter 之后被调用。
|
||||
-- 它被 tracing 类型插件用来在 body_filter 之后立即结束 span。
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 编写执行逻辑
|
||||
|
||||
在对应的阶段方法里编写功能的逻辑代码,在阶段方法中具有 `conf` 和 `ctx` 两个参数,以 `limit-conn` 插件配置为例。
|
||||
|
||||
#### conf 参数
|
||||
|
||||
`conf` 参数是插件的相关配置信息,您可以通过 `core.log.warn(core.json.encode(conf))` 将其输出到 `error.log` 中进行查看,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
function _M.access(conf, ctx)
|
||||
core.log.warn(core.json.encode(conf))
|
||||
......
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
conf:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"rejected_code": 503,
|
||||
"burst": 0,
|
||||
"default_conn_delay": 0.1,
|
||||
"conn": 1,
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### ctx 参数
|
||||
|
||||
`ctx` 参数缓存了请求相关的数据信息,您可以通过 `core.log.warn(core.json.encode(ctx, true))` 将其输出到 `error.log` 中进行查看,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
function _M.access(conf, ctx)
|
||||
core.log.warn(core.json.encode(ctx, true))
|
||||
......
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 其它注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
特别需要注意的是,如果你的插件有新建自己的代码目录,那么就需要修改 Makefile 文件,新增创建文件夹的操作,比如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$(INSTALL) -d $(INST_LUADIR)/apisix/plugins/skywalking
|
||||
$(INSTALL) apisix/plugins/skywalking/*.lua $(INST_LUADIR)/apisix/plugins/skywalking/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`_M` 中还有其他字段会影响到插件的行为。
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local _M = {
|
||||
...
|
||||
type = 'auth',
|
||||
run_policy = 'prefer_route',
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`run_policy` 字段可以用来控制插件执行。当这个字段设置成 `prefer_route` 时,且该插件同时配置在全局和路由级别,那么只有路由级别的配置生效。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的插件需要跟 `consumer` 一起使用,需要把 `type` 设置成 `auth`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 加载插件和替换插件
|
||||
|
||||
现在使用 `require "apisix.plugins.3rd-party"` 会加载你自己的插件,比如 `require "apisix.plugins.jwt-auth"`会加载 `jwt-auth` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
可能你会想覆盖一个文件中的函数,你可以在 `conf/config.yaml` 文件中配置 `lua_module_hook` 来使你的 hook 生效。
|
||||
|
||||
你的配置可以像下面这样:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
...
|
||||
extra_lua_path: "/path/to/example/?.lua"
|
||||
lua_module_hook: "my_hook"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当 APISIX 启动的时候,`example/my_hook.lua` 就会被加载,这时你可以使用这个钩子在 APISIX 中来全局替换掉一个方法。
|
||||
这个例子:[my_hook.lua](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/example/my_hook.lua) 可以在项目的 `example` 路径下被找到。
|
||||
|
||||
## 检查外部依赖
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的插件,涉及到一些外部的依赖和三方库,请首先检查一下依赖项的内容。如果插件需要用到共享内存,需要在 [自定义 Nginx 配置](./customize-nginx-configuration.md),例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# put this in config.yaml:
|
||||
nginx_config:
|
||||
http_configuration_snippet: |
|
||||
# for openid-connect plugin
|
||||
lua_shared_dict discovery 1m; # cache for discovery metadata documents
|
||||
lua_shared_dict jwks 1m; # cache for JWKs
|
||||
lua_shared_dict introspection 10m; # cache for JWT verification results
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
插件本身提供了 init 方法。方便插件加载后做初始化动作。如果你需要清理初始化动作创建出来的内容,你可以在对应的 destroy 方法里完成这一操作。
|
||||
|
||||
注:如果部分插件的功能实现,需要在 Nginx 初始化启动,则可能需要在 `apisix/init.lua` 文件的初始化方法 http_init 中添加逻辑,并且可能需要在 `apisix/cli/ngx_tpl.lua` 文件中,对 Nginx 配置文件生成的部分,添加一些你需要的处理。但是这样容易对全局产生影响,根据现有的插件机制,**我们不建议这样做,除非你已经对代码完全掌握**。
|
||||
|
||||
## 加密存储字段
|
||||
|
||||
有些插件需要将参数加密存储,比如 `basic-auth` 插件的 `password` 参数。这个插件需要在 `schema` 中指定哪些参数需要被加密存储。
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
encrypt_fields = {"password"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果是嵌套的参数,比如 `error-log-logger` 插件的 `clickhouse.password` 参数,需要用 `.` 来分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
encrypt_fields = {"clickhouse.password"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
目前还不支持:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 两层以上的嵌套
|
||||
2. 数组中的字段
|
||||
|
||||
通过在 `schema` 中指定 `encrypt_fields = {"password"}`,可以将参数加密存储。APISIX 将提供以下功能:
|
||||
|
||||
- 新增和更新资源时,对于 `encrypt_fields` 中声明的参数,APISIX 会自动加密存储在 etcd 中
|
||||
- 获取资源时,以及在运行插件时,对于 `encrypt_fields` 中声明的参数,APISIX 会自动解密
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,APISIX 启用数据加密并使用[两个默认的密钥](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/85563f016c35834763376894e45908b2fb582d87/apisix/cli/config.lua#L75),你可以在 `config.yaml` 中修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
data_encryption:
|
||||
enable: true
|
||||
keyring:
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`keyring` 是一个数组,可以指定多个 key,APISIX 会按照 keyring 中 key 的顺序,依次尝试用 key 来解密数据(只对在 `encrypt_fields` 声明的参数)。如果解密失败,会尝试下一个 key,直到解密成功。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 `keyring` 中的 key 都无法解密数据,则使用原始数据。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注册公共接口
|
||||
|
||||
插件可以注册暴露给公网的接口。以 batch-requests 插件为例,这个插件注册了 `POST /apisix/batch-requests` 接口,让客户端可以将多个 API 请求组合在一个请求/响应中:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
function batch_requests()
|
||||
-- ...
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.api()
|
||||
-- ...
|
||||
return {
|
||||
{
|
||||
methods = {"POST"},
|
||||
uri = "/apisix/batch-requests",
|
||||
handler = batch_requests,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意,注册的接口将不会默认暴露,需要使用[public-api 插件](../../en/latest/plugins/public-api.md)来暴露它。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注册控制接口
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想暴露 API 到 localhost 或内网,你可以通过 [Control API](./control-api.md) 来暴露它。
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at example-plugin plugin:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local function hello()
|
||||
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
|
||||
if args["json"] then
|
||||
return 200, {msg = "world"}
|
||||
else
|
||||
return 200, "world\n"
|
||||
end
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function _M.control_api()
|
||||
return {
|
||||
{
|
||||
methods = {"GET"},
|
||||
uris = {"/v1/plugin/example-plugin/hello"},
|
||||
handler = hello,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有改过默认的 control API 配置,这个插件暴露的 `GET /v1/plugin/example-plugin/hello` API 只有通过 `127.0.0.1` 才能访问它。通过以下命令进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -X GET "http://127.0.0.1:9090/v1/plugin/example-plugin/hello"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[查看更多有关 control API 介绍](./control-api.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 注册自定义变量
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在 APISIX 的许多地方使用变量。例如,在 http-logger 中自定义日志格式,用它作为 `limit-*` 插件的键。在某些情况下,内置的变量是不够的。因此,APISIX 允许开发者在全局范围内注册他们的变量,并将它们作为普通的内置变量使用。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,让我们注册一个叫做 `a6_labels_zone` 的变量来获取路由中 `zone` 标签的值。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
local core = require "apisix.core"
|
||||
|
||||
core.ctx.register_var("a6_labels_zone", function(ctx)
|
||||
local route = ctx.matched_route and ctx.matched_route.value
|
||||
if route and route.labels then
|
||||
return route.labels.zone
|
||||
end
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
end)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此后,任何对 `$a6_labels_zone` 的获取操作都会调用注册的获取器来获取数值。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,自定义变量不能用于依赖 Nginx 指令的功能,如 `access_log_format`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 编写测试用例
|
||||
|
||||
针对功能,完善各种维度的测试用例,对插件做个全方位的测试吧!插件的测试用例,都在 __t/plugin__ 目录下,可以前去了解。
|
||||
项目测试框架采用的 [****test-nginx****](https://github.com/openresty/test-nginx) 。
|
||||
一个测试用例 __.t__ 文件,通常用 \__DATA\__ 分割成 序言部分 和 数据部分。这里我们简单介绍下数据部分,
|
||||
也就是真正测试用例的部分,仍然以 key-auth 插件为例:
|
||||
|
||||
```perl
|
||||
=== TEST 1: sanity
|
||||
--- config
|
||||
location /t {
|
||||
content_by_lua_block {
|
||||
local plugin = require("apisix.plugins.key-auth")
|
||||
local ok, err = plugin.check_schema({key = 'test-key'}, core.schema.TYPE_CONSUMER)
|
||||
if not ok then
|
||||
ngx.say(err)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
ngx.say("done")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
--- request
|
||||
GET /t
|
||||
--- response_body
|
||||
done
|
||||
--- no_error_log
|
||||
[error]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
一个测试用例主要有三部分内容:
|
||||
|
||||
- 程序代码:Nginx location 的配置内容
|
||||
- 输入:http 的 request 信息
|
||||
- 输出检查:status,header,body,error_log 检查
|
||||
|
||||
这里请求 __/t__,经过配置文件 __location__,调用 __content_by_lua_block__ 指令完成 lua 的脚本,最终返回。
|
||||
用例的断言是 response_body 返回 "done",__no_error_log__ 表示会对 Nginx 的 error.log 检查,
|
||||
必须没有 ERROR 级别的记录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 附上 test-nginx 执行流程
|
||||
|
||||
根据我们在 Makefile 里配置的 PATH,和每一个 __.t__ 文件最前面的一些配置项,框架会组装成一个完整的 nginx.conf 文件,
|
||||
__t/servroot__ 会被当成 Nginx 的工作目录,启动 Nginx 实例。根据测试用例提供的信息,发起 http 请求并检查 http 的返回项,
|
||||
包括 http status,http response header,http response body 等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 相关资源
|
||||
|
||||
- 核心概念 - [插件](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/plugin/)
|
||||
- [Apache APISIX 扩展指南](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/blog/2021/10/26/extension-guide/)
|
||||
- [Create a Custom Plugin in Lua](https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/how-to-guide/custom-plugins/create-plugin-in-lua)
|
||||
- [example-plugin 代码](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/plugins/example-plugin.lua)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: api-breaker
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- API Breaker
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 Apache APISIX api-breaker 插件的相关操作,你可以使用此插件的 API 熔断机制来保护上游业务服务。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`api-breaker` 插件实现了 API 熔断功能,从而帮助我们保护上游业务服务。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
关于熔断超时逻辑,由代码逻辑自动按**触发不健康状态**的次数递增运算:
|
||||
|
||||
当上游服务返回 `unhealthy.http_statuses` 配置中的状态码(默认为 `500`),并达到 `unhealthy.failures` 预设次数时(默认为 3 次),则认为上游服务处于不健康状态。
|
||||
|
||||
第一次触发不健康状态时,熔断 2 秒。超过熔断时间后,将重新开始转发请求到上游服务,如果继续返回 `unhealthy.http_statuses` 状态码,记数再次达到 `unhealthy.failures` 预设次数时,熔断 4 秒。依次类推(2,4,8,16,……),直到达到预设的 `max_breaker_sec`值。
|
||||
|
||||
当上游服务处于不健康状态时,如果转发请求到上游服务并返回 `healthy.http_statuses` 配置中的状态码(默认为 `200`),并达到 `healthy.successes` 次时,则认为上游服务恢复至健康状态。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | -------------- | ------ | ---------- | --------------- | -------------------------------- |
|
||||
| break_response_code | integer | 是 | | [200, ..., 599] | 当上游服务处于不健康状态时返回的 HTTP 错误码。 |
|
||||
| break_response_body | string | 否 | | | 当上游服务处于不健康状态时返回的 HTTP 响应体信息。 |
|
||||
| break_response_headers | array[object] | 否 | | [{"key":"header_name","value":"can contain Nginx $var"}] | 当上游服务处于不健康状态时返回的 HTTP 响应头信息。该字段仅在配置了 `break_response_body` 属性时生效,并能够以 `$var` 的格式包含 APISIX 变量,比如 `{"key":"X-Client-Addr","value":"$remote_addr:$remote_port"}`。 |
|
||||
| max_breaker_sec | integer | 否 | 300 | >=3 | 上游服务熔断的最大持续时间,以秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| unhealthy.http_statuses | array[integer] | 否 | [500] | [500, ..., 599] | 上游服务处于不健康状态时的 HTTP 状态码。 |
|
||||
| unhealthy.failures | integer | 否 | 3 | >=1 | 上游服务在一定时间内触发不健康状态的异常请求次数。 |
|
||||
| healthy.http_statuses | array[integer] | 否 | [200] | [200, ..., 499] | 上游服务处于健康状态时的 HTTP 状态码。 |
|
||||
| healthy.successes | integer | 否 | 3 | >=1 | 上游服务触发健康状态的连续正常请求次数。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用 `api-breaker` 插件,该路由配置表示在一定时间内返回 `500` 或 `503` 状态码达到 3 次后触发熔断,返回 `200` 状态码 1 次后恢复健康:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1" \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"api-breaker": {
|
||||
"break_response_code": 502,
|
||||
"unhealthy": {
|
||||
"http_statuses": [500, 503],
|
||||
"failures": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"healthy": {
|
||||
"http_statuses": [200],
|
||||
"successes": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
按上述配置启用插件后,使用 `curl` 命令请求该路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果上游服务在一定时间内返回 `500` 状态码达到 3 次,客户端将会收到 `502 Bad Gateway` 的应答:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 502 Bad Gateway
|
||||
...
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head><title>502 Bad Gateway</title></head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<center><h1>502 Bad Gateway</h1></center>
|
||||
<hr><center>openresty</center>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: attach-consumer-label
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- API Consumer
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 Apache APISIX attach-consumer-label 插件的相关操作,你可以使用此插件向上游服务传递自定义的 Consumer labels。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`attach-consumer-label` 插件在 X-Consumer-Username 和 X-Credential-Indentifier 之外,还将自定义的消费者相关标签附加到经过身份验证的请求,以便上游服务区分消费者并实现额外的逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|----------|--------|--------|----------|--------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| headers | object | 是 | | | 要附加到请求标头的 Consumer 标签的键值对,其中键是请求标头名称,例如 "X-Consumer-Role",值是对客户标签键的引用,例如 "$role"。请注意,该值应始终以美元符号 (`$`) 开头。如果 Consumer 上没有配置引用的值,则相应的标头将不会附加到请求中。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例演示了如何在通过身份验证的请求转发到上游服务之前,将自定义标签附加到请求标头。如果请求被拒绝,就不会在请求标头上附加任何消费者标签。如果某个标签值未在消费者上配置,但在“attach-consumer-label”插件中被引用,相应的标头也不会被附加。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个有自定义标签的 Consumer `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${ADMIN_API_KEY}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john",
|
||||
# highlight-start
|
||||
"labels": {
|
||||
// Annotate 1
|
||||
"department": "devops",
|
||||
// Annotate 2
|
||||
"company": "api7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
# highlight-end
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
❶ Consumer 的 `department` 标签信息。
|
||||
|
||||
❷ Consumer 的 `company` 标签信息。
|
||||
|
||||
为 Consumer `john` 配置 `key-auth`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${ADMIN_API_KEY}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由并启用 `key-auth` 和 `attach-consumer-label` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${ADMIN_API_KEY}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "attach-consumer-label-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {},
|
||||
# highlight-start
|
||||
"attach-consumer-label": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
// Annotate 1
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Department": "$department",
|
||||
// Annotate 2
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Company": "$company",
|
||||
// Annotate 3
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Role": "$role"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
# highlight-end
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
❶ 将 Consumer 标签 `department` 的值附加到请求头的 `X-Consumer-Department` 字段。
|
||||
|
||||
❷ 将 Consumer 标签 `company` 的值附加到请求头的 `X-Consumer-Company` 字段。
|
||||
|
||||
❸ 将 Consumer 标签 `role` 的值附加到请求头的 `X-Consumer-Role` 字段。由于 Consumer 标签中没有配置 `role` 这个标签,该字段不会出现在发往上游的请求头中。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
引用标签的值必须以 `$` 符号开头。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
使用正确的 apikey 请求该路由,验证插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H 'apikey: john-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到类似的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Apikey": "john-key",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
# highlight-start
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Indentifier": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Company": "api7",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Department": "devops",
|
||||
# highlight-end
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66e5107c-5bb3e24f2de5baf733aec1cc",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 205.198.122.37",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/attach-consumer-label-route" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${ADMIN_API_KEY}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,272 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: authz-casbin
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Authz Casbin
|
||||
- authz-casbin
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `authz-casbin` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`authz-casbin` 插件是一个基于 [Lua Casbin](https://github.com/casbin/lua-casbin/) 的访问控制插件,该插件支持各种 [access control models](https://casbin.org/docs/en/supported-models) 的强大授权场景。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------- | ------ | ------- | ---------------------------------- |
|
||||
| model_path | string | 是 | Casbin 鉴权模型配置文件路径。 |
|
||||
| policy_path | string | 是 | Casbin 鉴权策略配置文件路径。 |
|
||||
| model | string | 是 | Casbin 鉴权模型的文本定义。 |
|
||||
| policy | string | 是 | Casbin 鉴权策略的文本定义。 |
|
||||
| username | string | 是 | 描述请求中有可以通过访问控制的用户名。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
你必须在插件配置中指定 `model_path`、`policy_path` 和 `username` 或者指定 `model`、`policy` 和 `username` 才能使插件生效。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要使所有的 Route 共享 Casbin 配置,你可以先在插件元数据中指定 `model` 和 `policy`,在插件配置中仅指定 `username`,这样所有 Route 都可以使用 Casbin 插件配置。
|
||||
|
||||
::::
|
||||
|
||||
## 元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------- | ------ | ------- | ------------------------------|
|
||||
| model | string | 是 | Casbin 鉴权模型的文本定义。 |
|
||||
| policy | string | 是 | Casbin 鉴权策略的文本定义。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 model/policy 文件路径或使用插件 configuration/metadata 中的 model/policy 文本配置在 Route 上启用插件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 model/policy 文件路径启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了通过 model/policy 配置文件来设置 Casbin 身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"authz-casbin": {
|
||||
"model_path": "/path/to/model.conf",
|
||||
"policy_path": "/path/to/policy.csv",
|
||||
"username": "user"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/*"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 model/policy 文本配置启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了通过你的 model/policy 文本来设置 Casbin 身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"authz-casbin": {
|
||||
"model": "[request_definition]
|
||||
r = sub, obj, act
|
||||
|
||||
[policy_definition]
|
||||
p = sub, obj, act
|
||||
|
||||
[role_definition]
|
||||
g = _, _
|
||||
|
||||
[policy_effect]
|
||||
e = some(where (p.eft == allow))
|
||||
|
||||
[matchers]
|
||||
m = (g(r.sub, p.sub) || keyMatch(r.sub, p.sub)) && keyMatch(r.obj, p.obj) && keyMatch(r.act, p.act)",
|
||||
|
||||
"policy": "p, *, /, GET
|
||||
p, admin, *, *
|
||||
g, alice, admin",
|
||||
|
||||
"username": "user"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/*"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 plugin metadata 配置模型/策略
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要使用 Admin API 发送一个 `PUT` 请求,将 `model` 和 `policy` 的配置添加到插件的元数据中。
|
||||
|
||||
所有通过这种方式创建的 Route 都会带有一个带插件元数据配置的 Casbin enforcer。你也可以使用这种方式更新 model/policy,该插件将会自动同步最新的配置信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/authz-casbin \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -i -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"model": "[request_definition]
|
||||
r = sub, obj, act
|
||||
|
||||
[policy_definition]
|
||||
p = sub, obj, act
|
||||
|
||||
[role_definition]
|
||||
g = _, _
|
||||
|
||||
[policy_effect]
|
||||
e = some(where (p.eft == allow))
|
||||
|
||||
[matchers]
|
||||
m = (g(r.sub, p.sub) || keyMatch(r.sub, p.sub)) && keyMatch(r.obj, p.obj) && keyMatch(r.act, p.act)",
|
||||
|
||||
"policy": "p, *, /, GET
|
||||
p, admin, *, *
|
||||
g, alice, admin"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
更新插件元数据后,可以将插件添加到指定 Route 中:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"authz-casbin": {
|
||||
"username": "user"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/*"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
插件路由的配置比插件元数据的配置有更高的优先级。因此,如果插件路由的配置中存在 model/policy 配置,插件将优先使用插件路由的配置而不是插件元数据中的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
首先定义测试鉴权模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```conf
|
||||
[request_definition]
|
||||
r = sub, obj, act
|
||||
|
||||
[policy_definition]
|
||||
p = sub, obj, act
|
||||
|
||||
[role_definition]
|
||||
g = _, _
|
||||
|
||||
[policy_effect]
|
||||
e = some(where (p.eft == allow))
|
||||
|
||||
[matchers]
|
||||
m = (g(r.sub, p.sub) || keyMatch(r.sub, p.sub)) && keyMatch(r.obj, p.obj) && keyMatch(r.act, p.act)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后添加测试鉴权策略:
|
||||
|
||||
```conf
|
||||
p, *, /, GET
|
||||
p, admin, *, *
|
||||
g, alice, admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要了解更多关于 `policy` 和 `model` 的配置,请参考 [examples](https://github.com/casbin/lua-casbin/tree/master/examples)。
|
||||
|
||||
上述配置将允许所有人使用 `GET` 请求访问主页(`/`),而只有具有管理员权限的用户才可以访问其他页面并使用其他请求方法。
|
||||
|
||||
简单举例来说,假设我们向主页发出 `GET` 请求,通常都可以返回正常结果。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/ -X GET
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但如果是一个未经授权的普通用户(例如:`bob`)访问除 `/` 以外的其他页面,将得到一个 403 错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/res -H 'user: bob' -X GET
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
而拥有管理权限的用户(如 `alice`)则可以访问其它页面。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/res -H 'user: alice' -X GET
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `authz-casbin` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: authz-casdoor
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Authz Casdoor
|
||||
- authz-casdoor
|
||||
description: 本篇文档介绍了 Apache APISIX auth-casdoor 插件的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `authz-casdoor` 插件可添加 [Casdoor](https://casdoor.org/) 集中认证方式。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
|---------------|--------|----------|----------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| endpoint_addr | string | 是 | Casdoor 的 URL。 |
|
||||
| client_id | string | 是 | Casdoor 的客户端 id。 |
|
||||
| client_secret | string | 是 | Casdoor 的客户端密钥。 |
|
||||
| callback_url | string | 是 | 用于接收 code 与 state 的回调地址。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"client_secret"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info IMPORTANT
|
||||
|
||||
指定 `endpoint_addr` 和 `callback_url` 属性时不要以“/”来结尾。
|
||||
|
||||
`callback_url` 必须是路由的 URI。具体细节可查看下方示例内容,了解相关配置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用 `auth-casdoor` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1" -H "X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/anything/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"authz-casdoor": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addr":"http://localhost:8000",
|
||||
"callback_url":"http://localhost:9080/anything/callback",
|
||||
"client_id":"7ceb9b7fda4a9061ec1c",
|
||||
"client_secret":"3416238e1edf915eac08b8fe345b2b95cdba7e04"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
一旦启用了该插件,访问该路由的新用户首先会经过 `authz-casdoor` 插件的处理,然后被重定向到 Casdoor 登录页面。
|
||||
|
||||
成功登录后,Casdoor 会将该用户重定向到 `callback_url`,并指定 GET 参数的 `code` 和 `state`。该插件还会向 Casdoor 请求一个访问 Token,并确认用户是否已登录。在成功认证后,该流程只出现一次并且后续请求不会被打断。
|
||||
|
||||
上述操作完成后,用户就会被重定向到目标 URL。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当需要禁用 `authz-casdoor` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/anything/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,216 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: authz-keycloak
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Authz Keycloak
|
||||
- authz-keycloak
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `authz-keycloak` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`authz-keycloak` 插件可用于通过 [Keycloak Identity Server](https://www.keycloak.org/) 添加身份验证。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
虽然该插件是为了与 Keycloak 一起使用而开发的,但是它也可以与任何符合 OAuth/OIDC 或 UMA 协议的身份认证软件一起使用。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解 Keycloak 的更多信息,请参考 [Authorization Services Guide](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/authorization_services/)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------|---------------|-------|-----------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| discovery | string | 否 | | https://host.domain/realms/foo/.well-known/uma2-configuration | Keycloak 授权服务的 [discovery document](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/authorization_services/index.html) 的 URL。 |
|
||||
| token_endpoint | string | 否 | | https://host.domain/realms/foo/protocol/openid-connect/token | 接受 OAuth2 兼容 token 的接口,需要支持 `urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:uma-ticket` 授权类型。 |
|
||||
| resource_registration_endpoint | string | 否 | | https://host.domain/realms/foo/authz/protection/resource_set | 符合 UMA 的资源注册端点。如果提供,则覆盖发现中的值。 |
|
||||
| client_id | string | 是 | | | 客户端正在寻求访问的资源服务器的标识符。 |
|
||||
| client_secret | string | 否 | | | 客户端密码(如果需要)。 |
|
||||
| grant_type | string | 否 | "urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:uma-ticket" | ["urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:uma-ticket"] | |
|
||||
| policy_enforcement_mode | string | 否 | "ENFORCING" | ["ENFORCING", "PERMISSIVE"] | |
|
||||
| permissions | array[string] | 否 | | | 描述客户端应用所需访问的资源和权限范围的字符串。格式必须为:`RESOURCE_ID#SCOPE_ID`。 |
|
||||
| lazy_load_paths | boolean | 否 | false | [true, false] | 当设置为 true 时,使用资源注册端点而不是静态权限将请求 URI 动态解析为资源。 |
|
||||
| http_method_as_scope | boolean | 否 | false | [true, false] | 设置为 true 时,将 HTTP 请求类型映射到同名范围并添加到所有请求的权限。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000 | [1000, ...] | 与 Identity Server 的 HTTP 连接超时(毫秒)。 |
|
||||
| access_token_expires_in | integer | 否 | 300 | [1, ...] | 访问令牌的有效期。token. |
|
||||
| access_token_expires_leeway | integer | 否 | 0 | [0, ...] | access_token 更新的到期余地。设置后,令牌将在到期前几秒更新 access_token_expires_leeway。这避免了 access_token 在到达 OAuth 资源服务器时刚刚过期的情况。 |
|
||||
| refresh_token_expires_in | integer | 否 | 3600 | [1, ...] | 刷新令牌的失效时间。 |
|
||||
| refresh_token_expires_leeway | integer | 否 | 0 | [0, ...] | refresh_token 更新的到期余地。设置后,令牌将在到期前几秒刷新 refresh_token_expires_leeway。这样可以避免在到达 OAuth 资源服务器时 refresh_token 刚刚过期的错误。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | [true, false] | 设置为 `true` 时,验证 TLS 证书是否与主机名匹配。 |
|
||||
| cache_ttl_seconds | integer | 否 | 86400 (equivalent to 24h) | positive integer >= 1 | 插件缓存插件用于向 Keycloak 进行身份验证的发现文档和令牌的最长时间(以秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | [true, false] | 当设置为 `true` 时,启用 HTTP keep-alive 保证在使用后仍然保持连接打开。如果您期望对 Keycloak 有很多请求,请设置为 `true`。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000 | positive integer >= 1000 | 已建立的 HTTP 连接将关闭之前的空闲时间。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | positive integer >= 1 | 连接池中的最大连接数。 |
|
||||
| access_denied_redirect_uri | string | 否 | | [1, 2048] | 需要将用户重定向到的 URI,而不是返回类似 `"error_description":"not_authorized"` 这样的错误消息。 |
|
||||
| password_grant_token_generation_incoming_uri | string | 否 | | /api/token | 将此设置为使用密码授予类型生成令牌。该插件会将传入的请求 URI 与此值进行比较。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"client_secret"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
除上述释义外,还有以下需要注意的点:
|
||||
|
||||
- Discovery and endpoints
|
||||
- 使用 `discovery` 属性后,`authz-keycloak` 插件就可以从其 URL 中发现 Keycloak API 的端点。该 URL 指向 Keyloak 针对相应领域授权服务的发现文档。
|
||||
- 如果发现文档可用,则插件将根据该文档确定令牌端点 URL。如果 URL 存在,则 `token_endpoint` 和 `resource_registration_endpoint` 的值将被其覆盖。
|
||||
- Client ID and secret
|
||||
- 该插件需配置 `client_id` 属性来标识自身。
|
||||
- 如果 `lazy_load_paths` 属性被设置为 `true`,那么该插件还需要从 Keycloak 中获得一个自身访问令牌。在这种情况下,如果客户端对 Keycloak 的访问是加密的,就需要配置 `client_secret` 属性。
|
||||
- Policy enforcement mode
|
||||
- `policy_enforcement_mode` 属性指定了在处理发送到服务器的授权请求时,该插件如何执行策略。
|
||||
- `ENFORCING` mode:即使没有与给定资源关联的策略,请求也会默认被拒绝。`policy_enforcement_mode` 默认设置为 `ENFORCING`。
|
||||
- `PERMISSIVE` mode:如果资源没有绑定任何访问策略,也被允许请求。
|
||||
- Permissions
|
||||
- 在处理传入的请求时,插件可以根据请求的参数确定静态或动态检查 Keycloak 的权限。
|
||||
- 如果 `lazy_load_paths` 参数设置为 `false`,则权限来自 `permissions` 属性。`permissions` 中的每个条目都需要按照令牌端点预设的 `permission` 属性进行格式化。详细信息请参考 [Obtaining Permissions](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/authorization_services/index.html#_service_obtaining_permissions).
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
有效权限可以是单个资源,也可以是与一个或多个范围配对的资源。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
如果 `lazy_load_paths` 属性设置为 `true`,则请求 URI 将解析为使用资源注册端点在 Keycloak 中配置的一个或多个资源。已经解析的资源被用作于检查的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
需要该插件从令牌端点为自己获取单独的访问令牌。因此,请确保在 Keycloak 的客户端设置中设置了 `Service Accounts Enabled` 选项。
|
||||
|
||||
还需要确保颁发的访问令牌包含具有 `uma_protection` 角色的 `resource_access` 声明,以保证插件能够通过 Protection API 查询资源。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
- 自动将 HTTP method 映射到作用域
|
||||
|
||||
`http_method_as_scope` 通常与 `lazy_load_paths` 一起使用,但也可以与静态权限列表一起使用。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果 `http_method_as_scope` 属性设置为 `true`,插件会将请求的 HTTP 方法映射到同名范围。然后将范围添加到每个要检查的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果 `lazy_load_paths` 属性设置为 `false`,则插件会将映射范围添加到 `permissions` 属性中配置的任意一个静态权限——即使它们已经包含一个或多个范围。
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用 `password` 授权生成令牌
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果要使用 `password` 授权生成令牌,你可以设置 `password_grant_token_generation_incoming_uri` 属性的值。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果传入的 URI 与配置的属性匹配并且请求方法是 POST,则使用 `token_endpoint` 生成一个令牌。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,你还需要添加 `application/x-www-form-urlencoded` 作为 `Content-Type` 标头,`username` 和 `password` 作为参数。
|
||||
|
||||
如下示例是当 `password_grant_token_generation_incoming_uri` 设置为 `/api/token` 时的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:9080/api/token' \
|
||||
--header 'Accept: application/json, text/plain, */*' \
|
||||
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
|
||||
--data-urlencode 'username=<User_Name>' \
|
||||
--data-urlencode 'password=<Password>'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何启用
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例为你展示了如何在指定 Route 中启用 `authz-keycloak` 插件,其中 `${realm}` 是 Keycloak 中的 `realm` 名称:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"authz-keycloak": {
|
||||
"token_endpoint": "http://127.0.0.1:8090/realms/${realm}/protocol/openid-connect/token",
|
||||
"permissions": ["resource name#scope name"],
|
||||
"client_id": "Client ID"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:8080": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以通过以下方法测试插件。
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要从 Keycloak 获取 JWT 令牌:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://<YOUR_KEYCLOAK_HOST>/realms/<YOUR_REALM>/protocol/openid-connect/token" \
|
||||
-d "client_id=<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>" \
|
||||
-d "client_secret=<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>" \
|
||||
-d "username=<YOUR_USERNAME>" \
|
||||
-d "password=<YOUR_PASSWORD>" \
|
||||
-d "grant_type=password"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你应该收到类似以下的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"access_token":"eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICJoT3ludlBPY2d6Y3VWWnYtTU42bXZKMUczb0dOX2d6MFo3WFl6S2FSa1NBIn0.eyJleHAiOjE3MDMyOTAyNjAsImlhdCI6MTcwMzI4OTk2MCwianRpIjoiMjJhOGFmMzItNDM5Mi00Yzg3LThkM2UtZDkyNDVmZmNiYTNmIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cDovLzE5Mi4xNjguMS44Mzo4MDgwL3JlYWxtcy9xdWlja3N0YXJ0LXJlYWxtIiwiYXVkIjoiYWNjb3VudCIsInN1YiI6IjAyZWZlY2VlLTBmYTgtNDg1OS1iYmIwLTgyMGZmZDdjMWRmYSIsInR5cCI6IkJlYXJlciIsImF6cCI6ImFwaXNpeC1xdWlja3N0YXJ0LWNsaWVudCIsInNlc3Npb25fc3RhdGUiOiI1YzIzZjVkZC1hN2ZhLTRlMmItOWQxNC02MmI1YzYyNmU1NDYiLCJhY3IiOiIxIiwicmVhbG1fYWNjZXNzIjp7InJvbGVzIjpbImRlZmF1bHQtcm9sZXMtcXVpY2tzdGFydC1yZWFsbSIsIm9mZmxpbmVfYWNjZXNzIiwidW1hX2F1dGhvcml6YXRpb24iXX0sInJlc291cmNlX2FjY2VzcyI6eyJhY2NvdW50Ijp7InJvbGVzIjpbIm1hbmFnZS1hY2NvdW50IiwibWFuYWdlLWFjY291bnQtbGlua3MiLCJ2aWV3LXByb2ZpbGUiXX19LCJzY29wZSI6ImVtYWlsIHByb2ZpbGUiLCJzaWQiOiI1YzIzZjVkZC1hN2ZhLTRlMmItOWQxNC02MmI1YzYyNmU1NDYiLCJlbWFpbF92ZXJpZmllZCI6ZmFsc2UsInByZWZlcnJlZF91c2VybmFtZSI6InF1aWNrc3RhcnQtdXNlciJ9.WNZQiLRleqCxw-JS-MHkqXnX_BPA9i6fyVHqF8l-L-2QxcqTAwbIp7AYKX-z90CG6EdRXOizAEkQytB32eVWXaRkLeTYCI7wIrT8XSVTJle4F88ohuBOjDfRR61yFh5k8FXXdAyRzcR7tIeE2YUFkRqw1gCT_VEsUuXPqm2wTKOmZ8fRBf4T-rP4-ZJwPkHAWc_nG21TmLOBCSulzYqoC6Lc-OvX5AHde9cfRuXx-r2HhSYs4cXtvX-ijA715MY634CQdedheoGca5yzPsJWrAlBbCruN2rdb4u5bDxKU62pJoJpmAsR7d5qYpYVA6AsANDxHLk2-W5F7I_IxqR0YQ","expires_in":300,"refresh_expires_in":1800,"refresh_token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICJjN2IwYmY4NC1kYjk0LTQ5YzctYWIyZC01NmU3ZDc1MmRkNDkifQ.eyJleHAiOjE3MDMyOTE3NjAsImlhdCI6MTcwMzI4OTk2MCwianRpIjoiYzcyZjAzMzctYmZhNS00MWEzLTlhYjEtZmJlNGY0NmZjMDgxIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cDovLzE5Mi4xNjguMS44Mzo4MDgwL3JlYWxtcy9xdWlja3N0YXJ0LXJlYWxtIiwiYXVkIjoiaHR0cDovLzE5Mi4xNjguMS44Mzo4MDgwL3JlYWxtcy9xdWlja3N0YXJ0LXJlYWxtIiwic3ViIjoiMDJlZmVjZWUtMGZhOC00ODU5LWJiYjAtODIwZmZkN2MxZGZhIiwidHlwIjoiUmVmcmVzaCIsImF6cCI6ImFwaXNpeC1xdWlja3N0YXJ0LWNsaWVudCIsInNlc3Npb25fc3RhdGUiOiI1YzIzZjVkZC1hN2ZhLTRlMmItOWQxNC02MmI1YzYyNmU1NDYiLCJzY29wZSI6ImVtYWlsIHByb2ZpbGUiLCJzaWQiOiI1YzIzZjVkZC1hN2ZhLTRlMmItOWQxNC02MmI1YzYyNmU1NDYifQ.7AH7ppbVOlkYc9CoJ7kLSlDUkmFuNga28Amugn2t724","token_type":"Bearer","not-before-policy":0,"session_state":"5c23f5dd-a7fa-4e2b-9d14-62b5c626e546","scope":"email profile"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后就可以使用获得的访问令牌发起请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/get -H 'Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `authz-keycloak` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:8080": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件 Roadmap
|
||||
|
||||
- 目前,`authz-keycloak` 插件通过要求定义资源名称和所需的范围,来强制执行路由策略。但 Keycloak 官方适配的其他语言客户端(Java、JavaScript)仍然可以通过动态查询 Keycloak 路径以及延迟加载身份资源的路径来提供路径匹配。在 Apache APISIX 之后发布的插件中即将支持此功能。
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持从 Keycloak JSON 文件中读取权限范畴和其他配置项。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: aws-lambda
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- AWS Lambda
|
||||
- aws-lambda
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX aws-lambda 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`aws-lambda` 插件用于将 [AWS Lambda](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/) 和 [Amazon API Gateway](https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/) 作为动态上游集成至 APISIX,从而实现将访问指定 URI 的请求代理到 AWS 云。
|
||||
|
||||
启用 `aws-lambda` 插件后,该插件会终止对已配置 URI 的请求,并代表客户端向 AWS Lambda Gateway URI 发起一个新的请求。这个新请求中携带了之前配置的授权详细信息,包括请求头、请求体和参数(以上参数都是从原始请求中传递的),然后 `aws-lambda` 插件会将带有响应头、状态码和响应体的响应信息返回给使用 APISIX 发起请求的客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持通过 AWS API key 和 AWS IAM secrets 进行授权。当使用 AWS IAM secrets 时,该插件支持 [AWS Signature Version 4 signing](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_aws-signing.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------------ - | ------- | -------- | ------- | ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| function_uri | string | 是 | | | 触发 lambda serverless 函数的 AWS API Gateway 端点。 |
|
||||
| authorization | object | 否 | | | 访问云函数的授权凭证。 |
|
||||
| authorization.apikey | string | 否 | | | 生成的 API 密钥,用于授权对 AWS Gateway 端点的请求。 |
|
||||
| authorization.iam | object | 否 | | | 用于通过 AWS v4 请求签名执行的基于 AWS IAM 角色的授权。请参考 [IAM 授权方案](#iam-授权方案)。 |
|
||||
| authorization.iam.accesskey | string | 是 | | 从 AWS IAM 控制台生成的访问密钥 ID。 |
|
||||
| authorization.iam.secretkey | string | 是 | | 从 AWS IAM 控制台生成的访问密钥。 |
|
||||
| authorization.iam.aws_region | string | 否 | "us-east-1" | 发出请求的 AWS 区域。有关更多 AWS 区域代码的信息请参考 [AWS 区域代码表](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/general/latest/gr/rande.html#region-names-codes)。 |
|
||||
| authorization.iam.service | string | 否 | "execute-api" | 接收该请求的服务。若使用 Amazon API gateway APIs, 应设置为 `execute-api`。若使用 Lambda function, 应设置为 `lambda`。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000 | [100,...] | 代理请求超时(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | true/false | 当设置为 `true` 时执行 SSL 验证。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | true/false | 当设置为 `true` 时,保持连接的活动状态以便重复使用。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | [1,...] | 在关闭该连接之前,可以在该连接上发送的最大请求数。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000 | [1000,...] | 当连接空闲时,保持该连接处于活动状态的时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令在指定路由中启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"aws-lambda": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "https://x9w6z07gb9.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/default/test-apisix",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"apikey": "<Generated API Key from aws console>"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ssl_verify":false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/aws"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述示例配置插件后,任何对 `/aws` URI 的请求(`HTTP/1.1`、`HTTPS`、`HTTP2`)都将调用已配置的 AWS 函数的 URI,并且会将响应信息返回给客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
下述命令的含义是:AWS Lambda 从请求中获取 `name` 参数,并返回一条 `"Hello $name"` 消息:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -XGET localhost:9080/aws\?name=APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
...
|
||||
"Hello, APISIX!"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例是客户端通过 HTTP/2 协议与 APISIX 进行通信。
|
||||
|
||||
在进行测试之前,由于该 `enable_http2: true` 默认是禁用状态,你可以通过在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中添加 `apisix.node_listen` 下的 `- port: 9081` 和 `enable_http2: true` 字段启用。示例如下
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
node_listen: # 支持监听多个端口
|
||||
- 9080
|
||||
- port: 9081
|
||||
enable_http2: true # 该字段如果不设置,默认值为 `false`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -XGET --http2 --http2-prior-knowledge localhost:9081/aws\?name=APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/2 200
|
||||
content-type: application/json
|
||||
...
|
||||
"Hello, APISIX!"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
与上面的示例类似,AWS Lambda 函数也可以通过 AWS API Gateway 触发,但需要使用 AWS IAM 权限进行授权。`aws-lambda` 插件的配置文件中包含了 `"authorization"` 字段,用户可以在 HTTP 调用中通过 AWS v4 请求签名。
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过配置文件实现授权:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"aws-lambda": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "https://ajycz5e0v9.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/default/test-apisix",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"iam": {
|
||||
"accesskey": "<access key>",
|
||||
"secretkey": "<access key secret>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ssl_verify": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/aws"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
使用该方法时已经假设你有一个启用了程序化访问的 IAM 用户,并具有访问端点的必要权限(AmazonAPIGatewayInvokeFullAccess)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置路径转发
|
||||
|
||||
`aws-lambda` 插件在代理请求到 AWS 上游时也支持 URL 路径转发。基本请求路径的扩展被附加到插件配置中指定的 `function_uri` 字段上。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 重要
|
||||
|
||||
因为 APISIX 路由是严格匹配的,所以为了使 `aws-lambda` 插件正常工作,在路由上配置的 `uri` 字段必须以 `*` 结尾,`*` 意味着这个 URI 的任何子路径都会被匹配到同一个路由。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过配置文件实现路径转发:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"aws-lambda": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "https://x9w6z07gb9.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"apikey": "<Generate API key>"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ssl_verify":false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/aws/*"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述示例配置插件后,任何访问 `aws/default/test-apisix` 的请求都会调用 AWS Lambda 函数,并转发附加的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -XGET http://127.0.0.1:9080/aws/default/test-apisix\?name\=APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
...
|
||||
"Hello, APISIX!"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/aws",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,215 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: azure-functions
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Azure Functions
|
||||
- azure-functions
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 API 网关 Apache APISIX azure-functions 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`azure-functions` 插件用于将 [Azure Serverless Function](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/services/functions/) 作为动态上游集成至 APISIX,从而实现将访问指定 URI 的请求代理到 Microsoft Azure 云服务。
|
||||
|
||||
启用 `azure-functions` 插件后,该插件会终止对已配置 URI 的请求,并代表客户端向 Azure Functions 发起一个新的请求。该新请求中携带了之前配置的授权详细信息,包括请求头、请求体和参数(以上参数都是从原始请求中传递的)。之后便会通过 `azure-functions` 插件,将带有响应头、状态码和响应体的信息返回给使用 APISIX 发起请求的客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | ------- | ------ | ------ | ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| function_uri | string | 是 | | | 触发 Serverless Functions 的 Azure Functions 端点。例如 `http://test-apisix.azurewebsites.net/api/HttpTrigger`。 |
|
||||
| authorization | object | 否 | | | 访问 Azure Functions 的授权凭证。 |
|
||||
| authorization.apikey | string | 否 | | | 授权凭证内的字段。生成 API 密钥来授权对端点的请求。 |
|
||||
| authorization.clientid | string | 否 | | | 授权凭证内的字段。生成客户端 ID(Azure Active Directory)来授权对端点的请求。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000 | [100,...] | 代理请求超时(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | true/false | 当设置为 `true` 时执行 SSL 验证。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | true/false | 当设置为 `true` 时,保持连接的活动状态以便重复使用。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | [1,...] | 连接断开之前,可接收的最大请求数。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000 | [1000,...] | 当连接空闲时,保持该连接处于活动状态的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| master_apikey | string | 否 | "" | 可用于访问 Azure Functions URI 的 API 密钥。 |
|
||||
| master_clientid | string | 否 | "" | 可用于授权 Azure Functions URI 的客户端 ID(Active Directory)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
`azure-functions` 插件的元数据提供了授权回退的功能。它定义了 `master_apikey` 和 `master_clientid` 字段,用户可以为关键任务的应用部署声明 API 密钥或客户端 ID。因此,如果在 `azure-functions` 插件属性中没有找到相关授权凭证,此时元数据中的授权凭证就会发挥作用。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
授权方式优先级排序如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先,`azure-functions` 插件在 APISIX 代理的请求头中寻找 `x-functions-key` 或 `x-functions-clientid` 键。
|
||||
2. 如果没有找到,`azure-functions` 插件会检查插件属性中的授权凭证。如果授权凭证存在,`azure-functions` 插件会将相应的授权标头添加到发送到 Azure Functions 的请求中。
|
||||
3. 如果未配置 `azure-functions` 插件的授权凭证属性,APISIX 将获取插件元数据配置并使用 API 密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想添加一个新的 API 密钥,请向 `/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata` 端点发出请求,并附上所需的元数据。示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/azure-functions \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"master_apikey" : "<Your Azure master access key>"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令在指定路由中启用该插件,请确保你的 Azure Functions 已提前部署好,并正常提供服务。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"azure-functions": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "http://test-apisix.azurewebsites.net/api/HttpTrigger",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"apikey": "${Generated API key to access the Azure-Function}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/azure"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述示例配置插件后,任何对 `/azure` URI 的请求(`HTTP/1.1`、`HTTPS`、`HTTP2`)都将调用已配置的 Azure Functions 的 URI,并且会将响应信息返回给客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
下述命令的含义是:Azure Functions 从请求中获取 `name` 参数,并返回一条 `"Hello $name"` 消息:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -XGET http://localhost:9080/azure\?name=APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
...
|
||||
Hello, APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例是客户端通过 HTTP/2 协议与 APISIX 进行通信。
|
||||
|
||||
在进行测试之前,由于该 `enable_http2: true` 默认是禁用状态,你可以通过在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中添加 `apisix.node_listen` 下的 `- port: 9081` 和 `enable_http2: true` 字段启用。示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
node_listen: # 支持监听多个端口
|
||||
- 9080
|
||||
- port: 9081
|
||||
enable_http2: true # 该字段如果不设置,默认值为 `false`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -XGET --http2 --http2-prior-knowledge http://localhost:9081/azure\?name=APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/2 200
|
||||
content-type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
...
|
||||
Hello, APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置路径转发
|
||||
|
||||
`azure-functions` 插件在代理请求到 Azure Functions 上游时也支持 URL 路径转发。基本请求路径的扩展被附加到插件配置中指定的 `function_uri` 字段上。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 重要
|
||||
|
||||
因为 APISIX 路由是严格匹配的,所以为了使 `azure-functions` 插件正常工作,在路由上配置的 `uri` 字段必须以 `*` 结尾,`*` 意味着这个 URI 的任何子路径都会被匹配到同一个路由。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过配置文件实现路径转发:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"azure-functions": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "http://app-bisakh.azurewebsites.net/api",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"apikey": "${Generated API key to access the Azure-Function}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/azure/*"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述示例配置插件后,任何访问 `azure/HttpTrigger1` 的请求都会调用 Azure Functions 并转发附加的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -XGET http://127.0.0.1:9080/azure/HttpTrigger1\?name\=APISIX\
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
...
|
||||
Hello, APISIX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/azure",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,512 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: basic-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Basic Auth
|
||||
- basic-auth
|
||||
description: basic-auth 插件为消费者添加了基本访问身份验证,以便消费者在访问上游资源之前进行身份验证。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/basic-auth" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`basic-auth` 插件为 [消费者](../terminology/consumer.md) 添加了 [基本访问身份验证](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_access_authentication),以便消费者在访问上游资源之前进行身份验证。
|
||||
|
||||
当消费者成功通过身份验证后,APISIX 会在将请求代理到上游服务之前向请求添加其他标头,例如 `X-Consumer-Username`、`X-Credential-Indentifier` 和其他消费者自定义标头(如果已配置)。上游服务将能够区分消费者并根据需要实现其他逻辑。如果这些值中的任何一个不可用,则不会添加相应的标头。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer/Credentials 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------- | ------ | -----| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| username | string | 是 | Consumer 的用户名并且该用户名是唯一,如果多个 Consumer 使用了相同的 `username`,将会出现请求匹配异常。|
|
||||
| password | string | 是 | 用户的密码。该字段支持使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源,将值保存在 Secret Manager 中。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"password"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
Route 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------ | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| hide_credentials | boolean | 否 | false | 该参数设置为 `true` 时,则不会将 Authorization 请求头传递给 Upstream。|
|
||||
| anonymous_consumer | boolean | 否 | false | 匿名消费者名称。如果已配置,则允许匿名用户绕过身份验证。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在不同场景中使用 `basic-auth` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在路由上实现基本身份验证
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在路由上实现基本身份验证。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `johndoe`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "johndoe"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `basic-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/johndoe/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"password": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `basic-auth` 的路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "basic-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用有效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用有效密钥发送请求至:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -u johndoe:john-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Apikey": "john-key",
|
||||
"Authorization": "Basic am9obmRvZTpqb2huLWtleQ==",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66e5107c-5bb3e24f2de5baf733aec1cc",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Indentifier": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 205.198.122.37",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用无效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用无效密钥发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -u johndoe:invalid-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"Invalid user authorization"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 无需密钥即可验证
|
||||
|
||||
无需密钥即可发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"Missing authorization in request"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 隐藏上游的身份验证信息
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何通过配置 `hide_credentials` 来防止密钥被发送到上游服务。APISIX 默认情况下会将身份验证密钥转发到上游服务,这在某些情况下可能会导致安全风险,您应该考虑更新 `hide_credentials`。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `johndoe` :
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "johndoe"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `basic-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/johndoe/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"password": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 不隐藏凭据
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `basic-auth` 创建路由,并将 `hide_credentials` 配置为 `false`,这是默认配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "basic-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"hide_credentials": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送带有有效密钥的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -u johndoe:john-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "Basic am9obmRvZTpqb2huLWtleQ==",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66cc2195-22bd5f401b13480e63c498c6",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Indentifier": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 43.228.226.23",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,凭证以 base64 编码格式对上游服务可见。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用 `Authorization` 标头在请求中传递 base64 编码的凭据,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H "Authorization: Basic am9obmRvZTpqb2huLWtleQ=="
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
#### 隐藏凭据
|
||||
|
||||
将插件的 `hide_credentials` 更新为 `true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/basic-auth-route" -X PATCH \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"hide_credentials": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送带有有效密钥的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -u johndoe:john-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66cc21a7-4f6ac87946e25f325167d53a",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Indentifier": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 43.228.226.23",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,上游服务不再可见这些凭据。
|
||||
|
||||
### 将消费者自定义 ID 添加到标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在 `Consumer-Custom-Id` 标头中将消费者自定义 ID 附加到经过身份验证的请求,该 ID 可用于根据需要实现其他逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
创建带有自定义 ID 标签的消费者 `johndoe`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"labels": {
|
||||
"custom_id": "495aec6a"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `basic-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/johndoe/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"password": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `basic-auth` 的路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "basic-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用有效密钥向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -u johndoe:john-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到一个带有 `X-Consumer-Custom-Id` 的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "Basic am9obmRvZTpqb2huLWtleQ==",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66ea8d64-33df89052ae198a706e18c2a",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Custom-Id": "495aec6a",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 205.198.122.37",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 匿名消费者的速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为普通消费者和匿名消费者配置不同的速率限制策略,其中匿名消费者不需要进行身份验证,并且配额较少。
|
||||
|
||||
创建普通消费者 `johndoe` 并配置 `limit-count` 插件以允许 30 秒内的配额为 3:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 3,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者 `johndoe` 创建 `basic-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/johndoe/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-basic-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username": "johndoe",
|
||||
"password": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建匿名用户 `anonymous`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内配额为 1:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "anonymous",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个路由并配置 `basic-auth` 插件来接受匿名消费者 `anonymous` 绕过身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "basic-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"anonymous_consumer": "anonymous"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了验证,请使用 `john` 的密钥发送五个连续的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -u johndoe:john-key -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,显示在 5 个请求中,3 个请求成功(状态代码 200),而其他请求被拒绝(状态代码 429)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 3, 429: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送五个匿名请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,表明只有一个请求成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 1, 429: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,234 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: batch-requests
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Batch Requests
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `batch-request` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
在启用 `batch-requests` 插件后,用户可以通过将多个请求组装成一个请求的形式,把请求发送给网关,网关会从请求体中解析出对应的请求,再分别封装成独立的请求,以 [HTTP pipeline](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_pipelining) 的方式代替用户向网关自身再发起多个 HTTP 请求,经历路由匹配,转发到对应上游等多个阶段,合并结果后再返回客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
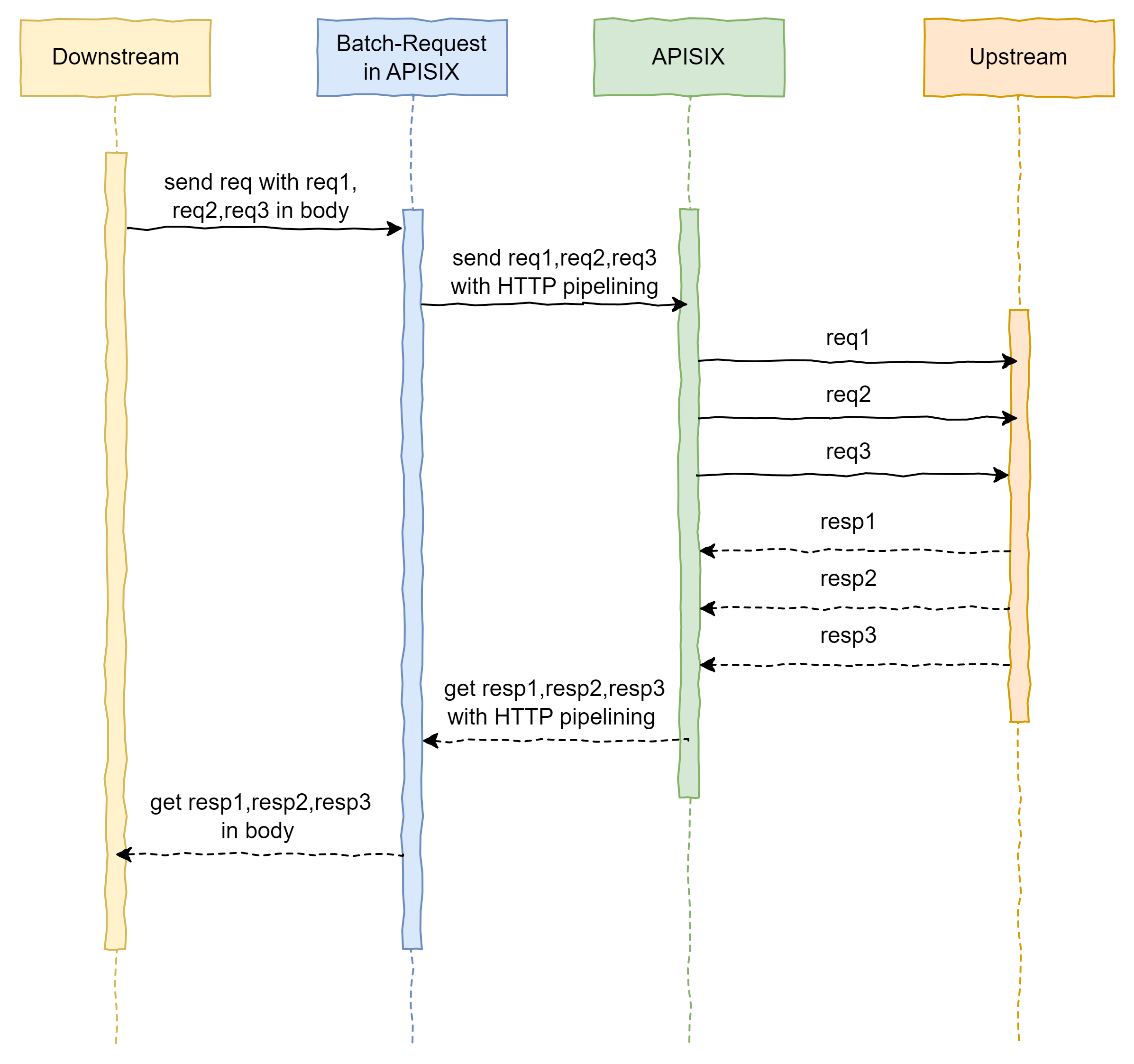
|
||||
|
||||
在客户端需要访问多个 API 的情况下,这将显著提高性能。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
用户原始请求中的请求头(除了以 `Content-` 开始的请求头,例如:`Content-Type`)将被赋给 HTTP pipeline 中的每个请求,因此对于网关来说,这些以 HTTP pipeline 方式发送给自身的请求与用户直接发起的外部请求没有什么不同,只能访问已经配置好的路由,并将经历完整的鉴权过程,因此不存在安全问题。
|
||||
|
||||
如果原始请求的请求头与插件中配置的请求头冲突,则以插件中配置的请求头优先(配置文件中指定的 real_ip_header 除外)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
无。
|
||||
|
||||
## 接口
|
||||
|
||||
该插件会增加 `/apisix/batch-requests` 接口。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
你需要通过 [public-api](../../../zh/latest/plugins/public-api.md) 插件来暴露它。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
该插件默认是禁用状态,你可以在配置文件(`./conf/config.yaml`)添加如下配置启用 `batch-requests` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
- batch-requests
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置插件
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,可以发送到 `/apisix/batch-requests` 的最大请求体不能大于 1 MiB。你可以通过 `apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/batch-requests` 更改插件的此配置:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/batch-requests \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"max_body_size": 4194304
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------- | -------| ------- | ------ | ---------------------------- |
|
||||
| max_body_size | integer | 是 | 1048576 |[1, ...]| 请求体的最大大小,单位:bytes。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 请求和响应格式
|
||||
|
||||
该插件会为 `apisix` 创建一个 `/apisix/batch-requests` 的接口,用来处理批量请求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 请求参数
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------- |------------------------------------| ------ | ------ | -------------------------------- |
|
||||
| query | object | 否 | | 给所有请求都携带的 `query string`。 |
|
||||
| headers | object | 否 | | 给所有请求都携带的 `header`。 |
|
||||
| timeout | number | 否 | 30000 | 聚合请求的超时时间,单位为 `ms`。 |
|
||||
| pipeline | array[[HttpRequest](#httprequest)] | 是 | | HTTP 请求的详细信息。 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### HttpRequest
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------- | -------- | ------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| version | string | 否 | 1.1 | [1.0, 1.1] | 请求所使用的 HTTP 协议版本。 |
|
||||
| method | string | 否 | GET | ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "PATCH", "HEAD", "OPTIONS", "CONNECT", "TRACE"] | 请求使用的 HTTP 方法。 |
|
||||
| query | object | 否 | | | 独立请求所携带的 `query string`, 如果 `Key` 和全局的有冲突,以此设置为主。 |
|
||||
| headers | object | 否 | | | 独立请求所携带的 `header`, 如果 `Key` 和全局的有冲突,以此设置为主。 |
|
||||
| path | string | 是 | | | HTTP 请求路径。 |
|
||||
| body | string | 否 | | | HTTP 请求体。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 验证 SSL 证书与主机名是否匹配。 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 响应参数
|
||||
|
||||
返回值是一个 [HttpResponse](#httpresponse) 的`数组`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### HttpResponse
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名 | 类型 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------- | ------- | ------------------- |
|
||||
| status | integer | HTTP 请求的状态码。 |
|
||||
| reason | string | HTTP 请求的返回信息。 |
|
||||
| body | string | HTTP 请求的响应体。 |
|
||||
| headers | object | HTTP 请求的响应头。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 修改自定义 URI
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过 [public-api](../../../en/latest/plugins/public-api.md) 插件设置自定义 URI。
|
||||
|
||||
只需要在创建路由时设置所需的 URI 并更改 `public-api` 插件的配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/br \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/batch-requests",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/batch-requests"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要为 `batch-requests` 插件的 API 创建一个路由,它将使用 [public-api](../../../en/latest/plugins/public-api.md) 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/batch-requests",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后,你就可以将要访问的请求信息传到网关的批量请求接口(`/apisix/batch-requests`)了,网关会以 [http pipeline](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_pipelining) 的方式自动帮你完成请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/batch-requests' \
|
||||
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
--data '{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Content-Type": "application/json",
|
||||
"admin-jwt":"xxxx"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"timeout": 500,
|
||||
"pipeline": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"path": "/community.GiftSrv/GetGifts",
|
||||
"body": "test"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"path": "/community.GiftSrv/GetGifts",
|
||||
"body": "test2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"reason": "OK",
|
||||
"body": "{\"ret\":500,\"msg\":\"error\",\"game_info\":null,\"gift\":[],\"to_gets\":0,\"get_all_msg\":\"\"}",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Connection": "keep-alive",
|
||||
"Date": "Sat, 11 Apr 2020 17:53:20 GMT",
|
||||
"Content-Type": "application/json",
|
||||
"Content-Length": "81",
|
||||
"Server": "APISIX web server"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"reason": "OK",
|
||||
"body": "{\"ret\":500,\"msg\":\"error\",\"game_info\":null,\"gift\":[],\"to_gets\":0,\"get_all_msg\":\"\"}",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Connection": "keep-alive",
|
||||
"Date": "Sat, 11 Apr 2020 17:53:20 GMT",
|
||||
"Content-Type": "application/json",
|
||||
"Content-Length": "81",
|
||||
"Server": "APISIX web server"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想禁用插件,可以将 `batch-requests` 从配置文件中的插件列表删除,重新加载 APISIX 后即可生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugins: # plugin list
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,609 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: body-transformer
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- BODY TRANSFORMER
|
||||
- body-transformer
|
||||
description: body-transformer 插件执行基于模板的转换,将请求和/或响应主体从一种格式转换为另一种格式,例如从 JSON 到 JSON、从 JSON 到 HTML 或从 XML 到 YAML。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/body-transformer" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`body-transformer` 插件执行基于模板的转换,将请求和/或响应主体从一种格式转换为另一种格式,例如从 JSON 到 JSON、从 JSON 到 HTML 或从 XML 到 YAML。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|--------------|----------------------|-------|---------------|--------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `request` | object | 否 | | | 请求体转换配置。 |
|
||||
| `request.input_format` | string | 否 | | [`xml`,`json`,`encoded`,`args`,`plain`,`multipart`] | 请求体原始媒体类型。若未指定,则该值将由 `Content-Type` 标头确定以应用相应的解码器。`xml` 选项对应于 `text/xml` 媒体类型。`json` 选项对应于 `application/json` 媒体类型。`encoded` 选项对应于 `application/x-www-form-urlencoded` 媒体类型。`args` 选项对应于 GET 请求。`plain` 选项对应于 `text/plain` 媒体类型。`multipart` 选项对应于 `multipart/related` 媒体类型。如果媒体类型不是这两种类型,则该值将保留未设置状态并直接应用转换模板。 |
|
||||
| `request.template` | string | True | | | 请求体转换模板。模板使用 [lua-resty-template](https://github.com/bungle/lua-resty-template) 语法。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 [模板语法](https://github.com/bungle/lua-resty-template#template-syntax)。您还可以使用辅助函数 `_escape_json()` 和 `_escape_xml()` 转义双引号等特殊字符,使用 `_body` 访问请求正文,使用 `_ctx` 访问上下文变量。|
|
||||
| `request.template_is_base64` | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果模板是 base64 编码的,则设置为 true。|
|
||||
| `response` | object | 否 | | | 响应体转换配置。|
|
||||
| `response.input_format` | string | 否 | | [`xml`,`json`] | 响应体原始媒体类型。如果未指定,则该值将由 `Content-Type` 标头确定以应用相应的解码器。如果媒体类型既不是 `xml` 也不是 `json`,则该值将保留未设置状态,并直接应用转换模板。|
|
||||
| `response.template` | string | True | | | 响应主体转换模板。|
|
||||
| `response.template_is_base64` | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果模板是 base64 编码的,则设置为 true。|
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何针对不同场景配置 `body-transformer`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
转换模板使用 [lua-resty-template](https://github.com/bungle/lua-resty-template) 语法。请参阅 [模板语法](https://github.com/bungle/lua-resty-template#template-syntax) 了解更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用辅助函数 `_escape_json()` 和 `_escape_xml()` 转义特殊字符(例如双引号)、`_body` 访问请求正文以及 `_ctx` 访问上下文变量。
|
||||
|
||||
在所有情况下,您都应确保转换模板是有效的 JSON 字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
### JSON 和 XML SOAP 之间的转换
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了在使用 SOAP 上游服务时如何将请求主体从 JSON 转换为 XML,将响应主体从 XML 转换为 JSON。
|
||||
|
||||
启动示例 SOAP 服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd /tmp
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-soap-service.git
|
||||
cd gs-soap-service/complete
|
||||
./mvnw spring-boot:run
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建请求和响应转换模板:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
req_template=$(cat <<EOF | awk '{gsub(/"/,"\\\"");};1' | awk '{$1=$1};1' | tr -d '\r\n'
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0"?>
|
||||
<soap-env:Envelope xmlns:soap-env="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
|
||||
<soap-env:Body>
|
||||
<ns0:getCountryRequest xmlns:ns0="http://spring.io/guides/gs-producing-web-service">
|
||||
<ns0:name>{{_escape_xml(name)}}</ns0:name>
|
||||
</ns0:getCountryRequest>
|
||||
</soap-env:Body>
|
||||
</soap-env:Envelope>
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
rsp_template=$(cat <<EOF | awk '{gsub(/"/,"\\\"");};1' | awk '{$1=$1};1' | tr -d '\r\n'
|
||||
{% if Envelope.Body.Fault == nil then %}
|
||||
{
|
||||
"status":"{{_ctx.var.status}}",
|
||||
"currency":"{{Envelope.Body.getCountryResponse.country.currency}}",
|
||||
"population":{{Envelope.Body.getCountryResponse.country.population}},
|
||||
"capital":"{{Envelope.Body.getCountryResponse.country.capital}}",
|
||||
"name":"{{Envelope.Body.getCountryResponse.country.name}}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
{% else %}
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message":{*_escape_json(Envelope.Body.Fault.faultstring[1])*},
|
||||
"code":"{{Envelope.Body.Fault.faultcode}}"
|
||||
{% if Envelope.Body.Fault.faultactor ~= nil then %}
|
||||
, "actor":"{{Envelope.Body.Fault.faultactor}}"
|
||||
{% end %}
|
||||
}
|
||||
{% end %}
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面使用了 `awk` 和 `tr` 来操作模板,使模板成为有效的 JSON 字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
使用之前创建的模板创建带有 `body-transformer` 的路由。在插件中,将请求输入格式设置为 JSON,将响应输入格式设置为 XML,并将 `Content-Type` 标头设置为 `text/xml`,以便上游服务正确响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["POST"],
|
||||
"uri": "/ws",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"template": "'"$req_template"'",
|
||||
"input_format": "json"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"template": "'"$rsp_template"'",
|
||||
"input_format": "xml"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"set": {
|
||||
"Content-Type": "text/xml"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"localhost:8080": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
如果将复杂的文本文件调整为有效的转换模板很麻烦,则可以使用 base64 实用程序对文件进行编码,例如以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"template": "'"$(base64 -w0 /path/to/request_template_file)"'"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"template": "'"$(base64 -w0 /path/to/response_template_file)"'"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
发送具有有效 JSON 主体的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/ws" -X POST -d '{"name": "Spain"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请求中发送的 JSON 主体将在转发到上游 SOAP 服务之前转换为 XML,响应主体将从 XML 转换回 JSON。
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"status": "200",
|
||||
"currency": "EUR",
|
||||
"population": 46704314,
|
||||
"capital": "Madrid",
|
||||
"name": "Spain"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 修改请求体
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何动态修改请求体。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `body-transformer` 创建一个路由,其中模板将单词 `world` 附加到 `name`,并将 `10` 添加到 `age`,以将它们分别设置为 `foo` 和 `bar` 的值:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"template": "{\"foo\":\"{{name .. \" world\"}}\",\"bar\":{{age+10}}}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路线发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -X POST \
|
||||
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
|
||||
-d '{"name":"hello","age":20}' \
|
||||
-i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "{\"foo\":\"hello world\",\"bar\":30}",
|
||||
...
|
||||
"json": {
|
||||
"bar": 30,
|
||||
"foo": "hello world"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用变量生成请求主体
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何使用 `ctx` 上下文变量动态生成请求主体。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `body-transformer` 创建路由,其中模板使用 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html) `arg_name` 访问请求参数:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"template": "{\"foo\":\"{{_ctx.var.arg_name .. \" world\"}}\"}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `name` 参数向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?name=hello"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到如下响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {
|
||||
"name": "hello"
|
||||
},
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"json": {
|
||||
"foo": "hello world"
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将正文从 YAML 转换为 JSON
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何将请求正文从 YAML 转换为 JSON。
|
||||
|
||||
创建请求转换模板:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
req_template=$(cat <<EOF | awk '{gsub(/"/,"\\\"");};1'
|
||||
{%
|
||||
local yaml = require("tinyyaml")
|
||||
local body = yaml.parse(_body)
|
||||
%}
|
||||
{"foobar":"{{body.foobar.foo .. " " .. body.foobar.bar}}"}
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下模板创建一个带有 `body-transformer` 的路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"template": "'"$req_template"'"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 YAML 主体向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
body='
|
||||
foobar:
|
||||
foo: hello
|
||||
bar: world'
|
||||
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -X POST \
|
||||
-d "$body" \
|
||||
-H "Content-Type: text/yaml" \
|
||||
-i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应,这验证了 YAML 主体已适当地转换为 JSON:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "{\"foobar\":\"hello world\"}",
|
||||
...
|
||||
"json": {
|
||||
"foobar": "hello world"
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将表单 URL 编码主体转换为 JSON
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何将 `form-urlencoded` 主体转换为 JSON。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `body-transformer` 创建路由,将 `input_format` 设置为 `encoded`,并配置一个模板,将字符串 `world` 附加到 `name` 输入,将 `10` 添加到 `age` 输入:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"input_format": "encoded",
|
||||
"template": "{\"foo\":\"{{name .. \" world\"}}\",\"bar\":{{age+10}}}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一个带有编码主体的 POST 请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -X POST \
|
||||
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
|
||||
-d 'name=hello&age=20'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {
|
||||
"{\"foo\":\"hello world\",\"bar\":30}": ""
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 GET 请求查询参数转换为正文
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何将 GET 请求查询参数转换为请求正文。请注意,这不会转换 HTTP 方法。要转换方法,请参阅 [`proxy-rewrite`](./proxy-rewrite.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `body-transformer` 创建路由,将 `input_format` 设置为 `args`,并配置一个向请求添加消息的模板:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"input_format": "args",
|
||||
"template": "{\"message\": \"hello {{name}}\"}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路线发送 GET 请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?name=john"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "{\"message\": \"hello john\"}",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": {
|
||||
"message": "hello john"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 转换纯文本媒体类型
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何转换具有 `plain` 媒体类型的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `body-transformer` 创建路由,将 `input_format` 设置为 `plain`,并配置模板以从正文字符串中删除 `not` 和后续空格:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"input_format": "plain",
|
||||
"template": "{\"message\": \"{* string.gsub(_body, \"not \", \"\") *}\"}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送 POST 请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -X POST \
|
||||
-d 'not actually json' \
|
||||
-i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {
|
||||
"{\"message\": \"actually json\"}": ""
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 转换多部分媒体类型
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何转换具有 `multipart` 媒体类型的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个请求转换模板,该模板根据请求正文中提供的 `age` 向正文添加 `status`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
req_template=$(cat <<EOF | awk '{gsub(/"/,"\\\"");};1'
|
||||
{%
|
||||
local core = require 'apisix.core'
|
||||
local cjson = require 'cjson'
|
||||
|
||||
if tonumber(context.age) > 18 then
|
||||
context._multipart:set_simple("status", "adult")
|
||||
else
|
||||
context._multipart:set_simple("status", "minor")
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
local body = context._multipart:tostring()
|
||||
%}{* body *}
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `body-transformer` 的路由,将 `input_format` 设置为 `multipart`,并使用之前创建的请求模板进行转换:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "body-transformer-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"body-transformer": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"input_format": "multipart",
|
||||
"template": "'"$req_template"'"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送多部分 POST 请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X POST \
|
||||
-F "name=john" \
|
||||
-F "age=10" \
|
||||
"http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {
|
||||
"age": "10",
|
||||
"name": "john",
|
||||
"status": "minor"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Content-Length": "361",
|
||||
"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data; boundary=------------------------qtPjk4c8ZjmGOXNKzhqnOP",
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: brotli
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- brotli
|
||||
description: 这个文档包含有关 Apache APISIX brotli 插件的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`brotli` 插件可以动态的设置 Nginx 中的 [brotli](https://github.com/google/ngx_brotli) 的行为。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前提条件
|
||||
|
||||
该插件依赖 brotli 共享库。
|
||||
|
||||
如下是构建和安装 brotli 共享库的示例脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
wget https://github.com/google/brotli/archive/refs/tags/v1.1.0.zip
|
||||
unzip v1.1.0.zip
|
||||
cd brotli-1.1.0 && mkdir build && cd build
|
||||
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/brotli ..
|
||||
sudo cmake --build . --config Release --target install
|
||||
sudo sh -c "echo /usr/local/brotli/lib >> /etc/ld.so.conf.d/brotli.conf"
|
||||
sudo ldconfig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|--------------|----------------------|-------|---------------|--------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| types | array[string] or "*" | False | ["text/html"] | | 动态设置 `brotli_types` 指令。特殊值 `"*"` 用于匹配任意的 MIME 类型。 |
|
||||
| min_length | integer | False | 20 | >= 1 | 动态设置 `brotli_min_length` 指令。 |
|
||||
| comp_level | integer | False | 6 | [0, 11] | 动态设置 `brotli_comp_level` 指令。 |
|
||||
| mode | integer | False | 0 | [0, 2] | 动态设置 `brotli decompress mode`,更多信息参考 [RFC 7932](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7932)。 |
|
||||
| lgwin | integer | False | 19 | [0, 10-24] | 动态设置 `brotli sliding window size`,`lgwin` 是滑动窗口大小的以 2 为底的对数,将其设置为 0 会让压缩器自行决定最佳值,更多信息请参考 [RFC 7932](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7932)。 |
|
||||
| lgblock | integer | False | 0 | [0, 16-24] | 动态设置 `brotli input block size`,`lgblock` 是最大输入块大小的以 2 为底的对数,将其设置为 0 会让压缩器自行决定最佳值,更多信息请参考 [RFC 7932](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7932)。 |
|
||||
| http_version | number | False | 1.1 | 1.1, 1.0 | 与 `gzip_http_version` 指令类似,用于识别 http 的协议版本。 |
|
||||
| vary | boolean | False | false | | 与 `gzip_vary` 指令类似,用于启用或禁用 `Vary: Accept-Encoding` 响应头。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
如下示例中,在指定的路由上启用 `brotli` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"brotli": {
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以通过以下方法测试插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/ -i -H "Accept-Encoding: br"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Tue, 05 Dec 2023 03:06:49 GMT
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.6.0
|
||||
Content-Encoding: br
|
||||
|
||||
Warning: Binary output can mess up your terminal. Use "--output -" to tell
|
||||
Warning: curl to output it to your terminal anyway, or consider "--output
|
||||
Warning: <FILE>" to save to a file.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当您需要禁用 `brotli` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,263 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: chaitin-waf
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- WAF
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `chaitin-waf` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
在启用 `chaitin-waf` 插件后,流量将被转发给长亭 WAF 服务,用以检测和防止各种 Web 应用程序攻击,以保护应用程序和用户数据的安全。
|
||||
|
||||
## 响应头
|
||||
|
||||
根据插件配置,可以选择是否附加额外的响应头。
|
||||
|
||||
响应头的信息如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF**:APISIX 是否将请求转发给 WAF 服务器。
|
||||
- yes:转发
|
||||
- no:不转发
|
||||
- unhealthy:符合匹配条件,但没有可用的 WAF 服务器
|
||||
- err:插件执行过程中出错。此时会附带 **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-ERROR** 请求头
|
||||
- waf-err:与 WAF 服务器交互时出错。此时会附带 **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-ERROR** 请求头
|
||||
- timeout:与 WAF 服务器的交互超时
|
||||
- **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-ERROR**:调试用响应头。APISIX 与 WAF 交互时的错误信息。
|
||||
- **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-TIME**:APISIX 与 WAF 交互所耗费的时间,单位是毫秒。
|
||||
- **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-STATUS**:WAF 服务器返回给 APISIX 的状态码。
|
||||
- **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-ACTION**:WAF 服务器返回给 APISIX 的处理结果。
|
||||
- pass:请求合法
|
||||
- reject:请求被 WAF 服务器拒绝
|
||||
- **X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-SERVER**:调试用响应头。所使用的 WAF 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|--------------------------|---------------|-----|-------|--------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| nodes | array(object) | 必选 | | 长亭 WAF 的地址列表。 |
|
||||
| nodes[0].host | string | 必选 | | 长亭 WAF 的地址,支持 IPV4、IPV6、Unix Socket 等配置方式。 |
|
||||
| nodes[0].port | string | 可选 | 80 | 长亭 WAF 的端口。 |
|
||||
| config | object | 否 | | 长亭 WAF 服务的配置参数值。当路由没有配置时将使用这里所配置的参数。 |
|
||||
| config.connect_timeout | integer | 否 | 1000 | connect timeout, 毫秒 |
|
||||
| config.send_timeout | integer | 否 | 1000 | send timeout, 毫秒 |
|
||||
| config.read_timeout | integer | 否 | 1000 | read timeout, 毫秒 |
|
||||
| config.req_body_size | integer | 否 | 1024 | 请求体大小,单位为 KB |
|
||||
| config.keepalive_size | integer | 否 | 256 | 长亭 WAF 服务的最大并发空闲连接数 |
|
||||
| config.keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000 | 空闲链接超时,毫秒 |
|
||||
|
||||
一个典型的示例配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/chaitin-waf -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"nodes":[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host": "unix:/path/to/safeline/resources/detector/snserver.sock",
|
||||
"port": 8000
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|--------------------------|---------------|-----|-------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| match | array[object] | 否 | | 匹配规则列表,默认为空且规则将被无条件执行。 |
|
||||
| match.vars | array[array] | 否 | | 由一个或多个 `{var, operator, val}` 元素组成的列表,例如:`{"arg_name", "==", "json"}`,表示当前请求参数 `name` 是 `json`。这里的 `var` 与 NGINX 内部自身变量命名是保持一致,所以也可以使用 `request_uri`、`host` 等;对于已支持的运算符,具体用法请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr#operator-list) 的 `operator-list` 部分。 |
|
||||
| append_waf_resp_header | bool | 否 | true | 是否添加响应头 |
|
||||
| append_waf_debug_header | bool | 否 | false | 是否添加调试用响应头,`add_header` 为 `true` 时才生效 |
|
||||
| config | object | 否 | | 长亭 WAF 服务的配置参数值。当路由没有配置时将使用元数据里所配置的参数。 |
|
||||
| config.connect_timeout | integer | 否 | | connect timeout, 毫秒 |
|
||||
| config.send_timeout | integer | 否 | | send timeout, 毫秒 |
|
||||
| config.read_timeout | integer | 否 | | read timeout, 毫秒 |
|
||||
| config.req_body_size | integer | 否 | | 请求体大小,单位为 KB |
|
||||
| config.keepalive_size | integer | 否 | | 长亭 WAF 服务的最大并发空闲连接数 |
|
||||
| config.keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | | 空闲链接超时,毫秒 |
|
||||
|
||||
一个典型的示例配置如下,这里使用 `httpbun.org` 作为示例后端,可以按需替换:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"chaitin-waf": {
|
||||
"match": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
["http_waf","==","true"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbun.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
以上述的示例配置为例进行测试。
|
||||
|
||||
不满足匹配条件时,请求可以正常触达:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -H "Host: httpbun.org" http://127.0.0.1:9080/get -i
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Content-Length: 408
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF: no
|
||||
Date: Wed, 19 Jul 2023 09:30:42 GMT
|
||||
X-Powered-By: httpbun/3c0dc05883dd9212ac38b04705037d50b02f2596
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Connection": "close",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbun.org",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.1.2",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-For": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbun.org",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Port": "9080",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Proto": "http",
|
||||
"X-Real-Ip": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 122.231.76.178",
|
||||
"url": "http://httpbun.org/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
面对潜在的注入请求也原样转发并遇到 404 错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -H "Host: httpbun.org" http://127.0.0.1:9080/getid=1%20AND%201=1 -i
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Content-Length: 19
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF: no
|
||||
Date: Wed, 19 Jul 2023 09:30:28 GMT
|
||||
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
|
||||
X-Powered-By: httpbun/3c0dc05883dd9212ac38b04705037d50b02f2596
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
404 page not found
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当满足匹配条件时,正常请求依然可以触达上游:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -H "Host: httpbun.org" -H "waf: true" http://127.0.0.1:9080/get -i
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Content-Length: 427
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-TIME: 2
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-STATUS: 200
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF: yes
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-ACTION: pass
|
||||
Date: Wed, 19 Jul 2023 09:29:58 GMT
|
||||
X-Powered-By: httpbun/3c0dc05883dd9212ac38b04705037d50b02f2596
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Connection": "close",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbun.org",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.1.2",
|
||||
"Waf": "true",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-For": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbun.org",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Port": "9080",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Proto": "http",
|
||||
"X-Real-Ip": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 122.231.76.178",
|
||||
"url": "http://httpbun.org/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
而潜在的攻击请求将会被拦截并返回 403 错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -H "Host: httpbun.org" -H "waf: true" http://127.0.0.1:9080/getid=1%20AND%201=1 -i
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
Date: Wed, 19 Jul 2023 09:29:06 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF: yes
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-TIME: 2
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-ACTION: reject
|
||||
X-APISIX-CHAITIN-WAF-STATUS: 403
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.3.0
|
||||
Set-Cookie: sl-session=UdywdGL+uGS7q8xMfnJlbQ==; Domain=; Path=/; Max-Age=86400
|
||||
|
||||
{"code": 403, "success":false, "message": "blocked by Chaitin SafeLine Web Application Firewall", "event_id": "51a268653f2c4189bfa3ec66afbcb26d"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/*",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbun.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: clickhouse-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- ClickHouse
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 API 网关 Apache APISIX 如何使用 clickhouse-logger 插件将日志数据发送到 ClickHouse 数据库中。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`clickhouse-logger` 插件可用于将日志数据推送到 [ClickHouse](https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse) 数据库中。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------------- | ----------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| endpoint_addr | 废弃 | 是 | | | ClickHouse 的 `endpoints`。请使用 `endpoint_addrs` 代替。 |
|
||||
| endpoint_addrs | array | 是 | | | ClickHouse 的 `endpoints。`。 |
|
||||
| database | string | 是 | | | 使用的数据库。 |
|
||||
| logtable | string | 是 | | | 写入的表名。 |
|
||||
| user | string | 是 | | | ClickHouse 的用户。 |
|
||||
| password | string | 是 | | | ClickHouse 的密码。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3 | [1,...] | 发送请求后保持连接活动的时间。 |
|
||||
| name | string | 否 | "clickhouse logger" | | 标识 logger 的唯一标识符。如果您使用 Prometheus 监视 APISIX 指标,名称将以 `apisix_batch_process_entries` 导出。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | [true,false] | 当设置为 `true` 时,验证证书。 |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含请求体。**注意**:如果请求体无法完全存放在内存中,由于 NGINX 的限制,APISIX 无法将它记录下来。|
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array | 否 | | | 当 `include_req_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时进行过滤。只有当此处设置的表达式计算结果为 `true` 时,才会记录请求体。更多信息,请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含响应体。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array | 否 | | | 当 `include_resp_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时进行过滤。只有当此处设置的表达式计算结果为 `true` 时才会记录响应体。更多信息,请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。|
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"password"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志/数据)。这样可以避免插件频繁地提交数据,默认情况下批处理器每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时提交数据,如需了解批处理器相关参数设置,请参考 [Batch-Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认日志格式示例
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"size": 118,
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "text/plain",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.7.0",
|
||||
"content-length": "12"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"client_ip": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 3,
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 98.999998092651,
|
||||
"upstream": "127.0.0.1:1982",
|
||||
"latency": 101.99999809265,
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"version": "3.7.0",
|
||||
"hostname": "localhost"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"route_id": "1",
|
||||
"start_time": 1704507612177,
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"querystring": {
|
||||
"foo": "unknown"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"host": "localhost",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"content-length": "18"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 110,
|
||||
"uri": "/hello?foo=unknown",
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:1984/hello?foo=unknown"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置插件元数据
|
||||
|
||||
`clickhouse-logger` 也支持自定义日志格式,与 [http-logger](./http-logger.md) 插件类似。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html) 变量。该配置全局生效。如果你指定了 `log_format`,该配置就会对所有绑定 `clickhouse-logger` 的路由或服务生效。|
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/clickhouse-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您可以使用 Clickhouse docker 镜像来创建一个容器,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d -p 8123:8123 -p 9000:9000 -p 9009:9009 --name some-clickhouse-server --ulimit nofile=262144:262144 clickhouse/clickhouse-server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后在您的 ClickHouse 数据库中创建一个表来存储日志。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:8123/' \
|
||||
--data-binary 'CREATE TABLE default.test (host String, client_ip String, route_id String, service_id String, `@timestamp` String, PRIMARY KEY(`@timestamp`)) ENGINE = MergeTree()' --user default:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令在指定路由中启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"clickhouse-logger": {
|
||||
"user": "default",
|
||||
"password": "",
|
||||
"database": "default",
|
||||
"logtable": "test",
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://127.0.0.1:8123"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
如果配置多个 `endpoints`,日志将会随机写入到各个 `endpoints`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以向 APISIX 发起请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果您检查表中的行,您将获得以下输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 'http://localhost:8123/?query=select%20*%20from%20default.test'
|
||||
127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 2023-05-08T19:15:53+05:30
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: client-control
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Client Control
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 Apache APISIX proxy-control 插件的相关操作,你可以使用此插件动态地控制 NGINX 处理客户端的请求的行为。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`client-control` 插件能够通过设置客户端请求体大小的上限来动态地控制 NGINX 处理客户端的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 重要
|
||||
|
||||
此插件需要 APISIX 在 [APISIX-Runtime](../FAQ.md#如何构建-apisix-Runtime-环境) 环境上运行。更多信息请参考 [apisix-build-tools](https://github.com/api7/apisix-build-tools)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------- | ----------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| max_body_size | integer | 否 | [0,...] | 设置客户端请求体的最大上限,动态调整 [`client_max_body_size`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#client_max_body_size) 的大小,单位为字节。当设置 `max_body_size` 为 0 时,将不会对客户端请求体大小进行检查。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用 `client-control` 插件,并设置 `max_body_size`:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"client-control": {
|
||||
"max_body_size" : 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
启用插件后,使用 `curl` 命令请求该路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html -d '123'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因为在配置插件时设置了 `max_body_size` 为 `1`,所以返回的 HTTP 响应头中如果带有 `413` 状态码,则表示插件生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 413 Request Entity Too Large
|
||||
...
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head><title>413 Request Entity Too Large</title></head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<center><h1>413 Request Entity Too Large</h1></center>
|
||||
<hr><center>openresty</center>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,353 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: consumer-restriction
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Consumer restriction
|
||||
description: Consumer Restriction 插件允许用户根据 Route、Service、Consumer 或 Consumer Group 来设置相应的访问限制。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`consumer-restriction` 插件允许用户根据 Route、Service、Consumer 或 Consumer Group 来设置相应的访问限制。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------------------------- | ------------- | ------ | ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| type | string | 否 | consumer_name | ["consumer_name", "consumer_group_id", "service_id", "route_id"] | 支持设置访问限制的对象类型。 |
|
||||
| whitelist | array[string] | 是 | | | 加入白名单的对象,优先级高于`allowed_by_methods`。 |
|
||||
| blacklist | array[string] | 是 | | | 加入黑名单的对象,优先级高于`whitelist`。 |
|
||||
| rejected_code | integer | 否 | 403 | [200,...] | 当请求被拒绝时,返回的 HTTP 状态码。 |
|
||||
| rejected_msg | string | 否 | | | 当请求被拒绝时,返回的错误信息。 |
|
||||
| allowed_by_methods | array[object] | 否 | | | 一组为 Consumer 设置允许的配置,包括用户名和允许的 HTTP 方法列表。 |
|
||||
| allowed_by_methods.user | string | 否 | | | 为 Consumer 设置的用户名。 |
|
||||
| allowed_by_methods.methods | array[string] | 否 | | ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "PATCH", "HEAD", "OPTIONS", "CONNECT", "TRACE", "PURGE"] | 为 Consumer 设置的允许的 HTTP 方法列表。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
不同的 `type` 属性值分别代表以下含义:
|
||||
|
||||
- `consumer_name`:把 Consumer 的 `username` 列入白名单或黑名单来限制 Consumer 对 Route 或 Service 的访问。
|
||||
- `consumer_group_id`: 把 Consumer Group 的 `id` 列入白名单或黑名单来限制 Consumer 对 Route 或 Service 的访问。
|
||||
- `service_id`:把 Service 的 `id` 列入白名单或黑名单来限制 Consumer 对 Service 的访问,需要结合授权插件一起使用。
|
||||
- `route_id`:把 Route 的 `id` 列入白名单或黑名单来限制 Consumer 对 Route 的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用并测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 `consumer_name` 限制访问
|
||||
|
||||
首先,创建两个 Consumer,分别为 `jack1` 和 `jack2`:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "jack1",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username":"jack2019",
|
||||
"password": "123456"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -i -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "jack2",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username":"jack2020",
|
||||
"password": "123456"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,在指定路由上启用并配置 `consumer-restriction` 插件,并通过将 `consumer_name` 加入 `whitelist` 来限制不同 Consumer 的访问:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {},
|
||||
"consumer-restriction": {
|
||||
"whitelist": [
|
||||
"jack1"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**测试插件**
|
||||
|
||||
`jack1` 发出访问请求,返回 `200` HTTP 状态码,代表访问成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -u jack2019:123456 http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`jack2` 发出访问请求,返回 `403` HTTP 状态码,代表访问被限制,插件生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -u jack2020:123456 http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"message":"The consumer_name is forbidden."}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 `allowed_by_methods` 限制访问
|
||||
|
||||
首先,创建两个 Consumer,分别为 `jack1` 和 `jack2`,创建方法请参考[通过 `consumer_name` 限制访问](#通过-consumername-限制访问)。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,在指定路由上启用并配置 `consumer-restriction` 插件,并且仅允许 `jack1` 使用 `POST` 方法进行访问:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {},
|
||||
"consumer-restriction": {
|
||||
"allowed_by_methods":[{
|
||||
"user": "jack1",
|
||||
"methods": ["POST"]
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**测试插件**
|
||||
|
||||
`jack1` 发出访问请求,返回 `403` HTTP 状态码,代表访问被限制:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -u jack2019:123456 http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"message":"The consumer_name is forbidden."}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在更新插件配置,增加 `jack1` 的 `GET` 访问能力:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {},
|
||||
"consumer-restriction": {
|
||||
"allowed_by_methods":[{
|
||||
"user": "jack1",
|
||||
"methods": ["POST","GET"]
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`jack1` 再次发出访问请求,返回 `200` HTTP 状态码,代表访问成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -u jack2019:123456 http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过 `service_id` 限制访问
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `service_id` 的方式需要与授权插件一起配合使用,这里以 [`key-auth`](./key-auth.md) 授权插件为例。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,创建两个 Service:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/services/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"desc": "new service 001"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/services/2 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"desc": "new service 002"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在指定 Consumer 上配置 `key-auth` 和 `consumer-restriction` 插件,并通过将 `service_id` 加入 `whitelist` 来限制 Consumer 对 Service 的访问:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "new_consumer",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "auth-jack"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"consumer-restriction": {
|
||||
"type": "service_id",
|
||||
"whitelist": [
|
||||
"1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"rejected_code": 403
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**测试插件**
|
||||
|
||||
在指定路由上启用并配置 `key-auth` 插件,并绑定 `service_id` 为 `1`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"service_id": 1,
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对 Service 发出访问请求,返回 `403` HTTP 状态码,说明在白名单列中的 `service_id` 允许访问,插件生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html -H 'apikey: auth-jack' -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
更新配置 `key-auth` 插件,并绑定 `service_id` 为 `2`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"service_id": 2,
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再次对 Service 发出访问请求,返回 `403` HTTP 状态码,说明不在白名单列表的 `service_id` 被拒绝访问,插件生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html -H 'apikey: auth-jack' -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"message":"The service_id is forbidden."}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: cors
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- CORS
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 Apache APISIX cors 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`cors` 插件可以让你轻松地为服务端启用 [CORS](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS)(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing,跨域资源共享)的返回头。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| allow_origins | string | 否 | "*" | 允许跨域访问的 Origin,格式为 `scheme://host:port`,示例如 `https://somedomain.com:8081`。如果你有多个 Origin,请使用 `,` 分隔。当 `allow_credential` 为 `false` 时,可以使用 `*` 来表示允许所有 Origin 通过。你也可以在启用了 `allow_credential` 后使用 `**` 强制允许所有 Origin 均通过,但请注意这样存在安全隐患。 |
|
||||
| allow_methods | string | 否 | "*" | 允许跨域访问的 Method,比如:`GET`,`POST` 等。如果你有多个 Method,请使用 `,` 分割。当 `allow_credential` 为 `false` 时,可以使用 `*` 来表示允许所有 Method 通过。你也可以在启用了 `allow_credential` 后使用 `**` 强制允许所有 Method 都通过,但请注意这样存在安全隐患。 |
|
||||
| allow_headers | string | 否 | "*" | 允许跨域访问时请求方携带哪些非 `CORS 规范` 以外的 Header。如果你有多个 Header,请使用 `,` 分割。当 `allow_credential` 为 `false` 时,可以使用 `*` 来表示允许所有 Header 通过。你也可以在启用了 `allow_credential` 后使用 `**` 强制允许所有 Header 都通过,但请注意这样存在安全隐患。 |
|
||||
| expose_headers | string | 否 | | 允许跨域访问时响应方携带哪些非 CORS 规范 以外的 Header。如果你有多个 Header,请使用 , 分割。当 allow_credential 为 false 时,可以使用 * 来表示允许任意 Header。如果不设置,插件不会修改 `Access-Control-Expose-Headers` 头,详情请参考 [Access-Control-Expose-Headers - MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Access-Control-Expose-Headers)。 |
|
||||
| max_age | integer | 否 | 5 | 浏览器缓存 CORS 结果的最大时间,单位为秒。在这个时间范围内,浏览器会复用上一次的检查结果,`-1` 表示不缓存。请注意各个浏览器允许的最大时间不同,详情请参考 [Access-Control-Max-Age - MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Access-Control-Max-Age#directives)。 |
|
||||
| allow_credential | boolean | 否 | false | 是否允许跨域访问的请求方携带凭据(如 Cookie 等)。根据 CORS 规范,如果设置该选项为 `true`,那么将不能在其他属性中使用 `*`。 |
|
||||
| allow_origins_by_regex | array | 否 | nil | 使用正则表达式数组来匹配允许跨域访问的 Origin,如 `[".*\.test.com$"]` 可以匹配任何 `test.com` 的子域名。如果 `allow_origins_by_regex` 属性已经指定,则会忽略 `allow_origins` 属性。 |
|
||||
| allow_origins_by_metadata | array | 否 | nil | 通过引用插件元数据的 `allow_origins` 配置允许跨域访问的 Origin。比如当插件元数据为 `"allow_origins": {"EXAMPLE": "https://example.com"}` 时,配置 `["EXAMPLE"]` 将允许 Origin `https://example.com` 的访问。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::info IMPORTANT
|
||||
|
||||
1. `allow_credential` 是一个很敏感的选项,请谨慎开启。开启之后,其他参数默认的 `*` 将失效,你必须显式指定它们的值。
|
||||
2. 在使用 `**` 时,需要清楚该参数引入的一些安全隐患,比如 CSRF,并确保这样的安全等级符合自己预期。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------- | ------ | ------ | ------------------ |
|
||||
| allow_origins | object | 否 | 定义允许跨域访问的 Origin;它的键为 `allow_origins_by_metadata` 使用的引用键,值则为允许跨域访问的 Origin,其语义与属性中的 `allow_origins` 相同。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在路由或服务上启用 `cors` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过如下命令在指定路由上启用 `cors` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"cors": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:8080": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果返回结果中出现 CORS 相关的 header,则代表插件生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
...
|
||||
< Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
< Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
< Access-Control-Allow-Methods: *
|
||||
< Access-Control-Allow-Headers: *
|
||||
< Access-Control-Max-Age: 5
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `cors` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:8080": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: csrf
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 跨站请求伪造攻击
|
||||
- Cross-site request forgery
|
||||
- csrf
|
||||
description: CSRF 插件基于 Double Submit Cookie 的方式,帮助用户阻止跨站请求伪造攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`csrf` 插件基于 [`Double Submit Cookie`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-site_request_forgery#Double_Submit_Cookie) 的方式,保护用户的 API 免于 CSRF 攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
在此插件运行时,`GET`、`HEAD` 和 `OPTIONS` 会被定义为 `safe-methods`,其他的请求方法则定义为 `unsafe-methods`。因此 `GET`、`HEAD` 和 `OPTIONS` 方法的调用不会被检查拦截。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ----------- | ------- | ----- |---------------------|
|
||||
| name | string | 否 | `apisix-csrf-token` | | 生成的 Cookie 中的 Token 名称,需要使用此名称在请求头携带 Cookie 中的内容。 |
|
||||
| expires | number | 否 | `7200` | | CSRF Cookie 的过期时间,单位为秒。当设置为 `0` 时,会忽略 CSRF Cookie 过期时间检查。|
|
||||
| key | string | 是 | | | 加密 Token 的密钥。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"key"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用并配置 `csrf` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"csrf": {
|
||||
"key": "edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:9001": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当你使用 `GET` 之外的方法访问被保护的路由时,请求会被拦截并返回 `401` HTTP 状态码。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `GET` 请求 `/hello` 时,在响应中会有一个携带了加密 Token 的 Cookie。Token 字段名称为插件配置中的 `name` 值,默认为 `apisix-csrf-token`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
每一个请求都会返回一个新的 Cookie。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
在后续对该路由进行的 `unsafe-methods` 请求中,需要从 Cookie 中读取加密的 Token,并在请求头中携带该 Token。请求头字段的名称为插件属性中的 `name`。
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
启用插件后,使用 `curl` 命令尝试直接对该路由发起 `POST` 请求,会返回 `Unauthorized` 字样的报错提示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -X POST
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"error_msg":"no csrf token in headers"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当发起 `GET` 请求时,返回结果中会有携带 Token 的 Cookie:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
Set-Cookie: apisix-csrf-token=eyJyYW5kb20iOjAuNjg4OTcyMzA4ODM1NDMsImV4cGlyZXMiOjcyMDAsInNpZ24iOiJcL09uZEF4WUZDZGYwSnBiNDlKREtnbzVoYkJjbzhkS0JRZXVDQm44MG9ldz0ifQ==;path=/;Expires=Mon, 13-Dec-21 09:33:55 GMT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在请求之前,用户需要从 Cookie 中读取 Token,并在后续的 `unsafe-methods` 请求的请求头中携带。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,你可以在客户端使用 [js-cookie](https://github.com/js-cookie/js-cookie) 读取 Cookie,使用 [axios](https://github.com/axios/axios) 发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const token = Cookie.get('apisix-csrf-token');
|
||||
|
||||
const instance = axios.create({
|
||||
headers: {'apisix-csrf-token': token}
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令发送请求,确保请求中携带了 Cookie 信息,如果返回 `200` HTTP 状态码则表示请求成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -X POST -H 'apisix-csrf-token: eyJyYW5kb20iOjAuNjg4OTcyMzA4ODM1NDMsImV4cGlyZXMiOjcyMDAsInNpZ24iOiJcL09uZEF4WUZDZGYwSnBiNDlKREtnbzVoYkJjbzhkS0JRZXVDQm44MG9ldz0ifQ==' -b 'apisix-csrf-token=eyJyYW5kb20iOjAuNjg4OTcyMzA4ODM1NDMsImV4cGlyZXMiOjcyMDAsInNpZ24iOiJcL09uZEF4WUZDZGYwSnBiNDlKREtnbzVoYkJjbzhkS0JRZXVDQm44MG9ldz0ifQ=='
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: datadog
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 简介
|
||||
|
||||
`datadog` 是 Apache APISIX 内置的监控插件,可与 [Datadog](https://www.datadoghq.com/)(云应用最常用的监控和可观测性平台之一)无缝集成。`datadog` 插件支持对每个请求和响应周期进行多种指标参数的获取,这些指标参数基本反映了系统的行为和健康状况。
|
||||
|
||||
`datadog` 插件通过 UDP 协议将其自定义指标推送给 DogStatsD 服务器,该服务器通过 UDP 连接与 Datadog Agent 捆绑在一起(关于如何安装 Datadog Agent,请参考[Agent](https://docs.datadoghq.com/agent/) )。DogStatsD 基本上是 StatsD 协议的实现,它为 Apache APISIX Agent 收集自定义指标,并将其聚合成单个数据点,发送到配置的 Datadog 服务器。更多关于 DogStatsD 的信息,请参考 [DogStatsD](https://docs.datadoghq.com/developers/dogstatsd/?tab=hostagent) 。
|
||||
|
||||
`datadog` 插件具有将多个指标参数组成一个批处理统一推送给外部 Datadog Agent 的能力,并且可以重复使用同一个数据包套接字。
|
||||
|
||||
此功能可以有效解决日志数据发送不及时的问题。在创建批处理器之后,如果对 `inactive_timeout` 参数进行配置,那么批处理器会在配置好的时间内自动发送日志数据。如果不进行配置,时间默认为 5s。
|
||||
|
||||
关于 Apache APISIX 的批处理程序的更多信息,请参考 [Batch-Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置)
|
||||
|
||||
## APISIX-Datadog plugin 工作原理
|
||||
|
||||
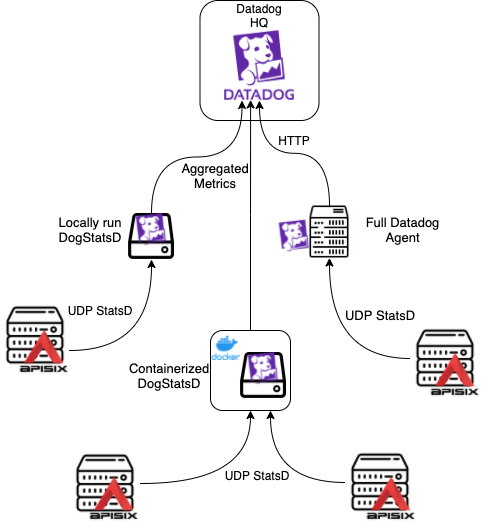
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX-Datadog 插件将其自定义指标推送到 DogStatsD server。而 DogStatsD server 通过 UDP 连接与 Datadog agent 捆绑在一起。DogStatsD 是 StatsD 协议的一个实现。它为 Apache APISIX agent 收集自定义指标,将其聚合成一个数据点,并将其发送到配置的 Datadog server。要了解更多关于 DogStatsD 的信息,请访问 DogStatsD 文档。
|
||||
|
||||
当你启用 APISIX-Datadog 插件时,Apache APISIX agent 会在每个请求响应周期向 DogStatsD server 输出以下指标:
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名称 | StatsD 类型 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ----------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Request Counter | Counter | 收到的请求数量。 |
|
||||
| Request Latency | Histogram | 处理该请求所需的时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| Upstream latency | Histogram | 上游 server agent 请求到收到响应所需的时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| APISIX Latency | Histogram | APISIX agent 处理该请求的时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| Ingress Size | Timer | 请求体大小,以字节为单位。 |
|
||||
| Egress Size | Timer | 响应体大小,以字节为单位。 |
|
||||
|
||||
这些指标将被发送到 DogStatsD agent,并带有以下标签。如果任何特定的标签没有合适的值,该标签将被直接省略。
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名称 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| route_name | 路由的名称,如果不存在,将显示路由 ID。 |
|
||||
| service_id | 如果一个路由是用服务的抽象概念创建的,那么特定的服务 ID 将被使用。 |
|
||||
| consumer | 如果路由有一个链接的消费者,消费者的用户名将被添加为一个标签。 |
|
||||
| balancer_ip | 处理了当前请求的上游复制均衡器的的 IP。 |
|
||||
| response_status | HTTP 响应状态代码。 |
|
||||
| scheme | 已用于提出请求的协议,如 HTTP、gRPC、gRPCs 等。 |
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX-Datadog 插件维护了一个带有 timer 的 buffer。当 timer 失效时,APISIX-Datadog 插件会将 buffer 的指标作为一个批量处理程序传送给本地运行的 DogStatsD server。这种方法通过重复使用相同的 UDP 套接字,对资源的占用较少,而且由于可以配置 timer,所以不会一直让网络过载。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何使用插件
|
||||
|
||||
### 前提:Datadog Agent
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先你必须在系统中安装一个 Datadog agent。它可以是一个 docker 容器,一个 pod 或是一个二进制的包管理器。你只需要确保 Apache APISIX agent 可以到达 Datadog agent 的 8125 端口。
|
||||
2. 如果你从没使用过 Datadog
|
||||
1. 首先访问 [www.datadoghq.com](http://www.datadoghq.com/) ,创建一个账户。
|
||||
2. 然后按照下图标注的步骤生成 API 密钥。 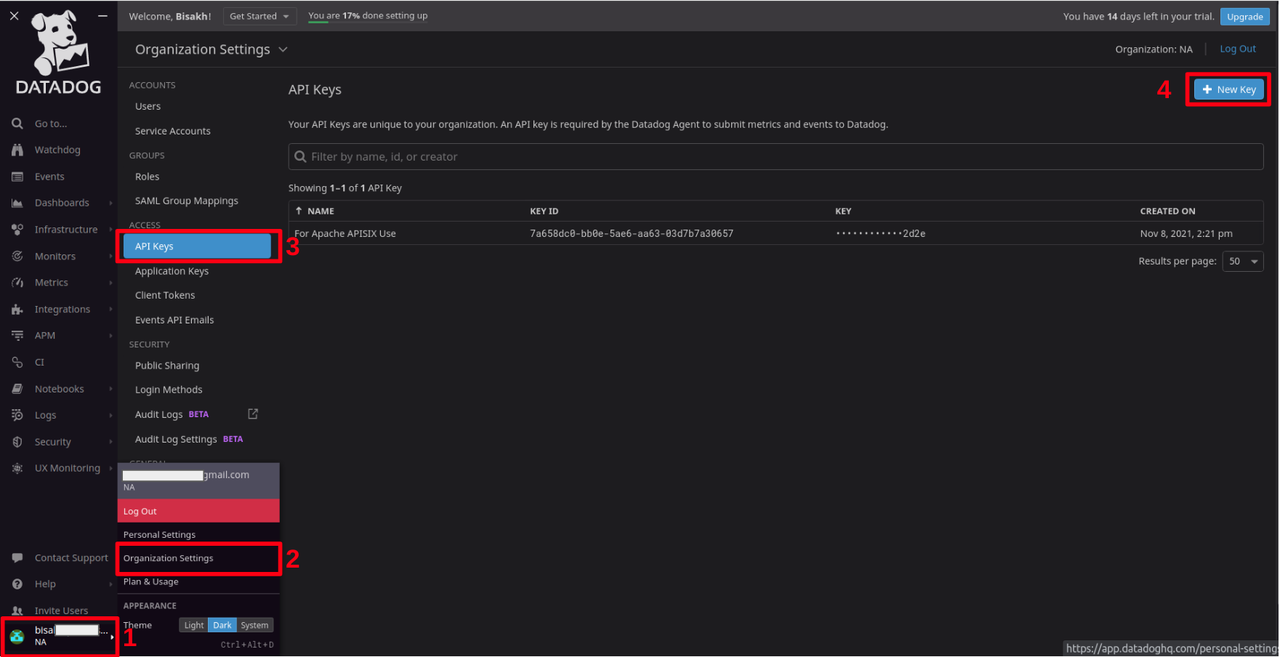
|
||||
3. APISIX-Datadog 插件只需要依赖 `datadog/agent` 的 dogstatsd 组件即可实现,因为该插件按照 statsd 协议通过标准的 UDP 套接字向 DogStatsD server 异步发送参数。我们推荐使用独立的 `datadog/dogstatsd` 镜像,而不是使用完整的`datadog/agent` ,因为 `datadog/dogstatsd` 的组件大小只有大约 11 MB,更加轻量化。而完整的 `datadog/agent` 镜像的大小为 2.8 GB。
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令,将它作为一个容器来运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# pull the latest image
|
||||
docker pull datadog/dogstatsd:latest
|
||||
# run a detached container
|
||||
docker run -d --name dogstatsd-agent -e DD_API_KEY=<Your API Key from step 2> -p 8125:8125/udp datadog/dogstatsd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在生产环境中使用 Kubernetes,你可以将 `dogstatsd` 作为一个 `Daemonset` 或 `Multi-Container Pod` 与 Apache APISIX agent 一起部署。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
本小节介绍了如何在指定路由上启用 `datadog` 插件。进行以下操作之前请确认您的 Datadog Agent 已经启动并正常运行。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"datadog": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,任何对 uri `/hello` 的请求都会生成上述指标,并推送到 Datadog Agent 的 DogStatsD 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
删除插件配置中相应的 JSON 配置以禁用 `datadog`。
|
||||
APISIX 插件是支持热加载的,所以不用重新启动 APISIX,配置就能生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 补充:自定义配置
|
||||
|
||||
在默认配置中,`datadog` 插件希望 Dogstatsd 服务在 `127.0.0.1:8125` 可用。如果你想更新配置,请更新插件的元数据。如果想要了解更多关于 `datadog` 插件元数据的字段,请参阅[元数据](#元数据)。
|
||||
|
||||
向 `/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/datadog` 发起请求,更改其元数据。操作示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/datadog -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host": "172.168.45.29",
|
||||
"port": 8126,
|
||||
"constant_tags": [
|
||||
"source:apisix",
|
||||
"service:custom"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"namespace": "apisix"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上述命令将会更新元数据,后续各指标将通过 UDP StatsD 推送到 `172.168.45.29:8126` 上对应的服务,并且配置将被热加载,不需要重新启动 APISIX 实例,就可以使配置生效。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想把 `datadog` 插件的元数据 schema 恢复到默认值,只需向同一个服务地址再发出一个 Body 为空的 PUT 请求。示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/datadog \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '{}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置属性
|
||||
|
||||
### 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------- | ------ | ----------- | ------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| prefer_name | boolean | optional | true | true/false | 如果设置为 `false`,将使用路由/服务的 id 值作为插件的 `route_name`,而不是带有参数的标签名称。 |
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理程序来聚集和处理条目(日志/数据)的批次。这就避免了插件频繁地提交数据,默认情况下,批处理程序每 `5` 秒或当队列中的数据达到 `1000` 时提交数据。有关信息或自定义批处理程序的参数设置,请参阅[批处理程序](../batch-processor.md#configuration) 配置部分。
|
||||
|
||||
### 元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------- | ------ | ----------- | ------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| host | string | optional | "127.0.0.1" | DogStatsD 服务器的主机地址 |
|
||||
| port | integer | optional | 8125 | DogStatsD 服务器的主机端口 |
|
||||
| namespace | string | optional | "apisix" | 由 APISIX 代理发送的所有自定义参数的前缀。对寻找指标图的实体很有帮助,例如:apisix.request.counter。 |
|
||||
| constant_tags | array | optional | [ "source:apisix" ] | 静态标签嵌入到生成的指标中。这对某些信号的度量进行分组很有用。 |
|
||||
|
||||
要了解更多关于如何有效地编写标签,请访问[这里](https://docs.datadoghq.com/getting_started/tagging/#defining-tags)
|
||||
|
||||
### 输出指标
|
||||
|
||||
启用 datadog 插件之后,APISIX 就会按照下面的指标格式,将数据整理成数据包最终发送到 DogStatsD server。
|
||||
|
||||
| Metric Name | StatsD Type | Description |
|
||||
| ----------- | ----------- | ------- |
|
||||
| Request Counter | Counter | 收到的请求数量。 |
|
||||
| Request Latency | Histogram | 处理该请求所需的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| Upstream latency | Histogram | 代理请求到上游服务器直到收到响应所需的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| APISIX Latency | Histogram | APISIX 代理处理该请求的时间(以毫秒为单位)。|
|
||||
| Ingress Size | Timer | 以字节为单位的请求体大小。 |
|
||||
| Egress Size | Timer | 以字节为单位的响应体大小。 |
|
||||
|
||||
这些指标会带有以下标签,并首先被发送到本地 DogStatsD Agent。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果一个标签没有合适的值,该标签将被直接省略。
|
||||
|
||||
- **route_name**:在路由模式定义中指定的名称,如果不存在或插件属性 `prefer_name` 被设置为 `false`,它将默认使用路由/服务的 id 值。
|
||||
- **service_name**:如果一个路由是用服务的抽象概念创建的,特定的服务 name/id(基于插件的 `prefer_name` 属性)将被使用。
|
||||
- **consumer**:如果路由有一个正在链接中的消费者,那么消费者的用户名将被添加为一个标签。
|
||||
- **balancer_ip**:处理当前请求的上游负载均衡器的 IP。
|
||||
- **response_status**:HTTP 响应状态代码。
|
||||
- **scheme**:已用于提出请求的协议,如 HTTP、gRPC、gRPCs 等。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: dubbo-proxy
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`dubbo-proxy` 插件允许将 `HTTP` 请求代理到 [**dubbo**](http://dubbo.apache.org)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 要求
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在使用 `OpenResty`, 你需要编译它来支持 `dubbo`, 参考 [APISIX-Runtime](../FAQ.md#如何构建-apisix-runtime-环境)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 运行时属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------ | ------ | ----------- | -------- | ------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| service_name | string | 必选 | | | dubbo 服务名字 |
|
||||
| service_version | string | 必选 | | | dubbo 服务版本 |
|
||||
| method | string | 可选 | uri 路径 | | dubbo 服务方法 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 静态属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------ | ------ | ----------- | -------- | ------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| upstream_multiplex_count | number | 必选 | 32 | >= 1 | 上游连接中最大的多路复用请求数 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何启用
|
||||
|
||||
首先,在 `config.yaml` 中启用 `dubbo-proxy` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Add this in config.yaml
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ... # plugin you need
|
||||
- dubbo-proxy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后重载 `APISIX`。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有个例子,在指定的路由中启用 `dubbo-proxy` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/upstreams/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:20880": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uris": [
|
||||
"/hello"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"dubbo-proxy": {
|
||||
"service_name": "org.apache.dubbo.sample.tengine.DemoService",
|
||||
"service_version": "0.0.0",
|
||||
"method": "tengineDubbo"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream_id": 1
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 `Tengine` 提供的 [快速开始](https://github.com/alibaba/tengine/tree/master/modules/mod_dubbo#quick-start) 例子中使用上述配置进行测试。
|
||||
|
||||
将会有同样的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
从上游 `dubbo` 服务返回的数据一定是 `Map<String, String>` 类型。
|
||||
|
||||
如果返回的数据如下
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"status": "200",
|
||||
"header1": "value1",
|
||||
"header2": "valu2",
|
||||
"body": "blahblah"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
则对应的 `HTTP` 响应如下
|
||||
|
||||
```http
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK # "status" will be the status code
|
||||
...
|
||||
header1: value1
|
||||
header2: value2
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
blahblah # "body" will be the body
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你想在某个路由或服务中禁用 `dubbo-proxy` 插件,非常简单,你可以直接删除插件配置中的 `json` 配置,不需要重启服务就能立即生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uris": [
|
||||
"/hello"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream_id": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在 `dubbo-proxy` 插件就已经被禁用了。此方法同样适用于其他插件。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想彻底禁用 `dubbo-proxy` 插件,
|
||||
你需要在 `config.yaml` 中注释掉以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ... # plugin you need
|
||||
#- dubbo-proxy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后重新加载 `APISIX`。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: echo
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Echo
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `echo` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`echo` 插件可以帮助用户尽可能地全面了解如何开发 APISIX 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件展示了如何在常见的 `phase` 中实现相应的功能,常见的 `phase` 包括:init, rewrite, access, balancer, header filter, body filter 以及 log。
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution WARNING
|
||||
|
||||
`echo` 插件只能用作示例,并不能处理一些特别的场景。**请勿将该插件用在生产环境中!**
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------- | ------ | ------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| before_body | string | 否 | 在 `body` 属性之前添加的内容,如果 `body` 属性没有指定,就会将其添加在上游 `response body` 之前。 |
|
||||
| body | string | 否 | 返回给客户端的响应内容,它将覆盖上游返回的响应 `body`。 |
|
||||
| after_body | string | 否 | 在 `body` 属性之后添加的内容,如果 body 属性没有指定将在上游响应 `body` 之后添加。 |
|
||||
| headers | object | 否 | 返回值的 headers。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
参数 `before_body`、`body` 和 `after_body` 至少要配置一个。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由中启用 `echo` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"echo": {
|
||||
"before_body": "before the body modification "
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,你可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
before the body modification hello world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `echo` 插件时,可通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,446 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: elasticsearch-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 插件
|
||||
- Elasticsearch-logger
|
||||
- 日志
|
||||
description: elasticsearch-logger Plugin 将请求和响应日志批量推送到 Elasticsearch,并支持日志格式的自定义。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/elasticsearch-logger" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`elasticsearch-logger` 插件将请求和响应日志批量推送到 [Elasticsearch](https://www.elastic.co),并支持自定义日志格式。启用后,插件会将请求上下文信息序列化为 [Elasticsearch Bulk 格式](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/docs-bulk.html#docs-bulk) 并将其添加到队列中,然后再推送到 Elasticsearch。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 [批处理器](../batch-processor.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------- | -------- | -------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| endup_addrs | array[string] | 是 | | Elasticsearch API 端点地址。如果配置了多个端点,则会随机写入。 |
|
||||
| field | object | 是 | | Elasticsearch `field` 配置。 |
|
||||
| field.index | string | 是 | | Elasticsearch [_index 字段](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-index-field.html#mapping-index-field)。 |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | JSON 格式的键值对中的自定义日志格式。值中支持 [APISIX](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| auth | array | 否 | | Elasticsearch [身份验证](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/setting-up-authentication.html) 配置。 |
|
||||
| auth.username | string | 是 | | Elasticsearch [身份验证](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/setting-up-authentication.html) 用户名。 |
|
||||
| auth.password | string | 是 | | Elasticsearch [身份验证](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/setting-up-authentication.html) 密码。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | 如果为 true,则执行 SSL 验证。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 10 | Elasticsearch 发送数据超时(秒)。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | false |如果为 true,则将请求主体包含在日志中。请注意,如果请求主体太大而无法保存在内存中,则由于 NGINX 的限制而无法记录。|
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array[array] | 否 | | 一个或多个条件的数组,形式为 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。在 `include_req_body` 为 true 时使用。仅当此处配置的表达式计算结果为 true 时,才会记录请求主体。|
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | false | 如果为 true,则将响应主体包含在日志中。|
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array[array] | 否 | | 一个或多个条件的数组,形式为 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。在 `include_resp_body` 为 true 时使用。仅当此处配置的表达式计算结果为 true 时,才会记录响应主体。|
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"auth.password"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
本插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志和数据)。这样可以避免插件频繁地提交数据,默认设置情况下批处理器会每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时提交数据,如需了解或自定义批处理器相关参数设置,请参考 [Batch-Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置) 配置部分。
|
||||
|
||||
## Plugin Metadata
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|
||||
|------|------|----------|---------|-------------|
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | |自定义日志格式为 JSON 格式的键值对。值中支持 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 和 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为不同场景配置 `elasticsearch-logger` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
要遵循示例,请在 Docker 中启动 Elasticsearch 实例:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d \
|
||||
--name elasticsearch \
|
||||
--network apisix-quickstart-net \
|
||||
-v elasticsearch_vol:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data/ \
|
||||
-p 9200:9200 \
|
||||
-p 9300:9300 \
|
||||
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx512m" \
|
||||
-e discovery.type=single-node \
|
||||
-e xpack.security.enabled=false \
|
||||
docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 Docker 中启动 Kibana 实例,以可视化 Elasticsearch 中的索引数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d \
|
||||
--name kibana \
|
||||
--network apisix-quickstart-net \
|
||||
-p 5601:5601 \
|
||||
-e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS="http://elasticsearch:9200" \
|
||||
docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果成功,您应该在 [localhost:5601](http://localhost:5601) 上看到 Kibana 仪表板。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 以默认日志格式记录
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在路由上启用 `elasticsearch-logger` 插件,该插件记录客户端对路由的请求和响应,并将日志推送到 Elasticsearch。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `elasticsearch-logger` 创建路由,将 `index` 字段配置为 `gateway`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "elasticsearch-logger-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"elasticsearch-logger": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://elasticsearch:9200"],
|
||||
"field": {
|
||||
"index": "gateway"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求以生成日志条目:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [localhost:5601](http://localhost:5601) 上的 Kibana 仪表板,并在 __Discover__ 选项卡下创建一个新的索引模式 `gateway` 以从 Elasticsearch 获取数据。配置完成后,导航回 __Discover__ 选项卡,您应该会看到生成的日志,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_index": "gateway",
|
||||
"_id": "CE-JL5QBOkdYRG7kEjTJ",
|
||||
"_version": 1,
|
||||
"_score": 1,
|
||||
"_source": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:9080",
|
||||
"accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/8.6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 85,
|
||||
"querystring": {},
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "application/json",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-credentials": "true",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.11.0",
|
||||
"content-length": "390",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-origin": "*",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"date": "Mon, 13 Jan 2025 10:18:14 GMT"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"size": 618
|
||||
},
|
||||
"route_id": "elasticsearch-logger-route",
|
||||
"latency": 585.00003814697,
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 18.000038146973,
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 567,
|
||||
"upstream": "50.19.58.113:80",
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"hostname": "0b9a772e68f8",
|
||||
"version": "3.11.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"client_ip": "192.168.65.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"fields": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Plugin Metadata 记录请求和响应标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何使用 [Plugin Metadata](../terminology/plugin-metadata.md) 和 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html) 自定义日志格式,以记录请求和响应中的特定标头。
|
||||
|
||||
在 APISIX 中,[Plugin Metadata](../terminology/plugin-metadata.md) 用于配置同一插件的所有插件实例的通用元数据字段。当插件在多个资源中启用并需要对其元数据字段进行通用更新时,它很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用 `elasticsearch-logger` 创建路由,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "elasticsearch-logger-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"elasticsearch-logger": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://elasticsearch:9200"],
|
||||
"field": {
|
||||
"index": "gateway"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,配置 `elasticsearch-logger` 的 Plugin Metadata:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/elasticsearch-logger" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr",
|
||||
"env": "$http_env",
|
||||
"resp_content_type": "$sent_http_Content_Type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `env` 标头向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H "env: dev"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [localhost:5601](http://localhost:5601) 上的 Kibana 仪表板,并在 __Discover__ 选项卡下创建一个新的索引模式 `gateway` 以从 Elasticsearch 获取数据(如果您尚未这样做)。配置完成后,导航回 __Discover__ 选项卡,您应该会看到生成的日志,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_index": "gateway",
|
||||
"_id": "Ck-WL5QBOkdYRG7kODS0",
|
||||
"_version": 1,
|
||||
"_score": 1,
|
||||
"_source": {
|
||||
"client_ip": "192.168.65.1",
|
||||
"route_id": "elasticsearch-logger-route",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "2025-01-06T10:32:36+00:00",
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"resp_content_type": "application/json"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"fields": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 有条件地记录请求主体
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何有条件地记录请求主体。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `elasticsearch-logger` 创建路由,仅在 URL 查询字符串 `log_body` 为 `true` 时记录请求主体:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"elasticsearch-logger": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://elasticsearch:9200"],
|
||||
"field": {
|
||||
"index": "gateway"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"include_req_body": true,
|
||||
"include_req_body_expr": [["arg_log_body", "==", "yes"]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"id": "elasticsearch-logger-route"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用满足以下条件的 URL 查询字符串向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?log_body=yes" -X POST -d '{"env": "dev"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [localhost:5601](http://localhost:5601) 上的 Kibana 仪表板,并在 __Discover__ 选项卡下创建一个新的索引模式 `gateway` 以从 Elasticsearch 获取数据(如果您尚未这样做)。配置完成后,导航回 __Discover__ 选项卡,您应该会看到生成的日志,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_index": "gateway",
|
||||
"_id": "Dk-cL5QBOkdYRG7k7DSW",
|
||||
"_version": 1,
|
||||
"_score": 1,
|
||||
"_source": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"content-length": "14",
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:9080",
|
||||
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 182,
|
||||
"querystring": {
|
||||
"log_body": "yes"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"body": "{\"env\": \"dev\"}",
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?log_body=yes",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything?log_body=yes"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"start_time": 1735965595203,
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "application/json",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.11.0",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-credentials": "true",
|
||||
"content-length": "548",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-origin": "*",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"date": "Mon, 13 Jan 2025 11:02:32 GMT"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"size": 776
|
||||
},
|
||||
"route_id": "elasticsearch-logger-route",
|
||||
"latency": 703.9999961853,
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 34.999996185303,
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 669,
|
||||
"upstream": "34.197.122.172:80",
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"hostname": "0b9a772e68f8",
|
||||
"version": "3.11.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"client_ip": "192.168.65.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"fields": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一个没有任何 URL 查询字符串的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -X POST -d '{"env": "dev"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 Kibana 仪表板 __Discover__ 选项卡,您应该看到生成的日志,但没有请求正文:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_index": "gateway",
|
||||
"_id": "EU-eL5QBOkdYRG7kUDST",
|
||||
"_version": 1,
|
||||
"_score": 1,
|
||||
"_source": {
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
|
||||
"accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"content-length": "14",
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:9080",
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/8.6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 169,
|
||||
"querystring": {},
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"start_time": 1735965686363,
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "application/json",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-credentials": "true",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.11.0",
|
||||
"content-length": "510",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-origin": "*",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"date": "Mon, 13 Jan 2025 11:15:54 GMT"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"size": 738
|
||||
},
|
||||
"route_id": "elasticsearch-logger-route",
|
||||
"latency": 680.99999427795,
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 4.9999942779541,
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 676,
|
||||
"upstream": "34.197.122.172:80",
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"hostname": "0b9a772e68f8",
|
||||
"version": "3.11.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"client_ip": "192.168.65.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"fields": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
如果您除了将 `include_req_body` 或 `include_resp_body` 设置为 `true` 之外还自定义了 `log_format`,则插件不会在日志中包含正文。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一种解决方法,您可以在日志格式中使用 NGINX 变量 `$request_body`,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"elasticsearch-logger": {
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"log_format": {"body": "$request_body"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,192 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: error-log-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 错误日志
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
description: API 网关 Apache APISIX error-log-logger 插件用于将 APISIX 的错误日志推送到 TCP、Apache SkyWalking、Apache Kafka 或 ClickHouse 服务器。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`error-log-logger` 插件用于将 APISIX 的错误日志 (`error.log`) 推送到 TCP、Apache SkyWalking、Apache Kafka 或 ClickHouse 服务器,你还可以设置错误日志级别以将日志发送到服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------------------------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------------------------ | ------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| tcp.host | string | 是 | | | TCP 服务的 IP 地址或主机名。 |
|
||||
| tcp.port | integer | 是 | | [0,...] | 目标端口。 |
|
||||
| tcp.tls | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时执行 SSL 验证。 |
|
||||
| tcp.tls_server_name | string | 否 | | | TLS 服务名称标记。 |
|
||||
| skywalking.endpoint_addr | string | 否 | http://127.0.0.1:12900/v3/logs | | SkyWalking 的 HTTP endpoint 地址,例如:http://127.0.0.1:12800。 |
|
||||
| skywalking.service_name | string | 否 | APISIX | | SkyWalking 上报的 service 名称。 |
|
||||
| skywalking.service_instance_name | String | 否 | APISIX Instance Name | | SkyWalking 上报的 service 实例名,如果希望直接获取本机主机名请设置为 `$hostname`。 |
|
||||
| clickhouse.endpoint_addr | String | 否 | http://127.0.0.1:8213 | | ClickHouse 的 HTTP endpoint 地址,例如 `http://127.0.0.1:8213`。 |
|
||||
| clickhouse.user | String | 否 | default | | ClickHouse 的用户名。 |
|
||||
| clickhouse.password | String | 否 | | | ClickHouse 的密码。 |
|
||||
| clickhouse.database | String | 否 | | | ClickHouse 的用于接收日志的数据库。 |
|
||||
| clickhouse.logtable | String | 否 | | | ClickHouse 的用于接收日志的表。 |
|
||||
| kafka.brokers | array | 是 | | | 需要推送的 Kafka broker 列表。 |
|
||||
| kafka.brokers.host | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 的节点 host 配置,例如 `192.168.1.1`|
|
||||
| kafka.brokers.port | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 的节点端口配置 |
|
||||
| kafka.brokers.sasl_config | object | 否 | | | Kafka broker 中的 sasl_config |
|
||||
| kafka.brokers.sasl_config.mechanism | string | 否 | "PLAIN" | ["PLAIN"] | Kafka broker 中的 sasl 认证机制 |
|
||||
| kafka.brokers.sasl_config.user | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 中 sasl 配置中的 user,如果 sasl_config 存在,则必须填写 |
|
||||
| kafka.brokers.sasl_config.password | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 中 sasl 配置中的 password,如果 sasl_config 存在,则必须填写 |
|
||||
| kafka.kafka_topic | string | 是 | | | 需要推送的 Kafka topic。|
|
||||
| kafka.producer_type | string | 否 | async | ["async", "sync"] | 生产者发送消息的模式。|
|
||||
| kafka.required_acks | integer | 否 | 1 | [0, 1, -1] | 生产者在确认一个请求发送完成之前需要收到的反馈信息的数量。该参数是为了保证发送请求的可靠性。该属性的配置与 Kafka `acks` 属性相同,具体配置请参考 [Apache Kafka 文档](https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#producerconfigs_acks)。 |
|
||||
| kafka.key | string | 否 | | | 用于消息分区而分配的密钥。 |
|
||||
| kafka.cluster_name | integer | 否 | 1 | [0,...] | Kafka 集群的名称,当有两个及以上 Kafka 集群时使用。只有当 `producer_type` 设为 `async` 模式时才可以使用该属性。|
|
||||
| kafka.meta_refresh_interval | integer | 否 | 30 | [1,...] | 对应 [lua-resty-kafka](https://github.com/doujiang24/lua-resty-kafka) 中的 `refresh_interval` 参数,用于指定自动刷新 metadata 的间隔时长,单位为秒。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3 | [1,...] | 连接和发送数据超时间,以秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | integer | 否 | 30 | [1,...] | 复用连接时,连接保持的时间,以秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| level | string | 否 | WARN | | 进行错误日志筛选的级别,默认为 `WARN`,取值 ["STDERR", "EMERG", "ALERT", "CRIT", "ERR", "ERROR", "WARN", "NOTICE", "INFO", "DEBUG"],其中 `ERR` 与 `ERROR` 级别一致。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"clickhouse.password"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
本插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志/数据)。这样可以避免插件频繁地提交数据,默认设置情况下批处理器会每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时提交数据,如需了解或自定义批处理器相关参数设置,请参考 [Batch-Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置) 配置部分。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认日志格式示例
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
["2024/01/06 16:04:30 [warn] 11786#9692271: *1 [lua] plugin.lua:205: load(): new plugins: {"error-log-logger":true}, context: init_worker_by_lua*","\n","2024/01/06 16:04:30 [warn] 11786#9692271: *1 [lua] plugin.lua:255: load_stream(): new plugins: {"limit-conn":true,"ip-restriction":true,"syslog":true,"mqtt-proxy":true}, context: init_worker_by_lua*","\n"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
该插件默认为禁用状态,你可以在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中启用 `error-log-logger` 插件。你可以参考如下示例启用插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugins: # plugin list
|
||||
......
|
||||
- request-id
|
||||
- hmac-auth
|
||||
- api-breaker
|
||||
- error-log-logger # enable plugin `error-log-logger
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
完成插件配置后,你需要重新加载 APISIX,插件才会生效。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
该插件属于 APISIX 全局性插件,不需要在任何路由或服务中绑定。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 TCP 服务器地址
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过配置插件元数据来设置 TCP 服务器地址,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/error-log-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"tcp": {
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port": 1999
|
||||
},
|
||||
"inactive_timeout": 1
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 SkyWalking OAP 服务器地址
|
||||
|
||||
通过以下配置插件元数据设置 SkyWalking OAP 服务器地址,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/error-log-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"skywalking": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addr": "http://127.0.0.1:12800/v3/logs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"inactive_timeout": 1
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 ClickHouse 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持将错误日志作为字符串发送到 ClickHouse 服务器中对应表的 `data` 字段。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以按照如下方式进行配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/error-log-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"clickhouse": {
|
||||
"user": "default",
|
||||
"password": "a",
|
||||
"database": "error_log",
|
||||
"logtable": "t",
|
||||
"endpoint_addr": "http://127.0.0.1:8123"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 Kafka
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持将错误日志发送到 Kafka,你可以按照如下方式进行配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/error-log-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kafka":{
|
||||
"brokers":[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host":"127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port":9092
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kafka_topic":"test2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"level":"ERROR",
|
||||
"inactive_timeout":1
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你不再需要该插件时,只需要在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中删除或注释该插件即可。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins: # plugin list
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
- request-id
|
||||
- hmac-auth
|
||||
- api-breaker
|
||||
#- error-log-logger # enable plugin `error-log-logger
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ext-plugin-post-req
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- ext-plugin-post-req
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `ext-plugin-post-req` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`ext-plugin-post-req` 插件的功能与 `ext-plugin-pre-req` 插件的不同之处在于:`ext-plugin-post-req` 插件是在内置 Lua 插件执行之后且在请求到达上游之前工作。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以参考 [ext-plugin-pre-req](./ext-plugin-pre-req.md) 文档,学习如何配置和使用 `ext-plugin-post-req` 插件。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ext-plugin-post-resp
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- ext-plugin-post-resp
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `ext-plugin-post-resp` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`ext-plugin-post-resp` 插件用于在执行内置 Lua 插件之前和在 Plugin Runner 内运行特定的 External Plugin。
|
||||
|
||||
`ext-plugin-post-resp` 插件将在请求获取到上游的响应之后执行。
|
||||
|
||||
启用本插件之后,APISIX 将使用 [lua-resty-http](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-http) 库向上游发起请求,这会导致:
|
||||
|
||||
- [proxy-control](./proxy-control.md) 插件不可用
|
||||
- [proxy-mirror](./proxy-mirror.md) 插件不可用
|
||||
- [proxy-cache](./proxy-cache.md) 插件不可用
|
||||
- [APISIX 与上游间的双向认证](../mtls.md#apisix-与上游间的双向认证) 功能尚不可用
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解更多关于 External Plugin 的信息,请参考 [External Plugin](../external-plugin.md) 。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
External Plugin 执行的结果会影响当前请求的响应。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------ | ------ | ------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| conf | array | 否 | | [{"name": "ext-plugin-A", "value": "{\"enable\":\"feature\"}"}] | 在 Plugin Runner 内执行的插件列表的配置。 |
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean| 否 | false | [false, true] | 当 Plugin Runner 临时不可用时是否允许请求继续,当值设置为 `true` 时则自动允许请求继续。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由中启用 `ext-plugin-post-resp` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"ext-plugin-post-resp": {
|
||||
"conf" : [
|
||||
{"name": "ext-plugin-A", "value": "{\"enable\":\"feature\"}"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在返回结果中可以看到刚刚配置的 Plugin Runner 已经被触发,同时 `ext-plugin-A` 插件也已经被执行。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `ext-plugin-post-resp` 插件时,可通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ext-plugin-pre-req
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- ext-plugin-pre-req
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `ext-plugin-pre-req` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`ext-plugin-pre-req` 插件用于在执行内置 Lua 插件之前和在 Plugin Runner 内运行特定的 External Plugin。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解更多关于 External Plugin 的信息,请参考 [External Plugin](../external-plugin.md) 。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
External Plugin 执行的结果会影响当前请求的行为。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------ | ------ | ------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| conf | array | 否 | | [{"name": "ext-plugin-A", "value": "{\"enable\":\"feature\"}"}] | 在 Plugin Runner 内执行的插件列表的配置。 |
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean| 否 | false | [false, true] | 当 Plugin Runner 临时不可用时是否允许请求继续,当值设置为 true 时则自动允许请求继续。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由中启用 `ext-plugin-pre-req` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"ext-plugin-pre-req": {
|
||||
"conf" : [
|
||||
{"name": "ext-plugin-A", "value": "{\"enable\":\"feature\"}"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在返回结果中可以看到刚刚配置的 Plugin Runner 已经被触发,同时 `ext-plugin-A` 插件也已经被执行。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `ext-plugin-pre-req` 插件时,可通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,299 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: fault-injection
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Fault Injection
|
||||
- fault-injection
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `fault-injection` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`fault-injection` 插件是故障注入插件,该插件可以和其他插件一起使用,并在其他插件执行前被执行。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------------------------- |
|
||||
| abort.http_status | integer | 是 | [200, ...] | 返回给客户端的 HTTP 状态码 |
|
||||
| abort.body | string | 否 | | 返回给客户端的响应数据。支持使用 NGINX 变量,如 `client addr: $remote_addr\n`|
|
||||
| abort.headers | object | 否 | | 返回给客户端的响应头,可以包含 NGINX 变量,如 `$remote_addr` |
|
||||
| abort.percentage | integer | 否 | [0, 100] | 将被中断的请求占比 |
|
||||
| abort.vars | array[] | 否 | | 执行故障注入的规则,当规则匹配通过后才会执行故障注。`vars` 是一个表达式的列表,来自 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr#operator-list)。 |
|
||||
| delay.duration | number | 是 | | 延迟时间,可以指定小数 |
|
||||
| delay.percentage | integer | 否 | [0, 100] | 将被延迟的请求占比 |
|
||||
| delay.vars | array[] | 否 | | 执行请求延迟的规则,当规则匹配通过后才会延迟请求。`vars` 是一个表达式列表,来自 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr#operator-list)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::info IMPORTANT
|
||||
|
||||
`abort` 属性将直接返回给客户端指定的响应码并且终止其他插件的执行。
|
||||
|
||||
`delay` 属性将延迟某个请求,并且还会执行配置的其他插件。
|
||||
|
||||
`abort` 和 `delay` 属性至少要配置一个。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
`vars` 是由 [`lua-resty-expr`](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 的表达式组成的列表,它可以灵活的实现规则之间的 AND/OR 关系,示例如下::
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ "arg_name","==","jack" ],
|
||||
[ "arg_age","==",18 ]
|
||||
],
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ "arg_name2","==","allen" ]
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以上示例表示前两个表达式之间的关系是 AND,而前两个和第三个表达式之间的关系是 OR。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在指定路由启用 `fault-injection` 插件,并指定 `abort` 属性。如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"fault-injection": {
|
||||
"abort": {
|
||||
"http_status": 200,
|
||||
"body": "Fault Injection!"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同样,我们也可以指定 `delay` 属性。如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"fault-injection": {
|
||||
"delay": {
|
||||
"duration": 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
还可以同时为指定路由启用 `fault-injection` 插件,并指定 `abort` 属性和 `delay` 属性的 `vars` 规则。如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"fault-injection": {
|
||||
"abort": {
|
||||
"http_status": 403,
|
||||
"body": "Fault Injection!\n",
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ "arg_name","==","jack" ]
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"delay": {
|
||||
"duration": 2,
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ "http_age","==","18" ]
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述示例启用插件后,可以向路由发起如下请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Date: Mon, 13 Jan 2020 13:50:04 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
|
||||
Fault Injection!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过如下命令可以向配置 `delay` 属性的路由发起请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
time curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
|
||||
Content-Length: 6
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
Date: Tue, 14 Jan 2020 14:30:54 GMT
|
||||
Last-Modified: Sat, 11 Jan 2020 12:46:21 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
hello
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m3.034s
|
||||
user 0m0.007s
|
||||
sys 0m0.010s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 标准匹配的故障注入
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 `fault-injection` 插件中使用 `vars` 规则设置特定规则:
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"fault-injection": {
|
||||
"abort": {
|
||||
"http_status": 403,
|
||||
"body": "Fault Injection!\n",
|
||||
"vars": [
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ "arg_name","==","jack" ]
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用不同的 `name` 参数测试路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello?name=allen" -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
没有故障注入的情况下,你可以得到如下结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Wed, 20 Jan 2021 07:21:57 GMT
|
||||
Server: APISIX/2.2
|
||||
|
||||
hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们将 `name` 设置为与配置相匹配的名称,`fault-injection` 插件将被执行:
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello?name=jack" -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
Date: Wed, 20 Jan 2021 07:23:37 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/2.2
|
||||
|
||||
Fault Injection!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `fault-injection` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,242 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: file-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- file-logger
|
||||
description: API 网关 Apache APISIX file-logger 插件可用于将日志数据存储到指定位置。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`file-logger` 插件可用于将日志数据存储到指定位置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
|
||||
`file-logger` 插件特点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 可将指定路由的日志发送到指定位置,方便你在本地统计各个路由的请求和响应数据。在使用 [debug mode](../../../en/latest/debug-mode.md) 时,你可以很轻松地将出现问题的路由的日志输出到指定文件中,从而更方便地排查问题。
|
||||
- 可以获取 [APISIX 变量](../../../en/latest/apisix-variable.md)和 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html),而 `access.log` 仅能使用 NGINX 变量。
|
||||
- 支持热加载,你可以在路由中随时更改其配置并立即生效。而修改 `access.log` 相关配置,则需要重新加载 APISIX。
|
||||
- 支持以 JSON 格式保存日志数据。
|
||||
- 可以在 `log phase` 阶段修改 `file-logger` 执行的函数来收集你所需要的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- |-----| ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| path | string | 是 | 自定义输出文件路径。例如:`logs/file.log`。 |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | 当设置为 `true` 时,日志中将包含请求体。如果请求体太大而无法在内存中保存,则由于 Nginx 的限制,无法记录请求体。|
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array | 否 | 当 `include_req_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时的过滤器。只有当此处设置的表达式求值为 `true` 时,才会记录请求体。有关更多信息,请参阅 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | 当设置为 `true` 时,生成的文件包含响应体。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array | 否 | 当 `include_resp_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时,使用该属性并基于 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 进行过滤。如果存在,则仅在表达式计算结果为 `true` 时记录响应。 |
|
||||
| match | array[array] | 否 | 当设置了这个选项后,只有匹配规则的日志才会被记录。`match` 是一个表达式列表,具体请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr#operator-list)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认日志格式示例
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 100.99999809265,
|
||||
"start_time": 1703907485819,
|
||||
"latency": 101.99999809265,
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 1,
|
||||
"client_ip": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"route_id": "1",
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"version": "3.7.0",
|
||||
"hostname": "localhost"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:1984",
|
||||
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
|
||||
"user-agent": "lua-resty-http/0.16.1 (Lua) ngx_lua/10025",
|
||||
"content-length": "12"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"size": 194,
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:1984/hello?log_body=no",
|
||||
"uri": "/hello?log_body=no",
|
||||
"querystring": {
|
||||
"log_body": "no"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "text/plain",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"content-length": "12",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.7.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"size": 123
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": "127.0.0.1:1982"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件元数据设置
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 可选 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../../../en/latest/apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
该设置全局生效。如果指定了 `log_format`,则所有绑定 `file-logger` 的路由或服务都将使用该日志格式。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过 Admin API 配置插件元数据:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/file-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
配置完成后,你可以在日志系统中看到如下类似日志:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
{"host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2020-09-23T19:05:05-04:00","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","route_id":"1"}
|
||||
{"host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2020-09-23T19:05:05-04:00","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","route_id":"1"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令在指定路由中启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"file-logger": {
|
||||
"path": "logs/file.log"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:9001": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令向 APISIX 发出请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
hello, world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问成功后,你可以在对应的 `logs` 目录下找到 `file.log` 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
## 过滤日志
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"file-logger": {
|
||||
"path": "logs/file.log",
|
||||
"match": [
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ "arg_name","==","jack" ]
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:9001": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello?name=jack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 `logs/file.log` 中可以看到日志记录
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello?name=rose
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 `logs/file.log` 中看不到日志记录
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:9001": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: forward-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Forward Authentication
|
||||
- forward-auth
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `forward-auth` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`forward-auth` 插件使用的是经典外部认证。当身份认证失败时,可以实现自定义错误或者重定向到认证页面的场景。
|
||||
|
||||
`forward-auth` 插件巧妙地将身份认证和授权逻辑移到了一个专门的外部服务中,APISIX 将用户的请求转发给认证服务并阻塞原始请求,然后在认证服务下以非 2xx 状态响应时进行结果替换。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------- | ------| ------- | -------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| uri | string | 是 | | | 设置 `authorization` 服务的地址 (例如:https://localhost:9188)。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | [true, false] | 当设置为 `true` 时,验证 SSL 证书。 |
|
||||
| request_method | string | 否 | GET | ["GET","POST"] | 客户端向 `authorization` 服务发送请求的方法。当设置为 POST 时,会将 `request body` 转发至 `authorization` 服务。 |
|
||||
| request_headers | array[string] | 否 | | | 设置需要由客户端转发到 `authorization` 服务的请求头。如果没有设置,则只发送 APISIX 提供的 headers (例如:X-Forwarded-XXX)。 |
|
||||
| upstream_headers | array[string] | 否 | | | 认证通过时,设置 `authorization` 服务转发至 `upstream` 的请求头。如果不设置则不转发任何请求头。 |
|
||||
| client_headers | array[string] | 否 | | | 认证失败时,由 `authorization` 服务向 `client` 发送的响应头。如果不设置则不转发任何响应头。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000ms | [1, 60000]ms | `authorization` 服务请求超时时间。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | [true, false] | HTTP 长连接。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000ms | [1000, ...]ms | 长连接超时时间。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | [1, ...]ms | 长连接池大小。 |
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean | 否 | false | | 当设置为 `true` 时,允许在身份验证服务器不可用时跳过身份验证。 |
|
||||
| status_on_error | integer | 否 | 403 | [200,...,599] | 设置授权服务出现网络错误时返回给客户端的 HTTP 状态。默认状态为“403”。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据定义
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 将生成并发送如下所示的请求头到认证服务:
|
||||
|
||||
| Scheme | HTTP Method | Host | URI | Source IP |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- | --------------- | --------------- |
|
||||
| X-Forwarded-Proto | X-Forwarded-Method | X-Forwarded-Host | X-Forwarded-Uri | X-Forwarded-For |
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要设置一个外部认证服务。以下示例使用的是 Apache APISIX 无服务器插件模拟服务:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT 'http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/auth' \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "/auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"serverless-pre-function": {
|
||||
"phase": "rewrite",
|
||||
"functions": [
|
||||
"return function (conf, ctx)
|
||||
local core = require(\"apisix.core\");
|
||||
local authorization = core.request.header(ctx, \"Authorization\");
|
||||
if authorization == \"123\" then
|
||||
core.response.exit(200);
|
||||
elseif authorization == \"321\" then
|
||||
core.response.set_header(\"X-User-ID\", \"i-am-user\");
|
||||
core.response.exit(200);
|
||||
else core.response.set_header(\"Location\", \"http://example.com/auth\");
|
||||
core.response.exit(403);
|
||||
end
|
||||
end"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以在指定 Route 上启用 `forward-auth` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT 'http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1' \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"forward-auth": {
|
||||
"uri": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/auth",
|
||||
"request_headers": ["Authorization"],
|
||||
"upstream_headers": ["X-User-ID"],
|
||||
"client_headers": ["Location"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
完成上述配置后,可通过以下三种方式进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
- 在请求头中发送认证的详细信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers -H 'Authorization: 123'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Authorization": "123",
|
||||
"Next": "More-headers"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 转发认证服务响应头到 Upstream。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers -H 'Authorization: 321'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Authorization": "321",
|
||||
"X-User-ID": "i-am-user",
|
||||
"Next": "More-headers"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 当授权失败时,认证服务可以向用户发送自定义响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
|
||||
Location: http://example.com/auth
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `forward-auth` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: GM
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- GM
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX gm 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`gm` 插件能启用国密相关的功能。目前支持通过该插件动态配置国密双证书。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 相关介绍
|
||||
国密就是国产化的密码算法。在我们日常开发过程中会接触到各种各样的密码算法,如 RSA、SHA256 等等。为了达到更高的安全等级,许多大公司和国家会制定自己的密码算法。国密就是这样一组由中国国家密码管理局制定的密码算法。在国际形势越发复杂多变的今天,密码算法的国产化替代,在一些领域已经成为了一股势不可挡的潮流。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
**该插件要求 Apache APISIX 运行在编译了 Tongsuo 的 APISIX-Runtime 上。**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要安装 Tongsuo(此处我们选择编译出 Tongsuo 的动态链接库):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# TODO: use a fixed release once they have created one.
|
||||
# See https://github.com/Tongsuo-Project/Tongsuo/issues/318
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/api7/tongsuo --depth 1
|
||||
pushd tongsuo
|
||||
./config shared enable-ntls -g --prefix=/usr/local/tongsuo
|
||||
make -j2
|
||||
sudo make install_sw
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其次,我们需要构建 APISIX-Runtime,让它使用 Tongsuo 作为 SSL 库:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export OR_PREFIX=/usr/local/openresty
|
||||
export openssl_prefix=/usr/local/tongsuo
|
||||
export zlib_prefix=$OR_PREFIX/zlib
|
||||
export pcre_prefix=$OR_PREFIX/pcre
|
||||
|
||||
export cc_opt="-DNGX_LUA_ABORT_AT_PANIC -I${zlib_prefix}/include -I${pcre_prefix}/include -I${openssl_prefix}/include"
|
||||
export ld_opt="-L${zlib_prefix}/lib -L${pcre_prefix}/lib -L${openssl_prefix}/lib64 -Wl,-rpath,${zlib_prefix}/lib:${pcre_prefix}/lib:${openssl_prefix}/lib64"
|
||||
./build-apisix-runtime.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该插件默认是禁用状态,你需要将其添加到配置文件(`./conf/config.yaml`)中才可以启用它:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
- gm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
由于 APISIX 的默认 cipher 中不包含国密 cipher,所以我们还需要在配置文件(`./conf/config.yaml`)中设置 cipher:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
...
|
||||
ssl:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 可按实际情况调整。错误的 cipher 会导致“no shared cipher”或“no ciphers available”报错。
|
||||
ssl_ciphers: HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
配置完成后,重新加载 APISIX,此时 APISIX 将会启用国密相关的逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
在测试插件之前,我们需要准备好国密双证书。Tongsuo 提供了生成[SM2 双证书](https://www.yuque.com/tsdoc/ts/sulazb)的教程。
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的例子中,我们将用到如下的证书:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 客户端加密证书和密钥
|
||||
t/certs/client_enc.crt
|
||||
t/certs/client_enc.key
|
||||
# 客户端签名证书和密钥
|
||||
t/certs/client_sign.crt
|
||||
t/certs/client_sign.key
|
||||
# CA 和中间 CA 打包在一起的文件,用于设置受信任的 CA
|
||||
t/certs/gm_ca.crt
|
||||
# 服务端加密证书和密钥
|
||||
t/certs/server_enc.crt
|
||||
t/certs/server_enc.key
|
||||
# 服务端签名证书和密钥
|
||||
t/certs/server_sign.crt
|
||||
t/certs/server_sign.key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此外,我们还需要准备 Tongsuo 命令行工具。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
./config enable-ntls -static
|
||||
make -j2
|
||||
# 生成的命令行工具在 apps 目录下
|
||||
mv apps/openssl ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以采用非静态编译的方式,不过就需要根据具体环境,自己解决动态链接库的路径问题了。
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定域名中启用 `gm` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
创建对应的 SSL 对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding: utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
# sudo pip install requests
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) <= 3:
|
||||
print("bad argument")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
with open(sys.argv[1]) as f:
|
||||
enc_cert = f.read()
|
||||
with open(sys.argv[2]) as f:
|
||||
enc_key = f.read()
|
||||
with open(sys.argv[3]) as f:
|
||||
sign_cert = f.read()
|
||||
with open(sys.argv[4]) as f:
|
||||
sign_key = f.read()
|
||||
api_key = "edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1"
|
||||
resp = requests.put("http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1", json={
|
||||
"cert": enc_cert,
|
||||
"key": enc_key,
|
||||
"certs": [sign_cert],
|
||||
"keys": [sign_key],
|
||||
"gm": True,
|
||||
"snis": ["localhost"],
|
||||
}, headers={
|
||||
"X-API-KEY": api_key,
|
||||
})
|
||||
print(resp.status_code)
|
||||
print(resp.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将上面的脚本保存为 `./create_gm_ssl.py`,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
./create_gm_ssl.py t/certs/server_enc.crt t/certs/server_enc.key t/certs/server_sign.crt t/certs/server_sign.key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
200
|
||||
{"key":"\/apisix\/ssls\/1","value":{"keys":["Yn...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
完成上述准备后,可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
./openssl s_client -connect localhost:9443 -servername localhost -cipher ECDHE-SM2-WITH-SM4-SM3 -enable_ntls -ntls -verifyCAfile t/certs/gm_ca.crt -sign_cert t/certs/client_sign.crt -sign_key t/certs/client_sign.key -enc_cert t/certs/client_enc.crt -enc_key t/certs/client_enc.key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里 `./openssl` 是前面得到的 Tongsuo 命令行工具。9443 是 APISIX 默认的 HTTPS 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切正常,可以看到连接建立了起来,并输出如下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
...
|
||||
New, NTLSv1.1, Cipher is ECDHE-SM2-SM4-CBC-SM3
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
如果不再使用此插件,可将 `gm` 插件从 `./conf/config.yaml` 配置文件中移除,然后重启 APISIX 或者通过插件热加载的接口触发插件的卸载。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: google-cloud-logging
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 插件
|
||||
- Google Cloud logging
|
||||
- 日志
|
||||
description: API 网关 Apache APISIX 的 google-cloud-logging 插件可用于将请求日志转发到 Google Cloud Logging Service 中进行分析和存储。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`google-cloud-logging` 插件可用于将请求日志发送到 [Google Cloud Logging Service](https://cloud.google.com/logging/) 进行分析和存储。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| auth_config | 是 | | `auth_config` 和 `auth_file` 必须配置一个。 |
|
||||
| auth_config.client_email | 是 | | 谷歌服务帐号的 email 参数。 |
|
||||
| auth_config.private_key | 是 | | 谷歌服务帐号的私钥参数。 |
|
||||
| auth_config.project_id | 是 | | 谷歌服务帐号的项目 ID。 |
|
||||
| auth_config.token_uri | 是 | https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token | 请求谷歌服务帐户的令牌的 URI。 |
|
||||
| auth_config.entries_uri | 否 | https://logging.googleapis.com/v2/entries:write | 谷歌日志服务写入日志条目的 API。 |
|
||||
| auth_config.scope | 否 | | 谷歌服务账号的访问范围,可参考 [OAuth 2.0 Scopes for Google APIs](https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/scopes#logging)。可选项:"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.read"、"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write"、"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.admin"、"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform"。|
|
||||
| auth_config.scopes | 废弃 | | 谷歌服务账号的访问范围,推荐使用 `auth_config.scope` |
|
||||
| auth_file | 是 | | `auth_config` 和 `auth_file` 必须配置一个。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | 否 | true | 当设置为 `true` 时,启用 `SSL` 验证。 |
|
||||
| resource | 否 | {"type": "global"} | 谷歌监控资源,请参考 [MonitoredResource](https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/reference/v2/rest/v2/MonitoredResource)。 |
|
||||
| log_id | 否 | apisix.apache.org%2Flogs | 谷歌日志 ID,请参考 [LogEntry](https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/reference/v2/rest/v2/LogEntry)。 |
|
||||
| log_format | 否 | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"auth_config.private_key"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志和数据)。这样可以避免该插件频繁地提交数据。默认情况下每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时,批处理器会自动提交数据,如需了解更多信息或自定义配置,请参考 [Batch Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认日志格式示例
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"insertId": "0013a6afc9c281ce2e7f413c01892bdc",
|
||||
"labels": {
|
||||
"source": "apache-apisix-google-cloud-logging"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"logName": "projects/apisix/logs/apisix.apache.org%2Flogs",
|
||||
"httpRequest": {
|
||||
"requestMethod": "GET",
|
||||
"requestUrl": "http://localhost:1984/hello",
|
||||
"requestSize": 59,
|
||||
"responseSize": 118,
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"remoteIp": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"serverIp": "127.0.0.1:1980",
|
||||
"latency": "0.103s"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resource": {
|
||||
"type": "global"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jsonPayload": {
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"route_id": "1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"timestamp": "2024-01-06T03:34:45.065Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头。则表明获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 注意
|
||||
|
||||
该设置全局生效。如果指定了 `log_format`,则所有绑定 `google-cloud-logging` 的路由或服务都将使用该日志格式。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过 Admin API 配置插件元数据:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/google-cloud-logging \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
配置完成后,你将在日志系统中看到如下类似日志:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{"partialSuccess":false,"entries":[{"jsonPayload":{"client_ip":"127.0.0.1","host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2023-01-09T14:47:25+08:00","route_id":"1"},"resource":{"type":"global"},"insertId":"942e81f60b9157f0d46bc9f5a8f0cc40","logName":"projects/apisix/logs/apisix.apache.org%2Flogs","timestamp":"2023-01-09T14:47:25+08:00","labels":{"source":"apache-apisix-google-cloud-logging"}}]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
**完整配置**
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"google-cloud-logging": {
|
||||
"auth_config":{
|
||||
"project_id":"apisix",
|
||||
"client_email":"your service account email@apisix.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
|
||||
"private_key":"-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----your private key-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----",
|
||||
"token_uri":"https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
|
||||
"scope":[
|
||||
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.admin"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"entries_uri":"https://logging.googleapis.com/v2/entries:write"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resource":{
|
||||
"type":"global"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"log_id":"apisix.apache.org%2Flogs",
|
||||
"inactive_timeout":10,
|
||||
"max_retry_count":0,
|
||||
"max_retry_count":0,
|
||||
"buffer_duration":60,
|
||||
"retry_delay":1,
|
||||
"batch_max_size":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**最小化配置**
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"google-cloud-logging": {
|
||||
"auth_config":{
|
||||
"project_id":"apisix",
|
||||
"client_email":"your service account email@apisix.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
|
||||
"private_key":"-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----your private key-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令向 APISIX 发出请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
hello, world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问成功后,你可以登录 [Google Cloud Logging Service](https://console.cloud.google.com/logs/viewer) 查看相关日志。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,396 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: grpc-transcode
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- gRPC Web
|
||||
- grpc-web
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `grpc-transcode` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `grpc-transcode` 插件可以在 HTTP 和 gRPC 请求之间进行转换。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 接收 HTTP 请求后,首先对请求进行转码,并将转码后的请求转发到 gRPC 服务,获取响应并以 HTTP 格式将其返回给客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TODO: use an image here to explain the concept better -->
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------------------------------------------- | ----- | ------ ------------------------------ |
|
||||
| proto_id | string/integer | 是 | | `.proto` 内容的 id。 |
|
||||
| service | string | 是 | | gRPC 服务名。 |
|
||||
| method | string | 是 | | gRPC 服务中要调用的方法名。 |
|
||||
| deadline | number | 否 | 0 | gRPC 服务的 deadline,单位为:ms。 |
|
||||
| pb_option | array[string([pb_option_def](#pb_option-的选项))] | 否 | | proto 编码过程中的转换选项。 |
|
||||
| show_status_in_body | boolean | 否 | false | 是否在返回体中展示解析过的 `grpc-status-details-bin` |
|
||||
| status_detail_type | string | 否 | | `grpc-status-details-bin` 中 [details](https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis/blob/b7cb84f5d42e6dba0fdcc2d8689313f6a8c9d7b9/google/rpc/status.proto#L46) 部分对应的 message type,如果不指定,此部分不进行解码 |
|
||||
|
||||
### pb_option 的选项
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 有效值 |
|
||||
|-----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| enum as result | `enum_as_name`, `enum_as_value` |
|
||||
| int64 as result | `int64_as_number`, `int64_as_string`, `int64_as_hexstring` |
|
||||
| default values | `auto_default_values`, `no_default_values`, `use_default_values`, `use_default_metatable` |
|
||||
| hooks | `enable_hooks`, `disable_hooks` |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
在启用插件之前,你必须将 `.proto` 或 `.pb` 文件的内容添加到 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用 `/admin/protos/id` 接口将文件的内容添加到 `content` 字段:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/protos/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"content" : "syntax = \"proto3\";
|
||||
package helloworld;
|
||||
service Greeter {
|
||||
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
message HelloRequest {
|
||||
string name = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
message HelloReply {
|
||||
string message = 1;
|
||||
}"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的 `.proto` 文件包含 `import`,或者想要把多个 `.proto` 文件合并成一个 proto,你可以生成一个 `.pb` 文件并在 APISIX 中使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
假设已经有一个 `.proto` 文件(`proto/helloworld.proto`),它导入了另一个 `proto` 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```proto
|
||||
syntax = "proto3";
|
||||
|
||||
package helloworld;
|
||||
import "proto/import.proto";
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
首先,让我们从 `.proto` 文件创建一个 `.pb` 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
protoc --include_imports --descriptor_set_out=proto.pb proto/helloworld.proto
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出的二进制文件 `proto.pb` 将同时包含 `helloworld.proto` 和 `import.proto`。
|
||||
|
||||
然后将 `proto.pb` 的内容作为 proto 的 `content` 字段提交。
|
||||
|
||||
由于 proto 的内容是二进制的,我们需要使用以下 shell 命令将其转换成 `base64`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/protos/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"content" : "'"$(base64 -w0 /path/to/proto.pb)"'"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
返回 `HTTP/1.1 201 Created` 结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{"node":{"value":{"create_time":1643879753,"update_time":1643883085,"content":"CmgKEnByb3RvL2ltcG9ydC5wcm90bxIDcGtnIhoKBFVzZXISEgoEbmFtZRgBIAEoCVIEbmFtZSIeCghSZXNwb25zZRISCgRib2R5GAEgASgJUgRib2R5QglaBy4vcHJvdG9iBnByb3RvMwq9AQoPcHJvdG8vc3JjLnByb3RvEgpoZWxsb3dvcmxkGhJwcm90by9pbXBvcnQucHJvdG8iPAoHUmVxdWVzdBIdCgR1c2VyGAEgASgLMgkucGtnLlVzZXJSBHVzZXISEgoEYm9keRgCIAEoCVIEYm9keTI5CgpUZXN0SW1wb3J0EisKA1J1bhITLmhlbGxvd29ybGQuUmVxdWVzdBoNLnBrZy5SZXNwb25zZSIAQglaBy4vcHJvdG9iBnByb3RvMw=="},"key":"\/apisix\/proto\/1"}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们可以在指定路由中启用 `grpc-transcode` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/grpctest",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"grpc-transcode": {
|
||||
"proto_id": "1",
|
||||
"service": "helloworld.Greeter",
|
||||
"method": "SayHello"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpc",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:50051": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
此处使用的 Upstream 应该是 gRPC 服务。请注意,`scheme` 需要设置为 `grpc`。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用 [grpc_server_example](https://github.com/api7/grpc_server_example) 进行测试。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述示例配置插件后,你可以向 APISIX 发出请求以从 gRPC 服务(通过 APISIX)获得响应:
|
||||
|
||||
访问上面配置的 route:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/grpctest?name=world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
返回结果
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Date: Fri, 16 Aug 2019 11:55:36 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
Proxy-Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
|
||||
{"message":"Hello world"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以配置 `pb_option`,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/23 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/zeebe/WorkflowInstanceCreate",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"grpc-transcode": {
|
||||
"proto_id": "1",
|
||||
"service": "gateway_protocol.Gateway",
|
||||
"method": "CreateWorkflowInstance",
|
||||
"pb_option":["int64_as_string"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpc",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:26500": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以通过如下命令检查刚刚配置的路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/zeebe/WorkflowInstanceCreate?bpmnProcessId=order-process&version=1&variables=\{\"orderId\":\"7\",\"ordervalue\":99\}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Date: Wed, 13 Nov 2019 03:38:27 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
grpc-encoding: identity
|
||||
grpc-accept-encoding: gzip
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
Trailer: grpc-status
|
||||
Trailer: grpc-message
|
||||
|
||||
{"workflowKey":"#2251799813685260","workflowInstanceKey":"#2251799813688013","bpmnProcessId":"order-process","version":1}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 在返回体中展示 `grpc-status-details-bin`
|
||||
|
||||
如果 gRPC 服务返回了错误,返回头中可能存在 `grpc-status-details-bin` 字段对错误进行描述,你可以解码该字段,并展示在返回体中。
|
||||
|
||||
上传 proto 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/protos/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"content" : "syntax = \"proto3\";
|
||||
package helloworld;
|
||||
service Greeter {
|
||||
rpc GetErrResp (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
message HelloRequest {
|
||||
string name = 1;
|
||||
repeated string items = 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
message HelloReply {
|
||||
string message = 1;
|
||||
repeated string items = 2;
|
||||
}"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启用 `grpc-transcode` 插件,并设置选项 `show_status_in_body` 为 `true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/grpctest",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"grpc-transcode": {
|
||||
"proto_id": "1",
|
||||
"service": "helloworld.Greeter",
|
||||
"method": "GetErrResp",
|
||||
"show_status_in_body": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpc",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:50051": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问上面配置的 route:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/grpctest?name=world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
返回结果
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable
|
||||
Date: Wed, 10 Aug 2022 08:59:46 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
grpc-status: 14
|
||||
grpc-message: Out of service
|
||||
grpc-status-details-bin: CA4SDk91dCBvZiBzZXJ2aWNlGlcKKnR5cGUuZ29vZ2xlYXBpcy5jb20vaGVsbG93b3JsZC5FcnJvckRldGFpbBIpCAESHFRoZSBzZXJ2ZXIgaXMgb3V0IG9mIHNlcnZpY2UaB3NlcnZpY2U
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
|
||||
{"error":{"details":[{"type_url":"type.googleapis.com\/helloworld.ErrorDetail","value":"\b\u0001\u0012\u001cThe server is out of service\u001a\u0007service"}],"message":"Out of service","code":14}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意返回体中还存在未解码的字段,如果需要解码该字段,需要在上传的 proto 文件中加上该字段对应的 `message type`。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/protos/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"content" : "syntax = \"proto3\";
|
||||
package helloworld;
|
||||
service Greeter {
|
||||
rpc GetErrResp (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
message HelloRequest {
|
||||
string name = 1;
|
||||
repeated string items = 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
message HelloReply {
|
||||
string message = 1;
|
||||
repeated string items = 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
message ErrorDetail {
|
||||
int64 code = 1;
|
||||
string message = 2;
|
||||
string type = 3;
|
||||
}"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时配置选项 `status_detail_type` 为 `helloworld.ErrorDetail`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/grpctest",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"grpc-transcode": {
|
||||
"proto_id": "1",
|
||||
"service": "helloworld.Greeter",
|
||||
"method": "GetErrResp",
|
||||
"show_status_in_body": true,
|
||||
"status_detail_type": "helloworld.ErrorDetail"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpc",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:50051": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时就能返回完全解码后的结果
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable
|
||||
Date: Wed, 10 Aug 2022 09:02:46 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
grpc-status: 14
|
||||
grpc-message: Out of service
|
||||
grpc-status-details-bin: CA4SDk91dCBvZiBzZXJ2aWNlGlcKKnR5cGUuZ29vZ2xlYXBpcy5jb20vaGVsbG93b3JsZC5FcnJvckRldGFpbBIpCAESHFRoZSBzZXJ2ZXIgaXMgb3V0IG9mIHNlcnZpY2UaB3NlcnZpY2U
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
|
||||
{"error":{"details":[{"type":"service","message":"The server is out of service","code":1}],"message":"Out of service","code":14}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `grpc-transcode` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/111 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/grpctest",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"scheme": "grpc",
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:50051": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: grpc-web
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- gRPC Web
|
||||
- grpc-web
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `grpc-web` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`grpc-web` 插件是一个代理插件,可以处理从 JavaScript 客户端到 gRPC Service 的 [gRPC Web](https://github.com/grpc/grpc-web) 请求。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|---------------------| ------- |----|-----------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| cors_allow_headers | string | 否 | "content-type,x-grpc-web,x-user-agent" | 允许跨域访问时请求方携带哪些非 `CORS 规范` 以外的 Header。如果你有多个 Header,请使用 `,` 分割。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过如下命令在指定路由上启用 `gRPC-web` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri":"/grpc/web/*",
|
||||
"plugins":{
|
||||
"grpc-web":{}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"scheme":"grpc",
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes":{
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::info IMPORTANT
|
||||
|
||||
在使用 `gRPC Web` 代理插件时,路由必须使用**前缀匹配**模式(例如:`/*` 或 `/grpc/example/*`),因为 `gRPC Web` 客户端会在 URI 中传递 `proto` 中声明的**包名称**、**服务接口名称**、**方法名称**等信息(例如:`/path/a6.RouteService/Insert`)。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,在使用**绝对匹配**时将无法命中插件和提取 `proto` 信息。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
请参考 [gRPC-Web Client Runtime Library](https://www.npmjs.com/package/grpc-web) 或 [Apache APISIX gRPC Web Test Framework](https://github.com/apache/apisix/tree/master/t/plugin/grpc-web) 了解如何配置你的 Web 客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
运行 gRPC Web 客户端后,你可以从浏览器或通过 Node.js 向 APISIX 发出请求。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
请求方式仅支持 `POST` 和 `OPTIONS`,详细信息请参考:[CORS support](https://github.com/grpc/grpc-web/blob/master/doc/browser-features.md#cors-support) 。
|
||||
|
||||
内容类型支持 `application/grpc-web`、`application/grpc-web-text`、`application/grpc-web+proto`、`application/grpc-web-text+proto`,详细信息请参考:[Protocol differences vs gRPC over HTTP2](https://github.com/grpc/grpc/blob/master/doc/PROTOCOL-WEB.md#protocol-differences-vs-grpc-over-http2) 。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `grpc-web` 插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 `JSON` 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri":"/grpc/web/*",
|
||||
"plugins":{},
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"scheme":"grpc",
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes":{
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: gzip
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- gzip
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `gzip` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`gzip` 插件能动态设置 [NGINX](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/web-server/compression/) 的压缩行为。
|
||||
当启用 `gzip` 插件时,客户端在发起请求时需要在请求头中添加 `Accept-Encoding: gzip`,以表明客户端支持 `gzip` 压缩。APISIX 在接收到请求后,会根据客户端的支持情况和服务器配置动态判断是否对响应内容进行 gzip 压缩。如果判定条件得到满足,APISIX 将在响应头中添加 `Content-Encoding: gzip` 字段,以指示响应内容已经通过 `gzip` 压缩。在客户端接收到响应后,根据响应头中的 `Content-Encoding` 字段使用相应的解压缩算法对响应内容进行解压,从而获取原始的响应内容。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info IMPORTANT
|
||||
|
||||
该插件要求 Apache APISIX 运行在 [APISIX-Runtime](../FAQ.md#如何构建-apisix-runtime-环境) 上。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------| -------------------- | ------- | -------------- | ------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| types | array[string] or "*" | 否 | ["text/html"] | | 动态设置 [`gzip_types`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_types) 指令,特殊值 `"*"` 匹配任何 MIME 类型。 |
|
||||
| min_length | integer | 否 | 20 | >= 1 | 动态设置 [`gzip_min_length`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_min_length) 指令。 |
|
||||
| comp_level | integer | 否 | 1 | [1, 9] | 动态设置 [`gzip_comp_level`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_comp_level) 指令。 |
|
||||
| http_version | number | 否 | 1.1 | 1.1, 1.0 | 动态设置 [`gzip_http_version`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_http_version) 指令。 |
|
||||
| buffers.number | integer | 否 | 32 | >= 1 | 动态设置 [`gzip_buffers`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_buffers) 指令 参数 `number`。 |
|
||||
| buffers.size | integer | 否 | 4096 | >= 1 | 动态设置 [`gzip_buffers`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_buffers) 指令参数 `size`。单位为字节。 |
|
||||
| vary | boolean | 否 | false | | 动态设置 [`gzip_vary`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_vary) 指令。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由中启用 `gzip` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"gzip": {
|
||||
"buffers": {
|
||||
"number": 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html -i -H "Accept-Encoding: gzip"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
|
||||
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Wed, 21 Jul 2021 03:52:55 GMT
|
||||
Server: APISIX/2.7
|
||||
Content-Encoding: gzip
|
||||
|
||||
Warning: Binary output can mess up your terminal. Use "--output -" to tell
|
||||
Warning: curl to output it to your terminal anyway, or consider "--output
|
||||
Warning: <FILE>" to save to a file.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `gzip` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,760 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: hmac-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- HMAC Authentication
|
||||
- hmac-auth
|
||||
description: hmac-auth 插件支持 HMAC 认证,保证请求的完整性,防止传输过程中的修改,增强 API 的安全性。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`hmac-auth` 插件支持 HMAC(基于哈希的消息认证码)认证,作为一种确保请求完整性的机制,防止它们在传输过程中被修改。要使用该插件,您需要在 [Consumers](../terminology/consumer.md) 上配置 HMAC 密钥,并在 Routes 或 Services 上启用该插件。
|
||||
|
||||
当消费者成功通过身份验证后,APISIX 会在将请求代理到上游服务之前向请求添加其他标头,例如 `X-Consumer-Username`、`X-Credential-Indentifier` 和其他消费者自定义标头(如果已配置)。上游服务将能够区分消费者并根据需要实现其他逻辑。如果这些值中的任何一个不可用,则不会添加相应的标头。
|
||||
|
||||
启用后,插件会验证请求的 `Authorization` 标头中的 HMAC 签名,并检查传入的请求是否来自受信任的来源。具体来说,当 APISIX 收到 HMAC 签名的请求时,会从 `Authorization` 标头中提取密钥 ID。然后,APISIX 会检索相应的消费者配置,包括密钥。如果密钥 ID 有效且存在,APISIX 将使用请求的 `Date` 标头和密钥生成 HMAC 签名。如果生成的签名与 `Authorization` 标头中提供的签名匹配,则请求通过身份验证并转发到上游服务。
|
||||
|
||||
插件实现基于 [draft-cavage-http-signatures](https://www.ietf.org/archive/id/draft-cavage-http-signatures-12.txt)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
以下属性可用于 Consumers 或 Credentials 的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------------- | ------ | ------------- | ------------------------------------------| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| access_key | string | 是 | | | 消费者的唯一标识符,用于标识相关配置,例如密钥。 |
|
||||
| secret_key | string | 是 | | | 用于生成 HMAC 的密钥。此字段支持使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源将值保存在 Secret Manager 中。 |
|
||||
|
||||
以下属性可用于 Routes 或 Services 的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------------- | ------ | ------------- | ------------------------------------------| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| allowed_algorithms | array[string] | 否 | ["hmac-sha1", "hmac-sha256", "hmac-sha512"] | "hmac-sha1"、"hmac-sha256" 和 "hmac-sha512" 的组合 | 允许的 HMAC 算法列表。 |
|
||||
| clock_skew | integer | 否 | 300 | >=1 | 客户端请求的时间戳与 APISIX 服务器当前时间之间允许的最大时间差(以秒为单位)。这有助于解决客户端和服务器之间的时间同步差异,并防止重放攻击。时间戳将根据 Date 头中的时间(必须为 GMT 格式)进行计算。 |
|
||||
| signed_headers | array[string] | 否 | | | 客户端请求的 HMAC 签名中应包含的 HMAC 签名头列表。 |
|
||||
| validate_request_body | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则验证请求正文的完整性,以确保在传输过程中没有被篡改。具体来说,插件会创建一个 SHA-256 的 base64 编码 digest,并将其与 `Digest` 头进行比较。如果 `Digest` 头丢失或 digest 不匹配,验证将失败。 |
|
||||
| hide_credentials | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则不会将授权请求头传递给上游服务。 |
|
||||
| anonymous_consumer | string | 否 | | | 匿名消费者名称。如果已配置,则允许匿名用户绕过身份验证。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"secret_key"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例说明了如何在不同场景中使用“hmac-auth”插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 在路由上实现 HMAC 身份验证
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在路由上实现 HMAC 身份验证。您还将在 `Consumer-Custom-Id` 标头中将消费者自定义 ID 附加到经过身份验证的请求,该 ID 可用于根据需要实现其他逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有自定义 ID 标签的消费者 `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john",
|
||||
"labels": {
|
||||
"custom_id": "495aec6a"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `hmac-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"key_id": "john-key",
|
||||
"secret_key": "john-secret-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `hmac-auth` 插件的默认配置创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "hmac-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成签名。您可以使用以下 Python 代码片段或其他技术栈:
|
||||
|
||||
```python title="hmac-sig-header-gen.py"
|
||||
import hmac
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
from datetime import datetime, timezone
|
||||
|
||||
key_id = "john-key" # key id
|
||||
secret_key = b"john-secret-key" # secret key
|
||||
request_method = "GET" # HTTP method
|
||||
request_path = "/get" # Route URI
|
||||
algorithm= "hmac-sha256" # can use other algorithms in allowed_algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
# get current datetime in GMT
|
||||
# note: the signature will become invalid after the clock skew (default 300s)
|
||||
# you can regenerate the signature after it becomes invalid, or increase the clock
|
||||
# skew to prolong the validity within the advised security boundary
|
||||
gmt_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the signing string (ordered)
|
||||
# the date and any subsequent custom headers should be lowercased and separated by a
|
||||
# single space character, i.e. `<key>:<space><value>`
|
||||
# https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-cavage-http-signatures-12#section-2.1.6
|
||||
signing_string = (
|
||||
f"{key_id}\n"
|
||||
f"{request_method} {request_path}\n"
|
||||
f"date: {gmt_time}\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# create signature
|
||||
signature = hmac.new(secret_key, signing_string.encode('utf-8'), hashlib.sha256).digest()
|
||||
signature_base64 = base64.b64encode(signature).decode('utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the request headers
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Date": gmt_time,
|
||||
"Authorization": (
|
||||
f'Signature keyId="{key_id}",algorithm="{algorithm}",'
|
||||
f'headers="@request-target date",'
|
||||
f'signature="{signature_base64}"'
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# print headers
|
||||
print(headers)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 hmac-sig-header-gen.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到打印的请求标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{'Date': 'Fri, 06 Sep 2024 06:41:29 GMT', 'Authorization': 'Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="wWfKQvPDr0wHQ4IHdluB4IzeNZcj0bGJs2wvoCOT5rM="'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用生成的标头,向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X GET "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" \
|
||||
-H "Date: Fri, 06 Sep 2024 06:41:29 GMT" \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="wWfKQvPDr0wHQ4IHdluB4IzeNZcj0bGJs2wvoCOT5rM="'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "Signature keyId=\"john-key\",algorithm=\"hmac-sha256\",headers=\"@request-target date\",signature=\"wWfKQvPDr0wHQ4IHdluB4IzeNZcj0bGJs2wvoCOT5rM=\"",
|
||||
"Date": "Fri, 06 Sep 2024 06:41:29 GMT",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66d96513-2e52d4f35c9b6a2772d667ea",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Custom-Id": "495aec6a",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 34.0.34.160",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Hide Authorization Information From Upstream
|
||||
|
||||
As seen the in the [last example](#implement-hmac-authentication-on-a-route), the `Authorization` header passed to the Upstream includes the signature and all other details. This could potentially introduce security risks.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to prevent these information from being sent to the Upstream service.
|
||||
|
||||
Update the plugin configuration to set `hide_credentials` to `true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/hmac-auth-route" -X PATCH \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"hide_credentials": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Send a request to the route:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X GET "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" \
|
||||
-H "Date: Fri, 06 Sep 2024 06:41:29 GMT" \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="wWfKQvPDr0wHQ4IHdluB4IzeNZcj0bGJs2wvoCOT5rM="'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You should see an `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` response and notice the `Authorization` header is entirely removed:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66d96513-2e52d4f35c9b6a2772d667ea",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 34.0.34.160",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Enable Body Validation
|
||||
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to enable body validation to ensure the integrity of the request body.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a consumer `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `hmac-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"key_id": "john-key",
|
||||
"secret_key": "john-secret-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a Route with the `hmac-auth` plugin as such:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "hmac-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/post",
|
||||
"methods": ["POST"],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"validate_request_body": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成签名。您可以使用以下 Python 代码片段或其他技术栈:
|
||||
|
||||
```python title="hmac-sig-digest-header-gen.py"
|
||||
import hmac
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
from datetime import datetime, timezone
|
||||
|
||||
key_id = "john-key" # key id
|
||||
secret_key = b"john-secret-key" # secret key
|
||||
request_method = "POST" # HTTP method
|
||||
request_path = "/post" # Route URI
|
||||
algorithm= "hmac-sha256" # can use other algorithms in allowed_algorithms
|
||||
body = '{"name": "world"}' # example request body
|
||||
|
||||
# get current datetime in GMT
|
||||
# note: the signature will become invalid after the clock skew (default 300s).
|
||||
# you can regenerate the signature after it becomes invalid, or increase the clock
|
||||
# skew to prolong the validity within the advised security boundary
|
||||
gmt_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the signing string (ordered)
|
||||
# the date and any subsequent custom headers should be lowercased and separated by a
|
||||
# single space character, i.e. `<key>:<space><value>`
|
||||
# https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-cavage-http-signatures-12#section-2.1.6
|
||||
signing_string = (
|
||||
f"{key_id}\n"
|
||||
f"{request_method} {request_path}\n"
|
||||
f"date: {gmt_time}\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# create signature
|
||||
signature = hmac.new(secret_key, signing_string.encode('utf-8'), hashlib.sha256).digest()
|
||||
signature_base64 = base64.b64encode(signature).decode('utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
# create the SHA-256 digest of the request body and base64 encode it
|
||||
body_digest = hashlib.sha256(body.encode('utf-8')).digest()
|
||||
body_digest_base64 = base64.b64encode(body_digest).decode('utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the request headers
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Date": gmt_time,
|
||||
"Digest": f"SHA-256={body_digest_base64}",
|
||||
"Authorization": (
|
||||
f'Signature keyId="{key_id}",algorithm="hmac-sha256",'
|
||||
f'headers="@request-target date",'
|
||||
f'signature="{signature_base64}"'
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# print headers
|
||||
print(headers)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 hmac-sig-digest-header-gen.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到打印的请求标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{'Date': 'Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:16:16 GMT', 'Digest': 'SHA-256=78qzJuLwSpZ8HacsTdFCQJWxzPMOf8bYctRk2ySLpS8=', 'Authorization': 'Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="rjS6NxOBKmzS8CZL05uLiAfE16hXdIpMD/L/HukOTYE="'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用生成的标头,向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/post" -X POST \
|
||||
-H "Date: Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:16:16 GMT" \
|
||||
-H "Digest: SHA-256=78qzJuLwSpZ8HacsTdFCQJWxzPMOf8bYctRk2ySLpS8=" \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="rjS6NxOBKmzS8CZL05uLiAfE16hXdIpMD/L/HukOTYE="' \
|
||||
-d '{"name": "world"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {
|
||||
"{\"name\": \"world\"}": ""
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "Signature keyId=\"john-key\",algorithm=\"hmac-sha256\",headers=\"@request-target date\",signature=\"rjS6NxOBKmzS8CZL05uLiAfE16hXdIpMD/L/HukOTYE=\"",
|
||||
"Content-Length": "17",
|
||||
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
|
||||
"Date": "Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:16:16 GMT",
|
||||
"Digest": "SHA-256=78qzJuLwSpZ8HacsTdFCQJWxzPMOf8bYctRk2ySLpS8=",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66d978c3-49f929ad5237da5340bbbeb4",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 34.0.34.160",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/post"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果您发送的请求没有摘要或摘要无效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/post" -X POST \
|
||||
-H "Date: Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:16:16 GMT" \
|
||||
-H "Digest: SHA-256=78qzJuLwSpZ8HacsTdFCQJWxzPMOf8bYctRk2ySLpS8=" \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="rjS6NxOBKmzS8CZL05uLiAfE16hXdIpMD/L/HukOTYE="' \
|
||||
-d '{"name": "world"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应,其中包含以下消息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"client request can't be validated"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 强制签名标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何强制在请求的 HMAC 签名中对某些标头进行签名。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `hmac-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"key_id": "john-key",
|
||||
"secret_key": "john-secret-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `hmac-auth` 插件创建路由,该插件要求 HMAC 签名中存在三个标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "hmac-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"signed_headers": ["date","x-custom-header-a","x-custom-header-b"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成签名。您可以使用以下 Python 代码片段或其他技术栈:
|
||||
|
||||
```python title="hmac-sig-req-header-gen.py"
|
||||
import hmac
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
from datetime import datetime, timezone
|
||||
|
||||
key_id = "john-key" # key id
|
||||
secret_key = b"john-secret-key" # secret key
|
||||
request_method = "GET" # HTTP method
|
||||
request_path = "/get" # Route URI
|
||||
algorithm= "hmac-sha256" # can use other algorithms in allowed_algorithms
|
||||
custom_header_a = "hello123" # required custom header
|
||||
custom_header_b = "world456" # required custom header
|
||||
|
||||
# get current datetime in GMT
|
||||
# note: the signature will become invalid after the clock skew (default 300s)
|
||||
# you can regenerate the signature after it becomes invalid, or increase the clock
|
||||
# skew to prolong the validity within the advised security boundary
|
||||
gmt_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the signing string (ordered)
|
||||
# the date and any subsequent custom headers should be lowercased and separated by a
|
||||
# single space character, i.e. `<key>:<space><value>`
|
||||
# https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-cavage-http-signatures-12#section-2.1.6
|
||||
signing_string = (
|
||||
f"{key_id}\n"
|
||||
f"{request_method} {request_path}\n"
|
||||
f"date: {gmt_time}\n"
|
||||
f"x-custom-header-a: {custom_header_a}\n"
|
||||
f"x-custom-header-b: {custom_header_b}\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# create signature
|
||||
signature = hmac.new(secret_key, signing_string.encode('utf-8'), hashlib.sha256).digest()
|
||||
signature_base64 = base64.b64encode(signature).decode('utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the request headers
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Date": gmt_time,
|
||||
"Authorization": (
|
||||
f'Signature keyId="{key_id}",algorithm="hmac-sha256",'
|
||||
f'headers="@request-target date x-custom-header-a x-custom-header-b",'
|
||||
f'signature="{signature_base64}"'
|
||||
),
|
||||
"x-custom-header-a": custom_header_a,
|
||||
"x-custom-header-b": custom_header_b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# print headers
|
||||
print(headers)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 hmac-sig-req-header-gen.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到打印的请求标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{'Date': 'Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:58:49 GMT', 'Authorization': 'Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date x-custom-header-a x-custom-header-b",signature="MwJR8JOhhRLIyaHlJ3Snbrf5hv0XwdeeRiijvX3A3yE="', 'x-custom-header-a': 'hello123', 'x-custom-header-b': 'world456'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用生成的标头,向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X GET "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" \
|
||||
-H "Date: Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:58:49 GMT" \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date x-custom-header-a x-custom-header-b",signature="MwJR8JOhhRLIyaHlJ3Snbrf5hv0XwdeeRiijvX3A3yE="' \
|
||||
-H "x-custom-header-a: hello123" \
|
||||
-H "x-custom-header-b: world456"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "Signature keyId=\"john-key\",algorithm=\"hmac-sha256\",headers=\"@request-target date x-custom-header-a x-custom-header-b\",signature=\"MwJR8JOhhRLIyaHlJ3Snbrf5hv0XwdeeRiijvX3A3yE=\"",
|
||||
"Date": "Fri, 06 Sep 2024 09:58:49 GMT",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66d98196-64a58db25ece71c077999ecd",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "john",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"X-Custom-Header-A": "hello123",
|
||||
"X-Custom-Header-B": "world456",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 103.97.2.206",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 匿名消费者的速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为常规消费者和匿名消费者配置不同的速率限制策略,其中匿名消费者不需要进行身份验证,配额较少。
|
||||
|
||||
创建常规消费者 `john`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内的配额为 3:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 3,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者 `john` 创建 `hmac-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-hmac-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"key_id": "john-key",
|
||||
"secret_key": "john-secret-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建匿名用户 `anonymous`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内配额为 1:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "anonymous",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由并配置 `hmac-auth` 插件以接受匿名消费者 `anonymous` 绕过身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "hmac-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"hmac-auth": {
|
||||
"anonymous_consumer": "anonymous"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成签名。您可以使用以下 Python 代码片段或其他技术栈:
|
||||
|
||||
```python title="hmac-sig-header-gen.py"
|
||||
import hmac
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
from datetime import datetime, timezone
|
||||
|
||||
key_id = "john-key" # key id
|
||||
secret_key = b"john-secret-key" # secret key
|
||||
request_method = "GET" # HTTP method
|
||||
request_path = "/get" # Route URI
|
||||
algorithm= "hmac-sha256" # can use other algorithms in allowed_algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
# get current datetime in GMT
|
||||
# note: the signature will become invalid after the clock skew (default 300s)
|
||||
# you can regenerate the signature after it becomes invalid, or increase the clock
|
||||
# skew to prolong the validity within the advised security boundary
|
||||
gmt_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the signing string (ordered)
|
||||
# the date and any subsequent custom headers should be lowercased and separated by a
|
||||
# single space character, i.e. `<key>:<space><value>`
|
||||
# https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-cavage-http-signatures-12#section-2.1.6
|
||||
signing_string = (
|
||||
f"{key_id}\n"
|
||||
f"{request_method} {request_path}\n"
|
||||
f"date: {gmt_time}\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# create signature
|
||||
signature = hmac.new(secret_key, signing_string.encode('utf-8'), hashlib.sha256).digest()
|
||||
signature_base64 = base64.b64encode(signature).decode('utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
# construct the request headers
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Date": gmt_time,
|
||||
"Authorization": (
|
||||
f'Signature keyId="{key_id}",algorithm="{algorithm}",'
|
||||
f'headers="@request-target date",'
|
||||
f'signature="{signature_base64}"'
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# print headers
|
||||
print(headers)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 hmac-sig-header-gen.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到打印的请求标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{'Date': 'Mon, 21 Oct 2024 17:31:18 GMT', 'Authorization': 'Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="ztFfl9w7LmCrIuPjRC/DWSF4gN6Bt8dBBz4y+u1pzt8="'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用生成的标头发送五个连续的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H "Date: Mon, 21 Oct 2024 17:31:18 GMT" -H 'Authorization: Signature keyId="john-key",algorithm="hmac-sha256",headers="@request-target date",signature="ztFfl9w7LmCrIuPjRC/DWSF4gN6Bt8dBBz4y+u1pzt8="' -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,显示在 5 个请求中,3 个请求成功(状态代码 200),而其他请求被拒绝(状态代码 429)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 3, 429: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送五个匿名请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,表明只有一个请求成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 1, 429: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
124
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/plugins/http-dubbo.md
Executable file
124
CloudronPackages/APISIX/apisix-source/docs/zh/latest/plugins/http-dubbo.md
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: http-dubbo
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- http-dubbo
|
||||
- http to dubbo
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `http-dubbo` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`http-dubbo` 插件可以将 http 请求 encode 为 dubbo 协议转发给上游服务(注意:在 dubbo2.x 时上游服务的序列化类型必须是 fastjson)
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | ------- |-----| ------ | ----------- |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| service_name | string | 是 | | | dubbo 服务名 |
|
||||
| service_version | string | 否 | 0.0.0 | | dubbo 服务版本 默认 0.0.0 |
|
||||
| method | string | 是 | | | dubbo 服务方法名 |
|
||||
| params_type_desc | string | 否 | | | dubbo 服务方法签名描述,入参如果是 void 可不填写 |
|
||||
| serialization_header_key | string | 否 | | | 插件会读取该请求头判断 body 是否已经按照 dubbo 协议序列化完毕。如果该请求头的值为 true 则插件不会更改 body 内容,直接把他当作 dubbo 请求参数。如果为 false 则要求开发者按照 dubbo 泛化调用的格式传递参数,由插件进行序列化。注意:由于 lua 和 java 的插件序列化精度不同,可能会导致参数精度不同。 |
|
||||
| serialized | boolean | 否 | false | [true, false] | 和`serialization_header_key`一样。优先级低于`serialization_header_key` |
|
||||
| connect_timeout | number | 否 | 6000 | | 上游服务 tcp connect_timeout |
|
||||
| read_timeout | number | 否 | 6000 | | 上游服务 tcp read_timeout |
|
||||
| send_timeout | number | 否 | 6000 | | 上游服务 tcp send_timeout |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由中启用 `http-dubbo` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/TestService/testMethod",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"http-dubbo": {
|
||||
"method": "testMethod",
|
||||
"params_type_desc": "Ljava/lang/Long;Ljava/lang/Integer;",
|
||||
"serialized": true,
|
||||
"service_name": "com.xxx.xxx.TestService",
|
||||
"service_version": "0.0.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以使用如下命令测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:9080/TestService/testMethod' \
|
||||
--data '1
|
||||
2'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何获取 params_type_desc
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
Method[] declaredMethods = YourService.class.getDeclaredMethods();
|
||||
String params_type_desc = ReflectUtils.getDesc(Arrays.stream(declaredMethods).filter(it->it.getName().equals("yourmethod")).findAny().get().getParameterTypes());
|
||||
|
||||
//方法重载情况下需要找自己需要暴露的方法 ReflectUtils 为 dubbo 实现
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何按照 dubbo 协议使用 json 进行序列化
|
||||
|
||||
为了防止精度丢失。我们推荐使用序列化好的 body 进行请求。
|
||||
dubbo 的 fastjson 序列化规则如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 每个参数之间使用 toJSONString 转化为 JSON 字符串
|
||||
|
||||
- 每个参数之间使用换行符 `\n` 分隔
|
||||
|
||||
部分语言和库在字符串或数字调用 toJSONString 后结果是不变的这可能需要你手动处理一些特殊情况例如:
|
||||
|
||||
- 字符串 `abc"` 需要被 encode 为 `"abc\""`
|
||||
|
||||
- 字符串 `123` 需要被 encode 为 `"123"`
|
||||
|
||||
抽象类,父类或者泛型作为入参签名,入参需要具体类型时。序列化需要写入具体的类型信息具体参考 [WriteClassName](https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/SerializerFeature_cn)
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `http-dubbo` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: http-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 插件
|
||||
- HTTP Logger
|
||||
- 日志
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 API 网关 Apache APISIX 的 http-logger 插件。使用该插件可以将 APISIX 的日志数据推送到 HTTP 或 HTTPS 服务器。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`http-logger` 插件可以将 APISIX 的日志数据推送到 HTTP 或 HTTPS 服务器。该插件提供了将日志数据请求作为 JSON 对象发送到监控工具或者其他 HTTP 服务器的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|-------------------------| ------- |-----| ------------- | -------------------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| uri | string | 是 | | | HTTP 或 HTTPS 服务器的 URI。 |
|
||||
| auth_header | string | 否 | | | 授权 header(如果需要)。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3 | [1,...] | 发送请求后保持连接处于活动状态的时间。 |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,将请求体包含在日志中。如果请求体太大而无法保存在内存中,由于 NGINX 的限制,无法记录。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array | 否 | | | 当 `include_req_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时的过滤器。只有当此处设置的表达式求值为 `true` 时,才会记录请求体。有关更多信息,请参阅 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含响应体。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array | 否 | | | 当 `include_resp_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时,使用该属性并基于 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 进行过滤。如果存在,则仅在表达式计算结果为 `true` 时记录响应。 |
|
||||
| concat_method | string | 否 | "json" | ["json", "new_line"] | 枚举类型: **json**:对所有待发日志使用 `json.encode` 编码。**new_line**:对每一条待发日志单独使用 `json.encode` 编码并使用 `\n` 连接起来。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时验证证书。 |
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志和数据)。这样可以避免该插件频繁地提交数据。默认情况下每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时,批处理器会自动提交数据,如需了解更多信息或自定义配置,请参考 [Batch Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认日志格式示例
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 100.99999809265,
|
||||
"start_time": 1703907485819,
|
||||
"latency": 101.99999809265,
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 1,
|
||||
"client_ip": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"route_id": "1",
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"version": "3.7.0",
|
||||
"hostname": "localhost"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:1984",
|
||||
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
|
||||
"user-agent": "lua-resty-http/0.16.1 (Lua) ngx_lua/10025",
|
||||
"content-length": "12"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"size": 194,
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:1984/hello?log_body=no",
|
||||
"uri": "/hello?log_body=no",
|
||||
"querystring": {
|
||||
"log_body": "no"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"content-type": "text/plain",
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"content-length": "12",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.7.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"size": 123
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": "127.0.0.1:1982"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头。则表明获取 [APISIX 变量](../../../en/latest/apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 注意
|
||||
|
||||
该设置全局生效。如果指定了 `log_format`,则所有绑定 `http-logger` 的路由或服务都将使用该日志格式。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过 Admin API 配置插件元数据:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/http-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
配置完成后,你将在日志系统中看到如下类似日志:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
{"host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2020-09-23T19:05:05-04:00","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","route_id":"1"}
|
||||
{"host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2020-09-23T19:05:05-04:00","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","route_id":"1"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过如下命令在指定路由上启用 `http-logger` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"http-logger": {
|
||||
"uri": "http://mockbin.org/bin/:ID"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[mockbin](http://mockbin.org/bin/create) 服务器用于模拟 HTTP 服务器,以方便查看 APISIX 生成的日志。
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令向 APISIX 发出请求,访问日志将记录在你的 `mockbin` 服务器中:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ip-restriction
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- IP restriction
|
||||
- ip-restriction
|
||||
description: ip-restriction 插件支持通过配置 IP 地址白名单或黑名单来限制 IP 地址对上游资源的访问。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/ip-restriction" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`ip-restriction` 插件支持通过配置 IP 地址白名单或黑名单来限制 IP 地址对上游资源的访问。限制 IP 对资源的访问有助于防止未经授权的访问并加强 API 安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | -------------------------------- |
|
||||
| whitelist | array[string] | 否 | | | 要列入白名单的 IP 列表。支持 IPv4、IPv6 和 CIDR 表示法。 |
|
||||
| blacklist | array[string] | 否 | | | 要列入黑名单的 IP 列表。支持 IPv4、IPv6 和 CIDR 表示法。 |
|
||||
| message | string | 否 | "Your IP address is not allowed" | [1, 1024] | 在未允许的 IP 访问的情况下返回的信息。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
`whitelist` 或 `blacklist` 至少配置一个,但不能同时配置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何针对不同场景配置 `ip-restriction` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过白名单限制访问
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何将有权访问上游资源的 IP 地址列表列入白名单,并自定义拒绝访问的错误消息。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `ip-restriction` 插件创建路由,将一系列 IP 列入白名单,并自定义拒绝访问时的错误消息:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "ip-restriction-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"ip-restriction": {
|
||||
"whitelist": [
|
||||
"192.168.0.1/24"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"message": "Access denied"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果您的 IP 被允许,您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。如果不允许,您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden` 响应,并显示以下错误消息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"Access denied"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用修改后的 IP 限制访问
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何使用 `real-ip` 插件修改用于 IP 限制的 IP。如果 APISIX 位于反向代理之后,并且 APISIX 无法获得真实客户端 IP,则此功能特别有用。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `ip-restriction` 插件创建路由,将特定 IP 地址列入白名单,并从 URL 参数 `realip` 获取客户端 IP 地址:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "ip-restriction-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"ip-restriction": {
|
||||
"whitelist": [
|
||||
"192.168.1.241"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"real-ip": {
|
||||
"source": "arg_realip"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?realip=192.168.1.241"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
使用不同的 IP 地址发送另一个请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?realip=192.168.10.24"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden` 响应。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: jwe-decrypt
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- APISIX 插件
|
||||
- JWE Decrypt
|
||||
- jwe-decrypt
|
||||
description: 本文档包含了关于 APISIX jwe-decrypt 插件的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`jwe-decrypt` 插件,用于解密 APISIX [Service](../terminology/service.md) 或者 [Route](../terminology/route.md) 请求中的 [JWE](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7516) 授权请求头。
|
||||
|
||||
插件增加了一个 `/apisix/plugin/jwe/encrypt` 的内部 API,提供给 JWE 加密使用。解密时,秘钥应该配置在 [Consumer](../terminology/consumer.md)内。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer 配置:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|---------------|---------|-------|-------|-----|-------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| key | string | True | | | Consumer 的唯一 key |
|
||||
| secret | string | True | | | 解密密钥,必须为 32 位。秘钥可以使用 [Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源保存在密钥管理服务中 |
|
||||
| is_base64_encoded | boolean | False | false | | 如果密钥是 Base64 编码,则需要配置为 `true` |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
注意,在启用 `is_base64_encoded` 后,你的 `secret` 长度可能会超过 32 位,你只需要保证在 Decode 后的长度仍然是 32 位即可。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Route 配置:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|----------------|---------|-------|---------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| header | string | True | Authorization | 指定请求头,用于获取加密令牌 |
|
||||
| forward_header | string | True | Authorization | 传递给 Upstream 的请求头名称 |
|
||||
| strict | boolean | False | true | 如果为配置为 true,请求中缺失 JWE token 则抛出 `403` 异常。如果为 `false`, 在缺失 JWE token 的情况下不会抛出异常 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
首先,基于 `jwe-decrypt` 插件创建一个 Consumer,并且配置解密密钥:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "jack",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwe-decrypt": {
|
||||
"key": "user-key",
|
||||
"secret": "-secret-length-must-be-32-chars-"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,基于 `jwe-decrypt` 插件创建一个路由,用于解密 authorization 请求头:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/anything*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwe-decrypt": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 JWE 加密数据
|
||||
|
||||
该插件创建了一个内部的 API `/apisix/plugin/jwe/encrypt` 以使用 JWE 进行加密。要公开它,需要创建一个对应的路由,并启用 [public-api](public-api.md) 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/jwenew -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/plugin/jwe/encrypt",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 API 发送一个请求,将 Consumer 中配置的密钥,以参数的方式传递给 URI,用于加密 payload 中的一些数据。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -G --data-urlencode 'payload={"uid":10000,"uname":"test"}' 'http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/plugin/jwe/encrypt?key=user-key' -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似于如下内容的响应结果,其中 JWE 加密的数据位于响应体中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Date: Mon, 25 Sep 2023 02:38:16 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.5.0
|
||||
Apisix-Plugins: public-api
|
||||
|
||||
eyJhbGciOiJkaXIiLCJraWQiOiJ1c2VyLWtleSIsImVuYyI6IkEyNTZHQ00ifQ..MTIzNDU2Nzg5MDEy.hfzMJ0YfmbMcJ0ojgv4PYAHxPjlgMivmv35MiA.7nilnBt2dxLR_O6kf-HQUA
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 JWE 解密数据
|
||||
|
||||
将加密数据放在 `Authorization` 请求头中,向 API 发起请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything/hello -H 'Authorization: eyJhbGciOiJkaXIiLCJraWQiOiJ1c2VyLWtleSIsImVuYyI6IkEyNTZHQ00ifQ..MTIzNDU2Nzg5MDEy.hfzMJ0YfmbMcJ0ojgv4PYAHxPjlgMivmv35MiA.7nilnBt2dxLR_O6kf-HQUA' -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该可以看到类似于如下的响应内容,其中 `Authorization` 响应头显示了有效的解密内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json
|
||||
Content-Length: 452
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Date: Mon, 25 Sep 2023 02:38:59 GMT
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
|
||||
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
|
||||
Server: APISIX/3.5.0
|
||||
Apisix-Plugins: jwe-decrypt
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "{\"uid\":10000,\"uname\":\"test\"}",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.1.2",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6510f2c3-1586ec011a22b5094dbe1896",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 119.143.79.94",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything/hello"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
要删除 `jwe-decrypt` 插件,您可以从插件配置中删除插件对应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 会自动加载,您不需要重新启动即可生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/anything*",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,907 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: jwt-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- JWT Auth
|
||||
- jwt-auth
|
||||
description: jwt-auth 插件支持使用 JSON Web Token (JWT) 作为客户端在访问上游资源之前进行身份验证的机制。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`jwt-auth` 插件支持使用 [JSON Web Token (JWT)](https://jwt.io/) 作为客户端在访问上游资源之前进行身份验证的机制。
|
||||
|
||||
启用后,该插件会公开一个端点,供 [消费者](../terminology/consumer.md) 创建 JWT 凭据。该过程会生成一个令牌,客户端请求应携带该令牌以向 APISIX 标识自己。该令牌可以包含在请求 URL 查询字符串、请求标头或 cookie 中。然后,APISIX 将验证该令牌以确定是否应允许或拒绝请求访问上游资源。
|
||||
|
||||
当消费者成功通过身份验证后,APISIX 会在将请求代理到上游服务之前向请求添加其他标头,例如 `X-Consumer-Username`、`X-Credential-Indentifier` 和其他消费者自定义标头(如已配置)。上游服务将能够区分消费者并根据需要实施其他逻辑。如果任何一个值不可用,则不会添加相应的标题。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer/Credential 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------- | ----- | ------- | --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| key | string | 是 | | | 消费者的唯一密钥。 |
|
||||
| secret | string | 否 | | | 当使用对称算法时,用于对 JWT 进行签名和验证的共享密钥。使用 `HS256` 或 `HS512` 作为算法时必填。如果未指定,后台将会自动生成。该字段支持使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源,将值保存在 Secret Manager 中。 |
|
||||
| public_key | string | 否 | | | RSA 或 ECDSA 公钥, `algorithm` 属性选择 `RS256` 或 `ES256` 算法时必选。该字段支持使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源,将值保存在 Secret Manager 中。 |
|
||||
| algorithm | string | 否 | "HS256" | ["HS256", "HS512", "RS256", "ES256"] | 加密算法。 |
|
||||
| exp | integer | 否 | 86400 | [1,...] | token 的超时时间。 |
|
||||
| base64_secret | boolean | 否 | false | | 当设置为 `true` 时,密钥为 base64 编码。 |
|
||||
| lifetime_grace_period | integer | 否 | 0 | [0,...] | 宽限期(以秒为单位)。用于解决生成 JWT 的服务器与验证 JWT 的服务器之间的时钟偏差。 |
|
||||
| key_claim_name | string | 否 | key | | JWT payload 中的声明用于标识相关的秘密,例如 `iss`。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"secret"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
Route 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------ | ------ | ------ | ------------- |---------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| header | string | 否 | authorization | 设置我们从哪个 header 获取 token。 |
|
||||
| query | string | 否 | jwt | 设置我们从哪个 query string 获取 token,优先级低于 header。 |
|
||||
| cookie | string | 否 | jwt | 设置我们从哪个 cookie 获取 token,优先级低于 query。 |
|
||||
| hide_credentials | boolean | 否 | false | 如果为 true,则不要将 header、query 或带有 JWT 的 cookie 传递给上游服务。 |
|
||||
| key_claim_name | string | 否 | key | 包含用户密钥(对应消费者的密钥属性)的 JWT 声明的名称。|
|
||||
| anonymous_consumer | string | 否 | false | 匿名消费者名称。如果已配置,则允许匿名用户绕过身份验证。 |
|
||||
| store_in_ctx | boolean | 否 | false | 设置为 `true` 将会将 JWT 负载存储在请求上下文 (`ctx.jwt_auth_payload`) 中。这允许在同一请求上随后运行的低优先级插件检索和使用 JWT 令牌。 |
|
||||
|
||||
您可以使用 [HashiCorp Vault](https://www.vaultproject.io/) 实施 `jwt-auth`,以从其[加密的 KV 引擎](https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/secrets/kv) 使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在不同场景中使用 `jwt-auth` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 JWT 进行消费者身份验证
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何实现 JWT 进行消费者密钥身份验证。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"secret": "jack-hs256-secret"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `jwt-auth` 插件创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要为 `jack` 签发 JWT,您可以使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 或其他实用程序。如果您使用的是 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io),请执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉菜单中选择 __HS256__。
|
||||
* 将 __Verify Signature__ 部分中的密钥更新为 `jack-hs256-secret`。
|
||||
* 使用消费者密钥 `jack-key` 更新有效 payload;并在 UNIX 时间戳中添加 `exp` 或 `nbf`。
|
||||
|
||||
您的 payload 应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"nbf": 1729132271
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将生成的 JWT 复制到 __Encoded__ 部分并保存到变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsIm5iZiI6MTcyOTEzMjI3MX0.0VDKUzNkSaa_H5g_rGNbNtDcKJ9fBGgcGC56AsVsV-I
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `Authorization` 标头中的 JWT 向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MjY2NDk2NDAsImtleSI6ImphY2sta2V5In0.kdhumNWrZFxjUvYzWLt4lFr546PNsr9TXuf0Az5opoM",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66ea951a-4d740d724bd2a44f174d4daf",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "jack",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
30 秒后,令牌将过期。使用相同令牌发送请求以验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"failed to verify jwt"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在请求标头、查询字符串或 Cookie 中携带 JWT
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在指定的标头、查询字符串和 Cookie 中接受 JWT。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"secret": "jack-hs256-secret"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `jwt-auth` 插件的路由,并指定请求可以在标头、查询或 cookie 中携带令牌:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"header": "jwt-auth-header",
|
||||
"query": "jwt-query",
|
||||
"cookie": "jwt-cookie"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要为 `jack` 签发 JWT,您可以使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 或其他实用程序。如果您使用的是 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io),请执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉菜单中选择 __HS256__。
|
||||
* 将 __Verify Signature__ 部分中的密钥更新为 `jack-hs256-secret`。
|
||||
* 使用消费者密钥 `jack-key` 更新有效 payload;并在 UNIX 时间戳中添加 `exp` 或 `nbf`。
|
||||
|
||||
您的有效 payload 应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"nbf": 1729132271
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将生成的 JWT 复制到 __Encoded__ 部分并保存到变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsIm5iZiI6MTcyOTEzMjI3MX0.0VDKUzNkSaa_H5g_rGNbNtDcKJ9fBGgcGC56AsVsV-I
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用标头中的 JWT 进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
发送标头中包含 JWT 的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H "jwt-auth-header: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"Jwt-Auth-Header": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJ1c2VyLWtleSIsImV4cCI6MTY5NTEyOTA0NH0.EiktFX7di_tBbspbjmqDKoWAD9JG39Wo_CAQ1LZ9voQ",
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在查询字符串中使用 JWT 进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
在查询字符串中使用 JWT 发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get?jwt-query=${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {
|
||||
"jwt-query": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJ1c2VyLWtleSIsImV4cCI6MTY5NTEyOTA0NH0.EiktFX7di_tBbspbjmqDKoWAD9JG39Wo_CAQ1LZ9voQ"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 183.17.233.107",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get?jwt-query=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJ1c2VyLWtleSIsImV4cCI6MTY5NTEyOTA0NH0.EiktFX7di_tBbspbjmqDKoWAD9JG39Wo_CAQ1LZ9voQ"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Cookie 中的 JWT 进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用 cookie 中的 JWT 发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" --cookie jwt-cookie=${jwt_token}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Cookie": "jwt-cookie=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJ1c2VyLWtleSIsImV4cCI6MTY5NTEyOTA0NH0.EiktFX7di_tBbspbjmqDKoWAD9JG39Wo_CAQ1LZ9voQ",
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 管理环境变量中的机密
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何将 `jwt-auth` 消费者密钥保存到环境变量并在配置中引用它。
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 支持引用通过 [NGINX `env` 指令](https://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#env) 配置的系统和用户环境变量。
|
||||
|
||||
将密钥保存到环境变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
JACK_JWT_AUTH_KEY=jack-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证并在密钥中引用环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "$env://JACK_JWT_AUTH_KEY",
|
||||
"secret": "jack-hs256-secret"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由并启用 `jwt-auth`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要为 `jack` 签发 JWT,您可以使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 或其他实用程序。如果您使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io),请执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉列表中选择 __HS256__。
|
||||
* 将 __Verify Signature__ 部分中的密钥更新为 `jack-hs256-secret` 。
|
||||
* 使用消费者密钥 `jack-key` 更新有效 payload;并在 UNIX 时间戳中添加 `exp` 或 `nbf`。
|
||||
|
||||
您的有效 payload 应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"nbf": 1729132271
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将生成的 JWT 复制到 __Encoded__ 部分并保存到变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsIm5iZiI6MTcyOTEzMjI3MX0.0VDKUzNkSaa_H5g_rGNbNtDcKJ9fBGgcGC56AsVsV-I
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送标头中包含 JWT 的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJleHAiOjE2OTUxMzMxNTUsImtleSI6Imp3dC1rZXkifQ.jiKuaAJqHNSSQCjXRomwnQXmdkC5Wp5VDPRsJlh1WAQ",
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在秘密管理器中管理秘密
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何管理 [HashiCorp Vault](https://www.vaultproject.io) 中的 `jwt-auth` 消费者密钥并在插件配置中引用它。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Docker 中启动 Vault 开发服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d \
|
||||
--name vault \
|
||||
-p 8200:8200 \
|
||||
--cap-add IPC_LOCK \
|
||||
-e VAULT_DEV_ROOT_TOKEN_ID=root \
|
||||
-e VAULT_DEV_LISTEN_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0:8200 \
|
||||
vault:1.9.0 \
|
||||
vault server -dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 目前支持 [Vault KV 引擎版本 1](https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/secrets/kv#kv-version-1)。在 Vault 中启用它:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker exec -i vault sh -c "VAULT_TOKEN='root' VAULT_ADDR='http://0.0.0.0:8200' vault secrets enable -path=kv -version=1 kv"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似于以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Success! Enabled the kv secrets engine at: kv/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个 secret 并配置 Vault 地址和其他连接信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/secrets/vault/jwt" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "https://127.0.0.1:8200",
|
||||
"prefix": "kv/apisix",
|
||||
"token": "root"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证并引用密钥中的秘密:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "$secret://vault/jwt/jack/jwt-key",
|
||||
"secret": "vault-hs256-secret"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由并启用 `jwt-auth`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 Vault 中将 `jwt-auth` 键值设置为 `jwt-vault-key`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker exec -i vault sh -c "VAULT_TOKEN='root' VAULT_ADDR='http://0.0.0.0:8200' vault kv put kv/apisix/jack jwt-key=jwt-vault-key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似于以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Success! Data written to: kv/apisix/jack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要签发 JWT,您可以使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 或其他实用程序。如果您使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io),请执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉列表中选择 __HS256__。
|
||||
* 将 __Verify Signature__ 部分中的密钥更新为 `vault-hs256-secret` 。
|
||||
* 使用消费者密钥 `jwt-vault-key` 更新有效 payload;并在 UNIX 时间戳中添加 `exp` 或 `nbf`。
|
||||
|
||||
您的有效 payload 应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "jwt-vault-key",
|
||||
"nbf": 1729132271
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将生成的 JWT 复制到 __Encoded__ 部分并保存到变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqd3QtdmF1bHQta2V5IiwibmJmIjoxNzI5MTMyMjcxfQ.faiN93LNP1lGSXqAb4empNJKMRWop8-KgnU58VQn1EE
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用令牌作为标头发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqd3QtdmF1bHQta2V5IiwiZXhwIjoxNjk1MTM4NjM1fQ.Au2liSZ8eQXUJR3SJESwNlIfqZdNyRyxIJK03L4dk_g",
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 RS256 算法签署 JWT
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了在实施 JWT 进行消费者身份验证时如何使用非对称算法(例如 RS256)来签名和验证 JWT。您将使用 [openssl](https://openssl-library.org/source/) 生成 RSA 密钥对,并使用 [JWT.io](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 生成 JWT,以更好地了解 JWT 的组成。
|
||||
|
||||
生成 2048 位的 RSA 私钥并提取对应的 PEM 格式的公钥:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
openssl genrsa -out jwt-rsa256-private.pem 2048
|
||||
openssl rsa -in jwt-rsa256-private.pem -pubout -out jwt-rsa256-public.pem
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到在当前工作目录中生成了 `jwt-rsa256-private.pem` 和 `jwt-rsa256-public.pem` 。
|
||||
|
||||
访问 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 并执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉列表中选择 __RS256__。
|
||||
* 将 key 复制并粘贴到 __Verify Signature__ 部分。
|
||||
* 使用与您想要使用的消费者密钥匹配的 `key` 更新有效 payload;以及 UNIX 时间戳中的 `exp` 或 `nbf`。
|
||||
|
||||
配置应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
src="https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2024/12/12/SRe7AXMw_jwt_token.png"
|
||||
alt="complete configuration of JWT generation on jwt.io"
|
||||
width="70%"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
复制左侧的 JWT 并保存到环境变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsImV4cCI6MTczNDIzMDQwMH0.XjqM0oszmCggwZs-8PUIlJv8wPJON1la2ET5v70E6TCE32Yq5ibrl-1azaK7IreAer3HtnVHeEfII2rR02v8xfR1TPIjU_oHov4qC-A4tLTbgqGVXI7fCy2WFm3PFh6MEKuRe6M3dCQtCAdkRRQrBr1gWFQZhV3TNeMmmtyIfuJpB7cp4DW5pYFsCcoE1Nw6Tz7dt8k0tPBTPI2Mv9AYfMJ30LHDscOaPNtz8YIk_TOkV9b9mhQudUJ7J_suCZMRxD3iL655jTp2gKsstGKdZa0_W9Reu4-HY3LSc5DS1XtfjuftpuUqgg9FvPU0mK_b0wT_Rq3lbYhcHb9GZ72qiQ
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证并配置 RSA 密钥:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"algorithm": "RS256",
|
||||
"public_key": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAnE0h4k/GWfEbYO/yE2MPjHtNKDLNz4mv1KNIPLxY2ccjPYOtjuug+iZ4MujLV59YfrHriTs0H8jweQfff3pRSMjyEK+4qWTY3TeKBXIEa3pVDeoedSJrgjLBVio6xH7et8ir+QScScfLaJHGB4/l3DDGyEhO782a9teY8brn5hsWX5uLmDJvxtTGAHYi847XOcx2UneW4tZ8wQ6JGBSiSg5qAHan4dFZ7CpixCNNqEcSK6EQ7lKOLeFGG8ys/dHBIEasU4oMlCuJH77+XQQ/shchy+vm9oZfP+grLZkV+nKAd8MQZsid7ZJ/fiB/BmnhGrjtIfh98jwxSx4DgdLhdwIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
|
||||
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEvwIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKkwggSlAgEAAoIBAQCcTSHiT8ZZ8Rtg7/ITYw+Me00oMs3Pia/Uo0g8vFjZxyM9g62O66D6Jngy6MtXn1h+seuJOzQfyPB5B99/elFIyPIQr7ipZNjdN4oFcgRrelUN6h51ImuCMsFWKjrEft63yKv5BJxJx8tokcYHj+XcMMbISE7vzZr215jxuufmGxZfm4uYMm/G1MYAdiLzjtc5zHZSd5bi1nzBDokYFKJKDmoAdqfh0VnsKmLEI02oRxIroRDuUo4t4UYbzKz90cEgRqxTigyUK4kfvv5dBD+yFyHL6+b2hl8/6CstmRX6coB3wxBmyJ3tkn9+IH8GaeEauO0h+H3yPDFLHgOB0uF3AgMBAAECggEARpY68Daw0Funzq5uN70r/3iLztSqx8hZpQEclXlF8wwQ6S33iqz1JSOMcwlZE7g9wfHd+jrHfndDypT4pVx7KxC86TZCghWuLrFvXqgwQM2dbcxGdwXVYZZEZAJsSeM19+/jYnFnl5ZoUVBMC4w79aX9j+O/6mKDUmjphHmxUuRCFjN0w7BRoYwmS796rSf1eoOcSXh2G9Ycc34DUFDfGpOzabndbmMfOz7W0DyUBG23fgLhNChTUGq8vMaqKXkQ8JKeKdEugSmRGz42HxjWoNlIGBDyB8tPNPT6SXsu/JBskdf9Gb71OWiub381oXC259sz+1K1REb1KSkgyC+bkQKBgQDKCnwXaf8aOIoJPCG53EqQfKScCIYQrvp1Uk3bs5tfYN4HcI3yAUnOqQ3Ux3eY9PfS37urlJXCfCbCnZ6P6xALZnN+aL2zWvZArlHvD6vnXiyevwK5IY+o2EW02h3A548wrGznQSsfX0tum22bEVlRuFfBbpZpizXwrV4ODSNhTwKBgQDGC27QQxah3yq6EbOhJJlJegjawVXEaEp/j4fD3qe/unLbUIFvCz6j9BAbgocDKzqXxlpTtIbnsesdLo7KM3MtYL0XO/87HIsBj9XCVgMkFCcM6YZ6fHnkJl0bs3haU4N9uI/wpokvfvXJp7iC9LUCseBdBj+N6T230HWiSbPjWQKBgQC8zzGKO/8vRNkSqkQmSczQ2/qE6p5G5w6eJy0lfOJdLswvDatJFpUf8PJA/6svoPYb9gOO5AtUNeuPAfeVLSnQTYzu+/kTrJTme0GMdAvE60gtjfmAgvGa64mw6gjWJk+1P92B+2/OIKMAmXXDbWIYMXqpBKzBs1vUMF/uJ68BlwKBgQDEivQem3YKj3/HyWmLstatpP7EmrqTgSzuC3OhX4b7L/5sySirG22/KKgTpSZ4bp5noeJiz/ZSWrAK9fmfkg/sKOV/+XsDHwCVPDnX86SKWbWnitp7FK2jTq94nlQC0H7edhvjqGLdUBJ9XoYu8MvzMLSJnXnVTHSDx832kU6FgQKBgQCbw4Eiu2IcOduIAokmsZl8Smh9ZeyhP2B/UBa1hsiPKQ6bw86QJr2OMbRXLBxtx+HYIfwDo4vXEE862PfoQyu6SjJBNmHiid7XcV06Z104UQNjP7IDLMMF+SASMqYoQWg/5chPfxBgIXnfWqw6TMmND3THY4Oj4Nhf4xeUg3HsaA==\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
您应该在开始行之后和结束行之前添加换行符,例如`-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n......\n-----END PRIVATE KEY -----`。
|
||||
|
||||
关键内容可以直接拼接。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `jwt-auth` 插件创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `Authorization` 标头中的 JWT 向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsImV4cCI6MTczNDIzMDQwMH0.XjqM0oszmCggwZs-8PUIlJv8wPJON1la2ET5v70E6TCE32Yq5ibrl-1azaK7IreAer3HtnVHeEfII2rR02v8xfR1TPIjU_oHov4qC-A4tLTbgqGVXI7fCy2WFm3PFh6MEKuRe6M3dCQtCAdkRRQrBr1gWFQZhV3TNeMmmtyIfuJpB7cp4DW5pYFsCcoE1Nw6Tz7dt8k0tPBTPI2Mv9AYfMJ30LHDscOaPNtz8YIk_TOkV9b9mhQudUJ7J_suCZMRxD3iL655jTp2gKsstGKdZa0_W9Reu4-HY3LSc5DS1XtfjuftpuUqgg9FvPU0mK_b0wT_Rq3lbYhcHb9GZ72qiQ",
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将消费者自定义 ID 添加到标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何将消费者自定义 ID 附加到 `Consumer-Custom-Id` 标头中经过身份验证的请求,该标头可用于根据需要实现其他逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有自定义 ID 标签的消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack",
|
||||
"labels": {
|
||||
"custom_id": "495aec6a"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"secret": "jack-hs256-secret"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `jwt-auth` 创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要为 `jack` 签发 JWT,您可以使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 或其他实用程序。如果您使用的是 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io),请执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉菜单中选择 __HS256__。
|
||||
* 将 __Verify Signature__ 部分中的密钥更新为 `jack-hs256-secret` 。
|
||||
* 使用消费者密钥 `jack-key` 更新有效 payload;并在 UNIX 时间戳中添加 `exp` 或 `nbf` 。
|
||||
|
||||
您的有效 payload 应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"nbf": 1729132271
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将生成的 JWT 复制到 __Encoded__ 部分并保存到变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsIm5iZiI6MTcyOTEzMjI3MX0.0VDKUzNkSaa_H5g_rGNbNtDcKJ9fBGgcGC56AsVsV-I
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `Authorization` 标头中的 JWT 向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似于以下内容的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,其中附加了 `X-Consumer-Custom-Id`:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Authorization": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MjY2NDk2NDAsImtleSI6ImphY2sta2V5In0.kdhumNWrZFxjUvYzWLt4lFr546PNsr9TXuf0Az5opoM",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66ea951a-4d740d724bd2a44f174d4daf",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "jack",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Custom-Id": "495aec6a",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 匿名消费者的速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为普通消费者和匿名消费者配置不同的速率限制策略,其中匿名消费者不需要进行身份验证,并且配额较少。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个普通消费者 `jack`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内的配额为 3:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 3,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者 `jack` 创建 `jwt-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-jwt-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"secret": "jack-hs256-secret"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建匿名用户 `anonymous`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内配额为 1:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "anonymous",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个路由并配置 `jwt-auth` 插件以接受匿名消费者 `anonymous` 绕过身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "jwt-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"jwt-auth": {
|
||||
"anonymous_consumer": "anonymous"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要为 `jack` 签发 JWT,您可以使用 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io) 或其他实用程序。如果您使用的是 [JWT.io 的调试器](https://jwt.io/#debugger-io),请执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在 __Algorithm__ 下拉菜单中选择 __HS256__。
|
||||
* 将 __Verify Signature__ 部分中的密钥更新为 `jack-hs256-secret`。
|
||||
* 使用角色 `user` 、权限 `read` 和消费者密钥 `jack-key` 以及 UNIX 时间戳中的 `exp` 或 `nbf` 更新有效 payload。
|
||||
|
||||
您的有效 payload 应类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "jack-key",
|
||||
"nbf": 1729132271
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将生成的 JWT 复制到 __Encoded__ 部分并保存到变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
jwt_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJrZXkiOiJqYWNrLWtleSIsIm5iZiI6MTcyOTEzMjI3MX0.hjtSsEILpko14zb8-ibyxrB2tA5biYY9JrFm3do69vs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了验证速率限制,请使用 jack 的 JWT 连续发送五个请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H "Authorization: ${jwt_token}" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,显示在 5 个请求中,3 个请求成功(状态代码 200),而其他请求被拒绝(状态代码 429)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 3, 429: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送五个匿名请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,表明只有一个请求成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 1, 429: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,247 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: kafka-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Kafka Logger
|
||||
description: API 网关 Apache APISIX 的 kafka-logger 插件用于将日志作为 JSON 对象推送到 Apache Kafka 集群中。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`kafka-logger` 插件用于将日志作为 JSON 对象推送到 Apache Kafka 集群中。可用作 `ngx_lua` NGINX 模块的 Kafka 客户端驱动程序。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | ------- | ------ | -------------- | --------------------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| broker_list | object | 是 | | | 已废弃,现使用 `brokers` 属性代替。原指需要推送的 Kafka 的 broker 列表。 |
|
||||
| brokers | array | 是 | | | 需要推送的 Kafka 的 broker 列表。 |
|
||||
| brokers.host | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 的节点 host 配置,例如 `192.168.1.1` |
|
||||
| brokers.port | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 的节点端口配置 |
|
||||
| brokers.sasl_config | object | 否 | | | Kafka broker 中的 sasl_config |
|
||||
| brokers.sasl_config.mechanism | string | 否 | "PLAIN" | ["PLAIN"] | Kafka broker 中的 sasl 认证机制 |
|
||||
| brokers.sasl_config.user | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 中 sasl 配置中的 user,如果 sasl_config 存在,则必须填写 |
|
||||
| brokers.sasl_config.password | string | 是 | | | Kafka broker 中 sasl 配置中的 password,如果 sasl_config 存在,则必须填写 |
|
||||
| kafka_topic | string | 是 | | | 需要推送的 topic。 |
|
||||
| producer_type | string | 否 | async | ["async", "sync"] | 生产者发送消息的模式。 |
|
||||
| required_acks | integer | 否 | 1 | [1, -1] | 生产者在确认一个请求发送完成之前需要收到的反馈信息的数量。该参数是为了保证发送请求的可靠性。该属性的配置与 Kafka `acks` 属性相同,具体配置请参考 [Apache Kafka 文档](https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#producerconfigs_acks)。required_acks 还不支持为 0。 |
|
||||
| key | string | 否 | | | 用于消息分区而分配的密钥。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3 | [1,...] | 发送数据的超时时间。 |
|
||||
| name | string | 否 | "kafka logger" | | 标识 logger 的唯一标识符。如果您使用 Prometheus 监视 APISIX 指标,名称将以 `apisix_batch_process_entries` 导出。 |
|
||||
| meta_format | enum | 否 | "default" | ["default","origin"] | `default`:获取请求信息以默认的 JSON 编码方式。`origin`:获取请求信息以 HTTP 原始请求方式。更多信息,请参考 [meta_format](#meta_format-示例)。|
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含请求体。**注意**:如果请求体无法完全存放在内存中,由于 NGINX 的限制,APISIX 无法将它记录下来。|
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array | 否 | | | 当 `include_req_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时进行过滤。只有当此处设置的表达式计算结果为 `true` 时,才会记录请求体。更多信息,请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。 |
|
||||
| max_req_body_bytes | integer | 否 | 524288 | >=1 | 允许的最大请求正文(以字节为单位)。在此限制内的请求体将被推送到 Kafka。如果大小超过配置值,则正文在推送到 Kafka 之前将被截断。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含响应体。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array | 否 | | | 当 `include_resp_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时进行过滤。只有当此处设置的表达式计算结果为 `true` 时才会记录响应体。更多信息,请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。|
|
||||
| max_resp_body_bytes | integer | 否 | 524288 | >=1 | 允许的最大响应正文(以字节为单位)。低于此限制的响应主体将被推送到 Kafka。如果大小超过配置值,则正文在推送到 Kafka 之前将被截断。 |
|
||||
| cluster_name | integer | 否 | 1 | [0,...] | Kafka 集群的名称,当有两个及以上 Kafka 集群时使用。只有当 `producer_type` 设为 `async` 模式时才可以使用该属性。|
|
||||
| producer_batch_num | integer | 否 | 200 | [1,...] | 对应 [lua-resty-kafka](https://github.com/doujiang24/lua-resty-kafka) 中的 `batch_num` 参数,聚合消息批量提交,单位为消息条数。 |
|
||||
| producer_batch_size | integer | 否 | 1048576 | [0,...] | 对应 [lua-resty-kafka](https://github.com/doujiang24/lua-resty-kafka) 中的 `batch_size` 参数,单位为字节。 |
|
||||
| producer_max_buffering | integer | 否 | 50000 | [1,...] | 对应 [lua-resty-kafka](https://github.com/doujiang24/lua-resty-kafka) 中的 `max_buffering` 参数,表示最大缓冲区,单位为条。 |
|
||||
| producer_time_linger | integer | 否 | 1 | [1,...] | 对应 [lua-resty-kafka](https://github.com/doujiang24/lua-resty-kafka) 中的 `flush_time` 参数,单位为秒。|
|
||||
| meta_refresh_interval | integer | 否 | 30 | [1,...] | 对应 [lua-resty-kafka](https://github.com/doujiang24/lua-resty-kafka) 中的 `refresh_interval` 参数,用于指定自动刷新 metadata 的间隔时长,单位为秒。 |
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志/数据)。这样可以避免插件频繁地提交数据,默认设置情况下批处理器会每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时提交数据,如需了解批处理器相关参数设置,请参考 [Batch-Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置) 配置部分。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
|
||||
数据首先写入缓冲区。当缓冲区超过 `batch_max_size` 或 `buffer_duration` 设置的值时,则会将数据发送到 Kafka 服务器并刷新缓冲区。
|
||||
|
||||
如果发送成功,则返回 `true`。如果出现错误,则返回 `nil`,并带有描述错误的字符串 `buffer overflow`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### meta_format 示例
|
||||
|
||||
- `default`:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"upstream": "127.0.0.1:1980",
|
||||
"start_time": 1619414294760,
|
||||
"client_ip": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"route_id": "1",
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"querystring": {
|
||||
"ab": "cd"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 90,
|
||||
"uri": "/hello?ab=cd",
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:1984/hello?ab=cd",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"host": "localhost",
|
||||
"content-length": "6",
|
||||
"connection": "close"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"body": "abcdef",
|
||||
"method": "GET"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"connection": "close",
|
||||
"content-type": "text/plain; charset=utf-8",
|
||||
"date": "Mon, 26 Apr 2021 05:18:14 GMT",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/2.5",
|
||||
"transfer-encoding": "chunked"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 190,
|
||||
"status": 200
|
||||
},
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"hostname": "localhost",
|
||||
"version": "2.5"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"latency": 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `origin`:
|
||||
|
||||
```http
|
||||
GET /hello?ab=cd HTTP/1.1
|
||||
host: localhost
|
||||
content-length: 6
|
||||
connection: close
|
||||
|
||||
abcdef
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件元数据
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------ | ------------- |------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../../../en/latest/apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
该设置全局生效。如果指定了 `log_format`,则所有绑定 `kafka-logger` 的路由或服务都将使用该日志格式。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何通过 Admin API 配置插件元数据:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/kafka-logger \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
配置完成后,你将在日志系统中看到如下类似日志:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
{"host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2020-09-23T19:05:05-04:00","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","route_id":"1"}
|
||||
{"host":"localhost","@timestamp":"2020-09-23T19:05:05-04:00","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","route_id":"1"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何启用
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过如下命令在指定路由上启用 `kafka-logger` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"kafka-logger": {
|
||||
"brokers" : [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port": 9092
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kafka_topic" : "test2",
|
||||
"key" : "key1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/hello"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该插件还支持一次推送到多个 Broker,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"brokers" : [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host" :"127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port" : 9092
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host" :"127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port" : 9093
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令向 APISIX 发出请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,570 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: key-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Key Auth
|
||||
- key-auth
|
||||
description: key-auth 插件支持使用身份验证密钥作为客户端在访问上游资源之前进行身份验证的机制。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/key-auth" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`key-auth` 插件支持使用身份验证密钥作为客户端在访问上游资源之前进行身份验证的机制。
|
||||
|
||||
要使用该插件,您需要在 [Consumers](../terminology/consumer.md) 上配置身份验证密钥,并在路由或服务上启用该插件。密钥可以包含在请求 URL 查询字符串或请求标头中。然后,APISIX 将验证密钥以确定是否应允许或拒绝请求访问上游资源。
|
||||
|
||||
当消费者成功通过身份验证后,APISIX 会在将请求代理到上游服务之前向请求添加其他标头,例如 `X-Consumer-Username`、`X-Credential-Indentifier` 和其他消费者自定义标头(如果已配置)。上游服务将能够区分消费者并根据需要实现其他逻辑。如果这些值中的任何一个不可用,则不会添加相应的标头。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer/Credential 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------ | ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| key | string | 是 | 不同的 Consumer 应有不同的 `key`,它应当是唯一的。如果多个 Consumer 使用了相同的 `key`,将会出现请求匹配异常。该字段支持使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源,将值保存在 Secret Manager 中。 |
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"key"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
Route 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------ | ----- | ------ |----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| header | string | 否 | apikey | 设置我们从哪个 header 获取 key。 |
|
||||
| query | string | 否 | apikey | 设置我们从哪个 query string 获取 key,优先级低于 `header`。 |
|
||||
| hide_credentials | boolean | 否 | false | 如果为 `true`,则不要将含有认证信息的 header 或 query string 传递给 Upstream。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在不同场景中使用 `key-auth` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 在路由上实现密钥认证
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在路由上实现密钥认证并将密钥包含在请求标头中。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `key-auth` 创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "key-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用有效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用有效密钥发送请求至:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H 'apikey: jack-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用无效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用无效密钥发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H 'apikey: wrong-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"Invalid API key in request"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 无需密钥即可验证
|
||||
|
||||
无需密钥即可发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"Missing API key found in request"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 隐藏上游的身份验证信息
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何通过配置 `hide_credentials` 来防止密钥被发送到上游服务。默认情况下,身份验证密钥被转发到上游服务,这在某些情况下可能会导致安全风险。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 不隐藏凭据
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `key-auth` 创建路由,并将 `hide_credentials` 配置为 `false` (默认配置):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "key-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"hide_credentials": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送带有有效密钥的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?apikey=jack-key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {
|
||||
"auth": "jack-key"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "jack",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6502d8a5-2194962a67aa21dd33f94bb2",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 103.248.35.179",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything?apikey=jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意凭证 `jack-key` 对于上游服务是可见的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 隐藏凭据
|
||||
|
||||
将插件的 `hide_credentials` 更新为 `true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/key-auth-route" -X PATCH \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"hide_credentials": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送带有有效密钥的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?apikey=jack-key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "jack",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6502d85c-16f34dbb5629a5960183e803",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 103.248.35.179",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意凭证 `jack-key` 对上游服务不再可见。
|
||||
|
||||
### 演示标头和查询中的密钥优先级
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在路由上实现消费者的密钥身份验证,并自定义应包含密钥的 URL 参数。该示例还显示,当在标头和查询字符串中都配置了 API 密钥时,请求标头具有更高的优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `key-auth` 创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "key-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"query": "auth"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用有效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用有效密钥发送请求至:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?auth=jack-key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用无效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
使用无效密钥发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?auth=wrong-key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下 `HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"message":"Invalid API key in request"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用查询字符串中的有效密钥进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
但是,如果您在标头中包含有效密钥,而 URL 查询字符串中仍包含无效密钥:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?auth=wrong-key" -H 'apikey: jack-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。这表明标头中包含的密钥始终具有更高的优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
### 将消费者自定义 ID 添加到标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在 `Consumer-Custom-Id` 标头中将消费者自定义 ID 附加到经过身份验证的请求,该 ID 可用于根据需要实现其他逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有自定义 ID 标签的消费者 `jack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack",
|
||||
"labels": {
|
||||
"custom_id": "495aec6a"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create `key-auth` credential for the consumer:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a Route with `key-auth`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "key-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To verify, send a request to the Route with the valid key:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?auth=jack-key"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You should see an `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` response similar to the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {
|
||||
"auth": "jack-key"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-66ea8d64-33df89052ae198a706e18c2a",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Username": "jack",
|
||||
"X-Credential-Identifier": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"X-Consumer-Custom-Id": "495aec6a",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "192.168.65.1, 205.198.122.37",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/anything?apikey=jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 匿名消费者的速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为常规消费者和匿名消费者配置不同的速率限制策略,其中匿名消费者不需要进行身份验证,并且配额较少。
|
||||
|
||||
创建常规消费者 `jack` 并配置 `limit-count` 插件以允许 30 秒内的配额为 3:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jack",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 3,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者 `jack` 创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jack/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jack-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jack-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建匿名用户 `anonymous`,并配置 `limit-count`插件,以允许 30 秒内配额为 1:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "anonymous",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由并配置 `key-auth` 插件以接受匿名消费者 `anonymous` 绕过身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "key-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"anonymous_consumer": "anonymous"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了验证,请使用 `jack` 的密钥发送五个连续的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H 'apikey: jack-key' -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,显示在 5 个请求中,3 个请求成功(状态代码 200),而其他请求被拒绝(状态代码 429)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 3, 429: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送五个匿名请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,表明只有一个请求成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 1, 429: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ldap-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- LDAP Authentication
|
||||
- ldap-auth
|
||||
description: 本篇文档介绍了 Apache APISIX ldap-auth 插件的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`ldap-auth` 插件可用于给路由或服务添加 LDAP 身份认证,该插件使用 [lua-resty-ldap](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-ldap) 连接 LDAP 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件需要与 Consumer 一起配合使用,API 的调用方可以使用 [basic authentication](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_access_authentication) 与 LDAP 服务器进行认证。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------- | ------ | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| user_dn | string | 是 | LDAP 客户端的 dn,例如:`cn=user01,ou=users,dc=example,dc=org`。该字段支持使用 [APISIX Secret](../terminology/secret.md) 资源,将值保存在 Secret Manager 中。 |
|
||||
|
||||
Route 端:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|----------|---------|----------|---------|------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| base_dn | string | 是 | | LDAP 服务器的 dn,例如:`ou=users,dc=example,dc=org`。|
|
||||
| ldap_uri | string | 是 | | LDAP 服务器的 URI。 |
|
||||
| use_tls | boolean | 否 | false | 如果设置为 `true` 则表示启用 TLS。 |
|
||||
| tls_verify| boolean | 否 | false | 是否校验 LDAP 服务器的证书。如果设置为 `true`,你必须设置 `config.yaml` 里面的 `ssl_trusted_certificate`,并且确保 `ldap_uri` 里的 host 和服务器证书中的 host 匹配。 |
|
||||
| uid | string | 否 | cn | UID 属性。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要创建一个 Consumer 并在其中配置该插件,具体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "foo",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"ldap-auth": {
|
||||
"user_dn": "cn=user01,ou=users,dc=example,dc=org"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后就可以在指定路由或服务中启用该插件,具体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"ldap-auth": {
|
||||
"base_dn": "ou=users,dc=example,dc=org",
|
||||
"ldap_uri": "localhost:1389",
|
||||
"uid": "cn"
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述方法配置插件后,可以通过以下命令测试插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -uuser01:password1 http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
hello, world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果授权信息请求头丢失或无效,则请求将被拒绝(如下展示了几种返回结果):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"message":"Missing authorization in request"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -uuser:password1 http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"message":"Invalid user authorization"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -uuser01:passwordfalse http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|
||||
...
|
||||
{"message":"Invalid user authorization"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `ldap-auth` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置。APISIX 将自动重新加载,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,420 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: limit-conn
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Limit Connection
|
||||
description: limit-conn 插件通过管理并发连接来限制请求速率。超过阈值的请求可能会被延迟或拒绝,以确保 API 使用受控并防止过载。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/limit-conn" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`limit-conn` 插件通过并发连接数来限制请求速率。超过阈值的请求将根据配置被延迟或拒绝,从而确保可控的资源使用并防止过载。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|------------|---------|----------|-------|----------------------------|------------------|
|
||||
| conn | integer | 是 | | > 0 | 允许的最大并发请求数。超过配置的限制且低于`conn + burst`的请求将被延迟。|
|
||||
| burst | integer | 是 | | >= 0 | 每秒允许延迟的过多并发请求数。超过限制的请求将被立即拒绝。|
|
||||
| default_conn_delay | number | 是 | | > 0 | 允许超过`conn + burst`的并发请求的处理延迟(秒),可根据`only_use_default_delay`设置动态调整。|
|
||||
| only_use_default_delay | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 false,则根据请求超出`conn`限制的程度按比例延迟请求。拥塞越严重,延迟就越大。例如,当 `conn` 为 `5`、`burst` 为 `3` 且 `default_conn_delay` 为 `1` 时,6 个并发请求将导致 1 秒的延迟,7 个请求将导致 2 秒的延迟,8 个请求将导致 3 秒的延迟,依此类推,直到达到 `conn + burst` 的总限制,超过此限制的请求将被拒绝。如果为 true,则使用 `default_conn_delay` 延迟 `burst` 范围内的所有超额请求。超出 `conn + burst` 的请求将被立即拒绝。例如,当 `conn` 为 `5`、`burst` 为 `3` 且 `default_conn_delay` 为 `1` 时,6、7 或 8 个并发请求都将延迟 1 秒。|
|
||||
| key_type | string | 否 | var | ["var","var_combination"] | key 的类型。如果`key_type` 为 `var`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量。如果 `key_type` 为 `var_combination`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量的组合。 |
|
||||
| key | string | 否 | remote_addr | | 用于计数请求的 key。如果 `key_type` 为 `var`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量。变量不需要以美元符号(`$`)为前缀。如果 `key_type` 为 `var_combination`,则 `key` 会被解释为变量的组合。所有变量都应该以美元符号 (`$`) 为前缀。例如,要配置 `key` 使用两个请求头 `custom-a` 和 `custom-b` 的组合,则 `key` 应该配置为 `$http_custom_a $http_custom_b`。|
|
||||
| rejection_code | integer | 否 | 503 | [200,...,599] | 请求因超出阈值而被拒绝时返回的 HTTP 状态代码。|
|
||||
| rejection_msg | string | 否 | | 非空 | 请求因超出阈值而被拒绝时返回的响应主体。|
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则允许 APISIX 在插件或其依赖项不可用时继续处理没有插件的请求。|
|
||||
| policy | string | 否 | local | ["local","redis","redis-cluster"] | 速率限制计数器的策略。如果是 `local`,则计数器存储在本地内存中。如果是 `redis`,则计数器存储在 Redis 实例上。如果是 `redis-cluster`,则计数器存储在 Redis 集群中。|
|
||||
| redis_host | string | 否 | | | Redis 节点的地址。当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时必填。 |
|
||||
| redis_port | integer | 否 | 6379 | [1,...] | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时,Redis 节点的端口。 |
|
||||
| redis_username | string | 否 | | | 如果使用 Redis ACL,则为 Redis 的用户名。如果使用旧式身份验证方法 `requirepass`,则仅配置 `redis_password`。当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时使用。 |
|
||||
| redis_password | string | 否 | | | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 或 `redis-cluster` 时,Redis 节点的密码。 |
|
||||
| redis_ssl | boolean | 否 | false |如果为 true,则在 `policy` 为 `redis` 时使用 SSL 连接到 Redis 集群。|
|
||||
| redis_ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则在 `policy` 为 `redis` 时验证服务器 SSL 证书。|
|
||||
| redis_database | integer | 否 | 0 | >= 0 | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时,Redis 中的数据库编号。|
|
||||
| redis_timeout | integer | 否 | 1000 | [1,...] | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 或 `redis-cluster` 时,Redis 超时值(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| redis_cluster_nodes | array[string] | 否 | | | 具有至少两个地址的 Redis 群集节点列表。当 policy 为 redis-cluster 时必填。 |
|
||||
redis_cluster_name | string | 否 | | | | Redis 集群的名称。当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster` 时必须使用。|
|
||||
| redis_cluster_ssl | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 `true`,当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster`时,使用 SSL 连接 Redis 集群。|
|
||||
| redis_cluster_ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 `true`,当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster` 时,验证服务器 SSL 证书。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在不同场景中配置 `limit-conn`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过远程地址应用速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何使用 `limit-conn` 通过 `remote_addr` 限制请求速率,并附带示例连接和突发阈值。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `limit-conn` 插件创建路由,以允许 2 个并发请求和 1 个过多的并发请求。此外:
|
||||
|
||||
* 配置插件,允许超过 `conn + burst` 的并发请求有 0.1 秒的处理延迟。
|
||||
* 将密钥类型设置为 `vars`,以将 `key` 解释为变量。
|
||||
* 根据请求的 `remote_address` 计算速率限制计数。
|
||||
* 将 `policy` 设置为 `local`,以使用内存中的本地计数器。
|
||||
* 将 `rejected_code` 自定义为 `429`。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-conn-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-conn": {
|
||||
"conn": 2,
|
||||
"burst": 1,
|
||||
"default_conn_delay": 0.1,
|
||||
"key_type": "var",
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"policy": "local",
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送五个并发请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seq 1 5 | xargs -n1 -P5 bash -c 'curl -s -o /dev/null -w "Response: %{http_code}\n" "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应,其中超过阈值的请求被拒绝:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过远程地址和消费者名称应用速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何使用 `limit-conn` 通过变量组合 `remote_addr` 和 `consumer_name` 对请求进行速率限制。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建第二个消费者 `jane`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jane"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jane/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jane-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jane-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `key-auth` 和 `limit-conn` 插件的路由,并在 `limit-conn` 插件中指定使用变量组合作为速率限制 key:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-conn-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {},
|
||||
"limit-conn": {
|
||||
"conn": 2,
|
||||
"burst": 1,
|
||||
"default_conn_delay": 0.1,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key_type": "var_combination",
|
||||
"key": "$remote_addr $consumer_name"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
作为消费者 `john` 发送五个并发请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seq 1 5 | xargs -n1 -P5 bash -c 'curl -s -o /dev/null -w "Response: %{http_code}\n" "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H "apikey: john-key"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应,其中超过阈值的请求被拒绝:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来立刻以消费者 `jane` 的身份发送五个并发请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seq 1 5 | xargs -n1 -P5 bash -c 'curl -s -o /dev/null -w "Response: %{http_code}\n" "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H "apikey: jane-key"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您还应该看到类似以下内容的响应,其中过多的请求被拒绝:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 限制 WebSocket 连接速率
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何使用 `limit-conn` 插件来限制并发 WebSocket 连接的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
启动 [上游 WebSocket 服务器](https://hub.docker.com/r/jmalloc/echo-server):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d \
|
||||
-p 8080:8080 \
|
||||
--name websocket-server \
|
||||
--network=apisix-quickstart-net \
|
||||
jmalloc/echo-server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建到服务器 WebSocket 端点的路由,并为路由启用 WebSocket。相应地调整 WebSocket 服务器地址。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "ws-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/.ws",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-conn": {
|
||||
"conn": 2,
|
||||
"burst": 1,
|
||||
"default_conn_delay": 0.1,
|
||||
"key_type": "var",
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"enable_websocket": true,
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"websocket-server:8080": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装 WebSocket 客户端,例如 [websocat](https://github.com/vi/websocat),通过以下路由与 WebSocket 服务器建立连接:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
websocat "ws://127.0.0.1:9080/.ws"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在终端中发送 `hello` 消息,您应该会看到 WebSocket 服务器回显相同的消息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Request served by 1cd244052136
|
||||
hello
|
||||
hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再打开三个终端会话并运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
websocat "ws://127.0.0.1:9080/.ws"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
由于速率限制的影响,当您尝试与服务器建立 WebSocket 连接时,您应该会看到最后一个终端会话打印 `429 Too Many Requests`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Redis 服务器在 APISIX 节点之间共享配额
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了使用 Redis 服务器对多个 APISIX 节点之间的请求进行速率限制,以便不同的 APISIX 节点共享相同的速率限制配额。
|
||||
|
||||
在每个 APISIX 实例上,使用以下配置创建路由。相应地调整管理 API、Redis 主机、端口、密码和数据库的地址。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-conn-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-conn": {
|
||||
"conn": 1,
|
||||
"burst": 1,
|
||||
"default_conn_delay": 0.1,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key_type": "var",
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"policy": "redis",
|
||||
"redis_host": "192.168.xxx.xxx",
|
||||
"redis_port": 6379,
|
||||
"redis_password": "p@ssw0rd",
|
||||
"redis_database": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送五个并发请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seq 1 5 | xargs -n1 -P5 bash -c 'curl -s -o /dev/null -w "Response: %{http_code}\n" "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应,其中超过阈值的请求被拒绝:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这表明在不同 APISIX 实例中配置的两个路由共享相同的配额。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Redis 集群在 APISIX 节点之间共享配额
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用 Redis 集群在多个 APISIX 节点之间应用相同的配额,以便不同的 APISIX 节点共享相同的速率限制配额。
|
||||
|
||||
确保您的 Redis 实例在 [集群模式](https://redis.io/docs/management/scaling/#create-and-use-a-redis-cluster) 下运行。`limit-conn` 插件配置至少需要两个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
在每个 APISIX 实例上,使用以下配置创建一个路由。相应地调整管理 API 的地址、Redis 集群节点、密码、集群名称和 SSL 验证。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-conn-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-conn": {
|
||||
"conn": 1,
|
||||
"burst": 1,
|
||||
"default_conn_delay": 0.1,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key_type": "var",
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"policy": "redis-cluster",
|
||||
"redis_cluster_nodes": [
|
||||
"192.168.xxx.xxx:6379",
|
||||
"192.168.xxx.xxx:16379"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"redis_password": "p@ssw0rd",
|
||||
"redis_cluster_name": "redis-cluster-1",
|
||||
"redis_cluster_ssl": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送五个并发请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seq 1 5 | xargs -n1 -P5 bash -c 'curl -s -o /dev/null -w "Response: %{http_code}\n" "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应,其中超过阈值的请求被拒绝:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 200
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
Response: 429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这表明在不同的 APISIX 实例中配置的两条路由共享相同的配额。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,508 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: limit-count
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Limit Count
|
||||
- 速率限制
|
||||
description: limit-count 插件使用固定窗口算法,通过给定时间间隔内的请求数量来限制请求速率。超过配置配额的请求将被拒绝。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/limit-count" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`limit-count` 插件使用固定窗口算法,通过给定时间间隔内的请求数量来限制请求速率。超过配置配额的请求将被拒绝。
|
||||
|
||||
您可能会在响应中看到以下速率限制标头:
|
||||
|
||||
* `X-RateLimit-Limit`:总配额
|
||||
* `X-RateLimit-Remaining`:剩余配额
|
||||
* `X-RateLimit-Reset`:计数器重置的剩余秒数
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------- | ---------- | ------------- | --------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| count | integer | 是 | | > 0 | 给定时间间隔内允许的最大请求数。 |
|
||||
| time_window | integer | 是 | | > 0 | 速率限制 `count` 对应的时间间隔(以秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| key_type | string | 否 | var | ["var","var_combination","constant"] | key 的类型。如果`key_type` 为 `var`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量。如果 `key_type` 为 `var_combination`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量的组合。如果 `key_type` 为 `constant`,则 `key` 将被解释为常量。 |
|
||||
| key | string | 否 | remote_addr | | 用于计数请求的 key。如果 `key_type` 为 `var`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量。变量不需要以美元符号(`$`)为前缀。如果 `key_type` 为 `var_combination`,则 `key` 会被解释为变量的组合。所有变量都应该以美元符号 (`$`) 为前缀。例如,要配置 `key` 使用两个请求头 `custom-a` 和 `custom-b` 的组合,则 `key` 应该配置为 `$http_custom_a $http_custom_b`。如果 `key_type` 为 `constant`,则 `key` 会被解释为常量值。|
|
||||
| rejection_code | integer | 否 | 503 | [200,...,599] | 请求因超出阈值而被拒绝时返回的 HTTP 状态代码。|
|
||||
| rejection_msg | string | 否 | | 非空 | 请求因超出阈值而被拒绝时返回的响应主体。|
|
||||
| policy | string | 否 | local | ["local","redis","redis-cluster"] | 速率限制计数器的策略。如果是 `local`,则计数器存储在本地内存中。如果是 `redis`,则计数器存储在 Redis 实例上。如果是 `redis-cluster`,则计数器存储在 Redis 集群中。|
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则允许 APISIX 在插件或其依赖项不可用时继续处理没有插件的请求。|
|
||||
| show_limit_quota_header | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则在响应标头中包含 `X-RateLimit-Limit` 以显示总配额和 `X-RateLimit-Remaining` 以显示剩余配额。|
|
||||
| group | string | 否 | | 非空 | 插件的 `group` ID,以便同一 `group` 的路由可以共享相同的速率限制计数器。 |
|
||||
| redis_host | string | 否 | | | Redis 节点的地址。当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时必填。 |
|
||||
| redis_port | integer | 否 | 6379 | [1,...] | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时,Redis 节点的端口。 |
|
||||
| redis_username | string | 否 | | | 如果使用 Redis ACL,则为 Redis 的用户名。如果使用旧式身份验证方法 `requirepass`,则仅配置 `redis_password`。当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时使用。 |
|
||||
| redis_password | string | 否 | | | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 或 `redis-cluster` 时,Redis 节点的密码。 |
|
||||
| redis_ssl | boolean | 否 | false |如果为 true,则在 `policy` 为 `redis` 时使用 SSL 连接到 Redis 集群。|
|
||||
| redis_ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则在 `policy` 为 `redis` 时验证服务器 SSL 证书。|
|
||||
| redis_database | integer | 否 | 0 | >= 0 | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时,Redis 中的数据库编号。|
|
||||
| redis_timeout | integer | 否 | 1000 | [1,...] | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 或 `redis-cluster` 时,Redis 超时值(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| redis_cluster_nodes | array[string] | 否 | | | 具有至少两个地址的 Redis 群集节点列表。当 policy 为 redis-cluster 时必填。 |
|
||||
redis_cluster_name | string | 否 | | | | Redis 集群的名称。当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster` 时必须使用。|
|
||||
| redis_cluster_ssl | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 `true`,当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster`时,使用 SSL 连接 Redis 集群。|
|
||||
| redis_cluster_ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 `true`,当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster` 时,验证服务器 SSL 证书。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例演示了如何在不同情况下配置 `limit-count` 。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 按远程地址应用速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例演示了通过单一变量 `remote_addr` 对请求进行速率限制。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `limit-count` 插件的路由,允许在 30 秒窗口内为每个远程地址设置 1 个配额:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key_type": "var",
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送验证请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
该请求已消耗了时间窗口允许的所有配额。如果您在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内再次发送该请求,您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应,表示该请求超出了配额阈值。
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过远程地址和消费者名称应用速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了通过变量 `remote_addr` 和 `consumer_name` 的组合对请求进行速率限制。它允许每个远程地址和每个消费者在 30 秒窗口内有 1 个配额。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建第二个消费者 `jane`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jane"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jane/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jane-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jane-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `key-auth` 和 `limit-count` 插件的路由,并在 `limit-count` 插件中指定使用变量组合作为速率限制键:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {},
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key_type": "var_combination",
|
||||
"key": "$remote_addr $consumer_name"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以消费者 `jane` 的身份发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H 'apikey: jane-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应以及相应的响应主体。
|
||||
|
||||
此请求已消耗了为时间窗口设置的所有配额。如果您在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内向消费者 `jane` 发送相同的请求,您应该会收到一个 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应,表示请求超出了配额阈值。
|
||||
|
||||
在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内向消费者 `john` 发送相同的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H 'apikey: john-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应和相应的响应主体,表明请求不受速率限制。
|
||||
|
||||
在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内再次以消费者 `john` 的身份发送相同的请求,您应该收到一个 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
这通过变量 `remote_addr` 和 `consumer_name` 的组合验证了插件速率限制。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在路由之间共享配额
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例通过配置 `limit-count` 插件的 `group` 演示了在多个路由之间共享速率限制配额。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,同一 `group` 的 `limit-count` 插件的配置应该相同。为了避免更新异常和重复配置,您可以创建一个带有 `limit-count` 插件和上游的服务,以供路由连接。
|
||||
|
||||
创建服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/services" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-service",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"group": "srv1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建两个路由,并将其 `service_id` 配置为 `limit-count-service`,以便它们对插件和上游共享相同的配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-route-1",
|
||||
"service_id": "limit-count-service",
|
||||
"uri": "/get1",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"uri": "/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-route-2",
|
||||
"service_id": "limit-count-service",
|
||||
"uri": "/get2",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"uri": "/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
[`proxy-rewrite`](./proxy-rewrite.md) 插件用于将 URI 重写为 `/get`,以便将请求转发到正确的端点。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
向路由 `/get1` 发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应以及相应的响应主体。
|
||||
|
||||
在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内向路由 `/get2` 发送相同的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应,这验证两个路由共享相同的速率限制配额。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Redis 服务器在 APISIX 节点之间共享配额
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了使用 Redis 服务器对多个 APISIX 节点之间的请求进行速率限制,以便不同的 APISIX 节点共享相同的速率限制配额。
|
||||
|
||||
在每个 APISIX 实例上,使用以下配置创建一个路由。相应地调整管理 API 的地址、Redis 主机、端口、密码和数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"policy": "redis",
|
||||
"redis_host": "192.168.xxx.xxx",
|
||||
"redis_port": 6379,
|
||||
"redis_password": "p@ssw0rd",
|
||||
"redis_database": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 APISIX 实例发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应以及相应的响应主体。
|
||||
|
||||
在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内向不同的 APISIX 实例发送相同的请求,您应该会收到一个 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应,验证在不同 APISIX 节点中配置的路由是否共享相同的配额。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Redis 集群在 APISIX 节点之间共享配额
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用 Redis 集群在多个 APISIX 节点之间应用相同的配额,以便不同的 APISIX 节点共享相同的速率限制配额。
|
||||
|
||||
确保您的 Redis 实例在 [集群模式](https://redis.io/docs/management/scaling/#create-and-use-a-redis-cluster) 下运行。`limit-count` 插件配置至少需要两个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
在每个 APISIX 实例上,使用以下配置创建路由。相应地调整管理 API 的地址、Redis 集群节点、密码、集群名称和 SSL 验证。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-count-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"policy": "redis-cluster",
|
||||
"redis_cluster_nodes": [
|
||||
"192.168.xxx.xxx:6379",
|
||||
"192.168.xxx.xxx:16379"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"redis_password": "p@ssw0rd",
|
||||
"redis_cluster_name": "redis-cluster-1",
|
||||
"redis_cluster_ssl": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 APISIX 实例发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应以及相应的响应主体。
|
||||
|
||||
在相同的 30 秒时间间隔内向不同的 APISIX 实例发送相同的请求,您应该会收到一个 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应,验证在不同 APISIX 节点中配置的路由是否共享相同的配额。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用匿名消费者进行速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为常规和匿名消费者配置不同的速率限制策略,其中匿名消费者不需要进行身份验证并且配额较少。虽然此示例使用 [`key-auth`](./key-auth.md) 进行身份验证,但匿名消费者也可以使用 [`basic-auth`](./basic-auth.md)、[`jwt-auth`](./jwt-auth.md) 和 [`hmac-auth`](./hmac-auth.md) 进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个消费者 `john`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内配额为 3:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 3,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者 `john` 创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建匿名用户 `anonymous`,并配置 `limit-count` 插件,以允许 30 秒内配额为 1:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "anonymous",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-count": {
|
||||
"count": 1,
|
||||
"time_window": 30,
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建路由并配置 `key-auth` 插件以接受匿名消费者 `anonymous` 绕过身份验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "key-auth-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"anonymous_consumer": "anonymous"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `john` 的密钥发送五个连续的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H 'apikey: john-key' -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,显示在 5 个请求中,3 个请求成功(状态代码 200),而其他请求被拒绝(状态代码 429)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 3, 429: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送五个匿名请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 5 | xargs -I{} curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200": $count_200, "429": $count_429
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到以下响应,表明只有一个请求成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200: 1, 429: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,289 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: limit-req
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Limit Request
|
||||
- limit-req
|
||||
description: limit-req 插件使用漏桶算法来限制请求的数量并允许节流。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/limit-req" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`limit-req` 插件使用 [leaky bucket](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leaky_bucket) 算法来限制请求的数量并允许节流。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------- | ------ | ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| rate | integer | True | | > 0 | 每秒允许的最大请求数。超过速率且低于突发的请求将被延迟。|
|
||||
| bust | integer | True | | >= 0 | 每秒允许延迟的请求数,以进行限制。超过速率和突发的请求将被拒绝。|
|
||||
| key_type | string | 否 | var | ["var","var_combination"] | key 的类型。如果 `key_type` 为 `var`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量。如果 `key_type` 为 `var_combination`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量的组合。 |
|
||||
| key | string | 否 | remote_addr | | 用于计数请求的 key。如果 `key_type` 为 `var`,则 `key` 将被解释为变量。变量不需要以美元符号(`$`)为前缀。如果 `key_type` 为 `var_combination`,则 `key` 会被解释为变量的组合。所有变量都应该以美元符号 (`$`) 为前缀。例如,要配置 `key` 使用两个请求头 `custom-a` 和 `custom-b` 的组合,则 `key` 应该配置为 `$http_custom_a $http_custom_b`。如果 `key_type` 为 `constant`,则 `key` 会被解释为常量值。|
|
||||
| rejection_code | integer | 否 | 503 | [200,...,599] | 请求因超出阈值而被拒绝时返回的 HTTP 状态代码。|
|
||||
| rejection_msg | string | 否 | | 非空 | 请求因超出阈值而被拒绝时返回的响应主体。|
|
||||
| nodelay | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则不要延迟突发阈值内的请求。 |
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则允许 APISIX 在插件或其依赖项不可用时继续处理没有插件的请求。|
|
||||
| policy | string | 否 | local | ["local","redis","redis-cluster"] | 速率限制计数器的策略。如果是 `local`,则计数器存储在本地内存中。如果是 `redis`,则计数器存储在 Redis 实例上。如果是 `redis-cluster`,则计数器存储在 Redis 集群中。|
|
||||
| allow_degradation | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则允许 APISIX 在插件或其依赖项不可用时继续处理没有插件的请求。|
|
||||
| show_limit_quota_header | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则在响应标头中包含 `X-RateLimit-Limit` 以显示总配额和 `X-RateLimit-Remaining` 以显示剩余配额。|
|
||||
| redis_host | string | 否 | | | Redis 节点的地址。当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时必填。 |
|
||||
| redis_port | integer | 否 | 6379 | [1,...] | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时,Redis 节点的端口。 |
|
||||
| redis_username | string | 否 | | | 如果使用 Redis ACL,则为 Redis 的用户名。如果使用旧式身份验证方法 `requirepass`,则仅配置 `redis_password`。当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时使用。 |
|
||||
| redis_password | string | 否 | | | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 或 `redis-cluster` 时,Redis 节点的密码。 |
|
||||
| redis_ssl | boolean | 否 | false |如果为 true,则在 `policy` 为 `redis` 时使用 SSL 连接到 Redis 集群。|
|
||||
| redis_ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则在 `policy` 为 `redis` 时验证服务器 SSL 证书。|
|
||||
| redis_database | integer | 否 | 0 | >= 0 | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 时,Redis 中的数据库编号。|
|
||||
| redis_timeout | integer | 否 | 1000 | [1,...] | 当 `policy` 为 `redis` 或 `redis-cluster` 时,Redis 超时值(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| redis_cluster_nodes | array[string] | 否 | | | 具有至少两个地址的 Redis 群集节点列表。当 policy 为 redis-cluster 时必填。 |
|
||||
redis_cluster_name | string | 否 | | | | Redis 集群的名称。当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster` 时必须使用。|
|
||||
| redis_cluster_ssl | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 `true`,当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster`时,使用 SSL 连接 Redis 集群。|
|
||||
| redis_cluster_ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 `true`,当 `policy` 为 `redis-cluster` 时,验证服务器 SSL 证书。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在不同场景中配置 `limit-req`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过远程地址应用速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了通过单个变量 `remote_addr` 对 HTTP 请求进行速率限制。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `limit-req` 插件创建允许每个远程地址 1 QPS 的路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "limit-req-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-req": {
|
||||
"rate": 1,
|
||||
"burst": 0,
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"key_type": "var",
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429,
|
||||
"nodelay": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送请求以验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
该请求已消耗了时间窗口允许的所有配额。如果您在同一秒内再次发送请求,您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应,表示请求超出了配额阈值。
|
||||
|
||||
### 允许速率限制阈值
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何配置 `burst` 以允许速率限制阈值超出配置的值并实现请求限制。您还将看到与未实施限制时的比较。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `limit-req` 插件创建一个路由,允许每个远程地址 1 QPS,并将 `burst` 设置为 1,以允许 1 个超过 `rate` 的请求延迟处理:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-req-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-req": {
|
||||
"rate": 1,
|
||||
"burst": 1,
|
||||
"key": "remote_addr",
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成三个对路由的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 3 | xargs -I{} curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200 responses: $count_200 ; 429 responses: $count_429"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您可能会看到所有三个请求都成功:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200 responses: 3 ; 429 responses: 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,将 `burst` 更新为 0 或将 `nodelay` 设置为 `true`,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/limit-req-route" -X PATCH \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"limit-req": {
|
||||
"nodelay": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再次向路由生成三个请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resp=$(seq 3 | xargs -I{} curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n") && \
|
||||
count_200=$(echo "$resp" | grep "200" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
count_429=$(echo "$resp" | grep "429" | wc -l) && \
|
||||
echo "200 responses: $count_200 ; 429 responses: $count_429"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应,表明超出速率的请求已被拒绝:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
200 responses: 1 ; 429 responses: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过远程地址和消费者名称应用速率限制
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了通过变量组合 `remote_addr` 和 `consumer_name` 来限制请求的速率。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `limit-req` 插件创建一个路由,允许每个远程地址和每个消费者 有 1 QPS。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `john`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "john"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/john/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建第二个消费者 `jane`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "jane"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/jane/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-jane-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "jane-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `key-auth` 和 `limit-req` 插件的路由,并在 `limit-req` 插件中指定使用变量组合作为速率限制 key:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "limit-req-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {},
|
||||
"limit-req": {
|
||||
"rate": 1,
|
||||
"burst": 0,
|
||||
"key": "$remote_addr $consumer_name",
|
||||
"key_type": "var_combination",
|
||||
"rejected_code": 429
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时发送两个请求,每个请求针对一个消费者:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H 'apikey: jane-key' & \
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H 'apikey: john-key' &
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到两个请求的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK`,表明请求未超过每个消费者的阈值。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在同一秒内以任一消费者身份发送更多请求,应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
这验证了插件速率限制是通过变量 `remote_addr` 和 `consumer_name` 的来实现的。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: log-rotate
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- 日志切分
|
||||
description: 云原生 API 网关 Apache APISIX log-rotate 插件用于定期切分日志目录下的访问日志和错误日志。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`log-rotate` 插件用于定期切分日志目录下的访问日志和错误日志。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以自定义日志轮换的频率以及要保留的日志数量。当日志数量超过限制时,旧的日志会被自动删除。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参数
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------- | ------ | ------- | ------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| interval | integer | 是 | 60 * 60 | | 每间隔多长时间切分一次日志,以秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| max_kept | integer | 是 | 24 * 7 | | 最多保留多少份历史日志,超过指定数量后,自动删除老文件。 |
|
||||
| max_size | integer | 否 | -1 | | 日志文件超过指定大小时进行切分,单位为 Byte。如果 `max_size` 小于 0 或者根据 `interval` 计算的时间到达时,将不会根据 `max_size` 切分日志。 |
|
||||
| enable_compression | boolean | 否 | false | [false, true] | 当设置为 `true` 时,启用日志文件压缩。该功能需要在系统中安装 `tar` 。 |
|
||||
|
||||
开启该插件后,就会按照参数自动切分日志文件了。比如以下示例是根据 `interval: 10` 和 `max_kept: 10` 得到的样本。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ll logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
total 44K
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 0 Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-33-40_access.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 2.8K Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-33-40_error.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 0 Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-33-50_access.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 2.4K Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-33-50_error.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 0 Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-34-00_access.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 2.4K Mar 20 20:34 2020-03-20_20-34-00_error.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 0 Mar 20 20:34 2020-03-20_20-34-10_access.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 2.4K Mar 20 20:34 2020-03-20_20-34-10_error.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 0 Mar 20 20:34 access.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 21:31 error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当开启日志文件压缩时,日志文件名称如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
ll logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
total 10.5K
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-33-50_access.log.tar.gz
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-33-50_error.log.tar.gz
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 20:33 2020-03-20_20-34-00_access.log.tar.gz
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 20:34 2020-03-20_20-34-00_error.log.tar.gz
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 20:34 2020-03-20_20-34-10_access.log.tar.gz
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 20:34 2020-03-20_20-34-10_error.log.tar.gz
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 0 Mar 20 20:34 access.log
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 resty resty 1.5K Mar 20 21:31 error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
**该插件默认为禁用状态**,你可以在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中启用 `log-rotate` 插件,不需要在任何路由或服务中绑定。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
# the plugins you enabled
|
||||
- log-rotate
|
||||
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
log-rotate:
|
||||
interval: 3600 # rotate interval (unit: second)
|
||||
max_kept: 168 # max number of log files will be kept
|
||||
max_size: -1 # max size of log files will be kept
|
||||
enable_compression: false # enable log file compression(gzip) or not, default false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
配置完成,你需要重新加载 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你不再需要该插件时,只需要在 `./conf/config.yaml` 中删除或注释该插件即可。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
# the plugins you enabled
|
||||
# - log-rotate
|
||||
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: loggly
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- SolarWinds Loggly
|
||||
description: API 网关 Apache APISIX loggly 插件可用于将日志转发到 SolarWinds Loggly 进行分析和存储。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`loggly` 插件可用于将日志转发到 [SolarWinds Loggly](https://www.solarwinds.com/loggly) 进行分析和存储。
|
||||
|
||||
当启用插件时,APISIX 会将请求上下文信息序列化为符合 [Loggly Syslog](https://documentation.solarwinds.com/en/success_center/loggly/content/admin/streaming-syslog-without-using-files.htm?cshid=loggly_streaming-syslog-without-using-files) 的数据格式,即具有 [RFC5424](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc5424) 兼容标头的 Syslog。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|------------------------|---------------|----------|---------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| customer_token | string | 是 | | 将日志发送到 Loggly 时使用的唯一标识符,以确保将日志发送到正确的组织帐户。 |
|
||||
| severity | string (enum) | 否 | INFO | Syslog 日志事件的严重性级别。包括:`DEBUG`、`INFO`、`NOTICE`、`WARNING`、`ERR`、`CRIT`、`ALERT` 和 `EMEGR`。 |
|
||||
| severity_map | object | 否 | nil | 一种将上游 HTTP 响应代码映射到 Syslog 中的方法。 `key-value`,其中 `key` 是 HTTP 响应代码,`value`是 Syslog 严重级别。例如`{"410": "CRIT"}`。 |
|
||||
| tags | array | 否 | | 元数据将包含在任何事件日志中,以帮助进行分段和过滤。 |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | false | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含请求体。**注意**:如果请求体无法完全存放在内存中,由于 NGINX 的限制,APISIX 无法将它记录下来。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array | 否 | | 当 `include_req_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时的过滤器。只有当此处设置的表达式求值为 `true` 时,才会记录请求体。有关更多信息,请参阅 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | false | 当设置为 `true` 时,包含响应体。 |
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array | 否 | | 当 `include_resp_body` 属性设置为 `true` 时进行过滤响应体,并且只有当此处设置的表达式计算结果为 `true` 时,才会记录响应体。更多信息,请参考 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理器来聚合并批量处理条目(日志或数据)。这样可以避免插件频繁地提交数据,默认设置情况下批处理器会每 `5` 秒钟或队列中的数据达到 `1000` 条时提交数据,如需了解批处理器相关参数设置,请参考 [Batch-Processor](../batch-processor.md#配置)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果要生成用户令牌,请在 Loggly 系统中的 `<your assigned subdomain>/loggly.com/tokens` 设置,或者在系统中单击 `Logs > Source setup > Customer tokens`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认日志格式示例
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<10>1 2024-01-06T06:50:51.739Z 127.0.0.1 apisix 58525 - [token-1@41058 tag="apisix"] {"service_id":"","server":{"version":"3.7.0","hostname":"localhost"},"apisix_latency":100.99985313416,"request":{"url":"http://127.0.0.1:1984/opentracing","headers":{"content-type":"application/x-www-form-urlencoded","user-agent":"lua-resty-http/0.16.1 (Lua) ngx_lua/10025","host":"127.0.0.1:1984"},"querystring":{},"uri":"/opentracing","size":155,"method":"GET"},"response":{"headers":{"content-type":"text/plain","server":"APISIX/3.7.0","transfer-encoding":"chunked","connection":"close"},"size":141,"status":200},"route_id":"1","latency":103.99985313416,"upstream_latency":3,"client_ip":"127.0.0.1","upstream":"127.0.0.1:1982","start_time":1704523851634}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件元数据设置
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以通过插件元数据配置插件。详细配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|------------|---------|-------|----------------------|--------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| host | string | 否 | "logs-01.loggly.com" | | 发送日志的主机的端点。 |
|
||||
| port | integer | 否 | 514 | | 要连接的 Loggly 端口。仅用于 `syslog` 协议。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 5000 | | 发送数据请求超时时间(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| protocol | string | 否 | "syslog" | [ "syslog", "http", "https" ] | 将日志发送到 Loggly 的协议。 |
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | nil | | 以 JSON 格式的键值对来声明日志格式。对于值部分,仅支持字符串。如果是以 `$` 开头,则表明是要获取 [APISIX 变量](../../../en/latest/apisix-variable.md) 或 [NGINX 内置变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
APISIX 支持 [Syslog](https://documentation.solarwinds.com/en/success_center/loggly/content/admin/streaming-syslog-without-using-files.htm)、[HTTP/S](https://documentation.solarwinds.com/en/success_center/loggly/content/admin/http-bulk-endpoint.htm)(批量端点)协议将日志事件发送到 Loggly。**默认情况下 `protocol` 的值为 `syslog`**。该协议允许你通过一些细粒度的控制(基于上游 HTTP 响应代码的日志严重性映射)发送符合 RFC5424 的系统日志事件。但是 HTTP/S 批量端点非常适合以更快的传输速度发送更大量的日志事件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
Syslog 协议允许你发送符合 RFC5424 的 syslog 事件并进行细粒度控制。但是在以快速传输速度发送大量日志时,使用 HTTP/S 批量端点会更好。你可以通过以下方式更新元数据以更新使用的协议:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/loggly \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"protocol": "http"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
**完整配置**
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins":{
|
||||
"loggly":{
|
||||
"customer_token":"0e6fe4bf-376e-40f4-b25f-1d55cb29f5a2",
|
||||
"tags":["apisix", "testroute"],
|
||||
"severity":"info",
|
||||
"severity_map":{
|
||||
"503": "err",
|
||||
"410": "alert"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"buffer_duration":60,
|
||||
"max_retry_count":0,
|
||||
"retry_delay":1,
|
||||
"inactive_timeout":2,
|
||||
"batch_max_size":10
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes":{
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:80":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri":"/index.html"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**最小化配置**
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins":{
|
||||
"loggly":{
|
||||
"customer_token":"0e6fe4bf-376e-40f4-b25f-1d55cb29f5a2",
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream":{
|
||||
"type":"roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes":{
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:80":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri":"/index.html"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令向 APISIX 发出请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/index.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发出请求后,你就可以在 Loggly 仪表盘上查看相关日志:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,407 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: loki-logger
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Loki-logger
|
||||
- Grafana Loki
|
||||
description: loki-logger 插件通过 Loki HTTP API /loki/api/v1/push 将请求和响应日志批量推送到 Grafana Loki。该插件还支持自定义日志格式。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/loki-logger" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`loki-logger` 插件通过 [Loki HTTP API](https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/reference/loki-http-api/#loki-http-api) `/loki/api/v1/push` 将请求和响应日志批量推送到 [Grafana Loki](https://grafana.com/oss/loki/)。该插件还支持自定义日志格式。
|
||||
|
||||
启用后,插件会将请求上下文信息序列化为 [JSON object](https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/api/#push-log-entries-to-loki) 并将其添加到队列中,然后再将其推送到 Loki。有关更多详细信息,请参阅批处理处理器 [batch processor](../batch-processor.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|--|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| end_addrs | array[string] | 是 | | | Loki API URL,例如 `http://127.0.0.1:3100`。如果配置了多个端点,日志将被推送到列表中随机确定的端点。 |
|
||||
| end_uri | string | 否 | /loki/api/v1/push | | Loki 提取端点的 URI 路径。 |
|
||||
| tenant_id | string | 否 | fake | | Loki 租户 ID。根据 Loki 的 [多租户文档](https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/operations/multi-tenancy/#multi-tenancy),在单租户下默认值设置为 `fake`。 |
|
||||
| headers | object | 否 | | | 请求头键值对(对 `X-Scope-OrgID` 和 `Content-Type` 的设置将会被忽略)。 |
|
||||
| log_labels | object | 否 | {job = "apisix"} | | Loki 日志标签。支持 [NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html) 和值中的常量字符串。变量应以 `$` 符号为前缀。例如,标签可以是 `{"origin" = "apisix"}` 或 `{"origin" = "$remote_addr"}`。|
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则验证 Loki 的 SSL 证书。|
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000 | [1, 60000] | Loki 服务 HTTP 调用的超时时间(以毫秒为单位)。|
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则保持连接以应对多个请求。|
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000 | >=1000 | Keepalive 超时时间(以毫秒为单位)。|
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | >=1 | 连接池中的最大连接数。|
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | |自定义日志格式为 JSON 格式的键值对。值中支持 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 和 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)。 |
|
||||
| name | string | 否 | loki-logger | | 批处理器插件的唯一标识符。如果使用 [Prometheus](./prometheus.md) 监控 APISIX 指标,则名称会导出到 `apisix_batch_process_entries`。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则将请求正文包含在日志中。请注意,如果请求正文太大而无法保存在内存中,则由于 NGINX 的限制而无法记录。 |
|
||||
| include_req_body_expr | array[array] | 否 | | |一个或多个 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 形式条件的数组。在 `include_req_body` 为 true 时使用。仅当此处配置的表达式计算结果为 true 时,才会记录请求正文。|
|
||||
| include_resp_body | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则将响应正文包含在日志中。|
|
||||
| include_resp_body_expr | array[array] | 否 | | | 一个或多个 [lua-resty-expr](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-expr) 形式条件的数组。在 `include_resp_body` 为 true 时使用。仅当此处配置的表达式计算结果为 true 时,才会记录响应正文。|
|
||||
|
||||
该插件支持使用批处理器对条目(日志/数据)进行批量聚合和处理,避免了频繁提交数据的需求。批处理器每隔 `5` 秒或当队列中的数据达到 `1000` 时提交数据。有关更多信息或设置自定义配置,请参阅 [批处理器](../batch-processor.md#configuration)。
|
||||
|
||||
## Plugin Metadata
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用 [Plugin Metadata](../terminology/plugin-metadata.md) 全局配置日志格式,该 Plugin Metadata 配置所有 `loki-logger` 插件实例的日志格式。如果在单个插件实例上配置的日志格式与在 Plugin Metadata 上配置的日志格式不同,则在单个插件实例上配置的日志格式优先。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|------|------|----------|--|-------------|
|
||||
| log_format | object | 否 | | 日志格式以 JSON 格式声明为键值对。值只支持字符串类型。可以通过在字符串前面加上 `$` 来使用 [APISIX 变量](../apisix-variable.md) 和 [NGINX 变量](http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html) 。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例演示了如何为不同场景配置 `loki-logger` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
为了遵循示例,请在 Docker 中启动一个示例 Loki 实例:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/grafana/loki/v3.0.0/cmd/loki/loki-local-config.yaml -O loki-config.yaml
|
||||
docker run --name loki -d -v $(pwd):/mnt/config -p 3100:3100 grafana/loki:3.2.1 -config.file=/mnt/config/loki-config.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此外,启动 Grafana 实例来查看和可视化日志:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d --name=apisix-quickstart-grafana \
|
||||
-p 3000:3000 \
|
||||
grafana/grafana-oss
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要连接 Loki 和 Grafana,请访问 Grafana,网址为 [`http://localhost:3000`](http://localhost:3000)。在 __Connections > Data sources__ 下,添加新数据源并选择 Loki。您的连接 URL 应遵循 `http://{your_ip_address}:3100` 的格式。保存新数据源时,Grafana 还应测试连接,您应该会看到 Grafana 通知数据源已成功连接。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 以默认日志格式记录请求和响应
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在路由上配置 `loki-logger` 插件以记录通过路由的请求和响应。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `loki-logger` 插件创建路由并配置 Loki 的地址:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "loki-logger-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"loki-logger": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://192.168.1.5:3100"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一些请求以生成日志条目:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到所有请求的“HTTP/1.1 200 OK”响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [Grafana explore view](http://localhost:3000/explore) 并运行查询 `job = apisix`。您应该会看到与您的请求相对应的许多日志,例如以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"route_id": "loki-logger-route",
|
||||
"response": {
|
||||
"status": 200,
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"date": "Fri, 03 Jan 2025 03:54:26 GMT",
|
||||
"server": "APISIX/3.11.0",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-credentials": "true",
|
||||
"content-length": "391",
|
||||
"access-control-allow-origin": "*",
|
||||
"content-type": "application/json",
|
||||
"connection": "close"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 619
|
||||
},
|
||||
"start_time": 1735876466,
|
||||
"client_ip": "192.168.65.1",
|
||||
"service_id": "",
|
||||
"apisix_latency": 5.0000038146973,
|
||||
"upstream": "34.197.122.172:80",
|
||||
"upstream_latency": 666,
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"hostname": "0b9a772e68f8",
|
||||
"version": "3.11.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/8.6.0",
|
||||
"accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:9080"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 85,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything",
|
||||
"querystring": {},
|
||||
"uri": "/anything"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"latency": 671.0000038147
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这验证了 Loki 已从 APISIX 接收日志。您还可以在 Grafana 中创建仪表板,以进一步可视化和分析日志。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Plugin Metadata 自定义日志格式
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何使用 [Plugin Metadata](../terminology/plugin-metadata.md) 自定义日志格式。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `loki-logger` 插件创建路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "loki-logger-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"loki-logger": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://192.168.1.5:3100"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为 `loki-logger` 配置 Plugin Metadata,它将更新所有需要记录请求的路由的日志格式:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/loki-logger" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H 'X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}' \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"host": "$host",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr",
|
||||
"route_id": "$route_id",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求以生成新的日志条目:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [Grafana explore view](http://localhost:3000/explore) 并运行查询 `job = apisix`。您应该会看到与您的请求相对应的日志条目,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"@timestamp":"2025-01-03T21:11:34+00:00",
|
||||
"client_ip":"192.168.65.1",
|
||||
"route_id":"loki-logger-route",
|
||||
"host":"127.0.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果路由上的插件指定了特定的日志格式,它将优先于 Plugin Metadata 中指定的日志格式。例如,按如下方式更新上一个路由上的插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/loki-logger-route" -X PATCH \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"loki-logger": {
|
||||
"log_format": {
|
||||
"route_id": "$route_id",
|
||||
"client_ip": "$remote_addr",
|
||||
"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求以生成新的日志条目:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [Grafana explore view](http://localhost:3000/explore) 并重新运行查询 `job = apisix`。您应该会看到与您的请求相对应的日志条目,与路由上配置的格式一致,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"client_ip":"192.168.65.1",
|
||||
"route_id":"loki-logger-route",
|
||||
"@timestamp":"2025-01-03T21:19:45+00:00"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 有条件地记录请求主体
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何有条件地记录请求主体。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `loki-logger` 创建路由,仅在 URL 查询字符串 `log_body` 为 `yes` 时记录请求主体:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "loki-logger-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"loki-logger": {
|
||||
"endpoint_addrs": ["http://192.168.1.5:3100"],
|
||||
"include_req_body": true,
|
||||
"include_req_body_expr": [["arg_log_body", "==", "yes"]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用满足条件的 URL 查询字符串向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?log_body=yes" -X POST -d '{"env": "dev"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [Grafana explore view](http://localhost:3000/explore) 并重新运行查询 `job = apisix`。您应该会看到与您的请求相对应的日志条目,与路由上配置的格式一致,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"route_id": "loki-logger-route",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"body": "{\"env\": \"dev\"}",
|
||||
"size": 182,
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?log_body=yes",
|
||||
"querystring": {
|
||||
"log_body": "yes"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uri": "/anything?log_body=yes"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"latency": 809.99994277954
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一个没有任何 URL 查询字符串的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -X POST -d '{"env": "dev"}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航到 [Grafana explore view](http://localhost:3000/explore) 并重新运行查询 `job = apisix`。您应该会看到与您的请求相对应的日志条目,与路由上配置的格式一致,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"route_id": "loki-logger-route",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"size": 169,
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything",
|
||||
"querystring": {},
|
||||
"uri": "/anything"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"latency": 557.00016021729
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
|
||||
如果您除了将 `include_req_body` 或 `include_resp_body` 设置为 `true` 之外还自定义了 `log_format`,则插件不会在日志中包含正文。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一种解决方法,您可以在日志格式中使用 NGINX 变量 `$request_body`,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kafka-logger": {
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"log_format": {"body": "$request_body"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### 日志未正确推送
|
||||
|
||||
请查看 `error.log` 文件以获取此类日志。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
2023/04/30 13:45:46 [error] 19381#19381: *1075673 [lua] batch-processor.lua:95: Batch Processor[loki logger] failed to process entries: loki server returned status: 401, body: no org id, context: ngx.timer, client: 127.0.0.1, server: 0.0.0.0:9081
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以根据错误代码 `failed to process entries: loki server returned status: 401, body: no org id` 和 loki 服务器的响应正文来诊断错误。
|
||||
|
||||
### 当请求每秒 (RPS) 较高时出现错误?
|
||||
|
||||
- 请确保 `keepalive` 相关的配置已正确设置。有关更多信息,请参阅[属性](#属性) 。
|
||||
- 请检查 `error.log` 中的日志,查找此类日志。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
2023/04/30 13:49:34 [error] 19381#19381: *1082680 [lua] batch-processor.lua:95: Batch Processor[loki logger] failed to process entries: loki server returned status: 429, body: Ingestion rate limit exceeded for user tenant_1 (limit: 4194304 bytes/sec) while attempting to ingest '1000' lines totaling '616307' bytes, reduce log volume or contact your Loki administrator to see if the limit can be increased, context: ngx.timer, client: 127.0.0.1, server: 0.0.0.0:9081
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 通常与高 QPS 相关的日志如上所示。错误信息为:`Ingestion rate limit exceeded for user tenant_1 (limit: 4194304 bytes/sec) while attempting to ingest '1000' lines totaling '616307' bytes, reduce log volume or contact your Loki administrator to see if the limit can be increased`。
|
||||
- 请参考 [Loki 文档](https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/configuration/#limits_config) ,添加默认日志量和突发日志量的限制,例如 `ingestion_rate_mb` 和 `ingestion_burst_size_mb`。
|
||||
|
||||
在开发过程中进行测试时,将 `ingestion_burst_size_mb` 设置为 100 可以确保 APISIX 以至少 10000 RPS 的速率正确推送日志。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: mocking
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Mocking
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX `mocking` 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`mocking` 插件用于模拟 API。当执行该插件时,它将随机返回指定格式的模拟数据,并且请求不会转发到上游。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------| ----- | ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| delay | integer| 否 | | 延时返回的时间,单位为秒。 |
|
||||
| response_status | integer| 否 | 200 | 返回响应的 HTTP 状态码。 |
|
||||
| content_type | string | 否 | application/json | 返回响应的 Header `Content-Type`。 |
|
||||
| response_example| string | 否 | | 返回响应的 Body,支持使用变量,例如 `$remote_addr $consumer_name`,与 `response_schema` 字段二选一。 |
|
||||
| response_schema | object | 否 | | 指定响应的 `jsonschema` 对象,未指定 `response_example` 字段时生效。 |
|
||||
| with_mock_header| boolean| 否 | true | 当设置为 `true` 时,将添加响应头 `x-mock-by: APISIX/{version}`。设置为 `false` 时则不添加该响应头。 |
|
||||
| response_headers| object | 否 | | 要在模拟响应中添加的标头。示例:`{"X-Foo": "bar", "X-Few": "baz"}` |
|
||||
|
||||
JSON Schema 在其字段中支持以下类型:
|
||||
|
||||
- `string`
|
||||
- `number`
|
||||
- `integer`
|
||||
- `boolean`
|
||||
- `object`
|
||||
- `array`
|
||||
|
||||
以下是一个 JSON Schema 示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"properties":{
|
||||
"field0":{
|
||||
"example":"abcd",
|
||||
"type":"string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field1":{
|
||||
"example":123.12,
|
||||
"type":"number"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field3":{
|
||||
"properties":{
|
||||
"field3_1":{
|
||||
"type":"string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field3_2":{
|
||||
"properties":{
|
||||
"field3_2_1":{
|
||||
"example":true,
|
||||
"type":"boolean"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field3_2_2":{
|
||||
"items":{
|
||||
"example":155.55,
|
||||
"type":"integer"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"array"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"object"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"object"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field2":{
|
||||
"items":{
|
||||
"type":"string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"array"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"object"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以下为上述 JSON Schema 可能生成的返回对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field1": 123.12,
|
||||
"field3": {
|
||||
"field3_1": "LCFE0",
|
||||
"field3_2": {
|
||||
"field3_2_1": true,
|
||||
"field3_2_2": [
|
||||
155,
|
||||
155
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field0": "abcd",
|
||||
"field2": [
|
||||
"sC"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过如下命令在指定路由上启用 `mocking` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"mocking": {
|
||||
"delay": 1,
|
||||
"content_type": "application/json",
|
||||
"response_status": 200,
|
||||
"response_schema": {
|
||||
"properties":{
|
||||
"field0":{
|
||||
"example":"abcd",
|
||||
"type":"string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field1":{
|
||||
"example":123.12,
|
||||
"type":"number"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field3":{
|
||||
"properties":{
|
||||
"field3_1":{
|
||||
"type":"string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field3_2":{
|
||||
"properties":{
|
||||
"field3_2_1":{
|
||||
"example":true,
|
||||
"type":"boolean"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field3_2_2":{
|
||||
"items":{
|
||||
"example":155.55,
|
||||
"type":"integer"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"array"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"object"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"object"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"field2":{
|
||||
"items":{
|
||||
"type":"string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"array"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type":"object"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令启用插件后,可以使用如下方式测试插件是否启用成功:
|
||||
|
||||
当 `mocking` 插件配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"delay":0,
|
||||
"content_type":"",
|
||||
"with_mock_header":true,
|
||||
"response_status":201,
|
||||
"response_example":"{\"a\":1,\"b\":2}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过如下命令进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/test-mock -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```Shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
|
||||
Date: Fri, 14 Jan 2022 11:49:34 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
x-mock-by: APISIX/2.10.0
|
||||
Server: APISIX/2.10.0
|
||||
|
||||
{"a":1,"b":2}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `mocking` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/index.html",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: mqtt-proxy
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- MQTT Proxy
|
||||
description: 本文档介绍了 Apache APISIX mqtt-proxy 插件的信息,通过 `mqtt-proxy` 插件可以使用 MQTT 的 `client_id` 进行动态负载平衡。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
通过 `mqtt-proxy` 插件可以使用 MQTT 的 `client_id` 进行动态负载平衡。它仅适用于 `stream` 模式。
|
||||
|
||||
这个插件支持 MQTT [3.1.*](http://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v3.1.1/os/mqtt-v3.1.1-os.html) 及 [5.0]( https://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v5.0/mqtt-v5.0.html ) 两个协议。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------------- | ------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| protocol_name | string | 是 | 协议名称,正常情况下应为 `MQTT`。 |
|
||||
| protocol_level | integer | 是 | 协议级别,MQTT `3.1.*` 为 `4`,MQTT `5.0` 应是`5`。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
为了启用该插件,需要先在配置文件(`./conf/config.yaml`)中加载 `stream_proxy` 相关配置。以下配置代表监听 `9100` TCP 端口:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
...
|
||||
router:
|
||||
http: 'radixtree_uri'
|
||||
ssl: 'radixtree_sni'
|
||||
stream_proxy: # TCP/UDP proxy
|
||||
tcp: # TCP proxy port list
|
||||
- 9100
|
||||
dns_resolver:
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以将请求发送到 `9100` 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以创建一个 stream 路由并启用 `mqtt-proxy` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"mqtt-proxy": {
|
||||
"protocol_name": "MQTT",
|
||||
"protocol_level": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": [{
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port": 1980,
|
||||
"weight": 1
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在 macOS 中使用 Docker,则 `host.docker.internal` 是 `host` 的正确属性。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件暴露了一个变量 `mqtt_client_id`,你可以使用它来通过客户端 ID 进行负载均衡。比如:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"mqtt-proxy": {
|
||||
"protocol_name": "MQTT",
|
||||
"protocol_level": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "chash",
|
||||
"key": "mqtt_client_id",
|
||||
"nodes": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"port": 1995,
|
||||
"weight": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.2",
|
||||
"port": 1995,
|
||||
"weight": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
不同客户端 ID 的 MQTT 连接将通过一致性哈希算法被转发到不同的节点。如果客户端 ID 为空,将会通过客户端 IP 进行均衡。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用 mqtt-proxy 插件启用 mTLS
|
||||
|
||||
Stream 代理可以使用 TCP 连接并且支持 TLS。请参考 [如何通过 tcp 连接接受 tls](../stream-proxy.md/#accept-tls-over-tcp-connection) 打开启用了 TLS 的 stream 代理。
|
||||
|
||||
`mqtt-proxy` 插件通过 Stream 代理的指定端口的 TCP 通信启用,如果 `tls` 设置为 `true`,则还要求客户端通过 TLS 进行身份验证。
|
||||
|
||||
配置 `ssl` 提供 CA 证书和服务器证书,以及 SNI 列表。使用 `ssl` 保护 `stream_routes` 的步骤等同于 [protect Routes](../mtls.md/#protect-route)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建 stream_route 并配置 mqtt-proxy 插件和 mTLS
|
||||
|
||||
通过以下示例可以创建一个配置了 `mqtt-proxy` 插件的 `stream_route`,需要提供 CA 证书、客户端证书和客户端密钥(对于不受主机信任的自签名证书,请使用 -k 选项):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"mqtt-proxy": {
|
||||
"protocol_name": "MQTT",
|
||||
"protocol_level": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sni": "${your_sni_name}",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
`sni` 名称必须与提供的 CA 和服务器证书创建的 SSL 对象的一个或多个 SNI 匹配。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X DELETE
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: multi-auth
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Multi Auth
|
||||
- multi-auth
|
||||
description: 本文档包含有关 Apache APISIX multi-auth 插件的信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
插件 `multi-auth` 用于向 `Route` 或者 `Service` 中,添加多种身份验证方式。它支持 `auth` 类型的插件。您可以使用 `multi-auth` 插件,来组合不同的身份认证方式。
|
||||
|
||||
插件通过迭代 `auth_plugins` 属性指定的插件列表,提供了灵活的身份认证机制。它允许多个 `Consumer` 在使用不同身份验证方式时共享相同的 `Route` ,同时。例如:一个 Consumer 使用 basic 认证,而另一个消费者使用 JWT 认证。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
For Route:
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|--------------|-------|------|-----|-------------------------|
|
||||
| auth_plugins | array | True | - | 添加需要支持的认证插件。至少需要 2 个插件。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
要启用插件,您必须创建两个或多个具有不同身份验证插件配置的 Consumer:
|
||||
|
||||
首先创建一个 Consumer 使用 basic-auth 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "foo1",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"basic-auth": {
|
||||
"username": "foo1",
|
||||
"password": "bar1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后再创建一个 Consumer 使用 key-auth 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"username": "foo2",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "auth-one"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建 Consumer 之后,您可以配置一个路由或服务来验证请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"multi-auth":{
|
||||
"auth_plugins":[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"basic-auth":{ }
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key-auth":{
|
||||
"query":"apikey",
|
||||
"hide_credentials":true,
|
||||
"header":"apikey"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
如上所述配置插件后,您可以向对应的 API 发起一个请求,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
请求开启 basic-auth 插件的 API
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -ufoo1:bar1 http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请求开启 key-auth 插件的 API
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -H 'apikey: auth-one' -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
...
|
||||
hello, world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果请求未授权,将会返回 `401 Unauthorized` 错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{"message":"Authorization Failed"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
要删除 `multi-auth` 插件,您可以从插件配置中删除插件对应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 会自动加载,您不需要重新启动即可生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: node-status
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 插件
|
||||
- Node status
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 API 网关 Apache APISIX node-status 插件的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`node-status` 插件可用于通过暴露的 API 查询 APISIX 的请求状态,并返回基本的状态信息。
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件属性
|
||||
|
||||
无。
|
||||
|
||||
## 插件接口
|
||||
|
||||
该插件将会增加 `/apisix/status` 的接口用来暴露 APISIX 的状态,你需要通过 [public-api](public-api.md) 插件来暴露该接口。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
`node-status` 插件默认为禁用状态,如果你需要使用该插件,请在配置文件 `./conf/config.yaml` 中启用它:
|
||||
|
||||
``` yaml title="./conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- limit-req
|
||||
- node-status
|
||||
- jwt-auth
|
||||
- zipkin
|
||||
......
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你需要为 `/apisix/status` API 配置路由,并使用 [public-api](public-api.md) 插件暴露它。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/ns -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/status",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
完成上述配置后,你可以通过以下命令向 `/apisix/status` 发送请求以获取状态信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/status -i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
Date: Tue, 03 Nov 2020 11:12:55 GMT
|
||||
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
|
||||
Connection: keep-alive
|
||||
Server: APISIX web server
|
||||
|
||||
{"status":{"total":"23","waiting":"0","accepted":"22","writing":"1","handled":"22","active":"1","reading":"0"},"id":"6790a064-8f61-44ba-a6d3-5df42f2b1bb3"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
返回结果中的参数释义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| status | APISIX 的状态信息。 |
|
||||
| total | 客户端请求总数。 |
|
||||
| waiting | 当前等待客户端请求的空闲连接数。 |
|
||||
| accepted | 当前已经接受的客户端连接总数。 |
|
||||
| writing | 当前正在写给客户端响应的连接数。 |
|
||||
| handled | 当前已经处理的连接总数,除非达到其他资源的限制,否则此值与 `accepted` 相同。 |
|
||||
| active | 当前活跃的客户端连接数。 |
|
||||
| reading | 当前正在读取请求头的连接数。 |
|
||||
| id | APISIX UID 信息,保存在 `./conf/apisix.uid` 文件中。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不再需要该插件,可以从配置文件 (`./conf/config.yaml`) 中删除它:
|
||||
|
||||
``` yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
- limit-req
|
||||
- jwt-auth
|
||||
- zipkin
|
||||
......
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以移除暴露 `/apisix/status` 接口的路由。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/ns -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X DELETE
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ocsp-stapling
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- 插件
|
||||
- ocsp-stapling
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 API 网关 Apache APISIX ocsp-stapling 插件的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`ocsp-stapling` 插件可以动态地设置 Nginx 中 [OCSP stapling](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_ssl_module.html#ssl_stapling) 的相关行为。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
这个插件是默认禁用的,通过修改配置文件 `./conf/config.yaml` 来启用它:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
- ocsp-stapling
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置文件之后,重启 APISIX 或者通过插件热加载接口来使配置生效:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugins/reload -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
插件属性存储在 SSL 资源的 `ocsp_stapling` 字段中。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|----------------|----------------------|----------|---------------|--------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| enabled | boolean | False | false | | 与 `ssl_stapling` 指令类似,用于启用或禁用 OCSP stapling 特性 |
|
||||
| skip_verify | boolean | False | false | | 与 `ssl_stapling_verify` 指令类似,用于启用或禁用对于 OCSP 响应结果的校验 |
|
||||
| cache_ttl | integer | False | 3600 | >= 60 | 指定 OCSP 响应结果的缓存时间 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
首先您应该创建一个 SSL 资源,并且证书资源中应该包含颁发者的证书。通常情况下,全链路证书就可以正常工作。
|
||||
|
||||
如下示例中,生成相关的 SSL 资源:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cert" : "'"$(cat server.crt)"'",
|
||||
"key": "'"$(cat server.key)"'",
|
||||
"snis": ["test.com"],
|
||||
"ocsp_stapling": {
|
||||
"enabled": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令生成 SSL 资源后,可以通过以下方法测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
echo -n "Q" | openssl s_client -status -connect localhost:9443 -servername test.com 2>&1 | cat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
...
|
||||
CONNECTED(00000003)
|
||||
OCSP response:
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
OCSP Response Data:
|
||||
OCSP Response Status: successful (0x0)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以通过以下方法禁用插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cert" : "'"$(cat server.crt)"'",
|
||||
"key": "'"$(cat server.key)"'",
|
||||
"snis": ["test.com"],
|
||||
"ocsp_stapling": {
|
||||
"enabled": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
在删除插件之前,需要确保所有的 SSL 资源都已经移除 `ocsp_stapling` 字段,可以通过以下命令实现对单个 SSL 资源的对应字段移除:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PATCH -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ocsp_stapling": null
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过修改配置文件 `./conf/config.yaml` 来禁用它:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
# - ocsp-stapling
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置文件之后,重启 APISIX 或者通过插件热加载接口来使配置生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugins/reload -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,329 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: opa
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Open Policy Agent
|
||||
- opa
|
||||
description: 本篇文档介绍了 Apache APISIX 通过 opa 插件与 Open Policy Agent 对接的相关信息。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`opa` 插件可用于与 [Open Policy Agent](https://www.openpolicyagent.org) 进行集成,实现后端服务的认证授权与访问服务等功能解耦,减少系统复杂性。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|-------------------|---------|----------|---------|---------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| host | string | 是 | | | OPA 服务的主机地址,例如 `https://localhost:8181`。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时,将验证 SSL 证书。 |
|
||||
| policy | string | 是 | | | OPA 策略路径,是 `package` 和 `decision` 配置的组合。当使用高级功能(如自定义响应)时,你可以省略 `decision` 配置。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000ms | [1, 60000]ms | 设置 HTTP 调用超时时间。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时,将为多个请求保持连接并处于活动状态。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000ms | [1000, ...]ms | 连接断开后的闲置时间。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | [1, ...]ms | 连接池限制。 |
|
||||
| with_route | boolean | 否 | false | | 当设置为 `true` 时,发送关于当前 Route 的信息。 |
|
||||
| with_service | boolean | 否 | false | | 当设置为 `true` 时,发送关于当前 Service 的信息。 |
|
||||
| with_consumer | boolean | 否 | false | | 当设置为 `true` 时,发送关于当前 Consumer 的信息。注意,这可能会发送敏感信息,如 API key。请确保在安全的情况下才打开它。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据定义
|
||||
|
||||
### APISIX 向 OPA 发送信息
|
||||
|
||||
下述示例代码展示了如何通过 APISIX 向 OPA 服务发送数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "http",
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
"scheme": "http",
|
||||
"path": "\/get",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl\/7.68.0",
|
||||
"accept": "*\/*",
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1:9080"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"query": {},
|
||||
"port": 9080,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"var": {
|
||||
"timestamp": 1701234567,
|
||||
"server_addr": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"server_port": "9080",
|
||||
"remote_port": "port",
|
||||
"remote_addr": "ip address"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"route": {},
|
||||
"service": {},
|
||||
"consumer": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上述代码具体释义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- `type` 代表请求类型(如 `http` 或 `stream`);
|
||||
- `request` 则需要在 `type` 为 `http` 时使用,包含基本的请求信息(如 URL、头信息等);
|
||||
- `var` 包含关于请求连接的基本信息(如 IP、端口、请求时间戳等);
|
||||
- `route`、`service` 和 `consumer` 包含的数据与 APISIX 中存储的数据相同,只有当这些对象上配置了 `opa` 插件时才会发送。
|
||||
|
||||
### OPA 向 APISIX 返回数据
|
||||
|
||||
下述示例代码展示了 OPA 服务对 APISIX 发送请求后的响应数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"result": {
|
||||
"allow": true,
|
||||
"reason": "test",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"an": "header"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status_code": 401
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上述响应中的代码释义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- `allow` 配置是必不可少的,它表示请求是否允许通过 APISIX 进行转发;
|
||||
- `reason`、`headers` 和 `status_code` 是可选的,只有当你配置一个自定义响应时才会返回这些选项信息,具体使用方法可查看后续测试用例。
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
首先启动 OPA 环境:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d --name opa -p 8181:8181 openpolicyagent/opa:0.35.0 run -s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本用法
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你运行了 OPA 服务,就可以进行基本策略的创建:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT '127.0.0.1:8181/v1/policies/example1' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: text/plain' \
|
||||
-d 'package example1
|
||||
|
||||
import input.request
|
||||
|
||||
default allow = false
|
||||
|
||||
allow {
|
||||
# HTTP method must GET
|
||||
request.method == "GET"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后在指定路由上配置 `opa` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT 'http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/r1' \
|
||||
-H 'X-API-KEY: <api-key>' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"opa": {
|
||||
"host": "http://127.0.0.1:8181",
|
||||
"policy": "example1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -X GET 127.0.0.1:9080/get
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果尝试向不同的端点发出请求,会出现请求失败的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -X POST 127.0.0.1:9080/post
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 403 FORBIDDEN
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用自定义响应
|
||||
|
||||
除了基础用法外,你还可以为更复杂的使用场景配置自定义响应,参考示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT '127.0.0.1:8181/v1/policies/example2' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: text/plain' \
|
||||
-d 'package example2
|
||||
|
||||
import input.request
|
||||
|
||||
default allow = false
|
||||
|
||||
allow {
|
||||
request.method == "GET"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# custom response body (Accepts a string or an object, the object will respond as JSON format)
|
||||
reason = "test" {
|
||||
not allow
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# custom response header (The data of the object can be written in this way)
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Location": "http://example.com/auth"
|
||||
} {
|
||||
not allow
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# custom response status code
|
||||
status_code = 302 {
|
||||
not allow
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时,你可以将 `opa` 插件的策略参数调整为 `example2`,然后发出请求进行测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -X GET 127.0.0.1:9080/get
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时如果你发出一个失败请求,将会收到来自 OPA 服务的自定义响应反馈,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i -X POST 127.0.0.1:9080/post
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 302 FOUND
|
||||
Location: http://example.com/auth
|
||||
|
||||
test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 发送 APISIX 数据
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的 OPA 服务需要根据 APISIX 的某些数据(如 Route 和 Consumer 的详细信息)来进行后续操作时,则可以通过配置插件来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
下述示例展示了一个简单的 `echo` 策略,它将原样返回 APISIX 发送的数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT '127.0.0.1:8181/v1/policies/echo' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: text/plain' \
|
||||
-d 'package echo
|
||||
|
||||
allow = false
|
||||
reason = input'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在就可以在路由上配置插件来发送 APISIX 数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X PUT 'http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/r1' \
|
||||
-H 'X-API-KEY: <api-key>' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"opa": {
|
||||
"host": "http://127.0.0.1:8181",
|
||||
"policy": "echo",
|
||||
"with_route": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时如果你提出一个请求,则可以通过自定义响应看到来自路由的数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -X GET 127.0.0.1:9080/get
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "http",
|
||||
"request": {
|
||||
xxx
|
||||
},
|
||||
"var": {
|
||||
xxx
|
||||
},
|
||||
"route": {
|
||||
xxx
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `opa` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,171 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: openfunction
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- OpenFunction
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 API 网关 Apache APISIX 的 openfunction 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`openfunction` 插件用于将开源的分布式无服务器平台 [CNCF OpenFunction](https://openfunction.dev/) 作为动态上游集成至 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
启用 `openfunction` 插件后,该插件会终止对已配置 URI 的请求,并代表客户端向 OpenFunction 的 function 发起一个新的请求,然后 `openfunction` 插件会将响应信息返回至客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------- | ------ | ------- | ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| function_uri | string | 是 | | | OpenFunction function uri,例如 `https://localhost:30858/default/function-sample`。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时执行 SSL 验证。 |
|
||||
| authorization | object | 否 | | | 访问 OpenFunction 的函数的授权凭证。|
|
||||
| authorization.service_token | string | 否 | | | OpenFunction service token,其格式为 `xxx:xxx`,支持函数入口的 basic auth 认证方式。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3000 ms | [100,...] ms | OpenFunction action 和 HTTP 调用超时时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时,保持连接的活动状态以便重复使用。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000 ms| [1000,...] ms| 当连接空闲时,保持该连接处于活动状态的时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | [1,...] | 连接断开之前,可接收的最大请求数。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
`timeout` 字段规定了 OpenFunction function 的最大执行时间,以及 APISIX 中 HTTP 客户端的请求超时时间。
|
||||
|
||||
因为 OpenFunction function 调用可能会耗费很长时间来拉取容器镜像和启动容器,如果 `timeout` 字段的值设置太小,可能会导致大量请求失败。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 前提条件
|
||||
|
||||
在使用 `openfunction` 插件之前,你需要通过以下命令运行 OpenFunction。详情参考 [OpenFunction 安装指南](https://openfunction.dev/docs/getting-started/installation/) 。
|
||||
|
||||
请确保当前环境中已经安装对应版本的 Kubernetes 集群。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建并推送函数
|
||||
|
||||
你可以参考 [OpenFunction 官方示例](https://github.com/OpenFunction/samples) 创建函数。构建函数时,你需要使用以下命令为容器仓库生成一个密钥,才可以将函数容器镜像推送到容器仓库 ( 例如 Docker Hub 或 Quay.io)。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
REGISTRY_SERVER=https://index.docker.io/v1/ REGISTRY_USER=<your_registry_user> REGISTRY_PASSWORD=<your_registry_password>
|
||||
kubectl create secret docker-registry push-secret \
|
||||
--docker-server=$REGISTRY_SERVER \
|
||||
--docker-username=$REGISTRY_USER \
|
||||
--docker-password=$REGISTRY_PASSWORD
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令在指定路由中启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"openfunction": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "http://localhost:3233/default/function-sample/test",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"service_token": "test:test"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello -X POST -d'test'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
hello, test!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置路径转发
|
||||
|
||||
`OpenFunction` 插件还支持 URL 路径转发,同时将请求代理到上游的 OpenFunction API 端点。基本请求路径的扩展(如路由 `/hello/*` 中 `*` 的部分)会被添加到插件配置中指定的 `function_uri`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 重要
|
||||
|
||||
路由上配置的 `uri` 必须以 `*` 结尾,此功能才能正常工作。APISIX 路由是严格匹配的,`*` 表示此 URI 的任何子路径都将匹配到同一路由。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例配置了此功能:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"openfunction": {
|
||||
"function_uri": "http://localhost:3233/default/function-sample",
|
||||
"authorization": {
|
||||
"service_token": "test:test"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,对路径 `hello/123` 的任何请求都将调用 OpenFunction 插件设置的对应的函数,并转发添加的路径:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello/123
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Hello, 123!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要禁用 `openfunction` 插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: openid-connect
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- OpenID Connect
|
||||
- OIDC
|
||||
description: openid-connect 插件支持与 OpenID Connect (OIDC) 身份提供商集成,例如 Keycloak、Auth0、Microsoft Entra ID、Google、Okta 等。它允许 APISIX 对客户端进行身份验证并从身份提供商处获取其信息,然后允许或拒绝其访问上游受保护资源。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/openid-connect" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`openid-connect` 插件支持与 [OpenID Connect (OIDC)](https://openid.net/connect/) 身份提供商集成,例如 Keycloak、Auth0、Microsoft Entra ID、Google、Okta 等。它允许 APISIX 对客户端进行身份验证,并从身份提供商处获取其信息,然后允许或拒绝其访问上游受保护资源。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------ | ------- | ------ | --------------------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| client_id | string | 是 | | | OAuth 客户端 ID。 |
|
||||
| client_secret | string | 是 | | | OAuth 客户端 secret。 |
|
||||
| discovery | string | 是 | | | OpenID 提供商的知名发现文档的 URL,其中包含 OP API 端点列表。插件可以直接利用发现文档中的端点。您也可以单独配置这些端点,这优先于发现文档中提供的端点。 |
|
||||
| scope | string | 否 | openid | | 与应返回的有关经过身份验证的用户的信息相对应的 OIDC 范围,也称为 [claim](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#StandardClaims)。这用于向用户授权适当的权限。默认值为 `openid`,这是 OIDC 返回唯一标识经过身份验证的用户的 `sub` 声明所需的范围。可以附加其他范围并用空格分隔,例如 `openid email profile`。 |
|
||||
| required_scopes | array[string] | 否 | | | 访问令牌中必须存在的范围。当 `bearer_only` 为 `true` 时与自省端点结合使用。如果缺少任何必需的范围,插件将以 403 禁止错误拒绝请求。|
|
||||
| realm | string | 否 | apisix | | 由于持有者令牌无效,[`WWW-Authenticate`](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6750#section-3) 响应标头中的领域伴随 401 未经授权的请求。 |
|
||||
| bearer_only | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则严格要求在身份验证请求中使用持有者访问令牌。 |
|
||||
| logout_path | string | 否 | /logout | | 激活注销的路径。 |
|
||||
| post_logout_redirect_uri | string | 否 | | | `logout_path` 收到注销请求后将用户重定向到的 URL。|
|
||||
| redirect_uri | string | 否 | | | 通过 OpenID 提供商进行身份验证后重定向到的 URI。请注意,重定向 URI 不应与请求 URI 相同,而应为请求 URI 的子路径。例如,如果路由的 `uri` 是 `/api/v1/*`,则 `redirect_uri` 可以配置为 `/api/v1/redirect`。如果未配置 `redirect_uri`,APISIX 将在请求 URI 后附加 `/.apisix/redirect` 以确定 `redirect_uri` 的值。|
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 3 | [1,...] | 请求超时时间(秒)。|
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则验证 OpenID 提供商的 SSL 证书。|
|
||||
| introspection_endpoint | string | 否 | | |用于自检访问令牌的 OpenID 提供程序的 [令牌自检](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7662) 端点的 URL。如果未设置,则将使用众所周知的发现文档中提供的自检端点[作为后备](https://github.com/zmartzone/lua-resty-openidc/commit/cdaf824996d2b499de4c72852c91733872137c9c)。|
|
||||
| introspection_endpoint_auth_method | string | 否 | client_secret_basic | | 令牌自检端点的身份验证方法。该值应为 `introspection_endpoint_auth_methods_supported` [授权服务器元数据](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8414.html) 中指定的身份验证方法之一,如众所周知的发现文档中所示,例如 `client_secret_basic`、`client_secret_post`、`private_key_jwt` 和 `client_secret_jwt`。|
|
||||
| token_endpoint_auth_method | string | 否 | client_secret_basic | | 令牌端点的身份验证方法。该值应为 `token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported` [授权服务器元数据](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8414.html) 中指定的身份验证方法之一,如众所周知的发现文档中所示,例如 `client_secret_basic`、`client_secret_post`、`private_key_jwt` 和 `client_secret_jwt`。如果配置的方法不受支持,则回退到 `token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported` 数组中的第一个方法。|
|
||||
| public_key | string | 否 | | | 用于验证 JWT 签名 id 的公钥使用非对称算法。提供此值来执行令牌验证将跳过客户端凭据流中的令牌自检。您可以以 `-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\\n……\\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----` 格式传递公钥。|
|
||||
| use_jwks | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true 并且未设置 `public_key`,则使用 JWKS 验证 JWT 签名并跳过客户端凭据流中的令牌自检。JWKS 端点是从发现文档中解析出来的。|
|
||||
| use_pkce | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则使用 [RFC 7636](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7636) 中定义的授权码流的代码交换证明密钥 (PKCE)。|
|
||||
| token_signing_alg_values_expected | string | 否 | | | 用于签署 JWT 的算法,例如 `RS256`。 |
|
||||
| set_access_token_header | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则在请求标头中设置访问令牌。默认情况下,使用 `X-Access-Token` 标头。|
|
||||
| access_token_in_authorization_header | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true 并且 `set_access_token_header` 也为 true,则在 `Authorization` 标头中设置访问令牌。 |
|
||||
| set_id_token_header | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true 并且 ID 令牌可用,则在 `X-ID-Token` 请求标头中设置值。 |
|
||||
| set_userinfo_header | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true 并且用户信息数据可用,则在 `X-Userinfo` 请求标头中设置值。 |
|
||||
| set_refresh_token_header | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true 并且刷新令牌可用,则在 `X-Refresh-Token` 请求标头中设置值。 |
|
||||
| session | object | 否 | | | 当 `bearer_only` 为 `false` 且插件使用 Authorization Code 流程时使用的 Session 配置。 |
|
||||
| session.secret | string | 是 | | 16 个字符以上 | 当 `bearer_only` 为 `false` 时,用于 session 加密和 HMAC 运算的密钥,若未配置则自动生成并保存到 etcd。当在独立模式下使用 APISIX 时,etcd 不再是配置中心,需要配置 `secret`。 |
|
||||
| session.cookie | object | 否 | | | Cookie 配置。 |
|
||||
| session.cookie.lifetime | integer | 否 | 3600 | | Cookie 生存时间(秒)。|
|
||||
| unauth_action | string | 否 | auth | ["auth","deny","pass"] | 未经身份验证的请求的操作。设置为 `auth` 时,重定向到 OpenID 提供程序的身份验证端点。设置为 `pass` 时,允许请求而无需身份验证。设置为 `deny` 时,返回 401 未经身份验证的响应,而不是启动授权代码授予流程。|
|
||||
| session_contents | object | 否 | | | 会话内容配置。如果未配置,将把所有数据存储在会话中。 |
|
||||
| session_contents.access_token | boolean | 否 | | | 若为 true,则将访问令牌存储在会话中。 |
|
||||
| session_contents.id_token | boolean | 否 | | | 若为 true,则将 ID 令牌存储在会话中。 |
|
||||
| session_contents.enc_id_token | boolean | 否 | | | 若为 true,则将加密的 ID 令牌存储在会话中。 |
|
||||
| session_contents.user | boolean | 否 | | | 若为 true,则将用户信息存储在会话中。 |
|
||||
| proxy_opts | object | 否 | | | OpenID 提供程序背后的代理服务器的配置。|
|
||||
| proxy_opts.http_proxy | string | 否 | | | HTTP 请求的代理服务器地址,例如 `http://<proxy_host>:<proxy_port>`。|
|
||||
| proxy_opts.https_proxy | string | 否 | | | HTTPS 请求的代理服务器地址,例如 `http://<proxy_host>:<proxy_port>`。 |
|
||||
| proxy_opts.http_proxy_authorization | string | 否 | | Basic [base64 用户名:密码] | 与 `http_proxy` 一起使用的默认 `Proxy-Authorization` 标头值。可以用自定义的 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求标头覆盖。 |
|
||||
| proxy_opts.https_proxy_authorization | string | 否 | | Basic [base64 用户名:密码] | 与 `https_proxy` 一起使用的默认 `Proxy-Authorization` 标头值。不能用自定义的 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求标头覆盖,因为使用 HTTPS 时,授权在连接时完成。 |
|
||||
| proxy_opts.no_proxy | string | 否 | | | 不应代理的主机的逗号分隔列表。|
|
||||
| authorization_params | object | 否 | | | 在请求中发送到授权端点的附加参数。 |
|
||||
| client_rsa_private_key | string | 否 | | | 用于签署 JWT 以向 OP 进行身份验证的客户端 RSA 私钥。当 `token_endpoint_auth_method` 为 `private_key_jwt` 时必需。 |
|
||||
| client_rsa_private_key_id | string | 否 | | | 用于计算签名的 JWT 的客户端 RSA 私钥 ID。当 `token_endpoint_auth_method` 为 `private_key_jwt` 时可选。 |
|
||||
| client_jwt_assertion_expires_in | integer | 否 | 60 | | 用于向 OP 进行身份验证的签名 JWT 的生命周期,以秒为单位。当 `token_endpoint_auth_method` 为 `private_key_jwt` 或 `client_secret_jwt` 时使用。 |
|
||||
| renew_access_token_on_expiry | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则在访问令牌过期或刷新令牌可用时尝试静默更新访问令牌。如果令牌无法更新,则重定向用户进行重新身份验证。|
|
||||
| access_token_expires_in | integer | 否 | | | 如果令牌端点响应中不存在 `expires_in` 属性,则访问令牌的有效期(以秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| refresh_session_interval | integer | 否 | | | 刷新用户 ID 令牌而无需重新认证的时间间隔。如果未设置,则不会检查网关向客户端发出的会话的到期时间。如果设置为 900,则表示在 900 秒后刷新用户的 `id_token`(或浏览器中的会话),而无需重新认证。 |
|
||||
| iat_slack | integer | 否 | 120 | | ID 令牌中 `iat` 声明的时钟偏差容忍度(以秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| accept_none_alg | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果 OpenID 提供程序未签署其 ID 令牌(例如当签名算法设置为`none` 时),则设置为 true。 |
|
||||
| accept_unsupported_alg | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果为 true,则忽略 ID 令牌签名以接受不支持的签名算法。 |
|
||||
| access_token_expires_leeway | integer | 否 | 0 | | 访问令牌续订的过期余地(以秒为单位)。当设置为大于 0 的值时,令牌续订将在令牌过期前设定的时间内进行。这样可以避免访问令牌在到达资源服务器时刚好过期而导致的错误。|
|
||||
| force_reauthorize | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,即使令牌已被缓存,也执行授权流程。 |
|
||||
| use_nonce | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,在授权请求中启用 nonce 参数。 |
|
||||
| revoke_tokens_on_logout | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则通知授权服务器,撤销端点不再需要先前获得的刷新或访问令牌。 |
|
||||
| jwk_expires_in | integer | 否 | 86400 | | JWK 缓存的过期时间(秒)。 |
|
||||
| jwt_verification_cache_ignore | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则强制重新验证承载令牌并忽略任何现有的缓存验证结果。 |
|
||||
| cache_segment | string | 否 | | | 缓存段的可选名称,用于分隔和区分令牌自检或 JWT 验证使用的缓存。|
|
||||
| introspection_interval | integer | 否 | 0 | | 缓存和自省访问令牌的 TTL(以秒为单位)。默认值为 0,这意味着不使用此选项,插件默认使用 `introspection_expiry_claim` 中定义的到期声明传递的 TTL。如果`introspection_interval` 大于 0 且小于 `introspection_expiry_claim` 中定义的到期声明传递的 TTL,则使用`introspection_interval`。|
|
||||
| introspection_expiry_claim | string | 否 | exp | | 到期声明的名称,它控制缓存和自省访问令牌的 TTL。|
|
||||
| introspection_addon_headers | array[string] | 否 | | | 用于将其他标头值附加到自省 HTTP 请求。如果原始请求中不存在指定的标头,则不会附加值。|
|
||||
| claim_validator.issuer.valid_issuers | string[] | 否 | | | 将经过审查的 jwt 发行者列入白名单。当用户未传递时,将使用发现端点返回的颁发者。如果两者均缺失,发行人将无法得到验证|
|
||||
|
||||
注意:schema 中还定义了 `encrypt_fields = {"client_secret"}`,这意味着该字段将会被加密存储在 etcd 中。具体参考 [加密存储字段](../plugin-develop.md#加密存储字段)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何针对不同场景配置 `openid-connect` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Authorization Code Flow
|
||||
|
||||
Authorization Code Flow 在 [RFC 6749,第 4.1 节](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6749#section-4.1) 中定义。它涉及用临时授权码交换访问令牌,通常由机密和公共客户端使用。
|
||||
|
||||
下图说明了实施 Authorization Code Flow 时不同实体之间的交互:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当传入请求的标头中或适当的会话 cookie 中不包含访问令牌时,插件将充当依赖方并重定向到授权服务器以继续授权码流程。
|
||||
|
||||
成功验证后,插件将令牌保留在会话 cookie 中,后续请求将使用存储在 cookie 中的令牌。
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅 [实现 Authorization Code Flow](../tutorials/keycloak-oidc.md#实现-authorization-code-grant)以获取使用`openid-connect`插件通过授权码流与 Keycloak 集成的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE)
|
||||
|
||||
Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) 在 [RFC 7636](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7636) 中定义。PKCE 通过添加代码质询和验证器来增强授权码流程,以防止授权码拦截攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
下图说明了使用 PKCE 实现授权码流程时不同实体之间的交互:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
请参阅 [实现 Authorization Code Grant](../tutorials/keycloak-oidc.md#实现-authorization-code-grant),了解使用 `openid-connect` 插件通过 PKCE 授权码流程与 Keycloak 集成的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### Client Credential Flow
|
||||
|
||||
Client Credential Flow 在 [RFC 6749,第 4.4 节](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6749#section-4.4) 中定义。它涉及客户端使用自己的凭证请求访问令牌以访问受保护的资源,通常用于机器对机器身份验证,并不代表特定用户。
|
||||
|
||||
下图说明了实施 Client Credential Flow 时不同实体之间的交互:
|
||||
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.api7.ai/uploads/2024/10/28/sbHxqnOz_client-credential-no-introspect.png" alt="Client credential flow diagram" style={{width: '70%'}} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅[实现 Client Credentials Grant](../tutorials/keycloak-oidc.md#实现-client-credentials-grant) 获取使用 `openid-connect` 插件通过客户端凭证流与 Keycloak 集成的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### Introspection Flow
|
||||
|
||||
Introspection Flow 在 [RFC 7662](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7662) 中定义。它涉及通过查询授权服务器的自省端点来验证访问令牌的有效性和详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
在此流程中,当客户端向资源服务器出示访问令牌时,资源服务器会向授权服务器的自省端点发送请求,如果令牌处于活动状态,则该端点会响应令牌详细信息,包括令牌到期时间、相关范围以及它所属的用户或客户端等信息。
|
||||
|
||||
下图说明了使用令牌自省实现 Introspection Flow 时不同实体之间的交互:
|
||||
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.api7.ai/uploads/2024/10/29/Y2RWIUV9_client-cred-flow-introspection.png" alt="Client credential with introspection diagram" style={{width: '55%'}} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅 [实现 Client Credentials Grant](../tutorials/keycloak-oidc.md#实现-client-credentials-grant) 以获取使用 `openid-connect` 插件通过带有令牌自省的客户端凭据流与 Keycloak 集成的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### Password Flow
|
||||
|
||||
Password Flow 在 [RFC 6749,第 4.3 节](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6749#section-4.3) 中定义。它专为受信任的应用程序而设计,允许它们使用用户的用户名和密码直接获取访问令牌。在此授权类型中,客户端应用程序将用户的凭据连同其自己的客户端 ID 和密钥一起发送到授权服务器,然后授权服务器对用户进行身份验证,如果有效,则颁发访问令牌。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然高效,但此流程仅适用于高度受信任的第一方应用程序,因为它要求应用程序直接处理敏感的用户凭据,如果在第三方环境中使用,则会带来重大安全风险。
|
||||
|
||||
下图说明了实施 Password Flow 时不同实体之间的交互:
|
||||
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.api7.ai/uploads/2024/10/30/njkWZVgX_pass-grant.png" alt="Password flow diagram" style={{width: '70%'}} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅 [实现 Password Grant](../tutorials/keycloak-oidc.md#实现-password-grant) 获取使用 `openid-connect` 插件通过密码流与 Keycloak 集成的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### Refresh Token Grant
|
||||
|
||||
Refresh Token Grant 在 [RFC 6749,第 6 节](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6749#section-6) 中定义。它允许客户端使用之前颁发的刷新令牌请求新的访问令牌,而无需用户重新进行身份验证。此流程通常在访问令牌过期时使用,允许客户端无需用户干预即可持续访问资源。刷新令牌与某些 OAuth 流程中的访问令牌一起颁发,其使用寿命和安全要求取决于授权服务器的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
下图说明了在实施 Password Grant 和 Refresh Token Grant 时不同实体之间的交互:
|
||||
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.api7.ai/uploads/2024/10/30/YBF7rI6M_password-with-refresh-token.png" alt="Password grant with refresh token flow diagram" style={{width: '100%'}} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅 [Refresh Token](../tutorials/keycloak-oidc.md#refresh-token) 获取使用 `openid-connect` 插件通过带令牌刷新的密码流与 Keycloak 集成的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
## 故障排除
|
||||
|
||||
本节介绍使用此插件时的一些常见问题,以帮助您排除故障。
|
||||
|
||||
### APISIX 无法连接到 OpenID 提供商
|
||||
|
||||
如果 APISIX 无法解析或无法连接到 OpenID 提供商,请仔细检查配置文件 `config.yaml` 中的 DNS 设置并根据需要进行修改。
|
||||
|
||||
### `No Session State Found`
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在使用[授权码流](#authorization-code-flow) 时遇到 500 内部服务器错误并在日志中显示以下消息,则可能有多种原因。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
the error request to the redirect_uri path, but there's no session state found
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 重定向 URI 配置错误
|
||||
|
||||
一个常见的错误配置是将 `redirect_uri` 配置为与路由的 URI 相同。当用户发起访问受保护资源的请求时,请求直接命中重定向 URI,且请求中没有 session cookie,从而导致 no session state found 错误。
|
||||
|
||||
要正确配置重定向 URI,请确保 `redirect_uri` 与配置插件的路由匹配,但不要完全相同。例如,正确的配置是将路由的 `uri` 配置为 `/api/v1/*`,并将 `redirect_uri` 的路径部分配置为 `/api/v1/redirect`。
|
||||
|
||||
您还应该确保 `redirect_uri` 包含 scheme,例如 `http` 或 `https` 。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 缺少 Session Secret
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在[standalone 模式](../../../en/latest/deployment-modes.md#standalone)下部署 APISIX,请确保配置了 `session.secret`。
|
||||
|
||||
用户 session 作为 cookie 存储在浏览器中,并使用 session 密钥进行加密。如果没有通过 `session.secret` 属性配置机密,则会自动生成机密并将其保存到 etcd。然而,在独立模式下,etcd 不再是配置中心。因此,您应该在 YAML 配置中心 `apisix.yaml` 中为此插件显式配置 `session.secret`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Cookie 未发送或不存在
|
||||
|
||||
检查 [`SameSite`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Set-Cookie#samesitesamesite-value) cookie 属性是否已正确设置(即您的应用程序是否需要跨站点发送 cookie),看看这是否会成为阻止 cookie 保存到浏览器的 cookie jar 或从浏览器发送的因素。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 上游发送的标头太大
|
||||
|
||||
如果您有 NGINX 位于 APISIX 前面来代理客户端流量,请查看 NGINX 的 `error.log` 中是否观察到以下错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
upstream sent too big header while reading response header from upstream
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果是这样,请尝试将 `proxy_buffers` 、 `proxy_buffer_size` 和 `proxy_busy_buffers_size` 调整为更大的值。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个选项是配置 `session_content` 属性来调整在会话中存储哪些数据。例如,你可以将 `session_content.access_token` 设置为 `true`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. 无效的客户端密钥
|
||||
|
||||
验证 `client_secret` 是否有效且正确。无效的 `client_secret` 将导致身份验证失败,并且不会返回任何令牌并将其存储在 session 中。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. PKCE IdP 配置
|
||||
|
||||
如果您使用授权码流程启用 PKCE,请确保您已将 IdP 客户端配置为使用 PKCE。例如,在 Keycloak 中,您应该在客户端的高级设置中配置 PKCE 质询方法:
|
||||
|
||||
<div style={{textAlign: 'center'}}>
|
||||
<img src="https://static.api7.ai/uploads/2024/11/04/xvnCNb20_pkce-keycloak-revised.jpeg" alt="PKCE keycloak configuration" style={{width: '70%'}} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,217 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: opentelemetry
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- OpenTelemetry
|
||||
description: opentelemetry 插件可用于根据 OpenTelemetry 协议规范上报 Traces 数据,该插件仅支持二进制编码的 OLTP over HTTP。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/opentelemetry" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`opentelemetry` 插件可用于根据 [OpenTelemetry Specification](https://opentelemetry.io/docs/reference/specification/) 协议规范上报 Traces 数据。该插件仅支持二进制编码的 OLTP over HTTP,即请求类型为 `application/x-protobuf` 的数据上报。
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,服务名称、租户 ID、collector 和 batch span processor 的配置已预配置在[默认配置](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/cli/config.lua)中。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过端点 `apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/opentelemetry` 更改插件的配置,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
您可以从“config.yaml”获取“admin_key”,并使用以下命令保存到环境变量中:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/plugin_metadata/opentelemetry -H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"trace_id_source": "x-request-id",
|
||||
"resource": {
|
||||
"service.name": "APISIX"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"collector": {
|
||||
"address": "127.0.0.1:4318",
|
||||
"request_timeout": 3,
|
||||
"request_headers": {
|
||||
"Authorization": "token"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"batch_span_processor": {
|
||||
"drop_on_queue_full": false,
|
||||
"max_queue_size": 1024,
|
||||
"batch_timeout": 2,
|
||||
"inactive_timeout": 1,
|
||||
"max_export_batch_size": 16
|
||||
},
|
||||
"set_ngx_var": false
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|---------------------------------------|---------------|----------|--------------|--------------|-------------|
|
||||
| sampler | object | 否 | - | - | 采样策略。 |
|
||||
| sampler.name | string | 否 | `always_off` | ["always_on", "always_off", "trace_id_ratio", "parent_base"] | 采样策略。<br />`always_on`:全采样;`always_off`:不采样;`trace_id_ratio`:基于 trace id 的百分比采样;`parent_base`:如果存在 tracing 上游,则使用上游的采样决定,否则使用配置的采样策略决策。|
|
||||
| sampler.options | object | 否 | - | - | 采样策略参数。 |
|
||||
| sampler.options.fraction | number | 否 | 0 | [0, 1] | `trace_id_ratio`:采样策略的百分比。 |
|
||||
| sampler.options.root | object | 否 | - | - | `parent_base`:采样策略在没有上游 tracing 时,会使用 root 采样策略做决策。|
|
||||
| sampler.options.root.name | string | 否 | - | ["always_on", "always_off", "trace_id_ratio"] | root 采样策略。 |
|
||||
| sampler.options.root.options | object | 否 | - | - | root 采样策略参数。 |
|
||||
| sampler.options.root.options.fraction | number | 否 | 0 | [0, 1] | `trace_id_ratio` root 采样策略的百分比|
|
||||
| additional_attributes | array[string] | 否 | - | - | 追加到 trace span 的额外属性,支持内置 NGINX 或 [APISIX 变量](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/apisix-variable/)。|
|
||||
| additional_header_prefix_attributes | array[string] | 否 | - | - | 附加到跟踪范围属性的标头或标头前缀。例如,使用 `x-my-header"` 或 `x-my-headers-*` 来包含带有前缀 `x-my-headers-` 的所有标头。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在不同场景下使用 `opentelemetry` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用 opentelemetry 插件
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,APISIX 中的 `opentelemetry` 插件是禁用的。要启用它,请将插件添加到配置文件中,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="config.yaml"
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
- opentelemetry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
有关 `config.yaml` 中可以配置的其他选项,请参阅[静态配置](#静态配置)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 Traces 上报到 OpenTelemetry
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何追踪对路由的请求并将 traces 发送到 OpenTelemetry。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Docker 启动一个 OpenTelemetry collector 实例:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -d --name otel-collector -p 4318:4318 otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个开启了 `opentelemetry` 插件的路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "otel-tracing-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"opentelemetry": {
|
||||
"sampler": {
|
||||
"name": "always_on"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你应该收到一个 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
在 OpenTelemetry collector 的日志中,你应该看到类似以下的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
2024-02-18T17:14:03.825Z info ResourceSpans #0
|
||||
Resource SchemaURL:
|
||||
Resource attributes:
|
||||
-> telemetry.sdk.language: Str(lua)
|
||||
-> telemetry.sdk.name: Str(opentelemetry-lua)
|
||||
-> telemetry.sdk.version: Str(0.1.1)
|
||||
-> hostname: Str(e34673e24631)
|
||||
-> service.name: Str(APISIX)
|
||||
ScopeSpans #0
|
||||
ScopeSpans SchemaURL:
|
||||
InstrumentationScope opentelemetry-lua
|
||||
Span #0
|
||||
Trace ID : fbd0a38d4ea4a128ff1a688197bc58b0
|
||||
Parent ID :
|
||||
ID : af3dc7642104748a
|
||||
Name : GET /anything
|
||||
Kind : Server
|
||||
Start time : 2024-02-18 17:14:03.763244032 +0000 UTC
|
||||
End time : 2024-02-18 17:14:03.920229888 +0000 UTC
|
||||
Status code : Unset
|
||||
Status message :
|
||||
Attributes:
|
||||
-> net.host.name: Str(127.0.0.1)
|
||||
-> http.method: Str(GET)
|
||||
-> http.scheme: Str(http)
|
||||
-> http.target: Str(/anything)
|
||||
-> http.user_agent: Str(curl/7.64.1)
|
||||
-> apisix.route_id: Str(otel-tracing-route)
|
||||
-> apisix.route_name: Empty()
|
||||
-> http.route: Str(/anything)
|
||||
-> http.status_code: Int(200)
|
||||
{"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "traces", "name": "debug"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要可视化这些追踪,你可以将 traces 导出到后端服务,例如 Zipkin 和 Prometheus。有关更多详细信息,请参阅[exporters](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/exporter)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在日志中使用 trace 变量
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何配置 `opentelemetry` 插件以设置以下内置变量,这些变量可以在日志插件或访问日志中使用:
|
||||
|
||||
- `opentelemetry_context_traceparent`: [W3C trace context](https://www.w3.org/TR/trace-context/#trace-context-http-headers-format)
|
||||
- `opentelemetry_trace_id`: 当前 span 的 trace_id
|
||||
- `opentelemetry_span_id`: 当前 span 的 span_id
|
||||
|
||||
如下更新配置文件。你应该自定义访问日志格式以使用 `opentelemetry` 插件变量,并在 `set_ngx_var` 字段中设置 `opentelemetry` 变量。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
nginx_config:
|
||||
http:
|
||||
enable_access_log: true
|
||||
access_log_format: '{"time": "$time_iso8601","opentelemetry_context_traceparent": "$opentelemetry_context_traceparent","opentelemetry_trace_id": "$opentelemetry_trace_id","opentelemetry_span_id": "$opentelemetry_span_id","remote_addr": "$remote_addr"}'
|
||||
access_log_format_escape: json
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
opentelemetry:
|
||||
set_ngx_var: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重新加载 APISIX 以使配置更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{"time": "18/Feb/2024:15:09:00 +0000","opentelemetry_context_traceparent": "00-fbd0a38d4ea4a128ff1a688197bc58b0-8f4b9d9970a02629-01","opentelemetry_trace_id": "fbd0a38d4ea4a128ff1a688197bc58b0","opentelemetry_span_id": "af3dc7642104748a","remote_addr": "172.10.0.1"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: openwhisk
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- OpenWhisk
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了关于 Apache APISIX openwhisk 插件的基本信息及使用方法。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`openwhisk` 插件用于将开源的分布式无服务器平台 [Apache OpenWhisk](https://openwhisk.apache.org) 作为动态上游集成至 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
启用 `openwhisk` 插件后,该插件会终止对已配置 URI 的请求,并代表客户端向 OpenWhisk 的 API Host 端点发起一个新的请求,然后 `openwhisk` 插件会将响应信息返回至客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------- | ------ | ------- | ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| api_host | string | 是 | | | OpenWhisk API Host 地址,例如 `https://localhost:3233`。 |
|
||||
| ssl_verify | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时执行 SSL 验证。 |
|
||||
| service_token | string | 是 | | | OpenWhisk service token,其格式为 `xxx:xxx` ,用于 API 调用时的身份认证。 |
|
||||
| namespace | string | 是 | | | OpenWhisk namespace,例如 `guest`。 |
|
||||
| action | string | 是 | | | OpenWhisk action,例如 `hello`。 |
|
||||
| result | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时,获得 action 元数据(执行函数并获得响应结果)。 |
|
||||
| timeout | integer | 否 | 60000ms | [1,60000]ms | OpenWhisk action 和 HTTP 调用超时时间(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| keepalive | boolean | 否 | true | | 当设置为 `true` 时,保持连接的活动状态以便重复使用。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_timeout | integer | 否 | 60000ms | [1000,...]ms | 当连接空闲时,保持该连接处于活动状态的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 |
|
||||
| keepalive_pool | integer | 否 | 5 | [1,...] | 连接断开之前,可接收的最大请求数。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note 注意
|
||||
|
||||
`timeout` 字段规定了 OpenWhisk action 的最大执行时间,以及 APISIX 中 HTTP 客户端的请求超时时间。
|
||||
|
||||
因为 OpenWhisk action 调用可能会耗费很长时间来拉取容器镜像和启动容器,所以如果 `timeout` 字段值设置太小,可能会导致大量的失败请求。
|
||||
|
||||
在 OpenWhisk 中 `timeout` 字段的值设置范围从 1 ms 到 60000 ms,建议用户将 `timeout` 字段的值至少设置为 1000ms。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
### 搭建 Apache OpenWhisk 测试环境
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在使用 `openwhisk` 插件之前,你需要通过以下命令运行 OpenWhisk standalone 模式。请确保当前环境中已经安装 Docker 软件。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run --rm -d \
|
||||
-h openwhisk --name openwhisk \
|
||||
-p 3233:3233 -p 3232:3232 \
|
||||
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
|
||||
openwhisk/standalone:nightly
|
||||
docker exec openwhisk waitready
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 安装 [openwhisk-cli](https://github.com/apache/openwhisk-cli) 工具:
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 [openwhisk-cli](https://github.com/apache/openwhisk-cli) 仓库下载已发布的适用于 Linux 系统的可执行二进制文件 wsk。
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在 OpenWhisk 中注册函数:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
wsk property set --apihost "http://localhost:3233" --auth "${service_token}"
|
||||
wsk action update test <(echo 'function main(){return {"ready":true}}') --kind nodejs:14
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建路由
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令在指定路由中启用该插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"openwhisk": {
|
||||
"api_host": "http://localhost:3233",
|
||||
"service_token": "${service_token}",
|
||||
"namespace": "guest",
|
||||
"action": "test"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试请求
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `curl` 命令测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
正常返回结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{ "ready": true }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过如下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/hello",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,474 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: prometheus
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Prometheus
|
||||
description: 本文将介绍 prometheus 插件,以及将 APISIX 与 Prometheus 集成以进行指标收集和持续监控。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/prometheus" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`prometheus` 插件提供将 APISIX 与 Prometheus 集成的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
启用该插件后,APISIX 将开始收集相关指标,例如 API 请求和延迟,并以[基于文本的展示格式](https://prometheus.io/docs/instrumenting/exposition_formats/#exposition-formats)导出到 Prometheus。然后,您可以在 Prometheus 中创建事件监控和警报,以监控 API 网关和 API 的健康状况。
|
||||
|
||||
## 静态配置
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,已在默认配置文件 [`config.lua`](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/cli/config.lua) 中对 `prometheus` 进行预配置。
|
||||
|
||||
要自定义这些值,请将相应的配置添加到 config.yaml 中。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
prometheus: # 插件:prometheus 属性
|
||||
export_uri: /apisix/prometheus/metrics # 设置 Prometheus 指标端点的 URI。
|
||||
metric_prefix: apisix_ # 设置 APISIX 生成的 Prometheus 指标的前缀。
|
||||
enable_export_server: true # 启用 Prometheus 导出服务器。
|
||||
export_addr: # 设置 Prometheus 导出服务器的地址。
|
||||
ip: 127.0.0.1 # 设置 IP。
|
||||
port: 9091 # 设置端口。
|
||||
# metrics: # 为指标创建额外的标签。
|
||||
# http_status: # 这些指标将以 `apisix_` 为前缀。
|
||||
# extra_labels: # 设置 http_status 指标的额外标签。
|
||||
# - upstream_addr: $upstream_addr
|
||||
# - status: $upstream_status
|
||||
# expire: 0 # 指标的过期时间(秒)。
|
||||
# 0 表示指标不会过期。
|
||||
# http_latency:
|
||||
# extra_labels: # 设置 http_latency 指标的额外标签。
|
||||
# - upstream_addr: $upstream_addr
|
||||
# expire: 0 # 指标的过期时间(秒)。
|
||||
# 0 表示指标不会过期。
|
||||
# bandwidth:
|
||||
# extra_labels: # 设置 bandwidth 指标的额外标签。
|
||||
# - upstream_addr: $upstream_addr
|
||||
# expire: 0 # 指标的过期时间(秒)。
|
||||
# 0 表示指标不会过期。
|
||||
# default_buckets: # 设置 `http_latency` 指标直方图的默认桶。
|
||||
# - 10
|
||||
# - 50
|
||||
# - 100
|
||||
# - 200
|
||||
# - 500
|
||||
# - 1000
|
||||
# - 2000
|
||||
# - 5000
|
||||
# - 10000
|
||||
# - 30000
|
||||
# - 60000
|
||||
# - 500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您可以使用 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html)创建 `extra_labels`。请参见[为指标添加额外标签](#为指标添加额外标签)。
|
||||
|
||||
重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------ | --------| ------ | ------ | ----------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
|prefer_name | boolean | 否 | False | 当设置为 `true` 时,则在`prometheus` 指标中导出路由/服务名称而非它们的 `id`。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 指标
|
||||
|
||||
Prometheus 中有不同类型的指标。要了解它们之间的区别,请参见[指标类型](https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/)。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是 `prometheus` 插件默认导出的指标。有关示例,请参见[获取 APISIX 指标](#获取 APISIX 指标)。请注意,一些指标,例如 `apisix_batch_process_entries`,如果没有数据,将不可见。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| apisix_bandwidth | counter | APISIX 中每个服务消耗的总流量(字节)。 |
|
||||
| apisix_etcd_modify_indexes | gauge | APISIX 键的 etcd 修改次数。 |
|
||||
| apisix_batch_process_entries | gauge | 发送数据时批处理中的剩余条目数,例如使用 `http logger` 和其他日志插件。 |
|
||||
| apisix_etcd_reachable | gauge | APISIX 是否可以访问 etcd。值为 `1` 表示可达,`0` 表示不可达。 |
|
||||
| apisix_http_status | counter | 从上游服务返回的 HTTP 状态代码。 |
|
||||
| apisix_http_requests_total | gauge | 来自客户端的 HTTP 请求数量。 |
|
||||
| apisix_nginx_http_current_connections | gauge | 当前与客户端的连接数量。 |
|
||||
| apisix_nginx_metric_errors_total | counter | `nginx-lua-prometheus` 错误的总数。 |
|
||||
| apisix_http_latency | histogram | HTTP 请求延迟(毫秒)。 |
|
||||
| apisix_node_info | gauge | APISIX 节点的信息,例如主机名和当前的 APISIX 版本号。 |
|
||||
| apisix_shared_dict_capacity_bytes | gauge | [NGINX 共享字典](https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module#ngxshareddict) 的总容量。 |
|
||||
| apisix_shared_dict_free_space_bytes | gauge | [NGINX 共享字典](https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module#ngxshareddict) 中剩余的空间。 |
|
||||
| apisix_upstream_status | gauge | 上游节点的健康检查状态,如果在上游配置了健康检查,则可用。值为 `1` 表示健康,`0` 表示不健康。 |
|
||||
| apisix_stream_connection_total | counter | 每个 Stream Route 处理的总连接数。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 标签
|
||||
|
||||
[标签](https://prometheus.io/docs/practices/naming/#labels) 是指标的属性,用于区分指标。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,`apisix_http_status` 指标可以使用 `route` 信息进行标记,以识别 HTTP 状态的来源路由。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是 APISIX 指标的非详尽标签及其描述。
|
||||
|
||||
### `apisix_http_status` 的标签
|
||||
|
||||
以下标签用于区分 `apisix_http_status` 指标。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| code | 上游节点返回的 HTTP 响应代码。 |
|
||||
| route | HTTP 状态来源的路由 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `false`(默认)时,使用路由 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `true` 时,使用路由名称。如果请求不匹配任何路由,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| matched_uri | 匹配请求的路由 URI。如果请求不匹配任何路由,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| matched_host | 匹配请求的路由主机。如果请求不匹配任何路由,或路由未配置主机,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| service | HTTP 状态来源的服务 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `false`(默认)时,使用服务 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `true` 时,使用服务名称。如果匹配的路由不属于任何服务,则默认为路由上配置的主机值。 |
|
||||
| consumer | 与请求关联的消费者名称。如果请求没有与之关联的消费者,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| node | 上游节点的 IP 地址。 |
|
||||
|
||||
### `apisix_bandwidth` 的标签
|
||||
|
||||
以下标签用于区分 `apisix_bandwidth` 指标。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| type | 流量类型,`egress` 或 `ingress`。 |
|
||||
| route | 带宽对应的路由 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `false`(默认)时,使用路由 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `true` 时,使用路由名称。如果请求不匹配任何路由,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| service | 带宽对应的服务 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `false`(默认)时,使用服务 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `true` 时,使用服务名称。如果匹配的路由不属于任何服务,则默认为路由上配置的主机值。 |
|
||||
| consumer | 与请求关联的消费者名称。如果请求没有与之关联的消费者,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| node | 上游节点的 IP 地址。 |
|
||||
|
||||
### `apisix_http_latency` 的标签
|
||||
|
||||
以下标签用于区分 `apisix_http_latency` 指标。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| type | 延迟类型。有关详细信息,请参见 [延迟类型](#延迟类型)。 |
|
||||
| route | 延迟对应的路由 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `false`(默认)时,使用路由 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `true` 时,使用路由名称。如果请求不匹配任何路由,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| service | 延迟对应的服务 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `false`(默认)时,使用服务 ID,当 `prefer_name` 为 `true` 时,使用服务名称。如果匹配的路由不属于任何服务,则默认为路由上配置的主机值。 |
|
||||
| consumer | 与延迟关联的消费者名称。如果请求没有与之关联的消费者,则默认为空字符串。 |
|
||||
| node | 与延迟关联的上游节点的 IP 地址。 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 延迟类型
|
||||
|
||||
`apisix_http_latency` 可以标记为以下三种类型之一:
|
||||
|
||||
* `request` 表示从客户端读取第一个字节到最后一个字节发送到客户端之间的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
* `upstream` 表示等待上游服务响应的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
* `apisix` 表示 `request` 延迟与 `upstream` 延迟之间的差异。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,APISIX 延迟不仅归因于 Lua 处理。应理解为:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
APISIX 延迟
|
||||
= 下游请求时间 - 上游响应时间
|
||||
= 下游流量延迟 + NGINX 延迟
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `apisix_upstream_status` 的标签
|
||||
|
||||
以下标签用于区分 `apisix_upstream_status` 指标。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| name | 与健康检查配置的上游对应的资源 ID,例如 `/apisix/routes/1` 和 `/apisix/upstreams/1`。 |
|
||||
| ip | 上游节点的 IP 地址。 |
|
||||
| port | 节点的端口号。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在不同场景中使用 `prometheus` 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 获取 APISIX 指标
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何从 APISIX 获取指标。
|
||||
|
||||
默认的 Prometheus 指标端点和其他与 Prometheus 相关的配置可以在 [静态配置](#静态配置) 中找到。如果您希望自定义这些配置,更新 `config.yaml` 并重新加载 APISIX。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在容器化环境中部署 APISIX,并希望外部访问 Prometheus 指标端点,请按如下方式更新配置文件并重新加载 APISIX:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
prometheus:
|
||||
export_addr:
|
||||
ip: 0.0.0.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 APISIX Prometheus 指标端点发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9091/apisix/prometheus/metrics"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似以下的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# HELP apisix_bandwidth Total bandwidth in bytes consumed per Service in Apisix
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_bandwidth counter
|
||||
apisix_bandwidth{type="egress",route="",service="",consumer="",node=""} 8417
|
||||
apisix_bandwidth{type="egress",route="1",service="",consumer="",node="127.0.0.1"} 1420
|
||||
apisix_bandwidth{type="egress",route="2",service="",consumer="",node="127.0.0.1"} 1420
|
||||
apisix_bandwidth{type="ingress",route="",service="",consumer="",node=""} 189
|
||||
apisix_bandwidth{type="ingress",route="1",service="",consumer="",node="127.0.0.1"} 332
|
||||
apisix_bandwidth{type="ingress",route="2",service="",consumer="",node="127.0.0.1"} 332
|
||||
# HELP apisix_etcd_modify_indexes Etcd modify index for APISIX keys
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_etcd_modify_indexes gauge
|
||||
apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="consumers"} 0
|
||||
apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="global_rules"} 0
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在公共 API 端点上公开 APISIX 指标
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何禁用默认情况下在端口 `9091` 上公开的 Prometheus 导出服务器,并在 APISIX 用于监听其他客户端请求的公共 API 端点上公开 APISIX Prometheus 指标。
|
||||
|
||||
在配置文件中禁用 Prometheus 导出服务器,并重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
prometheus:
|
||||
enable_export_server: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,使用 [`public-api`](../../../zh/latest/plugins/public-api.md) 插件创建一个路由,并为 APISIX 指标公开一个公共 API 端点:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/prometheus-metrics" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/prometheus/metrics",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向新指标端点发送请求以进行验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/prometheus/metrics"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似以下的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# HELP apisix_http_requests_total 自 APISIX 启动以来客户端请求的总数。
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_http_requests_total gauge
|
||||
apisix_http_requests_total 1
|
||||
# HELP apisix_nginx_http_current_connections 当前 HTTP 连接数量。
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_nginx_http_current_connections gauge
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="accepted"} 1
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="active"} 1
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="handled"} 1
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="reading"} 0
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="waiting"} 0
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="writing"} 1
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 监控上游健康状态
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何监控上游节点的健康状态。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `prometheus` 插件创建一个路由,并配置上游的主动健康检查:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "prometheus-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"prometheus": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1,
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:20001": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"checks": {
|
||||
"active": {
|
||||
"timeout": 5,
|
||||
"http_path": "/status",
|
||||
"healthy": {
|
||||
"interval": 2,
|
||||
"successes": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"unhealthy": {
|
||||
"interval": 1,
|
||||
"http_failures": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"passive": {
|
||||
"healthy": {
|
||||
"http_statuses": [200, 201],
|
||||
"successes": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"unhealthy": {
|
||||
"http_statuses": [500],
|
||||
"http_failures": 3,
|
||||
"tcp_failures": 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 APISIX Prometheus 指标端点发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9091/apisix/prometheus/metrics"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似以下的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# HELP apisix_upstream_status 上游健康检查的状态
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_upstream_status gauge
|
||||
apisix_upstream_status{name="/apisix/routes/1",ip="54.237.103.220",port="80"} 1
|
||||
apisix_upstream_status{name="/apisix/routes/1",ip="127.0.0.1",port="20001"} 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这显示上游节点 `httpbin.org:80` 是健康的,而上游节点 `127.0.0.1:20001` 是不健康的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为指标添加额外标签
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何为指标添加额外标签,并在标签值中使用 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
目前,仅以下指标支持额外标签:
|
||||
|
||||
* apisix_http_status
|
||||
* apisix_http_latency
|
||||
* apisix_bandwidth
|
||||
|
||||
在配置文件中包含以下配置以为指标添加标签,并重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
prometheus: # 插件:prometheus
|
||||
metrics: # 根据 NGINX 变量创建额外标签。
|
||||
http_status:
|
||||
extra_labels: # 设置 `http_status` 指标的额外标签。
|
||||
- upstream_addr: $upstream_addr # 添加一个额外的 `upstream_addr` 标签,其值为 NGINX 变量 $upstream_addr。
|
||||
- route_name: $route_name # 添加一个额外的 `route_name` 标签,其值为 APISIX 变量 $route_name。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,如果您在标签值中定义了一个变量,但它与任何现有的 [APISIX 变量](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/apisix-variable/) 和 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html) 不对应,则标签值将默认为空字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `prometheus` 插件创建一个路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "prometheus-route",
|
||||
"name": "extra-label",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"prometheus": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求以进行验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 的响应。
|
||||
|
||||
向 APISIX Prometheus 指标端点发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9091/apisix/prometheus/metrics"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似以下的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# HELP apisix_http_status APISIX 中每个服务的 HTTP 状态代码
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_http_status counter
|
||||
apisix_http_status{code="200",route="1",matched_uri="/get",matched_host="",service="",consumer="",node="54.237.103.220",upstream_addr="54.237.103.220:80",route_name="extra-label"} 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Prometheus 监控 TCP/UDP 流量
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何在 APISIX 中收集 TCP/UDP 流量指标。
|
||||
|
||||
在 `config.yaml` 中包含以下配置以启用 Stream proxy 和 `prometheus` 插件。重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
proxy_mode: http&stream # 启用 L4 和 L7 代理
|
||||
stream_proxy: # 配置 L4 代理
|
||||
tcp:
|
||||
- 9100 # 设置 TCP 代理监听端口
|
||||
udp:
|
||||
- 9200 # 设置 UDP 代理监听端口
|
||||
|
||||
stream_plugins:
|
||||
- prometheus # 为 stream proxy 启用 prometheus
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `prometheus` 插件创建一个 Stream Route:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"prometheus": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向该 Stream Route 发送请求以进行验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9100"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 的响应。
|
||||
|
||||
向 APISIX Prometheus 指标端点发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9091/apisix/prometheus/metrics"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似以下的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# HELP apisix_stream_connection_total APISIX 中每个 Stream Route 处理的总连接数
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_stream_connection_total counter
|
||||
apisix_stream_connection_total{route="1"} 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,379 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: proxy-cache
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Proxy Cache
|
||||
description: proxy-cache 插件根据键缓存响应,支持 GET、POST 和 HEAD 请求的磁盘和内存缓存,从而增强 API 性能。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/proxy-cache" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`proxy-cache` 插件提供了根据缓存键缓存响应的功能。该插件支持基于磁盘和基于内存的缓存选项,用于缓存 [GET](https://anything.org/learn/serving-over-http/#get-request)、[POST](https://anything.org/learn/serving-over-http/#post-request) 和 [HEAD](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Methods/HEAD) 请求。
|
||||
|
||||
可以根据请求 HTTP 方法、响应状态代码、请求标头值等有条件地缓存响应。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ------------------ | -------------- | ------ | ------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| cache_strategy | string | 否 | disk | ["disk","memory"] | 缓存策略。缓存在磁盘还是内存中。 |
|
||||
| cache_zone | string | 否 | disk_cache_one | | 与缓存策略一起使用的缓存区域。该值应与[配置文件](#static-configurations)中定义的缓存区域之一匹配,并与缓存策略相对应。例如,当使用内存缓存策略时,应该使用内存缓存区域。 |
|
||||
| cache_key | array[string] | 否 | ["$host", "$request_uri"] | | 用于缓存的键。支持[NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)和值中的常量字符串。变量应该以 `$` 符号为前缀。 |
|
||||
| cache_bypass | array[string] | 否 | | |一个或多个用于解析值的参数,如果任何值不为空且不等于 `0`,则不会从缓存中检索响应。支持值中的 [NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html) 和常量字符串。变量应该以 `$` 符号为前缀。|
|
||||
| cache_method | array[string] | 否 | ["GET", "HEAD"] | ["GET", "POST", "HEAD"] | 应缓存响应的请求方法。|
|
||||
| cache_http_status | array[integer] | 否 | [200, 301, 404] | [200, 599] | 应缓存响应的响应 HTTP 状态代码。|
|
||||
| hide_cache_headers | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则隐藏 `Expires` 和 `Cache-Control` 响应标头。|
|
||||
| cache_control | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 true,则遵守 HTTP 规范中的 `Cache-Control` 行为。仅对内存中策略有效。 |
|
||||
| no_cache | array[string] | 否 | | | 用于解析值的一个或多个参数,如果任何值不为空且不等于 `0`,则不会缓存响应。支持 [NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html) 和值中的常量字符串。变量应以 `$` 符号为前缀。 |
|
||||
| cache_ttl | integer | 否 | 300 | >=1 | 在内存中缓存时的缓存生存时间 (TTL),以秒为单位。要调整在磁盘上缓存时的 TTL,请更新[配置文件](#static-configurations) 中的 `cache_ttl`。TTL 值与从上游服务收到的响应标头 [`Cache-Control`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Cache-Control) 和 [`Expires`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Expires) 中的值一起评估。|
|
||||
|
||||
## 静态配置
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,磁盘缓存时的 `cache_ttl` 和缓存 `zones` 等值已在 [默认配置](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/cli/config.lua) 中预先配置。
|
||||
|
||||
要自定义这些值,请将相应的配置添加到 `config.yaml`。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apisix:
|
||||
proxy_cache:
|
||||
cache_ttl: 10s # 仅当 `Expires` 和 `Cache-Control` 响应标头均不存在,或者 APISIX 返回
|
||||
# 由于上游不可用导致 `502 Bad Gateway` 或 `504 Gateway Timeout` 时
|
||||
# 才会在磁盘上缓存时使用默认缓存 TTL
|
||||
zones:
|
||||
- name: disk_cache_one
|
||||
memory_size: 50m
|
||||
disk_size: 1G
|
||||
disk_path: /tmp/disk_cache_one
|
||||
cache_levels: 1:2
|
||||
# - name: disk_cache_two
|
||||
# memory_size: 50m
|
||||
# disk_size: 1G
|
||||
# disk_path: "/tmp/disk_cache_two"
|
||||
# cache_levels: "1:2"
|
||||
- name: memory_cache
|
||||
memory_size: 50m
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为不同场景配置 `proxy-cache`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 在磁盘上缓存数据
|
||||
|
||||
磁盘缓存策略具有系统重启时数据持久性以及与内存缓存相比具有更大存储容量的优势。它适用于优先考虑耐用性且可以容忍稍大的缓存访问延迟的应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在路由上使用 `proxy-cache` 插件将数据缓存在磁盘上。
|
||||
|
||||
使用磁盘缓存策略时,缓存 TTL 由响应标头 `Expires` 或 `Cache-Control` 中的值确定。如果这些标头均不存在,或者 APISIX 由于上游不可用而返回 `502 Bad Gateway` 或 `504 Gateway Timeout`,则缓存 TTL 默认为 [配置文件](#static-configuration) 中配置的值。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `proxy-cache` 插件创建路由以将数据缓存在磁盘上:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-cache-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-cache": {
|
||||
"cache_strategy": "disk"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,表明插件已成功启用:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: MISS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
由于在第一次响应之前没有可用的缓存,因此显示 `Apisix-Cache-Status: MISS`。
|
||||
|
||||
在缓存 TTL 窗口内再次发送相同的请求。您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,显示缓存已命中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: HIT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
等待缓存在 TTL 之后过期,然后再次发送相同的请求。您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,表明缓存已过期:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: EXPIRED
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在内存中缓存数据
|
||||
|
||||
内存缓存策略具有低延迟访问缓存数据的优势,因为从 RAM 检索数据比从磁盘存储检索数据更快。它还适用于存储不需要长期保存的临时数据,从而可以高效缓存频繁更改的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何在路由上使用 `proxy-cache` 插件在内存中缓存数据。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `proxy-cache` 创建路由并将其配置为使用基于内存的缓存:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-cache-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-cache": {
|
||||
"cache_strategy": "memory",
|
||||
"cache_zone": "memory_cache",
|
||||
"cache_ttl": 10
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,表明插件已成功启用:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: MISS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
由于在第一次响应之前没有可用的缓存,因此显示 `Apisix-Cache-Status: MISS`。
|
||||
|
||||
在缓存 TTL 窗口内再次发送相同的请求。您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,显示缓存已命中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: HIT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 有条件地缓存响应
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何配置 `proxy-cache` 插件以有条件地缓存响应。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `proxy-cache` 插件创建路由并配置 `no_cache` 属性,这样如果 URL 参数 `no_cache` 和标头 `no_cache` 的值中至少有一个不为空且不等于 `0`,则不会缓存响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-cache-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-cache": {
|
||||
"no_cache": ["$arg_no_cache", "$http_no_cache"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一些请求,其中 URL 参数的 `no_cache` 值表示绕过缓存:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?no_cache=1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到所有请求的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,并且每次都观察到以下标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: EXPIRED
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一些其他请求,其中 URL 参数 `no_cache` 值为零:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?no_cache=0"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到所有请求的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应,并开始看到缓存被命中:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: HIT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以在 `no_cache` 标头中指定以下值:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H "no_cache: 1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应不应该被缓存:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: EXPIRED
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 有条件地从缓存中检索响应
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何配置 `proxy-cache` 插件以有条件地从缓存中检索响应。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `proxy-cache` 插件创建路由并配置 `cache_bypass` 属性,这样如果 URL 参数 `bypass` 和标头 `bypass` 的值中至少有一个不为空且不等于 `0`,则不会从缓存中检索响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-cache-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-cache": {
|
||||
"cache_bypass": ["$arg_bypass", "$http_bypass"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送一个请求,其中 URL 参数值为 `bypass`,表示绕过缓存:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?bypass=1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: BYPASS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送另一个请求,其中 URL 参数 `bypass` 值为零:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything?bypass=0"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到带有以下标头的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: MISS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以在 `bypass` 标头中指定以下值:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/anything" -H "bypass: 1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
响应应该显示绕过缓存:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: BYPASS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 缓存 502 和 504 错误响应代码
|
||||
|
||||
当上游服务返回 500 范围内的服务器错误时,`proxy-cache` 插件将缓存响应,当且仅当返回的状态为 `502 Bad Gateway` 或 `504 Gateway Timeout`。
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了当上游服务返回 `504 Gateway Timeout` 时 `proxy-cache` 插件的行为。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `proxy-cache` 插件创建路由并配置虚拟上游服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-cache-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/timeout",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-cache": { }
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"12.34.56.78": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成一些对路由的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seq 4 | xargs -I{} curl -I "http://127.0.0.1:9080/timeout"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Time-out
|
||||
...
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: MISS
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Time-out
|
||||
...
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: HIT
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Time-out
|
||||
...
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: HIT
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Time-out
|
||||
...
|
||||
Apisix-Cache-Status: HIT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但是,如果上游服务返回 `503 Service Temporarily Unavailable`,则响应将不会被缓存。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: proxy-control
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Proxy Control
|
||||
description: 本文介绍了 Apache APISIX proxy-control 插件的相关操作,你可以使用此插件动态地控制 NGINX 代理的行为。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `proxy-control` 插件能够动态地控制 NGINX 代理的相关行为。
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 重要
|
||||
|
||||
此插件需要 APISIX 在 [APISIX-Runtime](../FAQ.md#如何构建-apisix-runtime-环境) 环境上运行。更多信息请参考 [apisix-build-tools](https://github.com/api7/apisix-build-tools)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------- | ----------- | ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| request_buffering | boolean | 否 | true | | 如果设置为 `true`,插件将动态设置 [`proxy_request_buffering`](http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html#proxy_request_buffering)。 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用插件
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在指定路由上启用 `proxy-control` 插件:
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/upload",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-control": {
|
||||
"request_buffering": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试插件
|
||||
|
||||
启用插件后,使用 `curl` 命令请求该路由进行一个大文件的上传测试:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/upload -d @very_big_file
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果在错误日志中没有找到关于 "a client request body is buffered to a temporary file" 的信息,则说明插件生效。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除插件
|
||||
|
||||
当你需要删除该插件时,可以通过以下命令删除相应的 JSON 配置,APISIX 将会自动重新加载相关配置,无需重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: $admin_key" -X PUT -d
|
||||
{
|
||||
"uri": "/upload",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"127.0.0.1:1980": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: proxy-mirror
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Proxy Mirror
|
||||
description: proxy-mirror 插件将入口流量复制到 APISIX 并将其转发到指定的上游,而不会中断常规服务。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/proxy-mirror" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`proxy-mirror` 插件将传入流量复制到 APISIX 并将其转发到指定的上游,而不会中断常规服务。您可以将插件配置为镜像所有流量或仅镜像一部分流量。该机制有利于一些用例,包括故障排除、安全检查、分析等。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,APISIX 会忽略接收镜像流量的上游主机的任何响应。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参数
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| host | string | 是 | | | 将镜像流量转发到的主机的地址。该地址应包含方案但不包含路径,例如 `http://127.0.0.1:8081`。 |
|
||||
| path | string | 否 | | | 将镜像流量转发到的主机的路径。如果未指定,则默认为路由的当前 URI 路径。如果插件正在镜像 gRPC 流量,则不适用。 |
|
||||
| path_concat_mode | string | 否 | replace | ["replace", "prefix"] | 指定 `path` 时的连接模式。设置为 `replace` 时,配置的 `path` 将直接用作将镜像流量转发到的主机的路径。设置为 `prefix` 时,转发到的路径将是配置的 `path`,附加路由的请求 URI 路径。如果插件正在镜像 gRPC 流量,则不适用。 |
|
||||
| sample_ratio | number | 否 | 1 | [0.00001, 1] | 将被镜像的请求的比例。默认情况下,所有流量都会被镜像。|
|
||||
|
||||
## 静态配置
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,插件的超时值在[默认配置](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/master/apisix/cli/config.lua)中预先配置。
|
||||
|
||||
要自定义这些值,请将相应的配置添加到 `config.yaml`。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
proxy-mirror:
|
||||
timeout:
|
||||
connect: 60s
|
||||
read: 60s
|
||||
send: 60s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何为不同场景配置 `proxy-mirror`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 镜像部分流量
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何配置 `proxy-mirror` 以将 50% 的流量镜像到路由并将其转发到另一个上游服务。
|
||||
|
||||
启动一个示例 NGINX 服务器以接收镜像流量:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run -p 8081:80 --name nginx nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该在终端会话中看到 NGINX 访问日志和错误日志。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个新的终端会话并使用 `proxy-mirror` 创建一个路由来镜像 50% 的流量:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "traffic-mirror-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-mirror": {
|
||||
"host": "http://127.0.0.1:8081",
|
||||
"sample_ratio": 0.5
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送生成几个请求到路由:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到所有请求的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应。
|
||||
|
||||
导航回 NGINX 终端会话,您应该会看到一些访问日志条目,大约是生成的请求数量的一半:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
172.17.0.1 - - [29/Jan/2024:23:11:01 +0000] "GET /get HTTP/1.1" 404 153 "-" "curl/7.64.1" "-"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这表明 APISIX 已将请求镜像到 NGINX 服务器。此处,HTTP 响应状态为 `404`,因为示例 NGINX 服务器未实现路由。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置镜像超时
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何更新插件的默认连接、读取和发送超时。当将流量镜像到非常慢的后端服务时,这可能很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
由于请求镜像是作为子请求实现的,子请求中的过度延迟可能导致原始请求被阻止。默认情况下,连接、读取和发送超时设置为 60 秒。要更新这些值,您可以在配置文件的 `plugin_attr` 部分中配置它们,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml title="conf/config.yaml"
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
proxy-mirror:
|
||||
timeout:
|
||||
connect: 2000ms
|
||||
read: 2000ms
|
||||
send: 2000ms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,509 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: proxy-rewrite
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Proxy Rewrite
|
||||
- proxy-rewrite
|
||||
description: proxy-rewrite 插件支持重写 APISIX 转发到上游服务的请求。使用此插件,您可以修改 HTTP 方法、请求目标上游地址、请求标头等。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/proxy-rewrite" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`proxy-rewrite` 插件支持重写 APISIX 转发到上游服务的请求。使用此插件,您可以修改 HTTP 方法、请求目标上游地址、请求标头等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必需 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|-----------------------------|-----------|----------|---------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| uri | string | 否 | | | 新的上游 URI 路径。值支持 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html)。例如,`$arg_name`。 |
|
||||
| method | string | 否 | | ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "HEAD", "DELETE", "OPTIONS","MKCOL", "COPY", "MOVE", "PROPFIND", "PROPFIND","LOCK", "UNLOCK", "PATCH", "TRACE"] | 要使用的重写请求的 HTTP 方法。 |
|
||||
| regex_uri | array[string] | 否 | | | 用于匹配客户端请求的 URI 路径并组成新的上游 URI 路径的正则表达式。当同时配置 `uri` 和 `regex_uri` 时,`uri` 具有更高的优先级。该数组应包含一个或多个 **键值对**,其中键是用于匹配 URI 的正则表达式,值是新的上游 URI 路径。例如,对于 `["^/iresty/(. *)/(. *)", "/$1-$2", ^/theothers/*", "/theothers"]`,如果请求最初发送到 `/iresty/hello/world`,插件会将上游 URI 路径重写为 `/iresty/hello-world`;如果请求最初发送到 `/theothers/hello/world`,插件会将上游 URI 路径重写为 `/theothers`。|
|
||||
| host | string | 否 | | | 设置 [`Host`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Host) 请求标头。|
|
||||
| headers | object | 否 | | | 要执行的标头操作。可以设置为动作动词 `add`、`remove` 和/或 `set` 的对象;或由要 `set` 的标头组成的对象。当配置了多个动作动词时,动作将按照“添加”、“删除”和“设置”的顺序执行。|
|
||||
| headers.add | object | 否 | | | 要附加到请求的标头。如果请求中已经存在标头,则会附加标头值。标头值可以设置为常量、一个或多个 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html),或者 `regex_uri` 的匹配结果(使用变量,例如 `$1-$2-$3`)。|
|
||||
| headers.set | object | 否 | | | 要设置请求的标头。如果请求中已经存在标头,则会覆盖标头值。标头值可以设置为常量、一个或多个 [Nginx 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html),或者 `regex_uri` 的匹配结果(使用变量,例如 `$1-$2-$3`)。不应将其用于设置 `Host`。|
|
||||
| headers.remove | array[string] | 否 | | | 从请求中删除的标头。
|
||||
| use_real_request_uri_unsafe | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 True,则绕过 URI 规范化并允许完整的原始请求 URI。启用此选项被视为不安全。|
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
下面的示例说明如何在不同场景中在路由上配置 `proxy-rewrite`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 重写主机标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何修改请求中的 `Host` 标头。请注意,您不应使用 `headers.set` 来设置 `Host` 标头。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"host": "myapisix.demo"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 `/headers` 发送请求以检查发送到上游的所有请求标头:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似于以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "myapisix.demo",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-64fef198-29da0970383150175bd2d76d",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 重写 URI 并设置标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何重写请求上游 URI 并设置其他标头值。如果客户端请求中存在相同的标头,则插件中设置的相应标头值将覆盖客户端请求中存在的值。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"set": {
|
||||
"X-Api-Version": "v1",
|
||||
"X-Api-Engine": "apisix"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送请求以验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/" -H '"X-Api-Version": "v2"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似于以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbin.org",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-64fed73a-59cd3bd640d76ab16c97f1f1",
|
||||
"X-Api-Engine": "apisix",
|
||||
"X-Api-Version": "v1",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"origin": "::1, 103.248.35.179",
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost/anything"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意到其中两个标头都存在,以及插件中配置的 `X-Api-Version` 标头值覆盖了请求中传递的标头值。
|
||||
|
||||
### 重写 URI 并附加标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何重写请求上游 URI 并附加其他标头值。如果客户端请求中存在相同的标头,则它们的标头值将附加到插件中配置的标头值。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"add": {
|
||||
"X-Api-Version": "v1",
|
||||
"X-Api-Engine": "apisix"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送请求以验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/" -H '"X-Api-Version": "v2"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbin.org",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-64fed73a-59cd3bd640d76ab16c97f1f1",
|
||||
"X-Api-Engine": "apisix",
|
||||
"X-Api-Version": "v1,v2",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,两个标头均存在,并且插件中配置的 `X-Api-Version` 标头值均附加在请求中传递的标头值上。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除现有标头
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何删除现有标头 `User-Agent`。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/headers",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"remove":[
|
||||
"User-Agent"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送请求来验证指定的标头是否被删除:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/headers"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该看到类似以下的响应,其中 `User-Agen` 标头已被移除:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "httpbin.org",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-64fef302-07f2b13e0eb006ba776ad91d",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 RegEx 重写 URI
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何解析原始上游 URI 路径中的文本并使用它们组成新的上游 URI 路径。在此示例中,APISIX 配置为将所有请求从 `/test/user/agent` 转发到 `/user-agent`。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/test/*",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
# highlight-start
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"regex_uri": ["^/test/(.*)/(.*)", "/$1-$2"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送请求到 `/test/user/agent`,检查是否被重定向到 `/user-agent`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/test/user/agent"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user-agent": "curl/8.2.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加 URL 参数
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何向请求添加 URL 参数。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"uri": "/get?arg1=apisix&arg2=plugin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发送请求来验证 URL 参数是否也转发给了上游:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {
|
||||
"arg1": "apisix",
|
||||
"arg2": "plugin"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-64fef6dc-2b0e09591db7353a275cdae4",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "127.0.0.1, 103.248.35.148",
|
||||
# highlight-next-line
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get?arg1=apisix&arg2=plugin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 重写 HTTP 方法
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何将 GET 请求重写为 POST 请求。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "proxy-rewrite-route",
|
||||
"methods": ["GET"],
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"method":"POST"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向 `/get` 发送 GET 请求,以验证它是否转换为向 `/anything` 发送 POST 请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会看到类似以下内容的响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"data": "",
|
||||
"files": {},
|
||||
"form": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.2.1",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-64fef7de-0c63387645353998196317f2",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"json": null,
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"origin": "::1, 103.248.35.179",
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost/anything"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将消费者名称转发到上游
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何将成功验证的消费者名称转发到上游服务。例如,您将使用 `key-auth` 作为身份验证方法。
|
||||
|
||||
创建消费者 `JohnDoe`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"username": "JohnDoe"
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为消费者创建 `key-auth` 凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/consumers/JohnDoe/credentials" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "cred-john-key-auth",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {
|
||||
"key": "john-key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,创建一个启用密钥认证的路由,配置 `proxy-rewrite` 以将消费者名称添加到标头,并删除认证密钥,以使其对上游服务不可见:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "consumer-restricted-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"key-auth": {},
|
||||
"proxy-rewrite": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"set": {
|
||||
"X-Apisix-Consumer": "$consumer_name"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"remove": [ "Apikey" ]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream" : {
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org":1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以消费者 `JohnDoe` 的身份向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" -H 'apikey: john-key'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到一个包含以下主体的 `HTTP/1.1 200 OK` 响应:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{
|
||||
"args": {},
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"Accept": "*/*",
|
||||
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
|
||||
"User-Agent": "curl/8.4.0",
|
||||
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-664b01a6-2163c0156ed4bff51d87d877",
|
||||
"X-Apisix-Consumer": "JohnDoe",
|
||||
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"origin": "172.19.0.1, 203.12.12.12",
|
||||
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送另一个请求,不带有有效凭证:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该收到 `HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden` 响应。
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,242 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: public-api
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Public API
|
||||
description: public-api 插件公开了一个内部 API 端点,使其可被公开访问。该插件的主要用途之一是公开由其他插件创建的内部端点。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/public-api" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`public-api` 插件公开了一个内部 API 端点,使其可被公开访问。该插件的主要用途之一是公开由其他插件创建的内部端点。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 必选项 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|------|--------|-------|-------|------|------|
|
||||
| uri | string | 否 | | | 内部端点的 URI。如果未配置,则暴露路由的 URI。|
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在不同场景中配置 `public-api`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在自定义端点暴露 Prometheus 指标
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示如何禁用默认在端口 `9091` 上暴露端点的 Prometheus 导出服务器,并在 APISIX 用于监听其他客户端请求的端口 `9080` 上,通过新的公共 API 端点暴露 APISIX 的 Prometheus 指标。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,还会配置路由,使内部端点 `/apisix/prometheus/metrics` 通过自定义端点对外公开。
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
|
||||
如果收集了大量指标,插件可能会占用大量 CPU 资源用于计算,从而影响正常请求的处理。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,APISIX 使用 [特权代理进程](https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-core/blob/master/lib/ngx/process.md#enable_privileged_agent) ,并将指标计算卸载至独立进程。如果使用配置文件中 `plugin_attr.prometheus.export_addr` 设定的指标端点,该优化将自动生效。但如果通过 `public-api` 插件暴露指标端点,则不会受益于此优化。
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
在配置文件中禁用 Prometheus 导出服务器,并重新加载 APISIX 以使更改生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
plugin_attr:
|
||||
prometheus:
|
||||
enable_export_server: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,创建一个带有 `public-api` 插件的路由,并为 APISIX 指标暴露一个公共 API 端点。你应将路由的 `uri` 设置为自定义端点路径,并将插件的 `uri` 设置为要暴露的内部端点。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H 'X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}' \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "prometheus-metrics",
|
||||
"uri": "/prometheus_metrics",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/prometheus/metrics"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向自定义指标端点发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/prometheus_metrics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你应看到类似以下的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# HELP apisix_http_requests_total The total number of client requests since APISIX started
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_http_requests_total gauge
|
||||
apisix_http_requests_total 1
|
||||
# HELP apisix_nginx_http_current_connections Number of HTTP connections
|
||||
# TYPE apisix_nginx_http_current_connections gauge
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="accepted"} 1
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="active"} 1
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="handled"} 1
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="reading"} 0
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="waiting"} 0
|
||||
apisix_nginx_http_current_connections{state="writing"} 1
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 暴露批量请求端点
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何使用 `public-api` 插件来暴露 `batch-requests` 插件的端点,该插件用于将多个请求组合成一个请求,然后将它们发送到网关。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个样本路由到 httpbin 的 `/anything` 端点,用于验证目的:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "httpbin-anything",
|
||||
"uri": "/anything",
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个带有 `public-api` 插件的路由,并将路由的 `uri` 设置为要暴露的内部端点:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "batch-requests",
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/batch-requests",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向暴露的批量请求端点发送一个包含 GET 和 POST 请求的流水线请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/batch-requests" -X POST -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pipeline": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"path": "/anything"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"path": "/anything",
|
||||
"body": "a post request"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到两个请求的响应,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"reason": "OK",
|
||||
"body": "{\n \"args\": {}, \n \"data\": \"\", \n \"files\": {}, \n \"form\": {}, \n \"headers\": {\n \"Accept\": \"*/*\", \n \"Host\": \"127.0.0.1\", \n \"User-Agent\": \"curl/8.6.0\", \n \"X-Amzn-Trace-Id\": \"Root=1-67b6e33b-5a30174f5534287928c54ca9\", \n \"X-Forwarded-Host\": \"127.0.0.1\"\n }, \n \"json\": null, \n \"method\": \"GET\", \n \"origin\": \"192.168.107.1, 43.252.208.84\", \n \"url\": \"http://127.0.0.1/anything\"\n}\n",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"reason": "OK",
|
||||
"body": "{\n \"args\": {}, \n \"data\": \"a post request\", \n \"files\": {}, \n \"form\": {}, \n \"headers\": {\n \"Accept\": \"*/*\", \n \"Content-Length\": \"14\", \n \"Host\": \"127.0.0.1\", \n \"User-Agent\": \"curl/8.6.0\", \n \"X-Amzn-Trace-Id\": \"Root=1-67b6e33b-0eddcec07f154dac0d77876f\", \n \"X-Forwarded-Host\": \"127.0.0.1\"\n }, \n \"json\": null, \n \"method\": \"POST\", \n \"origin\": \"192.168.107.1, 43.252.208.84\", \n \"url\": \"http://127.0.0.1/anything\"\n}\n",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果您希望在自定义端点处暴露批量请求端点,请创建一个带有 `public-api` 插件的路由。您应该将路由的 `uri` 设置为自定义端点路径,并将插件的 uri 设置为要暴露的内部端点。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "batch-requests",
|
||||
"uri": "/batch-requests",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"public-api": {
|
||||
"uri": "/apisix/batch-requests"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在批量请求端点应该被暴露为 `/batch-requests`,而不是 `/apisix/batch-requests`。
|
||||
向暴露的批量请求端点发送一个包含 GET 和 POST 请求的流水线请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9080/batch-requests" -X POST -d '
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pipeline": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"method": "GET",
|
||||
"path": "/anything"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"method": "POST",
|
||||
"path": "/anything",
|
||||
"body": "a post request"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应该会收到两个请求的响应,类似于以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"reason": "OK",
|
||||
"body": "{\n \"args\": {}, \n \"data\": \"\", \n \"files\": {}, \n \"form\": {}, \n \"headers\": {\n \"Accept\": \"*/*\", \n \"Host\": \"127.0.0.1\", \n \"User-Agent\": \"curl/8.6.0\", \n \"X-Amzn-Trace-Id\": \"Root=1-67b6e33b-5a30174f5534287928c54ca9\", \n \"X-Forwarded-Host\": \"127.0.0.1\"\n }, \n \"json\": null, \n \"method\": \"GET\", \n \"origin\": \"192.168.107.1, 43.252.208.84\", \n \"url\": \"http://127.0.0.1/anything\"\n}\n",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"reason": "OK",
|
||||
"body": "{\n \"args\": {}, \n \"data\": \"a post request\", \n \"files\": {}, \n \"form\": {}, \n \"headers\": {\n \"Accept\": \"*/*\", \n \"Content-Length\": \"14\", \n \"Host\": \"127.0.0.1\", \n \"User-Agent\": \"curl/8.6.0\", \n \"X-Amzn-Trace-Id\": \"Root=1-67b6e33b-0eddcec07f154dac0d77876f\", \n \"X-Forwarded-Host\": \"127.0.0.1\"\n }, \n \"json\": null, \n \"method\": \"POST\", \n \"origin\": \"192.168.107.1, 43.252.208.84\", \n \"url\": \"http://127.0.0.1/anything\"\n}\n",
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
...
|
||||
},
|
||||
"status": 200
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: real-ip
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
- Apache APISIX
|
||||
- API 网关
|
||||
- Plugin
|
||||
- Real IP
|
||||
description: real-ip 插件允许 Apache APISIX 通过 HTTP 请求头或 HTTP 查询字符串中传递的 IP 地址设置客户端的真实 IP。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<link rel="canonical" href="https://docs.api7.ai/hub/real-ip" />
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
## 描述
|
||||
|
||||
`real-ip` 插件允许 APISIX 通过 HTTP 请求头或 HTTP 查询字符串中传递的 IP 地址设置客户端的真实 IP。当 APISIX 位于反向代理之后时,此功能尤其有用,因为在这种情况下,代理可能会被视为请求发起客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
该插件在功能上类似于 NGINX 的 [ngx_http_realip_module](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_realip_module.html),但提供了更多的灵活性。
|
||||
|
||||
## 属性
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 类型 | 是否必需 | 默认值 | 有效值 | 描述 |
|
||||
|-------------------|---------------|----------|--------|----------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| source | string | 是 | | | 内置变量,例如 `http_x_forwarded_for` 或 `arg_realip`。变量值应为一个有效的 IP 地址,表示客户端的真实 IP 地址,可选地包含端口。 |
|
||||
| trusted_addresses | array[string] | 否 | | IPv4 或 IPv6 地址数组(接受 CIDR 表示法) | 已知会发送正确替代地址的可信地址。此配置设置 [`set_real_ip_from`](https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_realip_module.html#set_real_ip_from) 指令。 |
|
||||
| recursive | boolean | 否 | false | | 如果为 false,则将匹配可信地址之一的原始客户端地址替换为配置的 `source` 中发送的最后一个地址。<br />如果为 true,则将匹配可信地址之一的原始客户端地址替换为配置的 `source` 中发送的最后一个非可信地址。 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
如果 `source` 属性中设置的地址丢失或者无效,该插件将不会更改客户端地址。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了如何在不同场景中配置 `real-ip`。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
您可以这样从 `config.yaml` 中获取 `admin_key` 并存入环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
admin_key=$(yq '.deployment.admin.admin_key[0].key' conf/config.yaml | sed 's/"//g')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 从 URI 参数获取真实客户端地址
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例演示了如何使用 URI 参数更新客户端 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
创建如下路由。您应配置 `source` 以使用 [APISIX 变量](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/apisix-variable/)或者 [NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)从 URL 参数 `realip` 获取值。使用 `response-rewrite` 插件设置响应头,以验证客户端 IP 和端口是否实际更新。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "real-ip-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"real-ip": {
|
||||
"source": "arg_realip",
|
||||
"trusted_addresses": ["127.0.0.0/24"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response-rewrite": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"remote_addr": "$remote_addr",
|
||||
"remote_port": "$remote_port"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送带有 URL 参数中的真实 IP 和端口的请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get?realip=1.2.3.4:9080"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应看到响应包含以下头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
remote-addr: 1.2.3.4
|
||||
remote-port: 9080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 从请求头获取真实客户端地址
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了当 APISIX 位于反向代理(例如负载均衡器)之后时,如何设置真实客户端 IP,此时代理在 [`X-Forwarded-For`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Forwarded-For) 请求头中暴露了真实客户端 IP。
|
||||
|
||||
创建如下路由。您应配置 `source` 以使用 [APISIX 变量](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/apisix-variable/)或者 [NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)从请求头 `X-Forwarded-For` 获取值。使用 response-rewrite 插件设置响应头,以验证客户端 IP 是否实际更新。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "real-ip-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"real-ip": {
|
||||
"source": "http_x_forwarded_for",
|
||||
"trusted_addresses": ["127.0.0.0/24"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response-rewrite": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"remote_addr": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应看到响应包含以下头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
remote-addr: 10.26.3.19
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
IP 地址应对应于请求发起客户端的 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在多个代理之后获取真实客户端地址
|
||||
|
||||
以下示例展示了当 APISIX 位于多个代理之后时,如何获取真实客户端 IP,此时 [`X-Forwarded-For`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Forwarded-For) 请求头包含了一系列代理 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
创建如下路由。您应配置 `source` 以使用 [APISIX 变量](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/apisix-variable/)或者 [NGINX 变量](https://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html)从请求头 `X-Forwarded-For` 获取值。将 `recursive` 设置为 `true`,以便将匹配可信地址之一的原始客户端地址替换为配置的 `source` 中发送的最后一个非可信地址。然后,使用 `response-rewrite` 插件设置响应头,以验证客户端 IP 是否实际更新。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes" -X PUT \
|
||||
-H "X-API-KEY: ${admin_key}" \
|
||||
-d '{
|
||||
"id": "real-ip-route",
|
||||
"uri": "/get",
|
||||
"plugins": {
|
||||
"real-ip": {
|
||||
"source": "http_x_forwarded_for",
|
||||
"recursive": true,
|
||||
"trusted_addresses": ["192.128.0.0/16", "127.0.0.0/24"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"response-rewrite": {
|
||||
"headers": {
|
||||
"remote_addr": "$remote_addr"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"upstream": {
|
||||
"type": "roundrobin",
|
||||
"nodes": {
|
||||
"httpbin.org:80": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
向路由发送请求:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9080/get" \
|
||||
-H "X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.2, 192.128.1.1, 127.0.0.1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您应看到响应包含以下头:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
remote-addr: 127.0.0.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user