* Clean-up. Instructions on how template would be modified for production. * Change page titles to make it clearer make they contain. * Simple example of how to connect to node via RPC. Explanation of how to interact with node via RPC. * Bigger warning about deprecated webserver. Makes it clear that CordaRPCClient is THE way to interact with a node. * Review from Clinton. * Separating template info from general info.
2.4 KiB
What is a CorDapp?
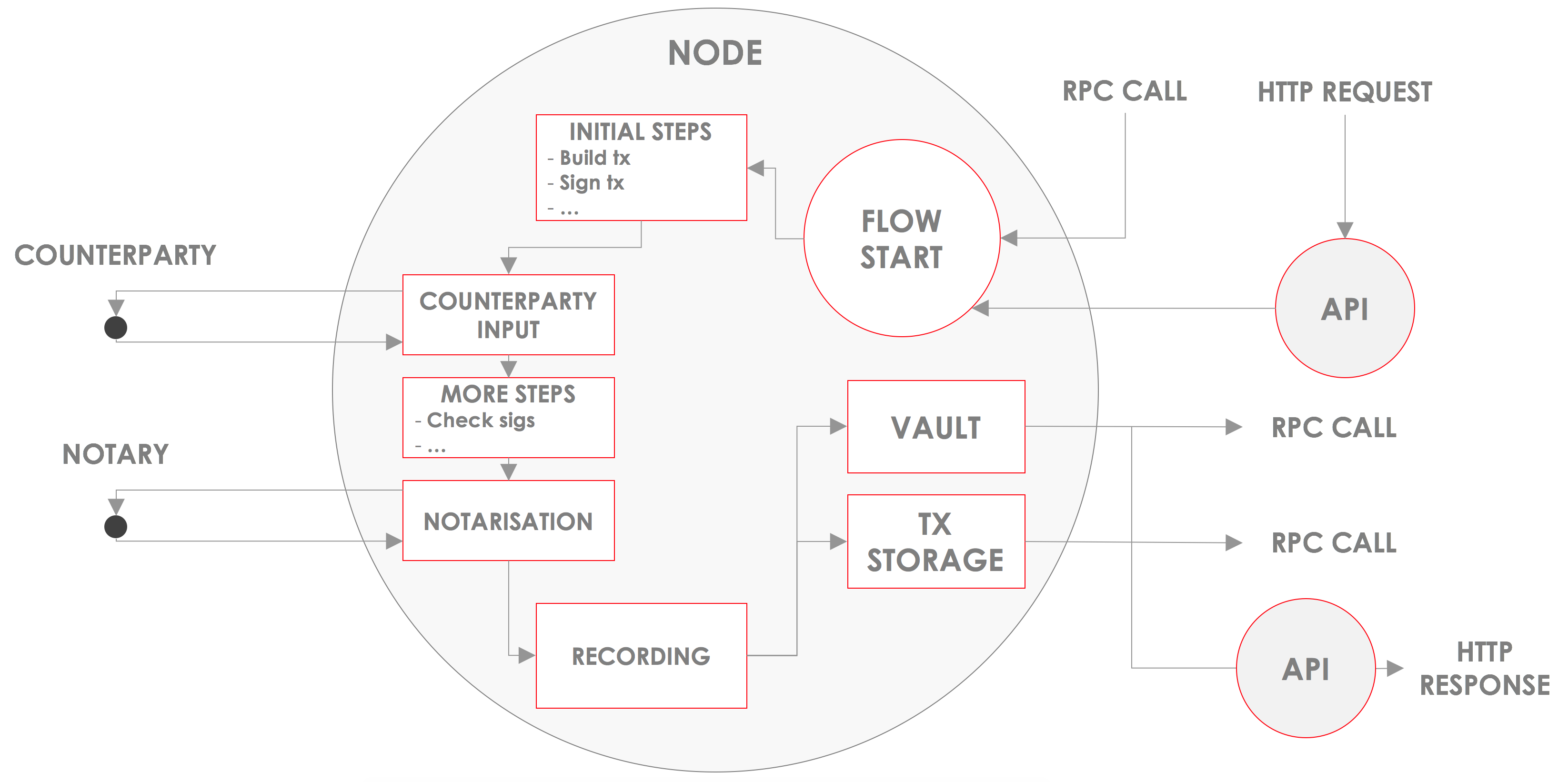
CorDapps (Corda Distributed Applications) are distributed applications that run on the Corda platform. The goal of a CorDapp is to allow nodes to reach agreement on updates to the ledger. They achieve this goal by defining flows that Corda node owners can invoke over RPC:
CorDapp components
CorDapps take the form of a set of JAR files containing class definitions written in Java and/or Kotlin.
These class definitions will commonly include the following elements:
- Flows: Define a routine for the node to run, usually to update the ledger (see
Key Concepts - Flows <key-concepts-flows>). They subclassFlowLogic - States: Define the facts over which agreement is reached (see
Key Concepts - States <key-concepts-states>). They implement theContractStateinterface - Contracts, defining what constitutes a valid ledger update (see
Key Concepts - Contracts <key-concepts-contracts>). They implement theContractinterface - Services, providing long-lived utilities within the node. They subclass
SingletonSerializationToken - Serialisation whitelists, restricting what types your node will receive off the wire. They implement the
SerializationWhitelistinterface
But the CorDapp JAR can also include other class definitions. These may include:
- APIs and static web content: These are served by Corda's built-in webserver. This webserver is not production-ready, and should be used for testing purposes only
- Utility classes
An example
Suppose a node owner wants their node to be able to trade bonds. They may choose to install a Bond Trading CorDapp with the following components:
A
BondState, used to represent bonds as shared facts on the ledgerA
BondContract, used to govern which ledger updates involvingBondStatestates are validThree flows:
- An
IssueBondFlow, allowing newBondStatestates to be issued onto the ledger - A
TradeBondFlow, allowing existingBondStatestates to be bought and sold on the ledger - An
ExitBondFlow, allowing existingBondStatestates to be exited from the ledger
- An
After installing this CorDapp, the node owner will be able to use the flows defined by the CorDapp to agree ledger updates related to issuance, sale, purchase and exit of bonds.