5.4 KiB
Network Permissioning
Corda networks are permissioned. To connect to a network, a node needs three keystores in its <workspace>/certificates/ folder:
truststore.jks, which stores trusted public keys and certificates (in our case, those of the network root CA)nodekeystore.jks, which stores the node’s identity keypairs and certificatessslkeystore.jks, which stores the node’s TLS keypairs and certificates
In development mode (i.e. when devMode = true, see corda-configuration-file for more information), pre-configured keystores are used if the required keystores do not exist. This ensures that developers can get the nodes working as quickly as possible.
However, these pre-configured keystores are not secure. Production deployments require a secure certificate authority. Most production deployments will use an existing certificate authority or construct one using software that will be made available in the coming months. Until then, the documentation below can be used to create your own certificate authority.
Network structure
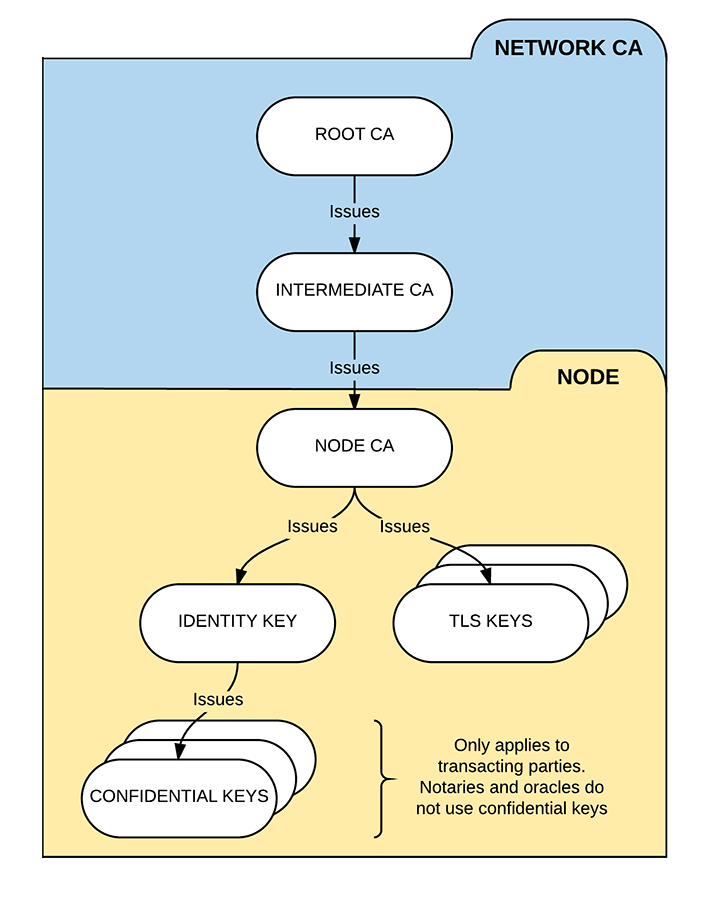
A Corda network has three types of certificate authorities (CAs):
- The root network CA
- The intermediate network CA
- The intermediate network CA is used instead of the root network CA for day-to-day key signing to reduce the risk of the root network CA's private key being compromised
- The node CAs
- Each node serves as its own CA in issuing the child certificates that it uses to sign its identity keys and TLS certificates
We can visualise the permissioning structure as follows:
Keypair and certificate formats
You can use any standard key tools or Corda's X509Utilities (which uses Bouncy Castle) to create the required public/private keypairs and certificates. The keypairs and certificates should obey the following restrictions:
The certificates must follow the X.509 standard
- We recommend X.509 v3 for forward compatibility
The TLS certificates must follow the TLS v1.2 standard
The root network CA, intermediate network CA and node CA keys, as well as the node TLS keys, must follow one of the following schemes:
- ECDSA using the NIST P-256 curve (secp256r1)
- RSA with 3072-bit key size
Creating the root and intermediate network CAs
Creating the root network CA's keystore and truststore
- Create a new keypair
- This will be used as the root network CA's keypair
- Create a self-signed certificate for the keypair. The basic constraints extension must be set to
true- This will be used as the root network CA's certificate
- Create a new keystore and store the root network CA's keypair and certificate in it for later use
- This keystore will be used by the root network CA to sign the intermediate network CA's certificate
- Create a new Java keystore named
truststore.jksand store the root network CA's certificate in it using the aliascordarootca- This keystore will be provisioned to the individual nodes later
Warning
The root network CA's private key should be protected and kept safe.
Creating the intermediate network CA's keystore
- Create a new keypair
- This will be used as the intermediate network CA's keypair
- Obtain a certificate for the keypair signed with the root network CA key. The basic constraints extension must be set to
true- This will be used as the intermediate network CA's certificate
- Create a new keystore and store the intermediate network CA's keypair and certificate chain (i.e. the intermediate network CA certificate and the root network CA certificate) in it for later use
- This keystore will be used by the intermediate network CA to sign the nodes' identity certificates
Creating the node CA keystores and TLS keystores
Creating the node CA keystores
- For each node, create a new keypair
- Obtain a certificate for the keypair signed with the intermediate network CA key. The basic constraints extension must be set to
true - Create a new Java keystore named
nodekeystore.jksand store the keypair in it using the aliascordaclientca- The node will store this keystore locally to sign its identity keys and anonymous keys
Creating the node TLS keystores
- For each node, create a new keypair
- Create a certificate for the keypair signed with the node CA key. The basic constraints extension must be set to
false - Create a new Java keystore named
sslkeystore.jksand store the key and certificates in it using the aliascordaclienttls- The node will store this keystore locally to sign its TLS certificates
Installing the certificates on the nodes
For each node, copy the following files to the node's certificate directory (<workspace>/certificates/):
- The node's
nodekeystore.jkskeystore - The node's
sslkeystore.jkskeystore - The root network CA's
truststore.jkskeystore