* Removes Identity page. Reworks it into the Network page. * Removes stray doorman reference. * Addresses review feedback.
2.1 KiB
The network
Summary
- A Corda network is made up of nodes running Corda and CorDapps
- Communication between nodes is point-to-point, instead of relying on global broadcasts
- Each node has a certificate mapping their network identity to a real-world legal identity
- The network is permissioned, with access requiring a certificate from the network operator
Network structure
A Corda network is a peer-to-peer network of nodes. Each node runs the Corda software as well as Corda applications known as CorDapps.
All communication between nodes is point-to-point and encrypted using transport-layer security. This means that data is shared only on a need-to-know basis. There are no global broadcasts.
Identity
Each node has a single well-known identity. The node's identity is used to represent the node in transactions, such as when purchasing an asset.
Note
These identities are distinct from the RPC user logins that are able to connect to the node via RPC.
Each network has a network map service that maps each well-known node identity to an IP address. These IP addresses are used for messaging between nodes.
Nodes can also generate confidential identities for individual transactions. The certificate chain linking a confidential identity to a well-known node identity or real-world legal identity is only distributed on a need-to-know basis. This ensures that even if an attacker gets access to an unencrypted transaction, they cannot identify the transaction's participants without additional information if confidential identities are being used.
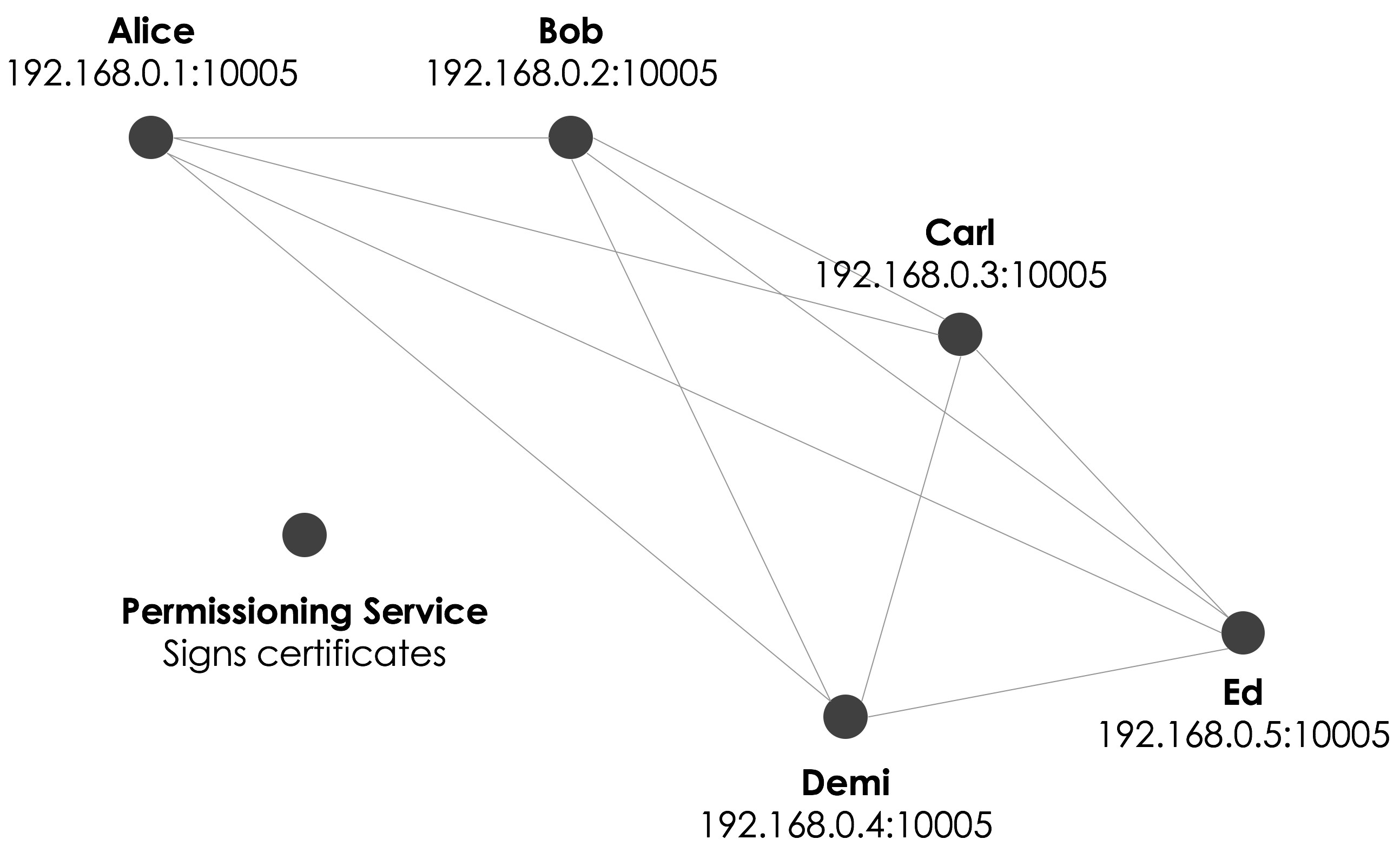
Admission to the network
Corda networks are semi-private. To join a network, a node must obtain a certificate from the network operator. This certificate maps a well-known node identity to:
- A real-world legal identity
- A public key
The network operator enforces rules regarding the information that nodes must provide and the know-your-customer processes they must undergo before being granted this certificate.