* Added an additional property on VaultQueryCriteria to specify an externalId/accountId when performing a vault query. Added logic in hibernate query criteria parser to handle the exernalId join and lookup. Added a test. * Fixed error in test. Fixed backwards incompatible changes. * Updated changelog. * Updated docs to remove incorrect instructions for querying by external ID.
29 KiB
API: Vault Query
Overview
Corda has been architected from the ground up to encourage usage of industry standard, proven query frameworks and libraries for accessing RDBMS backed transactional stores (including the Vault).
Corda provides a number of flexible query mechanisms for accessing the Vault:
- Vault Query API
- Using a JDBC session (as described in
Persistence <jdbc_session_ref>) - Custom JPA/JPQL queries
- Custom 3rd party Data Access frameworks such as Spring Data
The majority of query requirements can be satisfied by using the Vault Query API, which is exposed via the VaultService for use directly by flows:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/node/services/VaultService.kt
And via CordaRPCOps for use by RPC client applications:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/messaging/CordaRPCOps.kt
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/messaging/CordaRPCOps.kt
Helper methods are also provided with default values for arguments:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/messaging/CordaRPCOps.kt
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/messaging/CordaRPCOps.kt
The API provides both static (snapshot) and dynamic (snapshot with streaming updates) methods for a defined set of filter criteria:
- Use
queryByto obtain a current snapshot of data (for a givenQueryCriteria) - Use
trackByto obtain both a current snapshot and a future stream of updates (for a givenQueryCriteria)
Note
Streaming updates are only filtered based on contract type and state status (UNCONSUMED, CONSUMED, ALL). They will not respect any other criteria that the initial query has been filtered by.
Simple pagination (page number and size) and sorting (directional ordering using standard or custom property attributes) is also specifiable. Defaults are defined for paging (pageNumber = 1, pageSize = 200) and sorting (direction = ASC).
The QueryCriteria interface provides a flexible mechanism for specifying different filtering criteria, including and/or composition and a rich set of operators to include:
- Binary logical (AND, OR)
- Comparison (LESS_THAN, LESS_THAN_OR_EQUAL, GREATER_THAN, GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUAL)
- Equality (EQUAL, NOT_EQUAL)
- Likeness (LIKE, NOT_LIKE)
- Nullability (IS_NULL, NOT_NULL)
- Collection based (IN, NOT_IN)
- Standard SQL-92 aggregate functions (SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX, COUNT)
There are four implementations of this interface which can be chained together to define advanced filters.
VaultQueryCriteriaprovides filterable criteria on attributes within the Vault states table: status (UNCONSUMED, CONSUMED), state reference(s), contract state type(s), notaries, soft locked states, timestamps (RECORDED, CONSUMED), state constraints (seeConstraint Types <implicit_constraint_types>), relevancy (ALL, RELEVANT, NON_RELEVANT).Note
Sensible defaults are defined for frequently used attributes (status = UNCONSUMED, always include soft locked states).
FungibleAssetQueryCriteriaprovides filterable criteria on attributes defined in the Corda CoreFungibleAssetcontract state interface, used to represent assets that are fungible, countable and issued by a specific party (eg.Cash.StateandCommodityContract.Statein the Corda finance module). Filterable attributes include: participants(s), owner(s), quantity, issuer party(s) and issuer reference(s).Note
All contract states that extend the
FungibleAssetnow automatically persist that interfaces common state attributes to the vault_fungible_states table.LinearStateQueryCriteriaprovides filterable criteria on attributes defined in the Corda CoreLinearStateandDealStatecontract state interfaces, used to represent entities that continuously supersede themselves, all of which share the samelinearId(e.g. trade entity states such as theIRSStatedefined in the SIMM valuation demo). Filterable attributes include: participant(s), linearId(s), uuid(s), and externalId(s).Note
All contract states that extend
LinearStateorDealStatenow automatically persist those interfaces common state attributes to the vault_linear_states table.VaultCustomQueryCriteriaprovides the means to specify one or many arbitrary expressions on attributes defined by a custom contract state that implements its own schema as described in thePersistence </api-persistence>documentation and associated examples. Custom criteria expressions are expressed using one of several type-safeCriteriaExpression: BinaryLogical, Not, ColumnPredicateExpression, AggregateFunctionExpression. TheColumnPredicateExpressionallows for specification arbitrary criteria using the previously enumerated operator types. TheAggregateFunctionExpressionallows for the specification of an aggregate function type (sum, avg, max, min, count) with optional grouping and sorting. Furthermore, a rich DSL is provided to enable simple construction of custom criteria using any combination ofColumnPredicate. See theBuilderobject inQueryCriteriaUtilsfor a complete specification of the DSL.Note
Custom contract schemas are automatically registered upon node startup for CorDapps. Please refer to
Persistence </api-persistence>for mechanisms of registering custom schemas for different testing purposes.
All QueryCriteria implementations are composable using and and or operators.
All QueryCriteria implementations provide an explicitly specifiable set of common attributes:
- State status attribute (
Vault.StateStatus), which defaults to filtering on UNCONSUMED states. When chaining several criteria using AND / OR, the last value of this attribute will override any previous - Contract state types (
<Set<Class<out ContractState>>), which will contain at minimum one type (by default this will beContractStatewhich resolves to all state types). When chaining several criteria usingandandoroperators, all specified contract state types are combined into a single set
An example of a custom query is illustrated here:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
Custom contract states that implement the Queryable interface may now extend common schemas types FungiblePersistentState or, LinearPersistentState. Previously, all custom contracts extended the root PersistentState class and defined repeated mappings of FungibleAsset and LinearState attributes. See SampleCashSchemaV2 and DummyLinearStateSchemaV2 as examples.
Examples of these QueryCriteria objects are presented below for Kotlin and Java.
Note
When specifying the ContractType as a parameterised type to the QueryCriteria in Kotlin, queries now include all concrete implementations of that type if this is an interface. Previously, it was only possible to query on concrete types (or the universe of all ContractState).
The Vault Query API leverages the rich semantics of the underlying JPA Hibernate based Persistence </api-persistence> framework adopted by Corda.
Note
Permissioning at the database level will be enforced at a later date to ensure authenticated, role-based, read-only access to underlying Corda tables.
Note
API's now provide ease of use calling semantics from both Java and Kotlin. However, it should be noted that Java custom queries are significantly more verbose due to the use of reflection fields to reference schema attribute types.
An example of a custom query in Java is illustrated here:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Note
Queries by Party specify the AbstractParty which may be concrete or anonymous. In the later case, where an anonymous party does not resolve to an X500 name via the IdentityService, no query results will ever be produced. For performance reasons, queries do not use PublicKey as search criteria.
Custom queries can be either case sensitive or case insensitive. They are defined via a Boolean as one of the function parameters of each operator function. By default each operator is case sensitive.
An example of a case sensitive custom query operator is illustrated here:
val currencyIndex = PersistentCashState::currency.equal(USD.currencyCode, true)Note
The Boolean input of true in this example could be removed since the function will default to true when not provided.
An example of a case insensitive custom query operator is illustrated here:
val currencyIndex = PersistentCashState::currency.equal(USD.currencyCode, false)An example of a case sensitive custom query operator in Java is illustrated here:
FieldInfo attributeCurrency = getField("currency", CashSchemaV1.PersistentCashState.class);
CriteriaExpression currencyIndex = Builder.equal(attributeCurrency, "USD", true);An example of a case insensitive custom query operator in Java is illustrated here:
FieldInfo attributeCurrency = getField("currency", CashSchemaV1.PersistentCashState.class);
CriteriaExpression currencyIndex = Builder.equal(attributeCurrency, "USD", false);Pagination
The API provides support for paging where large numbers of results are expected (by default, a page size is set to 200 results). Defining a sensible default page size enables efficient checkpointing within flows, and frees the developer from worrying about pagination where result sets are expected to be constrained to 200 or fewer entries. Where large result sets are expected (such as using the RPC API for reporting and/or UI display), it is strongly recommended to define a PageSpecification to correctly process results with efficient memory utilisation. A fail-fast mode is in place to alert API users to the need for pagination where a single query returns more than 200 results and no PageSpecification has been supplied.
Here's a query that extracts every unconsumed ContractState from the vault in pages of size 200, starting from the default page number (page one):
val vaultSnapshot = proxy.vaultQueryBy<ContractState>(
QueryCriteria.VaultQueryCriteria(Vault.StateStatus.UNCONSUMED),
PageSpecification(DEFAULT_PAGE_NUM, 200))Note
A pages maximum size MAX_PAGE_SIZE is defined as Int.MAX_VALUE and should be used with extreme caution as results returned may exceed your JVM's memory footprint.
Example usage
Kotlin
General snapshot queries using VaultQueryCriteria:
Query for all unconsumed states (simplest query possible):
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states for some state references:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states for several contract state types:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states for specified contract state constraint types and sorted in ascending alphabetical order:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states for specified contract state constraints (type and data):
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states for a given notary:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states for a given set of participants:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed states recorded between two time intervals:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
This example illustrates usage of a Between ColumnPredicate.
Query for all states with pagination specification (10 results per page):
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
The result set metadata field totalStatesAvailable allows you to further paginate accordingly as demonstrated in the following example.
Query for all states using a pagination specification and iterate using the totalStatesAvailable field until no further pages available:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for only relevant states in the vault:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
LinearState and DealState queries using LinearStateQueryCriteria:
Query for unconsumed linear states for given linear ids:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for all linear states associated with a linear id:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed deal states with deals references:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for unconsumed deal states with deals parties:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for only relevant linear states in the vault:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
FungibleAsset and DealState queries using FungibleAssetQueryCriteria:
Query for fungible assets for a given currency:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for fungible assets for a minimum quantity:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
This example uses the builder DSL.
Query for fungible assets for a specific issuer party:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Query for only relevant fungible states in the vault:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Aggregate Function queries using VaultCustomQueryCriteria:
Note
Query results for aggregate functions are contained in the otherResults attribute of a results Page.
Aggregations on cash using various functions:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
otherResults will contain 5 items, one per calculated aggregate function.
Aggregations on cash grouped by currency for various functions:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
otherResults will contain 24 items, one result per calculated aggregate function per currency (the grouping attribute - currency in this case - is returned per aggregate result).
Sum aggregation on cash grouped by issuer party and currency and sorted by sum:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
otherResults will contain 12 items sorted from largest summed cash amount to smallest, one result per calculated aggregate function per issuer party and currency (grouping attributes are returned per aggregate result).
Dynamic queries (also using VaultQueryCriteria) are an extension to the snapshot queries by returning an additional QueryResults return type in the form of an Observable<Vault.Update>. Refer to ReactiveX Observable for a detailed understanding and usage of this type.
Track unconsumed cash states:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Track unconsumed linear states:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
This will return both DealState and LinearState states.
Track unconsumed deal states:
../../node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryTests.kt
Note
This will return only DealState states.
Java examples
Query for all unconsumed linear states:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Query for all consumed cash states:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Query for consumed deal states or linear ids, specify a paging specification and sort by unique identifier:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Query for all states using a pagination specification and iterate using the totalStatesAvailable field until no further pages available:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Aggregate Function queries using VaultCustomQueryCriteria:
Aggregations on cash using various functions:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Aggregations on cash grouped by currency for various functions:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Sum aggregation on cash grouped by issuer party and currency and sorted by sum:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Track unconsumed cash states:
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Track unconsumed deal states or linear states (with snapshot including specification of paging and sorting by unique identifier):
../../node/src/test/java/net/corda/node/services/vault/VaultQueryJavaTests.java
Troubleshooting
If the results your were expecting do not match actual returned query results we recommend you add an entry to your log4j2.xml configuration file to enable display of executed SQL statements:
<Logger name="org.hibernate.SQL" level="debug" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Console-Appender"/>
</Logger>Behavioural notes
TrackByupdates do not take into account the full criteria specification due to different and more restrictive syntax in observables filtering (vs full SQL-92 JDBC filtering as used in snapshot views). Specifically, dynamic updates are filtered bycontractStateTypeandstateType(UNCONSUMED, CONSUMED, ALL) onlyQueryByandTrackBysnapshot views using pagination may return different result sets as each paging request is a separate SQL query on the underlying database, and it is entirely conceivable that state modifications are taking place in between and/or in parallel to paging requests. When using pagination, always check the value of thetotalStatesAvailable(from theVault.Pageresult) and adjust further paging requests appropriately.
Other use case scenarios
For advanced use cases that require sophisticated pagination, sorting, grouping, and aggregation functions, it is recommended that the CorDapp developer utilise one of the many proven frameworks that ship with this capability out of the box. Namely, implementations of JPQL (JPA Query Language) such as Hibernate for advanced SQL access, and Spring Data for advanced pagination and ordering constructs.
The Corda Tutorials provide examples satisfying these additional Use Cases:
- Example CorDapp service using Vault API Custom Query to access attributes of IOU State
- Example CorDapp service query extension executing Named Queries via JPQL
- Advanced pagination queries using Spring Data JPA
Mapping owning keys to external IDs
When creating new public keys via the KeyManagementService, it is possible to create an association between the newly created public key and an external ID. This, in effect, allows CorDapp developers to group state ownership/participation keys by an account ID.
Note
This only works with freshly generated public keys and not the node's legal identity key. If you require that the freshly generated keys be for the node's identity then use PersistentKeyManagementService.freshKeyAndCert instead of freshKey. Currently, the generation of keys for other identities is not supported.
The code snippet below show how keys can be associated with an external ID by using the exposed JPA functionality:
public AnonymousParty freshKeyForExternalId(UUID externalId, ServiceHub services) {
// Create a fresh key pair and return the public key.
AnonymousParty anonymousParty = freshKey();
// Associate the fresh key to an external ID.
services.withEntityManager(entityManager -> {
PersistentKeyManagementService.PublicKeyHashToExternalId mapping = PersistentKeyManagementService.PublicKeyHashToExternalId(externalId, anonymousParty.owningKey);
entityManager.persist(mapping);
return null;
});
return anonymousParty;
}fun freshKeyForExternalId(externalId: UUID, services: ServiceHub): AnonymousParty {
// Create a fresh key pair and return the public key.
val anonymousParty = freshKey()
// Associate the fresh key to an external ID.
services.withEntityManager {
val mapping = PersistentKeyManagementService.PublicKeyHashToExternalId(externalId, anonymousParty.owningKey)
persist(mapping)
}
return anonymousParty
}As can be seen in the code snippet above, the PublicKeyHashToExternalId entity has been added to PersistentKeyManagementService, which allows you to associate your public keys with external IDs. So far, so good.
Note
Here, it is worth noting that we must map owning keys to external IDs, as opposed to state objects. This is because it might be the case that a LinearState is owned by two public keys generated by the same node.
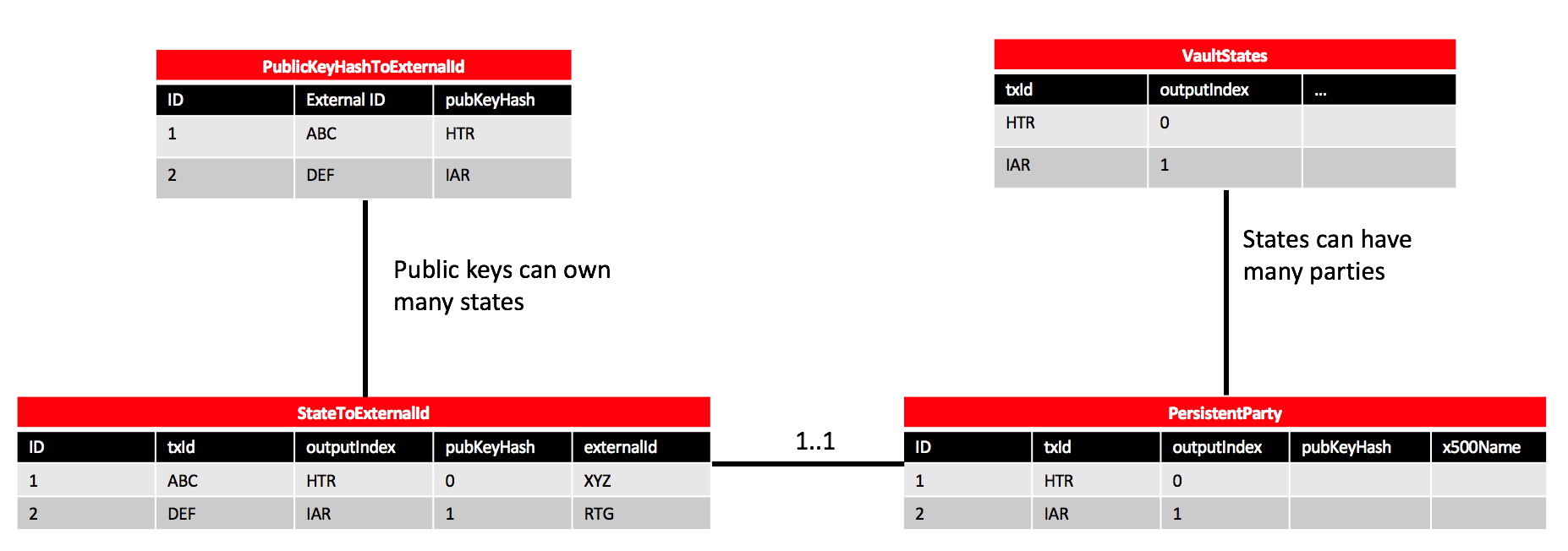
The intuition here is that when these public keys are used to own or participate in a state object, it is trivial to then associate those states with a particular external ID. Behind the scenes, when states are persisted to the vault, the owning keys for each state are persisted to a PersistentParty table. The PersistentParty table can be joined with the PublicKeyHashToExternalId table to create a view which maps each state to one or more external IDs. The entity relationship diagram below helps to explain how this works.
When performing a vault query, it is now possible to query for states by external ID using the externalIds parameter in VaultQueryCriteria.