* Updated corda release version to 1.0.0.RC2 (#1641) * Fixed Simm Valuation Demo Test and enable serializabe java 8 lambdas. (#1655) * [CORDA-624] Node Explorer on Issuing cash throws MissingContractAttachements exception (#1656) (cherry picked from commit27fea4d) * BIGINT fix for H2 coin selection. (#1658) * BIGINT fix for H2 coin selection. * Review feedback * CORDA-637 Node Explorer shows Network Map Service in Cash Issue dropdown (#1665) * [CORDA-637] Node Explorer shows Network Map Service in Cash Issue dropdown * add TODO to remove the hack * Declare this internal message string as "const". (#1676) * Merge "A variety of small fixes" into the 1.0 release branch (#1673) * Minor: improve javadocs in NodeInfo * Minor: use package descriptions in Kotlin build of api docs too, not just javadocs. * RPC: make RPCConnection non-internal, as it's a core API. Move docs around so they're on public API not internal API. * Add an IntelliJ scope that covers the currently supported Corda API. This is useful when used in combination with the "Highlight public declarations with missing KDoc" inspection. * Ironic: upgrade the version of the Gradle plugin that checks for upgraded versions of things. It had broken due being incompatible with the new versions of Gradle itself. * Docs: flesh out javadocs on ServiceHub * Docs: add @suppress to a few things that were polluting the Dokka docs. * Docs: mention RPC access in NodeInfo javadoc * IRS Fixes to bring UI closer to declared financial types (#1662) * Made problematic CordaRPCClient c'tor private (with internal bridge methods) and added correct c'tors for public use. (#1653) initialiseSerialization param has also been removed. * Fixing flow snapshot feature (#1685) * Fix validating notary flow to handle notary change transactions properly. (#1687) Add a notary change test for checking longer chains involving both regular and notary change transactions. * Unification of VaultQuery And VaultService APIs (into single VaultService interface) to simplify node bootstrapping and usability. (#1677) (#1688) * Identity documentation (#1620) * Sketch initial identity docs * Restructure confidential identity docs to better fit structure * Split confidential identities into API and concepts * Further expansion on basic identity conceptS * Merge Party type into api-identity.rst * Address feedback on written content * Rework inline code with literalinclude * Start addressing feedback from Richard * Clarify use of "counterparty" * Address comments on key concepts * Correct back to US english * Clarify distribution/publishing of identities * Update changelog around confidential identities * CORDA-642 Notary demo documentation fixes (#1682) * Notary demo documentation fixes. * One of the tables is prefixed. * CORDA-641: A temporary fix for contract upgrade transactions (#1700) * A temporary fix for contract upgrade transactions: during LedgerTransaction verification run the right logic based on whether it contains the UpgradeCommand. * Move ContractUpgradeFlowTest away from createSomeNodes() * Remove assembleBareTx as it's not used * Update corda version tag to 1.0.0-RC3 (#1705) * Hide SerializationContext from public API on TransactionBuilder (#1707) * Hide SerializationContext from public API on TransactionBuilder (cherry picked from commit 6ff7b7e) * Hide SerializationContext from public API on TransactionBuilder (cherry picked from commit 6ff7b7e) * Address feedback on confidential identities docs (#1701) * Address minor comments on confidential identities docs * Expand on implementation details of confidential identities * Cleanup * Clarify details of the data blob in the swap identites flow * Add that certificate path is not made public for confidential identities * FlowSession docs (#1693) * FlowSession docs (#1660) * FlowSession docs * PR comments * Milder example flow name * Fixes bugs with contract constraints (#1696) * Added schedulable flows to cordapp scanning Fixed a bug where the core flows are included in every cordapp. Added a test to prove the scheduled flows are loaded correctly. Added scheduled flow support to cordapp. Renabled broken test. Fixed test to prove cordapps aren't retreived from network. Review fixes. Fixed a test issue caused by gradle having slightly different paths to IntelliJ * Fixed test for real this time. * Consistent use of CordaException and CordaRuntimeException (#1710) * Custom exceptions in corda, should either derive from an appropriate closely related java exception, or CordaException, or CordaRuntimeException. They should not inherit just from Exception, or RuntimeException. Handle PR comments Add nicer constructors to CordaException and CordaRuntimeException * Fix ambiguous defaulted constructor * Add @suppress (#1725) * Git-ignore Node Explorer config. (#1709) * add message warning windows users they might need to manually kill explorer demo nodes started by gradle (#1717) (#1726) * Misc documentation fixes (#1694) (cherry picked from commit592896f) * Document -parameters compiler arg for Java CorDapps. (#1712) * Correct non-anonymous two party trade flow (#1731) * Parameterize TwoPartyTradeFlowTests to confirm deanonymised functionality works. * Correct handling of counterparty using well known identity in TWoPartyTradeFlow * CORDA-594 - SIMM Demo doc update (#1723) (#1735) * CORDA-594 - SIMM Demo doc update For V1 write a series of JSON / curl commands a user can follow to run the demo * Review Comments * Updated the rationale behind as to why SIMM was introduced. * typo * Cordapps now have a name field. (#1664) Corrected cordapp name generation. Added changelog entry. * Small API fixes against M16 (#1737) * Move CompositeSignaturesWithKeys into net.corda.core.crypto package. (cherry picked from commit 8f29562) * Rename and move CordaPluginRegistry to reflect its real purpose now. Simplify serialization code a bit. (cherry picked from commit e2ecd3a) * Docs: docsite improvements * Remove discussion of webserver from 'writing a cordapp' page. * Fixup some flow docs. * Add a couple more package descriptions. (cherry picked from commit 2aedc43) * Review comments (cherry picked from commit ba1d007) * Review comments - always apply default whitelist and no longer load it via ServiceLoader (cherry picked from commit 7d4d7bb) * Added wording about renaming services resource file * Update corda version tag to 1.0.0-RC4 (#1734) * Update corda version tag to 1.0.0-RC3 * Update corda version tag to 1.0.0-RC4 * Update build.gradle * V1 tests and fixes for the ContractConstraints work (#1739) * V1 tests and fixes for the ContractConstraints work * More fixes. * Added a contract constraints section to the key concepts doc. (#1704) Documentation for contract constraints. Added to index. Review fixes round 1. More review fixes. Review fixes. Explained package contents. review fixes. Addressed RGB's final review comments. Updated source code type to 'java' * Fixes dead links. (#1749) * Update gradle plugins version to 1.0.0 (#1753) * Update Readme (#1756) * Update Readme Minor tweaks to Readme -- consistent capitalisation and more descriptive list of features (also reordered to put the important things first) * Copied master readme. * Update Readme Minor tweaks to Readme -- consistent capitalisation and more descriptive list of features (also reordered to put the important things first) * Fixes .rst formatting. (#1751) * Updates tutorials. (#1649) * Updates tutorials. * Addresses review comments. * Tutorial refresh for v1.0 and moving of code into separate files. (#1758) * Moves code sections in tutorials to code files. * Removes wallet references. * Updates repo layout doc. * Removes remaining cordapp-tutorial references, replaced with cordapp-example. * Fixes broken link. * Misc docs fixes. * Refreshes the ServiceHub and rpc ops api pages. * Updates the cheat sheet. * Updates cookbooks. * Refreshes the running-a-notary tutorial. * Updates flow-testing tutorial * Updates tear-offs tutorial. * Refreshes integration-testing tutorial. * Updates to contract tutorial and accompanying code to bring inline with V1 release. * Refreshes contract-upgrade tutorial. * Fixed broken code sample in "writing a contract" and updated contracts dsl. * Added contract ref to java code. Fixed broken rst markup. * Updates transaction-building tutorial. * Updates the client-rpc and flow-state-machines tutorials. * Updates the oracles tutorial. * Amended country in X500 names from "UK" to "GB" * Update FlowCookbook.kt * Amended cheatsheet. Minor update on contract upgrades tutoraial. * Added `extraCordappPackagesToScan` to node driver. * Changes to match new function signature. * Update to reflect change in location of cash contract name. * CORDA-670: Correct scanned packages in network visualiser (#1763) * Add CorDapp dependency of IRS to network visualiser * Set CorDapp directories * Checking out the latest milestone will no longer be required. (#1761) * Updated documentation indices (#1754) * Update documentation indices. * Reference a moveable tag for V1 docs. Remove redundant warning text. * Reverted proposed usage of new docs release tag * Minor: print a deprecation warning when the web server starts. (#1767) * Release and upgrade notes for V1.0 (#1736) * Release and upgrade notes for V1.0 * Update changelog.rst * Update changelog.rst * Formatting. * Incorporating review feedback from KB and MN. * "guarantee" instead of "promise" * Updated with final review comments from KB and RGB. * Updated upgrade notes to describe migration from removed CordaPluginRegistry. * Minor clarification. * Minor updates following final RGB feedback. * Kat's further pedantic feedback * Minor changes following feedback from KB. * Incorporating review feedback from MH. * killed 'patent-pending' * Made the visualiser into a regular JVM module - not a CorDapp. (#1771) * Docs: more package descriptions and take non-stabilised APIs out of the docs build. (#1775) * Update corda version tag to 1.0.0 * Updated release notes to fix minor typos (#1779) Fixed bold type on simplified annotation driven scanning bullet and added bold type to module name bullets * Fixed drop down.. probably. (#1780) * fixed formatting for release notes. (#1782) * Improve API page wording (#1784) * Removed "unreleased" sections from the release notes and change log. * Merge remote-tracking branch 'origin/release-V1' into colljos-merge-v1-docs # Conflicts: # build.gradle # client/jfx/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/client/jfx/model/NodeMonitorModel.kt # client/rpc/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/client/rpc/CordaRPCClient.kt # client/rpc/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/client/rpc/PermissionException.kt # constants.properties # core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/flows/FlowSession.kt # core/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/core/contracts/DummyContractV2Tests.kt # core/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/core/flows/ContractUpgradeFlowTest.kt # docs/source/api-flows.rst # docs/source/api-index.rst # docs/source/changelog.rst # docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/tutorial/testdsl/CommercialPaperTest.java # docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt # docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/tutorial/contract/TutorialContract.kt # docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/tutorial/testdsl/TutorialTestDSL.kt # docs/source/hello-world-state.rst # docs/source/key-concepts-contract-constraints.rst # docs/source/serialization.rst # docs/source/tut-two-party-flow.rst # docs/source/tutorial-tear-offs.rst # node-api/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/nodeapi/internal/serialization/CordaClassResolver.kt # node-api/src/test/java/net/corda/nodeapi/internal/serialization/ForbiddenLambdaSerializationTests.java # node-api/src/test/java/net/corda/nodeapi/internal/serialization/LambdaCheckpointSerializationTest.java # node/src/integration-test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/AttachmentLoadingTests.kt # node/src/integration-test/kotlin/net/corda/services/messaging/MQSecurityTest.kt # node/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/node/internal/NodeStartup.kt # node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/internal/cordapp/CordappLoaderTest.kt # node/src/test/kotlin/net/corda/node/services/NotaryChangeTests.kt # samples/attachment-demo/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/attachmentdemo/AttachmentDemo.kt # samples/trader-demo/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/traderdemo/TraderDemo.kt # testing/node-driver/src/integration-test/kotlin/net/corda/testing/FlowStackSnapshotTest.kt # testing/node-driver/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/testing/driver/Driver.kt # testing/node-driver/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/testing/node/MockNode.kt # webserver/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/webserver/internal/NodeWebServer.kt
29 KiB
API: Flows
Note
Before reading this page, you should be familiar with the key concepts of key-concepts-flows.
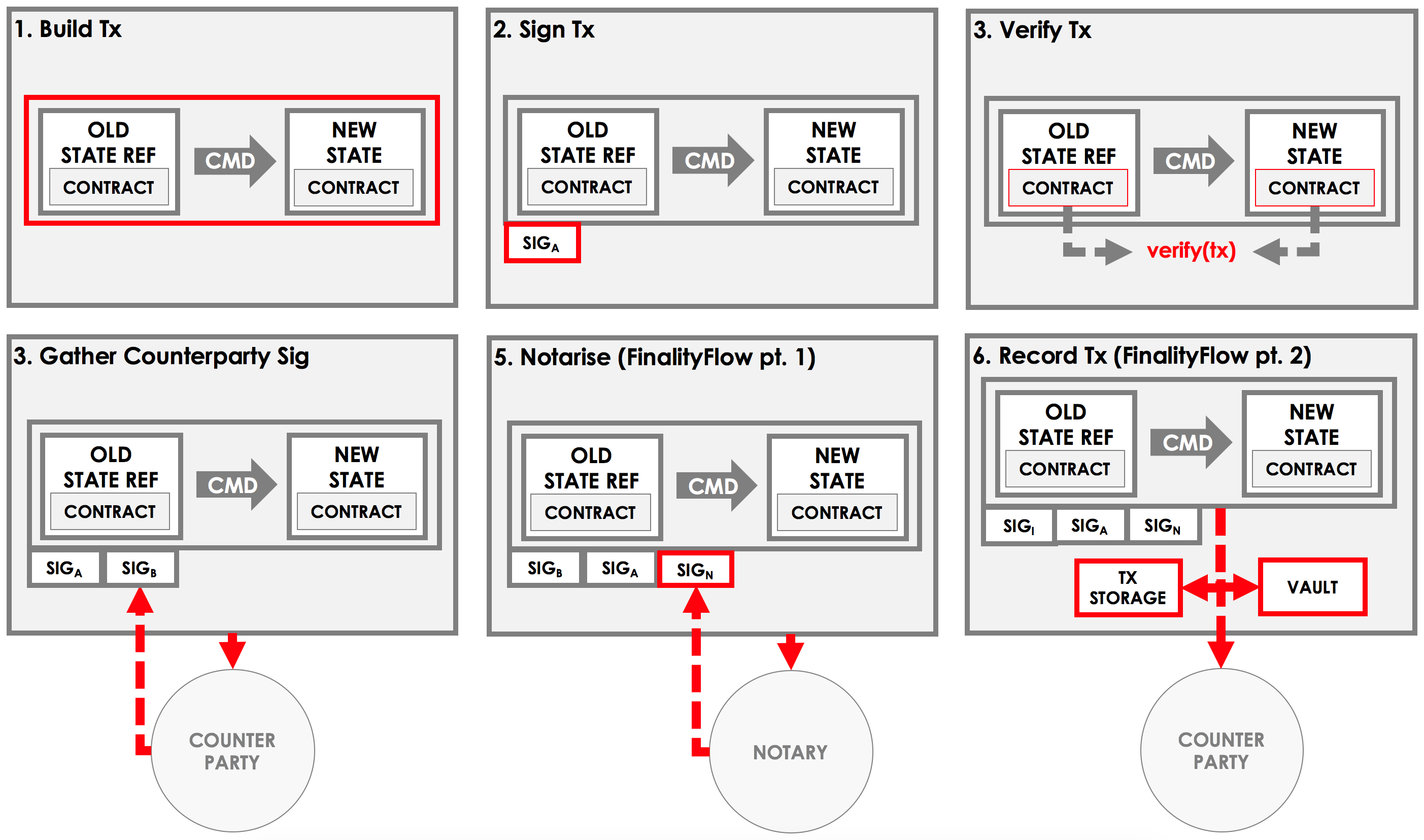
An example flow
Before we discuss the API offered by the flow, let's consider what a standard flow may look like.
Imagine a flow for agreeing a basic ledger update between Alice and Bob. This flow will have two sides:
- An
Initiatorside, that will initiate the request to update the ledger - A
Responderside, that will respond to the request to update the ledger
Initiator
In our flow, the Initiator flow class will be doing the majority of the work:
Part 1 - Build the transaction
- Choose a notary for the transaction
- Create a transaction builder
- Extract any input states from the vault and add them to the builder
- Create any output states and add them to the builder
- Add any commands, attachments and timestamps to the builder
Part 2 - Sign the transaction
- Sign the transaction builder
- Convert the builder to a signed transaction
Part 3 - Verify the transaction
- Verify the transaction by running its contracts
Part 4 - Gather the counterparty's signature
- Send the transaction to the counterparty
- Wait to receive back the counterparty's signature
- Add the counterparty's signature to the transaction
- Verify the transaction's signatures
Part 5 - Finalize the transaction
- Send the transaction to the notary
- Wait to receive back the notarised transaction
- Record the transaction locally
- Store any relevant states in the vault
- Send the transaction to the counterparty for recording
We can visualize the work performed by initiator as follows:
Responder
To respond to these actions, the responder takes the following steps:
Part 1 - Sign the transaction
- Receive the transaction from the counterparty
- Verify the transaction's existing signatures
- Verify the transaction by running its contracts
- Generate a signature over the transaction
- Send the signature back to the counterparty
Part 2 - Record the transaction
- Receive the notarised transaction from the counterparty
- Record the transaction locally
- Store any relevant states in the vault
FlowLogic
In practice, a flow is implemented as one or more communicating FlowLogic subclasses. The FlowLogic subclass's constructor can take any number of arguments of any type. The generic of FlowLogic (e.g. FlowLogic<SignedTransaction>) indicates the flow's return type.
class Initiator(val arg1: Boolean,
val arg2: Int,
val counterparty: Party): FlowLogic<SignedTransaction>() { }
class Responder(val otherParty: Party) : FlowLogic<Unit>() { }public static class Initiator extends FlowLogic<SignedTransaction> {
private final boolean arg1;
private final int arg2;
private final Party counterparty;
public Initiator(boolean arg1, int arg2, Party counterparty) {
this.arg1 = arg1;
this.arg2 = arg2;
this.counterparty = counterparty;
}
}
public static class Responder extends FlowLogic<Void> { }FlowLogic annotations
Any flow from which you want to initiate other flows must be annotated with the @InitiatingFlow annotation. Additionally, if you wish to start the flow via RPC, you must annotate it with the @StartableByRPC annotation:
@InitiatingFlow
@StartableByRPC
class Initiator(): FlowLogic<Unit>() { }@InitiatingFlow
@StartableByRPC
public static class Initiator extends FlowLogic<Unit> { }Meanwhile, any flow that responds to a message from another flow must be annotated with the @InitiatedBy annotation. @InitiatedBy takes the class of the flow it is responding to as its single parameter:
@InitiatedBy(Initiator::class)
class Responder(val otherSideSession: FlowSession) : FlowLogic<Unit>() { }@InitiatedBy(Initiator.class)
public static class Responder extends FlowLogic<Void> { }Additionally, any flow that is started by a SchedulableState must be annotated with the @SchedulableFlow annotation.
Call
Each FlowLogic subclass must override FlowLogic.call(), which describes the actions it will take as part of the flow. For example, the actions of the initiator's side of the flow would be defined in Initiator.call, and the actions of the responder's side of the flow would be defined in Responder.call.
In order for nodes to be able to run multiple flows concurrently, and to allow flows to survive node upgrades and restarts, flows need to be checkpointable and serializable to disk. This is achieved by marking FlowLogic.call(), as well as any function invoked from within FlowLogic.call(), with an @Suspendable annotation.
class Initiator(val counterparty: Party): FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() { }
}public static class InitiatorFlow extends FlowLogic<Void> {
private final Party counterparty;
public Initiator(Party counterparty) {
this.counterparty = counterparty;
}
@Suspendable
@Override
public Void call() throws FlowException { }
}ServiceHub
Within FlowLogic.call, the flow developer has access to the node's ServiceHub, which provides access to the various services the node provides. We will use the ServiceHub extensively in the examples that follow. You can also see api-service-hub for information about the services the ServiceHub offers.
Common flow tasks
There are a number of common tasks that you will need to perform within FlowLogic.call in order to agree ledger updates. This section details the API for common tasks.
Transaction building
The majority of the work performed during a flow will be to build, verify and sign a transaction. This is covered in api-transactions.
Extracting states from the vault
When building a transaction, you'll often need to extract the states you wish to consume from the vault. This is covered in api-vault-query.
Retrieving information about other nodes
We can retrieve information about other nodes on the network and the services they offer using ServiceHub.networkMapCache.
Notaries
Remember that a transaction generally needs a notary to:
- Prevent double-spends if the transaction has inputs
- Serve as a timestamping authority if the transaction has a time-window
There are several ways to retrieve a notary from the network map:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Specific counterparties
We can also use the network map to retrieve a specific counterparty:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Specific services
Finally, we can use the map to identify nodes providing a specific service (e.g. a regulator or an oracle):
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Communication between parties
In order to create a communication session between your initiator flow and the receiver flow you must call initiateFlow(party: Party): FlowSession
FlowSession instances in turn provide three functions:
send(payload: Any)- Sends the
payloadobject
- Sends the
receive(receiveType: Class<R>): R- Receives an object of type
receiveType
- Receives an object of type
sendAndReceive(receiveType: Class<R>, payload: Any): R- Sends the
payloadobject and receives an object of typereceiveTypeback
- Sends the
InitiateFlow
initiateFlow creates a communication session with the passed in Party.
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Note that at the time of call to this function no actual communication is done, this is deferred to the first send/receive, at which point the counterparty will either:
- Ignore the message if they are not registered to respond to messages from this flow.
- Start the flow they have registered to respond to this flow.
Send
Once we have a FlowSession object we can send arbitrary data to a counterparty:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
The flow on the other side must eventually reach a corresponding receive call to get this message.
Receive
We can also wait to receive arbitrary data of a specific type from a counterparty. Again, this implies a corresponding send call in the counterparty's flow. A few scenarios:
- We never receive a message back. In the current design, the flow is paused until the node's owner kills the flow.
- Instead of sending a message back, the counterparty throws a
FlowException. This exception is propagated back to us, and we can use the error message to establish what happened. - We receive a message back, but it's of the wrong type. In this case, a
FlowExceptionis thrown. - We receive back a message of the correct type. All is good.
Upon calling receive (or sendAndReceive), the FlowLogic is suspended until it receives a response.
We receive the data wrapped in an UntrustworthyData instance. This is a reminder that the data we receive may not be what it appears to be! We must unwrap the UntrustworthyData using a lambda:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We're not limited to sending to and receiving from a single counterparty. A flow can send messages to as many parties as it likes, and each party can invoke a different response flow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Warning
If you initiate several flows from the same @InitiatingFlow flow then on the receiving side you must be prepared to be initiated by any of the corresponding initiateFlow() calls! A good way of handling this ambiguity is to send as a first message a "role" message to the initiated flow, indicating which part of the initiating flow the rest of the counter-flow should conform to. For example send an enum, and on the other side start with a switch statement.
SendAndReceive
We can also use a single call to send data to a counterparty and wait to receive data of a specific type back. The type of data sent doesn't need to match the type of the data received back:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Counterparty response
Suppose we're now on the Responder side of the flow. We just received the following series of messages from the Initiator:
- They sent us an
Anyinstance - They waited to receive an
Integerinstance back - They sent a
Stringinstance and waited to receive aBooleaninstance back
Our side of the flow must mirror these calls. We could do this as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Why sessions?
Before FlowSession s were introduced the send/receive API looked a bit different. They were functions on FlowLogic and took the address Party as argument. The platform internally maintained a mapping from Party to session, hiding sessions from the user completely.
Although this is a convenient API it introduces subtle issues where a message that was originally meant for a specific session may end up in another.
Consider the following contrived example using the old Party based API:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/LaunchSpaceshipFlow.kt
The intention of the flows is very clear: LaunchSpaceshipFlow asks the president whether a spaceship should be launched. It is expecting a boolean reply. The president in return first tells the secretary that they need coffee, which is also communicated with a boolean. Afterwards the president replies to the launcher that they don't want to launch.
However the above can go horribly wrong when the launcher happens to be the same party getSecretary returns. In this case the boolean meant for the secretary will be received by the launcher!
This indicates that Party is not a good identifier for the communication sequence, and indeed the Party based API may introduce ways for an attacker to fish for information and even trigger unintended control flow like in the above case.
Hence we introduced FlowSession, which identifies the communication sequence. With FlowSession s the above set of flows would look like this:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/LaunchSpaceshipFlow.kt
Note how the president is now explicit about which session it wants to send to.
Porting from the old Party-based API
In the old API the first send or receive to a Party was the one kicking off the counter-flow. This is now explicit in the initiateFlow function call. To port existing code:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Subflows
Subflows are pieces of reusable flows that may be run by calling FlowLogic.subFlow. There are two broad categories of subflows, inlined and initiating ones. The main difference lies in the counter-flow's starting method, initiating ones initiate counter-flows automatically, while inlined ones expect some parent counter-flow to run the inlined counter-part.
Inlined subflows
Inlined subflows inherit their calling flow's type when initiating a new session with a counterparty. For example, say we have flow A calling an inlined subflow B, which in turn initiates a session with a party. The FlowLogic type used to determine which counter-flow should be kicked off will be A, not B. Note that this means that the other side of this inlined flow must therefore be implemented explicitly in the kicked off flow as well. This may be done by calling a matching inlined counter-flow, or by implementing the other side explicitly in the kicked off parent flow.
An example of such a flow is CollectSignaturesFlow. It has a counter-flow SignTransactionFlow that isn't annotated with InitiatedBy. This is because both of these flows are inlined; the kick-off relationship will be defined by the parent flows calling CollectSignaturesFlow and SignTransactionFlow.
In the code inlined subflows appear as regular FlowLogic instances, without either of the @InitiatingFlow or @InitiatedBy annotation.
Note
Inlined flows aren't versioned; they inherit their parent flow's version.
Initiating subflows
Initiating subflows are ones annotated with the @InitiatingFlow annotation. When such a flow initiates a session its type will be used to determine which @InitiatedBy flow to kick off on the counterparty.
An example is the @InitiatingFlow InitiatorFlow/@InitiatedBy ResponderFlow flow pair in the FlowCookbook.
Note
Initiating flows are versioned separately from their parents.
Core initiating subflows
Corda-provided initiating subflows are a little different to standard ones as they are versioned together with the platform, and their initiated counter-flows are registered explicitly, so there is no need for the InitiatedBy annotation.
An example is the FinalityFlow/FinalityHandler flow pair.
Built-in subflows
Corda provides a number of built-in flows that should be used for handling common tasks. The most important are:
CollectSignaturesFlow(inlined), which should be used to collect a transaction's required signaturesFinalityFlow(initiating), which should be used to notarise and record a transaction as well as to broadcast it to all relevant partiesSendTransactionFlow(inlined), which should be used to send a signed transaction if it needed to be resolved on the other side.ReceiveTransactionFlow(inlined), which should be used receive a signed transactionContractUpgradeFlow(initiating), which should be used to change a state's contractNotaryChangeFlow(initiating), which should be used to change a state's notary
Let's look at three very common examples.
FinalityFlow
FinalityFlow allows us to notarise the transaction and get it recorded in the vault of the participants of all the transaction's states:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We can also choose to send the transaction to additional parties who aren't one of the state's participants:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Only one party has to call FinalityFlow for a given transaction to be recorded by all participants. It does not need to be called by each participant individually.
CollectSignaturesFlow/SignTransactionFlow
The list of parties who need to sign a transaction is dictated by the transaction's commands. Once we've signed a transaction ourselves, we can automatically gather the signatures of the other required signers using CollectSignaturesFlow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Each required signer will need to respond by invoking its own SignTransactionFlow subclass to check the transaction and provide their signature if they are satisfied:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
SendTransactionFlow/ReceiveTransactionFlow
Verifying a transaction received from a counterparty also requires verification of every transaction in its dependency chain. This means the receiving party needs to be able to ask the sender all the details of the chain. The sender will use SendTransactionFlow for sending the transaction and then for processing all subsequent transaction data vending requests as the receiver walks the dependency chain using ReceiveTransactionFlow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We can receive the transaction using ReceiveTransactionFlow, which will automatically download all the dependencies and verify the transaction:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We can also send and receive a StateAndRef dependency chain and automatically resolve its dependencies:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Why inlined subflows?
Inlined subflows provide a way to share commonly used flow code while forcing users to create a parent flow. Take for example CollectSignaturesFlow. Say we made it an initiating flow that automatically kicks off SignTransactionFlow that signs the transaction. This would mean malicious nodes can just send any old transaction to us using CollectSignaturesFlow and we would automatically sign it!
By making this pair of flows inlined we provide control to the user over whether to sign the transaction or not by forcing them to nest it in their own parent flows.
In general if you're writing a subflow the decision of whether you should make it initiating should depend on whether the counter-flow needs broader context to achieve its goal.
FlowException
Suppose a node throws an exception while running a flow. Any counterparty flows waiting for a message from the node (i.e. as part of a call to receive or sendAndReceive) will be notified that the flow has unexpectedly ended and will themselves end. However, the exception thrown will not be propagated back to the counterparties.
If you wish to notify any waiting counterparties of the cause of the exception, you can do so by throwing a FlowException:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/flows/FlowException.kt
The flow framework will automatically propagate the FlowException back to the waiting counterparties.
There are many scenarios in which throwing a FlowException would be appropriate:
- A transaction doesn't
verify() - A transaction's signatures are invalid
- The transaction does not match the parameters of the deal as discussed
- You are reneging on a deal
ProgressTracker
We can give our flow a progress tracker. This allows us to see the flow's progress visually in our node's CRaSH shell.
To provide a progress tracker, we have to override FlowLogic.progressTracker in our flow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We then update the progress tracker's current step as we progress through the flow as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java