* Consistent separation of Java and Kotlin sources via package names only * Renamed the Kotlin tutorial files to match the class names * Added Java example of LaunchSpaceshipFlow
28 KiB
API: Transactions
Note
Before reading this page, you should be familiar with the key concepts of key-concepts-transactions.
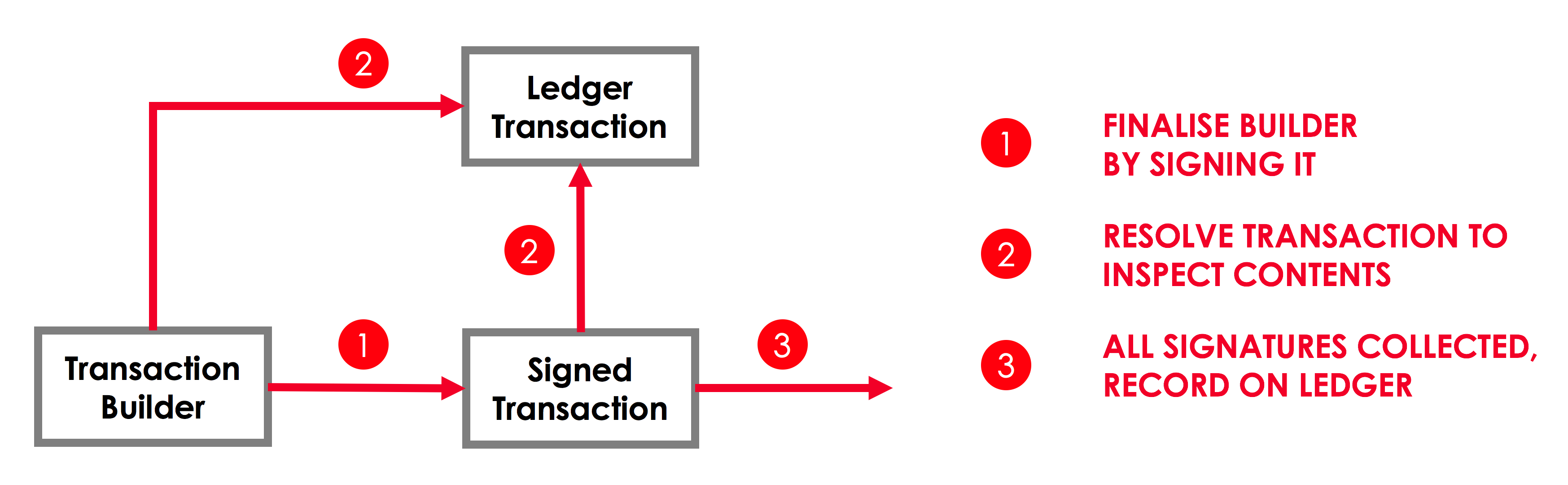
Transaction lifecycle
Between its creation and its final inclusion on the ledger, a transaction will generally occupy one of three states:
TransactionBuilder. A transaction's initial state. This is the only state during which the transaction is mutable, so we must add all the required components before moving on.SignedTransaction. The transaction now has one or more digital signatures, making it immutable. This is the transaction type that is passed around to collect additional signatures and that is recorded on the ledger.LedgerTransaction. The transaction has been "resolved" - for example, its inputs have been converted from references to actual states - allowing the transaction to be fully inspected.
We can visualise the transitions between the three stages as follows:
Transaction components
A transaction consists of six types of components:
- 1+ states:
- 0+ input states
- 0+ output states
- 0+ reference input states
- 1+ commands
- 0+ attachments
- 0 or 1 time-window
- A transaction with a time-window must also have a notary
Each component corresponds to a specific class in the Corda API. The following section describes each component class, and how it is created.
Input states
An input state is added to a transaction as a StateAndRef, which combines:
- The
ContractStateitself - A
StateRefidentifying thisContractStateas the output of a specific transaction
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
A StateRef uniquely identifies an input state, allowing the notary to mark it as historic. It is made up of:
- The hash of the transaction that generated the state
- The state's index in the outputs of that transaction
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
The StateRef links an input state back to the transaction that created it. This means that transactions form "chains" linking each input back to an original issuance transaction. This allows nodes verifying the transaction to "walk the chain" and verify that each input was generated through a valid sequence of transactions.
Reference input states
A reference input state is a ContractState which can be referred to in a transaction by the contracts of input and output states but whose contract is not executed as part of the transaction verification process. Furthermore, reference states are not consumed when the transaction is committed to the ledger but they are checked for "current-ness". In other words, the contract logic isn't run for the referencing transaction only. It's still a normal state when it occurs in an input or output position.
Reference data states enable many parties to "reuse" the same state in their transactions as reference data whilst still allowing the reference data state owner the capability to update the state.
A reference input state is added to a transaction as a ReferencedStateAndRef. A ReferencedStateAndRef can be obtained from a StateAndRef by calling the StateAndRef.referenced() method which returns a ReferencedStateAndRef.
Warning
Reference states are only available on Corda networks with a minimum platform version >= 4.
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
- language
kotlin :start-after: DOCSTART 55 :end-before: DOCEND 55 :dedent: 8
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
- language
java :start-after: DOCSTART 55 :end-before: DOCEND 55 :dedent: 12
Known limitations:
Notary change: It is likely the case that users of reference states do not have permission to change the notary assigned to a reference state. Even if users did have this permission the result would likely be a bunch of notary change races. As such, if a reference state is added to a transaction which is assigned to a different notary to the input and output states then all those inputs and outputs must be moved to the notary which the reference state uses.
If two or more reference states assigned to different notaries are added to a transaction then it follows that this transaction likely cannot be committed to the ledger as it unlikely that the party using the reference state can change the assigned notary for one of the reference states.
As such, if reference states assigned to multiple different notaries are added to a transaction builder then the check below will fail.
Output states
Since a transaction's output states do not exist until the transaction is committed, they cannot be referenced as the outputs of previous transactions. Instead, we create the desired output states as ContractState instances, and add them to the transaction directly:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
In cases where an output state represents an update of an input state, we may want to create the output state by basing it on the input state:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Before our output state can be added to a transaction, we need to associate it with a contract. We can do this by wrapping the output state in a StateAndContract, which combines:
- The
ContractStaterepresenting the output states - A
Stringidentifying the contract governing the state
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Commands
A command is added to the transaction as a Command, which combines:
- A
CommandDatainstance indicating the command's type - A
List<PublicKey>representing the command's required signers
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Attachments
Attachments are identified by their hash:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
The attachment with the corresponding hash must have been uploaded ahead of time via the node's RPC interface.
Time-windows
Time windows represent the period during which the transaction must be notarised. They can have a start and an end time, or be open at either end:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can also define a time window as an Instant plus/minus a time tolerance (e.g. 30 seconds):
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or as a start-time plus a duration:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
TransactionBuilder
Creating a builder
The first step when creating a transaction proposal is to instantiate a TransactionBuilder.
If the transaction has input states or a time-window, we need to instantiate the builder with a reference to the notary that will notarise the inputs and verify the time-window:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We discuss the selection of a notary in api-flows.
If the transaction does not have any input states or a time-window, it does not require a notary, and can be instantiated without one:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Adding items
The next step is to build up the transaction proposal by adding the desired components.
We can add components to the builder using the TransactionBuilder.withItems method:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/transactions/TransactionBuilder.kt
withItems takes a vararg of objects and adds them to the builder based on their type:
StateAndRefobjects are added as input statesReferencedStateAndRefobjects are added as reference input statesTransactionStateandStateAndContractobjects are added as output states- Both
TransactionStateandStateAndContractare wrappers around aContractStateoutput that link the output to a specific contract
- Both
Commandobjects are added as commandsSecureHashobjects are added as attachments- A
TimeWindowobject replaces the transaction's existingTimeWindow, if any
Passing in objects of any other type will cause an IllegalArgumentException to be thrown.
Here's an example usage of TransactionBuilder.withItems:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
There are also individual methods for adding components.
Here are the methods for adding inputs and attachments:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
An output state can be added as a ContractState, contract class name and notary:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can also leave the notary field blank, in which case the transaction's default notary is used:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or we can add the output state as a TransactionState, which already specifies the output's contract and notary:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Commands can be added as a Command:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or as CommandData and a vararg PublicKey:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
For the time-window, we can set a time-window directly:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or define the time-window as a time plus a duration (e.g. 45 seconds):
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Signing the builder
Once the builder is ready, we finalize it by signing it and converting it into a SignedTransaction.
We can either sign with our legal identity key:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or we can also choose to use another one of our public keys:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Either way, the outcome of this process is to create an immutable SignedTransaction with our signature over it.
SignedTransaction
A SignedTransaction is a combination of:
- An immutable transaction
- A list of signatures over that transaction
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/transactions/SignedTransaction.kt
Before adding our signature to the transaction, we'll want to verify both the transaction's contents and the transaction's signatures.
Verifying the transaction's contents
If a transaction has inputs, we need to retrieve all the states in the transaction's dependency chain before we can verify the transaction's contents. This is because the transaction is only valid if its dependency chain is also valid. We do this by requesting any states in the chain that our node doesn't currently have in its local storage from the proposer(s) of the transaction. This process is handled by a built-in flow called ReceiveTransactionFlow. See api-flows for more details.
We can now verify the transaction's contents to ensure that it satisfies the contracts of all the transaction's input and output states:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Checking that the transaction meets the contract constraints is only part of verifying the transaction's contents. We will usually also want to perform our own additional validation of the transaction contents before signing, to ensure that the transaction proposal represents an agreement we wish to enter into.
However, the SignedTransaction holds its inputs as StateRef instances, and its attachments as SecureHash instances, which do not provide enough information to properly validate the transaction's contents. We first need to resolve the StateRef and SecureHash instances into actual ContractState and Attachment instances, which we can then inspect.
We achieve this by using the ServiceHub to convert the SignedTransaction into a LedgerTransaction:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can now perform our additional verification. Here's a simple example:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Verifying the transaction's signatures
Aside from verifying that the transaction's contents are valid, we also need to check that the signatures are valid. A valid signature over the hash of the transaction prevents tampering.
We can verify that all the transaction's required signatures are present and valid as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
However, we'll often want to verify the transaction's existing signatures before all of them have been collected. For this we can use SignedTransaction.verifySignaturesExcept, which takes a vararg of the public keys for which the signatures are allowed to be missing:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
There is also an overload of SignedTransaction.verifySignaturesExcept, which takes a Collection of the public keys for which the signatures are allowed to be missing:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
If the transaction is missing any signatures without the corresponding public keys being passed in, a SignaturesMissingException is thrown.
We can also choose to simply verify the signatures that are present:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Be very careful, however - this function neither guarantees that the signatures that are present are required, nor checks whether any signatures are missing.
Signing the transaction
Once we are satisfied with the contents and existing signatures over the transaction, we add our signature to the SignedTransaction to indicate that we approve the transaction.
We can sign using our legal identity key, as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or we can choose to sign using another one of our public keys:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can also generate a signature over the transaction without adding it to the transaction directly.
We can do this with our legal identity key:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Or using another one of our public keys:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Notarising and recording
Notarising and recording a transaction is handled by a built-in flow called FinalityFlow. See api-flows for more details.