* Moves code sections in tutorials to code files. * Removes wallet references. * Updates repo layout doc. * Removes remaining cordapp-tutorial references, replaced with cordapp-example. * Fixes broken link. * Misc docs fixes. * Refreshes the ServiceHub and rpc ops api pages. * Updates the cheat sheet. * Updates cookbooks. * Refreshes the running-a-notary tutorial. * Updates flow-testing tutorial * Updates tear-offs tutorial. * Refreshes integration-testing tutorial. * Updates to contract tutorial and accompanying code to bring inline with V1 release. * Refreshes contract-upgrade tutorial. * Fixed broken code sample in "writing a contract" and updated contracts dsl. * Added contract ref to java code. Fixed broken rst markup. * Updates transaction-building tutorial. * Updates the client-rpc and flow-state-machines tutorials. * Updates the oracles tutorial. * Amended country in X500 names from "UK" to "GB" * Update FlowCookbook.kt * Amended cheatsheet. Minor update on contract upgrades tutoraial. * Added `extraCordappPackagesToScan` to node driver. * Changes to match new function signature. * Update to reflect change in location of cash contract name.
2.8 KiB
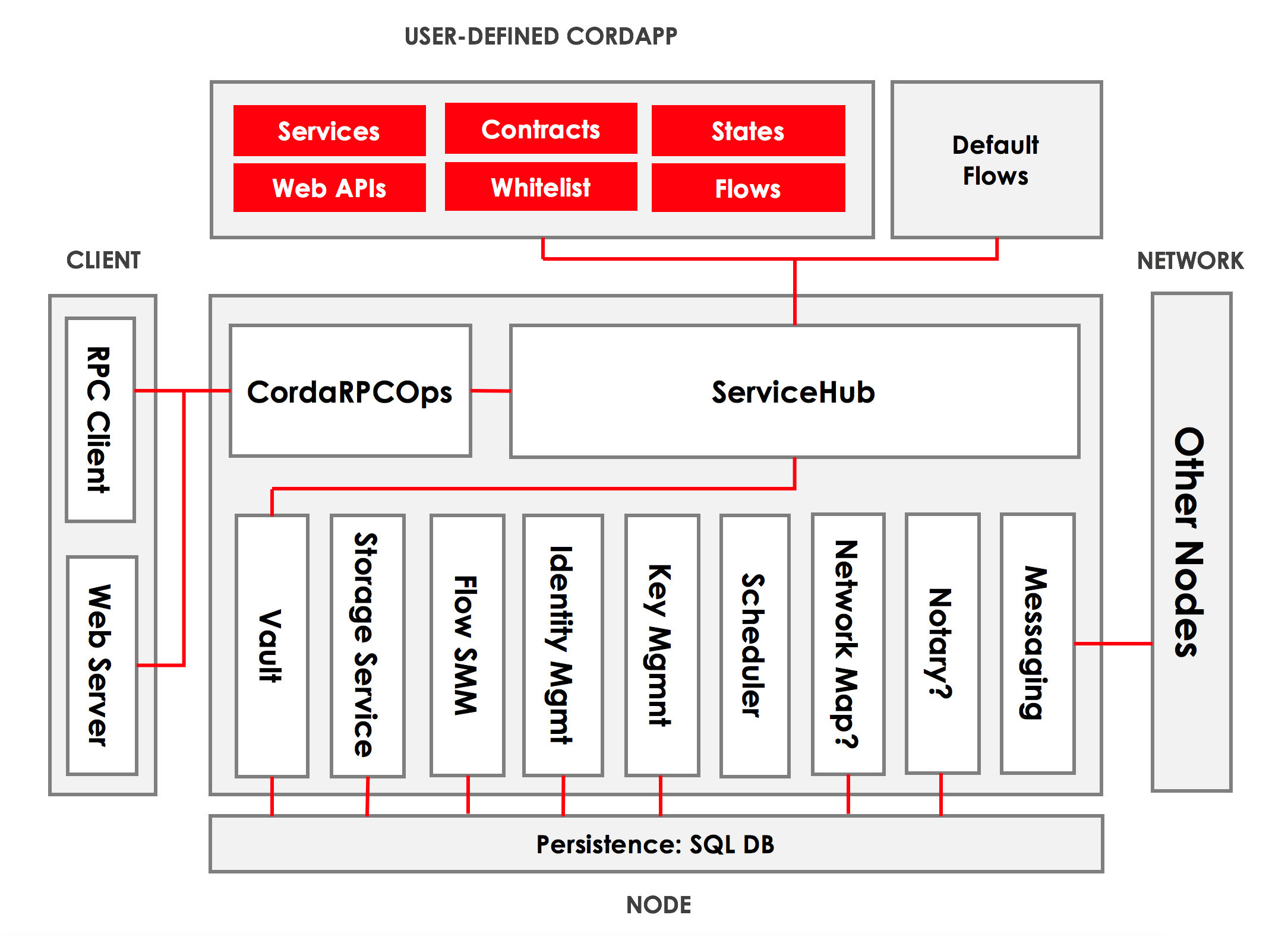
Nodes
Summary
A node is JVM run-time with a unique network identity running the Corda software
The node has two interfaces with the outside world:
- A network layer, for interacting with other nodes
- RPC, for interacting with the node's owner
The node's functionality is extended by installing CorDapps in the plugin registry
Video
Corda Node, CorDapps and Network
Node architecture
A Corda node is a JVM run-time environment with a unique identity on the network that hosts Corda services and CorDapps.
We can visualize the node's internal architecture as follows:
The core elements of the architecture are:
- A persistence layer for storing data
- A network interface for interacting with other nodes
- An RPC interface for interacting with the node's owner
- A service hub for allowing the node's flows to call upon the node's other services
- A plugin registry for extending the node by installing CorDapps
Persistence layer
The persistence layer has two parts:
- The vault, where the node stores any relevant current and historic states
- The storage service, where it stores transactions, attachments and flow checkpoints
The node's owner can query the node's storage using the RPC interface (see below).
Network interface
All communication with other nodes on the network is handled by the node itself, as part of running a flow. The node's owner does not interact with other network nodes directly.
RPC interface
The node's owner interacts with the node via remote procedure calls (RPC). The key RPC operations the node exposes are documented in api-rpc.
The service hub
Internally, the node has access to a rich set of services that are used during flow execution to coordinate ledger updates. The key services provided are:
- Information on other nodes on the network and the services they offer
- Access to the contents of the vault and the storage service
- Access to, and generation of, the node's public-private keypairs
- Information about the node itself
- The current time, as tracked by the node
The plugin registry
The plugin registry is where new CorDapps are installed to extend the behavior of the node.
The node also has several plugins installed by default to handle common tasks such as:
- Retrieving transactions and attachments from counterparties
- Upgrading contracts
- Broadcasting agreed ledger updates for recording by counterparties