65 KiB
API: Flows
Note
Before reading this page, you should be familiar with the key concepts of key-concepts-flows.
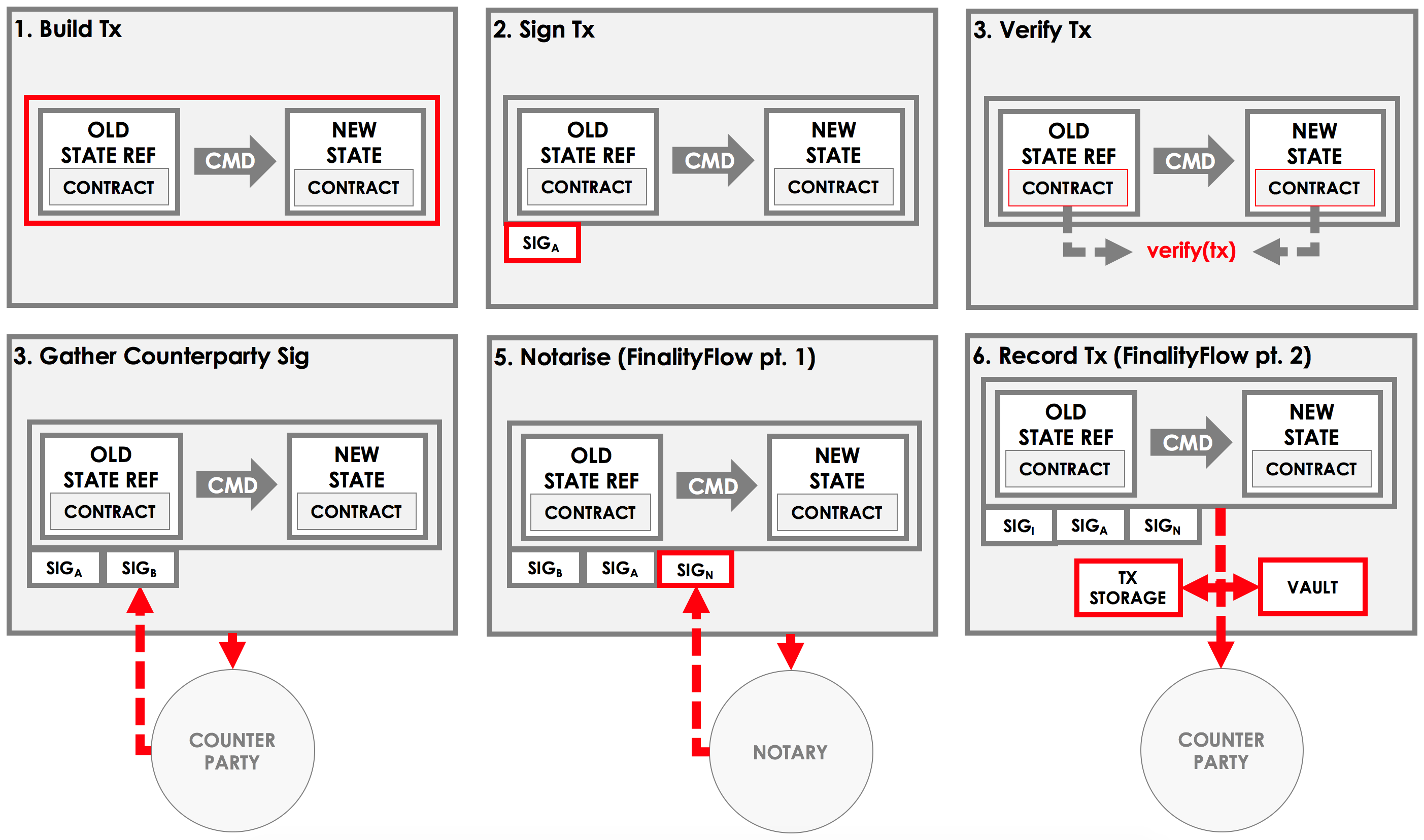
An example flow
Before we discuss the API offered by the flow, let's consider what a standard flow may look like.
Imagine a flow for agreeing a basic ledger update between Alice and Bob. This flow will have two sides:
- An
Initiatorside, that will initiate the request to update the ledger - A
Responderside, that will respond to the request to update the ledger
Initiator
In our flow, the Initiator flow class will be doing the majority of the work:
Part 1 - Build the transaction
- Choose a notary for the transaction
- Create a transaction builder
- Extract any input states from the vault and add them to the builder
- Create any output states and add them to the builder
- Add any commands, attachments and time-window to the builder
Part 2 - Sign the transaction
- Sign the transaction builder
- Convert the builder to a signed transaction
Part 3 - Verify the transaction
- Verify the transaction by running its contracts
Part 4 - Gather the counterparty's signature
- Send the transaction to the counterparty
- Wait to receive back the counterparty's signature
- Add the counterparty's signature to the transaction
- Verify the transaction's signatures
Part 5 - Finalize the transaction
- Send the transaction to the notary
- Wait to receive back the notarised transaction
- Record the transaction locally
- Store any relevant states in the vault
- Send the transaction to the counterparty for recording
We can visualize the work performed by initiator as follows:
Responder
To respond to these actions, the responder takes the following steps:
Part 1 - Sign the transaction
- Receive the transaction from the counterparty
- Verify the transaction's existing signatures
- Verify the transaction by running its contracts
- Generate a signature over the transaction
- Send the signature back to the counterparty
Part 2 - Record the transaction
- Receive the notarised transaction from the counterparty
- Record the transaction locally
- Store any relevant states in the vault
FlowLogic
In practice, a flow is implemented as one or more communicating FlowLogic subclasses. The FlowLogic subclass's constructor can take any number of arguments of any type. The generic of FlowLogic (e.g. FlowLogic<SignedTransaction>) indicates the flow's return type.
class Initiator(val arg1: Boolean,
val arg2: Int,
val counterparty: Party): FlowLogic<SignedTransaction>() { }
class Responder(val otherParty: Party) : FlowLogic<Unit>() { }public static class Initiator extends FlowLogic<SignedTransaction> {
private final boolean arg1;
private final int arg2;
private final Party counterparty;
public Initiator(boolean arg1, int arg2, Party counterparty) {
this.arg1 = arg1;
this.arg2 = arg2;
this.counterparty = counterparty;
}
}
public static class Responder extends FlowLogic<Void> { }FlowLogic annotations
Any flow from which you want to initiate other flows must be annotated with the @InitiatingFlow annotation. Additionally, if you wish to start the flow via RPC, you must annotate it with the @StartableByRPC annotation:
@InitiatingFlow
@StartableByRPC
class Initiator(): FlowLogic<Unit>() { }@InitiatingFlow
@StartableByRPC
public static class Initiator extends FlowLogic<Unit> { }Meanwhile, any flow that responds to a message from another flow must be annotated with the @InitiatedBy annotation. @InitiatedBy takes the class of the flow it is responding to as its single parameter:
@InitiatedBy(Initiator::class)
class Responder(val otherSideSession: FlowSession) : FlowLogic<Unit>() { }@InitiatedBy(Initiator.class)
public static class Responder extends FlowLogic<Void> { }Additionally, any flow that is started by a SchedulableState must be annotated with the @SchedulableFlow annotation.
Call
Each FlowLogic subclass must override FlowLogic.call(), which describes the actions it will take as part of the flow. For example, the actions of the initiator's side of the flow would be defined in Initiator.call, and the actions of the responder's side of the flow would be defined in Responder.call.
In order for nodes to be able to run multiple flows concurrently, and to allow flows to survive node upgrades and restarts, flows need to be checkpointable and serializable to disk. This is achieved by marking FlowLogic.call(), as well as any function invoked from within FlowLogic.call(), with an @Suspendable annotation.
class Initiator(val counterparty: Party): FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() { }
}public static class InitiatorFlow extends FlowLogic<Void> {
private final Party counterparty;
public Initiator(Party counterparty) {
this.counterparty = counterparty;
}
@Suspendable
@Override
public Void call() throws FlowException { }
}ServiceHub
Within FlowLogic.call, the flow developer has access to the node's ServiceHub, which provides access to the various services the node provides. We will use the ServiceHub extensively in the examples that follow. You can also see api-service-hub for information about the services the ServiceHub offers.
Common flow tasks
There are a number of common tasks that you will need to perform within FlowLogic.call in order to agree ledger updates. This section details the API for common tasks.
Transaction building
The majority of the work performed during a flow will be to build, verify and sign a transaction. This is covered in api-transactions.
Extracting states from the vault
When building a transaction, you'll often need to extract the states you wish to consume from the vault. This is covered in api-vault-query.
Retrieving information about other nodes
We can retrieve information about other nodes on the network and the services they offer using ServiceHub.networkMapCache.
Notaries
Remember that a transaction generally needs a notary to:
- Prevent double-spends if the transaction has inputs
- Serve as a timestamping authority if the transaction has a time-window
A notary can be retrieved from the network map as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Specific counterparties
We can also use the network map to retrieve a specific counterparty:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Communication between parties
In order to create a communication session between your initiator flow and the receiver flow you must call initiateFlow(party: Party): FlowSession
FlowSession instances in turn provide three functions:
send(payload: Any)- Sends the
payloadobject
- Sends the
receive(receiveType: Class<R>): R- Receives an object of type
receiveType
- Receives an object of type
sendAndReceive(receiveType: Class<R>, payload: Any): R- Sends the
payloadobject and receives an object of typereceiveTypeback
- Sends the
In addition FlowLogic provides functions that can receive messages from multiple sessions and send messages to multiple sessions:
receiveAllMap(sessions: Map<FlowSession, Class<out Any>>): Map<FlowSession, UntrustworthyData<Any>>- Receives from all
FlowSessionobjects specified in the passed in map. The received types may differ.
- Receives from all
receiveAll(receiveType: Class<R>, sessions: List<FlowSession>): List<UntrustworthyData<R>>- Receives from all
FlowSessionobjects specified in the passed in list. The received types must be the same.
- Receives from all
sendAll(payload: Any, sessions: Set<FlowSession>)- Sends the
payloadobject to all the providedFlowSessions.
- Sends the
sendAllMap(payloadsPerSession: Map<FlowSession, Any>)- Sends a potentially different payload to each
FlowSession, as specified by the providedpayloadsPerSession.
- Sends a potentially different payload to each
Note
It's more efficient to call sendAndReceive instead of calling send and then receive. It's also more efficient to call sendAll/receiveAll instead of multiple send/receive respectively.
InitiateFlow
initiateFlow creates a communication session with the passed in Party.
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Note that at the time of call to this function no actual communication is done, this is deferred to the first send/receive, at which point the counterparty will either:
- Ignore the message if they are not registered to respond to messages from this flow.
- Start the flow they have registered to respond to this flow.
Send
Once we have a FlowSession object we can send arbitrary data to a counterparty:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
The flow on the other side must eventually reach a corresponding receive call to get this message.
Receive
We can also wait to receive arbitrary data of a specific type from a counterparty. Again, this implies a corresponding send call in the counterparty's flow. A few scenarios:
- We never receive a message back. In the current design, the flow is paused until the node's owner kills the flow.
- Instead of sending a message back, the counterparty throws a
FlowException. This exception is propagated back to us, and we can use the error message to establish what happened. - We receive a message back, but it's of the wrong type. In this case, a
FlowExceptionis thrown. - We receive back a message of the correct type. All is good.
Upon calling receive (or sendAndReceive), the FlowLogic is suspended until it receives a response.
We receive the data wrapped in an UntrustworthyData instance. This is a reminder that the data we receive may not be what it appears to be! We must unwrap the UntrustworthyData using a lambda:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We're not limited to sending to and receiving from a single counterparty. A flow can send messages to as many parties as it likes, and each party can invoke a different response flow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Warning
If you initiate several flows from the same @InitiatingFlow flow then on the receiving side you must be prepared to be initiated by any of the corresponding initiateFlow() calls! A good way of handling this ambiguity is to send as a first message a "role" message to the initiated flow, indicating which part of the initiating flow the rest of the counter-flow should conform to. For example send an enum, and on the other side start with a switch statement.
SendAndReceive
We can also use a single call to send data to a counterparty and wait to receive data of a specific type back. The type of data sent doesn't need to match the type of the data received back:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Counterparty response
Suppose we're now on the Responder side of the flow. We just received the following series of messages from the Initiator:
- They sent us an
Anyinstance - They waited to receive an
Integerinstance back - They sent a
Stringinstance and waited to receive aBooleaninstance back
Our side of the flow must mirror these calls. We could do this as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Why sessions?
Before FlowSession s were introduced the send/receive API looked a bit different. They were functions on FlowLogic and took the address Party as argument. The platform internally maintained a mapping from Party to session, hiding sessions from the user completely.
Although this is a convenient API it introduces subtle issues where a message that was originally meant for a specific session may end up in another.
Consider the following contrived example using the old Party based API:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/LaunchSpaceshipFlow.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/LaunchSpaceshipFlow.java
The intention of the flows is very clear: LaunchSpaceshipFlow asks the president whether a spaceship should be launched. It is expecting a boolean reply. The president in return first tells the secretary that they need coffee, which is also communicated with a boolean. Afterwards the president replies to the launcher that they don't want to launch.
However the above can go horribly wrong when the launcher happens to be the same party getSecretary returns. In this case the boolean meant for the secretary will be received by the launcher!
This indicates that Party is not a good identifier for the communication sequence, and indeed the Party based API may introduce ways for an attacker to fish for information and even trigger unintended control flow like in the above case.
Hence we introduced FlowSession, which identifies the communication sequence. With FlowSession s the above set of flows would look like this:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/LaunchSpaceshipFlow.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/LaunchSpaceshipFlow.java
Note how the president is now explicit about which session it wants to send to.
Porting from the old Party-based API
In the old API the first send or receive to a Party was the one kicking off the counter-flow. This is now explicit in the initiateFlow function call. To port existing code:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Subflows
Subflows are pieces of reusable flows that may be run by calling FlowLogic.subFlow. There are two broad categories of subflows, inlined and initiating ones. The main difference lies in the counter-flow's starting method, initiating ones initiate counter-flows automatically, while inlined ones expect some parent counter-flow to run the inlined counterpart.
Inlined subflows
Inlined subflows inherit their calling flow's type when initiating a new session with a counterparty. For example, say we have flow A calling an inlined subflow B, which in turn initiates a session with a party. The FlowLogic type used to determine which counter-flow should be kicked off will be A, not B. Note that this means that the other side of this inlined flow must therefore be implemented explicitly in the kicked off flow as well. This may be done by calling a matching inlined counter-flow, or by implementing the other side explicitly in the kicked off parent flow.
An example of such a flow is CollectSignaturesFlow. It has a counter-flow SignTransactionFlow that isn't annotated with InitiatedBy. This is because both of these flows are inlined; the kick-off relationship will be defined by the parent flows calling CollectSignaturesFlow and SignTransactionFlow.
In the code inlined subflows appear as regular FlowLogic instances, without either of the @InitiatingFlow or @InitiatedBy annotation.
Note
Inlined flows aren't versioned; they inherit their parent flow's version.
Initiating subflows
Initiating subflows are ones annotated with the @InitiatingFlow annotation. When such a flow initiates a session its type will be used to determine which @InitiatedBy flow to kick off on the counterparty.
An example is the @InitiatingFlow InitiatorFlow/@InitiatedBy ResponderFlow flow pair in the FlowCookbook.
Note
Initiating flows are versioned separately from their parents.
Note
The only exception to this rule is FinalityFlow which is annotated with @InitiatingFlow but is an inlined flow. This flow was previously initiating and the annotation exists to maintain backwards compatibility with old code.
Core initiating subflows
Corda-provided initiating subflows are a little different to standard ones as they are versioned together with the platform, and their initiated counter-flows are registered explicitly, so there is no need for the InitiatedBy annotation.
Library flows
Corda installs four initiating subflow pairs on each node by default:
NotaryChangeFlow/NotaryChangeHandler, which should be used to change a state's notaryContractUpgradeFlow.Initiate/ContractUpgradeHandler, which should be used to change a state's contractSwapIdentitiesFlow/SwapIdentitiesHandler, which is used to exchange confidential identities with a counterparty
Warning
SwapIdentitiesFlow/SwapIdentitiesHandler are only installed if the confidential-identities module is included. The confidential-identities module is still not stabilised, so the SwapIdentitiesFlow/SwapIdentitiesHandler API may change in future releases. See api-stability-guarantees.
Corda also provides a number of built-in inlined subflows that should be used for handling common tasks. The most important are:
FinalityFlowwhich is used to notarise, record locally and then broadcast a signed transaction to its participants and any extra parties.ReceiveFinalityFlowto receive these notarised transactions from theFinalityFlowsender and record locally.CollectSignaturesFlow, which should be used to collect a transaction's required signaturesSendTransactionFlow, which should be used to send a signed transaction if it needed to be resolved on the other side.ReceiveTransactionFlow, which should be used receive a signed transaction
Let's look at some of these flows in more detail.
FinalityFlow
FinalityFlow allows us to notarise the transaction and get it recorded in the vault of the participants of all the transaction's states:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can also choose to send the transaction to additional parties who aren't one of the state's participants:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Only one party has to call FinalityFlow for a given transaction to be recorded by all participants. It must not be called by every participant. Instead, every other particpant must call ReceiveFinalityFlow in their responder flow to receive the transaction:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
idOfTxWeSigned is an optional parameter used to confirm that we got the right transaction. It comes from using SignTransactionFlow which is described in the error handling behaviour section.
Finalizing transactions with only one participant
In some cases, transactions will only have one participant, the initiator. In these instances, there are no other parties to send the transactions to during FinalityFlow. In these cases the counterpartySession list must exist, but be empty.
Error handling behaviour
Once a transaction has been notarised and its input states consumed by the flow initiator (eg. sender), should the participant(s) receiving the transaction fail to verify it, or the receiving flow (the finality handler) fails due to some other error, we then have a scenario where not all parties have the correct up to date view of the ledger (a condition where eventual consistency between participants takes longer than is normally the case under Corda's eventual consistency model). To recover from this scenario, the receiver's finality handler will automatically be sent to the node-flow-hospital where it's suspended and retried from its last checkpoint upon node restart, or according to other conditional retry rules explained in flow hospital runtime behaviour <flow-hospital-runtime>. This gives the node operator the opportunity to recover from the error. Until the issue is resolved the node will continue to retry the flow on each startup. Upon successful completion by the receiver's finality flow, the ledger will become fully consistent once again.
Warning
It's possible to forcibly terminate the erroring finality handler using the killFlow RPC but at the risk of an inconsistent view of the ledger.
Note
A future release will allow retrying hospitalised flows without restarting the node, i.e. via RPC.
CollectSignaturesFlow/SignTransactionFlow
The list of parties who need to sign a transaction is dictated by the transaction's commands. Once we've signed a transaction ourselves, we can automatically gather the signatures of the other required signers using CollectSignaturesFlow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Each required signer will need to respond by invoking its own SignTransactionFlow subclass to check the transaction (by implementing the checkTransaction method) and provide their signature if they are satisfied:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Types of things to check include:
- Ensuring that the transaction received is the expected type, i.e. has the expected type of inputs and outputs
- Checking that the properties of the outputs are expected, this is in the absence of integrating reference data sources to facilitate this
- Checking that the transaction is not incorrectly spending (perhaps maliciously) asset states, as potentially the transaction creator has access to some of signer's state references
SendTransactionFlow/ReceiveTransactionFlow
Verifying a transaction received from a counterparty also requires verification of every transaction in its dependency chain. This means the receiving party needs to be able to ask the sender all the details of the chain. The sender will use SendTransactionFlow for sending the transaction and then for processing all subsequent transaction data vending requests as the receiver walks the dependency chain using ReceiveTransactionFlow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can receive the transaction using ReceiveTransactionFlow, which will automatically download all the dependencies and verify the transaction:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We can also send and receive a StateAndRef dependency chain and automatically resolve its dependencies:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Why inlined subflows?
Inlined subflows provide a way to share commonly used flow code while forcing users to create a parent flow. Take for example CollectSignaturesFlow. Say we made it an initiating flow that automatically kicks off SignTransactionFlow that signs the transaction. This would mean malicious nodes can just send any old transaction to us using CollectSignaturesFlow and we would automatically sign it!
By making this pair of flows inlined we provide control to the user over whether to sign the transaction or not by forcing them to nest it in their own parent flows.
In general if you're writing a subflow the decision of whether you should make it initiating should depend on whether the counter-flow needs broader context to achieve its goal.
FlowException
Suppose a node throws an exception while running a flow. Any counterparty flows waiting for a message from the node (i.e. as part of a call to receive or sendAndReceive) will be notified that the flow has unexpectedly ended and will themselves end. However, the exception thrown will not be propagated back to the counterparties.
If you wish to notify any waiting counterparties of the cause of the exception, you can do so by throwing a FlowException:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/flows/FlowException.kt
The flow framework will automatically propagate the FlowException back to the waiting counterparties.
There are many scenarios in which throwing a FlowException would be appropriate:
- A transaction doesn't
verify() - A transaction's signatures are invalid
- The transaction does not match the parameters of the deal as discussed
- You are reneging on a deal
Below is an example using FlowException:
@InitiatingFlow
class SendMoneyFlow(private val moneyRecipient: Party) : FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() {
val money = Money(10.0, USD)
try {
initiateFlow(moneyRecipient).sendAndReceive<Unit>(money)
} catch (e: FlowException) {
if (e.cause is WrongCurrencyException) {
log.info(e.message, e)
}
}
}
}
@InitiatedBy(SendMoneyFlow::class)
class ReceiveMoneyFlow(private val moneySender: FlowSession) : FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() {
val receivedMoney = moneySender.receive<Money>().unwrap { it }
if (receivedMoney.currency != GBP) {
// Wrap a thrown Exception with a FlowException for the counter party to receive it.
throw FlowException(WrongCurrencyException("I only accept GBP, sorry!"))
}
}
}
class WrongCurrencyException(message: String) : CordaRuntimeException(message)HospitalizeFlowException
Some operations can fail intermittently and will succeed if they are tried again at a later time. Flows have the ability to halt their execution in such situations. By throwing a HospitalizeFlowException a flow will stop and retry at a later time (on the next node restart).
A HospitalizeFlowException can be defined in various ways:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/flows/HospitalizeFlowException.kt
Note
If a HospitalizeFlowException is wrapping or extending an exception already being handled by the node-flow-hospital, the outcome of a flow may change. For example, the flow could instantly retry or terminate if a critical error occurred.
Note
HospitalizeFlowException can be extended for customized exceptions. These exceptions will be treated in the same way when thrown.
Below is an example of a flow that should retry again in the future if an error occurs:
class TryAccessServiceFlow(): FlowLogic<Unit>() {
override fun call() {
try {
val code = serviceHub.cordaService(HTTPService::class.java).get() // throws UnknownHostException.
} catch (e: UnknownHostException) {
// Accessing the service failed! It might be offline. Let's hospitalize this flow, and have it retry again on next node startup.
throw HospitalizeFlowException("Service might be offline!", e)
}
}
}ProgressTracker
We can give our flow a progress tracker. This allows us to see the flow's progress visually in our node's CRaSH shell.
To provide a progress tracker, we have to override FlowLogic.progressTracker in our flow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
We then update the progress tracker's current step as we progress through the flow as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/kotlin/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/java/FlowCookbook.java
Calling external systems inside of flows
Flows provide the ability to await the result of an external operation running outside of the context of a flow. A flow will suspend while awaiting a result. This frees up a flow worker thread to continuing processing other flows.
Note
Flow worker threads belong to the thread pool that executes flows.
Examples of where this functionality is useful include:
- Triggering a long running process on an external system
- Retrieving information from a external service that might go down
FlowLogic provides two await functions that allow custom operations to be defined and executed outside of the context of a flow. Below are the interfaces that must be implemented and passed into await, along with brief descriptions of what they do:
FlowExternalOperation- An operation that returns a result which should be run using a thread from one of the node's thread pools.FlowExternalAsyncOperation- An operation that returns a future which should be run on a thread provided to its implementation. Threading needs to be explicitly handled when usingFlowExternalAsyncOperation.
FlowExternalOperation
FlowExternalOperation allows developers to write an operation that will run on a thread provided by the node's flow external operation thread pool.
Note
The size of the external operation thread pool can be configured, see the node configuration documentation <corda_configuration_flow_external_operation_thread_pool_size>.
Below is an example of how FlowExternalOperation can be called from a flow to run an operation on a new thread, allowing the flow to suspend:
@StartableByRPC
class FlowUsingFlowExternalOperation : FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() {
// Other flow operations
// Call [FlowLogic.await] to execute an external operation
// The result of the operation is returned to the flow
val response: Response = await(
// Pass in an implementation of [FlowExternalOperation]
RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(
serviceHub.cordaService(ExternalService::class.java),
Data("amount", 1)
)
)
// Other flow operations
}
class RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(
private val externalService: ExternalService,
private val data: Data
) : FlowExternalOperation<Response> {
// Implement [execute] which will be run on a thread outside of the flow's context
override fun execute(deduplicationId: String): Response {
return externalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId, data)
}
}
}
@CordaService
class ExternalService(serviceHub: AppServiceHub) : SingletonSerializeAsToken() {
private val client: OkHttpClient = OkHttpClient()
fun retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId: String, data: Data): Response {
return try {
// [DeduplicationId] passed into the request so the external system can handle deduplication
client.newCall(
Request.Builder().url("https://externalsystem.com/endpoint/$deduplicationId").post(
RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("text/plain"), data.toString()
)
).build()
).execute()
} catch (e: IOException) {
// Handle checked exception
throw HospitalizeFlowException("External API call failed", e)
}
}
}
data class Data(val name: String, val value: Any)@StartableByRPC
public class FlowUsingFlowExternalOperation extends FlowLogic<Void> {
@Override
@Suspendable
public Void call() {
// Other flow operations
// Call [FlowLogic.await] to execute an external operation
// The result of the operation is returned to the flow
Response response = await(
// Pass in an implementation of [FlowExternalOperation]
new RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(
getServiceHub().cordaService(ExternalService.class),
new Data("amount", 1)
)
);
// Other flow operations
return null;
}
public class RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem implements FlowExternalOperation<Response> {
private ExternalService externalService;
private Data data;
public RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(ExternalService externalService, Data data) {
this.externalService = externalService;
this.data = data;
}
// Implement [execute] which will be run on a thread outside of the flow's context
@Override
public Response execute(String deduplicationId) {
return externalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId, data);
}
}
}
@CordaService
public class ExternalService extends SingletonSerializeAsToken {
private OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
public ExternalService(AppServiceHub serviceHub) { }
public Response retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(String deduplicationId, Data data) {
try {
// [DeduplicationId] passed into the request so the external system can handle deduplication
return client.newCall(
new Request.Builder().url("https://externalsystem.com/endpoint/" + deduplicationId).post(
RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("text/plain"), data.toString()
)
).build()
).execute();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Must handle checked exception
throw new HospitalizeFlowException("External API call failed", e);
}
}
}
public class Data {
private String name;
private Object value;
public Data(String name, Object value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
}In summary, the following steps are taken in the code above:
ExternalServiceis a Corda service that provides a way to contact an external system (by HTTP in this example).ExternalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystemis passed adeduplicationIdwhich is included as part of the request to the external system. The external system, in this example, will handle deduplication and return the previous result if it was already computed.- An implementation of
FlowExternalOperation(RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem) is created that callsExternalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystem.RetrieveDataFromExternalSystemis then passed intoawaitto execute the code contained inRetrieveDataFromExternalSystem.execute.- The result of
RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem.executeis then returned to the flow once its execution finishes.
FlowExternalAsyncOperation
FlowExternalAsyncOperation allows developers to write an operation that returns a future whose threading is handled within the CorDapp.
Warning
Threading must be explicitly controlled when using FlowExternalAsyncOperation. A future will be run on its current flow worker thread if a new thread is not spawned or provided by a thread pool. This prevents the flow worker thread from freeing up and allowing another flow to take control and run.
Implementations of FlowExternalAsyncOperation must return a CompletableFuture. How this future is created is up to the developer. It is recommended to use CompletableFuture.supplyAsync and supply an executor to run the future on. Other libraries can be used to generate futures, as long as a CompletableFuture is returned out of FlowExternalAsyncOperation. An example of creating a future using Guava's ListenableFuture <api_flows_guava_future_conversion> is given in a following section.
Note
The future can be chained to execute further operations that continue using the same thread the future started on. For example, CompletableFuture's whenComplete, exceptionally or thenApply could be used (their async versions are also valid).
Below is an example of how FlowExternalAsyncOperation can be called from a flow:
@StartableByRPC
class FlowUsingFlowExternalAsyncOperation : FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() {
// Other flow operations
// Call [FlowLogic.await] to execute an external operation
// The result of the operation is returned to the flow
val response: Response = await(
// Pass in an implementation of [FlowExternalAsyncOperation]
RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(
serviceHub.cordaService(ExternalService::class.java),
Data("amount", 1)
)
)
// Other flow operations
}
class RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(
private val externalService: ExternalService,
private val data: Data
) : FlowExternalAsyncOperation<Response> {
// Implement [execute] which needs to be provided with a new thread to benefit from suspending the flow
override fun execute(deduplicationId: String): CompletableFuture<Response> {
return externalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId, data)
}
}
}
@CordaService
class ExternalService(serviceHub: AppServiceHub) : SingletonSerializeAsToken() {
private val client: OkHttpClient = OkHttpClient()
// [ExecutorService] created to provide a fixed number of threads to the futures created in this service
private val executor: ExecutorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
4,
ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("external-service-thread").build()
)
fun retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId: String, data: Data): CompletableFuture<Response> {
// Create a [CompletableFuture] to be executed by the [FlowExternalAsyncOperation]
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
Supplier {
try {
// [DeduplicationId] passed into the request so the external system can handle deduplication
client.newCall(
Request.Builder().url("https://externalsystem.com/endpoint/$deduplicationId").post(
RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("text/plain"), data.toString()
)
).build()
).execute()
} catch (e: IOException) {
// Handle checked exception
throw HospitalizeFlowException("External API call failed", e)
}
},
// The future must run on a new thread
executor
)
}
}
data class Data(val name: String, val value: Any)@StartableByRPC
public class FlowUsingFlowExternalAsyncOperation extends FlowLogic<Void> {
@Override
@Suspendable
public Void call() {
// Other flow operations
// Call [FlowLogic.await] to execute an external operation
// The result of the operation is returned to the flow
Response response = await(
// Pass in an implementation of [FlowExternalAsyncOperation]
new RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(
getServiceHub().cordaService(ExternalService.class),
new Data("amount", 1)
)
);
// Other flow operations
return null;
}
public class RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem implements FlowExternalAsyncOperation<Response> {
private ExternalService externalService;
private Data data;
public RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem(ExternalService externalService, Data data) {
this.externalService = externalService;
this.data = data;
}
// Implement [execute] which needs to be provided with a new thread to benefit from suspending the flow
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Response> execute(String deduplicationId) {
return externalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId, data);
}
}
}
@CordaService
public class ExternalService extends SingletonSerializeAsToken {
private OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
// [ExecutorService] created to provide a fixed number of threads to the futures created in this service
private ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
4,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("external-service-thread").build()
);
public ExternalService(AppServiceHub serviceHub) { }
public CompletableFuture<Response> retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(String deduplicationId, Data data) {
// Create a [CompletableFuture] to be executed by the [FlowExternalAsyncOperation]
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> {
try {
// [DeduplicationId] passed into the request so the external system can handle deduplication
return client.newCall(
new Request.Builder().url("https://externalsystem.com/endpoint/" + deduplicationId).post(
RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("text/plain"), data.toString()
)
).build()
).execute();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Must handle checked exception
throw new HospitalizeFlowException("External API call failed", e);
}
},
// The future must run on a new thread
executor
);
}
}
public class Data {
private String name;
private Object value;
public Data(String name, Object value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
}In summary, the following steps are taken in the code above:
ExternalServiceis a Corda service that provides a way to contact an external system (by HTTP in this example).ExternalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystemis passed adeduplicationIdwhich is included as part of the request to the external system. The external system, in this example, will handle deduplication and return the previous result if it was already computed.- A
CompletableFutureis created that contacts the external system.CompletableFuture.supplyAsynctakes in a reference to theExecutorServicewhich will provide a thread for the external operation to run on.- An implementation of
FlowExternalAsyncOperation(RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem) is created that calls theExternalService.retrieveDataFromExternalSystem.RetrieveDataFromExternalSystemis then passed intoawaitto execute the code contained inRetrieveDataFromExternalSystem.execute.- The result of
RetrieveDataFromExternalSystem.executeis then returned to the flow once its execution finishes.
Handling deduplication in external operations
A Flow has the ability to rerun from any point where it suspends. Due to this, a flow can execute code multiple times depending on where it retries. For context contained inside a flow, values will be reset to their state recorded at the last suspension point. This makes most properties existing inside a flow safe when retrying. External operations do not have the same guarantees as they are executed outside of the context of flows.
External operations are provided with a deduplicationId to allow CorDapps to decide whether to run the operation again or return a result retrieved from a previous attempt. How deduplication is handled depends on the CorDapp and how the external system works. For example, an external system might already handle this scenario and return the result from a previous calculation or it could be idempotent and can be safely executed multiple times.
Warning
There is no inbuilt deduplication for external operations. Any deduplication must be explicitly handled in whatever way is appropriate for the CorDapp and external system.
The deduplicationId passed to an external operation is constructed from its calling flow's ID and the number of suspends the flow has made. Therefore, the deduplicationId is guaranteed to be the same on a retry and will never be used again once the flow has successfully reached its next suspension point.
Note
Any external operations that did not finish processing (or were kept in the flow hospital due to an error) will be retried upon node restart.
Below are examples of how deduplication could be handled:
- The external system records successful computations and returns previous results if requested again.
- The external system is idempotent, meaning the computation can be made multiple times without altering any state (similar to the point above).
- An extra external service maintains a record of deduplication IDs.
- Recorded inside of the node's database.
Note
Handling deduplication on the external system's side is preferred compared to handling it inside of the node.
Warning
In-memory data structures should not be used for handling deduplication as their state will not survive node restarts.
Creating CompletableFutures from Guava's ListenableFutures
The code below demonstrates how to convert a ListenableFuture into a CompletableFuture, allowing the result to be executed using a FlowExternalAsyncOperation.
@CordaService
class ExternalService(serviceHub: AppServiceHub) : SingletonSerializeAsToken() {
private val client: OkHttpClient = OkHttpClient()
// Guava's [ListeningExecutorService] created to supply a fixed number of threads
private val guavaExecutor: ListeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
4,
ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("guava-thread").build()
)
)
fun retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(deduplicationId: String, data: Data): CompletableFuture<Response> {
// Create a Guava [ListenableFuture]
val guavaFuture: ListenableFuture<Response> = guavaExecutor.submit(Callable<Response> {
try {
// [DeduplicationId] passed into the request so the external system can handle deduplication
client.newCall(
Request.Builder().url("https://externalsystem.com/endpoint/$deduplicationId").post(
RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("text/plain"), data.toString()
)
).build()
).execute()
} catch (e: IOException) {
// Handle checked exception
throw HospitalizeFlowException("External API call failed", e)
}
})
// Create a [CompletableFuture]
return object : CompletableFuture<Response>() {
override fun cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning: Boolean): Boolean {
return guavaFuture.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning).also {
super.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning)
}
}
}.also { completableFuture ->
// Create a callback that completes the returned [CompletableFuture] when the underlying [ListenableFuture] finishes
val callback = object : FutureCallback<Response> {
override fun onSuccess(result: Response?) {
completableFuture.complete(result)
}
override fun onFailure(t: Throwable) {
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(t)
}
}
// Register the callback
Futures.addCallback(guavaFuture, callback, guavaExecutor)
}
}
}@CordaService
public class ExternalService extends SingletonSerializeAsToken {
private OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
public ExternalService(AppServiceHub serviceHub) { }
private ListeningExecutorService guavaExecutor = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
4,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("guava-thread").build()
)
);
public CompletableFuture<Response> retrieveDataFromExternalSystem(String deduplicationId, Data data) {
// Create a Guava [ListenableFuture]
ListenableFuture<Response> guavaFuture = guavaExecutor.submit(() -> {
try {
// [DeduplicationId] passed into the request so the external system can handle deduplication
return client.newCall(
new Request.Builder().url("https://externalsystem.com/endpoint/" + deduplicationId).post(
RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("text/plain"), data.toString()
)
).build()
).execute();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Must handle checked exception
throw new HospitalizeFlowException("External API call failed", e);
}
});
// Create a [CompletableFuture]
CompletableFuture<Response> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<Response>() {
// If the returned [CompletableFuture] is cancelled then the underlying [ListenableFuture] must be cancelled as well
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
boolean result = guavaFuture.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning);
super.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning);
return result;
}
};
// Create a callback that completes the returned [CompletableFuture] when the underlying [ListenableFuture] finishes
FutureCallback<Response> callback = new FutureCallback<Response>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Response result) {
completableFuture.complete(result);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(t);
}
};
// Register the callback
Futures.addCallback(guavaFuture, callback, guavaExecutor);
return completableFuture;
}
}In the code above:
- A
ListenableFutureis created and receives a thread from theListeningExecutorService. This future does all the processing.- A
CompletableFutureis created, so that it can be returned to and executed by aFlowExternalAsyncOperation.- A
FutureCallbackis registered to theListenableFuture, which will complete theCompletableFuture(either successfully or exceptionally) depending on the outcome of theListenableFuture.CompletableFuture.cancelis overridden to propagate its cancellation down to the underlyingListenableFuture.
Concurrency, Locking and Waiting
Corda is designed to:
- run many flows in parallel
- persist flows to storage and resurrect those flows much later
- (in the future) migrate flows between JVMs
Because of this, care must be taken when performing locking or waiting operations.
Locking
Flows should avoid using locks or interacting with objects that are shared between flows (except for ServiceHub and other carefully crafted services such as Oracles. See oracles). Locks will significantly reduce the scalability of the node, and can cause the node to deadlock if they remain locked across flow context switch boundaries (such as when sending and receiving from peers, as discussed above, or sleeping, as discussed below).
Waiting
A flow can wait until a specific transaction has been received and verified by the node using FlowLogic.waitForLedgerCommit. Outside of this, scheduling an activity to occur at some future time should be achieved using SchedulableState.
However, if there is a need for brief pauses in flows, you have the option of using FlowLogic.sleep in place of where you might have used Thread.sleep. Flows should expressly not use Thread.sleep, since this will prevent the node from processing other flows in the meantime, significantly impairing the performance of the node.
Even FlowLogic.sleep should not be used to create long running flows or as a substitute to using the SchedulableState scheduler, since the Corda ethos is for short-lived flows (long-lived flows make upgrading nodes or CorDapps much more complicated).
For example, the finance package currently uses FlowLogic.sleep to make several attempts at coin selection when many states are soft locked, to wait for states to become unlocked:
../../finance/workflows/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/finance/workflows/asset/selection/AbstractCashSelection.kt