22 KiB
API: Flows
Note
Before reading this page, you should be familiar with the key concepts of key-concepts-flows.
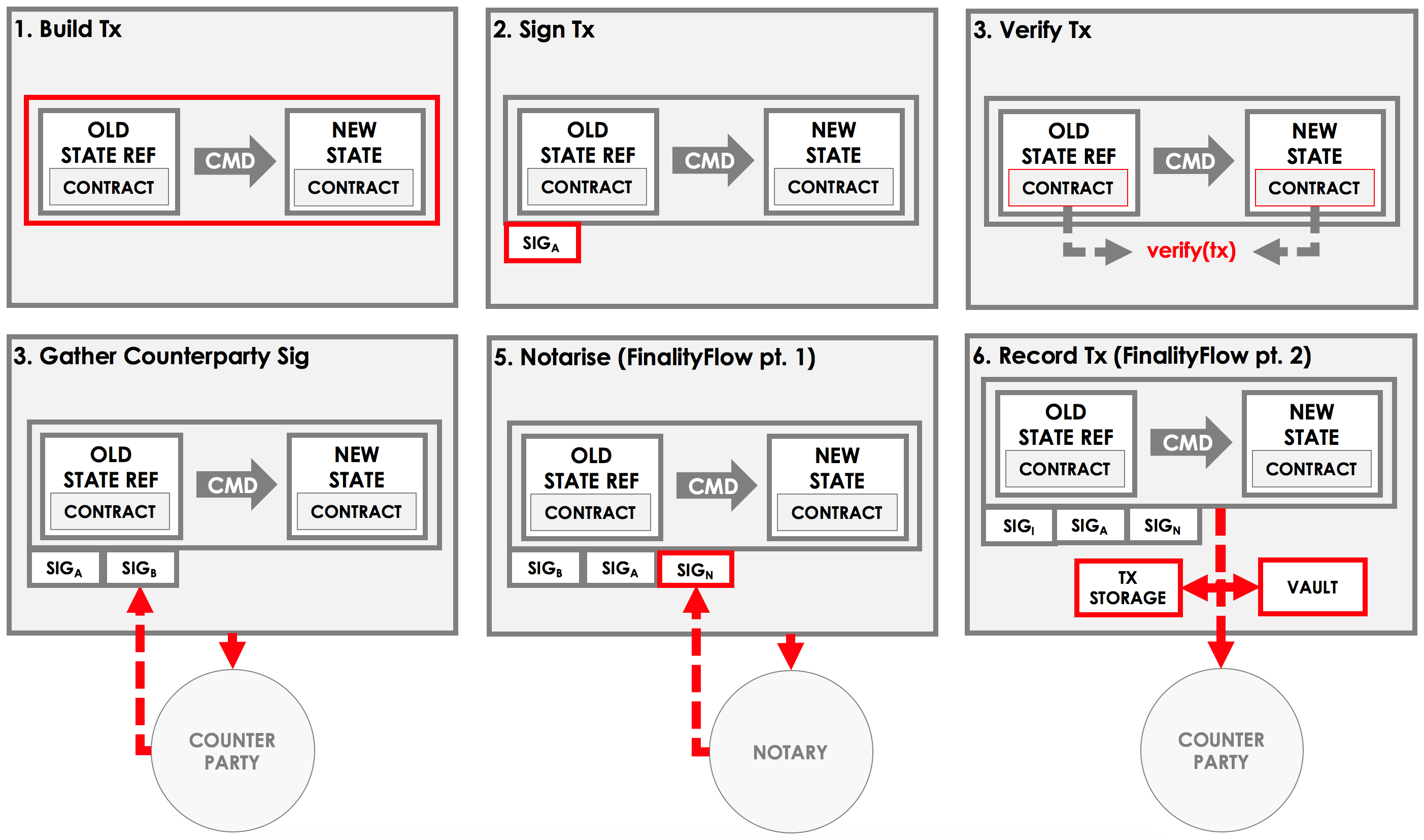
An example flow
Before we discuss the API offered by the flow, let's consider what a standard flow may look like.
Imagine a flow for agreeing a basic ledger update between Alice and Bob. This flow will have two sides:
- An
Initiatorside, that will initiate the request to update the ledger - A
Responderside, that will respond to the request to update the ledger
Initiator
In our flow, the Initiator flow class will be doing the majority of the work:
Part 1 - Build the transaction
- Choose a notary for the transaction
- Create a transaction builder
- Extract any input states from the vault and add them to the builder
- Create any output states and add them to the builder
- Add any commands, attachments and timestamps to the builder
Part 2 - Sign the transaction
- Sign the transaction builder
- Convert the builder to a signed transaction
Part 3 - Verify the transaction
- Verify the transaction by running its contracts
Part 4 - Gather the counterparty's signature
- Send the transaction to the counterparty
- Wait to receive back the counterparty's signature
- Add the counterparty's signature to the transaction
- Verify the transaction's signatures
Part 5 - Finalize the transaction
- Send the transaction to the notary
- Wait to receive back the notarised transaction
- Record the transaction locally
- Store any relevant states in the vault
- Send the transaction to the counterparty for recording
We can visualize the work performed by initiator as follows:
Responder
To respond to these actions, the responder takes the following steps:
Part 1 - Sign the transaction
- Receive the transaction from the counterparty
- Verify the transaction's existing signatures
- Verify the transaction by running its contracts
- Generate a signature over the transaction
- Send the signature back to the counterparty
Part 2 - Record the transaction
- Receive the notarised transaction from the counterparty
- Record the transaction locally
- Store any relevant states in the vault
FlowLogic
In practice, a flow is implemented as one or more communicating FlowLogic subclasses. The FlowLogic subclass's constructor can take any number of arguments of any type. The generic of FlowLogic (e.g. FlowLogic<SignedTransaction>) indicates the flow's return type.
class Initiator(val arg1: Boolean,
val arg2: Int,
val counterparty: Party): FlowLogic<SignedTransaction>() { }
class Responder(val otherParty: Party) : FlowLogic<Unit>() { }public static class Initiator extends FlowLogic<SignedTransaction> {
private final boolean arg1;
private final int arg2;
private final Party counterparty;
public Initiator(boolean arg1, int arg2, Party counterparty) {
this.arg1 = arg1;
this.arg2 = arg2;
this.counterparty = counterparty;
}
}
public static class Responder extends FlowLogic<Void> { }FlowLogic annotations
Any flow that you wish to start either directly via RPC or as a subflow must be annotated with the @InitiatingFlow annotation. Additionally, if you wish to start the flow via RPC, you must annotate it with the @StartableByRPC annotation:
@InitiatingFlow
@StartableByRPC
class Initiator(): FlowLogic<Unit>() { }@InitiatingFlow
@StartableByRPC
public static class Initiator extends FlowLogic<Unit> { }Meanwhile, any flow that responds to a message from another flow must be annotated with the @InitiatedBy annotation. @InitiatedBy takes the class of the flow it is responding to as its single parameter:
@InitiatedBy(Initiator::class)
class Responder(val otherParty: Party) : FlowLogic<Unit>() { }@InitiatedBy(Initiator.class)
public static class Responder extends FlowLogic<Void> { }Additionally, any flow that is started by a SchedulableState must be annotated with the @SchedulableFlow annotation.
Call
Each FlowLogic subclass must override FlowLogic.call(), which describes the actions it will take as part of the flow. For example, the actions of the initiator's side of the flow would be defined in Initiator.call, and the actions of the responder's side of the flow would be defined in Responder.call.
In order for nodes to be able to run multiple flows concurrently, and to allow flows to survive node upgrades and restarts, flows need to be checkpointable and serializable to disk. This is achieved by marking FlowLogic.call(), as well as any function invoked from within FlowLogic.call(), with an @Suspendable annotation.
class Initiator(val counterparty: Party): FlowLogic<Unit>() {
@Suspendable
override fun call() { }
}public static class InitiatorFlow extends FlowLogic<Void> {
private final Party counterparty;
public Initiator(Party counterparty) {
this.counterparty = counterparty;
}
@Suspendable
@Override
public Void call() throws FlowException { }
}ServiceHub
Within FlowLogic.call, the flow developer has access to the node's ServiceHub, which provides access to the various services the node provides. We will use the ServiceHub extensively in the examples that follow. You can also see api-service-hub for information about the services the ServiceHub offers.
Common flow tasks
There are a number of common tasks that you will need to perform within FlowLogic.call in order to agree ledger updates. This section details the API for common tasks.
Transaction building
The majority of the work performed during a flow will be to build, verify and sign a transaction. This is covered in api-transactions.
Extracting states from the vault
When building a transaction, you'll often need to extract the states you wish to consume from the vault. This is covered in api-vault-query.
Retrieving information about other nodes
We can retrieve information about other nodes on the network and the services they offer using ServiceHub.networkMapCache.
Notaries
Remember that a transaction generally needs a notary to:
- Prevent double-spends if the transaction has inputs
- Serve as a timestamping authority if the transaction has a time-window
There are several ways to retrieve a notary from the network map:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Specific counterparties
We can also use the network map to retrieve a specific counterparty:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Specific services
Finally, we can use the map to identify nodes providing a specific service (e.g. a regulator or an oracle):
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Communication between parties
FlowLogic instances communicate using three functions:
send(otherParty: Party, payload: Any)- Sends the
payloadobject to theotherParty
- Sends the
receive(receiveType: Class<R>, otherParty: Party)- Receives an object of type
receiveTypefrom theotherParty
- Receives an object of type
sendAndReceive(receiveType: Class<R>, otherParty: Party, payload: Any)- Sends the
payloadobject to theotherParty, and receives an object of typereceiveTypeback
- Sends the
Send
We can send arbitrary data to a counterparty:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
If this is the first send, the counterparty will either:
- Ignore the message if they are not registered to respond to messages from this flow.
- Start the flow they have registered to respond to this flow, and run the flow until the first call to
receive, at which point they process the message. In other words, we are assuming that the counterparty is registered to respond to this flow, and has a correspondingreceivecall.
Receive
We can also wait to receive arbitrary data of a specific type from a counterparty. Again, this implies a corresponding send call in the counterparty's flow. A few scenarios:
- We never receive a message back. In the current design, the flow is paused until the node's owner kills the flow.
- Instead of sending a message back, the counterparty throws a
FlowException. This exception is propagated back to us, and we can use the error message to establish what happened. - We receive a message back, but it's of the wrong type. In this case, a
FlowExceptionis thrown. - We receive back a message of the correct type. All is good.
Upon calling receive (or sendAndReceive), the FlowLogic is suspended until it receives a response.
We receive the data wrapped in an UntrustworthyData instance. This is a reminder that the data we receive may not be what it appears to be! We must unwrap the UntrustworthyData using a lambda:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We're not limited to sending to and receiving from a single counterparty. A flow can send messages to as many parties as it likes, and each party can invoke a different response flow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
SendAndReceive
We can also use a single call to send data to a counterparty and wait to receive data of a specific type back. The type of data sent doesn't need to match the type of the data received back:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Counterparty response
Suppose we're now on the Responder side of the flow. We just received the following series of messages from the Initiator:
- They sent us an
Anyinstance - They waited to receive an
Integerinstance back - They sent a
Stringinstance and waited to receive aBooleaninstance back
Our side of the flow must mirror these calls. We could do this as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Subflows
Corda provides a number of built-in flows that should be used for handling common tasks. The most important are:
CollectSignaturesFlow, which should be used to collect a transaction's required signaturesFinalityFlow, which should be used to notarise and record a transactionSendTransactionFlow, which should be used to send a signed transaction if it needed to be resolved on the other side.ReceiveTransactionFlow, which should be used receive a signed transactionContractUpgradeFlow, which should be used to change a state's contractNotaryChangeFlow, which should be used to change a state's notary
These flows are designed to be used as building blocks in your own flows. You invoke them by calling FlowLogic.subFlow from within your flow's call method. Let's look at three very common examples.
FinalityFlow
FinalityFlow allows us to notarise the transaction and get it recorded in the vault of the participants of all the transaction's states:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We can also choose to send the transaction to additional parties who aren't one of the state's participants:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Only one party has to call FinalityFlow for a given transaction to be recorded by all participants. It does not need to be called by each participant individually.
CollectSignaturesFlow/SignTransactionFlow
The list of parties who need to sign a transaction is dictated by the transaction's commands. Once we've signed a transaction ourselves, we can automatically gather the signatures of the other required signers using CollectSignaturesFlow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
Each required signer will need to respond by invoking its own SignTransactionFlow subclass to check the transaction and provide their signature if they are satisfied:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
SendTransactionFlow/ReceiveTransactionFlow
Verifying a transaction received from a counterparty also requires verification of every transaction in its dependency chain. This means the receiving party needs to be able to ask the sender all the details of the chain. The sender will use SendTransactionFlow for sending the transaction and then for processing all subsequent transaction data vending requests as the receiver walks the dependency chain using ReceiveTransactionFlow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We can receive the transaction using ReceiveTransactionFlow, which will automatically download all the dependencies and verify the transaction:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We can also send and receive a StateAndRef dependency chain and automatically resolve its dependencies:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
FlowException
Suppose a node throws an exception while running a flow. Any counterparty flows waiting for a message from the node (i.e. as part of a call to receive or sendAndReceive) will be notified that the flow has unexpectedly ended and will themselves end. However, the exception thrown will not be propagated back to the counterparties.
If you wish to notify any waiting counterparties of the cause of the exception, you can do so by throwing a FlowException:
../../core/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/core/flows/FlowException.kt
The flow framework will automatically propagate the FlowException back to the waiting counterparties.
There are many scenarios in which throwing a FlowException would be appropriate:
- A transaction doesn't
verify() - A transaction's signatures are invalid
- The transaction does not match the parameters of the deal as discussed
- You are reneging on a deal
ProgressTracker
We can give our flow a progress tracker. This allows us to see the flow's progress visually in our node's CRaSH shell.
To provide a progress tracker, we have to override FlowLogic.progressTracker in our flow:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java
We then update the progress tracker's current step as we progress through the flow as follows:
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/kotlin/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbook.kt
../../docs/source/example-code/src/main/java/net/corda/docs/FlowCookbookJava.java