| .. | ||
| examples | ||
| images | ||
| include | ||
| src | ||
| unittest | ||
| makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
Stand-Alone Integration Library
Contents
- Introduction
- class Integrator
- typedef derivsFunc
- class FirstOrderODEIntegrator
- typedef RootErrorFunc
- class FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator
- class EulerIntegrator
- class HeunsMethod
- class RK2Integrator
- class RK4Integrator
- class RK3_8Integrator
- class EulerCromerIntegrator
- class ABM2Integrator
- class ABM4Integrator
- enum SlopeConstraint
- class RootFinder
Introduction
The Stand-Alone Integration Library can be used within a Trick simulation, or independent of it.
Some examples of using these integrators can be found in the examples/ directory.
- CannonBall uses the RK2Integrator.
- MassSpringDamper uses the EulerCromerIntegrator.
- Orbit uses the EulerCromerIntegrator.
- DoubleIntegral shows an example of a double integral.
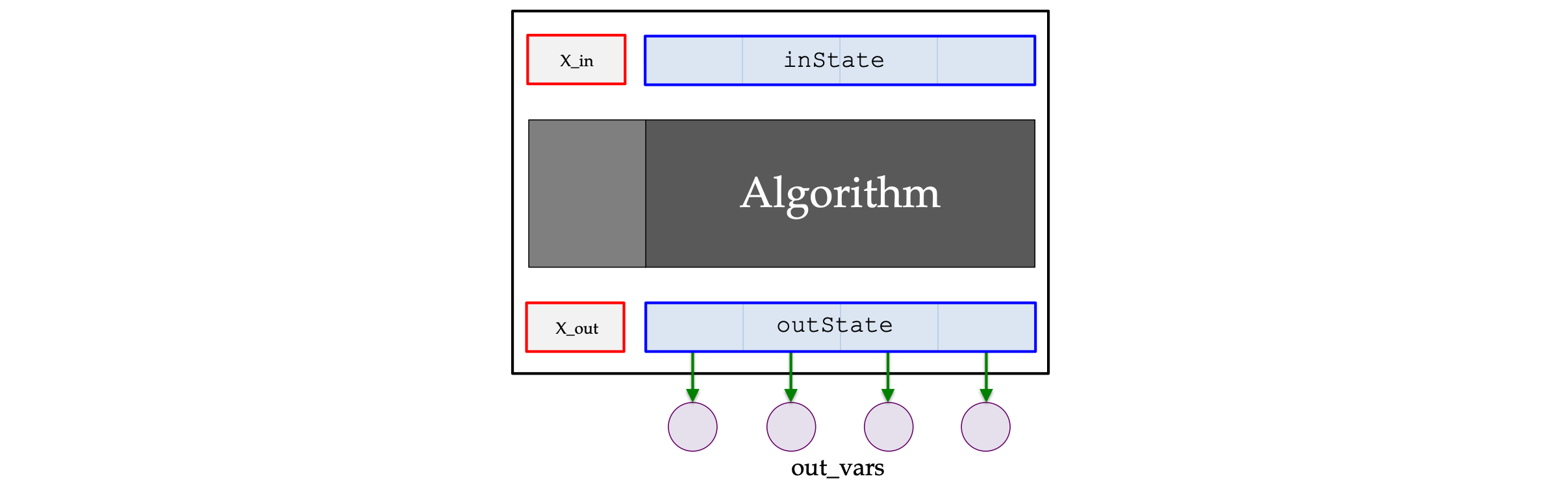
class Integrator
Description
This class represents an integrator.
| Member | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| X_in | double |
Independent variable value of the input state. |
| X_out | double |
Independent variable value of the output state. |
| default_h | double |
Default integration step-size |
| user_data | void* |
A pointer to user defined data that will be passed to user-defined functions when called by the Integrator. |
Constructor
Integrator(double h, void* udata);
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| h | double |
Default integration step-size |
| udata | void* |
A pointer to user defined data that will be passed to user-defined functions when called by the Integrator. |
Destructor
virtual ~Integrator() {}
Member Functions
virtual void step();
Derived classes should override this method to perform a numeric integration step. The default behavior is to simply increment the independent variable by the default integration step-size.
virtual void load();
Derived classes should override this method to load/prepare the integrator for the next integration step. The default behavior is to set the input value of the independent value to its previous output value, i.e, X_out = X_out.
virtual void unload() = 0;
Derived classes must override this method to disseminate the values of the output state to their respective destination variables.
double getIndyVar();
Return the value of the independent variable (i.e, the variable over which you are integrating) If you are integrating over time, this value will be the accumulated time.
double setIndyVar( double t);
Set the value of the independent variable. (i.e, the variable over which you are integrating) If you are integrating over time, this value will be the accumulated time.
typedef derivsFunc
typedef void (*derivsFunc)( double x, double state[], double derivs[], void* udata);
where:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | double |
independent variable |
| state | double* |
(input) an array of state variable values |
| derivs | double* |
(output) an array into which derivatives are to be returned |
| udata | void* |
a pointer to user_data. |
Example
void my_derivs( double t, double state[], double deriv[], void* udata) { ... }
class FirstOrderODEIntegrator
Derived from Integrator.
| Member | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| state_size | unsigned int |
Size of the state vector. |
| inState | double* |
Input state vector to the integrator. |
| outState | double* |
Output state vector from the integrator. |
| inVars | double** |
Array of pointers to the variables from which input state vector values are copied. |
| outVars | double** |
Array of pointers to the variables to which output state vector values are copied. |
| derivs_func | DerivsFunc |
Function thats generates the function (an array of state derivatives) to be integrated. |
| last_h | double |
the last integration step-size. |
Description
This class represents an integrator for a first order Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE).
Constructor
FirstOrderODEIntegrator( double h,
int N,
double* in_vars[],
double* out_vars[],
derivsFunc func,
void* user_data);
where:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| h | double |
Default integration step-size. |
| N | int |
Number of state variables to be integrated |
| in_vars | double* |
Array of pointers to the state variables from which we load() the integrator state (in_vars and out_vars will generally point to the same array of pointers.) |
| out_vars | double* |
Array of pointers to the state variables to which we unload() the integrator state (in_vars and out_vars will generally point to the same array of pointers.) |
| derivs_func | derivsFunc |
Function thats generates the function (the derivatives) to be integrated. |
| user_data | void* |
A pointer to user defined data that will be passed to a derivsFunc when called by the Integrator. |
Member Functions
void load()
Load the integrator's initial state from the variables specified by in_vars. Set the initial value of the independent variable for the next step to the final value of the previous step.

void unload()
Unload the integrator's result state to the variables specified by out_vars.
virtual void undo_step()
Undo the effect of the last integration step.

void load_from_outState()
Load the integrator's initial state from outState, rather than from the variables referenced by in_vars.

double** set_in_vars( double* in_vars[])
Specify the variables from which inState values are to be copied when load() is called. The number of elements in this array must equal the number of state variables.
Return a pointer to the previous array so that it can be deleted if necessary.

double** set_out_vars( double* out_vars[])
Specify the variables to which outState values are to be copied when unload() is called. The number of elements in this array must equal the number of state variables.
Return a pointer to the previous array so that it can be deleted if necessary.

typedef RootErrorFunc
typedef double (*RootErrorFunc)( double x, double state[], RootFinder* root_finder, void* udata);
where:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | double |
Independent variable |
| state | double* |
Array of state variable values |
| root_finder | RootFinder* |
Class for finding the roots of a function. |
| udata | void* |
A pointer to user_data. |
This user-supplied function should:
- Call
root_finder->find_roots(). - Specify what happens when the root is found, i.e., when
find_roots()returns 0.0. - Return the value returned by
root_finder->find_roots()as in the example below.
Example RootErrorFunc from the Cannonball example
double impact( double t, double state[], RootFinder* root_finder, void* udata) {
double root_error = root_finder->find_roots(t, state[1]);
if (root_error == 0.0) {
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Impact at t = %5.10f x = %5.10f y = %5.10f.\n", t, state[0], state[1]);
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------\n");
root_finder->init();
state[1] = 0.0000000001; // pos_y
state[2] = 0.0; // vel_x
state[3] = 0.0; // vel_y
state[4] = 0.0; // acc_x
state[5] = 0.0; // acc_y
}
return (root_error);
}
class FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
| Member | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| root_finder | RootFinder* |
Pointer to a RootFinder object. |
| root_error_func | RootErrorFunc |
Function that specifies what happens when a function-root is found. |
Description
This class represents a first order ODE integrator whose step-size can be varied.
Constructor
Member Functions
virtual void variable_step( double h)
Derived classes should override this method to calculate outState using some integration algorithm, given X_in, inState, and derivs_func. The over-riding method should also pass the user_data when calling the derivsFunc. The default behavior is to simply add the integration step-size (h) to X_in.

void step()
Call the virtual function (variable_step()) with the default step-size.
Then, if a RootFinder has been specified (using add_Rootfinder() below), search that interval for roots .
void add_Rootfinder( RootFinder* root_finder, RootErrorFunc rfunc)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| root_finder | RootFinder* |
Error tolerance. |
| rfunc | RootErrorFunc |
User supplied function that ??? |
Configure the integrator to find roots of state-element vs. independent-variable functions.
class EulerIntegrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator.
Description
The Euler method is a first order numerical integration method. It is the simplest, explicit Runge-Kutta method.
Constructor
EulerIntegrator(double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class HeunsMethod
Derived from FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator.
Description
This integrator implements Heun's Method.
Constructor
HeunsMethod( double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class RK2Integrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator.
Description
RK2Integrator implements the second order, explicit, Runge-Kutta method whose Butcher tableau is as follows.
Constructor
RK2Integrator( double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class RK4Integrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator.
Description
RK4Integrator implements the fourth order, explicit, Runge-Kutta method whose Butcher tableau is as follows.
Constructor
RK4Integrator( double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class RK3_8Integrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEVariableStepIntegrator.
Description
RK3_8Integrator implements the fourth order, explicit, Runge-Kutta method whose Butcher tableau is as follows.
Constructor
RK3_8Integrator( double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class ABM2Integrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
Description
The ABM2Integrator implements the second-order Adams-Bashforth-Moulton predictor/corrector method. Adams methods maintain a history of derivatives rather than calculating intermediate values like Runge-Kutta methods.
Constructor
ABM2Integrator ( double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class ABM4Integrator
Derived from FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
Description
The ABM2Integrator implements the second-order Adams-Bashforth-Moulton predictor/corrector method. Adams methods maintain a history of derivatives rather than calculating intermediate values like Runge-Kutta methods.
Constructor
ABM4Integrator ( double h, int N, double* in_vars[], double* out_vars[], derivsFunc func, void* user_data)
Constructor Parameters are those of FirstOrderODEIntegrator.
class EulerCromerIntegrator
Derived from Integrator.
Description
EulerCromer is integration method that conserves energy in oscillatory systems better than Runge-Kutta. So, it's good for mass-spring-damper systems, and orbital systems.
Constructor
SemiImplicitEuler(double dt, int N, double* xp[], double* vp[], derivsFunc gfunc, derivsFunc ffunc, void* user_data)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| dt | double |
Default time step value |
| N | int |
Number of state variables to be integrated |
| xp | double* |
Array of pointers to the variables from which we load() and to which we unload() the integrator's position values . |
| vp | double* |
Array of pointers to the variables from which we load() and to which we unload() the integrator's velocity values . |
| gfunc | derivsFunc |
A function that returns acceleration |
| ffunc | derivsFunc |
A function that returns velocity |
| user_data | void* |
A pointer to user defined data that will be passed to a derivsFunc when called by the Integrator. |
enum SlopeConstraint
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Negative | Require slope of the function to be negative at the root. |
| Unconstrained | No slope constraint. |
| Positive | Require slope of the function to be positive at the root. |
class RootFinder
Derived from RootFinder.
| Member | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| f_upper | double |
|
| x_upper | double |
|
| upper_set | bool |
|
| f_lower | double |
|
| x_lower | double |
|
| lower_set | bool |
|
| prev_f_error | double |
|
| f_error_tol | double |
|
| iterations | int |
|
| slope_constraint | SlopeConstraint |
|
| f_slope | SlopeConstraint |
Description
The RootFinder class uses the Regula-Falsi method to find roots of a math function. A root is a value of x such that f(x)=0.
Constructors
RootFinder()
Default constructor that calls void RootFinder::init() below.
RootFinder(double tolerance, SlopeConstraint constraint)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| tolerance | double |
Error tolerance. |
| constraint | SlopeConstraint |
Methods
void init( double tolerance, SlopeConstraint constraint)
Initialize the RootFinder with the given tolerance, and SlopeConstraint.
void RootFinder::init()
Initialize the RootFinder with the method above with:
- tolerance =
0.00000000001 - slope_constraint =
Unconstrained
double find_roots( double x, double f_error )
- Returns DBL_MAX if no root is detected.
- Returns 0.0 if a root is detected, and the estimated error in f(x) is within tolerance.
- Returns an estimated correction in x if a root is detected, but the estimated error in f(x) is not within tolerance.


