mirror of
https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus.git
synced 2025-06-08 08:11:34 +00:00
fix merge conflicts
This commit is contained in:
commit
cc57cc5f46
3
.github/FUNDING.yml
vendored
3
.github/FUNDING.yml
vendored
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# These are supported funding model platforms
|
||||
|
||||
github: # Replace with up to 4 GitHub Sponsors-enabled usernames e.g., [user1, user2]
|
||||
# Replace with up to 4 GitHub Sponsors-enabled usernames e.g., [user1, user2]
|
||||
github: AFLplusplus
|
||||
patreon: # Replace with a single Patreon username
|
||||
open_collective: AFLplusplusEU
|
||||
ko_fi: # Replace with a single Ko-fi username
|
||||
|
||||
10
GNUmakefile
10
GNUmakefile
@ -306,6 +306,7 @@ endif
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all
|
||||
all: test_x86 test_shm test_python ready $(PROGS) afl-as llvm gcc_plugin test_build all_done
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C utils/aflpp_driver
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: llvm
|
||||
llvm:
|
||||
@ -436,8 +437,8 @@ afl-showmap: src/afl-showmap.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-fork
|
||||
afl-tmin: src/afl-tmin.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o src/afl-performance.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(COMPILE_STATIC) $(CFLAGS_FLTO) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-forkserver.o src/afl-performance.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
afl-analyze: src/afl-analyze.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-performance.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(COMPILE_STATIC) $(CFLAGS_FLTO) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-performance.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
afl-analyze: src/afl-analyze.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-performance.o src/afl-forkserver.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(COMPILE_STATIC) $(CFLAGS_FLTO) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o src/afl-sharedmem.o src/afl-performance.o src/afl-forkserver.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
afl-gotcpu: src/afl-gotcpu.c src/afl-common.o $(COMM_HDR) | test_x86
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(COMPILE_STATIC) $(CFLAGS_FLTO) src/$@.c src/afl-common.o -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
@ -572,8 +573,9 @@ clean:
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/unsigaction clean
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/libcompcov clean
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/libqasan clean
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C frida_mode clean
|
||||
ifeq "$(IN_REPO)" "1"
|
||||
test -e qemu_mode/qemuafl/Makefile && $(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/qemuafl clean || true
|
||||
-test -e qemu_mode/qemuafl/Makefile && $(MAKE) -C qemu_mode/qemuafl clean || true
|
||||
test -e unicorn_mode/unicornafl/Makefile && $(MAKE) -C unicorn_mode/unicornafl clean || true
|
||||
else
|
||||
rm -rf qemu_mode/qemuafl
|
||||
@ -596,7 +598,6 @@ distrib: all
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -f GNUmakefile.gcc_plugin
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/libdislocator
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/libtokencap
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C utils/aflpp_driver
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/afl_network_proxy
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/socket_fuzzing
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/argv_fuzzing
|
||||
@ -621,7 +622,6 @@ source-only: all
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -f GNUmakefile.gcc_plugin
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/libdislocator
|
||||
$(MAKE) -C utils/libtokencap
|
||||
-$(MAKE) -C utils/aflpp_driver
|
||||
|
||||
%.8: %
|
||||
@echo .TH $* 8 $(BUILD_DATE) "afl++" > $@
|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ ifeq "$(SYS)" "SunOS"
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PROGS = ./afl-gcc-pass.so
|
||||
PROGS = ./afl-gcc-pass.so ./afl-compiler-rt.o ./afl-compiler-rt-32.o ./afl-compiler-rt-64.o
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all
|
||||
all: test_shm test_deps $(PROGS) test_build all_done
|
||||
@ -130,6 +130,17 @@ test_deps:
|
||||
afl-common.o: ./src/afl-common.c
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(CPPFLAGS) -c $< -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
./afl-compiler-rt.o: instrumentation/afl-compiler-rt.o.c
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS_SAFE) $(CPPFLAGS) -O3 -Wno-unused-result -fPIC -c $< -o $@
|
||||
|
||||
./afl-compiler-rt-32.o: instrumentation/afl-compiler-rt.o.c
|
||||
@printf "[*] Building 32-bit variant of the runtime (-m32)... "
|
||||
@$(CC) $(CFLAGS_SAFE) $(CPPFLAGS) -O3 -Wno-unused-result -m32 -fPIC -c $< -o $@ 2>/dev/null; if [ "$$?" = "0" ]; then echo "success!"; ln -sf afl-compiler-rt-32.o afl-llvm-rt-32.o; else echo "failed (that's fine)"; fi
|
||||
|
||||
./afl-compiler-rt-64.o: instrumentation/afl-compiler-rt.o.c
|
||||
@printf "[*] Building 64-bit variant of the runtime (-m64)... "
|
||||
@$(CC) $(CFLAGS_SAFE) $(CPPFLAGS) -O3 -Wno-unused-result -m64 -fPIC -c $< -o $@ 2>/dev/null; if [ "$$?" = "0" ]; then echo "success!"; ln -sf afl-compiler-rt-64.o afl-llvm-rt-64.o; else echo "failed (that's fine)"; fi
|
||||
|
||||
./afl-gcc-pass.so: instrumentation/afl-gcc-pass.so.cc | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXEFLAGS) $(PLUGIN_FLAGS) -shared $< -o $@
|
||||
ln -sf afl-cc afl-gcc-fast
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ LLVM_APPLE_XCODE = $(shell clang -v 2>&1 | grep -q Apple && echo 1 || echo 0)
|
||||
LLVM_LTO = 0
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(LLVMVER)" ""
|
||||
$(warning [!] llvm_mode needs llvm-config, which was not found)
|
||||
$(warning [!] llvm_mode needs llvm-config, which was not found. Set LLVM_CONFIG to its path and retry.)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(LLVM_UNSUPPORTED)" "1"
|
||||
@ -433,6 +433,9 @@ endif
|
||||
./cmplog-instructions-pass.so: instrumentation/cmplog-instructions-pass.cc instrumentation/afl-llvm-common.o | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CLANG_CPPFL) -shared $< -o $@ $(CLANG_LFL) instrumentation/afl-llvm-common.o
|
||||
|
||||
./cmplog-switches-pass.so: instrumentation/cmplog-switches-pass.cc instrumentation/afl-llvm-common.o | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CLANG_CPPFL) -shared $< -o $@ $(CLANG_LFL) instrumentation/afl-llvm-common.o
|
||||
|
||||
afl-llvm-dict2file.so: instrumentation/afl-llvm-dict2file.so.cc instrumentation/afl-llvm-common.o | test_deps
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CLANG_CPPFL) -shared $< -o $@ $(CLANG_LFL) instrumentation/afl-llvm-common.o
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
222
README.md
222
README.md
@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ With afl++ 3.10 we introduced the following changes from previous behaviours:
|
||||
|
||||
With afl++ 3.00 we introduced changes that break some previous afl and afl++
|
||||
behaviours and defaults:
|
||||
|
||||
* There are no llvm_mode and gcc_plugin subdirectories anymore and there is
|
||||
only one compiler: afl-cc. All previous compilers now symlink to this one.
|
||||
All instrumentation source code is now in the `instrumentation/` folder.
|
||||
@ -50,8 +49,8 @@ behaviours and defaults:
|
||||
shared libraries, etc. Additionally QEMU 5.1 supports more CPU targets so
|
||||
this is really worth it.
|
||||
* When instrumenting targets, afl-cc will not supersede optimizations anymore
|
||||
if any were given. This allows to fuzz targets as same as they are built
|
||||
for debug or release.
|
||||
if any were given. This allows to fuzz targets build regularly like those
|
||||
for debug or release versions.
|
||||
* afl-fuzz:
|
||||
* if neither -M or -S is specified, `-S default` is assumed, so more
|
||||
fuzzers can easily be added later
|
||||
@ -383,13 +382,62 @@ afl++ performs "never zero" counting in its bitmap. You can read more about this
|
||||
here:
|
||||
* [instrumentation/README.neverzero.md](instrumentation/README.neverzero.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### c) Modify the target
|
||||
#### c) Sanitizers
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to use sanitizers when instrumenting targets for fuzzing,
|
||||
which allows you to find bugs that would not necessarily result in a crash.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that sanitizers have a huge impact on CPU (= less executions per second)
|
||||
and RAM usage. Also you should only run one afl-fuzz instance per sanitizer type.
|
||||
This is enough because a use-after-free bug will be picked up, e.g. by
|
||||
ASAN (address sanitizer) anyway when syncing to other fuzzing instances,
|
||||
so not all fuzzing instances need to be instrumented with ASAN.
|
||||
|
||||
The following sanitizers have built-in support in afl++:
|
||||
* ASAN = Address SANitizer, finds memory corruption vulnerabilities like
|
||||
use-after-free, NULL pointer dereference, buffer overruns, etc.
|
||||
Enabled with `export AFL_USE_ASAN=1` before compiling.
|
||||
* MSAN = Memory SANitizer, finds read access to uninitialized memory, eg.
|
||||
a local variable that is defined and read before it is even set.
|
||||
Enabled with `export AFL_USE_MSAN=1` before compiling.
|
||||
* UBSAN = Undefined Behaviour SANitizer, finds instances where - by the
|
||||
C and C++ standards - undefined behaviour happens, e.g. adding two
|
||||
signed integers together where the result is larger than a signed integer
|
||||
can hold.
|
||||
Enabled with `export AFL_USE_UBSAN=1` before compiling.
|
||||
* CFISAN = Control Flow Integrity SANitizer, finds instances where the
|
||||
control flow is found to be illegal. Originally this was rather to
|
||||
prevent return oriented programming exploit chains from functioning,
|
||||
in fuzzing this is mostly reduced to detecting type confusion
|
||||
vulnerabilities - which is however one of the most important and dangerous
|
||||
C++ memory corruption classes!
|
||||
Enabled with `export AFL_USE_CFISAN=1` before compiling.
|
||||
* LSAN = Leak SANitizer, finds memory leaks in a program. This is not really
|
||||
a security issue, but for developers this can be very valuable.
|
||||
Note that unlike the other sanitizers above this needs
|
||||
`__AFL_LEAK_CHECK();` added to all areas of the target source code where you
|
||||
find a leak check necessary!
|
||||
Enabled with `export AFL_USE_LSAN=1` before compiling.
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to further modify the behaviour of the sanitizers at run-time
|
||||
by setting `ASAN_OPTIONS=...`, `LSAN_OPTIONS` etc. - the available parameters
|
||||
can be looked up in the sanitizer documentation of llvm/clang.
|
||||
afl-fuzz however requires some specific parameters important for fuzzing to be
|
||||
set. If you want to set your own, it might bail and report what it is missing.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that some sanitizers cannot be used together, e.g. ASAN and MSAN, and
|
||||
others often cannot work together because of target weirdness, e.g. ASAN and
|
||||
CFISAN. You might need to experiment which sanitizers you can combine in a
|
||||
target (which means more instances can be run without a sanitized target,
|
||||
which is more effective).
|
||||
|
||||
#### d) Modify the target
|
||||
|
||||
If the target has features that make fuzzing more difficult, e.g.
|
||||
checksums, HMAC, etc. then modify the source code so that this is
|
||||
removed.
|
||||
This can even be done for operational source code by eliminating
|
||||
these checks within this specific defines:
|
||||
checksums, HMAC, etc. then modify the source code so that checks for these
|
||||
values are removed.
|
||||
This can even be done safely for source code used in operational products
|
||||
by eliminating these checks within these AFL specific blocks:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#ifdef FUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION
|
||||
@ -401,7 +449,7 @@ these checks within this specific defines:
|
||||
|
||||
All afl++ compilers will set this preprocessor definition automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
#### d) Instrument the target
|
||||
#### e) Instrument the target
|
||||
|
||||
In this step the target source code is compiled so that it can be fuzzed.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -416,8 +464,8 @@ Then build the target. (Usually with `make`)
|
||||
|
||||
1. sometimes configure and build systems are fickle and do not like
|
||||
stderr output (and think this means a test failure) - which is something
|
||||
afl++ likes to do to show statistics. It is recommended to disable them via
|
||||
`export AFL_QUIET=1`.
|
||||
afl++ likes to do to show statistics. It is recommended to disable afl++
|
||||
instrumentation reporting via `export AFL_QUIET=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
2. sometimes configure and build systems error on warnings - these should be
|
||||
disabled (e.g. `--disable-werror` for some configure scripts).
|
||||
@ -458,20 +506,38 @@ non-standard way to set this, otherwise set up the build normally and edit the
|
||||
generated build environment afterwards manually to point it to the right compiler
|
||||
(and/or ranlib and ar).
|
||||
|
||||
#### d) Better instrumentation
|
||||
#### f) Better instrumentation
|
||||
|
||||
If you just fuzz a target program as-is you are wasting a great opportunity for
|
||||
much more fuzzing speed.
|
||||
|
||||
This requires the usage of afl-clang-lto or afl-clang-fast.
|
||||
This variant requires the usage of afl-clang-lto, afl-clang-fast or afl-gcc-fast.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the so-called `persistent mode`, which is much, much faster but
|
||||
It is the so-called `persistent mode`, which is much, much faster but
|
||||
requires that you code a source file that is specifically calling the target
|
||||
functions that you want to fuzz, plus a few specific afl++ functions around
|
||||
it. See [instrumentation/README.persistent_mode.md](instrumentation/README.persistent_mode.md) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
Basically if you do not fuzz a target in persistent mode then you are just
|
||||
doing it for a hobby and not professionally :-)
|
||||
doing it for a hobby and not professionally :-).
|
||||
|
||||
#### g) libfuzzer fuzzer harnesses with LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput()
|
||||
|
||||
libfuzzer `LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput()` harnesses are the defacto standard
|
||||
for fuzzing, and they can be used with afl++ (and honggfuzz) as well!
|
||||
Compiling them is as simple as:
|
||||
```
|
||||
afl-clang-fast++ -fsanitize=fuzzer -o harness harness.cpp targetlib.a
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can even use advanced libfuzzer features like `FuzzedDataProvider`,
|
||||
`LLVMFuzzerMutate()` etc. and they will work!
|
||||
|
||||
The generated binary is fuzzed with afl-fuzz like any other fuzz target.
|
||||
|
||||
Bonus: the target is already optimized for fuzzing due to persistent mode and
|
||||
shared-memory testcases and hence gives you the fastest speed possible.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information see [utils/aflpp_driver/README.md](utils/aflpp_driver/README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Preparing the fuzzing campaign
|
||||
|
||||
@ -503,6 +569,8 @@ Note that the INPUTFILE argument that the target program would read from has to
|
||||
If the target reads from stdin instead, just omit the `@@` as this is the
|
||||
default.
|
||||
|
||||
This step is highly recommended!
|
||||
|
||||
#### c) Minimizing all corpus files
|
||||
|
||||
The shorter the input files that still traverse the same path
|
||||
@ -518,7 +586,8 @@ for i in *; do
|
||||
done
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This step can also be parallelized, e.g. with `parallel`
|
||||
This step can also be parallelized, e.g. with `parallel`.
|
||||
Note that this step is rather optional though.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Done!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -554,6 +623,16 @@ step [2a. Collect inputs](#a-collect-inputs):
|
||||
`afl-fuzz -i input -o output -- bin/target -d @@`
|
||||
Note that the directory specified with -o will be created if it does not exist.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be valuable to run afl-fuzz in a screen or tmux shell so you can log off,
|
||||
or afl-fuzz is not aborted if you are running it in a remote ssh session where
|
||||
the connection fails in between.
|
||||
Only do that though once you have verified that your fuzzing setup works!
|
||||
Simply run it like `screen -dmS afl-main -- afl-fuzz -M main-$HOSTNAME -i ...`
|
||||
and it will start away in a screen session. To enter this session simply type
|
||||
`screen -r afl-main`. You see - it makes sense to name the screen session
|
||||
same as the afl-fuzz -M/-S naming :-)
|
||||
For more information on screen or tmux please check their documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to stop and re-start the fuzzing, use the same command line options
|
||||
(or even change them by selecting a different power schedule or another
|
||||
mutation mode!) and switch the input directory with a dash (`-`):
|
||||
@ -572,8 +651,15 @@ to use afl-clang-lto as the compiler. You also have the option to generate
|
||||
a dictionary yourself, see [utils/libtokencap/README.md](utils/libtokencap/README.md).
|
||||
|
||||
afl-fuzz has a variety of options that help to workaround target quirks like
|
||||
specific locations for the input file (`-f`), not performing deterministic
|
||||
fuzzing (`-d`) and many more. Check out `afl-fuzz -h`.
|
||||
specific locations for the input file (`-f`), performing deterministic
|
||||
fuzzing (`-D`) and many more. Check out `afl-fuzz -h`.
|
||||
|
||||
We highly recommend that you set a memory limit for running the target with `-m`
|
||||
which defines the maximum memory in MB. This prevents a potential
|
||||
out-of-memory problem for your system plus helps you detect missing `malloc()`
|
||||
failure handling in the target.
|
||||
Play around with various -m values until you find one that safely works for all
|
||||
your input seeds (if you have good ones and then double or quadrouple that.
|
||||
|
||||
By default afl-fuzz never stops fuzzing. To terminate afl++ simply press Control-C
|
||||
or send a signal SIGINT. You can limit the number of executions or approximate runtime
|
||||
@ -600,7 +686,7 @@ of the testcases. Depending on the average testcase size (and those found
|
||||
during fuzzing) and their number, a value between 50-500MB is recommended.
|
||||
You can set the cache size (in MB) by setting the environment variable `AFL_TESTCACHE_SIZE`.
|
||||
|
||||
There should be one main fuzzer (`-M main` option) and as many secondary
|
||||
There should be one main fuzzer (`-M main-$HOSTNAME` option) and as many secondary
|
||||
fuzzers (eg `-S variant1`) as you have cores that you use.
|
||||
Every -M/-S entry needs a unique name (that can be whatever), however the same
|
||||
-o output directory location has to be used for all instances.
|
||||
@ -614,23 +700,29 @@ For every secondary fuzzer there should be a variation, e.g.:
|
||||
* one to three fuzzers should fuzz a target compiled with laf-intel/COMPCOV
|
||||
(see above). Important note: If you run more than one laf-intel/COMPCOV
|
||||
fuzzer and you want them to share their intermediate results, the main
|
||||
fuzzer (`-M`) must be one of the them!
|
||||
fuzzer (`-M`) must be one of the them! (Although this is not really
|
||||
recommended.)
|
||||
|
||||
All other secondaries should be used like this:
|
||||
* A third to a half with the MOpt mutator enabled: `-L 0`
|
||||
* run with a different power schedule, available are:
|
||||
`fast (default), explore, coe, lin, quad, exploit, mmopt, rare, seek`
|
||||
which you can set with e.g. `-p seek`
|
||||
* A quarter to a third with the MOpt mutator enabled: `-L 0`
|
||||
* run with a different power schedule, recommended are:
|
||||
`fast (default), explore, coe, lin, quad, exploit and rare`
|
||||
which you can set with e.g. `-p explore`
|
||||
* a few instances should use the old queue cycling with `-Z`
|
||||
|
||||
Also it is recommended to set `export AFL_IMPORT_FIRST=1` to load testcases
|
||||
from other fuzzers in the campaign first.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a large corpus, a corpus from a previous run or are fuzzing in
|
||||
a CI, then also set `export AFL_CMPLOG_ONLY_NEW=1` and `export AFL_FAST_CAL=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use different fuzzers.
|
||||
If you are using afl spinoffs or afl conforming fuzzers, then just use the
|
||||
same -o directory and give it a unique `-S` name.
|
||||
Examples are:
|
||||
* [Fuzzolic](https://github.com/season-lab/fuzzolic)
|
||||
* [symcc](https://github.com/eurecom-s/symcc/)
|
||||
* [Eclipser](https://github.com/SoftSec-KAIST/Eclipser/)
|
||||
* [Untracer](https://github.com/FoRTE-Research/UnTracer-AFL)
|
||||
* [AFLsmart](https://github.com/aflsmart/aflsmart)
|
||||
* [FairFuzz](https://github.com/carolemieux/afl-rb)
|
||||
* [Neuzz](https://github.com/Dongdongshe/neuzz)
|
||||
@ -638,11 +730,52 @@ Examples are:
|
||||
|
||||
A long list can be found at [https://github.com/Microsvuln/Awesome-AFL](https://github.com/Microsvuln/Awesome-AFL)
|
||||
|
||||
However you can also sync afl++ with honggfuzz, libfuzzer with -entropic, etc.
|
||||
However you can also sync afl++ with honggfuzz, libfuzzer with `-entropic=1`, etc.
|
||||
Just show the main fuzzer (-M) with the `-F` option where the queue/work
|
||||
directory of a different fuzzer is, e.g. `-F /src/target/honggfuzz`.
|
||||
Using honggfuzz (with `-n 1` or `-n 2`) and libfuzzer in parallel is highly
|
||||
recommended!
|
||||
|
||||
#### c) The status of the fuzz campaign
|
||||
#### c) Using multiple machines for fuzzing
|
||||
|
||||
Maybe you have more than one machine you want to fuzz the same target on.
|
||||
Simply start the `afl-fuzz` (and perhaps libfuzzer, honggfuzz, ...)
|
||||
orchestra as you like, just ensure that your have one and only one `-M`
|
||||
instance per server, and that its name is unique, hence the recommendation
|
||||
for `-M main-$HOSTNAME`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now there are three strategies on how you can sync between the servers:
|
||||
* never: sounds weird, but this makes every server an island and has the
|
||||
chance the each follow different paths into the target. You can make
|
||||
this even more interesting by even giving different seeds to each server.
|
||||
* regularly (~4h): this ensures that all fuzzing campaigns on the servers
|
||||
"see" the same thing. It is like fuzzing on a huge server.
|
||||
* in intervals of 1/10th of the overall expected runtime of the fuzzing you
|
||||
sync. This tries a bit to combine both. have some individuality of the
|
||||
paths each campaign on a server explores, on the other hand if one
|
||||
gets stuck where another found progress this is handed over making it
|
||||
unstuck.
|
||||
|
||||
The syncing process itself is very simple.
|
||||
As the `-M main-$HOSTNAME` instance syncs to all `-S` secondaries as well
|
||||
as to other fuzzers, you have to copy only this directory to the other
|
||||
machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Lets say all servers have the `-o out` directory in /target/foo/out, and
|
||||
you created a file `servers.txt` which contains the hostnames of all
|
||||
participating servers, plus you have an ssh key deployed to all of them,
|
||||
then run:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
for FROM in `cat servers.txt`; do
|
||||
for TO in `cat servers.txt`; do
|
||||
rsync -rlpogtz --rsh=ssh $FROM:/target/foo/out/main-$FROM $TO:target/foo/out/
|
||||
done
|
||||
done
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can run this manually, per cron job - as you need it.
|
||||
There is a more complex and configurable script in `utils/distributed_fuzzing`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### d) The status of the fuzz campaign
|
||||
|
||||
afl++ comes with the `afl-whatsup` script to show the status of the fuzzing
|
||||
campaign.
|
||||
@ -651,11 +784,14 @@ Just supply the directory that afl-fuzz is given with the -o option and
|
||||
you will see a detailed status of every fuzzer in that campaign plus
|
||||
a summary.
|
||||
|
||||
To have only the summary use the `-s` switch e.g.: `afl-whatsup -s output/`
|
||||
To have only the summary use the `-s` switch e.g.: `afl-whatsup -s out/`
|
||||
|
||||
#### d) Checking the coverage of the fuzzing
|
||||
If you have multiple servers then use the command after a sync, or you have
|
||||
to execute this script per server.
|
||||
|
||||
The `paths found` value is a bad indicator how good the coverage is.
|
||||
#### e) Checking the coverage of the fuzzing
|
||||
|
||||
The `paths found` value is a bad indicator for checking how good the coverage is.
|
||||
|
||||
A better indicator - if you use default llvm instrumentation with at least
|
||||
version 9 - is to use `afl-showmap` with the collect coverage option `-C` on
|
||||
@ -683,12 +819,13 @@ then terminate it. The main node will pick it up and make it available to the
|
||||
other secondary nodes over time. Set `export AFL_NO_AFFINITY=1` or
|
||||
`export AFL_TRY_AFFINITY=1` if you have no free core.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you in nearly all cases can never reach full coverage. A lot of
|
||||
functionality is usually behind options that were not activated or fuzz e.g.
|
||||
if you fuzz a library to convert image formats and your target is the png to
|
||||
tiff API then you will not touch any of the other library APIs and features.
|
||||
Note that in nearly all cases you can never reach full coverage. A lot of
|
||||
functionality is usually dependent on exclusive options that would need individual
|
||||
fuzzing campaigns each with one of these options set. E.g. if you fuzz a library to
|
||||
convert image formats and your target is the png to tiff API then you will not
|
||||
touch any of the other library APIs and features.
|
||||
|
||||
#### e) How long to fuzz a target?
|
||||
#### f) How long to fuzz a target?
|
||||
|
||||
This is a difficult question.
|
||||
Basically if no new path is found for a long time (e.g. for a day or a week)
|
||||
@ -700,7 +837,7 @@ Keep the queue/ directory (for future fuzzings of the same or similar targets)
|
||||
and use them to seed other good fuzzers like libfuzzer with the -entropic
|
||||
switch or honggfuzz.
|
||||
|
||||
#### f) Improve the speed!
|
||||
#### g) Improve the speed!
|
||||
|
||||
* Use [persistent mode](instrumentation/README.persistent_mode.md) (x2-x20 speed increase)
|
||||
* If you do not use shmem persistent mode, use `AFL_TMPDIR` to point the input file on a tempfs location, see [docs/env_variables.md](docs/env_variables.md)
|
||||
@ -774,18 +911,19 @@ campaigns as these are much shorter runnings.
|
||||
* 10% for `AFL_LLVM_LAF_ALL`
|
||||
|
||||
3. Also randomize the afl-fuzz runtime options, e.g.
|
||||
* 60% for `AFL_DISABLE_TRIM`
|
||||
* 65% for `AFL_DISABLE_TRIM`
|
||||
* 50% use a dictionary generated by `AFL_LLVM_DICT2FILE`
|
||||
* 50% use MOpt (`-L 0`)
|
||||
* 40% use MOpt (`-L 0`)
|
||||
* 40% for `AFL_EXPAND_HAVOC_NOW`
|
||||
* 30% for old queue processing (`-Z`)
|
||||
* 20% for old queue processing (`-Z`)
|
||||
* for CMPLOG targets, 60% for `-l 2`, 40% for `-l 3`
|
||||
|
||||
4. Do *not* run any `-M` modes, just running `-S` modes is better for CI fuzzing.
|
||||
`-M` enables deterministic fuzzing, old queue handling etc. which is good for
|
||||
a fuzzing campaign but not good for short CI runs.
|
||||
`-M` enables old queue handling etc. which is good for a fuzzing campaign but
|
||||
not good for short CI runs.
|
||||
|
||||
How this can look like can e.g. be seen at afl++'s setup in Google's [oss-fuzz](https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz/blob/4bb61df7905c6005000f5766e966e6fe30ab4559/infra/base-images/base-builder/compile_afl#L69).
|
||||
How this can look like can e.g. be seen at afl++'s setup in Google's [oss-fuzz](https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz/blob/master/infra/base-images/base-builder/compile_afl)
|
||||
and [clusterfuzz](https://github.com/google/clusterfuzz/blob/master/src/python/bot/fuzzers/afl/launcher.py).
|
||||
|
||||
## Fuzzing binary-only targets
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1
TODO.md
1
TODO.md
@ -8,7 +8,6 @@
|
||||
- afl-plot to support multiple plot_data
|
||||
- afl_custom_fuzz_splice_optin()
|
||||
- afl_custom_splice()
|
||||
- intel-pt tracer
|
||||
- better autodetection of shifting runtime timeout values
|
||||
- cmplog: use colorization input for havoc?
|
||||
- parallel builds for source-only targets
|
||||
|
||||
42
afl-cmin
42
afl-cmin
@ -296,13 +296,13 @@ BEGIN {
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (0 == system( "test -d "in_dir"/default" )) {
|
||||
in_dir = in_dir "/default"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (0 == system( "test -d "in_dir"/queue" )) {
|
||||
in_dir = in_dir "/queue"
|
||||
}
|
||||
#if (0 == system( "test -d "in_dir"/default" )) {
|
||||
# in_dir = in_dir "/default"
|
||||
#}
|
||||
#
|
||||
#if (0 == system( "test -d "in_dir"/queue" )) {
|
||||
# in_dir = in_dir "/queue"
|
||||
#}
|
||||
|
||||
system("rm -rf "trace_dir" 2>/dev/null");
|
||||
system("rm "out_dir"/id[:_]* 2>/dev/null")
|
||||
@ -355,30 +355,35 @@ BEGIN {
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
stat_format = "-f '%z %N'" # *BSD, MacOS
|
||||
}
|
||||
cmdline = "(cd "in_dir" && find . \\( ! -name . -a -type d -prune \\) -o -type f -exec stat "stat_format" \\{\\} + | sort -k1n -k2r)"
|
||||
cmdline = "(cd "in_dir" && find . \\( ! -name \".*\" -a -type d \\) -o -type f -exec stat "stat_format" \\{\\} + | sort -k1n -k2r)"
|
||||
#cmdline = "ls "in_dir" | (cd "in_dir" && xargs stat "stat_format" 2>/dev/null) | sort -k1n -k2r"
|
||||
#cmdline = "(cd "in_dir" && stat "stat_format" *) | sort -k1n -k2r"
|
||||
#cmdline = "(cd "in_dir" && ls | xargs stat "stat_format" ) | sort -k1n -k2r"
|
||||
while (cmdline | getline) {
|
||||
sub(/^[0-9]+ (\.\/)?/,"",$0)
|
||||
infilesSmallToBig[i++] = $0
|
||||
infilesSmallToBigFull[i] = $0
|
||||
sub(/.*\//, "", $0)
|
||||
infilesSmallToBig[i] = $0
|
||||
infilesSmallToBigMap[infilesSmallToBig[i]] = infilesSmallToBigFull[i]
|
||||
infilesSmallToBigFullMap[infilesSmallToBigFull[i]] = infilesSmallToBig[i]
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
in_count = i
|
||||
|
||||
first_file = infilesSmallToBig[0]
|
||||
first_file = infilesSmallToBigFull[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Make sure that we're not dealing with a directory.
|
||||
#if (0 == system("test -d ""\""in_dir"/"first_file"\"")) {
|
||||
# print "[-] Error: The input directory is empty or contains subdirectories - please fix." > "/dev/stderr"
|
||||
# exit 1
|
||||
#}
|
||||
|
||||
if (0 == system("test -d ""\""in_dir"/"first_file"\"")) {
|
||||
print "[-] Error: The input directory is empty or contains subdirectories - please fix." > "/dev/stderr"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (0 == system("ln \""in_dir"/"first_file"\" "trace_dir"/.link_test")) {
|
||||
system(">\""in_dir"/.afl-cmin.test\"")
|
||||
if (0 == system("ln \""in_dir"/.afl-cmin.test\" "trace_dir"/.link_test")) {
|
||||
cp_tool = "ln"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
cp_tool = "cp"
|
||||
}
|
||||
system("rm -f \""in_dir"/.afl-cmin.test\"")
|
||||
|
||||
if (!ENVIRON["AFL_SKIP_BIN_CHECK"]) {
|
||||
# Make sure that we can actually get anything out of afl-showmap before we
|
||||
@ -511,7 +516,8 @@ BEGIN {
|
||||
|
||||
# copy file unless already done
|
||||
if (! (fn in file_already_copied)) {
|
||||
system(cp_tool" \""in_dir"/"fn"\" \""out_dir"/"fn"\"")
|
||||
realfile = infilesSmallToBigMap[fn]
|
||||
system(cp_tool" \""in_dir"/"realfile"\" \""out_dir"/"fn"\"")
|
||||
file_already_copied[fn] = ""
|
||||
++out_count
|
||||
#printf "tuple nr %d (%d cnt=%d) -> %s\n",tcnt,key,key_count[key],fn > trace_dir"/.log"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -135,6 +135,7 @@ For additional tips, please consult README.md.
|
||||
|
||||
Environment variables used:
|
||||
AFL_KEEP_TRACES: leave the temporary <out_dir>\.traces directory
|
||||
AFL_NO_FORKSRV: run target via execve instead of using the forkserver
|
||||
AFL_PATH: last resort location to find the afl-showmap binary
|
||||
AFL_SKIP_BIN_CHECK: skip check for target binary
|
||||
_EOF_
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,9 +246,9 @@ typedef struct {
|
||||
} timing;
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t val[256];
|
||||
uint8_t val[512];
|
||||
size_t len;
|
||||
} dictionary[1024];
|
||||
} dictionary[8192];
|
||||
size_t dictionaryCnt;
|
||||
const char* dictionaryFile;
|
||||
size_t mutationsMax;
|
||||
@ -263,6 +263,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
bool useVerifier;
|
||||
bool exitUponCrash;
|
||||
uint8_t exitCodeUponCrash;
|
||||
const char* reportFile;
|
||||
size_t dynFileIterExpire;
|
||||
bool only_printable;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,342 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#ifndef CUSTOM_MUTATOR_HELPERS
|
||||
#define CUSTOM_MUTATOR_HELPERS
|
||||
|
||||
#include "config.h"
|
||||
#include "types.h"
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#define INITIAL_GROWTH_SIZE (64)
|
||||
|
||||
#define RAND_BELOW(limit) (rand() % (limit))
|
||||
|
||||
/* Use in a struct: creates a name_buf and a name_size variable. */
|
||||
#define BUF_VAR(type, name) \
|
||||
type * name##_buf; \
|
||||
size_t name##_size;
|
||||
/* this filles in `&structptr->something_buf, &structptr->something_size`. */
|
||||
#define BUF_PARAMS(struct, name) \
|
||||
(void **)&struct->name##_buf, &struct->name##_size
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
||||
} afl_t;
|
||||
|
||||
static void surgical_havoc_mutate(u8 *out_buf, s32 begin, s32 end) {
|
||||
|
||||
static s8 interesting_8[] = {INTERESTING_8};
|
||||
static s16 interesting_16[] = {INTERESTING_8, INTERESTING_16};
|
||||
static s32 interesting_32[] = {INTERESTING_8, INTERESTING_16, INTERESTING_32};
|
||||
|
||||
switch (RAND_BELOW(12)) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 0: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Flip a single bit somewhere. Spooky! */
|
||||
|
||||
s32 bit_idx = ((RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin) << 3) + RAND_BELOW(8);
|
||||
|
||||
out_buf[bit_idx >> 3] ^= 128 >> (bit_idx & 7);
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 1: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set byte to interesting value. */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 val = interesting_8[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_8))];
|
||||
out_buf[(RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin)] = val;
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 2: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set word to interesting value, randomly choosing endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 2) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 1) break;
|
||||
|
||||
switch (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
interesting_16[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_16) >> 1)];
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
SWAP16(interesting_16[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_16) >> 1)]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 3: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set dword to interesting value, randomly choosing endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 4) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 3) break;
|
||||
|
||||
switch (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
interesting_32[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_32) >> 2)];
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
SWAP32(interesting_32[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_32) >> 2)]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 4: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set qword to interesting value, randomly choosing endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 8) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 7) break;
|
||||
|
||||
switch (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
*(u64 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
(s64)interesting_32[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_32) >> 2)];
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
*(u64 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) = SWAP64(
|
||||
(s64)interesting_32[RAND_BELOW(sizeof(interesting_32) >> 2)]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 5: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Randomly subtract from byte. */
|
||||
|
||||
out_buf[(RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin)] -= 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 6: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Randomly add to byte. */
|
||||
|
||||
out_buf[(RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin)] += 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 7: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Randomly subtract from word, random endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 2) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 1) break;
|
||||
|
||||
if (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) -= 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
u16 num = 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
SWAP16(SWAP16(*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx)) - num);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 8: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Randomly add to word, random endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 2) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 1) break;
|
||||
|
||||
if (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) += 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
u16 num = 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
SWAP16(SWAP16(*(u16 *)(out_buf + byte_idx)) + num);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 9: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Randomly subtract from dword, random endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 4) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 3) break;
|
||||
|
||||
if (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) -= 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 num = 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
SWAP32(SWAP32(*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx)) - num);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 10: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Randomly add to dword, random endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (end - begin < 4) break;
|
||||
|
||||
s32 byte_idx = (RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (byte_idx >= end - 3) break;
|
||||
|
||||
if (RAND_BELOW(2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) += 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 num = 1 + RAND_BELOW(ARITH_MAX);
|
||||
|
||||
*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx) =
|
||||
SWAP32(SWAP32(*(u32 *)(out_buf + byte_idx)) + num);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 11: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Just set a random byte to a random value. Because,
|
||||
why not. We use XOR with 1-255 to eliminate the
|
||||
possibility of a no-op. */
|
||||
|
||||
out_buf[(RAND_BELOW(end - begin) + begin)] ^= 1 + RAND_BELOW(255);
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* This function calculates the next power of 2 greater or equal its argument.
|
||||
@return The rounded up power of 2 (if no overflow) or 0 on overflow.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static inline size_t next_pow2(size_t in) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (in == 0 || in > (size_t)-1)
|
||||
return 0; /* avoid undefined behaviour under-/overflow */
|
||||
size_t out = in - 1;
|
||||
out |= out >> 1;
|
||||
out |= out >> 2;
|
||||
out |= out >> 4;
|
||||
out |= out >> 8;
|
||||
out |= out >> 16;
|
||||
return out + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* This function makes sure *size is > size_needed after call.
|
||||
It will realloc *buf otherwise.
|
||||
*size will grow exponentially as per:
|
||||
https://blog.mozilla.org/nnethercote/2014/11/04/please-grow-your-buffers-exponentially/
|
||||
Will return NULL and free *buf if size_needed is <1 or realloc failed.
|
||||
@return For convenience, this function returns *buf.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static inline void *maybe_grow(void **buf, size_t *size, size_t size_needed) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* No need to realloc */
|
||||
if (likely(size_needed && *size >= size_needed)) return *buf;
|
||||
|
||||
/* No initial size was set */
|
||||
if (size_needed < INITIAL_GROWTH_SIZE) size_needed = INITIAL_GROWTH_SIZE;
|
||||
|
||||
/* grow exponentially */
|
||||
size_t next_size = next_pow2(size_needed);
|
||||
|
||||
/* handle overflow */
|
||||
if (!next_size) { next_size = size_needed; }
|
||||
|
||||
/* alloc */
|
||||
*buf = realloc(*buf, next_size);
|
||||
*size = *buf ? next_size : 0;
|
||||
|
||||
return *buf;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Swaps buf1 ptr and buf2 ptr, as well as their sizes */
|
||||
static inline void afl_swap_bufs(void **buf1, size_t *size1, void **buf2,
|
||||
size_t *size2) {
|
||||
|
||||
void * scratch_buf = *buf1;
|
||||
size_t scratch_size = *size1;
|
||||
*buf1 = *buf2;
|
||||
*size1 = *size2;
|
||||
*buf2 = scratch_buf;
|
||||
*size2 = scratch_size;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#undef INITIAL_GROWTH_SIZE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
1
custom_mutators/radamsa/custom_mutator_helpers.h
Symbolic link
1
custom_mutators/radamsa/custom_mutator_helpers.h
Symbolic link
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
../examples/custom_mutator_helpers.h
|
||||
37
docs/FAQ.md
37
docs/FAQ.md
@ -3,6 +3,7 @@
|
||||
## Contents
|
||||
|
||||
* [What is the difference between afl and afl++?](#what-is-the-difference-between-afl-and-afl)
|
||||
* [I got a weird compile error from clang](#i-got-a-weird-compile-error-from-clang)
|
||||
* [How to improve the fuzzing speed?](#how-to-improve-the-fuzzing-speed)
|
||||
* [How do I fuzz a network service?](#how-do-i-fuzz-a-network-service)
|
||||
* [How do I fuzz a GUI program?](#how-do-i-fuzz-a-gui-program)
|
||||
@ -35,6 +36,26 @@ flexible and feature rich guided fuzzer available as open source.
|
||||
And in independent fuzzing benchmarks it is one of the best fuzzers available,
|
||||
e.g. [Fuzzbench Report](https://www.fuzzbench.com/reports/2020-08-03/index.html)
|
||||
|
||||
## I got a weird compile error from clang
|
||||
|
||||
If you see this kind of error when trying to instrument a target with afl-cc/
|
||||
afl-clang-fast/afl-clang-lto:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/prg/tmp/llvm-project/build/bin/clang-13: symbol lookup error: /usr/local/bin/../lib/afl//cmplog-instructions-pass.so: undefined symbol: _ZNK4llvm8TypeSizecvmEv
|
||||
clang-13: error: unable to execute command: No such file or directory
|
||||
clang-13: error: clang frontend command failed due to signal (use -v to see invocation)
|
||||
clang version 13.0.0 (https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project 1d7cf550721c51030144f3cd295c5789d51c4aad)
|
||||
Target: x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
|
||||
Thread model: posix
|
||||
InstalledDir: /prg/tmp/llvm-project/build/bin
|
||||
clang-13: note: diagnostic msg:
|
||||
********************
|
||||
```
|
||||
Then this means that your OS updated the clang installation from an upgrade
|
||||
package and because of that the afl++ llvm plugins do not match anymore.
|
||||
|
||||
Solution: `git pull ; make clean install` of afl++
|
||||
|
||||
## How to improve the fuzzing speed?
|
||||
|
||||
1. Use [llvm_mode](docs/llvm_mode/README.md): afl-clang-lto (llvm >= 11) or afl-clang-fast (llvm >= 9 recommended)
|
||||
@ -167,13 +188,7 @@ Four steps are required to do this and it also requires quite some knowledge
|
||||
of coding and/or disassembly and is effectively possible only with
|
||||
afl-clang-fast PCGUARD and afl-clang-lto LTO instrumentation.
|
||||
|
||||
1. First step: Identify which edge ID numbers are unstable
|
||||
|
||||
run the target with `export AFL_DEBUG=1` for a few minutes then terminate.
|
||||
The out/fuzzer_stats file will then show the edge IDs that were identified
|
||||
as unstable.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Second step: Find the responsible function(s).
|
||||
1. First step: Instrument to be able to find the responsible function(s).
|
||||
|
||||
a) For LTO instrumented binaries this can be documented during compile
|
||||
time, just set `export AFL_LLVM_DOCUMENT_IDS=/path/to/a/file`.
|
||||
@ -196,6 +211,14 @@ afl-clang-fast PCGUARD and afl-clang-lto LTO instrumentation.
|
||||
recompile with the two mentioned above. This is just for
|
||||
identifying the functions that have unstable edges.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Second step: Identify which edge ID numbers are unstable
|
||||
|
||||
run the target with `export AFL_DEBUG=1` for a few minutes then terminate.
|
||||
The out/fuzzer_stats file will then show the edge IDs that were identified
|
||||
as unstable in the `var_bytes` entry. You can match these numbers
|
||||
directly to the data you created in the first step.
|
||||
Now you know which functions are responsible for the instability
|
||||
|
||||
3. Third step: create a text file with the filenames/functions
|
||||
|
||||
Identify which source code files contain the functions that you need to
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,22 +65,17 @@ The QEMU mode is currently supported only on Linux. I think it's just a QEMU
|
||||
problem, I couldn't get a vanilla copy of user-mode emulation support working
|
||||
correctly on BSD at all.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. MacOS X on x86
|
||||
## 3. MacOS X on x86 and arm64 (M1)
|
||||
|
||||
MacOS X should work, but there are some gotchas due to the idiosyncrasies of
|
||||
the platform. On top of this, I have limited release testing capabilities
|
||||
and depend mostly on user feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
To build AFL, install Xcode and follow the general instructions for Linux.
|
||||
To build AFL, install llvm (and perhaps gcc) from brew and follow the general
|
||||
instructions for Linux. If possible avoid Xcode at all cost.
|
||||
|
||||
The Xcode 'gcc' tool is just a wrapper for clang, so be sure to use afl-clang
|
||||
to compile any instrumented binaries; afl-gcc will fail unless you have GCC
|
||||
installed from another source (in which case, please specify `AFL_CC` and
|
||||
`AFL_CXX` to point to the "real" GCC binaries).
|
||||
|
||||
Only 64-bit compilation will work on the platform; porting the 32-bit
|
||||
instrumentation would require a fair amount of work due to the way OS X
|
||||
handles relocations, and today, virtually all MacOS X boxes are 64-bit.
|
||||
afl-gcc will fail unless you have GCC installed, but that is using outdated
|
||||
instrumentation anyway. You don't want that.
|
||||
|
||||
The crash reporting daemon that comes by default with MacOS X will cause
|
||||
problems with fuzzing. You need to turn it off by following the instructions
|
||||
@ -98,10 +93,42 @@ and definitely don't look POSIX-compliant. This means two things:
|
||||
|
||||
User emulation mode of QEMU does not appear to be supported on MacOS X, so
|
||||
black-box instrumentation mode (`-Q`) will not work.
|
||||
However Frida mode (`-O`) should work on x86 and arm64 MacOS boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
The llvm instrumentation requires a fully-operational installation of clang. The one that
|
||||
comes with Xcode is missing some of the essential headers and helper tools.
|
||||
See README.llvm.md for advice on how to build the compiler from scratch.
|
||||
MacOS X supports SYSV shared memory used by AFL's instrumentation, but the
|
||||
default settings aren't usable with AFL++. The default settings on 10.14 seem
|
||||
to be:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ ipcs -M
|
||||
IPC status from <running system> as of XXX
|
||||
shminfo:
|
||||
shmmax: 4194304 (max shared memory segment size)
|
||||
shmmin: 1 (min shared memory segment size)
|
||||
shmmni: 32 (max number of shared memory identifiers)
|
||||
shmseg: 8 (max shared memory segments per process)
|
||||
shmall: 1024 (max amount of shared memory in pages)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To temporarily change your settings to something minimally usable with AFL++,
|
||||
run these commands as root:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sysctl kern.sysv.shmmax=8388608
|
||||
sysctl kern.sysv.shmall=4096
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're running more than one instance of AFL you likely want to make `shmall`
|
||||
bigger and increase `shmseg` as well:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sysctl kern.sysv.shmmax=8388608
|
||||
sysctl kern.sysv.shmseg=48
|
||||
sysctl kern.sysv.shmall=98304
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See http://www.spy-hill.com/help/apple/SharedMemory.html for documentation for
|
||||
these settings and how to make them permanent.
|
||||
|
||||
MacOS X supports SYSV shared memory used by AFL's instrumentation, but the
|
||||
default settings aren't usable with AFL++. The default settings on 10.14 seem
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,14 +18,12 @@ how to hit the ground running:
|
||||
custom SIGSEGV or SIGABRT handlers and background processes. For tips on
|
||||
detecting non-crashing flaws, see section 11 in [README.md](README.md) .
|
||||
|
||||
3) Compile the program / library to be fuzzed using afl-gcc. A common way to
|
||||
3) Compile the program / library to be fuzzed using afl-cc. A common way to
|
||||
do this would be:
|
||||
|
||||
CC=/path/to/afl-gcc CXX=/path/to/afl-g++ ./configure --disable-shared
|
||||
CC=/path/to/afl-cc CXX=/path/to/afl-c++ ./configure --disable-shared
|
||||
make clean all
|
||||
|
||||
If program build fails, ping <afl-users@googlegroups.com>.
|
||||
|
||||
4) Get a small but valid input file that makes sense to the program. When
|
||||
fuzzing verbose syntax (SQL, HTTP, etc), create a dictionary as described in
|
||||
dictionaries/README.md, too.
|
||||
@ -41,9 +39,6 @@ how to hit the ground running:
|
||||
6) Investigate anything shown in red in the fuzzer UI by promptly consulting
|
||||
[status_screen.md](status_screen.md).
|
||||
|
||||
7) compile and use llvm_mode (afl-clang-fast/afl-clang-fast++) as it is way
|
||||
faster and has a few cool features
|
||||
|
||||
8) There is a basic docker build with 'docker build -t aflplusplus .'
|
||||
|
||||
That's it. Sit back, relax, and - time permitting - try to skim through the
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# MOpt(imized) AFL by <puppet@zju.edu.cn>
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Description
|
||||
MOpt-AFL is a AFL-based fuzzer that utilizes a customized Particle Swarm
|
||||
Optimization (PSO) algorithm to find the optimal selection probability
|
||||
distribution of operators with respect to fuzzing effectiveness.
|
||||
More details can be found in the technical report.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Cite Information
|
||||
Chenyang Lyu, Shouling Ji, Chao Zhang, Yuwei Li, Wei-Han Lee, Yu Song and
|
||||
Raheem Beyah, MOPT: Optimized Mutation Scheduling for Fuzzers,
|
||||
USENIX Security 2019.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Seed Sets
|
||||
We open source all the seed sets used in the paper
|
||||
"MOPT: Optimized Mutation Scheduling for Fuzzers".
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Experiment Results
|
||||
The experiment results can be found in
|
||||
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/184GOzkZGls1H2NuLuUfSp9gfqp1E2-lL?usp=sharing.
|
||||
We only open source the crash files since the space is limited.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Technical Report
|
||||
MOpt_TechReport.pdf is the technical report of the paper
|
||||
"MOPT: Optimized Mutation Scheduling for Fuzzers", which contains more deatails.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Parameter Introduction
|
||||
Most important, you must add the parameter `-L` (e.g., `-L 0`) to launch the
|
||||
MOpt scheme.
|
||||
|
||||
Option '-L' controls the time to move on to the pacemaker fuzzing mode.
|
||||
'-L t': when MOpt-AFL finishes the mutation of one input, if it has not
|
||||
discovered any new unique crash or path for more than t minutes, MOpt-AFL will
|
||||
enter the pacemaker fuzzing mode.
|
||||
|
||||
Setting 0 will enter the pacemaker fuzzing mode at first, which is
|
||||
recommended in a short time-scale evaluation.
|
||||
|
||||
Setting -1 will enable both pacemaker mode and normal aflmutation fuzzing in
|
||||
parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
Other important parameters can be found in afl-fuzz.c, for instance,
|
||||
|
||||
'swarm_num': the number of the PSO swarms used in the fuzzing process.
|
||||
'period_pilot': how many times MOpt-AFL will execute the target program
|
||||
in the pilot fuzzing module, then it will enter the core fuzzing module.
|
||||
'period_core': how many times MOpt-AFL will execute the target program in the
|
||||
core fuzzing module, then it will enter the PSO updating module.
|
||||
'limit_time_bound': control how many interesting test cases need to be found
|
||||
before MOpt-AFL quits the pacemaker fuzzing mode and reuses the deterministic stage.
|
||||
0 < 'limit_time_bound' < 1, MOpt-AFL-tmp.
|
||||
'limit_time_bound' >= 1, MOpt-AFL-ever.
|
||||
|
||||
Have fun with MOpt in AFL!
|
||||
@ -122,7 +122,7 @@
|
||||
[https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dyninst](https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/afl-dyninst)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## RETROWRITE
|
||||
## RETROWRITE, ZAFL, ... other binary rewriter
|
||||
|
||||
If you have an x86/x86_64 binary that still has its symbols, is compiled
|
||||
with position independant code (PIC/PIE) and does not use most of the C++
|
||||
@ -131,6 +131,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
It is at about 80-85% performance.
|
||||
|
||||
[https://git.zephyr-software.com/opensrc/zafl](https://git.zephyr-software.com/opensrc/zafl)
|
||||
[https://github.com/HexHive/retrowrite](https://github.com/HexHive/retrowrite)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -204,9 +204,7 @@ trimmed input. Here's a quick API description:
|
||||
arguments because we already have the initial buffer from `init_trim` and we
|
||||
can memorize the current state in the data variables. This can also save
|
||||
reparsing steps for each iteration. It should return the trimmed input
|
||||
buffer, where the returned data must not exceed the initial input data in
|
||||
length. Returning anything that is larger than the original data (passed to
|
||||
`init_trim`) will result in a fatal abort of AFL++.
|
||||
buffer.
|
||||
|
||||
- `post_trim` (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -108,9 +108,6 @@ make fairly broad use of environmental variables instead:
|
||||
- Setting `AFL_QUIET` will prevent afl-cc and afl-as banners from being
|
||||
displayed during compilation, in case you find them distracting.
|
||||
|
||||
- Setting `AFL_CAL_FAST` will speed up the initial calibration, if the
|
||||
application is very slow.
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) Settings for LLVM and LTO: afl-clang-fast / afl-clang-fast++ / afl-clang-lto / afl-clang-lto++
|
||||
|
||||
The native instrumentation helpers (instrumentation and gcc_plugin) accept a subset
|
||||
@ -386,6 +383,7 @@ checks or alter some of the more exotic semantics of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- `AFL_FAST_CAL` keeps the calibration stage about 2.5x faster (albeit less
|
||||
precise), which can help when starting a session against a slow target.
|
||||
`AFL_CAL_FAST` works too.
|
||||
|
||||
- The CPU widget shown at the bottom of the screen is fairly simplistic and
|
||||
may complain of high load prematurely, especially on systems with low core
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Historical notes
|
||||
|
||||
This doc talks about the rationale of some of the high-level design decisions
|
||||
for American Fuzzy Lop. It's adopted from a discussion with Rob Graham.
|
||||
See README.md for the general instruction manual, and technical_details.md for
|
||||
additional implementation-level insights.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Influences
|
||||
|
||||
In short, `afl-fuzz` is inspired chiefly by the work done by Tavis Ormandy back
|
||||
in 2007. Tavis did some very persuasive experiments using `gcov` block coverage
|
||||
to select optimal test cases out of a large corpus of data, and then using
|
||||
them as a starting point for traditional fuzzing workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
(By "persuasive", I mean: netting a significant number of interesting
|
||||
vulnerabilities.)
|
||||
|
||||
In parallel to this, both Tavis and I were interested in evolutionary fuzzing.
|
||||
Tavis had his experiments, and I was working on a tool called bunny-the-fuzzer,
|
||||
released somewhere in 2007.
|
||||
|
||||
Bunny used a generational algorithm not much different from `afl-fuzz`, but
|
||||
also tried to reason about the relationship between various input bits and
|
||||
the internal state of the program, with hopes of deriving some additional value
|
||||
from that. The reasoning / correlation part was probably in part inspired by
|
||||
other projects done around the same time by Will Drewry and Chris Evans.
|
||||
|
||||
The state correlation approach sounded very sexy on paper, but ultimately, made
|
||||
the fuzzer complicated, brittle, and cumbersome to use; every other target
|
||||
program would require a tweak or two. Because Bunny didn't fare a whole lot
|
||||
better than less sophisticated brute-force tools, I eventually decided to write
|
||||
it off. You can still find its original documentation at:
|
||||
|
||||
https://code.google.com/p/bunny-the-fuzzer/wiki/BunnyDoc
|
||||
|
||||
There has been a fair amount of independent work, too. Most notably, a few
|
||||
weeks earlier that year, Jared DeMott had a Defcon presentation about a
|
||||
coverage-driven fuzzer that relied on coverage as a fitness function.
|
||||
|
||||
Jared's approach was by no means identical to what afl-fuzz does, but it was in
|
||||
the same ballpark. His fuzzer tried to explicitly solve for the maximum coverage
|
||||
with a single input file; in comparison, afl simply selects for cases that do
|
||||
something new (which yields better results - see [technical_details.md](technical_details.md)).
|
||||
|
||||
A few years later, Gabriel Campana released fuzzgrind, a tool that relied purely
|
||||
on Valgrind and a constraint solver to maximize coverage without any brute-force
|
||||
bits; and Microsoft Research folks talked extensively about their still
|
||||
non-public, solver-based SAGE framework.
|
||||
|
||||
In the past six years or so, I've also seen a fair number of academic papers
|
||||
that dealt with smart fuzzing (focusing chiefly on symbolic execution) and a
|
||||
couple papers that discussed proof-of-concept applications of genetic
|
||||
algorithms with the same goals in mind. I'm unconvinced how practical most of
|
||||
these experiments were; I suspect that many of them suffer from the
|
||||
bunny-the-fuzzer's curse of being cool on paper and in carefully designed
|
||||
experiments, but failing the ultimate test of being able to find new,
|
||||
worthwhile security bugs in otherwise well-fuzzed, real-world software.
|
||||
|
||||
In some ways, the baseline that the "cool" solutions have to compete against is
|
||||
a lot more impressive than it may seem, making it difficult for competitors to
|
||||
stand out. For a singular example, check out the work by Gynvael and Mateusz
|
||||
Jurczyk, applying "dumb" fuzzing to ffmpeg, a prominent and security-critical
|
||||
component of modern browsers and media players:
|
||||
|
||||
http://googleonlinesecurity.blogspot.com/2014/01/ffmpeg-and-thousand-fixes.html
|
||||
|
||||
Effortlessly getting comparable results with state-of-the-art symbolic execution
|
||||
in equally complex software still seems fairly unlikely, and hasn't been
|
||||
demonstrated in practice so far.
|
||||
|
||||
But I digress; ultimately, attribution is hard, and glorying the fundamental
|
||||
concepts behind AFL is probably a waste of time. The devil is very much in the
|
||||
often-overlooked details, which brings us to...
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Design goals for afl-fuzz
|
||||
|
||||
In short, I believe that the current implementation of afl-fuzz takes care of
|
||||
several itches that seemed impossible to scratch with other tools:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Speed. It's genuinely hard to compete with brute force when your "smart"
|
||||
approach is resource-intensive. If your instrumentation makes it 10x more
|
||||
likely to find a bug, but runs 100x slower, your users are getting a bad
|
||||
deal.
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid starting with a handicap, `afl-fuzz` is meant to let you fuzz most of
|
||||
the intended targets at roughly their native speed - so even if it doesn't
|
||||
add value, you do not lose much.
|
||||
|
||||
On top of this, the tool leverages instrumentation to actually reduce the
|
||||
amount of work in a couple of ways: for example, by carefully trimming the
|
||||
corpus or skipping non-functional but non-trimmable regions in the input
|
||||
files.
|
||||
|
||||
2) Rock-solid reliability. It's hard to compete with brute force if your
|
||||
approach is brittle and fails unexpectedly. Automated testing is attractive
|
||||
because it's simple to use and scalable; anything that goes against these
|
||||
principles is an unwelcome trade-off and means that your tool will be used
|
||||
less often and with less consistent results.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the approaches based on symbolic execution, taint tracking, or
|
||||
complex syntax-aware instrumentation are currently fairly unreliable with
|
||||
real-world targets. Perhaps more importantly, their failure modes can render
|
||||
them strictly worse than "dumb" tools, and such degradation can be difficult
|
||||
for less experienced users to notice and correct.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, `afl-fuzz` is designed to be rock solid, chiefly by keeping it
|
||||
simple. In fact, at its core, it's designed to be just a very good
|
||||
traditional fuzzer with a wide range of interesting, well-researched
|
||||
strategies to go by. The fancy parts just help it focus the effort in
|
||||
places where it matters the most.
|
||||
|
||||
3) Simplicity. The author of a testing framework is probably the only person
|
||||
who truly understands the impact of all the settings offered by the tool -
|
||||
and who can dial them in just right. Yet, even the most rudimentary fuzzer
|
||||
frameworks often come with countless knobs and fuzzing ratios that need to
|
||||
be guessed by the operator ahead of the time. This can do more harm than
|
||||
good.
|
||||
|
||||
AFL is designed to avoid this as much as possible. The three knobs you
|
||||
can play with are the output file, the memory limit, and the ability to
|
||||
override the default, auto-calibrated timeout. The rest is just supposed to
|
||||
work. When it doesn't, user-friendly error messages outline the probable
|
||||
causes and workarounds, and get you back on track right away.
|
||||
|
||||
4) Chainability. Most general-purpose fuzzers can't be easily employed
|
||||
against resource-hungry or interaction-heavy tools, necessitating the
|
||||
creation of custom in-process fuzzers or the investment of massive CPU
|
||||
power (most of which is wasted on tasks not directly related to the code
|
||||
we actually want to test).
|
||||
|
||||
AFL tries to scratch this itch by allowing users to use more lightweight
|
||||
targets (e.g., standalone image parsing libraries) to create small
|
||||
corpora of interesting test cases that can be fed into a manual testing
|
||||
process or a UI harness later on.
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned in [technical_details.md](technical_details.md), AFL does all this not by systematically
|
||||
applying a single overarching CS concept, but by experimenting with a variety
|
||||
of small, complementary methods that were shown to reliably yields results
|
||||
better than chance. The use of instrumentation is a part of that toolkit, but is
|
||||
far from being the most important one.
|
||||
|
||||
Ultimately, what matters is that `afl-fuzz` is designed to find cool bugs - and
|
||||
has a pretty robust track record of doing just that.
|
||||
@ -1,157 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Notes for using ASAN with afl-fuzz
|
||||
|
||||
This file discusses some of the caveats for fuzzing under ASAN, and suggests
|
||||
a handful of alternatives. See README.md for the general instruction manual.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Short version
|
||||
|
||||
ASAN on 64-bit systems requests a lot of memory in a way that can't be easily
|
||||
distinguished from a misbehaving program bent on crashing your system.
|
||||
|
||||
Because of this, fuzzing with ASAN is recommended only in four scenarios:
|
||||
|
||||
- On 32-bit systems, where we can always enforce a reasonable memory limit
|
||||
(-m 800 or so is a good starting point),
|
||||
|
||||
- On 64-bit systems only if you can do one of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Compile the binary in 32-bit mode (gcc -m32),
|
||||
|
||||
- Precisely gauge memory needs using http://jwilk.net/software/recidivm .
|
||||
|
||||
- Limit the memory available to process using cgroups on Linux (see
|
||||
utils/asan_cgroups).
|
||||
|
||||
To compile with ASAN, set AFL_USE_ASAN=1 before calling 'make clean all'. The
|
||||
afl-gcc / afl-clang wrappers will pick that up and add the appropriate flags.
|
||||
Note that ASAN is incompatible with -static, so be mindful of that.
|
||||
|
||||
(You can also use AFL_USE_MSAN=1 to enable MSAN instead.)
|
||||
|
||||
When compiling with AFL_USE_LSAN, the leak sanitizer will normally run
|
||||
when the program exits. In order to utilize this check at different times,
|
||||
such as at the end of a loop, you may use the macro __AFL_LEAK_CHECK();.
|
||||
This macro will report a crash in afl-fuzz if any memory is left leaking
|
||||
at this stage. You can also use LSAN_OPTIONS and a supressions file
|
||||
for more fine-tuned checking, however make sure you keep exitcode=23.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: if you run several secondary instances, only one should run the target
|
||||
compiled with ASAN (and UBSAN, CFISAN), the others should run the target with
|
||||
no sanitizers compiled in.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also the option of generating a corpus using a non-ASAN binary, and
|
||||
then feeding it to an ASAN-instrumented one to check for bugs. This is faster,
|
||||
and can give you somewhat comparable results. You can also try using
|
||||
libdislocator (see [utils/libdislocator/README.dislocator.md](../utils/libdislocator/README.dislocator.md) in the parent directory) as a
|
||||
lightweight and hassle-free (but less thorough) alternative.
|
||||
|
||||
## 2) Long version
|
||||
|
||||
ASAN allocates a huge region of virtual address space for bookkeeping purposes.
|
||||
Most of this is never actually accessed, so the OS never has to allocate any
|
||||
real pages of memory for the process, and the VM grabbed by ASAN is essentially
|
||||
"free" - but the mapping counts against the standard OS-enforced limit
|
||||
(RLIMIT_AS, aka ulimit -v).
|
||||
|
||||
On our end, afl-fuzz tries to protect you from processes that go off-rails
|
||||
and start consuming all the available memory in a vain attempt to parse a
|
||||
malformed input file. This happens surprisingly often, so enforcing such a limit
|
||||
is important for almost any fuzzer: the alternative is for the kernel OOM
|
||||
handler to step in and start killing random processes to free up resources.
|
||||
Needless to say, that's not a very nice prospect to live with.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, un*x systems offer no portable way to limit the amount of
|
||||
pages actually given to a process in a way that distinguishes between that
|
||||
and the harmless "land grab" done by ASAN. In principle, there are three standard
|
||||
ways to limit the size of the heap:
|
||||
|
||||
- The RLIMIT_AS mechanism (ulimit -v) caps the size of the virtual space -
|
||||
but as noted, this pays no attention to the number of pages actually
|
||||
in use by the process, and doesn't help us here.
|
||||
|
||||
- The RLIMIT_DATA mechanism (ulimit -d) seems like a good fit, but it applies
|
||||
only to the traditional sbrk() / brk() methods of requesting heap space;
|
||||
modern allocators, including the one in glibc, routinely rely on mmap()
|
||||
instead, and circumvent this limit completely.
|
||||
|
||||
- Finally, the RLIMIT_RSS limit (ulimit -m) sounds like what we need, but
|
||||
doesn't work on Linux - mostly because nobody felt like implementing it.
|
||||
|
||||
There are also cgroups, but they are Linux-specific, not universally available
|
||||
even on Linux systems, and they require root permissions to set up; I'm a bit
|
||||
hesitant to make afl-fuzz require root permissions just for that. That said,
|
||||
if you are on Linux and want to use cgroups, check out the contributed script
|
||||
that ships in utils/asan_cgroups/.
|
||||
|
||||
In settings where cgroups aren't available, we have no nice, portable way to
|
||||
avoid counting the ASAN allocation toward the limit. On 32-bit systems, or for
|
||||
binaries compiled in 32-bit mode (-m32), this is not a big deal: ASAN needs
|
||||
around 600-800 MB or so, depending on the compiler - so all you need to do is
|
||||
to specify -m that is a bit higher than that.
|
||||
|
||||
On 64-bit systems, the situation is more murky, because the ASAN allocation
|
||||
is completely outlandish - around 17.5 TB in older versions, and closer to
|
||||
20 TB with newest ones. The actual amount of memory on your system is
|
||||
(probably!) just a tiny fraction of that - so unless you dial the limit
|
||||
with surgical precision, you will get no protection from OOM bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
On my system, the amount of memory grabbed by ASAN with a slightly older
|
||||
version of gcc is around 17,825,850 MB; for newest clang, it's 20,971,600.
|
||||
But there is no guarantee that these numbers are stable, and if you get them
|
||||
wrong by "just" a couple gigs or so, you will be at risk.
|
||||
|
||||
To get the precise number, you can use the recidivm tool developed by Jakub
|
||||
Wilk (http://jwilk.net/software/recidivm). In absence of this, ASAN is *not*
|
||||
recommended when fuzzing 64-bit binaries, unless you are confident that they
|
||||
are robust and enforce reasonable memory limits (in which case, you can
|
||||
specify '-m none' when calling afl-fuzz).
|
||||
|
||||
Using recidivm or running with no limits aside, there are two other decent
|
||||
alternatives: build a corpus of test cases using a non-ASAN binary, and then
|
||||
examine them with ASAN, Valgrind, or other heavy-duty tools in a more
|
||||
controlled setting; or compile the target program with -m32 (32-bit mode)
|
||||
if your system supports that.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3) Interactions with the QEMU mode
|
||||
|
||||
ASAN, MSAN, and other sanitizers appear to be incompatible with QEMU user
|
||||
emulation, so please do not try to use them with the -Q option; QEMU doesn't
|
||||
seem to appreciate the shadow VM trick used by these tools, and will likely
|
||||
just allocate all your physical memory, then crash.
|
||||
|
||||
You can, however, use QASan to run binaries that are not instrumented with ASan
|
||||
under QEMU with the AFL++ instrumentation.
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/andreafioraldi/qasan
|
||||
|
||||
## 4) ASAN and OOM crashes
|
||||
|
||||
By default, ASAN treats memory allocation failures as fatal errors, immediately
|
||||
causing the program to crash. Since this is a departure from normal POSIX
|
||||
semantics (and creates the appearance of security issues in otherwise
|
||||
properly-behaving programs), we try to disable this by specifying
|
||||
allocator_may_return_null=1 in ASAN_OPTIONS.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, it's been reported that this setting still causes ASAN to
|
||||
trigger phantom crashes in situations where the standard allocator would
|
||||
simply return NULL. If this is interfering with your fuzzing jobs, you may
|
||||
want to cc: yourself on this bug:
|
||||
|
||||
https://bugs.llvm.org/show_bug.cgi?id=22026
|
||||
|
||||
## 5) What about UBSAN?
|
||||
|
||||
New versions of UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer offers the
|
||||
-fsanitize=undefined-trap-on-error compiler flag that tells UBSan to insert an
|
||||
istruction that will cause SIGILL (ud2 on x86) when an undefined behaviour
|
||||
is detected. This is the option that you want to use when combining AFL++
|
||||
and UBSan.
|
||||
|
||||
AFL_USE_UBSAN=1 env var will add this compiler flag to afl-clang-fast,
|
||||
afl-gcc-fast and afl-gcc for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Old versions of UBSAN don't offer a consistent way
|
||||
to abort() on fault conditions or to terminate with a distinctive exit code
|
||||
but there are some versions of the library can be binary-patched to address this
|
||||
issue. You can also preload a shared library that substitute all the UBSan
|
||||
routines used to report errors with abort().
|
||||
@ -3,6 +3,10 @@
|
||||
This document talks about synchronizing afl-fuzz jobs on a single machine
|
||||
or across a fleet of systems. See README.md for the general instruction manual.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this document is rather outdated. please refer to the main document
|
||||
section on multiple core usage [../README.md#Using multiple cores](../README.md#b-using-multiple-coresthreads)
|
||||
for up to date strategies!
|
||||
|
||||
## 1) Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Every copy of afl-fuzz will take up one CPU core. This means that on an
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,13 +48,9 @@ be then manually fed to a more resource-hungry program later on.
|
||||
Also note that reading the fuzzing input via stdin is faster than reading from
|
||||
a file.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. Use LLVM instrumentation
|
||||
## 3. Use LLVM persistent instrumentation
|
||||
|
||||
When fuzzing slow targets, you can gain 20-100% performance improvement by
|
||||
using the LLVM-based instrumentation mode described in [the instrumentation README](../instrumentation/README.llvm.md).
|
||||
Note that this mode requires the use of clang and will not work with GCC.
|
||||
|
||||
The LLVM mode also offers a "persistent", in-process fuzzing mode that can
|
||||
The LLVM mode offers a "persistent", in-process fuzzing mode that can
|
||||
work well for certain types of self-contained libraries, and for fast targets,
|
||||
can offer performance gains up to 5-10x; and a "deferred fork server" mode
|
||||
that can offer huge benefits for programs with high startup overhead. Both
|
||||
@ -138,8 +134,7 @@ misses, or similar factors, but they are less likely to be a concern.)
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. Keep memory use and timeouts in check
|
||||
|
||||
If you have increased the `-m` or `-t` limits more than truly necessary, consider
|
||||
dialing them back down.
|
||||
Consider setting low values for `-m` and `-t`.
|
||||
|
||||
For programs that are nominally very fast, but get sluggish for some inputs,
|
||||
you can also try setting `-t` values that are more punishing than what `afl-fuzz`
|
||||
@ -164,6 +159,20 @@ There are several OS-level factors that may affect fuzzing speed:
|
||||
- Network filesystems, either used for fuzzer input / output, or accessed by
|
||||
the fuzzed binary to read configuration files (pay special attention to the
|
||||
home directory - many programs search it for dot-files).
|
||||
- Disable all the spectre, meltdown etc. security countermeasures in the
|
||||
kernel if your machine is properly separated:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ibpb=off ibrs=off kpti=off l1tf=off mds=off mitigations=off
|
||||
no_stf_barrier noibpb noibrs nopcid nopti nospec_store_bypass_disable
|
||||
nospectre_v1 nospectre_v2 pcid=off pti=off spec_store_bypass_disable=off
|
||||
spectre_v2=off stf_barrier=off
|
||||
```
|
||||
In most Linux distributions you can put this into a `/etc/default/grub`
|
||||
variable.
|
||||
|
||||
The following list of changes are made when executing `afl-system-config`:
|
||||
|
||||
- On-demand CPU scaling. The Linux `ondemand` governor performs its analysis
|
||||
on a particular schedule and is known to underestimate the needs of
|
||||
short-lived processes spawned by `afl-fuzz` (or any other fuzzer). On Linux,
|
||||
@ -196,26 +205,4 @@ There are several OS-level factors that may affect fuzzing speed:
|
||||
Setting a different scheduling policy for the fuzzer process - say
|
||||
`SCHED_RR` - can usually speed things up, too, but needs to be done with
|
||||
care.
|
||||
- Use the `afl-system-config` script to set all proc/sys settings above in one go.
|
||||
- Disable all the spectre, meltdown etc. security countermeasures in the
|
||||
kernel if your machine is properly separated:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ibpb=off ibrs=off kpti=off l1tf=off mds=off mitigations=off
|
||||
no_stf_barrier noibpb noibrs nopcid nopti nospec_store_bypass_disable
|
||||
nospectre_v1 nospectre_v2 pcid=off pti=off spec_store_bypass_disable=off
|
||||
spectre_v2=off stf_barrier=off
|
||||
```
|
||||
In most Linux distributions you can put this into a `/etc/default/grub`
|
||||
variable.
|
||||
|
||||
## 9. If all other options fail, use `-d`
|
||||
|
||||
For programs that are genuinely slow, in cases where you really can't escape
|
||||
using huge input files, or when you simply want to get quick and dirty results
|
||||
early on, you can always resort to the `-d` mode.
|
||||
|
||||
The mode causes `afl-fuzz` to skip all the deterministic fuzzing steps, which
|
||||
makes output a lot less neat and can ultimately make the testing a bit less
|
||||
in-depth, but it will give you an experience more familiar from other fuzzing
|
||||
tools.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# afl++'s power schedules based on AFLfast
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://mboehme.github.io/paper/CCS16.pdf"><img src="https://mboehme.github.io/paper/CCS16.png" align="right" width="250"></a>
|
||||
Power schedules implemented by Marcel Böhme \<marcel.boehme@acm.org\>.
|
||||
AFLFast is an extension of AFL which is written and maintained by
|
||||
Michal Zalewski \<lcamtuf@google.com\>.
|
||||
|
||||
AFLfast has helped in the success of Team Codejitsu at the finals of the DARPA Cyber Grand Challenge where their bot Galactica took **2nd place** in terms of #POVs proven (see red bar at https://www.cybergrandchallenge.com/event#results). AFLFast exposed several previously unreported CVEs that could not be exposed by AFL in 24 hours and otherwise exposed vulnerabilities significantly faster than AFL while generating orders of magnitude more unique crashes.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, we observed that most generated inputs exercise the same few "high-frequency" paths and developed strategies to gravitate towards low-frequency paths, to stress significantly more program behavior in the same amount of time. We devised several **search strategies** that decide in which order the seeds should be fuzzed and **power schedules** that smartly regulate the number of inputs generated from a seed (i.e., the time spent fuzzing a seed). We call the number of inputs generated from a seed, the seed's **energy**.
|
||||
|
||||
We find that AFL's exploitation-based constant schedule assigns **too much energy to seeds exercising high-frequency paths** (e.g., paths that reject invalid inputs) and not enough energy to seeds exercising low-frequency paths (e.g., paths that stress interesting behaviors). Technically, we modified the computation of a seed's performance score (`calculate_score`), which seed is marked as favourite (`update_bitmap_score`), and which seed is chosen next from the circular queue (`main`). We implemented the following schedules (in the order of their effectiveness, best first):
|
||||
|
||||
| AFL flag | Power Schedule |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------------------------- |
|
||||
| `-p explore` | 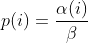 |
|
||||
| `-p fast` (default)| 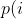=\\min\\left(\\frac{\\alpha(i)}{\\beta}\\cdot\\frac{2^{s(i)}}{f(i)},M\\right)) |
|
||||
| `-p coe` | 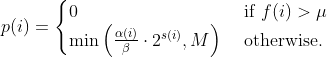 |
|
||||
| `-p quad` | 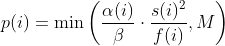 |
|
||||
| `-p lin` | 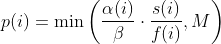 |
|
||||
| `-p exploit` (AFL) | 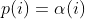 |
|
||||
| `-p mmopt` | Experimental: `explore` with no weighting to runtime and increased weighting on the last 5 queue entries |
|
||||
| `-p rare` | Experimental: `rare` puts focus on queue entries that hit rare edges |
|
||||
| `-p seek` | Experimental: `seek` is EXPLORE but ignoring the runtime of the queue input and less focus on the size |
|
||||
where *α(i)* is the performance score that AFL uses to compute for the seed input *i*, *β(i)>1* is a constant, *s(i)* is the number of times that seed *i* has been chosen from the queue, *f(i)* is the number of generated inputs that exercise the same path as seed *i*, and *μ* is the average number of generated inputs exercising a path.
|
||||
|
||||
More details can be found in the paper that was accepted at the [23rd ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS'16)](https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2016/accepted-papers/).
|
||||
|
||||
PS: In parallel mode (several instances with shared queue), we suggest to run the main node using the exploit schedule (-p exploit) and the secondary nodes with a combination of cut-off-exponential (-p coe), exponential (-p fast; default), and explore (-p explore) schedules. In single mode, the default settings will do. **EDIT:** In parallel mode, AFLFast seems to perform poorly because the path probability estimates are incorrect for the imported seeds. Pull requests to fix this issue by syncing the estimates across instances are appreciated :)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Released under terms and conditions of Apache License, Version 2.0.
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# Technical "whitepaper" for afl-fuzz
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this document is rather outdated!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This document provides a quick overview of the guts of American Fuzzy Lop.
|
||||
See README.md for the general instruction manual; and for a discussion of
|
||||
motivations and design goals behind AFL, see historical_notes.md.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,29 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"__afl_already_initialized_first";
|
||||
"__afl_already_initialized_forkserver";
|
||||
"__afl_already_initialized_second";
|
||||
"__afl_already_initialized_shm";
|
||||
"__afl_area_ptr";
|
||||
"__afl_manual_init";
|
||||
"__afl_persistent_loop";
|
||||
"__afl_auto_early";
|
||||
"__afl_auto_first";
|
||||
"__afl_auto_init";
|
||||
"__afl_area_initial";
|
||||
"__afl_prev_loc";
|
||||
"__afl_prev_caller";
|
||||
"__afl_prev_ctx";
|
||||
"__afl_final_loc";
|
||||
"__afl_map_addr";
|
||||
"__afl_auto_second";
|
||||
"__afl_coverage_discard";
|
||||
"__afl_coverage_interesting";
|
||||
"__afl_coverage_off";
|
||||
"__afl_coverage_on";
|
||||
"__afl_coverage_skip";
|
||||
"__afl_dictionary";
|
||||
"__afl_dictionary_len";
|
||||
"__afl_final_loc";
|
||||
"__afl_fuzz_len";
|
||||
"__afl_fuzz_ptr";
|
||||
"__afl_manual_init";
|
||||
"__afl_map_addr";
|
||||
"__afl_persistent_loop";
|
||||
"__afl_prev_caller";
|
||||
"__afl_prev_ctx";
|
||||
"__afl_prev_loc";
|
||||
"__afl_selective_coverage";
|
||||
"__afl_selective_coverage_start_off";
|
||||
"__afl_selective_coverage_temp";
|
||||
@ -25,24 +38,27 @@
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard_init";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hook1";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hook16";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hook2";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hook4";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hook8";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hookN";
|
||||
"__cmplog_ins_hook16";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp1";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp1";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp2";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp2";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp4";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp4";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp8";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp8";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp16";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp16";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_switch";
|
||||
"__cmplog_rtn_hook";
|
||||
"__cmplog_rtn_gcc_stdstring_cstring";
|
||||
"__cmplog_rtn_gcc_stdstring_stdstring";
|
||||
"__cmplog_rtn_hook";
|
||||
"__cmplog_rtn_llvm_stdstring_cstring";
|
||||
"__cmplog_rtn_llvm_stdstring_stdstring";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp1";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp16";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp2";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp4";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp8";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp1";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp16";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp2";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp4";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp8";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_pc_guard_init";
|
||||
"__sanitizer_cov_trace_switch";
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
147
frida_mode/MapDensity.md
Normal file
147
frida_mode/MapDensity.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
|
||||
# Map Density
|
||||
|
||||
# How Coverage Works
|
||||
The coverage in AFL++ works by assigning each basic block of code a unique ID
|
||||
and during execution when transitioning between blocks (e.g. by calls or jumps)
|
||||
assigning each of these edges an ID based upon the source and destination block
|
||||
ID.
|
||||
|
||||
For each individual execution of the target, a single dimensional byte array
|
||||
indexed by the edge ID is used to count how many times each edge is traversed.
|
||||
|
||||
A single dimensional cumulative byte array is also constructed where each byte
|
||||
again represents an individual edge ID, but this time, the value of the byte
|
||||
represents a range of how many times that edge has been traversed.
|
||||
|
||||
```1, 2, 3, 4-7, 8-15, 16-31, 32-127, 128+```
|
||||
|
||||
The theory is that a new path isn't particularly interesting if an edge has been
|
||||
traversed `23` instead of `24` times for example, but is interesting if an edge
|
||||
has been traversed for the very first time, or the number of times fits within a different bucket.
|
||||
|
||||
After each run, the count of times each edge is hit is compared to the values in
|
||||
the cumulative map and if it is different, then the input is kept as a new seed
|
||||
and the cumulative map is updated.
|
||||
|
||||
This mechanism is described in greater detail in the seminal
|
||||
[paper](https://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl/technical_details.txt) on AFL by
|
||||
[lcamtuf](https://github.com/lcamtuf).
|
||||
|
||||
# Collisions
|
||||
In black-box fuzzing, we must assume that control may flow from any block to any
|
||||
other block, since we don't know any better. Thus for a target with `n` basic
|
||||
blocks of code, there are `n * n` potential edges. As we can see, even with a
|
||||
small number of edges, a very large map will be required so that we have space
|
||||
to fit them all. Even if our target only had `1024` blocks, this would require a
|
||||
map containing `1048576` entries (or 1Mb in size).
|
||||
|
||||
Whilst this may not seem like a lot of memory, it causes problems for two reasons. Firstly, the processing step after each execution must now process much more
|
||||
data, and secondly a map this size is unlikely to fit within the L2 cache of the processor. Since this is a very hot code path, we are likely to pay a very heavy
|
||||
performance cost.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we must accept that not all edges can have a unique and that
|
||||
therefore there will be collisions. This means that if the fuzzer finds a new
|
||||
path by uncovering an edge which was not previously found, but that the same
|
||||
edge ID is used by another edge, then it may go completely unnoticed. This is
|
||||
obviously undesirable, but equally if our map is too large, then we will not be
|
||||
able to process as many potential inputs in the same time and hence not uncover
|
||||
edges for that reason. Thus a careful trade-off of map size must be made.
|
||||
|
||||
# Block & Edge Numbering
|
||||
Since the original AFL, blocks and edges have always been numbered in the same
|
||||
way as we can see from the following C snippet from the whitepaper.
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
cur_location = (block_address >> 4) ^ (block_address << 8);
|
||||
shared_mem[cur_location ^ prev_location]++;
|
||||
prev_location = cur_location >> 1;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each block ID is generated by performing a shift and XOR on its address. Then
|
||||
the edge ID is calculated as `E = B ^ (B' >> 1)`. Here, we can make two
|
||||
observations. In fact, the edge ID is also masked to ensure it is less than the
|
||||
size of the map being used.
|
||||
|
||||
## Block IDs
|
||||
Firstly, the block ID doesn't have very good entropy. If we consider the address
|
||||
of the block, then whilst each block has a unique ID, it isn't necessarily very
|
||||
evenly distributed.
|
||||
|
||||
We start with a large address, and need to discard a large number of the bits to
|
||||
generate a block ID which is within range. But how do we choose the unique bits
|
||||
of the address verus those which are the same for every block? The high bits of
|
||||
the address may simply be all `0s` or all `1s` to make the address cannonical,
|
||||
the middle portion of the address may be the same for all blocks (since if they
|
||||
are all within the same binary, then they will all be adjacent in memory), and
|
||||
on some systems, even the low bits may have poor entropy as some use fixed
|
||||
length aligned instructions. Then we need to consider that a portion of each
|
||||
binary may contain the `.data` or `.bss` sections and so may not contain any
|
||||
blocks of code at all.
|
||||
|
||||
## Edge IDs
|
||||
Secondly, we can observe that when we generate an edge ID from the source and
|
||||
destination block IDs, we perform a right shift on the source block ID. Whilst
|
||||
there are good reasons as set out in the whitepaper why such a transform is
|
||||
applied, in so doing, we dispose of `1` bit of precious entropy in our source
|
||||
block ID.
|
||||
|
||||
All together, this means that some edge IDs may be more popular than others.
|
||||
This means that some portions of the map may be very densly populated with large
|
||||
numbers of edges, whilst others may be very sparsely populated, or not populated
|
||||
at all.
|
||||
|
||||
# Improvements
|
||||
One of the main reaons why this algorithm selected, is performance. All of the
|
||||
operations are very quick to perform and given we may be carrying this out for
|
||||
every block of code we execute, performance is critical.
|
||||
|
||||
However, the design of the binary instrumentation modes of AFL++ has moved on.
|
||||
Both QEMU and FRIDA modes use a two stage process when executing a target
|
||||
application. Each block is first compiled or instrumented, and then it is
|
||||
executed. The compiled blocks can be re-used each time the target executes them.
|
||||
|
||||
Since a blocks ID is based on its address, and this is known at compile time, we
|
||||
only need to generate this ID once per block and so this ID generation no longer
|
||||
needs to be as performant. We can therefore use a hash algorithm to generate
|
||||
this ID and therefore ensure that the block IDs are more evenly distributed.
|
||||
|
||||
Edge IDs however, can only be determined at run-time. Since we don't know which
|
||||
blocks a given input will traverse until we run it. However, given our block IDs
|
||||
are now evenly distributed, generating an evenly distributed edge ID becomes
|
||||
simple. Here, the only change we make is to use a rotate operation rather than
|
||||
a shift operation so we don't lose a bit of entropy from the source ID.
|
||||
|
||||
So our new algorithm becomes:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
cur_location = hash(block_address)
|
||||
shared_mem[cur_location ^ prev_location]++;
|
||||
prev_location = rotate(cur_location, 1);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, in the original design, the `cur_location` was always set to `0`, at the
|
||||
beginning of a run, we instead set the value of `cur_location` to `hash(0)`.
|
||||
|
||||
# Parallel Fuzzing
|
||||
Another sub-optimal aspect of the original design is that no matter how many
|
||||
instances of the fuzzer you ran in parallel, each instance numbered each block
|
||||
and so each edge with the same ID. Each instance would therefore find the same
|
||||
subset of edges collide with each other. In the event of a collision, all
|
||||
instances will hit the same road block.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if we instead use a different seed for our hashing function for each
|
||||
instance, then each will ascribe each block a different ID and hence each edge
|
||||
will be given a different edge ID. This means that whilst one instance of the
|
||||
fuzzer may find a given pair of edges collide, it is very unlikely that another
|
||||
instance will find the same pair also collide.
|
||||
|
||||
Due to the collaborative nature of parallel fuzzing, this means that whilst one
|
||||
instance may struggle to find a particular new path because the new edge
|
||||
collides, another instance will likely not encounter the same collision and thus
|
||||
be able to differentiate this new path and share it with the other instances.
|
||||
|
||||
If only a single new edge is found, and the new path is shared with an instance
|
||||
for which that edge collides, that instance may disregard it as irrelevant. In
|
||||
practice, however, the discovery of a single new edge, likely leads to several
|
||||
more edges beneath it also being found and therefore the likelihood of all of
|
||||
these being collisions is very slim.
|
||||
863
frida_mode/Scripting.md
Normal file
863
frida_mode/Scripting.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,863 @@
|
||||
# Scripting
|
||||
FRIDA now supports the ability to configure itself using JavaScript. This allows
|
||||
the user to make use of the convenience of FRIDA's scripting engine (along with
|
||||
it's support for debug symbols and exports) to configure all of the things which
|
||||
were traditionally configured using environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
By default FRIDA mode will look for the file `afl.js` in the current working
|
||||
directory of the target. Alternatively, a script file can be configured using
|
||||
the environment variable `AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT`.
|
||||
|
||||
This script can make use of all of the standard [frida api functions](https://frida.re/docs/javascript-api/), but FRIDA mode adds some additional functions to allow
|
||||
you to interact with FRIDA mode itself. These can all be accessed via the global
|
||||
`Afl` parameter. e.g. `Afl.print("HELLO WORLD");`,
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter a problem with your script, then you should set the environment
|
||||
variable `AFL_DEBUG_CHILD=1` to view any diagnostic information.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Example
|
||||
Most of the time, users will likely be wanting to call the functions which configure an address (e.g. for the entry point, or the persistent address).
|
||||
|
||||
The example below uses the API [`DebugSymbol.fromName()`](https://frida.re/docs/javascript-api/#debugsymbol). Another use API is [`Module.getExportByName()`](https://frida.re/docs/javascript-api/#module).
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
/* Use Afl.print instead of console.log */
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
/* Print some useful diagnostics stuff */
|
||||
Afl.print(`PID: ${Process.id}`);
|
||||
|
||||
new ModuleMap().values().forEach(m => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`${m.base}-${m.base.add(m.size)} ${m.name}`);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Configure entry-point, persistence etc. This will be what most
|
||||
* people want to do.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const persistent_addr = DebugSymbol.fromName('main');
|
||||
Afl.print(`persistent_addr: ${persistent_addr.address}`);
|
||||
|
||||
if (persistent_addr.address.equals(ptr(0))) {
|
||||
Afl.error('Cannot find symbol main');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const persistent_ret = DebugSymbol.fromName('slow');
|
||||
Afl.print(`persistent_ret: ${persistent_ret.address}`);
|
||||
|
||||
if (persistent_ret.address.equals(ptr(0))) {
|
||||
Afl.error('Cannot find symbol slow');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(persistent_addr.address);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentReturn(persistent_ret.address);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentCount(1000000);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Control instrumentation, you may want to do this too */
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentLibraries();
|
||||
const mod = Process.findModuleByName("libc-2.31.so")
|
||||
Afl.addExcludedRange(mod.base, mod.size);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Some useful options to configure logging */
|
||||
Afl.setStdOut("/tmp/stdout.txt");
|
||||
Afl.setStdErr("/tmp/stderr.txt");
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show the address layout. Sometimes helpful */
|
||||
Afl.setDebugMaps();
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* If you are using these options, then things aren't going
|
||||
* very well for you.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentDebugFile("/tmp/instr.log");
|
||||
Afl.setPrefetchDisable();
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentNoOptimize();
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentEnableTracing();
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentTracingUnique();
|
||||
Afl.setStatsFile("/tmp/stats.txt");
|
||||
Afl.setStatsInterval(1);
|
||||
Afl.setStatsTransitions();
|
||||
|
||||
/* *ALWAYS* call this when you have finished all your configuration */
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Stripped Binaries
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, if the binary you attempting to fuzz has no symbol information, and no
|
||||
exports, then the following approach can be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const module = Process.getModuleByName('target.exe');
|
||||
/* Hardcoded offset within the target image */
|
||||
const address = module.base.add(0xdeadface);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(address);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Persisent Hook
|
||||
A persistent hook can be implemented using a conventional shared object, sample
|
||||
source code for a hook suitable for the prototype of `LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput`
|
||||
can be found [here](hook/hook.c). This can be configured using code similar to
|
||||
the following.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const path = Afl.module.path;
|
||||
const dir = path.substring(0, path.lastIndexOf("/"));
|
||||
const mod = Module.load(`${dir}/frida_mode/build/hook.so`);
|
||||
const hook = mod.getExportByName('afl_persistent_hook');
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentHook(hook);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, the hook can be provided by using FRIDAs built in support for `CModule`, powered by TinyCC.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const cm = new CModule(`
|
||||
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <gum/gumdefs.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void afl_persistent_hook(GumCpuContext *regs, uint8_t *input_buf,
|
||||
uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy((void *)regs->rdi, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
regs->rsi = input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
`,
|
||||
{
|
||||
memcpy: Module.getExportByName(null, 'memcpy')
|
||||
});
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentHook(cm.afl_persistent_hook);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Advanced Persistence
|
||||
Consider the following target code...
|
||||
```c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <stdbool.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (len < 1) return;
|
||||
buf[len] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// we support three input cases
|
||||
if (buf[0] == '0')
|
||||
printf("Looks like a zero to me!\n");
|
||||
else if (buf[0] == '1')
|
||||
printf("Pretty sure that is a one!\n");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Neither one or zero? How quaint!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int run(char *file) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = -1;
|
||||
off_t len;
|
||||
char * buf = NULL;
|
||||
size_t n_read;
|
||||
int result = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
do {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "Running: %s\n", file);
|
||||
|
||||
fd = open(file, O_RDONLY);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("open");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
|
||||
if (len < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("lseek (SEEK_END)");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) != 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("lseek (SEEK_SET)");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf = malloc(len);
|
||||
if (buf == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("malloc");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n_read = read(fd, buf, len);
|
||||
if (n_read != len) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("read");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "Running: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", file, n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(buf, len);
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "Done: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", file, n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
result = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
} while (false);
|
||||
|
||||
if (buf != NULL) { free(buf); }
|
||||
|
||||
if (fd != -1) { close(fd); }
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void slow() {
|
||||
|
||||
usleep(100000);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc != 2) { return 1; }
|
||||
slow();
|
||||
return run(argv[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
FRIDA mode supports the replacement of any function, with an implementation
|
||||
generated by CModule. This allows for a bespoke harness to be written as
|
||||
follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
const slow = DebugSymbol.fromName('slow').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`slow: ${slow}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput = DebugSymbol.fromName('LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput: ${LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const cm = new CModule(`
|
||||
|
||||
extern unsigned char * __afl_fuzz_ptr;
|
||||
extern unsigned int * __afl_fuzz_len;
|
||||
extern void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len);
|
||||
|
||||
void slow(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(__afl_fuzz_ptr, *__afl_fuzz_len);
|
||||
}
|
||||
`,
|
||||
{
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput: LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput,
|
||||
__afl_fuzz_ptr: Afl.getAflFuzzPtr(),
|
||||
__afl_fuzz_len: Afl.getAflFuzzLen()
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(cm.slow);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(cm.slow);
|
||||
Afl.setInMemoryFuzzing();
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(slow, cm.slow);
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we replace the function `slow` with our own code. This code is then
|
||||
selected as the entry point as well as the persistent loop address.
|
||||
|
||||
**WARNING** There are two key limitations in replacing a function in this way:
|
||||
- The function which is to be replaced must not be `main` this is because this
|
||||
is the point at which FRIDA mode is initialized and at the point the the JS has
|
||||
been run, the start of the `main` function has already been instrumented and
|
||||
cached.
|
||||
- The replacement function must not call itself. e.g. in this example we
|
||||
couldn't replace `LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput` and call itself.
|
||||
|
||||
# Patching
|
||||
Consider the [following](test/js/test2.c) test code...
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - a trivial program to test the build
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019-2020 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <stdbool.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
const uint32_t crc32_tab[] = {
|
||||
0x00000000, 0x77073096, 0xee0e612c, 0x990951ba, 0x076dc419, 0x706af48f,
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
0xb40bbe37, 0xc30c8ea1, 0x5a05df1b, 0x2d02ef8d
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t
|
||||
crc32(const void *buf, size_t size)
|
||||
{
|
||||
const uint8_t *p = buf;
|
||||
uint32_t crc;
|
||||
crc = ~0U;
|
||||
while (size--)
|
||||
crc = crc32_tab[(crc ^ *p++) & 0xFF] ^ (crc >> 8);
|
||||
return crc ^ ~0U;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Don't you hate those contrived examples which CRC their data. We can use
|
||||
* FRIDA to patch this function out and always return success. Otherwise, we
|
||||
* could change it to actually correct the checksum.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int crc32_check (char * buf, int len) {
|
||||
if (len < sizeof(uint32_t)) { return 0; }
|
||||
uint32_t expected = *(uint32_t *)&buf[len - sizeof(uint32_t)];
|
||||
uint32_t calculated = crc32(buf, len - sizeof(uint32_t));
|
||||
return expected == calculated;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* So you've found a really boring bug in an earlier campaign which results in
|
||||
* a NULL dereference or something like that. That bug can get in the way,
|
||||
* causing the persistent loop to exit whenever it is triggered, and can also
|
||||
* cloud your output unnecessarily. Again, we can use FRIDA to patch it out.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void some_boring_bug(char c) {
|
||||
switch (c) {
|
||||
case 'A'...'Z':
|
||||
case 'a'...'z':
|
||||
__builtin_trap();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!crc32_check(buf, len)) return;
|
||||
|
||||
some_boring_bug(buf[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
if (buf[0] == '0') {
|
||||
printf("Looks like a zero to me!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (buf[0] == '1') {
|
||||
printf("Pretty sure that is a one!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (buf[0] == '2') {
|
||||
if (buf[1] == '3') {
|
||||
if (buf[2] == '4') {
|
||||
printf("Oh we, weren't expecting that!");
|
||||
__builtin_trap();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Neither one or zero? How quaint!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = -1;
|
||||
off_t len;
|
||||
char * buf = NULL;
|
||||
size_t n_read;
|
||||
int result = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc != 2) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Running: %s\n", argv[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
|
||||
if (len < 0) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) != 0) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
buf = malloc(len);
|
||||
if (buf == NULL) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
n_read = read(fd, buf, len);
|
||||
if (n_read != len) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Running: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", argv[1], n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(buf, len);
|
||||
printf("Done: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", argv[1], n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are a couple of obstacles with our target application. Unlike when fuzzing
|
||||
source code, though, we can't simply edit it and recompile it. The following
|
||||
script shows how we can use the normal functionality of FRIDA to modify any
|
||||
troublesome behaviour.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
const main = DebugSymbol.fromName('main').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`main: ${main}`);
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(main);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(main);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentCount(10000000);
|
||||
|
||||
const crc32_check = DebugSymbol.fromName('crc32_check').address;
|
||||
const crc32_replacement = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(buf, len) => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`len: ${len}`);
|
||||
if (len < 4) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
},
|
||||
'int',
|
||||
['pointer', 'int']);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(crc32_check, crc32_replacement);
|
||||
|
||||
const some_boring_bug = DebugSymbol.fromName('some_boring_bug').address
|
||||
const boring_replacement = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(c) => { },
|
||||
'void',
|
||||
['char']);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(some_boring_bug, boring_replacement);
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Advanced Patching
|
||||
Consider the following code fragment...
|
||||
```c
|
||||
extern void some_boring_bug2(char c);
|
||||
|
||||
__asm__ (
|
||||
".text \n"
|
||||
"some_boring_bug2: \n"
|
||||
".global some_boring_bug2 \n"
|
||||
".type some_boring_bug2, @function \n"
|
||||
"mov %edi, %eax \n"
|
||||
"cmp $0xb4, %al \n"
|
||||
"jne ok \n"
|
||||
"ud2 \n"
|
||||
"ok: \n"
|
||||
"ret \n");
|
||||
|
||||
void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len) {
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
some_boring_bug2(buf[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rather than using FRIDAs `Interceptor.replace` or `Interceptor.attach` APIs, it
|
||||
is possible to apply much more fine grained modification to the target
|
||||
application by means of using the Stalker APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
The following code locates the function of interest and patches out the UD2
|
||||
instruction signifying a crash.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
/* Modify the instructions */
|
||||
const some_boring_bug2 = DebugSymbol.fromName('some_boring_bug2').address
|
||||
const pid = Memory.alloc(4);
|
||||
pid.writeInt(Process.id);
|
||||
|
||||
const cm = new CModule(`
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <gum/gumstalker.h>
|
||||
|
||||
typedef int pid_t;
|
||||
|
||||
#define STDERR_FILENO 2
|
||||
#define BORING2_LEN 10
|
||||
|
||||
extern int dprintf(int fd, const char *format, ...);
|
||||
extern void some_boring_bug2(char c);
|
||||
extern pid_t getpid(void);
|
||||
extern pid_t pid;
|
||||
|
||||
gboolean js_stalker_callback(const cs_insn *insn, gboolean begin,
|
||||
gboolean excluded, GumStalkerOutput *output)
|
||||
{
|
||||
pid_t my_pid = getpid();
|
||||
GumX86Writer *cw = output->writer.x86;
|
||||
|
||||
if (GUM_ADDRESS(insn->address) < GUM_ADDRESS(some_boring_bug2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
return TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (GUM_ADDRESS(insn->address) >=
|
||||
GUM_ADDRESS(some_boring_bug2) + BORING2_LEN) {
|
||||
|
||||
return TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (my_pid == pid) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (begin) {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "\n> 0x%016lX: %s %s\n", insn->address,
|
||||
insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, " 0x%016lX: %s %s\n", insn->address,
|
||||
insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (insn->id == X86_INS_UD2) {
|
||||
|
||||
gum_x86_writer_put_nop(cw);
|
||||
return FALSE;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
return TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
`,
|
||||
{
|
||||
dprintf: Module.getExportByName(null, 'dprintf'),
|
||||
getpid: Module.getExportByName(null, 'getpid'),
|
||||
some_boring_bug2: some_boring_bug2,
|
||||
pid: pid
|
||||
});
|
||||
Afl.setStalkerCallback(cm.js_stalker_callback)
|
||||
Afl.setStdErr("/tmp/stderr.txt");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you will more likely want to find the
|
||||
patch address by using:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const module = Process.getModuleByName('target.exe');
|
||||
/* Hardcoded offset within the target image */
|
||||
const address = module.base.add(0xdeadface);
|
||||
```
|
||||
OR
|
||||
```
|
||||
const address = DebugSymbol.fromName("my_function").address.add(0xdeadface);
|
||||
```
|
||||
OR
|
||||
```
|
||||
const address = Module.getExportByName(null, "my_function").add(0xdeadface);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The function `js_stalker_callback` should return `TRUE` if the original
|
||||
instruction should be emitted in the instrumented code, or `FALSE` otherwise.
|
||||
In the example above, we can see it is replaced with a `NOP`.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, note that the same callback will be called when compiling instrumented
|
||||
code both in the child of the forkserver (as it is executed) and also in the
|
||||
parent of the forserver (when prefetching is enabled) so that it can be
|
||||
inherited by the next forked child. It is **VERY** important that the same
|
||||
instructions be generated in both the parent and the child, or if prefetching is
|
||||
disabled that the same instructions are generated every time the block is
|
||||
compiled. Failure to do so will likely lead to bugs which are incredibly
|
||||
difficult to diagnose. The code above only prints the instructions when running
|
||||
in the parent process (the one provided by `Process.id` when the JS script is
|
||||
executed).
|
||||
|
||||
# OSX
|
||||
Note that the JavaScript debug symbol api for OSX makes use of the
|
||||
`CoreSymbolication` APIs and as such the `CoreFoundation` module must be loaded
|
||||
into the target to make use of it. This can be done by setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
AFL_PRELOAD=/System/Library/Frameworks/CoreFoundation.framework/CoreFoundation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It should be noted that `CoreSymbolication` API may take a while to initialize
|
||||
and build its caches. For this reason, it may be nescessary to also increase the
|
||||
value of the `-t` flag passed to `afl-fuzz`.
|
||||
|
||||
# API
|
||||
```js
|
||||
class Afl {
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Field containing the `Module` object for `afl-frida-trace.so` (the FRIDA mode
|
||||
* implementation).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static module: Module = Process.getModuleByName("afl-frida-trace.so");
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting a value in `AFL_FRIDA_EXCLUDE_RANGES`,
|
||||
* it takes as arguments a `NativePointer` and a `number`. It can be
|
||||
* called multiple times to exclude several ranges.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static addExcludedRange(addressess: NativePointer, size: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddExcludeRange(addressess, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting a value in `AFL_FRIDA_INST_RANGES`,
|
||||
* it takes as arguments a `NativePointer` and a `number`. It can be
|
||||
* called multiple times to include several ranges.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static addIncludedRange(addressess: NativePointer, size: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddIncludeRange(addressess, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This must always be called at the end of your script. This lets
|
||||
* FRIDA mode know that your configuration is finished and that
|
||||
* execution has reached the end of your script. Failure to call
|
||||
* this will result in a fatal error.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static done(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiDone();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This function can be called within your script to cause FRIDA
|
||||
* mode to trigger a fatal error. This is useful if for example you
|
||||
* discover a problem you weren't expecting and want everything to
|
||||
* stop. The user will need to enable `AFL_DEBUG_CHILD=1` to view
|
||||
* this error message.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static error(msg: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(msg);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiError(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to provide access to `__afl_fuzz_ptr`, which contains the length of
|
||||
* fuzzing data when using in-memory test case fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static getAflFuzzLen(): NativePointer {
|
||||
|
||||
return Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_fuzz_len");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to provide access to `__afl_fuzz_ptr`, which contains the fuzzing
|
||||
* data when using in-memory test case fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static getAflFuzzPtr(): NativePointer {
|
||||
|
||||
return Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_fuzz_ptr");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Print a message to the STDOUT. This should be preferred to
|
||||
* FRIDA's `console.log` since FRIDA will queue it's log messages.
|
||||
* If `console.log` is used in a callback in particular, then there
|
||||
* may no longer be a thread running to service this queue.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static print(msg: string): void {
|
||||
const STDOUT_FILENO = 2;
|
||||
const log = `${msg}\n`;
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(log);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiWrite(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, log.length);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_DEBUG_MAPS`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setDebugMaps(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetDebugMaps();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This has the same effect as setting `AFL_ENTRYPOINT`, but has the
|
||||
* convenience of allowing you to use FRIDAs APIs to determine the
|
||||
* address you would like to configure, rather than having to grep
|
||||
* the output of `readelf` or something similarly ugly. This
|
||||
* function should be called with a `NativePointer` as its
|
||||
* argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setEntryPoint(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetEntryPoint(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to enable in-memory test cases for fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInMemoryFuzzing(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAflSharedMemFuzzing.writeInt(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_DEBUG_FILE`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentDebugFile(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentDebugFile(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentEnableTracing(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTrace();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_INST_LIBS`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentLibraries(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentLibraries();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_OPTIMIZE`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentNoOptimize(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentNoOptimize();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE_UNIQUE`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentTracingUnique(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTraceUnique();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR`, again a
|
||||
* `NativePointer` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentAddress(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentAddress(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_CNT`, a
|
||||
* `number` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentCount(count: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentCount(count);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_DEBUG`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentDebug(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentDebug();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR`. This function takes a NativePointer as an
|
||||
* argument. See above for examples of use.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentHook(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentHook(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_RET`, again a
|
||||
* `NativePointer` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentReturn(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentReturn(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_PREFETCH`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPrefetchDisable(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPrefetchDisable();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Set a function to be called for each instruction which is instrumented
|
||||
* by AFL FRIDA mode.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStalkerCallback(callback: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStalkerCallback(callback);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_FILE`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStatsFile(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsFile(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_INTERVAL`. This function takes a `number` as an
|
||||
* argument
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStatsInterval(interval: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsInterval(interval);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_TRANSITIONS`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStatsTransitions(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsTransitions();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_OUTPUT_STDERR`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStdErr(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdErr(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_OUTPUT_STDOUT`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStdOut(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdOut(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
35
frida_mode/frida.map
Normal file
35
frida_mode/frida.map
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
global:
|
||||
__afl_fuzz_len;
|
||||
__afl_fuzz_ptr;
|
||||
__afl_sharedmem_fuzzing;
|
||||
afl_frida_start;
|
||||
js_api_add_exclude_range;
|
||||
js_api_add_include_range;
|
||||
js_api_done;
|
||||
js_api_error;
|
||||
js_api_set_debug_maps;
|
||||
js_api_set_entrypoint;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_debug_file;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_jit;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_libraries;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_no_optimize;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_seed;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_trace;
|
||||
js_api_set_instrument_trace_unique;
|
||||
js_api_set_persistent_address;
|
||||
js_api_set_persistent_count;
|
||||
js_api_set_persistent_debug;
|
||||
js_api_set_persistent_hook;
|
||||
js_api_set_persistent_return;
|
||||
js_api_set_prefetch_disable;
|
||||
js_api_set_stalker_callback;
|
||||
js_api_set_stats_file;
|
||||
js_api_set_stats_interval;
|
||||
js_api_set_stats_transitions;
|
||||
js_api_set_stderr;
|
||||
js_api_set_stdout;
|
||||
|
||||
local:
|
||||
*;
|
||||
};
|
||||
64
frida_mode/hook/frida_hook.c
Normal file
64
frida_mode/hook/frida_hook.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Modify this file to set the right registers with the fuzz input and length.
|
||||
* It is a good idea to check input_buf_len to be not larger than the
|
||||
* destination buffer!
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__x86_64__)
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void afl_persistent_hook(
|
||||
GumCpuContext *regs, uint8_t *input_buf, uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
// do a length check matching the target!
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy((void *)regs->rdi, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
regs->rsi = input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__i386__)
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void afl_persistent_hook(
|
||||
GumCpuContext *regs, uint8_t *input_buf, uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
// do a length check matching the target!
|
||||
|
||||
void **esp = (void **)regs->esp;
|
||||
void * arg1 = esp[0];
|
||||
void **arg2 = &esp[1];
|
||||
memcpy(arg1, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
*arg2 = (void *)input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__aarch64__)
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void afl_persistent_hook(
|
||||
GumCpuContext *regs, uint8_t *input_buf, uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
// do a length check matching the target!
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy((void *)regs->x[0], input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
regs->x[1] = input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#pragma error "Unsupported architecture"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) int afl_persistent_hook_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
// 1 for shared memory input (faster), 0 for normal input (you have to use
|
||||
// read(), input_buf will be NULL)
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
195
frida_mode/hook/qemu_hook.c
Normal file
195
frida_mode/hook/qemu_hook.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__x86_64__)
|
||||
|
||||
struct x86_64_regs {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t rax, rbx, rcx, rdx, rdi, rsi, rbp, r8, r9, r10, r11, r12, r13, r14,
|
||||
r15;
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t rip;
|
||||
uint64_t pc;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t rsp;
|
||||
uint64_t sp;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t rflags;
|
||||
uint64_t flags;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t zmm_regs[32][64];
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
void afl_persistent_hook(struct x86_64_regs *regs, uint64_t guest_base,
|
||||
uint8_t *input_buf, uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
(void)guest_base; /* unused */
|
||||
memcpy((void *)regs->rdi, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
regs->rsi = input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__i386__)
|
||||
|
||||
struct x86_regs {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t eax, ebx, ecx, edx, edi, esi, ebp;
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t eip;
|
||||
uint32_t pc;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t esp;
|
||||
uint32_t sp;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t eflags;
|
||||
uint32_t flags;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t xmm_regs[8][16];
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
void afl_persistent_hook(struct x86_regs *regs, uint64_t guest_base,
|
||||
uint8_t *input_buf, uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
(void)guest_base; /* unused */
|
||||
void **esp = (void **)regs->esp;
|
||||
void * arg1 = esp[1];
|
||||
void **arg2 = &esp[2];
|
||||
memcpy(arg1, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
*arg2 = (void *)input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
#elif defined(__aarch64__)
|
||||
|
||||
struct arm64_regs {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10;
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x11;
|
||||
uint32_t fp_32;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x12;
|
||||
uint32_t ip_32;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x13;
|
||||
uint32_t sp_32;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x14;
|
||||
uint32_t lr_32;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x15;
|
||||
uint32_t pc_32;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x16;
|
||||
uint64_t ip0;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x17;
|
||||
uint64_t ip1;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x18, x19, x20, x21, x22, x23, x24, x25, x26, x27, x28;
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x29;
|
||||
uint64_t fp;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x30;
|
||||
uint64_t lr;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
union {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t x31;
|
||||
uint64_t sp;
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// the zero register is not saved here ofc
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t pc;
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t cpsr;
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t vfp_zregs[32][16 * 16];
|
||||
uint8_t vfp_pregs[17][32];
|
||||
uint32_t vfp_xregs[16];
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
void afl_persistent_hook(struct arm64_regs *regs, uint64_t guest_base,
|
||||
uint8_t *input_buf, uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
(void)guest_base; /* unused */
|
||||
memcpy((void *)regs->x0, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
regs->x1 = input_buf_len;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#pragma error "Unsupported architecture"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
int afl_persistent_hook_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
// 1 for shared memory input (faster), 0 for normal input (you have to use
|
||||
// read(), input_buf will be NULL)
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
11
frida_mode/include/intercept.h
Normal file
11
frida_mode/include/intercept.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
#ifndef _INTERCEPTOR_H
|
||||
#define _INTERCEPTOR_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void intercept_hook(void *address, gpointer replacement, gpointer user_data);
|
||||
void intercept_unhook(void *address);
|
||||
void intercept_unhook_self(void);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
26
frida_mode/include/js.h
Normal file
26
frida_mode/include/js.h
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
#ifndef _JS_H
|
||||
#define _JS_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
typedef gboolean (*js_api_stalker_callback_t)(const cs_insn *insn,
|
||||
gboolean begin, gboolean excluded,
|
||||
GumStalkerOutput *output);
|
||||
|
||||
extern unsigned char api_js[];
|
||||
extern unsigned int api_js_len;
|
||||
|
||||
extern gboolean js_done;
|
||||
extern js_api_stalker_callback_t js_user_callback;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Frida Mode */
|
||||
|
||||
void js_config(void);
|
||||
|
||||
void js_start(void);
|
||||
|
||||
gboolean js_stalker_callback(const cs_insn *insn, gboolean begin,
|
||||
gboolean excluded, GumStalkerOutput *output);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
24
frida_mode/many-linux/Dockerfile
Normal file
24
frida_mode/many-linux/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
FROM fridadotre/manylinux-x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
COPY realpath /bin/realpath
|
||||
RUN chmod +x /bin/realpath
|
||||
|
||||
RUN yum -y install xz
|
||||
RUN yum -y install vim-common
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus.git
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /AFLplusplus
|
||||
RUN mkdir -p /AFLplusplus/frida_mode/build/frida/
|
||||
RUN curl -L -o /AFLplusplus/frida_mode/build/frida/frida-gumjs-devkit-15.0.0-linux-x86_64.tar.xz "https://github.com/frida/frida/releases/download/15.0.0/frida-gumjs-devkit-15.0.0-linux-x86_64.tar.xz"
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /AFLplusplus
|
||||
RUN git checkout dev
|
||||
WORKDIR /AFLplusplus/frida_mode
|
||||
ENV CFLAGS="\
|
||||
-DADDR_NO_RANDOMIZE=0x0040000 \
|
||||
-Wno-implicit-function-declaration \
|
||||
"
|
||||
ENV CXX=$CC
|
||||
RUN make
|
||||
21
frida_mode/many-linux/GNUmakefile
Normal file
21
frida_mode/many-linux/GNUmakefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
PWD:=$(shell pwd)/
|
||||
BUILD_DIR:=$(PWD)build/
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all clean shell
|
||||
|
||||
all: | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
docker build --tag many-afl-frida .
|
||||
docker run --rm \
|
||||
-v $(PWD)build/:/export \
|
||||
many-afl-frida \
|
||||
cp /AFLplusplus/afl-frida-trace.so /export
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR):
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
docker images --filter 'dangling=true' -q --no-trunc | xargs -L1 docker rmi --force
|
||||
|
||||
shell:
|
||||
docker run -ti --rm many-afl-frida /bin/bash
|
||||
9
frida_mode/many-linux/Makefile
Normal file
9
frida_mode/many-linux/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
all:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake all || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@gmake clean
|
||||
|
||||
shell:
|
||||
@gmake shell
|
||||
8
frida_mode/many-linux/README.md
Normal file
8
frida_mode/many-linux/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
# many-linux
|
||||
|
||||
This folder contains a Docker image to allow the building of
|
||||
`afl-frida-trace.so` using the `many-linux` docker image. This docker image is
|
||||
based on CentOS Linux 5. By building `afl-frida-trace.so` for such an old
|
||||
version of Linux, given the strong backward compatibility of Linux, this should
|
||||
work on the majority of Linux environments. This may be useful for targetting
|
||||
Linux distributions other than your development environment.
|
||||
2
frida_mode/many-linux/realpath
Normal file
2
frida_mode/many-linux/realpath
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
readlink -f -- "$@"
|
||||
28
frida_mode/src/asan/asan_arm32.c
Normal file
28
frida_mode/src/asan/asan_arm32.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "asan.h"
|
||||
#include "util.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__arm__)
|
||||
void asan_instrument(const cs_insn *instr, GumStalkerIterator *iterator) {
|
||||
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(instr);
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(iterator);
|
||||
if (asan_initialized) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("ASAN mode not supported on this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void asan_arch_init(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("ASAN mode not supported on this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
19
frida_mode/src/cmplog/cmplog_arm32.c
Normal file
19
frida_mode/src/cmplog/cmplog_arm32.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "frida_cmplog.h"
|
||||
#include "util.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__arm__)
|
||||
void cmplog_instrument(const cs_insn *instr, GumStalkerIterator *iterator) {
|
||||
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(instr);
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(iterator);
|
||||
if (__afl_cmp_map == NULL) { return; }
|
||||
FATAL("CMPLOG mode not supported on this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
16
frida_mode/src/ctx/ctx_arm32.c
Normal file
16
frida_mode/src/ctx/ctx_arm32.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "ctx.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__arm__)
|
||||
|
||||
gsize ctx_read_reg(GumArmCpuContext *ctx, arm_reg reg) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("ctx_read_reg unimplemented for this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
303
frida_mode/src/ctx/ctx_arm64.c
Normal file
303
frida_mode/src/ctx/ctx_arm64.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,303 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "ctx.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__aarch64__)
|
||||
|
||||
#define ARM64_REG_8(LABEL, REG) \
|
||||
case LABEL: { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
return REG & GUM_INT8_MASK; \
|
||||
\
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define ARM64_REG_16(LABEL, REG) \
|
||||
case LABEL: { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
return (REG & GUM_INT16_MASK); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define ARM64_REG_32(LABEL, REG) \
|
||||
case LABEL: { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
return (REG & GUM_INT32_MASK); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define ARM64_REG_64(LABEL, REG) \
|
||||
case LABEL: { \
|
||||
\
|
||||
return (REG); \
|
||||
\
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gsize ctx_read_reg(GumArm64CpuContext *ctx, arm64_reg reg) {
|
||||
|
||||
switch (reg) {
|
||||
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_WZR:
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_XZR:
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B0, ctx->x[0])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B1, ctx->x[1])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B2, ctx->x[2])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B3, ctx->x[3])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B4, ctx->x[4])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B5, ctx->x[5])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B6, ctx->x[6])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B7, ctx->x[7])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B8, ctx->x[8])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B9, ctx->x[9])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B10, ctx->x[10])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B11, ctx->x[11])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B12, ctx->x[12])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B13, ctx->x[13])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B14, ctx->x[14])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B15, ctx->x[15])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B16, ctx->x[16])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B17, ctx->x[17])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B18, ctx->x[18])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B19, ctx->x[19])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B20, ctx->x[20])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B21, ctx->x[21])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B22, ctx->x[22])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B23, ctx->x[23])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B24, ctx->x[24])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B25, ctx->x[25])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B26, ctx->x[26])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B27, ctx->x[27])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B28, ctx->x[28])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B29, ctx->fp)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B30, ctx->lr)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_8(ARM64_REG_B31, ctx->sp)
|
||||
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H0, ctx->x[0])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H1, ctx->x[1])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H2, ctx->x[2])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H3, ctx->x[3])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H4, ctx->x[4])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H5, ctx->x[5])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H6, ctx->x[6])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H7, ctx->x[7])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H8, ctx->x[8])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H9, ctx->x[9])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H10, ctx->x[10])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H11, ctx->x[11])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H12, ctx->x[12])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H13, ctx->x[13])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H14, ctx->x[14])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H15, ctx->x[15])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H16, ctx->x[16])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H17, ctx->x[17])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H18, ctx->x[18])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H19, ctx->x[19])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H20, ctx->x[20])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H21, ctx->x[21])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H22, ctx->x[22])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H23, ctx->x[23])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H24, ctx->x[24])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H25, ctx->x[25])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H26, ctx->x[26])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H27, ctx->x[27])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H28, ctx->x[28])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H29, ctx->fp)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H30, ctx->lr)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_16(ARM64_REG_H31, ctx->sp)
|
||||
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W0, ctx->x[0])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W1, ctx->x[1])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W2, ctx->x[2])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W3, ctx->x[3])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W4, ctx->x[4])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W5, ctx->x[5])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W6, ctx->x[6])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W7, ctx->x[7])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W8, ctx->x[8])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W9, ctx->x[9])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W10, ctx->x[10])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W11, ctx->x[11])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W12, ctx->x[12])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W13, ctx->x[13])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W14, ctx->x[14])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W15, ctx->x[15])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W16, ctx->x[16])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W17, ctx->x[17])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W18, ctx->x[18])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W19, ctx->x[19])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W20, ctx->x[20])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W21, ctx->x[21])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W22, ctx->x[22])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W23, ctx->x[23])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W24, ctx->x[24])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W25, ctx->x[25])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W26, ctx->x[26])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W27, ctx->x[27])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W28, ctx->x[28])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W29, ctx->fp)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_32(ARM64_REG_W30, ctx->lr)
|
||||
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X0, ctx->x[0])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X1, ctx->x[1])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X2, ctx->x[2])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X3, ctx->x[3])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X4, ctx->x[4])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X5, ctx->x[5])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X6, ctx->x[6])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X7, ctx->x[7])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X8, ctx->x[8])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X9, ctx->x[9])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X10, ctx->x[10])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X11, ctx->x[11])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X12, ctx->x[12])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X13, ctx->x[13])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X14, ctx->x[14])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X15, ctx->x[15])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X16, ctx->x[16])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X17, ctx->x[17])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X18, ctx->x[18])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X19, ctx->x[19])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X20, ctx->x[20])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X21, ctx->x[21])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X22, ctx->x[22])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X23, ctx->x[23])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X24, ctx->x[24])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X25, ctx->x[25])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X26, ctx->x[26])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X27, ctx->x[27])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_X28, ctx->x[28])
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_FP, ctx->fp)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_LR, ctx->lr)
|
||||
ARM64_REG_64(ARM64_REG_SP, ctx->sp)
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
FATAL("Failed to read register: %d", reg);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
size_t ctx_get_size(const cs_insn *instr, cs_arm64_op *operand) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t num_registers;
|
||||
uint8_t count_byte;
|
||||
char vas_digit;
|
||||
size_t mnemonic_len;
|
||||
|
||||
switch (instr->id) {
|
||||
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_STP:
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_STXP:
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_STNP:
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_STLXP:
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_LDP:
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_LDXP:
|
||||
case ARM64_INS_LDNP:
|
||||
num_registers = 2;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
num_registers = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
mnemonic_len = strlen(instr->mnemonic);
|
||||
if (mnemonic_len == 0) { FATAL("No mnemonic found"); };
|
||||
|
||||
char last = instr->mnemonic[mnemonic_len - 1];
|
||||
switch (last) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 'b':
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
case 'h':
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
case 'w':
|
||||
return 4 * num_registers;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (operand->vas == ARM64_VAS_INVALID) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (operand->type == ARM64_OP_REG) {
|
||||
|
||||
switch (operand->reg) {
|
||||
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_WZR:
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_WSP:
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_W0 ... ARM64_REG_W30:
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_S0 ... ARM64_REG_S31:
|
||||
return 4 * num_registers;
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_D0 ... ARM64_REG_D31:
|
||||
return 8 * num_registers;
|
||||
case ARM64_REG_Q0 ... ARM64_REG_Q31:
|
||||
return 16;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return 8 * num_registers;
|
||||
;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 8 * num_registers;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (g_str_has_prefix(instr->mnemonic, "st") ||
|
||||
g_str_has_prefix(instr->mnemonic, "ld")) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (mnemonic_len < 3) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("VAS Mnemonic too short: %s\n", instr->mnemonic);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
vas_digit = instr->mnemonic[2];
|
||||
if (vas_digit < '0' || vas_digit > '9') {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("VAS Mnemonic digit out of range: %s\n", instr->mnemonic);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
count_byte = vas_digit - '0';
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
count_byte = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch (operand->vas) {
|
||||
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_1B:
|
||||
return 1 * count_byte;
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_1H:
|
||||
return 2 * count_byte;
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_4B:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_1S:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_1D:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_2H:
|
||||
return 4 * count_byte;
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_8B:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_4H:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_2S:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_2D:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_1Q:
|
||||
return 8 * count_byte;
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_8H:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_4S:
|
||||
case ARM64_VAS_16B:
|
||||
return 16 * count_byte;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
FATAL("Unexpected VAS type: %s %d", instr->mnemonic, operand->vas);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
35
frida_mode/src/intercept.c
Normal file
35
frida_mode/src/intercept.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "intercept.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void intercept_hook(void *address, gpointer replacement, gpointer user_data) {
|
||||
|
||||
GumInterceptor *interceptor = gum_interceptor_obtain();
|
||||
gum_interceptor_begin_transaction(interceptor);
|
||||
GumReplaceReturn ret =
|
||||
gum_interceptor_replace(interceptor, address, replacement, user_data);
|
||||
if (ret != GUM_REPLACE_OK) { FATAL("gum_interceptor_attach: %d", ret); }
|
||||
gum_interceptor_end_transaction(interceptor);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void intercept_unhook(void *address) {
|
||||
|
||||
GumInterceptor *interceptor = gum_interceptor_obtain();
|
||||
|
||||
gum_interceptor_begin_transaction(interceptor);
|
||||
gum_interceptor_revert(interceptor, address);
|
||||
gum_interceptor_end_transaction(interceptor);
|
||||
gum_interceptor_flush(interceptor);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void intercept_unhook_self(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
GumInvocationContext *ctx = gum_interceptor_get_current_invocation();
|
||||
intercept_unhook(ctx->function);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
257
frida_mode/src/js/api.js
Normal file
257
frida_mode/src/js/api.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
|
||||
"use strict";
|
||||
class Afl {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting a value in `AFL_FRIDA_EXCLUDE_RANGES`,
|
||||
* it takes as arguments a `NativePointer` and a `number`. It can be
|
||||
* called multiple times to exclude several ranges.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static addExcludedRange(addressess, size) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddExcludeRange(addressess, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting a value in `AFL_FRIDA_INST_RANGES`,
|
||||
* it takes as arguments a `NativePointer` and a `number`. It can be
|
||||
* called multiple times to include several ranges.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static addIncludedRange(addressess, size) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddIncludeRange(addressess, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This must always be called at the end of your script. This lets
|
||||
* FRIDA mode know that your configuration is finished and that
|
||||
* execution has reached the end of your script. Failure to call
|
||||
* this will result in a fatal error.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static done() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiDone();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This function can be called within your script to cause FRIDA
|
||||
* mode to trigger a fatal error. This is useful if for example you
|
||||
* discover a problem you weren't expecting and want everything to
|
||||
* stop. The user will need to enable `AFL_DEBUG_CHILD=1` to view
|
||||
* this error message.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static error(msg) {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(msg);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiError(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to provide access to `__afl_fuzz_ptr`, which contains the length of
|
||||
* fuzzing data when using in-memory test case fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static getAflFuzzLen() {
|
||||
return Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_fuzz_len");
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to provide access to `__afl_fuzz_ptr`, which contains the fuzzing
|
||||
* data when using in-memory test case fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static getAflFuzzPtr() {
|
||||
return Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_fuzz_ptr");
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Print a message to the STDOUT. This should be preferred to
|
||||
* FRIDA's `console.log` since FRIDA will queue it's log messages.
|
||||
* If `console.log` is used in a callback in particular, then there
|
||||
* may no longer be a thread running to service this queue.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static print(msg) {
|
||||
const STDOUT_FILENO = 2;
|
||||
const log = `${msg}\n`;
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(log);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiWrite(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, log.length);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_DEBUG_MAPS`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setDebugMaps() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetDebugMaps();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This has the same effect as setting `AFL_ENTRYPOINT`, but has the
|
||||
* convenience of allowing you to use FRIDAs APIs to determine the
|
||||
* address you would like to configure, rather than having to grep
|
||||
* the output of `readelf` or something similarly ugly. This
|
||||
* function should be called with a `NativePointer` as its
|
||||
* argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setEntryPoint(address) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetEntryPoint(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to enable in-memory test cases for fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInMemoryFuzzing() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAflSharedMemFuzzing.writeInt(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_DEBUG_FILE`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentDebugFile(file) {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentDebugFile(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentEnableTracing() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTrace();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_JIT`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentJit() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentJit();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_INST_LIBS`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentLibraries() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentLibraries();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_OPTIMIZE`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentNoOptimize() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentNoOptimize();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_SEED`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentSeed(seed) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentSeed(seed);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE_UNIQUE`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setInstrumentTracingUnique() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTraceUnique();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR`, again a
|
||||
* `NativePointer` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setPersistentAddress(address) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentAddress(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_CNT`, a
|
||||
* `number` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setPersistentCount(count) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentCount(count);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_DEBUG`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setPersistentDebug() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentDebug();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR`. This function takes a NativePointer as an
|
||||
* argument. See above for examples of use.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setPersistentHook(address) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentHook(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_RET`, again a
|
||||
* `NativePointer` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setPersistentReturn(address) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentReturn(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_PREFETCH`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setPrefetchDisable() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPrefetchDisable();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Set a function to be called for each instruction which is instrumented
|
||||
* by AFL FRIDA mode.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setStalkerCallback(callback) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStalkerCallback(callback);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_FILE`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setStatsFile(file) {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsFile(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_INTERVAL`. This function takes a `number` as an
|
||||
* argument
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setStatsInterval(interval) {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsInterval(interval);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_TRANSITIONS`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setStatsTransitions() {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsTransitions();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_OUTPUT_STDERR`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setStdErr(file) {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdErr(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_OUTPUT_STDOUT`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static setStdOut(file) {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdOut(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
static jsApiGetFunction(name, retType, argTypes) {
|
||||
const addr = Afl.module.getExportByName(name);
|
||||
return new NativeFunction(addr, retType, argTypes);
|
||||
}
|
||||
static jsApiGetSymbol(name) {
|
||||
return Afl.module.getExportByName(name);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Field containing the `Module` object for `afl-frida-trace.so` (the FRIDA mode
|
||||
* implementation).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
Afl.module = Process.getModuleByName("afl-frida-trace.so");
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddExcludeRange = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_add_exclude_range", "void", ["pointer", "size_t"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddIncludeRange = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_add_include_range", "void", ["pointer", "size_t"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAflSharedMemFuzzing = Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_sharedmem_fuzzing");
|
||||
Afl.jsApiDone = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_done", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiError = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_error", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetDebugMaps = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_debug_maps", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetEntryPoint = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_entrypoint", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentDebugFile = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_debug_file", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentJit = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_jit", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentLibraries = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_libraries", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentNoOptimize = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_no_optimize", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentSeed = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_seed", "void", ["uint64"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTrace = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_trace", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTraceUnique = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_instrument_trace_unique", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentAddress = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_persistent_address", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentCount = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_persistent_count", "void", ["uint64"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentDebug = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_persistent_debug", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentHook = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_persistent_hook", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentReturn = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_persistent_return", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPrefetchDisable = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_prefetch_disable", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStalkerCallback = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_stalker_callback", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsFile = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_stats_file", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsInterval = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_stats_interval", "void", ["uint64"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsTransitions = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_stats_transitions", "void", []);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdErr = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_stderr", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdOut = Afl.jsApiGetFunction("js_api_set_stdout", "void", ["pointer"]);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiWrite = new NativeFunction(
|
||||
/* tslint:disable-next-line:no-null-keyword */
|
||||
Module.getExportByName(null, "write"), "int", ["int", "pointer", "int"]);
|
||||
142
frida_mode/src/js/js.c
Normal file
142
frida_mode/src/js/js.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "js.h"
|
||||
#include "util.h"
|
||||
|
||||
static char * js_script = NULL;
|
||||
gboolean js_done = FALSE;
|
||||
js_api_stalker_callback_t js_user_callback = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
static gchar * filename = "afl.js";
|
||||
static gchar * contents;
|
||||
static GumScriptBackend * backend;
|
||||
static GCancellable * cancellable = NULL;
|
||||
static GError * error = NULL;
|
||||
static GumScript * script;
|
||||
static GumScriptScheduler *scheduler;
|
||||
static GMainContext * context;
|
||||
static GMainLoop * main_loop;
|
||||
|
||||
static void js_msg(GumScript *script, const gchar *message, GBytes *data,
|
||||
gpointer user_data) {
|
||||
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(script);
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(data);
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(user_data);
|
||||
OKF("%s", message);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void js_config(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
js_script = getenv("AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static gchar *js_get_script() {
|
||||
|
||||
gsize length;
|
||||
if (js_script != NULL) { filename = js_script; }
|
||||
|
||||
filename = g_canonicalize_filename(filename, g_get_current_dir());
|
||||
|
||||
if (!g_file_get_contents(filename, &contents, &length, NULL)) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (js_script == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Could not load script file: %s", filename);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
OKF("Loaded AFL script: %s, %" G_GSIZE_MODIFIER "d bytes", filename,
|
||||
length);
|
||||
|
||||
gchar *source = g_malloc0(api_js_len + length + 1);
|
||||
memcpy(source, api_js, api_js_len);
|
||||
memcpy(&source[api_js_len], contents, length);
|
||||
|
||||
return source;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void js_print_script(gchar *source) {
|
||||
|
||||
gchar **split = g_strsplit(source, "\n", 0);
|
||||
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; split[i] != NULL; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
OKF("%3" G_GSIZE_MODIFIER "d. %s", i + 1, split[i]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
g_strfreev(split);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void load_cb(GObject *source_object, GAsyncResult *result,
|
||||
gpointer user_data) {
|
||||
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(source_object);
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(user_data);
|
||||
gum_script_load_finish(script, result);
|
||||
if (error != NULL) { FATAL("Failed to load script - %s", error->message); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void create_cb(GObject *source_object, GAsyncResult *result,
|
||||
gpointer user_data) {
|
||||
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(source_object);
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(user_data);
|
||||
script = gum_script_backend_create_finish(backend, result, &error);
|
||||
if (error != NULL) { FATAL("Failed to create script: %s", error->message); }
|
||||
|
||||
gum_script_set_message_handler(script, js_msg, NULL, NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
gum_script_load(script, cancellable, load_cb, NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void js_start(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
gchar *source = js_get_script();
|
||||
if (source == NULL) { return; }
|
||||
js_print_script(source);
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = gum_script_backend_get_scheduler();
|
||||
gum_script_scheduler_disable_background_thread(scheduler);
|
||||
|
||||
backend = gum_script_backend_obtain_qjs();
|
||||
|
||||
context = gum_script_scheduler_get_js_context(scheduler);
|
||||
main_loop = g_main_loop_new(context, true);
|
||||
g_main_context_push_thread_default(context);
|
||||
|
||||
gum_script_backend_create(backend, "example", source, cancellable, create_cb,
|
||||
&error);
|
||||
|
||||
while (g_main_context_pending(context))
|
||||
g_main_context_iteration(context, FALSE);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!js_done) { FATAL("Script didn't call Afl.done()"); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gboolean js_stalker_callback(const cs_insn *insn, gboolean begin,
|
||||
gboolean excluded, GumStalkerOutput *output) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (js_user_callback == NULL) { return TRUE; }
|
||||
return js_user_callback(insn, begin, excluded, output);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
201
frida_mode/src/js/js_api.c
Normal file
201
frida_mode/src/js/js_api.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "entry.h"
|
||||
#include "instrument.h"
|
||||
#include "js.h"
|
||||
#include "output.h"
|
||||
#include "persistent.h"
|
||||
#include "prefetch.h"
|
||||
#include "ranges.h"
|
||||
#include "stats.h"
|
||||
#include "util.h"
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_done() {
|
||||
|
||||
js_done = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_error(char *msg) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("%s", msg);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_entrypoint(
|
||||
void *address) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (address == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
js_api_error("js_api_set_entrypoint called with NULL");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
entry_point = GPOINTER_TO_SIZE(address);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_persistent_address(
|
||||
void *address) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (address == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
js_api_error("js_api_set_persistent_address called with NULL");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
persistent_start = GPOINTER_TO_SIZE(address);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_persistent_return(
|
||||
void *address) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (address == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
js_api_error("js_api_set_persistent_return called with NULL");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
persistent_ret = GPOINTER_TO_SIZE(address);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_persistent_count(
|
||||
uint64_t count) {
|
||||
|
||||
persistent_count = count;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_persistent_debug() {
|
||||
|
||||
persistent_debug = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_debug_maps() {
|
||||
|
||||
ranges_debug_maps = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_add_include_range(
|
||||
void *address, gsize size) {
|
||||
|
||||
GumMemoryRange range = {.base_address = GUM_ADDRESS(address), .size = size};
|
||||
ranges_add_include(&range);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_add_exclude_range(
|
||||
void *address, gsize size) {
|
||||
|
||||
GumMemoryRange range = {.base_address = GUM_ADDRESS(address), .size = size};
|
||||
ranges_add_exclude(&range);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_jit() {
|
||||
|
||||
ranges_inst_jit = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_libraries() {
|
||||
|
||||
ranges_inst_libs = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_debug_file(
|
||||
char *path) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrument_debug_filename = g_strdup(path);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_prefetch_disable(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
prefetch_enable = FALSE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_no_optimize(
|
||||
void) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrument_optimize = FALSE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_seed(
|
||||
guint64 seed) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrument_use_fixed_seed = TRUE;
|
||||
instrument_fixed_seed = seed;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_trace(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrument_tracing = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_instrument_trace_unique(
|
||||
void) {
|
||||
|
||||
instrument_unique = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_stdout(char *file) {
|
||||
|
||||
output_stdout = g_strdup(file);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_stderr(char *file) {
|
||||
|
||||
output_stderr = g_strdup(file);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_stats_file(char *file) {
|
||||
|
||||
stats_filename = g_strdup(file);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_stats_interval(
|
||||
uint64_t interval) {
|
||||
|
||||
stats_interval = interval;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_stats_transitions() {
|
||||
|
||||
stats_transitions = TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_persistent_hook(
|
||||
void *address) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (address == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
js_api_error("js_api_set_persistent_hook called with NULL");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
persistent_hook = address;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void js_api_set_stalker_callback(
|
||||
const js_api_stalker_callback_t callback) {
|
||||
|
||||
js_user_callback = callback;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
36
frida_mode/src/stats/stats_arm32.c
Normal file
36
frida_mode/src/stats/stats_arm32.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
#include "frida-gumjs.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "debug.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "stats.h"
|
||||
#include "util.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__arm__)
|
||||
|
||||
gboolean stats_is_supported_arch(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
return FALSE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
size_t stats_data_size_arch(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Stats not supported on this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void stats_write_arch(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Stats not supported on this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void stats_collect_arch(const cs_insn *instr) {
|
||||
|
||||
UNUSED_PARAMETER(instr);
|
||||
FATAL("Stats not supported on this architecture");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
166
frida_mode/test/jpeg/GNUmakefile
Normal file
166
frida_mode/test/jpeg/GNUmakefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
PWD:=$(shell pwd)/
|
||||
ROOT:=$(shell realpath $(PWD)../../..)/
|
||||
BUILD_DIR:=$(PWD)build/
|
||||
|
||||
AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ=$(ROOT)frida_mode/build/frida_hook.so
|
||||
|
||||
LIBJPEG_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)libjpeg/
|
||||
HARNESS_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)harness/
|
||||
JPEGTEST_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)jpegtest/
|
||||
|
||||
LIBJPEG_URL:=https://github.com/libjpeg-turbo/libjpeg-turbo.git
|
||||
LIBJPEG_DIR:=$(LIBJPEG_BUILD_DIR)libjpeg/
|
||||
LIBJPEG_CONFIGURE:=$(LIBJPEG_DIR)configure.ac
|
||||
LIBJPEG_MAKEFILE:=$(LIBJPEG_DIR)Makefile
|
||||
LIBJPEG_LIB:=$(LIBJPEG_DIR).libs/libturbojpeg.a
|
||||
|
||||
HARNESS_FILE:=$(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR)StandaloneFuzzTargetMain.c
|
||||
HARNESS_OBJ:=$(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR)StandaloneFuzzTargetMain.o
|
||||
HARNESS_URL:="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus/stable/utils/aflpp_driver/aflpp_qemu_driver.c"
|
||||
|
||||
JPEGTEST_FILE:=$(JPEGTEST_BUILD_DIR)target.cc
|
||||
JPEGTEST_OBJ:=$(JPEGTEST_BUILD_DIR)target.o
|
||||
JPEGTEST_URL:="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google/fuzzbench/master/benchmarks/libjpeg-turbo-07-2017/libjpeg_turbo_fuzzer.cc"
|
||||
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lpthread
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_BIN:=$(BUILD_DIR)test
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "Darwin"
|
||||
TEST_BIN_LDFLAGS:=-undefined dynamic_lookup -Wl,-no_pie
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_DATA_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)in/
|
||||
TEST_DATA_FILE:=$(TEST_DATA_DIR)default_seed
|
||||
|
||||
FRIDA_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)frida-out
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef ARCH
|
||||
|
||||
ARCH=$(shell uname -m)
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
ARCH:=arm64
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "i686"
|
||||
ARCH:=x86
|
||||
endif
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
GET_SYMBOL_ADDR:=$(ROOT)frida_mode/util/get_symbol_addr.sh
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x0000aaaaaaaaa000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86_64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x0000555555554000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x56555000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all clean frida hook
|
||||
|
||||
all: $(TEST_BIN)
|
||||
make -C $(ROOT)frida_mode/
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
CXXFLAGS="-m32" LDFLAGS="-m32" ARCH="x86" make all
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR):
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
######### HARNESS ########
|
||||
$(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(HARNESS_FILE): | $(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(HARNESS_URL)
|
||||
|
||||
$(HARNESS_OBJ): $(HARNESS_FILE)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CXXFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) $(TEST_BIN_LDFLAGS) -o $@ -c $<
|
||||
|
||||
######### JPEGTEST ########
|
||||
|
||||
$(JPEGTEST_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(JPEGTEST_FILE): | $(JPEGTEST_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(JPEGTEST_URL)
|
||||
|
||||
$(JPEGTEST_OBJ): $(JPEGTEST_FILE) | $(LIBJPEG_MAKEFILE)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -std=c++11 -I $(LIBJPEG_DIR) -o $@ -c $<
|
||||
|
||||
######### LIBJPEG ########
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBJPEG_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBJPEG_CONFIGURE): $(LIBJPEG_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
git clone $(LIBJPEG_URL) $(LIBJPEG_DIR)
|
||||
cd $(LIBJPEG_DIR) && git checkout b0971e47d76fdb81270e93bbf11ff5558073350d
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBJPEG_MAKEFILE): $(LIBJPEG_CONFIGURE)
|
||||
cd $(LIBJPEG_DIR) && autoreconf -fiv
|
||||
cd $(LIBJPEG_DIR) && ./configure
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBJPEG_LIB): $(LIBJPEG_MAKEFILE)
|
||||
make -C $(LIBJPEG_DIR) -j $(shell nproc)
|
||||
|
||||
######### TEST ########
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN): $(HARNESS_OBJ) $(JPEGTEST_OBJ) $(LIBJPEG_LIB)
|
||||
$(CXX) \
|
||||
$(CFLAGS) \
|
||||
-o $@ \
|
||||
$(HARNESS_OBJ) $(JPEGTEST_OBJ) $(LIBJPEG_LIB) \
|
||||
-lz \
|
||||
$(LDFLAGS) \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN_LDFLAGS) \
|
||||
|
||||
########## DUMMY #######
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_DATA_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_DATA_FILE): | $(TEST_DATA_DIR)
|
||||
echo "hi" > $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
|
||||
###### TEST DATA #######
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
frida: $(TEST_BIN) $(AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_DEBUG_CHILD=1 \
|
||||
AFL_DISABLE_TRIM=1 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_CNT=1000000 \
|
||||
AFL_I_DONT_CARE_ABOUT_MISSING_CRASHES=1 \
|
||||
AFL_NO_AFFINITY=1 \
|
||||
X__AFL_NO_UI=1 \
|
||||
AFL_PATH=/out \
|
||||
AFL_SHUFFLE_QUEUE=1 \
|
||||
AFL_SKIP_CPUFREQ=1 \
|
||||
AFL_SKIP_CRASHES=1 \
|
||||
AFL_TESTCACHE_SIZE=2 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_HOOK=$(AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
AFL_ENTRYPOINT=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-i $(TEST_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-m none \
|
||||
-t 1000+ \
|
||||
-d \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-c 0\
|
||||
-V 30 \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN) 2147483647
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
gdb \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment LD_PRELOAD=$(ROOT)afl-frida-trace.so' \
|
||||
--ex 'set disassembly-flavor intel' \
|
||||
--args $(TEST_BIN) $(TEST_DATA_DIR)basn0g01.jpeg
|
||||
16
frida_mode/test/jpeg/Makefile
Normal file
16
frida_mode/test/jpeg/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
all:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake all || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake 32 || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@gmake clean
|
||||
|
||||
frida:
|
||||
@gmake frida
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
@gmake debug
|
||||
36
frida_mode/test/jpeg/get_symbol_addr.py
Executable file
36
frida_mode/test/jpeg/get_symbol_addr.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python3
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
from elftools.elf.elffile import ELFFile
|
||||
|
||||
def process_file(file, symbol, base):
|
||||
with open(file, 'rb') as f:
|
||||
elf = ELFFile(f)
|
||||
symtab = elf.get_section_by_name('.symtab')
|
||||
mains = symtab.get_symbol_by_name(symbol)
|
||||
if len(mains) != 1:
|
||||
print ("Failed to find main")
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
|
||||
main_addr = mains[0]['st_value']
|
||||
main = base + main_addr
|
||||
print ("0x%016x" % main)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def hex_value(x):
|
||||
return int(x, 16)
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Process some integers.')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('-f', '--file', dest='file', type=str,
|
||||
help='elf file name', required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('-s', '--symbol', dest='symbol', type=str,
|
||||
help='symbol name', required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('-b', '--base', dest='base', type=hex_value,
|
||||
help='elf base address', required=True)
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
return process_file (args.file, args.symbol, args.base)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
ret = main()
|
||||
exit(ret)
|
||||
98
frida_mode/test/js/GNUmakefile
Normal file
98
frida_mode/test/js/GNUmakefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
PWD:=$(shell pwd)/
|
||||
ROOT:=$(shell realpath $(PWD)../../..)/
|
||||
BUILD_DIR:=$(PWD)build/
|
||||
TEST_DATA_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)in/
|
||||
TEST_DATA_FILE:=$(TEST_DATA_DIR)in
|
||||
|
||||
TESTINSTBIN:=$(BUILD_DIR)test
|
||||
TESTINSTSRC:=$(PWD)test.c
|
||||
|
||||
TESTINSTBIN2:=$(BUILD_DIR)test2
|
||||
TESTINSTSRC2:=$(PWD)test2.c
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)qemu-out
|
||||
FRIDA_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)frida-out
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "Darwin"
|
||||
AFL_PRELOAD=/System/Library/Frameworks/CoreFoundation.framework/CoreFoundation
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all 32 clean qemu frida debug
|
||||
|
||||
all: $(TESTINSTBIN) $(TESTINSTBIN2)
|
||||
make -C $(ROOT)frida_mode/
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
CFLAGS="-m32" LDFLAGS="-m32" ARCH="x86" make all
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR):
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_DATA_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_DATA_FILE): | $(TEST_DATA_DIR)
|
||||
echo -n "000" > $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(TESTINSTBIN): $(TESTINSTSRC) | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@ $<
|
||||
|
||||
$(TESTINSTBIN2): $(TESTINSTSRC2) | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@ $<
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_entry: $(TESTINSTBIN) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_PRELOAD=$(AFL_PRELOAD) \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT=entry.js \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-i $(TEST_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-t 10000+ \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TESTINSTBIN) @@
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_replace: $(TESTINSTBIN) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT=replace.js \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-i $(TEST_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TESTINSTBIN) @@
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_patch: $(TESTINSTBIN2) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT=patch.js \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-i $(TEST_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TESTINSTBIN2) @@
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_stalker: $(TESTINSTBIN2) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT=stalker.js \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-i $(TEST_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TESTINSTBIN2) @@
|
||||
|
||||
debug: $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
gdb \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment LD_PRELOAD=$(ROOT)afl-frida-trace.so' \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT=entry.js' \
|
||||
--ex 'set disassembly-flavor intel' \
|
||||
--args $(TESTINSTBIN) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
|
||||
strace: $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
LD_PRELOAD=$(ROOT)afl-frida-trace.so \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_JS_SCRIPT=entry.js \
|
||||
strace $(TESTINSTBIN) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
25
frida_mode/test/js/Makefile
Normal file
25
frida_mode/test/js/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
all:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake all || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake 32 || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@gmake clean
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_entry:
|
||||
@gmake frida_js_entry
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_replace:
|
||||
@gmake frida_js_replace
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_patch:
|
||||
@gmake frida_js_patch
|
||||
|
||||
frida_js_stalker:
|
||||
@gmake frida_js_stalker
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
@gmake debug
|
||||
26
frida_mode/test/js/entry.js
Normal file
26
frida_mode/test/js/entry.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print(`PID: ${Process.id}`);
|
||||
|
||||
new ModuleMap().values().forEach(m => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`${m.base}-${m.base.add(m.size)} ${m.name}`);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const name = Process.enumerateModules()[0].name;
|
||||
Afl.print(`Name: ${name}`);
|
||||
|
||||
if (name === 'test') {
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print('Searching...\n');
|
||||
const entry_point = DebugSymbol.fromName('run');
|
||||
Afl.print(`entry_point: ${entry_point}`);
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(entry_point.address);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
34
frida_mode/test/js/patch.js
Normal file
34
frida_mode/test/js/patch.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
const main = DebugSymbol.fromName('main').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`main: ${main}`);
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(main);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(main);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentCount(10000000);
|
||||
|
||||
const crc32_check = DebugSymbol.fromName('crc32_check').address;
|
||||
const crc32_replacement = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(buf, len) => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`len: ${len}`);
|
||||
if (len < 4) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
},
|
||||
'int',
|
||||
['pointer', 'int']);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(crc32_check, crc32_replacement);
|
||||
|
||||
const some_boring_bug = DebugSymbol.fromName('some_boring_bug').address
|
||||
const boring_replacement = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(c) => { },
|
||||
'void',
|
||||
['char']);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(some_boring_bug, boring_replacement);
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
43
frida_mode/test/js/replace.js
Normal file
43
frida_mode/test/js/replace.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print(`PID: ${Process.id}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const name = Process.enumerateModules()[0].name;
|
||||
Afl.print(`Name: ${name}`);
|
||||
|
||||
new ModuleMap().values().forEach(m => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`${m.base}-${m.base.add(m.size)} ${m.name}`);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const slow = DebugSymbol.fromName('slow').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`slow: ${slow}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput = DebugSymbol.fromName('LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput: ${LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const cm = new CModule(`
|
||||
|
||||
extern unsigned char * __afl_fuzz_ptr;
|
||||
extern unsigned int * __afl_fuzz_len;
|
||||
extern void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len);
|
||||
|
||||
void slow(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(__afl_fuzz_ptr, *__afl_fuzz_len);
|
||||
}
|
||||
`,
|
||||
{
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput: LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput,
|
||||
__afl_fuzz_ptr: Afl.getAflFuzzPtr(),
|
||||
__afl_fuzz_len: Afl.getAflFuzzLen()
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(cm.slow);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(cm.slow);
|
||||
Afl.setInMemoryFuzzing();
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(slow, cm.slow);
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
109
frida_mode/test/js/stalker.js
Normal file
109
frida_mode/test/js/stalker.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
const main = DebugSymbol.fromName('main').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`main: ${main}`);
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(main);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(main);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentCount(10000000);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Replace CRC-32 check */
|
||||
const crc32_check = DebugSymbol.fromName('crc32_check').address;
|
||||
const crc32_replacement = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(buf, len) => {
|
||||
if (len < 4) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
},
|
||||
'int',
|
||||
['pointer', 'int']);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(crc32_check, crc32_replacement);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Patch out the first boring bug */
|
||||
const some_boring_bug = DebugSymbol.fromName('some_boring_bug').address
|
||||
const boring_replacement = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(c) => { },
|
||||
'void',
|
||||
['char']);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(some_boring_bug, boring_replacement);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Modify the instructions */
|
||||
const some_boring_bug2 = DebugSymbol.fromName('some_boring_bug2').address
|
||||
const pid = Memory.alloc(4);
|
||||
pid.writeInt(Process.id);
|
||||
|
||||
const cm = new CModule(`
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <gum/gumstalker.h>
|
||||
|
||||
typedef int pid_t;
|
||||
|
||||
#define STDERR_FILENO 2
|
||||
#define BORING2_LEN 10
|
||||
|
||||
extern int dprintf(int fd, const char *format, ...);
|
||||
extern void some_boring_bug2(char c);
|
||||
extern pid_t getpid(void);
|
||||
extern pid_t pid;
|
||||
|
||||
gboolean js_stalker_callback(const cs_insn *insn, gboolean begin,
|
||||
gboolean excluded, GumStalkerOutput *output)
|
||||
{
|
||||
pid_t my_pid = getpid();
|
||||
GumX86Writer *cw = output->writer.x86;
|
||||
|
||||
if (GUM_ADDRESS(insn->address) < GUM_ADDRESS(some_boring_bug2)) {
|
||||
|
||||
return TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (GUM_ADDRESS(insn->address) >=
|
||||
GUM_ADDRESS(some_boring_bug2) + BORING2_LEN) {
|
||||
|
||||
return TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (my_pid == pid) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (begin) {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "\n> 0x%016lX: %s %s\n", insn->address,
|
||||
insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, " 0x%016lX: %s %s\n", insn->address,
|
||||
insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (insn->id == X86_INS_UD2) {
|
||||
|
||||
gum_x86_writer_put_nop(cw);
|
||||
return FALSE;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
return TRUE;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
`,
|
||||
{
|
||||
dprintf: Module.getExportByName(null, 'dprintf'),
|
||||
getpid: Module.getExportByName(null, 'getpid'),
|
||||
some_boring_bug2: some_boring_bug2,
|
||||
pid: pid
|
||||
});
|
||||
Afl.setStalkerCallback(cm.js_stalker_callback)
|
||||
Afl.setStdErr("/tmp/stderr.txt");
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
115
frida_mode/test/js/test.c
Normal file
115
frida_mode/test/js/test.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - a trivial program to test the build
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019-2020 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <stdbool.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (len < 1) return;
|
||||
buf[len] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// we support three input cases
|
||||
if (buf[0] == '0')
|
||||
printf("Looks like a zero to me!\n");
|
||||
else if (buf[0] == '1')
|
||||
printf("Pretty sure that is a one!\n");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Neither one or zero? How quaint!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int run(char *file) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = -1;
|
||||
off_t len;
|
||||
char * buf = NULL;
|
||||
size_t n_read;
|
||||
int result = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
do {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "Running: %s\n", file);
|
||||
|
||||
fd = open(file, O_RDONLY);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("open");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
|
||||
if (len < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("lseek (SEEK_END)");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) != 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("lseek (SEEK_SET)");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf = malloc(len);
|
||||
if (buf == NULL) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("malloc");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n_read = read(fd, buf, len);
|
||||
if (n_read != len) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror("read");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "Running: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", file, n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(buf, len);
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "Done: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", file, n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
result = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
} while (false);
|
||||
|
||||
if (buf != NULL) { free(buf); }
|
||||
|
||||
if (fd != -1) { close(fd); }
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void slow() {
|
||||
|
||||
usleep(100000);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc != 2) { return 1; }
|
||||
slow();
|
||||
return run(argv[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
177
frida_mode/test/js/test2.c
Normal file
177
frida_mode/test/js/test2.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - a trivial program to test the build
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019-2020 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <stdarg.h>
|
||||
#include <stdbool.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#define IGNORED_RETURN(x) (void)!(x)
|
||||
|
||||
const uint32_t crc32_tab[] = {
|
||||
0x00000000, 0x77073096, 0xee0e612c, 0x990951ba, 0x076dc419, 0x706af48f,
|
||||
0xe963a535, 0x9e6495a3, 0x0edb8832, 0x79dcb8a4, 0xe0d5e91e, 0x97d2d988,
|
||||
0x09b64c2b, 0x7eb17cbd, 0xe7b82d07, 0x90bf1d91, 0x1db71064, 0x6ab020f2,
|
||||
0xf3b97148, 0x84be41de, 0x1adad47d, 0x6ddde4eb, 0xf4d4b551, 0x83d385c7,
|
||||
0x136c9856, 0x646ba8c0, 0xfd62f97a, 0x8a65c9ec, 0x14015c4f, 0x63066cd9,
|
||||
0xfa0f3d63, 0x8d080df5, 0x3b6e20c8, 0x4c69105e, 0xd56041e4, 0xa2677172,
|
||||
0x3c03e4d1, 0x4b04d447, 0xd20d85fd, 0xa50ab56b, 0x35b5a8fa, 0x42b2986c,
|
||||
0xdbbbc9d6, 0xacbcf940, 0x32d86ce3, 0x45df5c75, 0xdcd60dcf, 0xabd13d59,
|
||||
0x26d930ac, 0x51de003a, 0xc8d75180, 0xbfd06116, 0x21b4f4b5, 0x56b3c423,
|
||||
0xcfba9599, 0xb8bda50f, 0x2802b89e, 0x5f058808, 0xc60cd9b2, 0xb10be924,
|
||||
0x2f6f7c87, 0x58684c11, 0xc1611dab, 0xb6662d3d, 0x76dc4190, 0x01db7106,
|
||||
0x98d220bc, 0xefd5102a, 0x71b18589, 0x06b6b51f, 0x9fbfe4a5, 0xe8b8d433,
|
||||
0x7807c9a2, 0x0f00f934, 0x9609a88e, 0xe10e9818, 0x7f6a0dbb, 0x086d3d2d,
|
||||
0x91646c97, 0xe6635c01, 0x6b6b51f4, 0x1c6c6162, 0x856530d8, 0xf262004e,
|
||||
0x6c0695ed, 0x1b01a57b, 0x8208f4c1, 0xf50fc457, 0x65b0d9c6, 0x12b7e950,
|
||||
0x8bbeb8ea, 0xfcb9887c, 0x62dd1ddf, 0x15da2d49, 0x8cd37cf3, 0xfbd44c65,
|
||||
0x4db26158, 0x3ab551ce, 0xa3bc0074, 0xd4bb30e2, 0x4adfa541, 0x3dd895d7,
|
||||
0xa4d1c46d, 0xd3d6f4fb, 0x4369e96a, 0x346ed9fc, 0xad678846, 0xda60b8d0,
|
||||
0x44042d73, 0x33031de5, 0xaa0a4c5f, 0xdd0d7cc9, 0x5005713c, 0x270241aa,
|
||||
0xbe0b1010, 0xc90c2086, 0x5768b525, 0x206f85b3, 0xb966d409, 0xce61e49f,
|
||||
0x5edef90e, 0x29d9c998, 0xb0d09822, 0xc7d7a8b4, 0x59b33d17, 0x2eb40d81,
|
||||
0xb7bd5c3b, 0xc0ba6cad, 0xedb88320, 0x9abfb3b6, 0x03b6e20c, 0x74b1d29a,
|
||||
0xead54739, 0x9dd277af, 0x04db2615, 0x73dc1683, 0xe3630b12, 0x94643b84,
|
||||
0x0d6d6a3e, 0x7a6a5aa8, 0xe40ecf0b, 0x9309ff9d, 0x0a00ae27, 0x7d079eb1,
|
||||
0xf00f9344, 0x8708a3d2, 0x1e01f268, 0x6906c2fe, 0xf762575d, 0x806567cb,
|
||||
0x196c3671, 0x6e6b06e7, 0xfed41b76, 0x89d32be0, 0x10da7a5a, 0x67dd4acc,
|
||||
0xf9b9df6f, 0x8ebeeff9, 0x17b7be43, 0x60b08ed5, 0xd6d6a3e8, 0xa1d1937e,
|
||||
0x38d8c2c4, 0x4fdff252, 0xd1bb67f1, 0xa6bc5767, 0x3fb506dd, 0x48b2364b,
|
||||
0xd80d2bda, 0xaf0a1b4c, 0x36034af6, 0x41047a60, 0xdf60efc3, 0xa867df55,
|
||||
0x316e8eef, 0x4669be79, 0xcb61b38c, 0xbc66831a, 0x256fd2a0, 0x5268e236,
|
||||
0xcc0c7795, 0xbb0b4703, 0x220216b9, 0x5505262f, 0xc5ba3bbe, 0xb2bd0b28,
|
||||
0x2bb45a92, 0x5cb36a04, 0xc2d7ffa7, 0xb5d0cf31, 0x2cd99e8b, 0x5bdeae1d,
|
||||
0x9b64c2b0, 0xec63f226, 0x756aa39c, 0x026d930a, 0x9c0906a9, 0xeb0e363f,
|
||||
0x72076785, 0x05005713, 0x95bf4a82, 0xe2b87a14, 0x7bb12bae, 0x0cb61b38,
|
||||
0x92d28e9b, 0xe5d5be0d, 0x7cdcefb7, 0x0bdbdf21, 0x86d3d2d4, 0xf1d4e242,
|
||||
0x68ddb3f8, 0x1fda836e, 0x81be16cd, 0xf6b9265b, 0x6fb077e1, 0x18b74777,
|
||||
0x88085ae6, 0xff0f6a70, 0x66063bca, 0x11010b5c, 0x8f659eff, 0xf862ae69,
|
||||
0x616bffd3, 0x166ccf45, 0xa00ae278, 0xd70dd2ee, 0x4e048354, 0x3903b3c2,
|
||||
0xa7672661, 0xd06016f7, 0x4969474d, 0x3e6e77db, 0xaed16a4a, 0xd9d65adc,
|
||||
0x40df0b66, 0x37d83bf0, 0xa9bcae53, 0xdebb9ec5, 0x47b2cf7f, 0x30b5ffe9,
|
||||
0xbdbdf21c, 0xcabac28a, 0x53b39330, 0x24b4a3a6, 0xbad03605, 0xcdd70693,
|
||||
0x54de5729, 0x23d967bf, 0xb3667a2e, 0xc4614ab8, 0x5d681b02, 0x2a6f2b94,
|
||||
0xb40bbe37, 0xc30c8ea1, 0x5a05df1b, 0x2d02ef8d
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t
|
||||
crc32(const void *buf, size_t size)
|
||||
{
|
||||
const uint8_t *p = buf;
|
||||
uint32_t crc;
|
||||
crc = ~0U;
|
||||
while (size--)
|
||||
crc = crc32_tab[(crc ^ *p++) & 0xFF] ^ (crc >> 8);
|
||||
return crc ^ ~0U;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Don't you hate those contrived examples which CRC their data. We can use
|
||||
* FRIDA to patch this function out and always return success. Otherwise, we
|
||||
* could change it to actually correct the checksum.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int crc32_check (char * buf, int len) {
|
||||
if (len < sizeof(uint32_t)) { return 0; }
|
||||
uint32_t expected = *(uint32_t *)&buf[len - sizeof(uint32_t)];
|
||||
uint32_t calculated = crc32(buf, len - sizeof(uint32_t));
|
||||
return expected == calculated;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* So you've found a really boring bug in an earlier campaign which results in
|
||||
* a NULL dereference or something like that. That bug can get in the way,
|
||||
* causing the persistent loop to exit whenever it is triggered, and can also
|
||||
* cloud your output unnecessarily. Again, we can use FRIDA to patch it out.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void some_boring_bug(char c) {
|
||||
switch (c) {
|
||||
case 'A'...'Z':
|
||||
case 'a'...'z':
|
||||
__builtin_trap();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
extern void some_boring_bug2(char c);
|
||||
|
||||
__asm__ (
|
||||
".text \n"
|
||||
"some_boring_bug2: \n"
|
||||
".global some_boring_bug2 \n"
|
||||
".type some_boring_bug2, @function \n"
|
||||
"mov %edi, %eax \n"
|
||||
"cmp $0xb4, %al \n"
|
||||
"jne ok \n"
|
||||
"ud2 \n"
|
||||
"ok: \n"
|
||||
"ret \n");
|
||||
|
||||
void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(char *buf, int len) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!crc32_check(buf, len)) return;
|
||||
|
||||
some_boring_bug(buf[0]);
|
||||
some_boring_bug2(buf[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
if (buf[0] == '0') {
|
||||
printf("Looks like a zero to me!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (buf[0] == '1') {
|
||||
printf("Pretty sure that is a one!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (buf[0] == '2') {
|
||||
printf("Oh we, weren't expecting that!");
|
||||
__builtin_trap();
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Neither one or zero? How quaint!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = -1;
|
||||
off_t len;
|
||||
char * buf = NULL;
|
||||
size_t n_read;
|
||||
int result = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc != 2) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Running: %s\n", argv[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
|
||||
if (len < 0) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) != 0) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
buf = malloc(len);
|
||||
if (buf == NULL) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
n_read = read(fd, buf, len);
|
||||
if (n_read != len) { return 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Running: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", argv[1], n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(buf, len);
|
||||
printf("Done: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", argv[1], n_read);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
48
frida_mode/test/persistent_ret/test.js
Normal file
48
frida_mode/test/persistent_ret/test.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print(`PID: ${Process.id}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const name = Process.enumerateModules()[0].name;
|
||||
Afl.print(`Name: ${name}`);
|
||||
|
||||
new ModuleMap().values().forEach(m => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`${m.base}-${m.base.add(m.size)} ${m.name}`);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
if (name === 'testinstr') {
|
||||
const persistent_addr = DebugSymbol.fromName('LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`persistent_addr: ${persistent_addr}`);
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(persistent_addr);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(persistent_addr);
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentDebugFile("/dev/stdout");
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentDebug();
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentNoOptimize();
|
||||
Afl.setInstrumentEnableTracing();
|
||||
|
||||
const LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput = new NativeFunction(
|
||||
persistent_addr,
|
||||
'void',
|
||||
['pointer', 'uint64'],
|
||||
{traps: "all"});
|
||||
|
||||
const persistentHook = new NativeCallback(
|
||||
(data, size) => {
|
||||
const input = Afl.aflFuzzPtr.readPointer();
|
||||
const len = Afl.aflFuzzLen.readPointer().readU32();
|
||||
const hd = hexdump(input, {length: len, header: false, ansi: true});
|
||||
Afl.print(`input: ${hd}`);
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(input, len);
|
||||
},
|
||||
'void',
|
||||
['pointer', 'uint64']);
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.aflSharedMemFuzzing.writeInt(1);
|
||||
Interceptor.replace(persistent_addr, persistentHook);
|
||||
Interceptor.flush();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
39
frida_mode/test/png/persistent/hook/cmodule.js
Normal file
39
frida_mode/test/png/persistent/hook/cmodule.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print(`PID: ${Process.id}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const name = Process.enumerateModules()[0].name;
|
||||
Afl.print(`Name: ${name}`);
|
||||
|
||||
new ModuleMap().values().forEach(m => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`${m.base}-${m.base.add(m.size)} ${m.name}`);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const persistent_addr = DebugSymbol.fromName('LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`persistent_addr: ${persistent_addr}`);
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(persistent_addr);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(persistent_addr);
|
||||
|
||||
const cm = new CModule(`
|
||||
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <gum/gumdefs.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void afl_persistent_hook(GumCpuContext *regs, uint8_t *input_buf,
|
||||
uint32_t input_buf_len) {
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy((void *)regs->rdi, input_buf, input_buf_len);
|
||||
regs->rsi = input_buf_len;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
`,
|
||||
{
|
||||
memcpy: Module.getExportByName(null, 'memcpy')
|
||||
});
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentHook(cm.afl_persistent_hook);
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
27
frida_mode/test/png/persistent/hook/load.js
Normal file
27
frida_mode/test/png/persistent/hook/load.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('* AFL FRIDA MODE *');
|
||||
Afl.print('******************');
|
||||
Afl.print('');
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print(`PID: ${Process.id}`);
|
||||
|
||||
const name = Process.enumerateModules()[0].name;
|
||||
Afl.print(`Name: ${name}`);
|
||||
|
||||
new ModuleMap().values().forEach(m => {
|
||||
Afl.print(`${m.base}-${m.base.add(m.size)} ${m.name}`);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const persistent_addr = DebugSymbol.fromName('LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput').address;
|
||||
Afl.print(`persistent_addr: ${persistent_addr}`);
|
||||
Afl.setEntryPoint(persistent_addr);
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentAddress(persistent_addr);
|
||||
|
||||
const path = Afl.module.path;
|
||||
const dir = path.substring(0, path.lastIndexOf("/"));
|
||||
const mod = Module.load(`${dir}/frida_mode/build/frida_hook.so`);
|
||||
const hook = mod.getExportByName('afl_persistent_hook');
|
||||
Afl.setPersistentHook(hook);
|
||||
|
||||
Afl.print("done");
|
||||
Afl.done();
|
||||
166
frida_mode/test/proj4/GNUmakefile
Normal file
166
frida_mode/test/proj4/GNUmakefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
PWD:=$(shell pwd)/
|
||||
ROOT:=$(shell realpath $(PWD)../../..)/
|
||||
BUILD_DIR:=$(PWD)build/
|
||||
|
||||
AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ=$(ROOT)frida_mode/build/frida_hook.so
|
||||
|
||||
LIBPROJ4_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)libproj4/
|
||||
HARNESS_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)harness/
|
||||
PROJ4TEST_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)proj4test/
|
||||
|
||||
LIBPROJ4_URL:=https://github.com/OSGeo/PROJ
|
||||
LIBPROJ4_DIR:=$(LIBPROJ4_BUILD_DIR)libproj4/
|
||||
LIBPROJ4_CONFIGURE:=$(LIBPROJ4_DIR)configure.ac
|
||||
LIBPROJ4_MAKEFILE:=$(LIBPROJ4_DIR)Makefile
|
||||
LIBPROJ4_LIB:=$(LIBPROJ4_DIR)src/.libs/libproj.a
|
||||
|
||||
HARNESS_FILE:=$(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR)StandaloneFuzzTargetMain.c
|
||||
HARNESS_OBJ:=$(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR)StandaloneFuzzTargetMain.o
|
||||
HARNESS_URL:="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus/stable/utils/aflpp_driver/aflpp_qemu_driver.c"
|
||||
|
||||
PROJ4TEST_FILE:=$(PROJ4TEST_BUILD_DIR)target.cc
|
||||
PROJ4TEST_OBJ:=$(PROJ4TEST_BUILD_DIR)target.o
|
||||
PROJ4TEST_URL:="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OSGeo/PROJ/d00501750b210a73f9fb107ac97a683d4e3d8e7a/test/fuzzers/standard_fuzzer.cpp"
|
||||
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lpthread
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_BIN:=$(BUILD_DIR)test
|
||||
ifeq "$(shell uname)" "Darwin"
|
||||
TEST_BIN_LDFLAGS:=-undefined dynamic_lookup -Wl,-no_pie
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_DATA_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)in/
|
||||
TEST_DATA_FILE:=$(TEST_DATA_DIR)default_seed
|
||||
|
||||
FRIDA_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)frida-out
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef ARCH
|
||||
|
||||
ARCH=$(shell uname -m)
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
ARCH:=arm64
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "i686"
|
||||
ARCH:=x86
|
||||
endif
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
GET_SYMBOL_ADDR:=$(ROOT)frida_mode/util/get_symbol_addr.sh
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x0000aaaaaaaaa000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86_64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x0000555555554000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x56555000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all clean frida hook
|
||||
|
||||
all: $(TEST_BIN)
|
||||
make -C $(ROOT)frida_mode/
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
CXXFLAGS="-m32" LDFLAGS="-m32" ARCH="x86" make all
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR):
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
######### HARNESS ########
|
||||
$(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(HARNESS_FILE): | $(HARNESS_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(HARNESS_URL)
|
||||
|
||||
$(HARNESS_OBJ): $(HARNESS_FILE)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CXXFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@ -c $<
|
||||
|
||||
######### PROJ4TEST ########
|
||||
|
||||
$(PROJ4TEST_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(PROJ4TEST_FILE): | $(PROJ4TEST_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
wget -O $@ $(PROJ4TEST_URL)
|
||||
|
||||
$(PROJ4TEST_OBJ): $(PROJ4TEST_FILE) | $(LIBPROJ4_MAKEFILE)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -std=c++11 -I $(LIBPROJ4_DIR)src/ -o $@ -c $<
|
||||
|
||||
######### LIBPROJ4 ########
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBPROJ4_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBPROJ4_CONFIGURE): $(LIBPROJ4_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
git clone $(LIBPROJ4_URL) $(LIBPROJ4_DIR)
|
||||
cd $(LIBPROJ4_DIR) && git checkout d00501750b210a73f9fb107ac97a683d4e3d8e7a
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBPROJ4_MAKEFILE): $(LIBPROJ4_CONFIGURE)
|
||||
cd $(LIBPROJ4_DIR) && ./autogen.sh
|
||||
cd $(LIBPROJ4_DIR) && ./configure
|
||||
|
||||
$(LIBPROJ4_LIB): $(LIBPROJ4_MAKEFILE)
|
||||
make -C $(LIBPROJ4_DIR) -j $(shell nproc)
|
||||
|
||||
######### TEST ########
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN): $(HARNESS_OBJ) $(PROJ4TEST_OBJ) $(LIBPROJ4_LIB)
|
||||
$(CXX) \
|
||||
$(CFLAGS) \
|
||||
-o $@ \
|
||||
$(HARNESS_OBJ) $(PROJ4TEST_OBJ) $(LIBPROJ4_LIB) \
|
||||
-lz \
|
||||
$(LDFLAGS) \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN_LDFLAGS) \
|
||||
|
||||
########## DUMMY #######
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_DATA_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_DATA_FILE): | $(TEST_DATA_DIR)
|
||||
echo "hi" > $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
|
||||
###### TEST DATA #######
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
frida: $(TEST_BIN) $(AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) $(TEST_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_DEBUG_CHILD=1 \
|
||||
AFL_DISABLE_TRIM=1 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_CNT=1000000 \
|
||||
AFL_I_DONT_CARE_ABOUT_MISSING_CRASHES=1 \
|
||||
AFL_NO_AFFINITY=1 \
|
||||
X__AFL_NO_UI=1 \
|
||||
AFL_PATH=/out \
|
||||
AFL_SHUFFLE_QUEUE=1 \
|
||||
AFL_SKIP_CPUFREQ=1 \
|
||||
AFL_SKIP_CRASHES=1 \
|
||||
AFL_TESTCACHE_SIZE=2 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_HOOK=$(AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
AFL_ENTRYPOINT=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-i $(TEST_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-m none \
|
||||
-t 1000+ \
|
||||
-d \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-c 0\
|
||||
-V 30 \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN) 2147483647
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
gdb \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment LD_PRELOAD=$(ROOT)afl-frida-trace.so' \
|
||||
--ex 'set disassembly-flavor intel' \
|
||||
--args $(TEST_BIN) $(TEST_DATA_DIR)basn0g01.proj4
|
||||
17
frida_mode/test/proj4/Makefile
Normal file
17
frida_mode/test/proj4/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
all:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake all || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake 32 || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@gmake clean
|
||||
|
||||
frida:
|
||||
@gmake frida
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
@gmake debug
|
||||
|
||||
36
frida_mode/test/proj4/get_symbol_addr.py
Executable file
36
frida_mode/test/proj4/get_symbol_addr.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python3
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
from elftools.elf.elffile import ELFFile
|
||||
|
||||
def process_file(file, symbol, base):
|
||||
with open(file, 'rb') as f:
|
||||
elf = ELFFile(f)
|
||||
symtab = elf.get_section_by_name('.symtab')
|
||||
mains = symtab.get_symbol_by_name(symbol)
|
||||
if len(mains) != 1:
|
||||
print ("Failed to find main")
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
|
||||
main_addr = mains[0]['st_value']
|
||||
main = base + main_addr
|
||||
print ("0x%016x" % main)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def hex_value(x):
|
||||
return int(x, 16)
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Process some integers.')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('-f', '--file', dest='file', type=str,
|
||||
help='elf file name', required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('-s', '--symbol', dest='symbol', type=str,
|
||||
help='symbol name', required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('-b', '--base', dest='base', type=hex_value,
|
||||
help='elf base address', required=True)
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
return process_file (args.file, args.symbol, args.base)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
ret = main()
|
||||
exit(ret)
|
||||
166
frida_mode/test/sqlite/GNUmakefile
Normal file
166
frida_mode/test/sqlite/GNUmakefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
PWD:=$(shell pwd)/
|
||||
ROOT:=$(shell realpath $(PWD)../../..)/
|
||||
BUILD_DIR:=$(PWD)build/
|
||||
|
||||
SQLITE_BUILD_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)sqlite/
|
||||
SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR:=$(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)src/
|
||||
|
||||
AFLPP_DRIVER:=$(ROOT)utils/aflpp_driver/libAFLQemuDriver.a
|
||||
|
||||
AFLPP_DRIVER:=$(ROOT)utils/aflpp_driver/libAFLQemuDriver.a
|
||||
AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ=$(ROOT)frida_mode/build/frida_hook.so
|
||||
AFLPP_QEMU_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ=$(ROOT)frida_mode/build/qemu_hook.so
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
CFLAGS += -fpermissive
|
||||
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lpthread
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_BIN:=$(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)ossfuzz
|
||||
SQLITE_TEST_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)in/
|
||||
AFLPP_DRIVER_DUMMY_INPUT:=$(SQLITE_TEST_DIR)in
|
||||
|
||||
SQLITE_CFLAGS:= -DSQLITE_MAX_LENGTH=128000000 \
|
||||
-DSQLITE_MAX_SQL_LENGTH=128000000 \
|
||||
-DSQLITE_MAX_MEMORY=25000000 \
|
||||
-DSQLITE_PRINTF_PRECISION_LIMIT=1048576 \
|
||||
-DSQLITE_DEBUG=1 \
|
||||
-DSQLITE_MAX_PAGE_COUNT=16384
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)qemu-out
|
||||
FRIDA_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)frida-out
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef ARCH
|
||||
|
||||
ARCH=$(shell uname -m)
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
ARCH:=arm64
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "i686"
|
||||
ARCH:=x86
|
||||
endif
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
GET_SYMBOL_ADDR:=$(ROOT)frida_mode/util/get_symbol_addr.sh
|
||||
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x4000000000)
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x0000aaaaaaaaa000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86_64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x0000555555554000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(TEST_BIN) LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput 0x56555000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all clean qemu frida hook sqlite
|
||||
|
||||
all: $(TEST_BIN)
|
||||
make -C $(ROOT)frida_mode/
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
CXXFLAGS="-m32" LDFLAGS="-m32" ARCH="x86" make all
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR):
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
########## SQLITE #######
|
||||
|
||||
$(AFLPP_DRIVER):
|
||||
make -C $(ROOT)
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)sqlite3.tar.gz: | $(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
curl 'https://sqlite.org/src/tarball/sqlite.tar.gz?r=c78cbf2e86850cc6' -o $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR): $(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)sqlite3.tar.gz
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
tar xzvf $< --strip-components 1 -C $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_TEST_DIR): | $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
find $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR) -name "*.test" | xargs -L1 -I%% cp -v %% $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)Makefile: | $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)
|
||||
cd $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR) && \
|
||||
CFLAGS="$(SQLITE_CFLAGS)" \
|
||||
ASAN_OPTIONS=detect_leaks=0 \
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR).libs/libsqlite3.so: $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)Makefile
|
||||
CFLAGS="$(SQLITE_CFLAGS)" \
|
||||
ASAN_OPTIONS=detect_leaks=0 \
|
||||
make -C $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR) -j $(shell nproc)
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)sqlite3.o: $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR).libs/libsqlite3.so
|
||||
CFLAGS="$(SQLITE_CFLAGS)" \
|
||||
ASAN_OPTIONS=detect_leaks=0 \
|
||||
make -C $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR) -j $(shell nproc) sqlite3.c
|
||||
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)ossfuzz.o: $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)sqlite3.o
|
||||
$(CC) -I $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR) -c $(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)test/ossfuzz.c -o $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN): $(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)ossfuzz.o
|
||||
$(CXX) -o $(TEST_BIN) \
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_DIR)ossfuzz.o \
|
||||
$(SQLITE_BUILD_SRC_DIR)sqlite3.o \
|
||||
$(AFLPP_DRIVER) \
|
||||
-l pthread \
|
||||
-l dl
|
||||
|
||||
sqlite: $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR) $(TEST_BIN)
|
||||
|
||||
########## DUMMY #######
|
||||
|
||||
$(AFLPP_DRIVER_DUMMY_INPUT): | $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR)
|
||||
truncate -s 1M $@
|
||||
|
||||
###### TEST DATA #######
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
qemu: $(TEST_BIN) $(AFLPP_QEMU_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) $(AFLPP_DRIVER_DUMMY_INPUT) | $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR)
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_CNT=1000000 \
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_HOOK=$(AFLPP_QEMU_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) \
|
||||
AFL_ENTRYPOINT=$(AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_GPR=1 \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-V 30 \
|
||||
-Q \
|
||||
-i $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(QEMU_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN) $(AFLPP_DRIVER_DUMMY_INPUT)
|
||||
|
||||
frida: $(TEST_BIN) $(AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) $(AFLPP_DRIVER_DUMMY_INPUT) | $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR)
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_CNT=1000000 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_HOOK=$(AFLPP_FRIDA_DRIVER_HOOK_OBJ) \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
AFL_ENTRYPOINT=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-V 30 \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-i $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN) $(AFLPP_DRIVER_DUMMY_INPUT)
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
gdb \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment LD_PRELOAD=$(ROOT)afl-frida-trace.so' \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment AFL_QEMU_DRIVER_NO_HOOK=1' \
|
||||
--ex 'set disassembly-flavor intel' \
|
||||
--ex 'b main' \
|
||||
--ex 'r < $(SQLITE_TEST_DIR)0034ecacd5427aafc6b97413da2053b36de5059f' \
|
||||
$(TEST_BIN)
|
||||
17
frida_mode/test/sqlite/Makefile
Normal file
17
frida_mode/test/sqlite/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
all:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake all || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake 32 || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@gmake clean
|
||||
|
||||
frida:
|
||||
@gmake frida
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
@gmake debug
|
||||
|
||||
92
frida_mode/test/unstable/GNUmakefile
Normal file
92
frida_mode/test/unstable/GNUmakefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
PWD:=$(shell pwd)/
|
||||
ROOT:=$(shell realpath $(PWD)../../..)/
|
||||
BUILD_DIR:=$(PWD)build/
|
||||
UNSTABLE_DATA_DIR:=$(BUILD_DIR)in/
|
||||
UNSTABLE_DATA_FILE:=$(UNSTABLE_DATA_DIR)in
|
||||
|
||||
UNSTABLE_BIN:=$(BUILD_DIR)unstable
|
||||
UNSTABLE_SRC:=$(PWD)unstable.c
|
||||
|
||||
QEMU_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)qemu-out
|
||||
FRIDA_OUT:=$(BUILD_DIR)frida-out
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef ARCH
|
||||
|
||||
ARCH=$(shell uname -m)
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
ARCH:=arm64
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "i686"
|
||||
ARCH:=x86
|
||||
endif
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
GET_SYMBOL_ADDR:=$(ROOT)frida_mode/util/get_symbol_addr.sh
|
||||
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(UNSTABLE_BIN) run_test 0x4000000000)
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "aarch64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(UNSTABLE_BIN) run_test 0x0000aaaaaaaaa000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86_64"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(UNSTABLE_BIN) run_test 0x0000555555554000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
ifeq "$(ARCH)" "x86"
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(shell $(GET_SYMBOL_ADDR) $(UNSTABLE_BIN) run_test 0x56555000)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: all 32 clean qemu frida
|
||||
|
||||
all: $(UNSTABLE_BIN)
|
||||
make -C $(ROOT)frida_mode/
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
CFLAGS="-m32" LDFLAGS="-m32" ARCH="x86" make all
|
||||
|
||||
$(BUILD_DIR):
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(UNSTABLE_DATA_DIR): | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
mkdir -p $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(UNSTABLE_DATA_FILE): | $(UNSTABLE_DATA_DIR)
|
||||
echo -n "000" > $@
|
||||
|
||||
$(UNSTABLE_BIN): $(UNSTABLE_SRC) | $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@ $<
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
qemu: $(UNSTABLE_BIN) $(UNSTABLE_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(AFL_QEMU_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-Q \
|
||||
-i $(UNSTABLE_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(QEMU_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(UNSTABLE_BIN) @@
|
||||
|
||||
frida: $(UNSTABLE_BIN) $(UNSTABLE_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
AFL_DEBUG=1 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR=$(AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR) \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE_UNIQUE=1 \
|
||||
AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_OPTIMIZE=1 \
|
||||
$(ROOT)afl-fuzz \
|
||||
-D \
|
||||
-O \
|
||||
-i $(UNSTABLE_DATA_DIR) \
|
||||
-o $(FRIDA_OUT) \
|
||||
-- \
|
||||
$(UNSTABLE_BIN) @@
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
gdb \
|
||||
--ex 'set environment LD_PRELOAD=$(ROOT)afl-frida-trace.so' \
|
||||
--ex 'set disassembly-flavor intel' \
|
||||
--args $(UNSTABLE_BIN) $(UNSTABLE_DATA_FILE)
|
||||
19
frida_mode/test/unstable/Makefile
Normal file
19
frida_mode/test/unstable/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
all:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake all || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
32:
|
||||
@echo trying to use GNU make...
|
||||
@gmake 32 || echo please install GNUmake
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@gmake clean
|
||||
|
||||
qemu:
|
||||
@gmake qemu
|
||||
|
||||
frida:
|
||||
@gmake frida
|
||||
|
||||
debug:
|
||||
@gmake debug
|
||||
67
frida_mode/test/unstable/unstable.c
Normal file
67
frida_mode/test/unstable/unstable.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - a trivial program to test the build
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Originally written by Michal Zalewski
|
||||
Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019-2020 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
#define TESTINSTR_SECTION
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define TESTINSTR_SECTION __attribute__((section(".testinstr")))
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
void LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (size < 1) return;
|
||||
|
||||
int r = rand();
|
||||
if ((r % 2) == 0) {
|
||||
printf ("Hooray all even\n");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
printf ("Hmm that's odd\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// we support three input cases
|
||||
if (data[0] == '0')
|
||||
printf("Looks like a zero to me!\n");
|
||||
else if (data[0] == '1')
|
||||
printf("Pretty sure that is a one!\n");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Neither one or zero? How quaint!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void run_test(char * file) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "Running: %s\n", file);
|
||||
FILE *f = fopen(file, "r");
|
||||
assert(f);
|
||||
fseek(f, 0, SEEK_END);
|
||||
size_t len = ftell(f);
|
||||
fseek(f, 0, SEEK_SET);
|
||||
unsigned char *buf = (unsigned char*)malloc(len);
|
||||
size_t n_read = fread(buf, 1, len, f);
|
||||
fclose(f);
|
||||
assert(n_read == len);
|
||||
LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(buf, len);
|
||||
free(buf);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "Done: %s: (%zd bytes)\n", file, n_read);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
srand(1);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "StandaloneFuzzTargetMain: running %d inputs\n", argc - 1);
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
|
||||
run_test(argv[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
399
frida_mode/ts/lib/afl.ts
Normal file
399
frida_mode/ts/lib/afl.ts
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,399 @@
|
||||
class Afl {
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Field containing the `Module` object for `afl-frida-trace.so` (the FRIDA mode
|
||||
* implementation).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static module: Module = Process.getModuleByName("afl-frida-trace.so");
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting a value in `AFL_FRIDA_EXCLUDE_RANGES`,
|
||||
* it takes as arguments a `NativePointer` and a `number`. It can be
|
||||
* called multiple times to exclude several ranges.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static addExcludedRange(addressess: NativePointer, size: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddExcludeRange(addressess, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting a value in `AFL_FRIDA_INST_RANGES`,
|
||||
* it takes as arguments a `NativePointer` and a `number`. It can be
|
||||
* called multiple times to include several ranges.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static addIncludedRange(addressess: NativePointer, size: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAddIncludeRange(addressess, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This must always be called at the end of your script. This lets
|
||||
* FRIDA mode know that your configuration is finished and that
|
||||
* execution has reached the end of your script. Failure to call
|
||||
* this will result in a fatal error.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static done(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiDone();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This function can be called within your script to cause FRIDA
|
||||
* mode to trigger a fatal error. This is useful if for example you
|
||||
* discover a problem you weren't expecting and want everything to
|
||||
* stop. The user will need to enable `AFL_DEBUG_CHILD=1` to view
|
||||
* this error message.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static error(msg: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(msg);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiError(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to provide access to `__afl_fuzz_ptr`, which contains the length of
|
||||
* fuzzing data when using in-memory test case fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static getAflFuzzLen(): NativePointer {
|
||||
|
||||
return Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_fuzz_len");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to provide access to `__afl_fuzz_ptr`, which contains the fuzzing
|
||||
* data when using in-memory test case fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static getAflFuzzPtr(): NativePointer {
|
||||
|
||||
return Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_fuzz_ptr");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Print a message to the STDOUT. This should be preferred to
|
||||
* FRIDA's `console.log` since FRIDA will queue it's log messages.
|
||||
* If `console.log` is used in a callback in particular, then there
|
||||
* may no longer be a thread running to service this queue.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static print(msg: string): void {
|
||||
const STDOUT_FILENO = 2;
|
||||
const log = `${msg}\n`;
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(log);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiWrite(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, log.length);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_DEBUG_MAPS`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setDebugMaps(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetDebugMaps();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This has the same effect as setting `AFL_ENTRYPOINT`, but has the
|
||||
* convenience of allowing you to use FRIDAs APIs to determine the
|
||||
* address you would like to configure, rather than having to grep
|
||||
* the output of `readelf` or something similarly ugly. This
|
||||
* function should be called with a `NativePointer` as its
|
||||
* argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setEntryPoint(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetEntryPoint(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Function used to enable in-memory test cases for fuzzing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInMemoryFuzzing(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiAflSharedMemFuzzing.writeInt(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_DEBUG_FILE`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentDebugFile(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentDebugFile(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentEnableTracing(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTrace();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_JIT`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentJit(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentJit();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_INST_LIBS`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentLibraries(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentLibraries();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_OPTIMIZE`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentNoOptimize(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentNoOptimize();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_SEED`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentSeed(seed: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentSeed(seed);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_TRACE_UNIQUE`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setInstrumentTracingUnique(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetInstrumentTraceUnique();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR`, again a
|
||||
* `NativePointer` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentAddress(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentAddress(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_CNT`, a
|
||||
* `number` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentCount(count: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentCount(count);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_DEBUG`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentDebug(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentDebug();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_ADDR`. This function takes a NativePointer as an
|
||||
* argument. See above for examples of use.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentHook(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentHook(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* This is equivalent to setting `AFL_FRIDA_PERSISTENT_RET`, again a
|
||||
* `NativePointer` should be provided as it's argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPersistentReturn(address: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPersistentReturn(address);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_INST_NO_PREFETCH`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setPrefetchDisable(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetPrefetchDisable();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Set a function to be called for each instruction which is instrumented
|
||||
* by AFL FRIDA mode.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStalkerCallback(callback: NativePointer): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStalkerCallback(callback);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_FILE`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStatsFile(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsFile(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_INTERVAL`. This function takes a `number` as an
|
||||
* argument
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStatsInterval(interval: number): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsInterval(interval);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_STATS_TRANSITIONS`
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStatsTransitions(): void {
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStatsTransitions();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_OUTPUT_STDERR`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStdErr(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdErr(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* See `AFL_FRIDA_OUTPUT_STDOUT`. This function takes a single `string` as
|
||||
* an argument.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public static setStdOut(file: string): void {
|
||||
const buf = Memory.allocUtf8String(file);
|
||||
Afl.jsApiSetStdOut(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiAddExcludeRange = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_add_exclude_range",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer", "size_t"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiAddIncludeRange = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_add_include_range",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer", "size_t"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiAflSharedMemFuzzing = Afl.jsApiGetSymbol("__afl_sharedmem_fuzzing");
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiDone = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_done",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiError = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_error",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetDebugMaps = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_debug_maps",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetEntryPoint = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_entrypoint",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentDebugFile = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_debug_file",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentJit = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_jit",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentLibraries = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_libraries",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentNoOptimize = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_no_optimize",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentSeed = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_seed",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["uint64"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentTrace = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_trace",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetInstrumentTraceUnique = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_instrument_trace_unique",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetPersistentAddress = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_persistent_address",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetPersistentCount = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_persistent_count",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["uint64"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetPersistentDebug = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_persistent_debug",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetPersistentHook = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_persistent_hook",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetPersistentReturn = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_persistent_return",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetPrefetchDisable = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_prefetch_disable",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetStalkerCallback = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_stalker_callback",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetStatsFile = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_stats_file",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetStatsInterval = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_stats_interval",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["uint64"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetStatsTransitions = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_stats_transitions",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
[]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetStdErr = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_stderr",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiSetStdOut = Afl.jsApiGetFunction(
|
||||
"js_api_set_stdout",
|
||||
"void",
|
||||
["pointer"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static readonly jsApiWrite = new NativeFunction(
|
||||
/* tslint:disable-next-line:no-null-keyword */
|
||||
Module.getExportByName(null, "write"),
|
||||
"int",
|
||||
["int", "pointer", "int"]);
|
||||
|
||||
private static jsApiGetFunction(name: string, retType: NativeType, argTypes: NativeType[]): NativeFunction {
|
||||
const addr: NativePointer = Afl.module.getExportByName(name);
|
||||
|
||||
return new NativeFunction(addr, retType, argTypes);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static jsApiGetSymbol(name: string): NativePointer {
|
||||
|
||||
return Afl.module.getExportByName(name);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export { Afl };
|
||||
12
frida_mode/ts/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
12
frida_mode/ts/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"requires": true,
|
||||
"lockfileVersion": 1,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"tsc": {
|
||||
"version": "2.0.3",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/tsc/-/tsc-2.0.3.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-SN+9zBUtrpUcOpaUO7GjkEHgWtf22c7FKbKCA4e858eEM7Qz86rRDpgOU2lBIDf0fLCsEg65ms899UMUIB2+Ow==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
32
frida_mode/ts/package.json
Normal file
32
frida_mode/ts/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@worksbutnottested/aflplusplus-frida",
|
||||
"version": "1.0.1",
|
||||
"description": "AFLplusplus Frida Mode",
|
||||
"main": "./dist/afl.js",
|
||||
"types": "./dist/afl.d.ts",
|
||||
"files": [
|
||||
"/dist/"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"repository": {
|
||||
"type": "git",
|
||||
"url": "git@github.com:worksbutnottested/AFLplusplus.git"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"publishConfig": {
|
||||
"cache": "~/.npm",
|
||||
"registry": "https://npm.pkg.github.com/@worksbutnottested"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"prepare": "npm run build",
|
||||
"build": "tsc",
|
||||
"lint": "tslint -p tslint.json"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"devDependencies": {
|
||||
"@types/node": "^14.14.2",
|
||||
"typescript": "^4.0.3",
|
||||
"typescript-tslint-plugin": "^0.5.5",
|
||||
"tslint": "^6.1.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@types/frida-gum": "^16.2.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
14
frida_mode/ts/tsconfig.json
Normal file
14
frida_mode/ts/tsconfig.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"compilerOptions": {
|
||||
"target": "es2020",
|
||||
"lib": ["es2020"],
|
||||
"strict": true,
|
||||
"module": "commonjs",
|
||||
"esModuleInterop": true,
|
||||
"declaration": true,
|
||||
"outDir": "./dist"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"include": [
|
||||
"lib/**/*"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
256
frida_mode/ts/tslint.json
Normal file
256
frida_mode/ts/tslint.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,256 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"rules": {
|
||||
"adjacent-overload-signatures": true,
|
||||
"ban-types": {
|
||||
"options": [
|
||||
["Object", "Avoid using the `Object` type. Did you mean `object`?"],
|
||||
[
|
||||
"Function",
|
||||
"Avoid using the `Function` type. Prefer a specific function type, like `() => void`."
|
||||
],
|
||||
["Boolean", "Avoid using the `Boolean` type. Did you mean `boolean`?"],
|
||||
["Number", "Avoid using the `Number` type. Did you mean `number`?"],
|
||||
["String", "Avoid using the `String` type. Did you mean `string`?"],
|
||||
["Symbol", "Avoid using the `Symbol` type. Did you mean `symbol`?"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ban-ts-ignore": true,
|
||||
"member-access": {
|
||||
"options": ["check-accessor", "check-constructor", "check-parameter-property"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"member-ordering": {
|
||||
"options": {
|
||||
"order": "statics-first",
|
||||
"alphabetize": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"no-any": true,
|
||||
"no-empty-interface": true,
|
||||
"no-for-in": true,
|
||||
"no-import-side-effect": true,
|
||||
"no-inferrable-types": { "options": ["ignore-params"] },
|
||||
"no-internal-module": true,
|
||||
"no-magic-numbers": true,
|
||||
"no-namespace": true,
|
||||
"no-non-null-assertion": true,
|
||||
"no-reference": true,
|
||||
"no-restricted-globals": true,
|
||||
"no-this-assignment": true,
|
||||
"no-var-requires": true,
|
||||
"only-arrow-functions": true,
|
||||
"prefer-for-of": true,
|
||||
"prefer-readonly": true,
|
||||
"promise-function-async": true,
|
||||
"typedef": {
|
||||
"options": [
|
||||
"call-signature",
|
||||
"parameter",
|
||||
"property-declaration"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"typedef-whitespace": {
|
||||
"options": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"call-signature": "nospace",
|
||||
"index-signature": "nospace",
|
||||
"parameter": "nospace",
|
||||
"property-declaration": "nospace",
|
||||
"variable-declaration": "nospace"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"call-signature": "onespace",
|
||||
"index-signature": "onespace",
|
||||
"parameter": "onespace",
|
||||
"property-declaration": "onespace",
|
||||
"variable-declaration": "onespace"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"unified-signatures": true,
|
||||
"await-promise": true,
|
||||
"ban-comma-operator": true,
|
||||
"curly": true,
|
||||
"forin": true,
|
||||
"function-constructor": true,
|
||||
"label-position": true,
|
||||
"no-arg": true,
|
||||
"no-async-without-await": true,
|
||||
"no-bitwise": true,
|
||||
"no-conditional-assignment": true,
|
||||
"no-console": true,
|
||||
"no-construct": true,
|
||||
"no-debugger": true,
|
||||
"no-duplicate-super": true,
|
||||
"no-duplicate-switch-case": true,
|
||||
"no-duplicate-variable": { "options": ["check-parameters"] },
|
||||
"no-dynamic-delete": true,
|
||||
"no-empty": true,
|
||||
"no-eval": true,
|
||||
"no-floating-promises": true,
|
||||
"no-for-in-array": true,
|
||||
"no-implicit-dependencies": true,
|
||||
"no-inferred-empty-object-type": true,
|
||||
"no-invalid-template-strings": true,
|
||||
"no-misused-new": true,
|
||||
"no-null-keyword": true,
|
||||
"no-null-undefined-union": true,
|
||||
"no-object-literal-type-assertion": true,
|
||||
"no-promise-as-boolean": true,
|
||||
"no-return-await": true,
|
||||
"no-shadowed-variable": true,
|
||||
"no-string-literal": true,
|
||||
"no-string-throw": true,
|
||||
"no-sparse-arrays": true,
|
||||
"no-submodule-imports": true,
|
||||
"no-tautology-expression": true,
|
||||
"no-unbound-method": true,
|
||||
"no-unnecessary-class": { "options": ["allow-empty-class", "allow-static-only"] },
|
||||
"no-unsafe-any": false,
|
||||
"no-unsafe-finally": true,
|
||||
"no-unused-expression": true,
|
||||
"no-var-keyword": true,
|
||||
"no-void-expression": true,
|
||||
"prefer-conditional-expression": true,
|
||||
"radix": true,
|
||||
"restrict-plus-operands": true,
|
||||
"static-this": true,
|
||||
"strict-boolean-expressions": true,
|
||||
"strict-string-expressions": true,
|
||||
"strict-comparisons": true,
|
||||
"strict-type-predicates": true,
|
||||
"switch-default": true,
|
||||
"triple-equals": true,
|
||||
"unnecessary-constructor": true,
|
||||
"use-default-type-parameter": true,
|
||||
"use-isnan": true,
|
||||
"cyclomatic-complexity": true,
|
||||
"eofline": true,
|
||||
"indent": { "options": ["spaces"] },
|
||||
"invalid-void": true,
|
||||
"linebreak-style": { "options": "LF" },
|
||||
"max-classes-per-file": { "options": 1 },
|
||||
"max-file-line-count": { "options": 1000 },
|
||||
"max-line-length": {
|
||||
"options": { "limit": 120 }
|
||||
},
|
||||
"no-default-export": true,
|
||||
"no-default-import": true,
|
||||
"no-duplicate-imports": true,
|
||||
"no-irregular-whitespace": true,
|
||||
"no-mergeable-namespace": true,
|
||||
"no-parameter-reassignment": true,
|
||||
"no-require-imports": true,
|
||||
"no-trailing-whitespace": true,
|
||||
"object-literal-sort-keys": true,
|
||||
"prefer-const": true,
|
||||
"trailing-comma": {
|
||||
"options": {
|
||||
"esSpecCompliant": true,
|
||||
"multiline": "always",
|
||||
"singleline": "never"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"align": {
|
||||
"options": ["parameters", "arguments", "statements", "elements", "members"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"array-type": { "options": "array-simple" },
|
||||
"arrow-parens": true,
|
||||
"arrow-return-shorthand": { "options": "multiline" },
|
||||
"binary-expression-operand-order": true,
|
||||
"callable-types": true,
|
||||
"class-name": true,
|
||||
"comment-format": { "options": ["check-space", "check-uppercase"] },
|
||||
"comment-type": { "options": ["singleline", "multiline", "doc", "directive"] },
|
||||
"completed-docs": [
|
||||
true,
|
||||
{
|
||||
"enums": true,
|
||||
"methods": {"locations": "all", "privacies": ["public", "protected"]},
|
||||
"properties": {"locations": "all", "privacies": ["public", "protected"]}
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"deprecation": true,
|
||||
"encoding": true,
|
||||
"file-name-casing": { "options": "camel-case" },
|
||||
"import-spacing": true,
|
||||
"increment-decrement": true,
|
||||
"interface-name": true,
|
||||
"interface-over-type-literal": true,
|
||||
"jsdoc-format": { "options": "check-multiline-start" },
|
||||
"match-default-export-name": true,
|
||||
"new-parens": true,
|
||||
"newline-before-return": true,
|
||||
"newline-per-chained-call": true,
|
||||
"no-angle-bracket-type-assertion": true,
|
||||
"no-boolean-literal-compare": true,
|
||||
"no-consecutive-blank-lines": true,
|
||||
"no-parameter-properties": true,
|
||||
"no-redundant-jsdoc": true,
|
||||
"no-reference-import": true,
|
||||
"no-unnecessary-callback-wrapper": true,
|
||||
"no-unnecessary-initializer": true,
|
||||
"no-unnecessary-qualifier": true,
|
||||
"no-unnecessary-type-assertion": true,
|
||||
"number-literal-format": true,
|
||||
"object-literal-key-quotes": { "options": "consistent-as-needed" },
|
||||
"object-literal-shorthand": true,
|
||||
"one-line": {
|
||||
"options": [
|
||||
"check-catch",
|
||||
"check-else",
|
||||
"check-finally",
|
||||
"check-open-brace",
|
||||
"check-whitespace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"one-variable-per-declaration": true,
|
||||
"ordered-imports": {
|
||||
"options": {
|
||||
"grouped-imports": true,
|
||||
"import-sources-order": "case-insensitive",
|
||||
"named-imports-order": "case-insensitive",
|
||||
"module-source-path": "full"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"prefer-function-over-method": true,
|
||||
"prefer-method-signature": true,
|
||||
"prefer-object-spread": true,
|
||||
"prefer-switch": true,
|
||||
"prefer-template": true,
|
||||
"prefer-while": true,
|
||||
"quotemark": {
|
||||
"options": ["double", "avoid-escape", "avoid-template"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"return-undefined": true,
|
||||
"semicolon": { "options": ["always"] },
|
||||
"space-before-function-paren": {
|
||||
"options": {
|
||||
"anonymous": "never",
|
||||
"asyncArrow": "always",
|
||||
"constructor": "never",
|
||||
"method": "never",
|
||||
"named": "never"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"space-within-parens": { "options": 0 },
|
||||
"switch-final-break": true,
|
||||
"type-literal-delimiter": true,
|
||||
"unnecessary-bind": true,
|
||||
"unnecessary-else": true,
|
||||
"variable-name": { "options": ["ban-keywords", "check-format", "require-const-for-all-caps"] },
|
||||
"whitespace": {
|
||||
"options": [
|
||||
"check-branch",
|
||||
"check-decl",
|
||||
"check-operator",
|
||||
"check-module",
|
||||
"check-separator",
|
||||
"check-type",
|
||||
"check-typecast",
|
||||
"check-preblock",
|
||||
"check-type-operator",
|
||||
"check-rest-spread"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
117
frida_mode/util/bin2c.c
Normal file
117
frida_mode/util/bin2c.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
|
||||
#include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void fatal(char *msg) {
|
||||
|
||||
perror(msg);
|
||||
exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void bin2c_write(char *name, char *output, unsigned char *buff, size_t size) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = open(output, O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC, 00660);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) { fatal("open"); }
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write the array definition */
|
||||
dprintf(fd, "unsigned char %s[] = {\n", name);
|
||||
|
||||
/* 12 bytes per row, just like xxd means we fit an 80 character width */
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i += 12) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (size_t j = 0; j < 12; j++) {
|
||||
|
||||
size_t idx = i + j;
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we get to the end of the input, then break */
|
||||
if (idx >= size) { break; }
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we are writing the first column, then we need a leading indent */
|
||||
if (j == 0) { dprintf(fd, " "); }
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write the hexadecimal byte value */
|
||||
dprintf(fd, "0x%02x", buff[idx]);
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we have just written the last byte, then stop */
|
||||
if (idx == size - 1) { break; }
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* If we have written the last byte in a row, then follow with a comma
|
||||
* and a newline
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (j == 11) {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(fd, ",\n");
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Otherwise, follow with a command and a space
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(fd, ", ");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write the closing brace for the array */
|
||||
dprintf(fd, "\n};\n");
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write a parameter describing the length of the array */
|
||||
dprintf(fd, "unsigned int %s_len = %lu;\n", name, size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (close(fd) < 0) { fatal("close"); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void bin2c(char *name, char *input, char *output) {
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = open(input, O_RDONLY);
|
||||
if (fd < 0) { fatal("open(input)"); }
|
||||
|
||||
size_t size = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
|
||||
if (size < 0) { fatal("lseek(SEEK_END)"); }
|
||||
|
||||
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0) { fatal("lseek(SEEK_SET)"); }
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned char *buff = malloc(size);
|
||||
if (buff == NULL) { fatal("malloc(size)"); }
|
||||
|
||||
if (read(fd, buff, size) != size) { fatal("read(size)"); }
|
||||
|
||||
bin2c_write(name, output, buff, size);
|
||||
|
||||
free(buff);
|
||||
if (close(fd) < 0) { fatal("close(fd_in)"); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc < 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDERR_FILENO, "%s <name> <input> <output>\n", argv[0]);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
char *name = argv[1];
|
||||
char *input = argv[2];
|
||||
char *output = argv[3];
|
||||
|
||||
dprintf(STDOUT_FILENO, "bin2c:\n");
|
||||
dprintf(STDOUT_FILENO, "\tname: %s\n", name);
|
||||
dprintf(STDOUT_FILENO, "\tinput: %s\n", input);
|
||||
dprintf(STDOUT_FILENO, "\toutput: %s\n", output);
|
||||
|
||||
bin2c(name, input, output);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
32
frida_mode/util/get_symbol_addr.sh
Executable file
32
frida_mode/util/get_symbol_addr.sh
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# Copyright 2020 Google LLC
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
# set -x
|
||||
target="$1"
|
||||
symbol="$2"
|
||||
base="$3"
|
||||
|
||||
test -z "$target" -o -z "$symbol" -o '!' -e "$target" && exit 0
|
||||
|
||||
test $(uname -s) = "Darwin" && symbol=_"$symbol"
|
||||
|
||||
file "$target" | grep -q executable && {
|
||||
nm "$target" | grep -i "T $symbol" | awk '{print"0x"$1}'
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
hex_base=$(echo "$3" | awk '{sub("^0x","");print $0}' | tr a-f A-F )
|
||||
nm "$target" | grep -i "T $symbol" | awk '{print$1}' | tr a-f A-F | \
|
||||
xargs echo "ibase=16;obase=10;$hex_base + " | bc | tr A-F a-f | awk '{print "0x"$0}'
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
@ -478,9 +478,7 @@ typedef struct afl_state {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 hang_tmout; /* Timeout used for hang det (ms) */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 cal_cycles, /* Calibration cycles defaults */
|
||||
cal_cycles_long, /* Calibration cycles defaults */
|
||||
havoc_stack_pow2, /* HAVOC_STACK_POW2 */
|
||||
u8 havoc_stack_pow2, /* HAVOC_STACK_POW2 */
|
||||
no_unlink, /* do not unlink cur_input */
|
||||
debug, /* Debug mode */
|
||||
custom_only, /* Custom mutator only mode */
|
||||
@ -521,7 +519,8 @@ typedef struct afl_state {
|
||||
shmem_testcase_mode, /* If sharedmem testcases are used */
|
||||
expand_havoc, /* perform expensive havoc after no find */
|
||||
cycle_schedules, /* cycle power schedules? */
|
||||
old_seed_selection; /* use vanilla afl seed selection */
|
||||
old_seed_selection, /* use vanilla afl seed selection */
|
||||
reinit_table; /* reinit the queue weight table */
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *virgin_bits, /* Regions yet untouched by fuzzing */
|
||||
*virgin_tmout, /* Bits we haven't seen in tmouts */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,6 +54,7 @@ typedef struct afl_forkserver {
|
||||
u32 exec_tmout; /* Configurable exec timeout (ms) */
|
||||
u32 init_tmout; /* Configurable init timeout (ms) */
|
||||
u32 map_size; /* map size used by the target */
|
||||
u32 real_map_size; /* real map size, unaligned */
|
||||
u32 snapshot; /* is snapshot feature used */
|
||||
u64 mem_limit; /* Memory cap for child (MB) */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -516,6 +516,8 @@ bool ModuleSanitizerCoverage::instrumentModule(
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isInInstrumentList(&F) || !F.size()) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &IN : BB) {
|
||||
@ -759,6 +761,12 @@ bool ModuleSanitizerCoverage::instrumentModule(
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = Str2.size();
|
||||
uint64_t optLength = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
if (optLength > literalLength + 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
optLength = Str2.length() + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (literalLength + 1 == optLength) {
|
||||
|
||||
Str2.append("\0", 1); // add null byte
|
||||
@ -862,6 +870,12 @@ bool ModuleSanitizerCoverage::instrumentModule(
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = optLen;
|
||||
optLen = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
if (optLen > thestring.length() + 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
optLen = thestring.length() + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (optLen < 2) { continue; }
|
||||
if (literalLength + 1 == optLen) { // add null byte
|
||||
thestring.append("\0", 1);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ u64 __afl_map_addr;
|
||||
// for the __AFL_COVERAGE_ON/__AFL_COVERAGE_OFF features to work:
|
||||
int __afl_selective_coverage __attribute__((weak));
|
||||
int __afl_selective_coverage_start_off __attribute__((weak));
|
||||
int __afl_selective_coverage_temp = 1;
|
||||
static int __afl_selective_coverage_temp = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__ANDROID__) || defined(__HAIKU__)
|
||||
PREV_LOC_T __afl_prev_loc[NGRAM_SIZE_MAX];
|
||||
@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ static int __afl_dummy_fd[2] = {2, 2};
|
||||
|
||||
/* ensure we kill the child on termination */
|
||||
|
||||
void at_exit(int signal) {
|
||||
static void at_exit(int signal) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_pid > 0) { kill(child_pid, SIGKILL); }
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ void __afl_trace(const u32 x) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Error reporting to forkserver controller */
|
||||
|
||||
void send_forkserver_error(int error) {
|
||||
static void send_forkserver_error(int error) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 status;
|
||||
if (!error || error > 0xffff) return;
|
||||
@ -270,12 +270,6 @@ static void __afl_map_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_final_loc) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_final_loc % 64) {
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_final_loc = (((__afl_final_loc + 63) >> 6) << 6);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_map_size = __afl_final_loc;
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_final_loc > MAP_SIZE) {
|
||||
@ -304,8 +298,9 @@ static void __afl_map_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!getenv("AFL_QUIET"))
|
||||
fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"Warning: AFL++ tools will need to set AFL_MAP_SIZE to %u "
|
||||
"to be able to run this instrumented program!\n",
|
||||
"Warning: AFL++ tools might need to set AFL_MAP_SIZE to %u "
|
||||
"to be able to run this instrumented program if this "
|
||||
"crashes!\n",
|
||||
__afl_final_loc);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -622,6 +617,7 @@ static void __afl_unmap_shm(void) {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_cmp_map = NULL;
|
||||
__afl_cmp_map_backup = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -629,6 +625,34 @@ static void __afl_unmap_shm(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define write_error(text) write_error_with_location(text, __FILE__, __LINE__)
|
||||
|
||||
void write_error_with_location(char *text, char *filename, int linenumber) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 * o = getenv("__AFL_OUT_DIR");
|
||||
char *e = strerror(errno);
|
||||
|
||||
if (o) {
|
||||
|
||||
char buf[4096];
|
||||
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%s/error.txt", o);
|
||||
FILE *f = fopen(buf, "a");
|
||||
|
||||
if (f) {
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(f, "File %s, line %d: Error(%s): %s\n", filename, linenumber,
|
||||
text, e);
|
||||
fclose(f);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "File %s, line %d: Error(%s): %s\n", filename, linenumber,
|
||||
text, e);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __linux__
|
||||
static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -655,7 +679,12 @@ static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_sharedmem_fuzzing || (__afl_dictionary_len && __afl_dictionary)) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) { _exit(1); }
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("read to afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (__afl_debug) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -724,7 +753,12 @@ static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Wait for parent by reading from the pipe. Abort if read fails. */
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("reading from afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -761,7 +795,12 @@ static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
if (child_stopped && was_killed) {
|
||||
|
||||
child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) < 0) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("child_stopped && was_killed");
|
||||
_exit(1); // TODO why exit?
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -770,7 +809,12 @@ static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. */
|
||||
|
||||
child_pid = fork();
|
||||
if (child_pid < 0) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (child_pid < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("fork");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -810,9 +854,19 @@ static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &child_pid, 4) != 4) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &child_pid, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, WUNTRACED) < 0) _exit(1);
|
||||
write_error("write to afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, WUNTRACED) < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("waitpid");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* In persistent mode, the child stops itself with SIGSTOP to indicate
|
||||
a successful run. In this case, we want to wake it up without forking
|
||||
@ -822,7 +876,12 @@ static void __afl_start_snapshots(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &status, 4) != 4) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &status, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("writing to afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -955,7 +1014,12 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (read(FORKSRV_FD, &was_killed, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
// write_error("read from afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -992,7 +1056,12 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
if (child_stopped && was_killed) {
|
||||
|
||||
child_stopped = 0;
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) < 0) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("child_stopped && was_killed");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1001,7 +1070,12 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
/* Once woken up, create a clone of our process. */
|
||||
|
||||
child_pid = fork();
|
||||
if (child_pid < 0) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (child_pid < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("fork");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* In child process: close fds, resume execution. */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1030,11 +1104,20 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* In parent process: write PID to pipe, then wait for child. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &child_pid, 4) != 4) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &child_pid, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, is_persistent ? WUNTRACED : 0) < 0)
|
||||
write_error("write to afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, is_persistent ? WUNTRACED : 0) < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("waitpid");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* In persistent mode, the child stops itself with SIGSTOP to indicate
|
||||
a successful run. In this case, we want to wake it up without forking
|
||||
again. */
|
||||
@ -1043,7 +1126,12 @@ static void __afl_start_forkserver(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Relay wait status to pipe, then loop back. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &status, 4) != 4) _exit(1);
|
||||
if (write(FORKSRV_FD + 1, &status, 4) != 4) {
|
||||
|
||||
write_error("writing to afl-fuzz");
|
||||
_exit(1);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1599,7 +1687,7 @@ void __cmplog_ins_hookN(uint128_t arg1, uint128_t arg2, uint8_t attr,
|
||||
|
||||
void __cmplog_ins_hook16(uint128_t arg1, uint128_t arg2, uint8_t attr) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
|
||||
uintptr_t k = (uintptr_t)__builtin_return_address(0);
|
||||
k = (k >> 4) ^ (k << 8);
|
||||
@ -1668,7 +1756,7 @@ void __sanitizer_cov_trace_cmp4(uint32_t arg1, uint32_t arg2) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void __sanitizer_cov_trace_cost_cmp4(uint32_t arg1, uint32_t arg2) {
|
||||
void __sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp4(uint32_t arg1, uint32_t arg2) {
|
||||
|
||||
__cmplog_ins_hook4(arg1, arg2, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1703,7 +1791,7 @@ void __sanitizer_cov_trace_const_cmp16(uint128_t arg1, uint128_t arg2) {
|
||||
|
||||
void __sanitizer_cov_trace_switch(uint64_t val, uint64_t *cases) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < cases[0]; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1800,7 +1888,7 @@ void __cmplog_rtn_hook(u8 *ptr1, u8 *ptr2) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "RTN1 %p %p\n", ptr1, ptr2);
|
||||
int l1, l2;
|
||||
if ((l1 = area_is_valid(ptr1, 32)) <= 0 ||
|
||||
@ -1884,7 +1972,7 @@ static u8 *get_llvm_stdstring(u8 *string) {
|
||||
|
||||
void __cmplog_rtn_gcc_stdstring_cstring(u8 *stdstring, u8 *cstring) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (area_is_valid(stdstring, 32) <= 0 || area_is_valid(cstring, 32) <= 0)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1894,7 +1982,7 @@ void __cmplog_rtn_gcc_stdstring_cstring(u8 *stdstring, u8 *cstring) {
|
||||
|
||||
void __cmplog_rtn_gcc_stdstring_stdstring(u8 *stdstring1, u8 *stdstring2) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (area_is_valid(stdstring1, 32) <= 0 || area_is_valid(stdstring2, 32) <= 0)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1905,7 +1993,7 @@ void __cmplog_rtn_gcc_stdstring_stdstring(u8 *stdstring1, u8 *stdstring2) {
|
||||
|
||||
void __cmplog_rtn_llvm_stdstring_cstring(u8 *stdstring, u8 *cstring) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (area_is_valid(stdstring, 32) <= 0 || area_is_valid(cstring, 32) <= 0)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1915,7 +2003,7 @@ void __cmplog_rtn_llvm_stdstring_cstring(u8 *stdstring, u8 *cstring) {
|
||||
|
||||
void __cmplog_rtn_llvm_stdstring_stdstring(u8 *stdstring1, u8 *stdstring2) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (likely(!__afl_cmp_map)) return;
|
||||
if (area_is_valid(stdstring1, 32) <= 0 || area_is_valid(stdstring2, 32) <= 0)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1949,7 +2037,7 @@ void __afl_coverage_on() {
|
||||
if (likely(__afl_selective_coverage && __afl_selective_coverage_temp)) {
|
||||
|
||||
__afl_area_ptr = __afl_area_ptr_backup;
|
||||
__afl_cmp_map = __afl_cmp_map_backup;
|
||||
if (__afl_cmp_map_backup) { __afl_cmp_map = __afl_cmp_map_backup; }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1990,3 +2078,5 @@ void __afl_coverage_interesting(u8 val, u32 id) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#undef write_error
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,9 +96,8 @@ bool isIgnoreFunction(const llvm::Function *F) {
|
||||
|
||||
static constexpr const char *ignoreSubstringList[] = {
|
||||
|
||||
"__asan", "__msan", "__ubsan", "__lsan",
|
||||
"__san", "__sanitize", "__cxx", "_GLOBAL__",
|
||||
"DebugCounter", "DwarfDebug", "DebugLoc"
|
||||
"__asan", "__msan", "__ubsan", "__lsan", "__san", "__sanitize",
|
||||
"__cxx", "DebugCounter", "DwarfDebug", "DebugLoc"
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -154,6 +154,7 @@ bool AFLdict2filePass::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (isIgnoreFunction(&F)) continue;
|
||||
if (!isInInstrumentList(&F) || !F.size()) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
/* Some implementation notes.
|
||||
*
|
||||
@ -428,6 +429,12 @@ bool AFLdict2filePass::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = Str2.length();
|
||||
uint64_t optLength = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
if (optLength > literalLength + 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
optLength = Str2.length() + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (literalLength + 1 == optLength) {
|
||||
|
||||
Str2.append("\0", 1); // add null byte
|
||||
|
||||
@ -546,6 +546,12 @@ bool AFLLTOPass::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = Str2.size();
|
||||
uint64_t optLength = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
if (optLength > literalLength + 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
optLength = Str2.length() + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (literalLength + 1 == optLength) {
|
||||
|
||||
Str2.append("\0", 1); // add null byte
|
||||
@ -649,6 +655,7 @@ bool AFLLTOPass::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = optLen;
|
||||
optLen = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
if (optLen > literalLength + 1) { optLen = literalLength + 1; }
|
||||
if (optLen < 2) { continue; }
|
||||
if (literalLength + 1 == optLen) { // add null byte
|
||||
thestring.append("\0", 1);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -438,9 +438,9 @@ bool AFLCoverage::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "FUNCTION: %s (%zu)\n", F.getName().str().c_str(),
|
||||
F.size());
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isInInstrumentList(&F)) continue;
|
||||
if (!isInInstrumentList(&F)) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
if (F.size() < function_minimum_size) continue;
|
||||
if (F.size() < function_minimum_size) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
std::list<Value *> todo;
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -104,7 +104,6 @@ Iterator Unique(Iterator first, Iterator last) {
|
||||
bool CmpLogInstructions::hookInstrs(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Instruction *> icomps;
|
||||
std::vector<SwitchInst *> switches;
|
||||
LLVMContext & C = M.getContext();
|
||||
|
||||
Type * VoidTy = Type::getVoidTy(C);
|
||||
@ -222,6 +221,18 @@ bool CmpLogInstructions::hookInstrs(Module &M) {
|
||||
FunctionCallee cmplogHookInsN = cN;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
GlobalVariable *AFLCmplogPtr = M.getNamedGlobal("__afl_cmp_map");
|
||||
|
||||
if (!AFLCmplogPtr) {
|
||||
|
||||
AFLCmplogPtr = new GlobalVariable(M, PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0), false,
|
||||
GlobalValue::ExternalWeakLinkage, 0,
|
||||
"__afl_cmp_map");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Constant *Null = Constant::getNullValue(PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0));
|
||||
|
||||
/* iterate over all functions, bbs and instruction and add suitable calls */
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -238,164 +249,6 @@ bool CmpLogInstructions::hookInstrs(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
SwitchInst *switchInst = nullptr;
|
||||
if ((switchInst = dyn_cast<SwitchInst>(BB.getTerminator()))) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (switchInst->getNumCases() > 1) { switches.push_back(switchInst); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unique the collected switches
|
||||
switches.erase(Unique(switches.begin(), switches.end()), switches.end());
|
||||
|
||||
// Instrument switch values for cmplog
|
||||
if (switches.size()) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet)
|
||||
errs() << "Hooking " << switches.size() << " switch instructions\n";
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &SI : switches) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value * Val = SI->getCondition();
|
||||
unsigned int max_size = Val->getType()->getIntegerBitWidth(), cast_size;
|
||||
unsigned char do_cast = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!SI->getNumCases() || max_size < 16) {
|
||||
|
||||
// if (!be_quiet) errs() << "skip trivial switch..\n";
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (max_size % 8) {
|
||||
|
||||
max_size = (((max_size / 8) + 1) * 8);
|
||||
do_cast = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(SI->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(SI);
|
||||
|
||||
if (max_size > 128) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) {
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"Cannot handle this switch bit size: %u (truncating)\n",
|
||||
max_size);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
max_size = 128;
|
||||
do_cast = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// do we need to cast?
|
||||
switch (max_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 8:
|
||||
case 16:
|
||||
case 32:
|
||||
case 64:
|
||||
case 128:
|
||||
cast_size = max_size;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
cast_size = 128;
|
||||
do_cast = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Value *CompareTo = Val;
|
||||
|
||||
if (do_cast) {
|
||||
|
||||
CompareTo =
|
||||
IRB.CreateIntCast(CompareTo, IntegerType::get(C, cast_size), false);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (SwitchInst::CaseIt i = SI->case_begin(), e = SI->case_end(); i != e;
|
||||
++i) {
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
ConstantInt *cint = i.getCaseValue();
|
||||
#else
|
||||
ConstantInt *cint = i->getCaseValue();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
if (cint) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
args.push_back(CompareTo);
|
||||
|
||||
Value *new_param = cint;
|
||||
|
||||
if (do_cast) {
|
||||
|
||||
new_param =
|
||||
IRB.CreateIntCast(cint, IntegerType::get(C, cast_size), false);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (new_param) {
|
||||
|
||||
args.push_back(new_param);
|
||||
ConstantInt *attribute = ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1);
|
||||
args.push_back(attribute);
|
||||
if (cast_size != max_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
ConstantInt *bitsize =
|
||||
ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, (max_size / 8) - 1);
|
||||
args.push_back(bitsize);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch (cast_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 8:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns1, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 16:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns2, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 32:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns4, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 64:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns8, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 128:
|
||||
#ifdef WORD_SIZE_64
|
||||
if (max_size == 128) {
|
||||
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns16, args);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookInsN, args);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -409,8 +262,15 @@ bool CmpLogInstructions::hookInstrs(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &selectcmpInst : icomps) {
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(selectcmpInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(selectcmpInst);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(selectcmpInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(selectcmpInst);
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm =
|
||||
SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, selectcmpInst, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
Value *op0 = selectcmpInst->getOperand(0);
|
||||
Value *op1 = selectcmpInst->getOperand(1);
|
||||
@ -601,7 +461,7 @@ bool CmpLogInstructions::hookInstrs(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (switches.size() || icomps.size())
|
||||
if (icomps.size())
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -184,6 +184,18 @@ bool CmpLogRoutines::hookRtns(Module &M) {
|
||||
FunctionCallee cmplogGccStdC = c4;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
GlobalVariable *AFLCmplogPtr = M.getNamedGlobal("__afl_cmp_map");
|
||||
|
||||
if (!AFLCmplogPtr) {
|
||||
|
||||
AFLCmplogPtr = new GlobalVariable(M, PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0), false,
|
||||
GlobalValue::ExternalWeakLinkage, 0,
|
||||
"__afl_cmp_map");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Constant *Null = Constant::getNullValue(PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0));
|
||||
|
||||
/* iterate over all functions, bbs and instruction and add suitable calls */
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -289,8 +301,15 @@ bool CmpLogRoutines::hookRtns(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value *v1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *v2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, callInst, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
Value * v1Pcasted = IRB.CreatePointerCast(v1P, i8PtrTy);
|
||||
@ -308,8 +327,15 @@ bool CmpLogRoutines::hookRtns(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value *v1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *v2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, callInst, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
Value * v1Pcasted = IRB.CreatePointerCast(v1P, i8PtrTy);
|
||||
@ -327,8 +353,15 @@ bool CmpLogRoutines::hookRtns(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value *v1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *v2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, callInst, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
Value * v1Pcasted = IRB.CreatePointerCast(v1P, i8PtrTy);
|
||||
@ -346,8 +379,15 @@ bool CmpLogRoutines::hookRtns(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value *v1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *v2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, callInst, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
Value * v1Pcasted = IRB.CreatePointerCast(v1P, i8PtrTy);
|
||||
@ -365,8 +405,15 @@ bool CmpLogRoutines::hookRtns(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value *v1P = callInst->getArgOperand(0), *v2P = callInst->getArgOperand(1);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(callInst->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, callInst, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
Value * v1Pcasted = IRB.CreatePointerCast(v1P, i8PtrTy);
|
||||
|
||||
414
instrumentation/cmplog-switches-pass.cc
Normal file
414
instrumentation/cmplog-switches-pass.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,414 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
american fuzzy lop++ - LLVM CmpLog instrumentation
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Andrea Fioraldi <andreafioraldi@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright 2015, 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright 2019-2020 AFLplusplus Project. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
#include <sys/time.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "llvm/Config/llvm-config.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/ADT/Statistic.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/IRBuilder.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/LegacyPassManager.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Module.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Support/Debug.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Support/raw_ostream.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Transforms/IPO/PassManagerBuilder.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Transforms/Utils/BasicBlockUtils.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Pass.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/Analysis/ValueTracking.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR > 3 || \
|
||||
(LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR == 3 && LLVM_VERSION_MINOR > 4)
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/Verifier.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/IR/DebugInfo.h"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "llvm/Analysis/Verifier.h"
|
||||
#include "llvm/DebugInfo.h"
|
||||
#define nullptr 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <set>
|
||||
#include "afl-llvm-common.h"
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace llvm;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
class CmpLogInstructions : public ModulePass {
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static char ID;
|
||||
CmpLogInstructions() : ModulePass(ID) {
|
||||
|
||||
initInstrumentList();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override;
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 4
|
||||
const char *getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
StringRef getPassName() const override {
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return "cmplog instructions";
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool hookInstrs(Module &M);
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
char CmpLogInstructions::ID = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
template <class Iterator>
|
||||
Iterator Unique(Iterator first, Iterator last) {
|
||||
|
||||
while (first != last) {
|
||||
|
||||
Iterator next(first);
|
||||
last = std::remove(++next, last, *first);
|
||||
first = next;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return last;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool CmpLogInstructions::hookInstrs(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<SwitchInst *> switches;
|
||||
LLVMContext & C = M.getContext();
|
||||
|
||||
Type * VoidTy = Type::getVoidTy(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int8Ty = IntegerType::getInt8Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int16Ty = IntegerType::getInt16Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int32Ty = IntegerType::getInt32Ty(C);
|
||||
IntegerType *Int64Ty = IntegerType::getInt64Ty(C);
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Constant *
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
c1 = M.getOrInsertFunction("__cmplog_ins_hook1", VoidTy, Int8Ty, Int8Ty,
|
||||
Int8Ty
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
,
|
||||
NULL
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
);
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Function *cmplogHookIns1 = cast<Function>(c1);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee cmplogHookIns1 = c1;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Constant *
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
c2 = M.getOrInsertFunction("__cmplog_ins_hook2", VoidTy, Int16Ty, Int16Ty,
|
||||
Int8Ty
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
,
|
||||
NULL
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
);
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Function *cmplogHookIns2 = cast<Function>(c2);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee cmplogHookIns2 = c2;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Constant *
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
c4 = M.getOrInsertFunction("__cmplog_ins_hook4", VoidTy, Int32Ty, Int32Ty,
|
||||
Int8Ty
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
,
|
||||
NULL
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
);
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Function *cmplogHookIns4 = cast<Function>(c4);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee cmplogHookIns4 = c4;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Constant *
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
c8 = M.getOrInsertFunction("__cmplog_ins_hook8", VoidTy, Int64Ty, Int64Ty,
|
||||
Int8Ty
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
,
|
||||
NULL
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
);
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 9
|
||||
Function *cmplogHookIns8 = cast<Function>(c8);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
FunctionCallee cmplogHookIns8 = c8;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
GlobalVariable *AFLCmplogPtr = M.getNamedGlobal("__afl_cmp_map");
|
||||
|
||||
if (!AFLCmplogPtr) {
|
||||
|
||||
AFLCmplogPtr = new GlobalVariable(M, PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0), false,
|
||||
GlobalValue::ExternalWeakLinkage, 0,
|
||||
"__afl_cmp_map");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Constant *Null = Constant::getNullValue(PointerType::get(Int8Ty, 0));
|
||||
|
||||
/* iterate over all functions, bbs and instruction and add suitable calls */
|
||||
for (auto &F : M) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isInInstrumentList(&F)) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &BB : F) {
|
||||
|
||||
SwitchInst *switchInst = nullptr;
|
||||
if ((switchInst = dyn_cast<SwitchInst>(BB.getTerminator()))) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (switchInst->getNumCases() > 1) { switches.push_back(switchInst); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unique the collected switches
|
||||
switches.erase(Unique(switches.begin(), switches.end()), switches.end());
|
||||
|
||||
// Instrument switch values for cmplog
|
||||
if (switches.size()) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet)
|
||||
errs() << "Hooking " << switches.size() << " switch instructions\n";
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto &SI : switches) {
|
||||
|
||||
Value * Val = SI->getCondition();
|
||||
unsigned int max_size = Val->getType()->getIntegerBitWidth(), cast_size;
|
||||
unsigned char do_cast = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!SI->getNumCases() || max_size < 16) {
|
||||
|
||||
// if (!be_quiet) errs() << "skip trivial switch..\n";
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (max_size % 8) {
|
||||
|
||||
max_size = (((max_size / 8) + 1) * 8);
|
||||
do_cast = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB2(SI->getParent());
|
||||
IRB2.SetInsertPoint(SI);
|
||||
|
||||
LoadInst *CmpPtr = IRB2.CreateLoad(AFLCmplogPtr);
|
||||
CmpPtr->setMetadata(M.getMDKindID("nosanitize"), MDNode::get(C, None));
|
||||
auto is_not_null = IRB2.CreateICmpNE(CmpPtr, Null);
|
||||
auto ThenTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen(is_not_null, SI, false);
|
||||
|
||||
IRBuilder<> IRB(ThenTerm);
|
||||
|
||||
if (max_size > 128) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) {
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"Cannot handle this switch bit size: %u (truncating)\n",
|
||||
max_size);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
max_size = 128;
|
||||
do_cast = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// do we need to cast?
|
||||
switch (max_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 8:
|
||||
case 16:
|
||||
case 32:
|
||||
case 64:
|
||||
case 128:
|
||||
cast_size = max_size;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
cast_size = 128;
|
||||
do_cast = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Value *CompareTo = Val;
|
||||
|
||||
if (do_cast) {
|
||||
|
||||
CompareTo =
|
||||
IRB.CreateIntCast(CompareTo, IntegerType::get(C, cast_size), false);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (SwitchInst::CaseIt i = SI->case_begin(), e = SI->case_end(); i != e;
|
||||
++i) {
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR < 5
|
||||
ConstantInt *cint = i.getCaseValue();
|
||||
#else
|
||||
ConstantInt *cint = i->getCaseValue();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
if (cint) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<Value *> args;
|
||||
args.push_back(CompareTo);
|
||||
|
||||
Value *new_param = cint;
|
||||
|
||||
if (do_cast) {
|
||||
|
||||
new_param =
|
||||
IRB.CreateIntCast(cint, IntegerType::get(C, cast_size), false);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (new_param) {
|
||||
|
||||
args.push_back(new_param);
|
||||
ConstantInt *attribute = ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, 1);
|
||||
args.push_back(attribute);
|
||||
if (cast_size != max_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
ConstantInt *bitsize =
|
||||
ConstantInt::get(Int8Ty, (max_size / 8) - 1);
|
||||
args.push_back(bitsize);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch (cast_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 8:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns1, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 16:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns2, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 32:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns4, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 64:
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns8, args);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 128:
|
||||
#ifdef WORD_SIZE_64
|
||||
if (max_size == 128) {
|
||||
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookIns16, args);
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
IRB.CreateCall(cmplogHookInsN, args);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (switches.size())
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool CmpLogInstructions::runOnModule(Module &M) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_QUIET") == NULL)
|
||||
printf("Running cmplog-switches-pass by andreafioraldi@gmail.com\n");
|
||||
else
|
||||
be_quiet = 1;
|
||||
hookInstrs(M);
|
||||
verifyModule(M);
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void registerCmpLogInstructionsPass(const PassManagerBuilder &,
|
||||
legacy::PassManagerBase &PM) {
|
||||
|
||||
auto p = new CmpLogInstructions();
|
||||
PM.add(p);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterCmpLogInstructionsPass(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_OptimizerLast, registerCmpLogInstructionsPass);
|
||||
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterCmpLogInstructionsPass0(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_EnabledOnOptLevel0, registerCmpLogInstructionsPass);
|
||||
|
||||
#if LLVM_VERSION_MAJOR >= 11
|
||||
static RegisterStandardPasses RegisterCmpLogInstructionsPassLTO(
|
||||
PassManagerBuilder::EP_FullLinkTimeOptimizationLast,
|
||||
registerCmpLogInstructionsPass);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -313,22 +313,11 @@ bool CompareTransform::transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp,
|
||||
ConstantInt *ilen = dyn_cast<ConstantInt>(op2);
|
||||
if (ilen) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t len = ilen->getZExtValue();
|
||||
// if len is zero this is a pointless call but allow real
|
||||
// implementation to worry about that
|
||||
if (len < 2) continue;
|
||||
if (ilen->getZExtValue() < 2) { continue; }
|
||||
|
||||
if (isMemcmp) {
|
||||
|
||||
// if size of compare is larger than constant string this is
|
||||
// likely a bug but allow real implementation to worry about
|
||||
// that
|
||||
uint64_t literalLength = HasStr1 ? Str1.size() : Str2.size();
|
||||
if (literalLength + 1 < ilen->getZExtValue()) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (isMemcmp)
|
||||
} else if (isMemcmp) {
|
||||
|
||||
// this *may* supply a len greater than the constant string at
|
||||
// runtime so similarly we don't want to have to handle that
|
||||
@ -336,6 +325,8 @@ bool CompareTransform::transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
calls.push_back(callInst);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -421,7 +412,7 @@ bool CompareTransform::transformCmps(Module &M, const bool processStrcmp,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (TmpConstStr.length() < 2 ||
|
||||
(TmpConstStr.length() == 2 && !TmpConstStr[1])) {
|
||||
(TmpConstStr.length() == 2 && TmpConstStr[1] == 0)) {
|
||||
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -55,12 +55,7 @@
|
||||
#include <sys/types.h>
|
||||
#include <sys/resource.h>
|
||||
|
||||
static s32 child_pid; /* PID of the tested program */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 *trace_bits; /* SHM with instrumentation bitmap */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 *in_file, /* Analyzer input test case */
|
||||
*prog_in; /* Targeted program input file */
|
||||
static u8 *in_file; /* Analyzer input test case */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 *in_data; /* Input data for analysis */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,20 +68,19 @@ static u64 orig_cksum; /* Original checksum */
|
||||
|
||||
static u64 mem_limit = MEM_LIMIT; /* Memory limit (MB) */
|
||||
|
||||
static s32 dev_null_fd = -1; /* FD to /dev/null */
|
||||
|
||||
static bool edges_only, /* Ignore hit counts? */
|
||||
use_hex_offsets, /* Show hex offsets? */
|
||||
use_stdin = true; /* Use stdin for program input? */
|
||||
|
||||
static volatile u8 stop_soon, /* Ctrl-C pressed? */
|
||||
child_timed_out; /* Child timed out? */
|
||||
static volatile u8 stop_soon; /* Ctrl-C pressed? */
|
||||
|
||||
static u8 *target_path;
|
||||
static u8 frida_mode;
|
||||
static u8 qemu_mode;
|
||||
static u32 map_size = MAP_SIZE;
|
||||
|
||||
static afl_forkserver_t fsrv = {0}; /* The forkserver */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Constants used for describing byte behavior. */
|
||||
|
||||
#define RESP_NONE 0x00 /* Changing byte is a no-op. */
|
||||
@ -156,7 +150,7 @@ static void classify_counts(u8 *mem) {
|
||||
|
||||
static inline u8 anything_set(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 *ptr = (u32 *)trace_bits;
|
||||
u32 *ptr = (u32 *)fsrv.trace_bits;
|
||||
u32 i = (map_size >> 2);
|
||||
|
||||
while (i--) {
|
||||
@ -173,7 +167,7 @@ static inline u8 anything_set(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
static void at_exit_handler(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
unlink(prog_in); /* Ignore errors */
|
||||
unlink(fsrv.out_file); /* Ignore errors */
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -205,116 +199,29 @@ static void read_initial_file(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write output file. */
|
||||
|
||||
static s32 write_to_file(u8 *path, u8 *mem, u32 len) {
|
||||
|
||||
s32 ret;
|
||||
|
||||
unlink(path); /* Ignore errors */
|
||||
|
||||
ret = open(path, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, DEFAULT_PERMISSION);
|
||||
|
||||
if (ret < 0) { PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", path); }
|
||||
|
||||
ck_write(ret, mem, len, path);
|
||||
|
||||
lseek(ret, 0, SEEK_SET);
|
||||
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Execute target application. Returns exec checksum, or 0 if program
|
||||
times out. */
|
||||
|
||||
static u32 analyze_run_target(char **argv, u8 *mem, u32 len, u8 first_run) {
|
||||
static u32 analyze_run_target(u8 *mem, u32 len, u8 first_run) {
|
||||
|
||||
static struct itimerval it;
|
||||
int status = 0;
|
||||
afl_fsrv_write_to_testcase(&fsrv, mem, len);
|
||||
fsrv_run_result_t ret = afl_fsrv_run_target(&fsrv, exec_tmout, &stop_soon);
|
||||
|
||||
s32 prog_in_fd;
|
||||
u64 cksum;
|
||||
if (ret == FSRV_RUN_ERROR) {
|
||||
|
||||
memset(trace_bits, 0, map_size);
|
||||
MEM_BARRIER();
|
||||
FATAL("Error in forkserver");
|
||||
|
||||
prog_in_fd = write_to_file(prog_in, mem, len);
|
||||
} else if (ret == FSRV_RUN_NOINST) {
|
||||
|
||||
child_pid = fork();
|
||||
FATAL("Target not instrumented");
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_pid < 0) { PFATAL("fork() failed"); }
|
||||
} else if (ret == FSRV_RUN_NOBITS) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (!child_pid) {
|
||||
|
||||
struct rlimit r;
|
||||
|
||||
if (dup2(use_stdin ? prog_in_fd : dev_null_fd, 0) < 0 ||
|
||||
dup2(dev_null_fd, 1) < 0 || dup2(dev_null_fd, 2) < 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
*(u32 *)trace_bits = EXEC_FAIL_SIG;
|
||||
PFATAL("dup2() failed");
|
||||
FATAL("Failed to run target");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
close(dev_null_fd);
|
||||
close(prog_in_fd);
|
||||
|
||||
if (mem_limit) {
|
||||
|
||||
r.rlim_max = r.rlim_cur = ((rlim_t)mem_limit) << 20;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef RLIMIT_AS
|
||||
|
||||
setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &r); /* Ignore errors */
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
setrlimit(RLIMIT_DATA, &r); /* Ignore errors */
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* ^RLIMIT_AS */
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r.rlim_max = r.rlim_cur = 0;
|
||||
setrlimit(RLIMIT_CORE, &r); /* Ignore errors */
|
||||
|
||||
execv(target_path, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
*(u32 *)trace_bits = EXEC_FAIL_SIG;
|
||||
exit(0);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
close(prog_in_fd);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Configure timeout, wait for child, cancel timeout. */
|
||||
|
||||
child_timed_out = 0;
|
||||
it.it_value.tv_sec = (exec_tmout / 1000);
|
||||
it.it_value.tv_usec = (exec_tmout % 1000) * 1000;
|
||||
|
||||
setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &it, NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
if (waitpid(child_pid, &status, 0) <= 0) { FATAL("waitpid() failed"); }
|
||||
|
||||
child_pid = 0;
|
||||
it.it_value.tv_sec = 0;
|
||||
it.it_value.tv_usec = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &it, NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
MEM_BARRIER();
|
||||
|
||||
/* Clean up bitmap, analyze exit condition, etc. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (*(u32 *)trace_bits == EXEC_FAIL_SIG) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Unable to execute '%s'", argv[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
classify_counts(trace_bits);
|
||||
classify_counts(fsrv.trace_bits);
|
||||
total_execs++;
|
||||
|
||||
if (stop_soon) {
|
||||
@ -326,22 +233,20 @@ static u32 analyze_run_target(char **argv, u8 *mem, u32 len, u8 first_run) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Always discard inputs that time out. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_timed_out) {
|
||||
if (fsrv.last_run_timed_out) {
|
||||
|
||||
exec_hangs++;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cksum = hash64(trace_bits, map_size, HASH_CONST);
|
||||
u64 cksum = hash64(fsrv.trace_bits, fsrv.map_size, HASH_CONST);
|
||||
|
||||
if (ret == FSRV_RUN_CRASH) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* We don't actually care if the target is crashing or not,
|
||||
except that when it does, the checksum should be different. */
|
||||
|
||||
if (WIFSIGNALED(status) ||
|
||||
(WIFEXITED(status) && WEXITSTATUS(status) == MSAN_ERROR) ||
|
||||
(WIFEXITED(status) && WEXITSTATUS(status))) {
|
||||
|
||||
cksum ^= 0xffffffff;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -604,7 +509,7 @@ static void dump_hex(u32 len, u8 *b_data) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Actually analyze! */
|
||||
|
||||
static void analyze(char **argv) {
|
||||
static void analyze() {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 i;
|
||||
u32 boring_len = 0, prev_xff = 0, prev_x01 = 0, prev_s10 = 0, prev_a10 = 0;
|
||||
@ -630,16 +535,16 @@ static void analyze(char **argv) {
|
||||
code. */
|
||||
|
||||
in_data[i] ^= 0xff;
|
||||
xor_ff = analyze_run_target(argv, in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
xor_ff = analyze_run_target(in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
in_data[i] ^= 0xfe;
|
||||
xor_01 = analyze_run_target(argv, in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
xor_01 = analyze_run_target(in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
in_data[i] = (in_data[i] ^ 0x01) - 0x10;
|
||||
sub_10 = analyze_run_target(argv, in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
sub_10 = analyze_run_target(in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
in_data[i] += 0x20;
|
||||
add_10 = analyze_run_target(argv, in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
add_10 = analyze_run_target(in_data, in_len, 0);
|
||||
in_data[i] -= 0x10;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Classify current behavior. */
|
||||
@ -712,7 +617,7 @@ static void handle_stop_sig(int sig) {
|
||||
(void)sig;
|
||||
stop_soon = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_pid > 0) { kill(child_pid, SIGKILL); }
|
||||
afl_fsrv_killall();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -724,10 +629,10 @@ static void set_up_environment(char **argv) {
|
||||
char *afl_preload;
|
||||
char *frida_afl_preload = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
dev_null_fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);
|
||||
if (dev_null_fd < 0) { PFATAL("Unable to open /dev/null"); }
|
||||
fsrv.dev_null_fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);
|
||||
if (fsrv.dev_null_fd < 0) { PFATAL("Unable to open /dev/null"); }
|
||||
|
||||
if (!prog_in) {
|
||||
if (!fsrv.out_file) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *use_dir = ".";
|
||||
|
||||
@ -738,10 +643,17 @@ static void set_up_environment(char **argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
prog_in = alloc_printf("%s/.afl-analyze-temp-%u", use_dir, (u32)getpid());
|
||||
fsrv.out_file =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/.afl-analyze-temp-%u", use_dir, (u32)getpid());
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
unlink(fsrv.out_file);
|
||||
fsrv.out_fd =
|
||||
open(fsrv.out_file, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, DEFAULT_PERMISSION);
|
||||
|
||||
if (fsrv.out_fd < 0) { PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", fsrv.out_file); }
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set sane defaults... */
|
||||
|
||||
x = get_afl_env("ASAN_OPTIONS");
|
||||
@ -977,9 +889,9 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 'f':
|
||||
|
||||
if (prog_in) { FATAL("Multiple -f options not supported"); }
|
||||
use_stdin = 0;
|
||||
prog_in = optarg;
|
||||
if (fsrv.out_file) { FATAL("Multiple -f options not supported"); }
|
||||
fsrv.use_stdin = 0;
|
||||
fsrv.out_file = ck_strdup(optarg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 'e':
|
||||
@ -1000,6 +912,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
if (!strcmp(optarg, "none")) {
|
||||
|
||||
mem_limit = 0;
|
||||
fsrv.mem_limit = 0;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1038,6 +951,8 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fsrv.mem_limit = mem_limit;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
@ -1057,6 +972,17 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fsrv.exec_tmout = exec_tmout;
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 'O': /* FRIDA mode */
|
||||
|
||||
if (frida_mode) { FATAL("Multiple -O options not supported"); }
|
||||
|
||||
frida_mode = 1;
|
||||
fsrv.frida_mode = frida_mode;
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 'O': /* FRIDA mode */
|
||||
@ -1073,6 +999,8 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
if (!mem_limit_given) { mem_limit = MEM_LIMIT_QEMU; }
|
||||
|
||||
qemu_mode = 1;
|
||||
fsrv.mem_limit = mem_limit;
|
||||
fsrv.qemu_mode = qemu_mode;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 'U':
|
||||
@ -1081,6 +1009,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
if (!mem_limit_given) { mem_limit = MEM_LIMIT_UNICORN; }
|
||||
|
||||
unicorn_mode = 1;
|
||||
fsrv.mem_limit = mem_limit;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 'W': /* Wine+QEMU mode */
|
||||
@ -1090,6 +1019,8 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
use_wine = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!mem_limit_given) { mem_limit = 0; }
|
||||
fsrv.qemu_mode = qemu_mode;
|
||||
fsrv.mem_limit = mem_limit;
|
||||
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1108,6 +1039,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
if (optind == argc || !in_file) { usage(argv[0]); }
|
||||
|
||||
map_size = get_map_size();
|
||||
fsrv.map_size = map_size;
|
||||
|
||||
use_hex_offsets = !!get_afl_env("AFL_ANALYZE_HEX");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1117,14 +1049,15 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
/* initialize cmplog_mode */
|
||||
shm.cmplog_mode = 0;
|
||||
trace_bits = afl_shm_init(&shm, map_size, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
atexit(at_exit_handler);
|
||||
setup_signal_handlers();
|
||||
|
||||
set_up_environment(argv);
|
||||
|
||||
target_path = find_binary(argv[optind]);
|
||||
detect_file_args(argv + optind, prog_in, &use_stdin);
|
||||
fsrv.target_path = find_binary(argv[optind]);
|
||||
fsrv.trace_bits = afl_shm_init(&shm, map_size, 0);
|
||||
detect_file_args(argv + optind, fsrv.out_file, &use_stdin);
|
||||
|
||||
if (qemu_mode) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1148,14 +1081,31 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
SAYF("\n");
|
||||
|
||||
if (getenv("AFL_FORKSRV_INIT_TMOUT")) {
|
||||
|
||||
s32 forksrv_init_tmout = atoi(getenv("AFL_FORKSRV_INIT_TMOUT"));
|
||||
if (forksrv_init_tmout < 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Bad value specified for AFL_FORKSRV_INIT_TMOUT");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fsrv.init_tmout = (u32)forksrv_init_tmout;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fsrv.kill_signal =
|
||||
parse_afl_kill_signal_env(getenv("AFL_KILL_SIGNAL"), SIGKILL);
|
||||
|
||||
read_initial_file();
|
||||
|
||||
ACTF("Performing dry run (mem limit = %llu MB, timeout = %u ms%s)...",
|
||||
mem_limit, exec_tmout, edges_only ? ", edges only" : "");
|
||||
|
||||
analyze_run_target(use_argv, in_data, in_len, 1);
|
||||
afl_fsrv_start(&fsrv, use_argv, &stop_soon, false);
|
||||
analyze_run_target(in_data, in_len, 1);
|
||||
|
||||
if (child_timed_out) {
|
||||
if (fsrv.last_run_timed_out) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL("Target binary times out (adjusting -t may help).");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1167,13 +1117,14 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv_orig, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
analyze(use_argv);
|
||||
analyze();
|
||||
|
||||
OKF("We're done here. Have a nice day!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
if (target_path) { ck_free(target_path); }
|
||||
|
||||
afl_shm_deinit(&shm);
|
||||
afl_fsrv_deinit(&fsrv);
|
||||
if (fsrv.target_path) { ck_free(fsrv.target_path); }
|
||||
if (in_data) { ck_free(in_data); }
|
||||
|
||||
exit(0);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
33
src/afl-cc.c
33
src/afl-cc.c
@ -315,7 +315,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
u8 fortify_set = 0, asan_set = 0, x_set = 0, bit_mode = 0, shared_linking = 0,
|
||||
preprocessor_only = 0, have_unroll = 0, have_o = 0, have_pic = 0,
|
||||
have_c = 0;
|
||||
have_c = 0, partial_linking = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params = ck_alloc((argc + 128) * sizeof(u8 *));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -514,14 +514,14 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
unsetenv("AFL_LD");
|
||||
unsetenv("AFL_LD_CALLER");
|
||||
|
||||
if (cmplog_mode) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (lto_mode && !have_c) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf(
|
||||
"-Wl,-mllvm=-load=%s/cmplog-routines-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf(
|
||||
"-Wl,-mllvm=-load=%s/cmplog-instructions-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
"-Wl,-mllvm=-load=%s/cmplog-switches-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = alloc_printf(
|
||||
"-Wl,-mllvm=-load=%s/split-switches-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -531,13 +531,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-load";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/cmplog-routines-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-load";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/cmplog-instructions-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/cmplog-switches-pass.so", obj_path);
|
||||
|
||||
// reuse split switches from laf
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-Xclang";
|
||||
@ -746,6 +740,11 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = afllib;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __APPLE__
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "-undefined";
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] = "dynamic_lookup";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
@ -767,6 +766,10 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-x")) x_set = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-E")) preprocessor_only = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-shared")) shared_linking = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-Wl,-r")) partial_linking = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-Wl,--relocatable")) partial_linking = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-r")) partial_linking = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "--relocatable")) partial_linking = 1;
|
||||
if (!strcmp(cur, "-c")) have_c = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strncmp(cur, "-O", 2)) have_o = 1;
|
||||
@ -996,7 +999,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
switch (bit_mode) {
|
||||
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
if (!shared_linking)
|
||||
if (!shared_linking && !partial_linking)
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/afl-compiler-rt.o", obj_path);
|
||||
if (lto_mode)
|
||||
@ -1005,7 +1008,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 32:
|
||||
if (!shared_linking) {
|
||||
if (!shared_linking && !partial_linking) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/afl-compiler-rt-32.o", obj_path);
|
||||
@ -1026,7 +1029,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 64:
|
||||
if (!shared_linking) {
|
||||
if (!shared_linking && !partial_linking) {
|
||||
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("%s/afl-compiler-rt-64.o", obj_path);
|
||||
@ -1049,7 +1052,7 @@ static void edit_params(u32 argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if !defined(__APPLE__) && !defined(__sun)
|
||||
if (!shared_linking)
|
||||
if (!shared_linking && !partial_linking)
|
||||
cc_params[cc_par_cnt++] =
|
||||
alloc_printf("-Wl,--dynamic-list=%s/dynamic_list.txt", obj_path);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -751,6 +751,8 @@ void read_bitmap(u8 *fname, u8 *map, size_t len) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Get unix time in milliseconds */
|
||||
|
||||
u64 get_cur_time(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
struct timeval tv;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,6 +90,7 @@ void afl_fsrv_init(afl_forkserver_t *fsrv) {
|
||||
/* exec related stuff */
|
||||
fsrv->child_pid = -1;
|
||||
fsrv->map_size = get_map_size();
|
||||
fsrv->real_map_size = fsrv->map_size;
|
||||
fsrv->use_fauxsrv = false;
|
||||
fsrv->last_run_timed_out = false;
|
||||
fsrv->debug = false;
|
||||
@ -110,6 +111,7 @@ void afl_fsrv_init_dup(afl_forkserver_t *fsrv_to, afl_forkserver_t *from) {
|
||||
fsrv_to->init_tmout = from->init_tmout;
|
||||
fsrv_to->mem_limit = from->mem_limit;
|
||||
fsrv_to->map_size = from->map_size;
|
||||
fsrv_to->real_map_size = from->real_map_size;
|
||||
fsrv_to->support_shmem_fuzz = from->support_shmem_fuzz;
|
||||
fsrv_to->out_file = from->out_file;
|
||||
fsrv_to->dev_urandom_fd = from->dev_urandom_fd;
|
||||
@ -691,15 +693,15 @@ void afl_fsrv_start(afl_forkserver_t *fsrv, char **argv,
|
||||
|
||||
if (!fsrv->map_size) { fsrv->map_size = MAP_SIZE; }
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(tmp_map_size % 64)) {
|
||||
fsrv->real_map_size = tmp_map_size;
|
||||
|
||||
if (tmp_map_size % 64) {
|
||||
|
||||
// should not happen
|
||||
WARNF("Target reported non-aligned map size of %u", tmp_map_size);
|
||||
tmp_map_size = (((tmp_map_size + 63) >> 6) << 6);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) { ACTF("Target map size: %u", tmp_map_size); }
|
||||
if (!be_quiet) { ACTF("Target map size: %u", fsrv->real_map_size); }
|
||||
if (tmp_map_size > fsrv->map_size) {
|
||||
|
||||
FATAL(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -551,19 +551,18 @@ save_if_interesting(afl_state_t *afl, void *mem, u32 len, u8 fault) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (cksum)
|
||||
afl->queue_top->exec_cksum = cksum;
|
||||
else
|
||||
cksum = afl->queue_top->exec_cksum =
|
||||
hash64(afl->fsrv.trace_bits, afl->fsrv.map_size, HASH_CONST);
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl->schedule >= FAST && afl->schedule <= RARE) {
|
||||
/* AFLFast schedule? update the new queue entry */
|
||||
if (cksum) {
|
||||
|
||||
afl->queue_top->n_fuzz_entry = cksum % N_FUZZ_SIZE;
|
||||
afl->n_fuzz[afl->queue_top->n_fuzz_entry] = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* due to classify counts we have to recalculate the checksum */
|
||||
cksum = afl->queue_top->exec_cksum =
|
||||
hash64(afl->fsrv.trace_bits, afl->fsrv.map_size, HASH_CONST);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Try to calibrate inline; this also calls update_bitmap_score() when
|
||||
successful. */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -480,13 +480,22 @@ void read_foreign_testcases(afl_state_t *afl, int first) {
|
||||
|
||||
for (iter = 0; iter < afl->foreign_sync_cnt; iter++) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir != NULL &&
|
||||
afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir[0] != 0) {
|
||||
if (afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir && afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir[0]) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (first) ACTF("Scanning '%s'...", afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir);
|
||||
time_t mtime_max = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
u8 *name = strrchr(afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir, '/');
|
||||
if (!name) { name = afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir; }
|
||||
if (!name) {
|
||||
|
||||
name = afl->foreign_syncs[iter].dir;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
++name;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp(name, "queue") || !strcmp(name, "out") ||
|
||||
!strcmp(name, "default")) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -701,10 +710,14 @@ void read_testcases(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *directory) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (i = 0; i < (u32)nl_cnt; ++i) {
|
||||
if (nl_cnt) {
|
||||
|
||||
i = nl_cnt;
|
||||
do {
|
||||
|
||||
--i;
|
||||
|
||||
struct stat st;
|
||||
|
||||
u8 dfn[PATH_MAX];
|
||||
snprintf(dfn, PATH_MAX, "%s/.state/deterministic_done/%s", afl->in_dir,
|
||||
nl[i]->d_name);
|
||||
@ -741,7 +754,8 @@ void read_testcases(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *directory) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (st.st_size > MAX_FILE) {
|
||||
|
||||
WARNF("Test case '%s' is too big (%s, limit is %s), partial reading", fn2,
|
||||
WARNF("Test case '%s' is too big (%s, limit is %s), partial reading",
|
||||
fn2,
|
||||
stringify_mem_size(val_buf[0], sizeof(val_buf[0]), st.st_size),
|
||||
stringify_mem_size(val_buf[1], sizeof(val_buf[1]), MAX_FILE));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -792,6 +806,8 @@ void read_testcases(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *directory) {
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
} while (i > 0);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
free(nl); /* not tracked */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -393,6 +393,7 @@ u8 trim_case_custom(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q, u8 *in_buf,
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl->stop_soon || fault == FSRV_RUN_ERROR) { goto abort_trimming; }
|
||||
|
||||
classify_counts(&afl->fsrv);
|
||||
cksum = hash64(afl->fsrv.trace_bits, afl->fsrv.map_size, HASH_CONST);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ static int select_algorithm(afl_state_t *afl, u32 max_algorithm) {
|
||||
/* Helper to choose random block len for block operations in fuzz_one().
|
||||
Doesn't return zero, provided that max_len is > 0. */
|
||||
|
||||
static u32 choose_block_len(afl_state_t *afl, u32 limit) {
|
||||
static inline u32 choose_block_len(afl_state_t *afl, u32 limit) {
|
||||
|
||||
u32 min_value, max_value;
|
||||
u32 rlim = MIN(afl->queue_cycle, (u32)3);
|
||||
@ -2057,7 +2057,7 @@ havoc_stage:
|
||||
temp_len = new_len;
|
||||
if (out_buf != custom_havoc_buf) {
|
||||
|
||||
afl_realloc(AFL_BUF_PARAM(out), temp_len);
|
||||
out_buf = afl_realloc(AFL_BUF_PARAM(out), temp_len);
|
||||
if (unlikely(!afl->out_buf)) { PFATAL("alloc"); }
|
||||
memcpy(out_buf, custom_havoc_buf, temp_len);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2102,9 +2102,9 @@ havoc_stage:
|
||||
|
||||
case 8 ... 9: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set word to interesting value, randomly choosing endian. */
|
||||
case 8 ... 9: {
|
||||
|
||||
if (temp_len < 2) { break; }
|
||||
/* Set word to interesting value, little endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef INTROSPECTION
|
||||
snprintf(afl->m_tmp, sizeof(afl->m_tmp), " INTERESTING16");
|
||||
@ -2136,9 +2136,9 @@ havoc_stage:
|
||||
|
||||
case 12 ... 13: {
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set dword to interesting value, randomly choosing endian. */
|
||||
case 12 ... 13: {
|
||||
|
||||
if (temp_len < 4) { break; }
|
||||
/* Set dword to interesting value, little endian. */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef INTROSPECTION
|
||||
snprintf(afl->m_tmp, sizeof(afl->m_tmp), " INTERESTING32");
|
||||
@ -2862,6 +2862,7 @@ abandon_entry:
|
||||
|
||||
--afl->pending_not_fuzzed;
|
||||
afl->queue_cur->was_fuzzed = 1;
|
||||
afl->reinit_table = 1;
|
||||
if (afl->queue_cur->favored) { --afl->pending_favored; }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +58,8 @@ double compute_weight(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q,
|
||||
if (likely(afl->schedule < RARE)) { weight *= (avg_exec_us / q->exec_us); }
|
||||
weight *= (log(q->bitmap_size) / avg_bitmap_size);
|
||||
weight *= (1 + (q->tc_ref / avg_top_size));
|
||||
if (unlikely(q->favored)) weight *= 5;
|
||||
if (unlikely(q->favored)) { weight *= 5; }
|
||||
if (unlikely(!q->was_fuzzed)) { weight *= 2; }
|
||||
|
||||
return weight;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -198,6 +199,8 @@ void create_alias_table(afl_state_t *afl) {
|
||||
while (nS)
|
||||
afl->alias_probability[S[--nS]] = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
afl->reinit_table = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
#ifdef INTROSPECTION
|
||||
u8 fn[PATH_MAX];
|
||||
@ -1132,12 +1135,10 @@ inline u8 *queue_testcase_get(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q) {
|
||||
|
||||
do_once = 1;
|
||||
// release unneeded memory
|
||||
u8 *ptr = ck_realloc(
|
||||
afl->q_testcase_cache = ck_realloc(
|
||||
afl->q_testcase_cache,
|
||||
(afl->q_testcase_max_cache_entries + 1) * sizeof(size_t));
|
||||
|
||||
if (ptr) { afl->q_testcase_cache = (struct queue_entry **)ptr; }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Cache full. We neet to evict one or more to map one.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -252,7 +252,7 @@ static u8 colorization(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *buf, u32 len,
|
||||
u64 start_time = get_cur_time();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
u32 screen_update = 1000000 / afl->queue_cur->exec_us;
|
||||
u32 screen_update;
|
||||
u64 orig_hit_cnt, new_hit_cnt, exec_cksum;
|
||||
orig_hit_cnt = afl->queued_paths + afl->unique_crashes;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -261,6 +261,24 @@ static u8 colorization(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *buf, u32 len,
|
||||
afl->stage_max = (len << 1);
|
||||
afl->stage_cur = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (likely(afl->queue_cur->exec_us)) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (likely((100000 / 2) >= afl->queue_cur->exec_us)) {
|
||||
|
||||
screen_update = 100000 / afl->queue_cur->exec_us;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
screen_update = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
screen_update = 100000;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// in colorization we do not classify counts, hence we have to calculate
|
||||
// the original checksum.
|
||||
if (unlikely(get_exec_checksum(afl, buf, len, &exec_cksum))) {
|
||||
@ -905,8 +923,7 @@ static u8 cmp_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, struct cmp_header *h,
|
||||
// test for arithmetic, eg. "if ((user_val - 0x1111) == 0x1234) ..."
|
||||
s64 diff = pattern - b_val;
|
||||
s64 o_diff = o_pattern - o_b_val;
|
||||
/*
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "DIFF1 idx=%03u shape=%02u %llx-%llx=%lx\n", idx,
|
||||
/* fprintf(stderr, "DIFF1 idx=%03u shape=%02u %llx-%llx=%lx\n", idx,
|
||||
h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "DIFF1 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern,
|
||||
b_val, diff); */
|
||||
@ -936,8 +953,10 @@ static u8 cmp_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, struct cmp_header *h,
|
||||
s64 o_diff = o_pattern ^ o_b_val;
|
||||
|
||||
/* fprintf(stderr, "DIFF2 idx=%03u shape=%02u %llx-%llx=%lx\n",
|
||||
idx, h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff); fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"DIFF2 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern, b_val, diff);*/
|
||||
idx, h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"DIFF2 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern, b_val, diff);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (diff == o_diff && diff) {
|
||||
|
||||
// this could be a XOR transformation
|
||||
@ -983,8 +1002,10 @@ static u8 cmp_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, struct cmp_header *h,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* fprintf(stderr, "DIFF3 idx=%03u shape=%02u %llx-%llx=%lx\n",
|
||||
idx, h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff); fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"DIFF3 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern, b_val, diff);*/
|
||||
idx, h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"DIFF3 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern, b_val, diff);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (o_diff && diff) {
|
||||
|
||||
// this could be a lower to upper
|
||||
@ -1030,8 +1051,10 @@ static u8 cmp_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, struct cmp_header *h,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* fprintf(stderr, "DIFF4 idx=%03u shape=%02u %llx-%llx=%lx\n",
|
||||
idx, h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff); fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"DIFF4 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern, b_val, diff);*/
|
||||
idx, h->shape + 1, o_pattern, o_b_val, o_diff);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"DIFF4 %016llx %llx-%llx=%lx\n", repl, pattern, b_val, diff);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (o_diff && diff) {
|
||||
|
||||
// this could be a lower to upper
|
||||
@ -1383,7 +1406,8 @@ static u8 cmp_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, struct cmp_header *h,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//#endif /* CMPLOG_SOLVE_ARITHMETIC
|
||||
//#endif /*
|
||||
// CMPLOG_SOLVE_ARITHMETIC
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2152,7 +2176,8 @@ static u8 rtn_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *pattern, u8 *repl,
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(buf + idx, tmp, i + 1);
|
||||
if (unlikely(its_fuzz(afl, buf, len, status))) { return 1; }
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "RTN ATTEMPT tohex %u result %u\n", tohex, *status);
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "RTN ATTEMPT tohex %u result %u\n", tohex,
|
||||
// *status);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2235,7 +2260,8 @@ static u8 rtn_extend_encoding(afl_state_t *afl, u8 *pattern, u8 *repl,
|
||||
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++)
|
||||
buf[idx + j] = repl[j] - arith_val[j];
|
||||
if (unlikely(its_fuzz(afl, buf, len, status))) { return 1; }
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "RTN ATTEMPT arith %u result %u\n", arith, *status);
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "RTN ATTEMPT arith %u result %u\n", arith,
|
||||
// *status);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2328,15 +2354,16 @@ static u8 rtn_fuzz(afl_state_t *afl, u32 key, u8 *orig_buf, u8 *buf, u8 *cbuf,
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
struct cmp_header *hh = &afl->orig_cmp_map->headers[key];
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "RTN N hits=%u id=%u shape=%u attr=%u v0=", h->hits, h->id,
|
||||
h->shape, h->attribute); for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) fprintf(stderr, "%02x",
|
||||
o->v0[j]); fprintf(stderr, " v1="); for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) fprintf(stderr,
|
||||
"%02x", o->v1[j]); fprintf(stderr, "\nRTN O hits=%u id=%u shape=%u attr=%u
|
||||
o0=", hh->hits, hh->id, hh->shape, hh->attribute); for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%02x", orig_o->v0[j]);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "RTN N hits=%u id=%u shape=%u attr=%u v0=", h->hits,
|
||||
h->id, h->shape, h->attribute);
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) fprintf(stderr, "%02x", o->v0[j]);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " v1=");
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) fprintf(stderr, "%02x", o->v1[j]);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\nRTN O hits=%u id=%u shape=%u attr=%u o0=",
|
||||
hh->hits, hh->id, hh->shape, hh->attribute);
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) fprintf(stderr, "%02x", orig_o->v0[j]);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " o1=");
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%02x", orig_o->v1[j]);
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) fprintf(stderr, "%02x", orig_o->v1[j]);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2663,7 +2690,12 @@ exit_its:
|
||||
|
||||
afl->queue_cur->colorized = CMPLOG_LVL_MAX;
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl->queue_cur->cmplog_colorinput) {
|
||||
|
||||
ck_free(afl->queue_cur->cmplog_colorinput);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
while (taint) {
|
||||
|
||||
t = taint->next;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -314,7 +314,7 @@ u8 calibrate_case(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q, u8 *use_mem,
|
||||
++q->cal_failed;
|
||||
|
||||
afl->stage_name = "calibration";
|
||||
afl->stage_max = afl->fast_cal ? 3 : CAL_CYCLES;
|
||||
afl->stage_max = afl->afl_env.afl_cal_fast ? 3 : CAL_CYCLES;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make sure the forkserver is up before we do anything, and let's not
|
||||
count its spin-up time toward binary calibration. */
|
||||
@ -333,7 +333,6 @@ u8 calibrate_case(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q, u8 *use_mem,
|
||||
|
||||
if (afl->fsrv.support_shmem_fuzz && !afl->fsrv.use_shmem_fuzz) {
|
||||
|
||||
unsetenv(SHM_FUZZ_ENV_VAR);
|
||||
afl_shm_deinit(afl->shm_fuzz);
|
||||
ck_free(afl->shm_fuzz);
|
||||
afl->shm_fuzz = NULL;
|
||||
@ -356,6 +355,12 @@ u8 calibrate_case(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q, u8 *use_mem,
|
||||
|
||||
for (afl->stage_cur = 0; afl->stage_cur < afl->stage_max; ++afl->stage_cur) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(afl->debug)) {
|
||||
|
||||
DEBUGF("calibration stage %d/%d\n", afl->stage_cur + 1, afl->stage_max);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
u64 cksum;
|
||||
|
||||
write_to_testcase(afl, use_mem, q->len);
|
||||
@ -403,6 +408,21 @@ u8 calibrate_case(afl_state_t *afl, struct queue_entry *q, u8 *use_mem,
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (unlikely(!var_detected)) {
|
||||
|
||||
// note: from_queue seems to only be set during initialization
|
||||
if (afl->afl_env.afl_no_ui || from_queue) {
|
||||
|
||||
WARNF("instability detected during calibration");
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (afl->debug) {
|
||||
|
||||
DEBUGF("instability detected during calibration\n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var_detected = 1;
|
||||
afl->stage_max = afl->fast_cal ? CAL_CYCLES : CAL_CYCLES_LONG;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,8 +96,6 @@ void afl_state_init(afl_state_t *afl, uint32_t map_size) {
|
||||
afl->splicing_with = -1; /* Splicing with which test case? */
|
||||
afl->cpu_to_bind = -1;
|
||||
afl->havoc_stack_pow2 = HAVOC_STACK_POW2;
|
||||
afl->cal_cycles = CAL_CYCLES;
|
||||
afl->cal_cycles_long = CAL_CYCLES_LONG;
|
||||
afl->hang_tmout = EXEC_TIMEOUT;
|
||||
afl->exit_on_time = 0;
|
||||
afl->stats_update_freq = 1;
|
||||
@ -341,6 +339,13 @@ void read_afl_environment(afl_state_t *afl, char **envp) {
|
||||
afl->afl_env.afl_cal_fast =
|
||||
get_afl_env(afl_environment_variables[i]) ? 1 : 0;
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (!strncmp(env, "AFL_FAST_CAL",
|
||||
|
||||
afl_environment_variable_len)) {
|
||||
|
||||
afl->afl_env.afl_cal_fast =
|
||||
get_afl_env(afl_environment_variables[i]) ? 1 : 0;
|
||||
|
||||
} else if (!strncmp(env, "AFL_STATSD",
|
||||
|
||||
afl_environment_variable_len)) {
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user